A model symbiosis reveals a role for sheathed-flagellum rotation in the release of immunogenic lipopolysaccharide
Figures
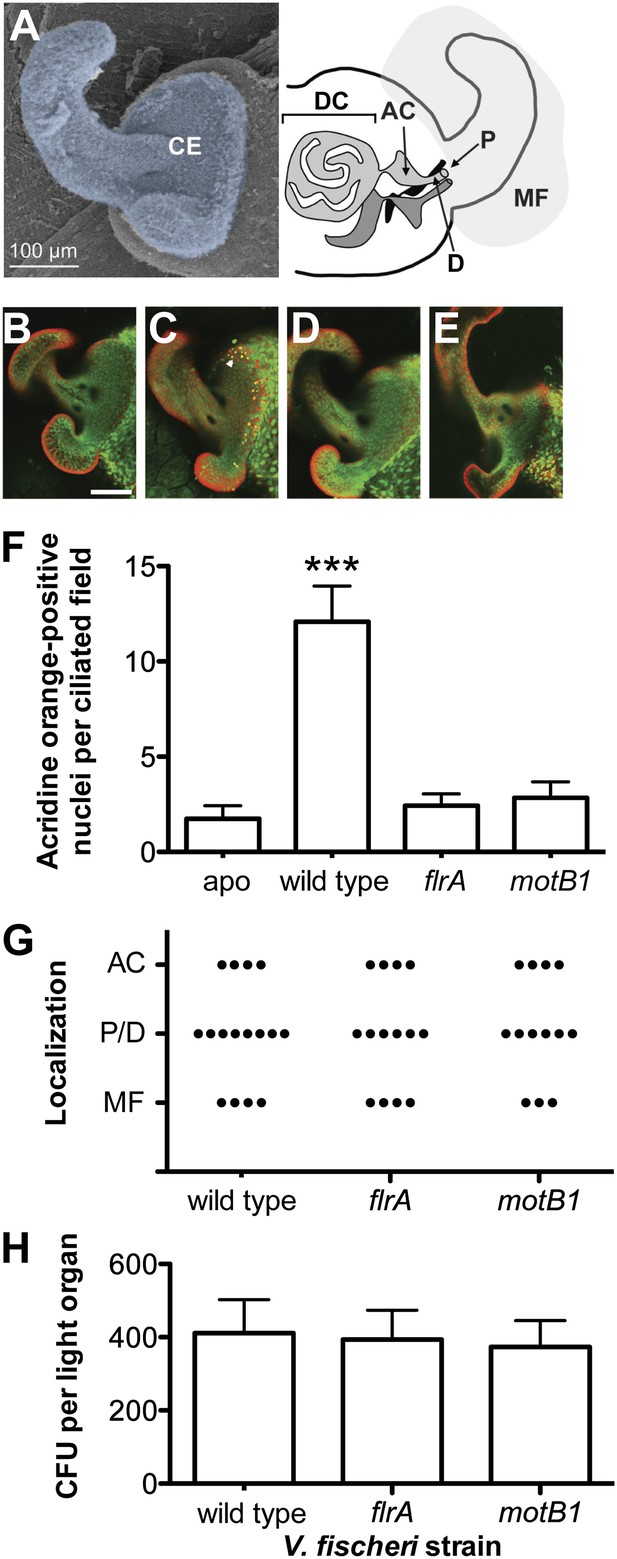
Motility mutants of V. fischeri do not induce early-stage apoptosis.
(A) Morphology of the juvenile light organ, highlighting the external ciliated epithelium (CE; false-colored blue) in a scanning electron micrograph (left), and the internal features with which the bacteria interact during initiation of symbiotic colonization in a schematic diagram (right). DC, deep crypts; AC, antechamber; D, duct; P, pore; and MF, mucus field. (B–E) Representative laser-scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM) images of acridine orange (AO)-stained juvenile light organs, after exposure to either: no V. fischeri (B, apo); wild type (C); flrA (D); or motB1 (E), as described in the ‘Materials and methods’. White arrowhead in (C) indicates one of the numerous AO-positive nuclei (yellow). Scale bar in (B) represents 100 μm for all the images. (F) Counts of AO-positive nuclei in the light-organ ciliated epithelium of squid exposed to either the indicated V. fischeri strains, or no V. fischeri (apo). (***), p<0.001 by Kruskal–Wallis Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), followed by Dunn’s Multiple Comparison test. The absence of apoptosis in the aposymbiotic squid confirms that the experimental addition of peptidoglycan (PGN) (‘Materials and methods’) is insufficient to induce AO staining. (G) Bacterial localization under conditions used for measurement of early-stage apoptosis (panel F). Localization was determined by examining squid exposed to the indicated strains, genetically labeled to express GFP, using LSCM. Each point represents the bacterial localization in a single light-organ lobe. (H) Level of colonization (colony-forming units, CFU) under conditions used for measurement of early-stage apoptosis (panel F). Light organs were dissected from anesthetized and pithed squid, and then homogenized and plated to determine symbiont number.
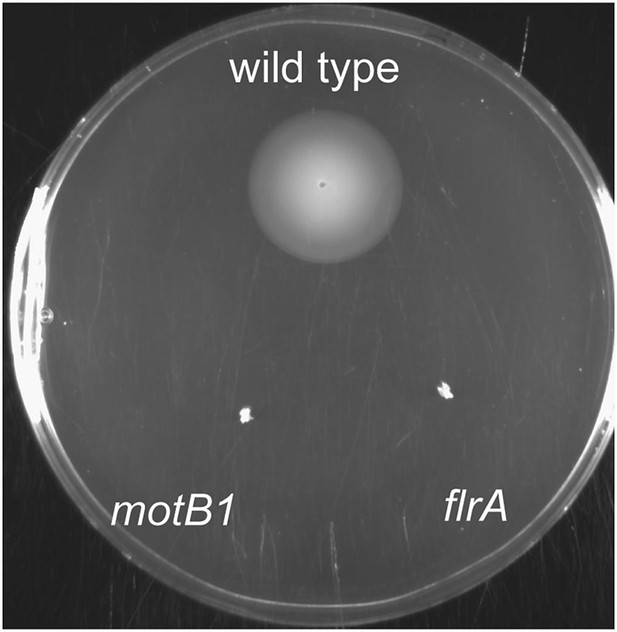
Soft-agar motility of wild-type, flrA and motB1 strains.
Wild-type, motB1 and flrA strains were grown to mid-log phase and inoculated into SWT medium supplemented with 0.3% agar. Plates were visualized after incubating for 11 hr at 28°C.
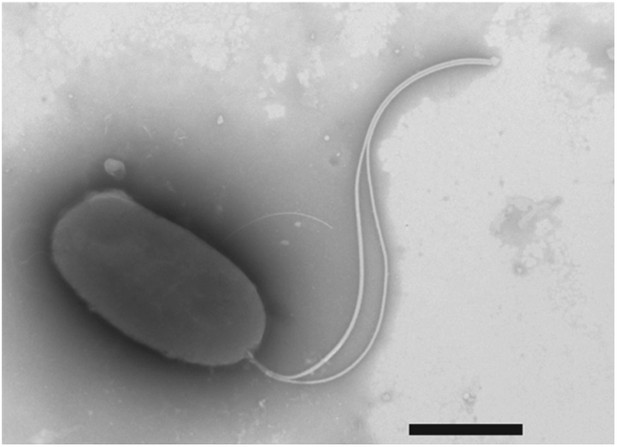
Negative-stain transmission electron micrograph of a representative flagellated motB1 cell.
The motB1 mutant was grown to mid-log phase in SWT broth, and visualized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) after negative-staining. Scale bar indicates 1 µm.
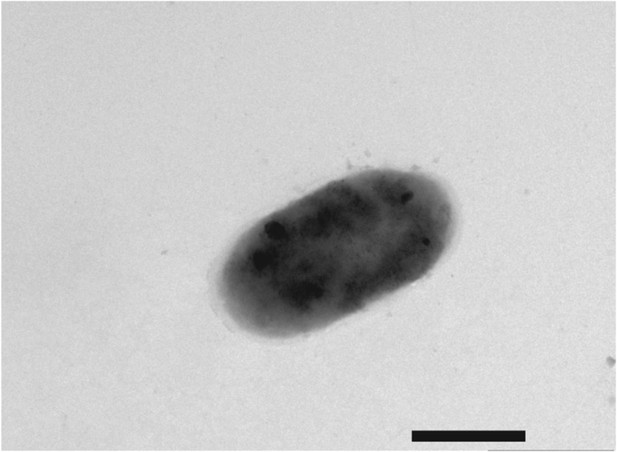
Negative-stain transmission electron micrograph of a representative aflagellate flrA cell.
The flrA mutant was grown to mid-log phase in SWT broth, and visualized by negative-stain TEM. Scale bar indicates 1 µm.
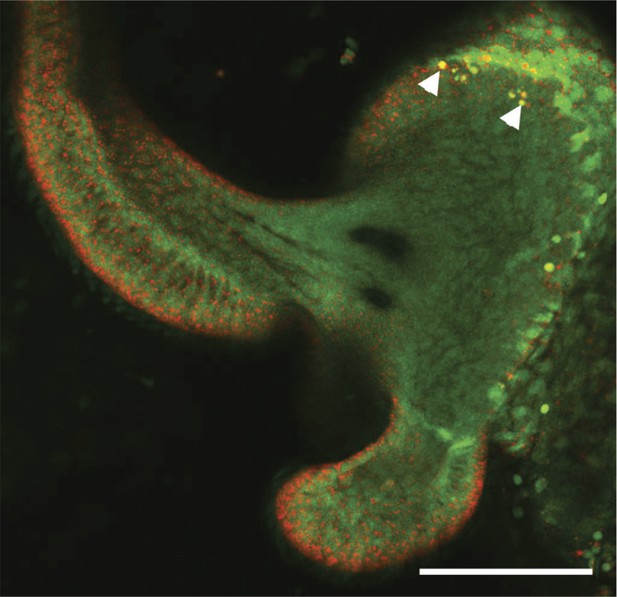
Representative LSCM image of an AO-stained light-organ lobe isolated from a squid treated with exogenous V. fischeri lipid A.
As described in the ‘Materials and methods’, squid were exposed for 10 hr to purified V. fischeri lipid A, then stained with acridine orange. White arrowheads indicate two of the AO-positive nuclei (yellow). Scale bar represents 100 μm.
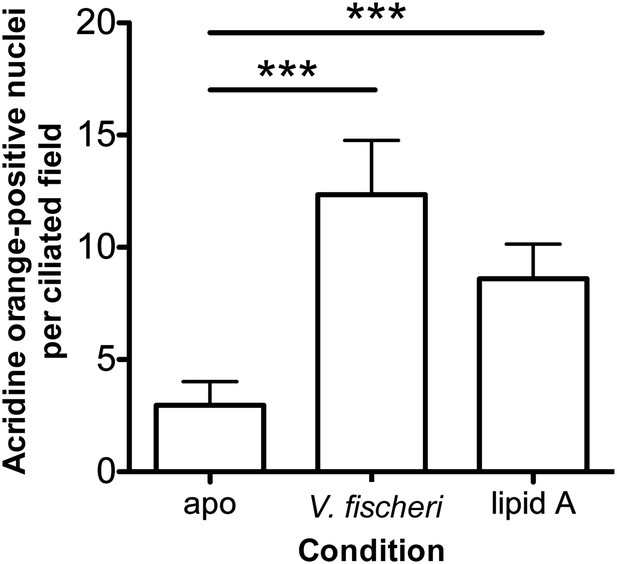
Induction of early-stage apoptosis in response to exogenous lipid A.
As described in the ‘Materials and methods’, squid were exposed for 10 hr to either no V. fischeri (apo), wild-type V. fischeri, or purified V. fischeri lipid A alone. Early-stage apoptosis was determined by counting the number of acridine orange (AO)-positive nuclei in the ciliated field of one lobe of the light organ. (***), p<0.001 by Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA, followed by Dunn's Multiple Comparison test.
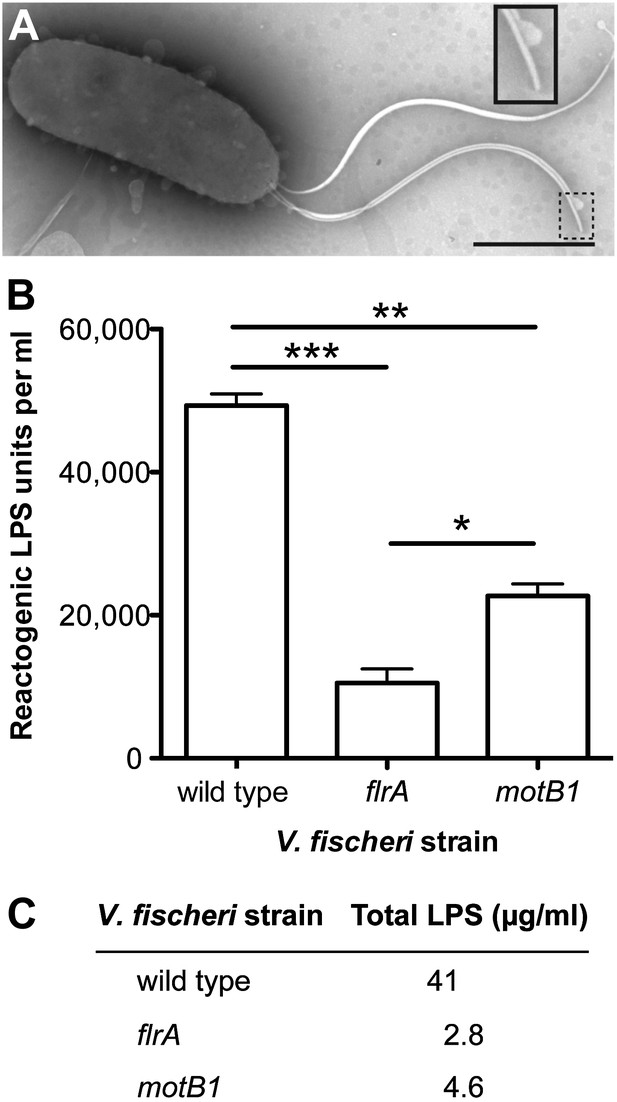
Motility mutants of V. fischeri release less LPS into culture supernatants.
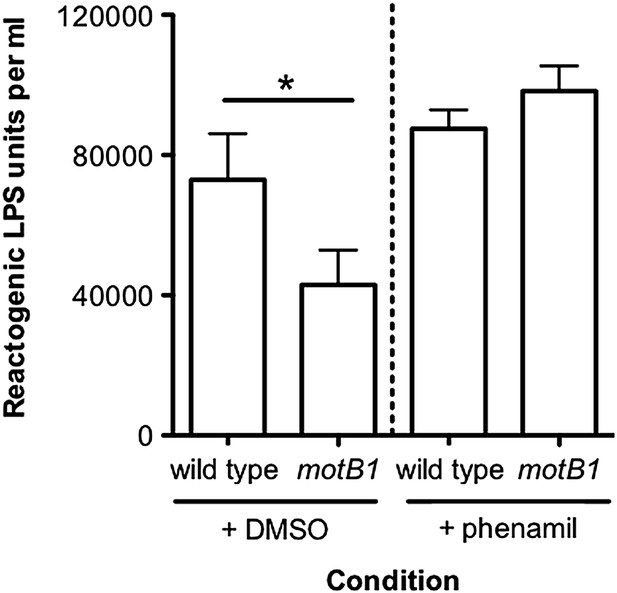
(A) Negative-stain TEM of a wild-type V. fischeri cell. Dashed box, shown larger within the solid box, highlights the distal tip of two flagella, one of which displays dissociation of the sheath from the filament in the form of a membrane vesicle-like structure. Scale bar indicates 1 μm. (B) Reactogenic LPS in cell-free supernatants of V. fischeri mid-log (OD600 ≈ 0.5) cultures grown in seawater tryptone (SWT) medium at 28°C was measured by LAL assay. (*), p<0.05; (**), p<0.01; and (***), p<0.001, as analyzed by one-way repeated measures ANOVA, with a posthoc Bonferroni correction. (C) Total LPS levels in cell-free supernatants from mid-log (OD600 ≈ 0.5) cultures grown in SWT at 28°C for indicated strains were determined by quantitative SDS-PAGE analysis (detailed in Figure 2—figure supplement 1).
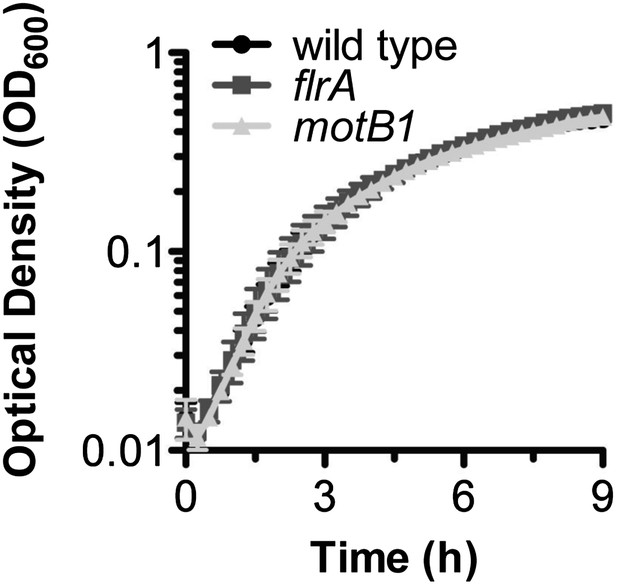
Growth of V. fischeri wild-type, motB1 and flrA strains.
Indicated strains were inoculated into SWT and grown at 28°C under microaerobic conditions.
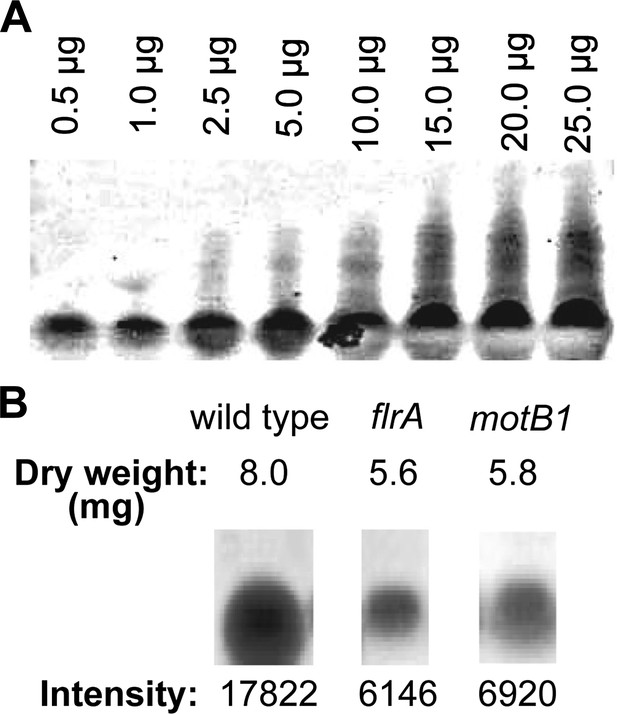
Quantification of total LPS in cell-free supernatants by SDS-PAGE analysis.
(A) Silver-stained gel image of purified V. fischeri LPS separated by SDS-PAGE used to generate a standard curve by densitometry. (B) Total dry weight following dialysis of 50 ml of cell-free supernatants of the indicated strains, and band intensity of 125 μg samples of the purified lipid fractions, visualized by silver staining after SDS-PAGE analysis. Image has been cropped to remove irrelevant lanes, but all samples were separated on the same gel.
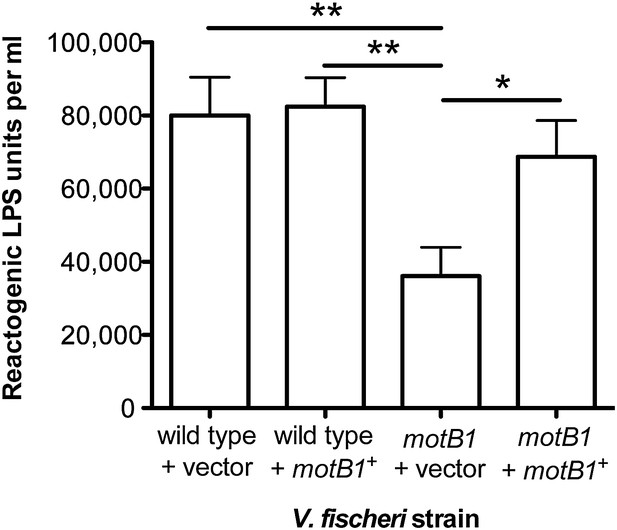
Genetic complementation restores supernatant LPS levels to the motB1 mutant strain.
Levels of reactogenic LPS in mid-log culture supernatants (OD600 ≈ 0.5) of indicated strains, as measured using the LAL assay. (*), p<0.05, and (**), p<0.01, as analyzed by one-way repeated measures ANOVA with a posthoc Bonferroni correction.
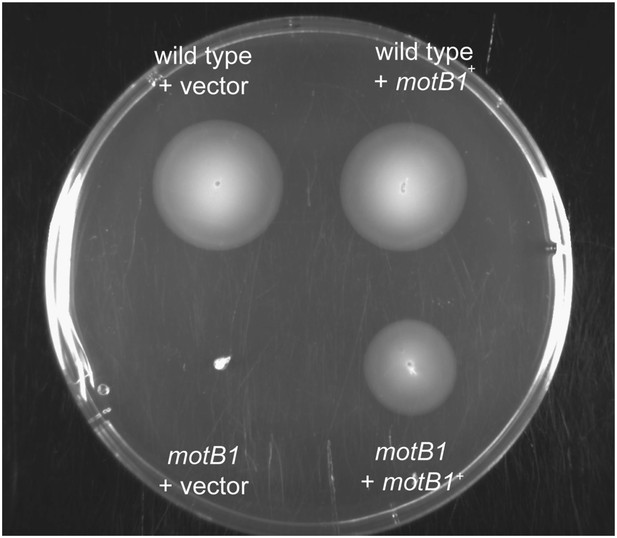
Soft-agar motility of genetically complemented motB1 strains.
Indicated strains were grown to mid-log phase and inoculated into SWT medium containing 0.3% agar. Plates were visualized after incubation for 11 hr at 28°C.
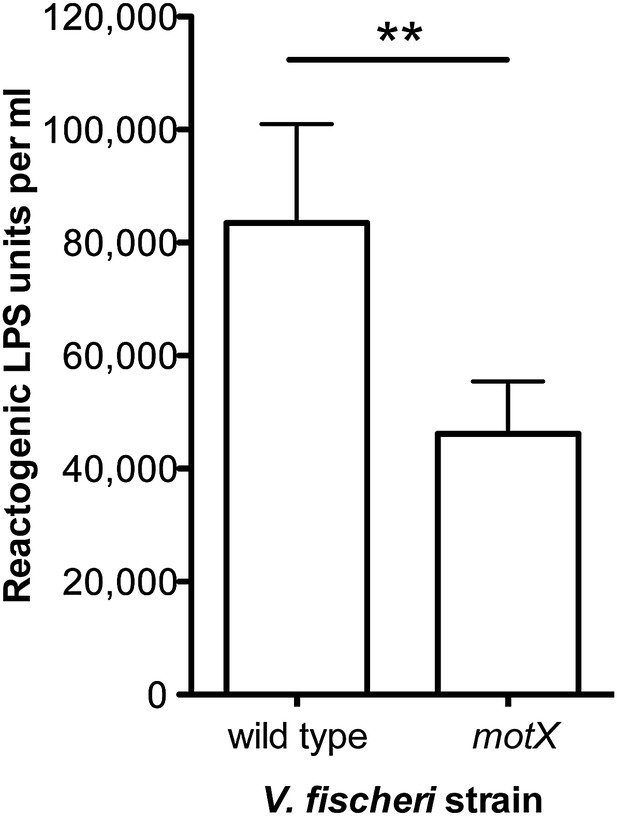
Disruption of motX in V. fischeri reduces supernatant LPS levels.
Levels of reactogenic LPS, as measured using the LAL assay, in cell-free supernatants of mid-log cultures (OD600 ≈ 0.5) of V. fischeri wild-type and motX strains. (**), p<0.01 as determined by paired Student’s t test.
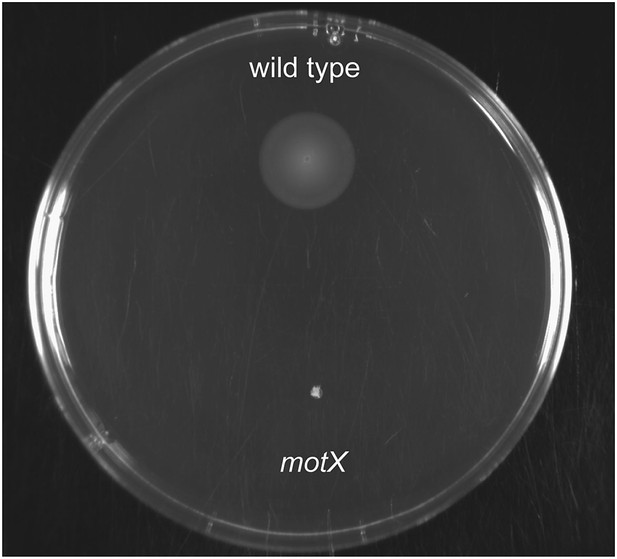
Soft-agar motility of V. fischeri motX mutant.
Wild-type and motX strains were grown to mid-log phase and inoculated into SWT medium containing 0.3% agar. Plates were visualized after incubating for 8 hr at 28°C.
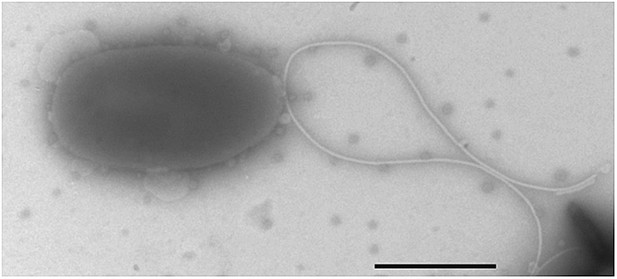
Negative-stain transmission electron micrograph of a representative motX cell.
The motX mutant was grown to mid-log phase in SWT broth, and visualized by negative-stain TEM, revealing normal sheathed flagella. Scale bar indicates 1 µm.
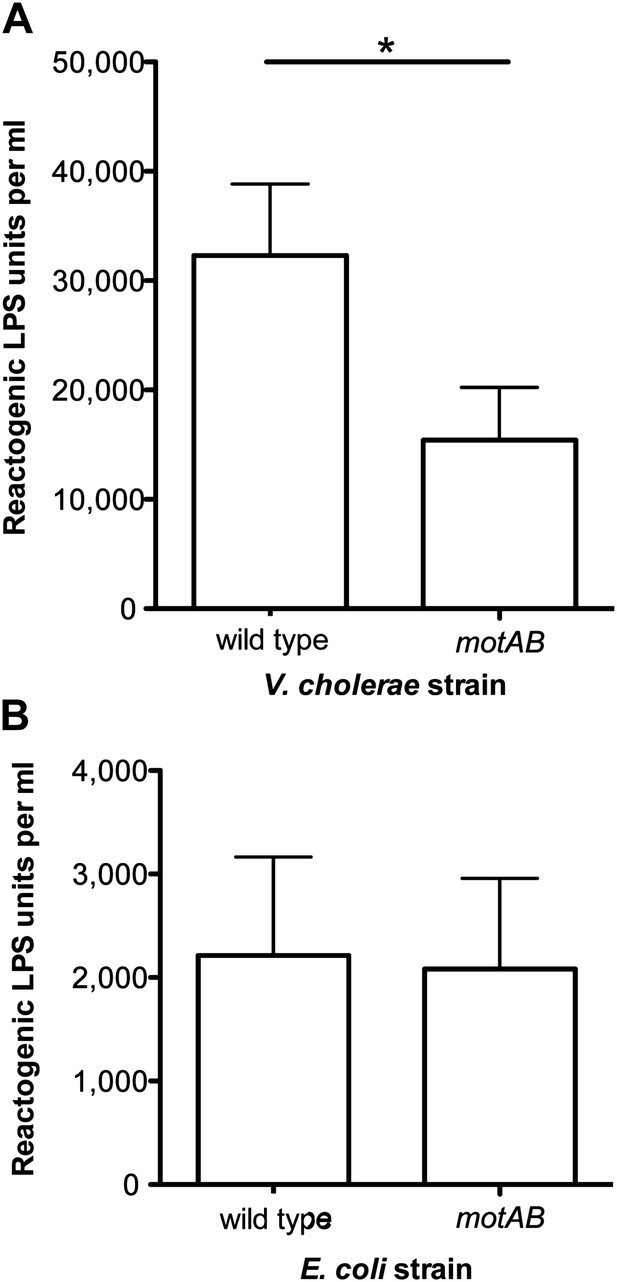
Loss of flagellar rotation reduces LPS release by sheathed V. cholerae, but not unsheathed E. coli.
(A) Reactogenic LPS released into mid-log (OD600 ≈ 0.5) culture supernatants by wild-type V. cholerae O395N1 and its motAB (i.e., pomAB) derivative, grown in SWT at 37°C, was measured by the LAL assay. (*), p<0.05 by paired Student’s t test. (B) Reactogenic LPS in mid-log (OD600 ≈ 0.5) culture supernatants of wild-type E. coli and its motAB derivative grown in tryptone medium at 30°C, as measured using the LAL assay.