DNA Repair: Rad51, friend or foe?
Imagine your frustration if, in the event of a breakdown, the emergency mechanic not only failed to repair your vehicle but actually damaged it even further. A similar situation can arise with our own DNA which, when damaged, is subjected to a system of rigorous checks and balances by the DNA repair machinery. However, DNA can also be damaged through the actions of structures called R-loops. These are RNA-DNA hybrids formed when an RNA transcript invades the DNA double helix, and they are a natural byproduct of the transcription process (Aguilera and Garcia-Muse, 2012). Now, in eLife, Douglas Koshland at the University of California, Berkeley, and co-workers reveal that proteins normally involved in DNA repair can also facilitate the formation of R-loops, thus increasing DNA damage (Wahba et al., 2013).
Initial work in bacteria showed that the repair protein RecA (Kasahara et al., 2000) can potentiate the formation of R-loops in the absence of active transcription. Building on this study, Koshland and colleagues—including Lamia Wahba, who is also at Johns Hopkins University, and Steven Gore—report three sets of experiments on the yeast counterpart of RecA, which is known as Rad51. Firstly, they provide evidence that Rad51 is also involved in R-loop formation. Secondly, they show that Rad51 is already present at R-loops before DNA damage occurs, suggesting that it may be oncogenic (i.e., have the potential to cause cancer). Thirdly, through elegant experimentation, they challenge the dogma that R-loop formation must invariably occur at the site of transcription (cis-acting) by revealing that R-loops can also be formed by RNA invading the DNA duplex at a remote genomic location (trans-acting).
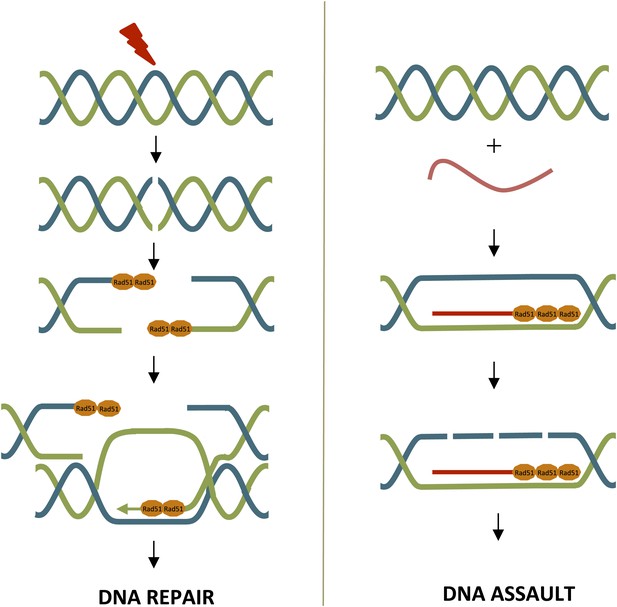
Rad51 can contribute to DNA repair or DNA assault.
Left: DNA repair through homologous recombination, where one strand is used as a template to repair the other. DNA damage (red bolt) leads to double-strand breaks. At the break point, one strand of the DNA is slightly longer than the other and Rad52 (not shown) promotes the loading of Rad51 (orange) onto these single-strand overhangs. This initiates the process of DNA repair via homologous recombination. Rad51 is removed from the single-strand overhangs by the negative regulator Srs2 (not shown) before the final stages of DNA repair. Right: Rad51 can promote the formation of DNA-RNA hybrids (R-loops), which can damage DNA. R-loops form when Rad51 binds repeatedly to RNA (red lines). Srs2 (not shown) inhibits R-loop formation by removing Rad51.
Wahba et al. show that the accumulation of R-loops is dependent on Rad51 activity: in the absence of Rad51, aberrant transcription does not result in the formation of R-loops and the genome remains intact. To measure the destabilizing effects of R-loops on DNA, Wahba et al. used a yeast artificial chromosome (or YAC), which they introduced into the yeast nucleus. They found that Rad51 does not work alone but is regulated by other factors: removing a positive protein regulator of Rad51, called Rad52, blocks the formation of R-loops, whereas removing a negative protein regulator, Srs2, increases their formation.
Koshland and colleagues reveal, in addition, that Rad51 localizes to R-loops. Previous work has shown that Rad51 binds at break points in DNA to initiate DNA repair (Sugawara et al., 2003). Moreover, mammalian Rad51 is known to help cells resist the damaging effects of ionizing radiation, chemotherapeutic agents, and the spontaneous breaks and aberrations that occur during DNA replication. A natural assumption therefore is that the high levels of Rad51 expression seen in tumour cells (Klein, 2008) reflect the protein’s role in DNA repair; in other words, that Rad51 may act as a tumour suppressor.
So what is Rad51 doing at R-loop sites? To address this question, Wahba et al. studied the deposition of a histone called H2AX—a well-defined marker for the formation of double-strand DNA breaks—and compared the timing of this event with the accumulation of Rad51 at an R-loop site. They confirmed that Rad51 was present prior to DNA damage, suggesting that rather than contributing to repair, Rad51 could be driving R-loop-mediated genome instability in cancer cells, and promoting tumour biogenesis.
Having established that Rad51 induces the formation of R-loops, and drawing encouragement from bacterial work, Koshland and colleagues went on to show that R-loop formation is not directly dependent on the act of transcription. To do this, they created yeast cells that contained two copies of a particular DNA sequence—one in a YAC and the other in one of the yeast’s own chromosomes—and placed the latter under the control of a transcriptional switch. When the switch was triggered, the induced chromosomal transcript—with the help of Rad51—invaded the homologous DNA in the YAC. This resulted in the formation of an R-loop, distinct and distant from the original site of transcription. And sure enough, this trans induced R-loop destabilized the YAC DNA.
It is noteworthy that R-loops are not always deleterious. As obligatory intermediates, they are essential for mitochondrial DNA replication (Pohjoismaki et al., 2010) and immunoglobulin gene class-switch recombination (Yu et al., 2003)—a complex process in which antibody genes genetically rearrange during the development of immune cells called B cells. They are also implicated in transcription termination (Skourti-Stathaki et al., 2011) and in transcription activation of CpG island promoters (Ginno et al., 2012). However, when R-loops occur out of their natural context and pose a threat to cell survival, all is not lost. Cells have the innate capacity to counteract such hazardous structures. One line of defense is Srs2, which can remove Rad51 from DNA. Other options include Sen1 helicase, an enzyme that can unwind R-loops formed in the wake of transcription (Mischo et al., 2011), and RNAse H, which can degrade RNA that is base-paired with DNA in R-loops (Cerritelli and Crouch, 2009). All of these proteins serve to protect the cellular genome from destruction.
Exploring and harnessing the potential applications of Rad51-dependent R-loop formation is an exciting prospect. The current findings have intriguing parallels with the CRISPR system (Horvath and Barrangou, 2013), which is a mechanism used by bacteria and archaea to defend themselves against invading phages. In brief, short DNA fragments from phage genomes are integrated into the bacterial or archael genome within the CRISPR locus, and transcripts from the CRISPR regions then form R-loops with the infecting phage DNA. These R-loops recruit enzymes to destroy the phage genome. Engineered CRISPR-derived constructs have been used to successfully target specific DNA sequences for replacement or modification in mammalian cells (Wang et al., 2013). Koshland and colleagues now potentially add Rad51 to the arsenal available for genetic search and destroy missions. Consequently, their work may have broad implications for synthetic biology, gene function studies and gene therapy.
References
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
Copyright
© 2013, Tan-Wong and Proudfoot
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 1,639
- views
-
- 123
- downloads
-
- 1
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Chromosomes and Gene Expression
The association between late replication timing and low transcription rates in eukaryotic heterochromatin is well known, yet the specific mechanisms underlying this link remain uncertain. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the histone deacetylase Sir2 is required for both transcriptional silencing and late replication at the repetitive ribosomal DNA (rDNA) arrays. We have previously reported that in the absence of SIR2, a de-repressed RNA PolII repositions MCM replicative helicases from their loading site at the ribosomal origin, where they abut well-positioned, high-occupancy nucleosomes, to an adjacent region with lower nucleosome occupancy. By developing a method that can distinguish activation of closely spaced MCM complexes, here we show that the displaced MCMs at rDNA origins have increased firing propensity compared to the nondisplaced MCMs. Furthermore, we found that both activation of the repositioned MCMs and low occupancy of the adjacent nucleosomes critically depend on the chromatin remodeling activity of FUN30. Our study elucidates the mechanism by which Sir2 delays replication timing, and it demonstrates, for the first time, that activation of a specific replication origin in vivo relies on the nucleosome context shaped by a single chromatin remodeler.
-
- Chromosomes and Gene Expression
Specialized magnetic beads that bind target proteins to a cryogenic electron microscopy grid make it possible to study the structure of protein complexes from dilute samples.





