Hidden synaptic differences in a neural circuit underlie differential behavioral susceptibility to a neural injury
Figures
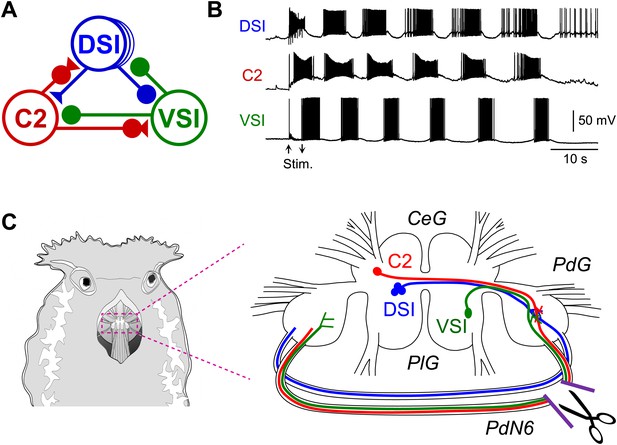
The Tritonia swim central pattern generator.
(A) A schematic diagram of the swim central pattern generator (CPG). The CPG consists of three types of interneurons: C2, cerebral cell 2; DSI, dorsal swim interneuron; VSI, ventral swim interneuron. Based on Getting et al. (1980) and Getting (1983a, 1983b). All neurons are electrically coupled to contralateral counterparts, which are not represented here. There are three DSIs, but C2 and VSI are individual neurons. Filled triangles represent excitatory synapses and filled circles represent inhibitory synapses. Combinations of triangles and circles are multi-component synapses. (B) An example of the swim motor pattern recorded from an isolated brain preparation. Simultaneous intracellular recordings from the three CPG neurons are shown. The bursting pattern was elicited by electrical stimulation of the left body wall nerve, pedal nerve 3 (cf., Figure 3A), using voltage pulses (8 V, 1 ms) at 5 Hz for 3 s. Arrows show onset and offset of the nerve stimulation. (C) The Tritonia brain and the site where PdN6 was cut in vivo. The body wall above the buccal mass was cut open (left). A schematic drawing shows a dorsal view of the Tritonia brain (right) with the locations of the interneurons and their axonal projections. DSI and C2 are located on the dorsal surface of the cerebral ganglion (CeG). VSI is located on the ventral side of the pleural ganglion (PlG). C2 and VSI project axons through the Pedal commissure (PdN6), which connects the two pedal ganglia (PdG) (Sakurai and Katz, 2009b). PdN6 was transected near the right pedal ganglion with scissors.
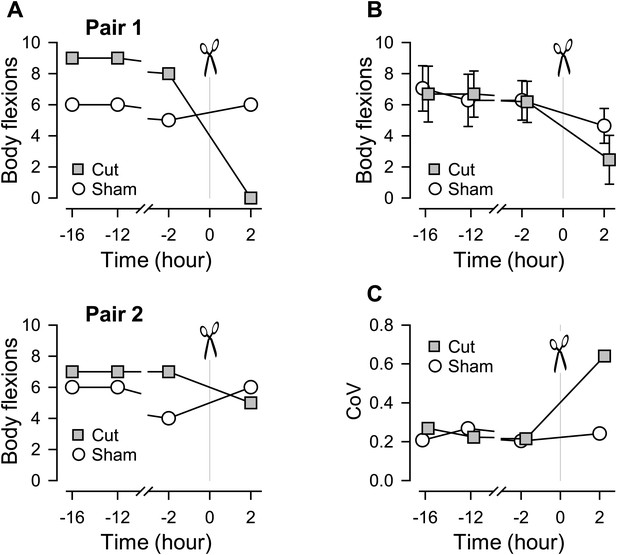
Individual variability in the extent of swim impairment by a lesion.
(A) Nerve-transected animals were blindly paired with sham-operated animals. Two examples (Pair 1 and Pair 2) show different effects on the number of body flexions during the escape swim behavior for animals in response to PdN6 transection (gray squares) compared to sham-operated controls (white circles). In one animal, cutting PdN6 caused a large decrease in the number of body flexions compared to sham (Pair 1), whereas the same lesion caused a small decrease in other experimental preparation (Pair 2). (B) Mean number of body flexions during the escape swim behavior for animals with PdN6 transected (gray squares) and sham-operated controls (white circles). The surgery caused a significant decrease in the number of flexions in both cut and sham animals (cut animals, F(3,30) = 21.0, p< 0.001, N = 11; sham animals, F(3,30) = 7.47, p< 0.001, N = 11 by One-way Repeated Measures ANOVA). A two-way repeated measures ANOVA with post-hoc pairwise comparison revealed a significant difference in the number of flexions between cut and sham animals 2 hr after the surgery (p<0.001). Prior to the cut, there was no significant difference between the test and sham-operated animals in the number of flexions (16 hr, p = 0.57; −12 hr, p = 0.52; −2hr, p = 0.89). (C) The coefficient of variance (CoV) of the number of body flexions for the transected animals (gray squares) showed a threefold increase after the cut, but only a slight increase in sham-operated animals (white circles). There is a significant difference in variance between the cut group and the sham group after the surgery (by Levene median test, N = 19).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.005
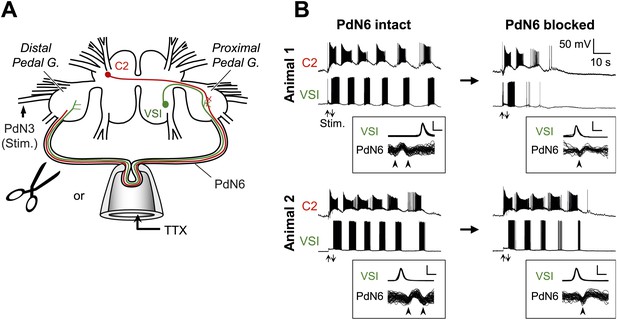
Individuals differed in the extent of motor pattern impairment by disconnection of PdN6.
(A) A schematic drawing of the Tritonia brain showing how axonal impulse propagation was blocked in PdN6 either by delivering TTX (1 × 10−4M) into a suction pipette or by physical transection. The stimulus was delivered to the left pedal nerve 3 (PdN3). The pedal ganglion closer to the VSI cell body was called the proximal pedal ganglion whereas the other pedal ganglion was called the distal pedal ganglion. (B) Simultaneous intracellular recordings from C2 and VSI from two representative animals (Animals 1 and 2). Arrows (Stim) indicate the time of PdN3 stimulation. Animal 1 showed a large decrease (from 6 to 2) in the number of VSI bursts after PdN6 was blocked, whereas in Animal 2 the number of VSI bursts was less affected (from 6 to 5). The boxed insets show overlaid traces of VSI spikes recorded from the soma and the corresponding axonal impulses recorded from PdN6 with an en passant suction electrode during the swim motor program. The traces were triggered at the peak of the somatic action potential and overlaid. The shapes of the impulses show that the action potentials were blocked (see text for explanation). Calibration: 50 mV, 10 ms.
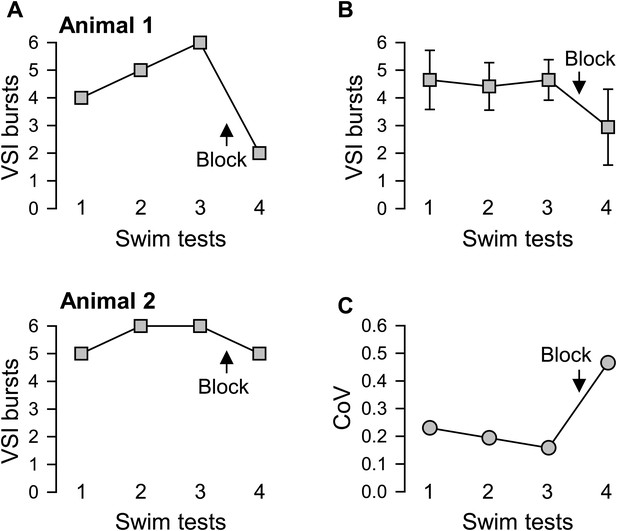
Individual variability in the extent of motor pattern impairment by disconnection of PdN6.
(A) The number of VSI bursts per swim motor pattern episode recorded from Animal 1 was more affected by blocking PdN6 than that from Animal 2 (same individuals as in Figure 3B). The swim motor pattern was evoked 3 or 4 times at constant intervals (approximately 10 min), and PdN6 was blocked between the last two swim motor pattern bouts. (B) The average number of the VSI bursts decreased significantly after PdN6 block (p<0.001 by one-way repeated measures ANOVA, N = 34). Post-hoc pairwise comparisons (Tukey test) show significant differences of the 4th swim test from all other swim tests. (C) The coefficient of variance (CoV) of the number of bursts increased after PdN6 block. There is a significant increase in variance in the number of VSI bursts after PdN6 disconnection (p<0.05 by Levene median test, N = 34).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.008
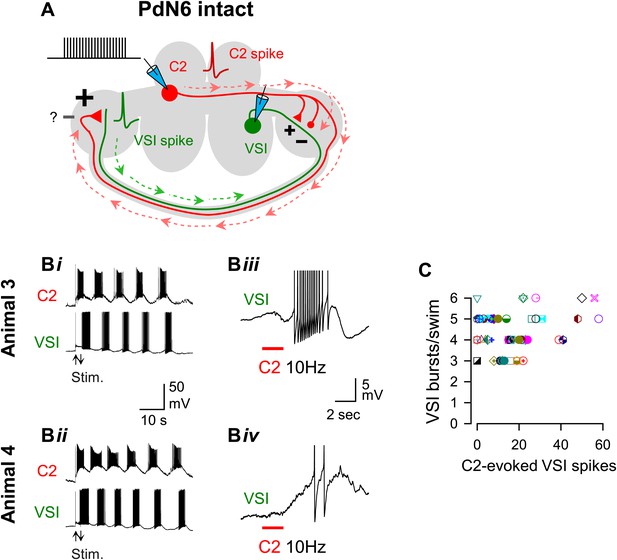
The extent of motor impairment showed little or no correlation with the C2-evoked VSI spiking recorded before blocking PdN6.
(A) A schematic illustration showing the stimulus (C2) and recording (VSI) microelectrodes, the direction of action potential propagation (dashed arrows) in C2 and VSI, and synaptic action (+, excitatory; −, inhibitory) of C2 onto VSI before blocking PdN6. Repetitive square current pulses (10 nA, 20 ms) were injected into the C2 soma to evoke a train of action potentials at a constant frequency (10 Hz). (B) Two examples of swim motor patterns (Bi, Bii) and the membrane potential responses (Biii, Biv) of VSI to C2 stimulation are shown for two animals (Animals 3 and 4). With PdN6 intact, Animal 3 showed five VSI bursts (Bi) and Animal 4 had six VSI bursts (Bii). The effect of C2 stimulation on VSI varied among individuals; causing an intense burst in VSI of Animal 3 (Biii) but only two spikes in Animal 4 (Biv). VSI exhibited antidromic spikes in the majority of preparations (see text) that were presumably caused by the C2 excitatory action in the distal terminal of VSI (Sakurai and Katz, 2009b). In Biii and Biv action potentials are truncated to show underlying membrane potential. (C) No correlation was detected between the number of VSI bursts per swim episode and the number of C2-evoked VSI spikes with PdN6 intact (R2 = 0.05, p = 0.10 by linear regression, N = 52). Graph symbols in this and Figures 6 and 7 each represent data from the same individuals.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for panel C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.010
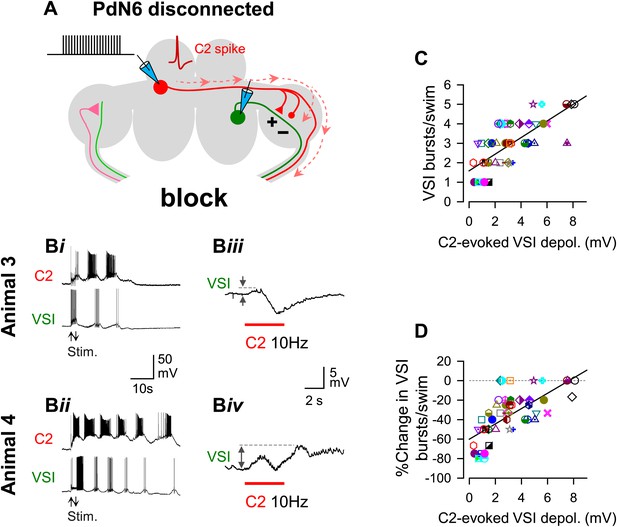
The extent of motor impairment showed a strong correlation with C2-evoked VSI depolarization recorded after blocking PdN6.
(A) A schematic illustration showing the stimulus (C2) and recording (VSI) microelectrodes, the direction of action potential propagation (dashed arrows) in C2, and synaptic action (+, excitatory; -, inhibitory) after blocking PdN6. (B) Two examples (Animals 3 and 4) of swim motor patterns (Bi, Bii) and the membrane potential responses (Biii, Biv) of VSI to C2 stimulation are shown after blocking PdN6. Animal 3 and 4 are the same animals as in Figure 5B. The effects of blocking PdN6 on the swim motor pattern were different: Animal 3 showed 40% reduction (5 to 3) in the number of VSI bursts (Bi), whereas Animal 4 showed a 16.7% reduction (6 to 5) (Bii). With PdN6 blocked, C2 stimulation (10 Hz, 4 s) no longer caused VSI to spike in either animal, but instead evoked a complex membrane potential change consisting of both depolarization and hyperpolarization (Biii, Biv). (C) After PdN6 disconnection, there was a significant correlation between the number of VSI bursts per swim episode and the amplitude of the C2-evoked VSI depolarization (R2 = 0.53, p< 0.001 by linear regression, N = 50). (D) The percent change in the number of VSI bursts caused by PdN6 disconnection showed a significant correlation with the amplitude of the C2-evoked depolarization in VSI (p<0.001 by linear regression, R2 = 0.47, p<0.001, N = 50).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Source data for panels C and D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.012
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Source data for figure supplement 1 panel B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.013
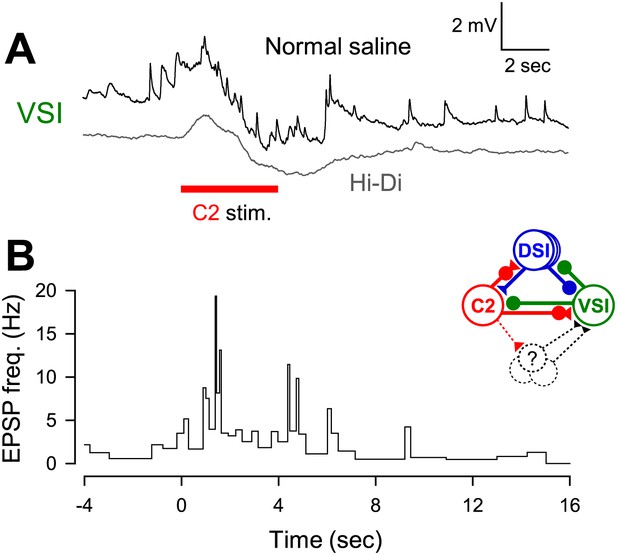
C2 recruited unidentified neurons to excite VSI.
(A) C2 stimulation caused a bombardment of small EPSPs that lasted longer than the duration of stimulation (black trace). Recruitment of these polysynaptic EPSPs was minimized by superfusion of high-divalent cation (Hi-Di) saline (gray trace). Positions of the two traces were offset for visualization. (B) A graph showing that C2 stimulation increased the instantaneous frequency of the recruited EPSPs in VSI. Inset diagram shows C2-evoked polysynaptic recruitment of unidentified neurons making excitatory synapses onto VSI.
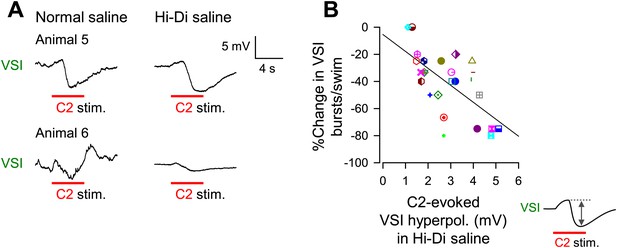
The extent of motor impairment correlated with the inhibitory component of C2-to-VSI synapse.
(A) Two examples (Animals 5 and 6) of VSI membrane potential responses to C2 stimulation recorded with PdN6 disconnected in normal saline (left) and in high divalent cation (Hi-Di) saline (right) to decrease the contribution of polysynaptic inputs. (B) The impairment, measured as the percent change in the number of VSI bursts, showed a significant correlation with the amplitude of the hyperpolarization phase (R2 = 0.44, p<0.001 by linear regression, N = 26) of the C2-evoked synaptic potential in VSI.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Source data for panel B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.016
-
Figure 7—source data 2
Source data for figure supplement 1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.017
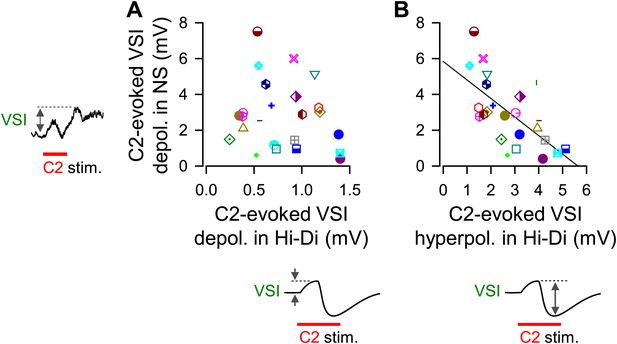
The magnitude of C2-evoked depolarization in VSI in normal saline correlated with the amplitude of hyperpolarizing phase of C2-to-VSI synaptic potential.
The magnitude of C2-evoked VSI depolarization in normal saline did not correlate to the direct C2-evoked depolarization measured in Hi-Di saline (A, R2 = 0.04, p=0.37 by linear regression, N = 24), but did correlate with the C2-evoked hyperpolarization (B, R2 = 0.43, p<0.001 by linear regression, N = 24).
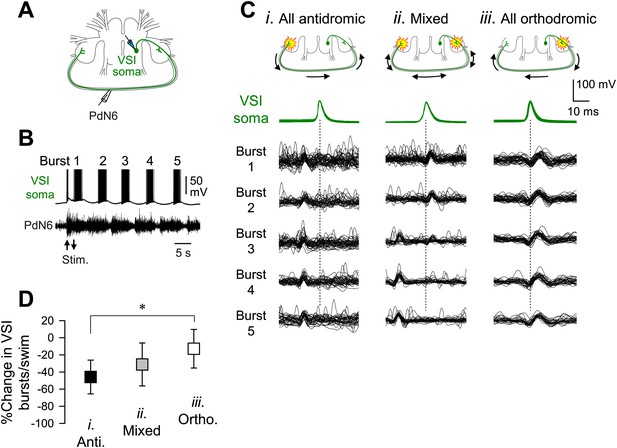
The direction of spike propagation in VSI axon was predictive of susceptibility of the swim motor pattern to PdN6 disconnection.
(A) A schematic diagram showing the recording configuration. VSI action potentials were recorded with an intracellular microelectrode in the soma and an extracellular en passant suction electrode on PdN6. To initiate a swim motor pattern, the left PdN3 was stimulated via a suction electrode (see Figure 3A). (B) Intracellular activity recorded from VSI and the axonal impulses recorded extracellularly from PdN6 during a swim motor pattern. Arrows indicate the time of PdN3 stimulation to initiate the swim program. Each VSI burst is indicated by a number (1–5). (C) Overlaid spike-triggered impulses for each burst recorded from PdN6 in three individuals show variability in the direction of VSI spike propagation (Ci, antidromic; Cii, mixed; Ciii, orthodromic). Schematic drawings above the traces show the presumptive spike-initiation zones (yellow explosion symbols) and the direction of action potential propagation (arrows) in the VSI axons. In Ci, all five bursts in the swim program consisted of antidromic VSI spikes (the nerve impulse appearing earlier than the soma spike), whereas in Cii, VSI spike propagation shifted from orthodromic to antidromic during the course of the swim motor pattern. In Ciii, all VSI spikes were evoked near the soma and propagated orthodromically. Traces in Cii were reused from Sakurai and Katz (2009b). (D) The direction of VSI spike propagation in PdN6 was predictive of the extent of impairment after PdN disconnection. The extent of impairment by PdN6 disconnection, shown as the percent change in the number of VSI bursts per swim episode, is plotted in three groups categorized by the direction of VSI spike propagations (black, all VSI bursts were antidromic; gray, mixed; white, all bursts were orthodromic). One-way ANOVA with a post-hoc pairwise comparison (Holm-Sidak method) revealed that individuals exhibiting only orthodromic VSI bursts were significantly less impaired than those with only antidromic VSI bursts as indicated by an asterisk (F(2,66) = 4.64, p = 0.015, N = 5 and 16).
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Source data for panel D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.020
-
Figure 8—source data 2
Source data for figure supplement 1 panels B and C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.021
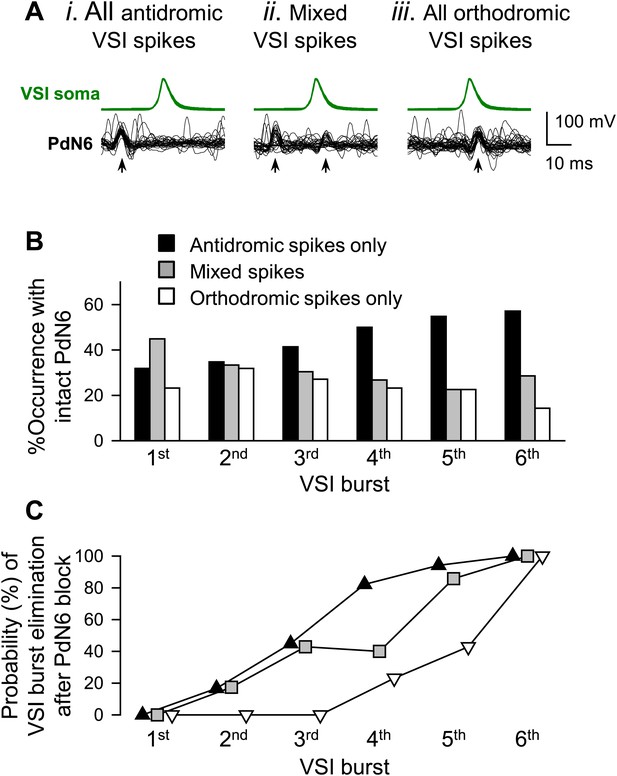
Inter- and intra-individual variation in the direction of VSI spike propagation during the swim motor pattern.
(A) Individual bursts were categorized into three groups: (i) burst with all antidromic spikes, (ii) burst with mixture of antidromic and orthodromic spikes, and (iii) burst with all orthodromic spikes. (B) More individuals showed antidromic VSI bursts later in the swim motor pattern. For each VSI burst (1st through 6th), bars represent the percentages of individuals before PdN6 disconnection that exhibited bursts with only antidromic spikes (black), mixed spikes (gray), and only orthodromic spikes (white). The 1st burst, N = 69; the 2nd burst, N = 69; the 3rd burst, N = 69; the 4th burst, N = 56; the 5th burst, N = 31; the 6th burst, N = 7. (C) After disconnecting PdN6, the swim motor pattern was more likely to be terminated at the VSI burst that had consisted of antidromic spikes. The graph shows the probability of elimination of each VSI burst (from 1st to 6th) for the three VSI burst types with PdN6 intact. For example, if the 4th burst consisted of all antidromic VSI spikes (black triangles), then 82% of animals lost that burst after PdN6 disconnection, causing the swim motor pattern to be less than four bursts. In contrast, only 23% of animals lost the 4th burst if it had consisted of all orthodromic spikes (white triangles) prior to PdN6 disconnection or 40% if it consisted of mixed spikes (gray boxes).
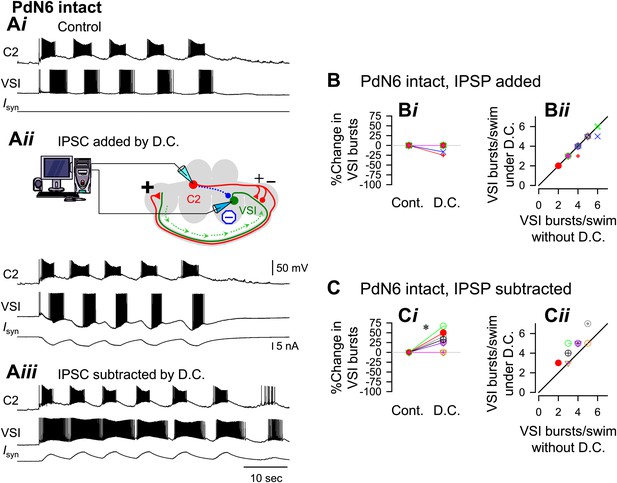
An artificial synaptic conductance created a hidden circuit change that caused no motor impairment with PdN6 intact.
A) Recordings of a five-cycle swim motor pattern with PdN6 intact (Ai). Introduction of an artificial synaptic conductance from C2 to VSI using dynamic clamp (D.C.) had no effect on the number of VSI bursts (Aii). The artificial synapse is represented as a dotted blue line with a filled blue circle in the schematic. VSI displayed unnaturally large hyperpolarizations on each burst because the currents were injected at the site of the electrode impalement in the soma instead of occurring in the neuropil. The spikes rode on the hyperpolarizing phase of the burst, indicating that they were antidromic spikes, generated in the distal pedal ganglion (green arrows in schematic). When the inhibitory synaptic conductances were subtracted by applying negative conductances of the same amount as in Aii, the number of bursts increased (Aiii). B, With PdN6 intact, addition of synaptic inhibition with dynamic clamp (D.C.) did not change the number of VSI bursts compared to control (Cont) (Bi, p = 0.16 by paired t-test, N = 18). A plot of the number of bursts under dynamic clamp vs the number of bursts without dynamic clamp has a slope close to one (Bii). C, With PdN6 intact, subtraction of synaptic inhibition significantly increased the number of VSI bursts 26.6% compared to control. (p = 0.01 by paired t-test, N = 9) (Ci). All of the preparations either produced the same number of bursts or increased by up to 2 bursts (Cii). Graph symbols in Figures 9 and 10 each represent data from same specimens.
-
Figure 9—source data 1
Source data for panels B and C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.024
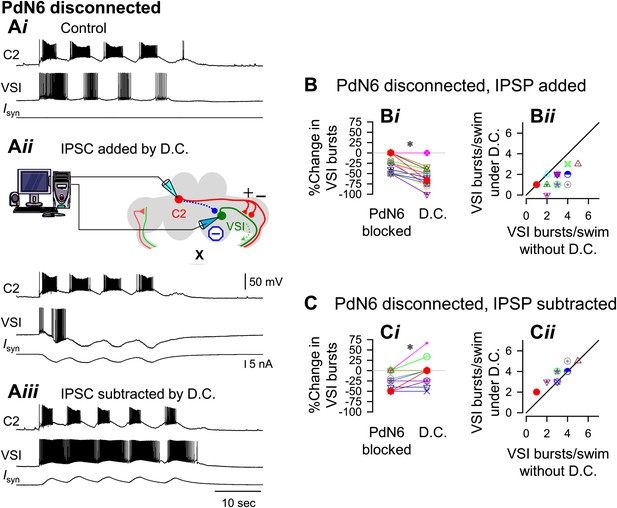
With PdN6 disconnected, an artificial synaptic conductance reduced the number of VSI bursts.
(A) Recordings from the same preparation as Figure 9, but with PdN6 disconnected. PdN6 disconnection reduced the number of VSI bursts from five to four bursts per swim episode (Ai) (Compare with Figure 9Ai). Addition of an artificial inhibitory synaptic conductance using dynamic clamp (D.C) further decreased the number of VSI bursts to one (Aii). Subtraction of the inhibitory synaptic conductance with the dynamic clamp restored the number of VSI bursts to five (Aiii). (B) With PdN6 blocked, addition of synaptic inhibition with dynamic clamp significantly decreased the number of VSI bursts (Bi, PdN6 blocked vs D.C., p<0.0001 by paired t-test, N = 20). PdN6 disconnection decreased the number of VSI bursts by 24.7 ± 20.8% from control. Addition of an artificial synaptic conductance using dynamic clamp decreased the number of VSI bursts further to 57.7 ± 22.0%. Comparison of the number of VSI bursts with dynamic clamp to control shows the points falling below the unity line (Bii). (C) With PdN6 blocked, subtracting the synaptic inhibition restored the motor pattern. With dynamic clamp, number of VSI bursts was increased from −21.9 ± 20.7% below control to −3.1 ± 30.0% (Ci, p = 0.003 by paired t-test, N = 19). For most preparations, the effect of dynamic clamp was to increase the number of VSI bursts (Cii).
-
Figure 10—source data 1
Source data for panel B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02598.026





