SETD2 is required for DNA double-strand break repair and activation of the p53-mediated checkpoint
Figures
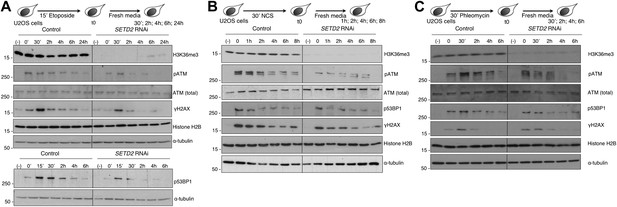
SETD2 is necessary for ATM activation during the DNA damage response.
Control and SETD2 RNAi-depleted U2OS cells were challenged with etoposide (A), NCS (B) or phleomycin (C) and chased in fresh media during the indicated time points. Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies against the indicated proteins. Molecular weight markers (KDa) are shown on the left of each blot. Data are from one representative experiment of at least three independent experiments performed with similar results.
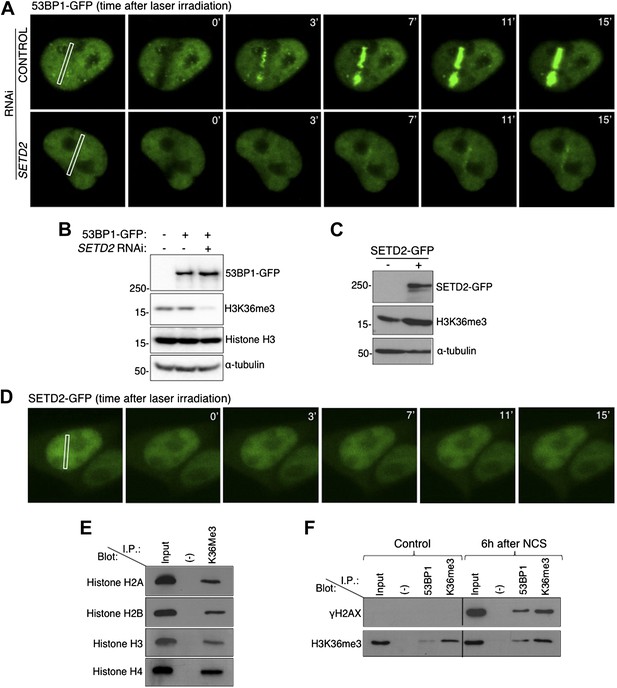
SETD2 promotes 53BP1 recruitment to DNA damage sites.
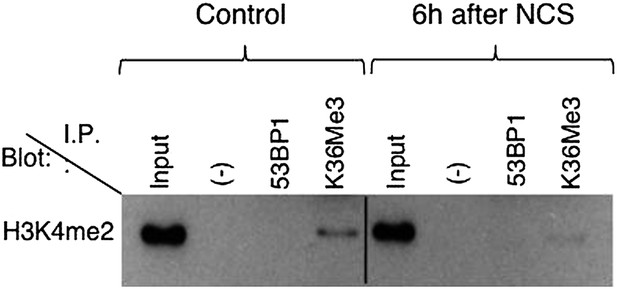
(A) 53BP1-GFP transfected U2OS cells were damaged by laser irradiation of the indicated nuclear region. The dynamics of 53BP1-GFP during the DNA damage response on control and SETD2-depleted cells was monitored by live cell imaging for 15 min after laser irradiation. One representative experiment from over 50 individual cells recorded is shown. (B) Control and SETD2 RNAi-depleted U2OS cells were transfected with a 53BP1-GFP expression plasmid. Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies against GFP (to detect 53BP1-GFP), H3K36me3, total histone H3, and α-tubulin. Molecular weight markers (KDa) are shown on the left. (C) SETD2-GFP transfected U2OS cells were lysed and processed for western blot with antibodies against GFP (to reveal SETD2-GFP), H3K36me3 and α-tubulin. Molecular weight markers (KDa) are shown on the left. (D) Live-cell images of SETD2-GFP dynamics were recorded upon laser-induced DNA damage of the indicated nuclear region of U2OS cells during 15 min (E) H3K36me3 was immunoprecipitated from MNase-digested U2OS cell extracts and each of the four nucleosomal histones was detected by immunoblotting of the SDS-PAGE resolved complexes. (F) Nuclear co-immunoprecipitations before and 6 hr after NCS treatment were performed on U2OS cells using the indicated antibodies (I.P.: 53BP1 and H3K36me3). The Input lane represents total cell lysates and (−) denotes the negative control immunoprecipitation (beads only). Purified complexes were resolved by SDS-PAGE and blotted with antibodies against γH2AX or H3K36me3.
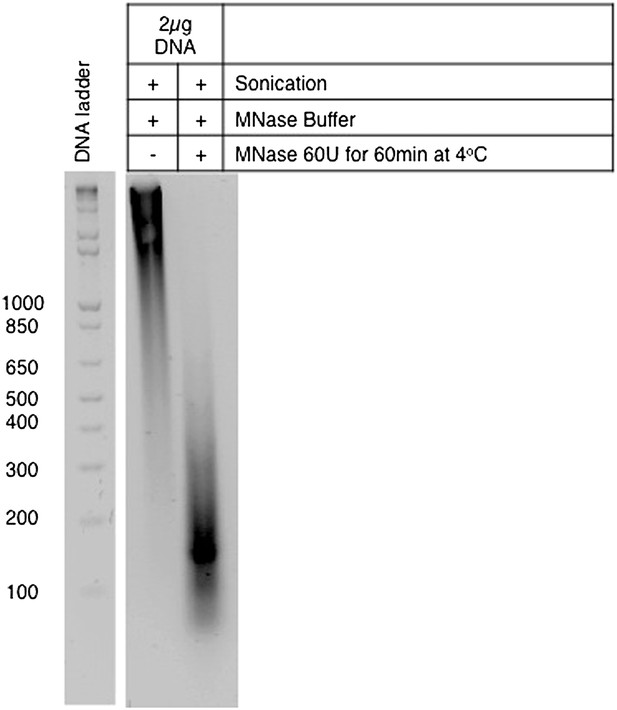

Preparation of single-nucleosome extracts for the co-immunoprecipitation experiments.
DNA was purified from MNase-digested samples and resolved on a 1.8% agarose gel. The length of the DNA fragments is indicated on the left.
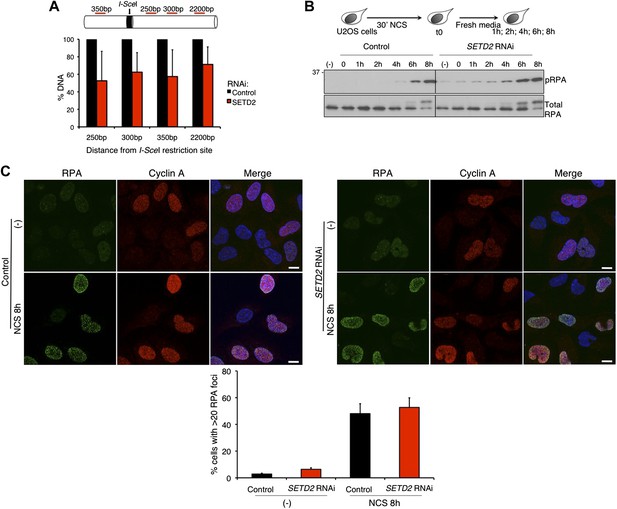
SETD2-independent DNA 5′ end resection and RPA recruitment to DSBs.
(A) Direct measurement of DNA 5′ end resection at the I-SceI site of the GFP gene in control and SETD2-depleted U2OS DR-GFP cells. The percentage of non-resected DNA at 250 bp, 300 bp, 350 bp, and 2200 bp from the I-SceI restriction site is shown. The percentage of DNA at each location was set to 100% in control cells. Means and standard deviations from five independent experiments using two distinct siRNAs targeting SETD2 are shown. (B) Control and SETD2 RNAi-depleted U2OS cells were challenged with NCS during 30 min and chased in fresh media during the indicated time points. Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies against pRPA and total RPA. Molecular weight markers (KDa) are shown on the left. (C) Immunofluorescence of control and SETD2 RNAi depleted U2OS cells before and 8 hr after NCS treatment was performed with antibodies against RPA and cyclin A. Dapi was added to the mounting medium to stain the DNA. Scale bars: 5 μm. The graph shows the percentage of cells with more than 20 RPA foci. A minimum of 400 cells on each of three independent experiments was scored.
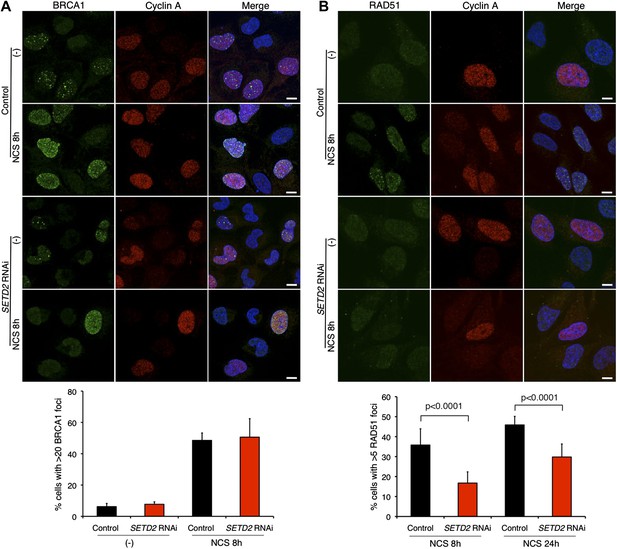
SETD2 promotes RAD51 recruitment to DSBs during DNA repair.
Immunofluorescence of control and SETD2 RNAi-depleted U2OS cells before and 8 hr after NCS treatment was performed with antibodies against BRCA1 (A) or RAD51 (B). Cyclin A staining was performed in parallel. Dapi was added to the mounting medium to stain the DNA. Scale bars: 5 μm. The graphs represent the average and standard deviations of the percentage of cells with BRCA1 or RAD51 foci after NCS treatment. A minimum of 500 cells from each of three individual experiments was scored for each experimental condition.
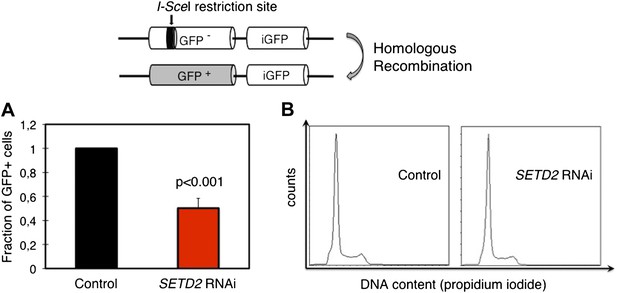
SETD2 is required for homologous recombination DNA repair.
(A) The efficiency of homologous recombination in control and SETD2 RNAi-depleted cells was investigated by measuring the fraction of GFP + cells in the U2OS DR-GFP reporter assay. Means and standard deviations from five independent experiments using two distinct siRNAs targeting SETD2 are shown. (B) Cell cycle progression of control and SETD2-depleted U2OS DR-GFP cells was obtained by flow cytometry analysis of propidium iodide staining.
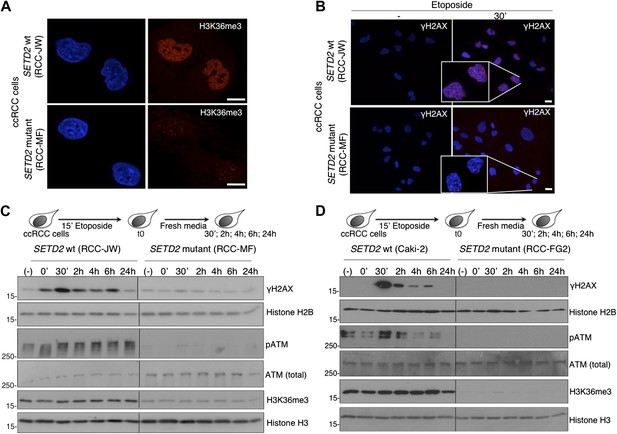
ccRCC cells with inactivating mutations on SETD2 show impaired DNA damage signalling.
The H3K36me3 levels of SETD2 wt and mutant ccRCC cells were inspected with an antibody against H3K36me3 by immunofluorescence (A). (B) Immunofluorescence of SETD2 wt and mutant ccRCC cells before and 30 min after etoposide treatment for 15 min was performed with an antibody against γH2AX. Dapi was added to the mounting medium to stain the DNA. Scale bars: 5 μm. (C and D) Two SETD2 wt (RCC-JW and Caki-2) and two SETD2 mutant (RCC-MF and RCC-FG2) cell lines were challenged with etoposide during 15 min and chased in fresh media during the indicated time points. Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies against the indicated proteins. Molecular weight markers (KDa) are shown on the left.
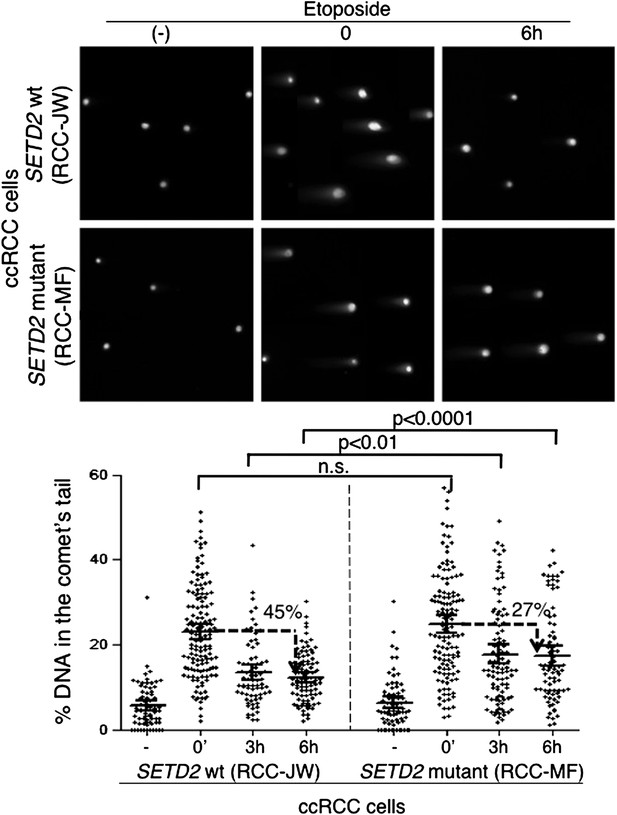
Repair of double-strand breaks is compromised in SETD2 mutant ccRCC cells.
The amount of DNA damage immediately after induction of DSBs with etoposide and 3 and 6 hr after treatment was estimated by comet assay on SETD2 wt and mutant ccRCC cells. Graphs depict the % of DNA in the tail of each individual comet. The horizontal solid lines represent the mean and 95% confidence intervals. At least 70 individual comets were analyzed for each time point.
Repair of double-strand breaks in SETD2 wt and mutant ccRCC cells.
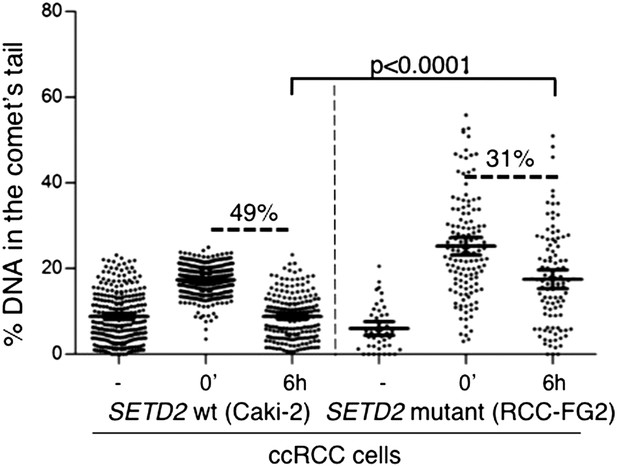
The amount of DNA damage 6 hr after etoposide treatment was estimated by comet assay on an additional pair of SETD2 wt (Caki-2) and mutant (RCC-FG2) cells. Graphs depict the % of DNA in the tail of each individual comet. The horizontal solid lines represent the mean and 95% confidence intervals.
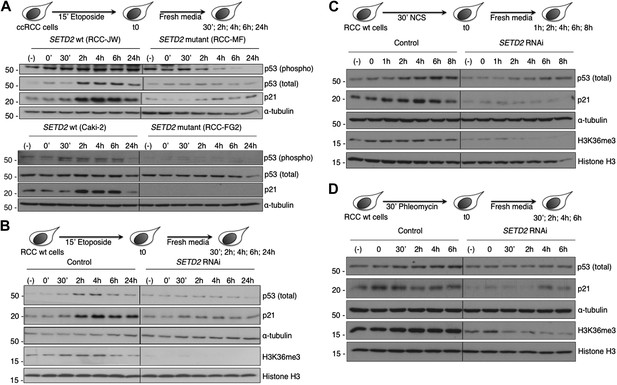
SETD2 is required for p53 activation following DNA damage.
(A) SETD2 wt and mutant ccRCC cells were challenged with etoposide during 15 min and chased in fresh media during the indicated time points. Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies against the proteins indicated on the right. SETD2 wt ccRCC cells were depleted for SETD2 by RNAi, treated with etoposide (B), NCS (C) or phleomycin (D) during the indicated periods of time and chased in fresh media. Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies against the proteins indicated on the right. Molecular weight markers (KDa) are shown on the left. Data are from one representative experiments of a total of three independent experiments performed with similar results.
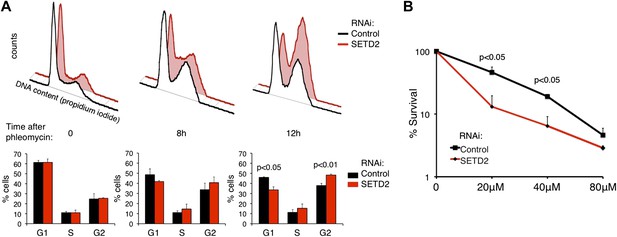
SETD2 regulates the p53-dependent cell-cycle checkpoint and cell survival following DNA damage.
(A) Control and SETD2 RNAi-depleted cells were treated with 40 μM of phleomycin to induce cell-cycle checkpoints. Cells were harvested at 0, 8, or 12 hr after treatment, fixed and stained with propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Graphs show means and standard deviations of the percentage of cells at each phase of the cell cycle. Data are from four individual experiments. (B) Control and SETD2 RNAi-depleted cells were treated with phleomycin at indicated concentrations and clonogenic survival was measured 10 days after treatment. Means and standard deviations from 6 individual cell cultures treated with each drug concentration are shown.
Tables
Sequence of primers used in this study
| Gene Name | Primer designation | Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| I-SceI Flank | Flank_Fw | GAG CAG GAA CCT GAG GAG |
| Flank_Rv | GCC GTA GGT ATT ACC CTG | |
| I-SceI 250bp | 250bp_Fw | CAT GCC CGA AGG CTA CGT |
| 250bp_Rv | CGG CGC GGG TCT TGT A | |
| I-SceI 300bp | 300bp_Fw | CTT CTT CAA GGA CGA CGG C |
| 300bp_Rv | GTA GTT GTA CTC CAG CTT GTG | |
| I-SceI 350bp | 350bp_Fw | CTA CAG CTC CTG GGC AAC |
| 350bp_Rv | CTT CGG CAC CTT TCT CTT C | |
| I-SceI 2200bp | 2200bp_Fw | CGC GAC GTC TGT CGA GAA G |
| 2200bp_Rv | GCC GAT GCA AAG TGC CGA TA | |
| GAPDH | GAPDH_Fw | GAA GGT GGA GGT CGG AGT C |
| GAPDH_Rv | GAA GAT GGT GAT GGG ATT TC |