Essential yet limited role for CCR2+ inflammatory monocytes during Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific T cell priming
Figures
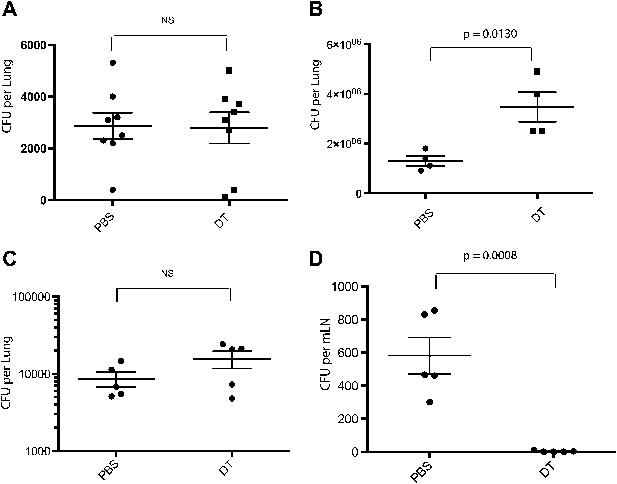
Depletion of inflammatory monocytes during the second week of M. tuberculosis infection abrogates transport of live bacteria to mLNs and increases pulmonary bacterial burden.
(A) CFU plots from the lungs of CCR2-DTR mice receiving DT or PBS on days −1, 0 and 1 and harvested on day 7. (B) CFU plots of the lungs of CCR2-DTR mice receiving DT or PBS on days 7, 9 and 11 and harvested on day 15 post infection. CFU counts from the lungs (C) and mLN (D) of CCR2-DTR mice given DT treatment on days 7, 9 and 11 and harvested on day 12. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Error bars denote SEM. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
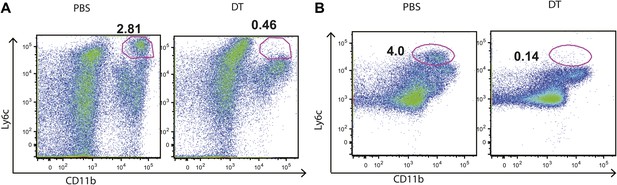
DT administration depletes IMs from the lungs and mLNs of infected mice.
CCR2-DTR mice received PBS or DT on days 7, 9 and 11 post infection and were harvested on day 12 when flow cytometry was performed to quantify the IM population in the lungs (A) and mLN (B). Data are representative of three independent experiments.
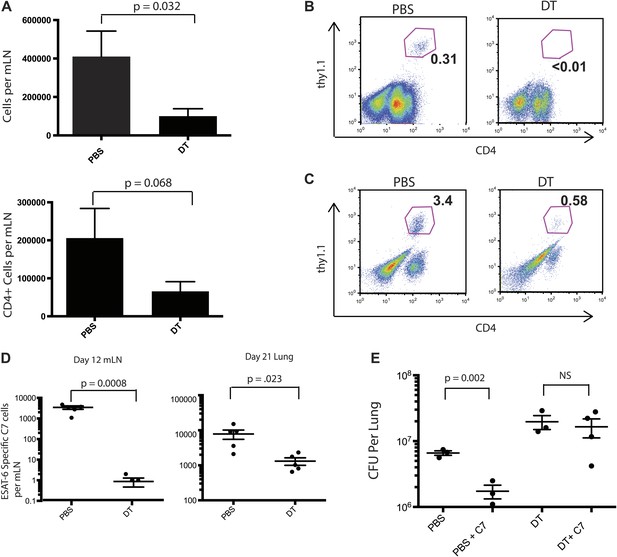
Priming of ESAT-6-specific CD4 T cells is reduced in CCR2-DTR mice depleted during the second week of infection.
(A) Total cell counts and CD4 T cell counts in mLNs of mice on day 12 post infection after treatment with DT or PBS on days 7, 9 and 11. CCR2-DTR mice received naive ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells the day before infection and were treated with DT or PBS on days 7, 9 and 11, mLNs (B) were harvested on day 12, lungs (C) were harvested on day 21 and ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells were visualized. (D) Cumulative data from experiments shown in (B) and (C) showing the total number of ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells in mLNs and lungs. (E) CFU plots of lungs of mice that received naive EAST-6-specific C7 T cells and were treated with DT or PBS, as indicated, and were harvested on day 21 post infection. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Five mice per group are included in the bar graphs shown in (A). Error bars denote SEM. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
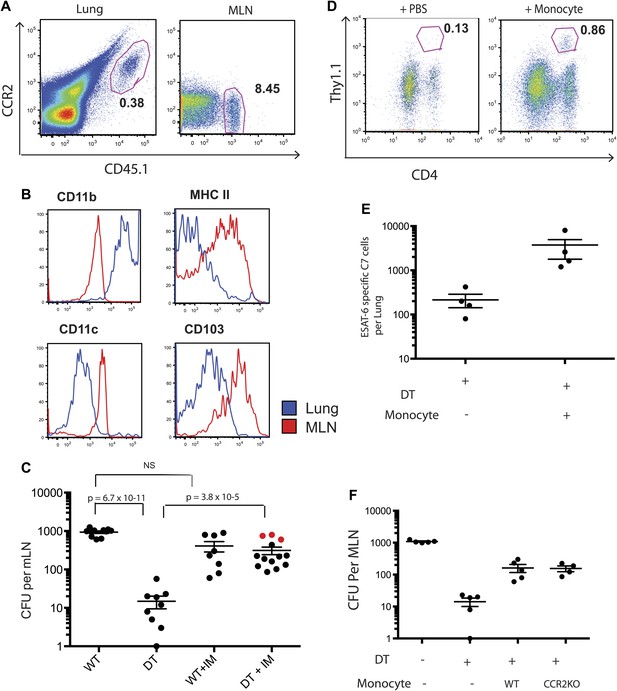
Adoptive transfer of highly purified inflammatory monocytes can rescue antigen transport and CD4 T cell priming in DT treated CCR2-DTR mice.
CCR2-DTR mice were infected and treated with DT or PBS on days 7, 9 and 11 and received highly purified CD45.1+ IMs on days 8 and 10. (A) Mice were euthanized on day 12 post infection and flow cytometry was performed on lungs and mLNs to track the engraftment of adoptively transferred IMs. (B) The expression of cell surface markers CD11b, MHC II, CDIIc and CD103 by adoptively transferred IMs in the lung and mLN was determined. (C) CFU plots from day 12 mLNs of CCR2-DTR mice rescued with IMs. Dots marked in red represent mice that received double sorted IMs of greater than 99% purity. (D) CCR2-DTR mice received a dose of naive ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells the day before infection and were treated with DT on days 7, 9 and 11 and received purified IMs or PBS on days 8 and 10. Lungs were harvested on day 15 and ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells were visualized. (E) Cumulative data of experiment shown in (D) showing the total number of ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells in day 15 lungs. (F) CCR2-DTR mice were depleted on days 7, 9 and 11 and received CCR2 WT or CCR2 KO IMs on days 8 and 10. Day 12 mLNs were harvested for CFU counts. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Error bars denote SEM. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
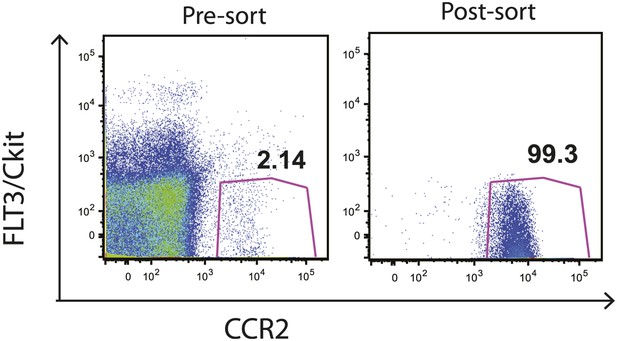
Sorting of IMs from CCR2-GFP mice. FLT3-, cKit-, GFP+ cells were sorted from the bone marrow of CCR2-GFP mice.
FACS plots show pre- and post sorting purity of the cells. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
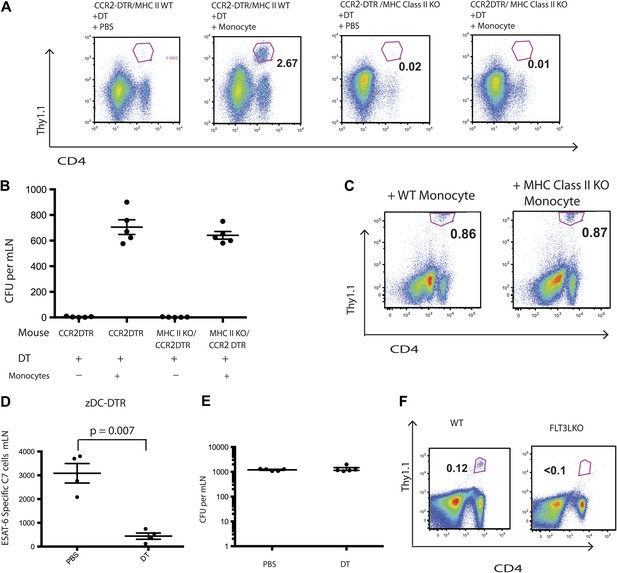
IMs do not prime CD4 T cells directly.
CCR2-DTR mice that were either MHC class II KO or WT received naive ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells the day before infection and were treated with DT or PBS on days 7, 9 and 11 and received purified IMs on days 8 and 10. (A) ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells in lungs harvested on day 15. (B) Mtb CFUs from mLNs of mice harvested on day 12. (C) CCR2-DTR mice received naive ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells the day before infection and were treated with DT or PBS on days 7, 9 and 11 and received either MHCII WT or MHCII KO IMs on days 8 and 10. Flow cytometry was performed on lungs harvested on day 15. (D) zDC-DTR mice received naive ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells the day before infection and cDCs were depleted on day 7, 9 and 11, and the number of ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells was determined in mLNs harvested on day 12. (E) The number of CFU in mLNs of PBS and DT treated zDC-DTR mice. (F) FLT3LKO mice received naive ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells the day before infection and lungs were harvested on day 15 to quantify the ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Error bars denote SEM. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
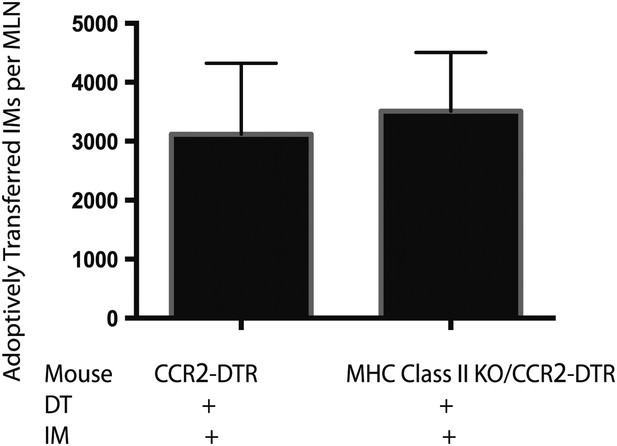
Adoptively transferred IMs traffick to the mLNs of MHC Class II KO mice.
MHC class II KO/CCR2-DTR mice infected with Mtb and depleted on days 7, 9, and 11 received a dose of purified IMs on days 8 and 10 and were harvested on day 12 when the total number of transferred IMs per mLN was quantified. Each group contains five mice. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
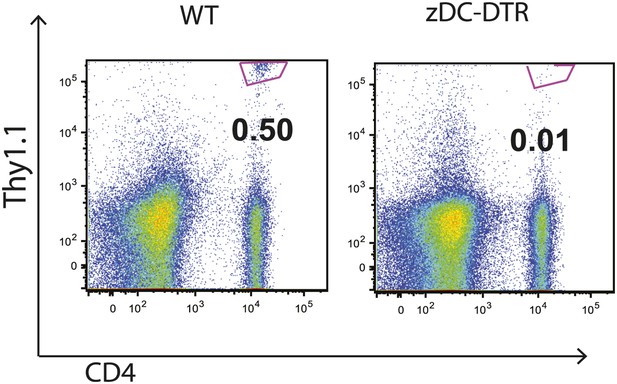
Priming of ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells is reduced in zDC-DTR mice.
zDC-DTR mice received naive ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells the day before infection and cDCs were depleted on days 7, 9 and 11. On day 12 mLNs were harvested to quantify the number of ESAT-6-specific C7 T cells. Data are representative of two independent experiments containing four mice per group.
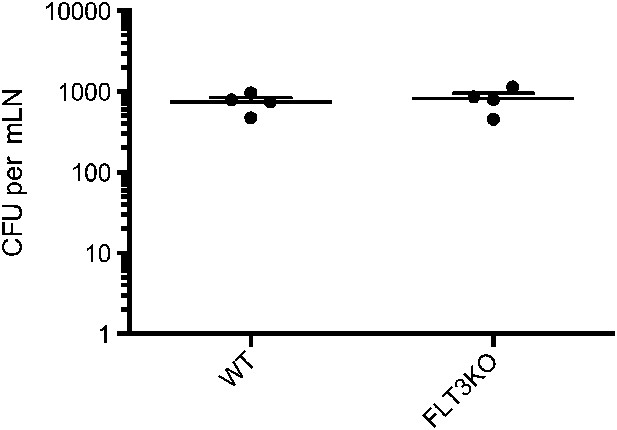
Mtb traffick to the mLN of FLT3LKO mice is unimpaired.
FLT3LKO mice were infected with Mtb and mLNs were harvested on day 12 for CFU analysis. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Data are representative of two independent experiments.





