GSK-3 signaling in developing cortical neurons is essential for radial migration and dendritic orientation
Figures
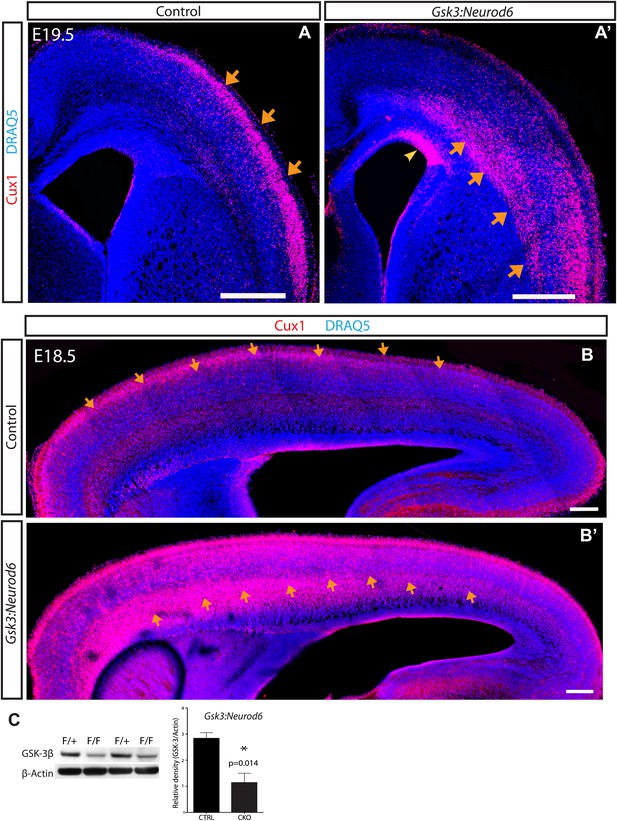
GSK-3 signaling is essential for proper lamination of the developing cortex.
(A–A') Cux-1 staining (red) in coronal sections from control and Gsk3:Neurod6 mice at E19.5. Cux-1 neurons are strikingly mislocalized in Gsk3:Neurod6 mutants (orange arrows) including a small population of neurons that remain in the ventricular zone (yellow arrowhead). Nuclei were counterstained with DRAQ5. Scale bar = 500 μm. (n = 4). (B–B') Cux-1 staining in parasagittal vibratome sections from control and Gsk3:Neurod6 mutants at E18.5. Cux-1 expressing neurons (arrows) are mislocalized in Gsk3:Neurod6 mutants and populate the deeper layers of the cortex along the entire rostrol/caudal axis. Scale bar = 200 μm. (C) Representative Western blot confirms strongly reduced GSK-3β protein levels in the E19.5 Gsk3:Neurod6 cortex compared to heterozygous control (n = 3 het control, n = 3 CKO). Relative Density *p<0.05, unpaired t-test.
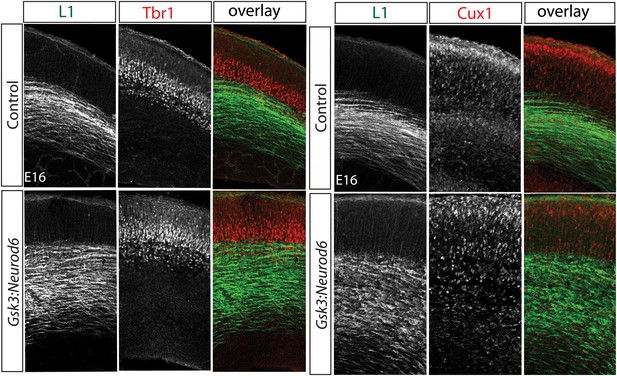
Migration defect apparent by E16 after Gsk3 deletion in cortical excitatory neurons.
Coronal cryostat sections at E16. Layer 6 TBR1 neurons populate appropriate layers in control and Gsk3:Neurod6 mutants. Cux-1 (red) expressing neurons, marker for upper layer 2/3 neurons, are mislocalized in Gsk3:Neurod6 mutant coronal sections. L1 staining labels axon tracts.
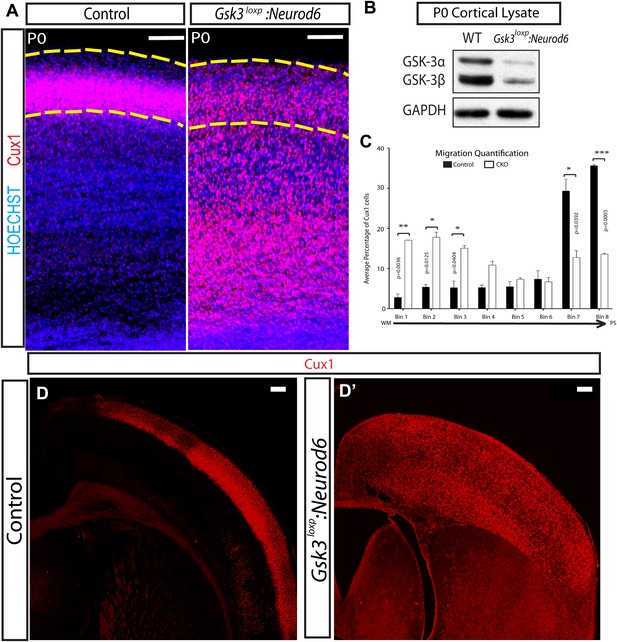
Migration defects in Gsk3-deleted mice are persistent.
(A) P0:Cux 1 staining (red) in coronal sections of Gsk3loxp:Neurod6 mutants and littermate heterozygote controls. Cux1-expressing neurons are localized to layer2/3 in controls (denoted by yellow dashed lines) while Cux1-expressing neurons are localized throughout the cortical plate in the mutants. (n = 5, scale bar = 100 μm). (B) Representative Western blot of P0 cortical lysates confirms strongly reduced GSK-3α and GSK-3β protein levels in Gsk3loxp:Neurod6 mutants when compared to Gsk3aloxp/loxpGsk3bloxp/loxp controls. GAPDH was probed as a loading control (n = 3 control, n = 3 CKO). (C) P0 quantification of control and Gsk3loxp:Neurod6 Cux1 neurons using 8 bin analysis spanning white matter (WM) to the pial surface (PS), (n = 2 het control, n = 2 CKO). (D–D') P7: Gsk3loxp:Neurod6 mutants stained with Cux1 (red) show persistent altered lamination with Cux1-expressing neurons spread throughout all layers of the cortex. Littermate controls show normal Cux1 distribution in layer 2/3. Scale bar = 200 μm.
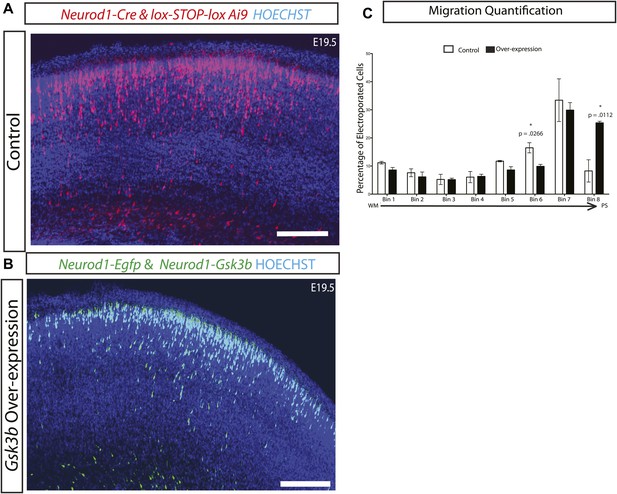
Gsk3 overexpression enhances radial migration.
(A) E19.5 coronal sections showing normal migration after in utero electroporation of Neurod1-Cre and lox-STOP-lox-Ai9 (red neurons) and (B) Coronal sections showing abnormal neuronal migration after electroporation of Neurod1-Gsk3b and Neurod1-GFP (green neurons). Enhanced migration is apparent in B. Scale bar = 200 μm. (C) E19.5 quantification of migration in control and Gsk3 over-expressing neurons using 8 bin analysis as previously described. Significantly more Gsk3 over-expressing neurons were found in the outermost bin 8 and fewer Gsk3 over-expressing neurons populated bin 6. p-values shown in figure, unpaired t-test. (control n = 2 mice from two individual litters, 1276 neurons vs Gsk3 overexpression n = 3 mice from two individual litters, 1959 neurons).
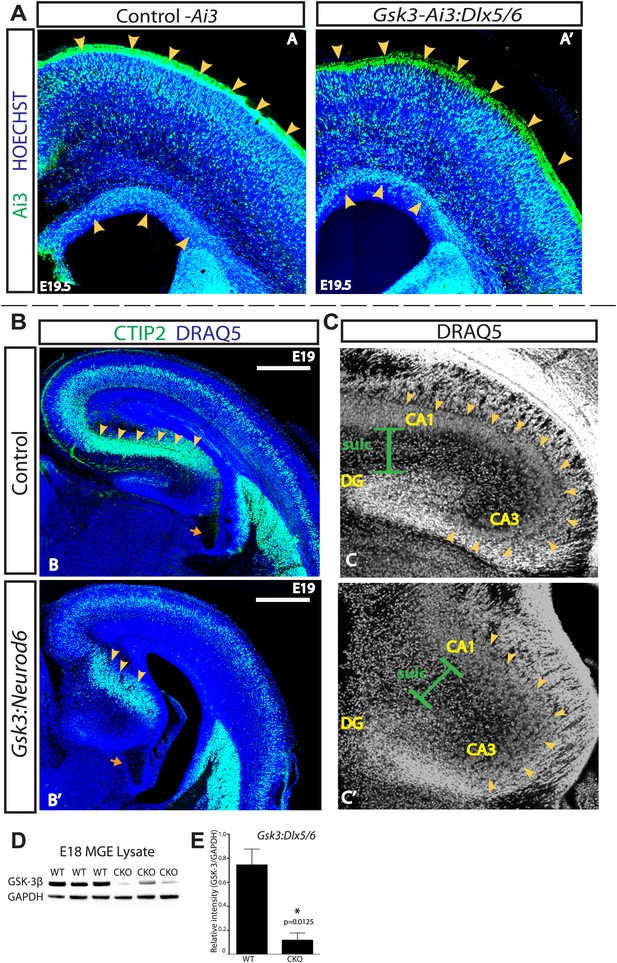
GSK-3 signaling is dispensable for tangential migration, but required for radial hippocampal migration.
(A–A') E19.5 coronal sections showing EYFP-expressing interneurons in heterozygous control and Gsk3:Dlx5/6 mutants crossed with the Ai3 reporter line. Gsk3-deleted interneurons (green) enter the cortex in two streams in both controls and mutants (arrowheads). Mutants showed no overt migration defect. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst. (n = 3). (B–B') E19 coronal sections of control and Gsk3:Neurod6 mutants showing CTIP2 (green) expressing neurons in the hippocampus. In the Gsk3:Neurod6 mutants, the pyramidal cell layer (green) does not extend laterally into a compact CA1 region and remains dispersed (yellow arrowheads). Fimbrial axonal projections appear normal in Gsk3:Neurod6 mutants (orange arrow). Nuclei were counterstained with DRAQ5. Scale bar = 500 μm. (n = 3). (C–C') Higher magnification of hippocampal area shown in (B). The Gsk3:Neurod6 mutants show disrupted cytoarchitecture. In the mutants, DRAQ5-labeled cells are mislocalized and diffuse (arrowheads) and fail to form clearly defined CA1/CA3 regions of the hippocampus. The Gsk3:Neurod6 mutant mice also lack a clearly defined hippocampal sulcus (green bars) and dentate gyrus (DG). (D) Representative Western blot of E18 MGE lysates confirm strongly reduced GSK-3β protein after recombination with Dlx5/6-Cre. (E) Quantification of protein knockdown in D (n = 3 WT, n = 3 CKO, unpaired t-test).
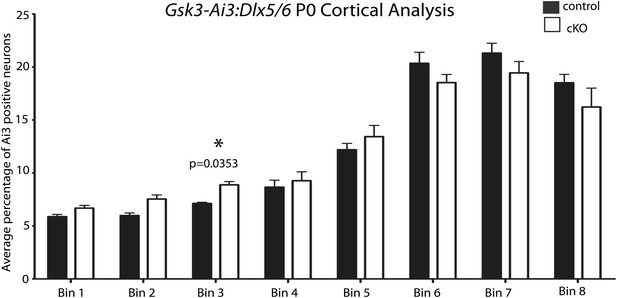
No apparent migration defect in Gsk3:Dlx5/6 mice.
P0 quantification of Ai3-positive neurons in control and Gsk3-deleted interneurons using 8 bin analysis spanning white matter to the dorsal stream. p-values reaching significance are shown in figure, unpaired t-test. (n = 2 controls, 3894 total cux1 neurons, n = 2 cko, 3681 total cux1 neurons).
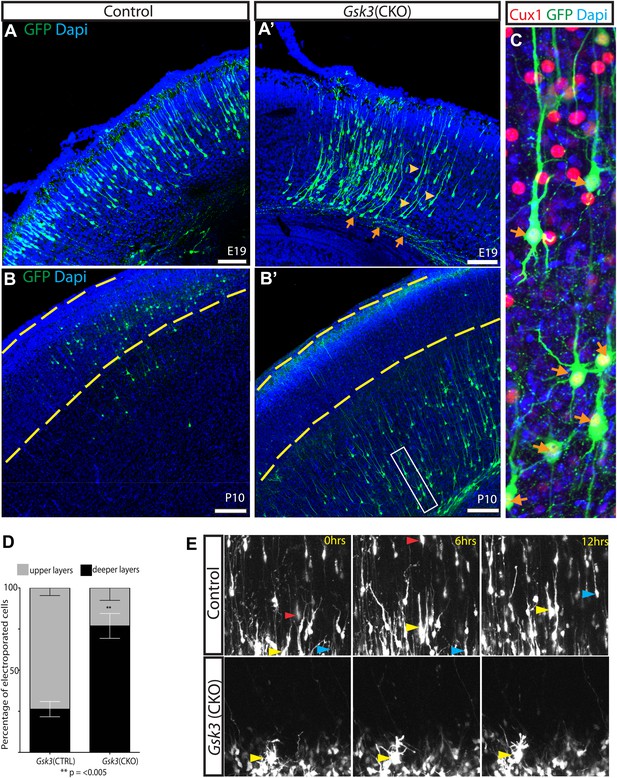
GSK-3 deletion delays the multipolar to bipolar transition.
(A–A') Representative E19 coronal sections after in utero electroporation at E14.5 with Neurod1-Cre and Z/EG plasmids. Electroporated cells were visualized with anti-EGFP (green), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Gsk3-deleted neurons remain in the deeper layers of the cortex but elaborate a long pial-directed process (yellow arrowheads). Gsk3-deleted neurons elaborate axons projecting towards the corpus callosum (orange arrows). Scale bar = 200 μm (n = 5, two independent litters). (B–B') Coronal sections at P10 after E14.5 electroporation, as in A. Gsk3-deleted neurons remain in the deeper layers of the cortical plate and fail to reach layer 2/3 (denoted with yellow bars). Scale bar = 200 μm (n = 3, 2 independent litters). (C) Higher magnification of Gsk3-deleted neurons in B' (box). Gsk3-deleted neurons (green) in deeper layers co-label with Cux (red) (orange arrows). Nuclei were stained with Dapi. (D) Quantification of control and Gsk3-deleted neurons in upper (layer 2–3) vs deeper layers of the cortex at P10. (n = 3, 4209 total neurons counted, 2234 control vs 1975 Gsk3 deleted) **p=0.003, unpaired t-test. (E) Gsk3 deletion delays the multipolar to bipolar transition. Still images from time-lapse imaging of slice cultures at 3DIV. pCAG-dsRED or Neurod1-Cre;Z/EG was injected into the ventricles of Gsk3a−/−Gsk3bloxp/loxp embryos and electroporated at E15. Representative images were taken at time 0, 6, and 12 hr. Control dsRed neurons migrate through the cortical plate (yellow, red, and blue arrows show individual neurons at the different time points). (n = 2 controls). Gsk3-deleted neurons fail to migrate through the cortical plate and exhibit persistent multi-polar morphology (yellow arrowheads). (n = 4 mutants).
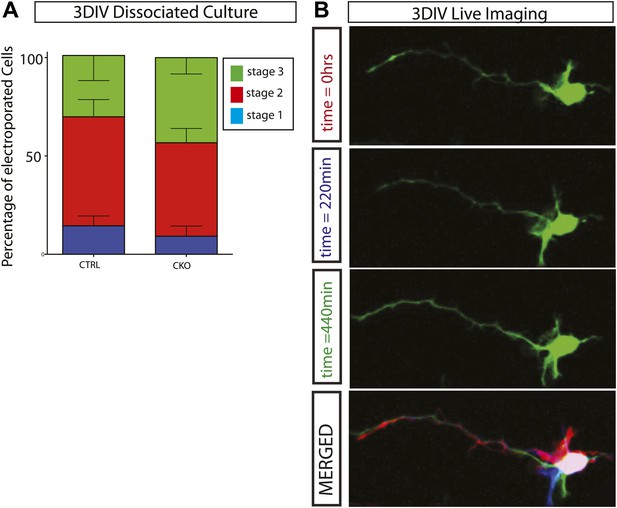
Gsk3-deleted neurons polarize and are highly dynamic.
(A) Stage progression analysis of dissociated control and Gsk3-deleted neurons. Stage 1 immature neurons display lamellapodial and filopodial protrusions. Stage 2 neurons have transitioned to form multiple short neurites (multipolar morphology), and stage 3 neurons exhibit a single neurite extending to become an axon (see Dotti et al., 1988). There is no significant delay in polarization (n = 3, 1341 neurons). (B) Live imaging of dissociated Gsk3-deleted neurons reveal dynamic neurites. Images were taken every 11 min. Representative images at time 0 (red), 220 min (blue), and 440 min (green). Merged image is pseudo colored.
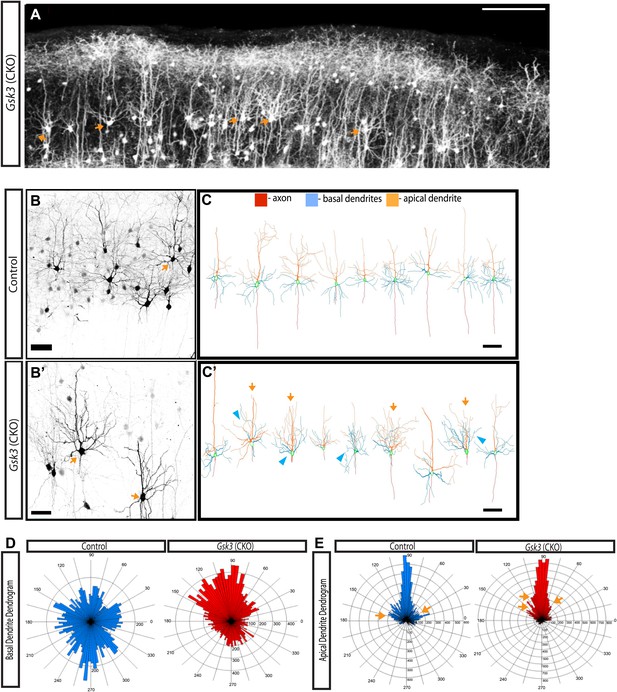
GSK-3 signaling is required for proper dendrite orientation.
(A) Gsk3 deleted neurons at P15 shown after in utero electroporation at E14.5 with Neurod1-Cre and Z/EG plasmids. Multiple neurons with obvious abnormalities in dendritic orientation were observed in the upper layers of the cortex (orange arrows). Scale bar = 200 μm. (B–B') Control and Gsk3-deleted neurons in the upper layers at P15, immunostained with antibodies against eGFP (black) using same methods as Figure 4. Gsk3-deleted neurons have abnormally polarized arbors indicated by orange arrows. Scale bar = 50 μm. (C–C') Neurolucida reconstructions of control and Gsk3-deleted neurons in the upper layers of the cortex. The axon (red) projects towards the ventricle in control and Gsk3-deleted neurons. Both apical dendrites (orange) and basal dendrites (blue) are more branched (orange arrows) and basal dendrites (blue) are mispolarized (blue arrowheads) in Gsk3-deleted neurons. Scale bar = 100 μm. (D) Basal dendrite quantification. Dendrogram shows that basal dendrites more frequently project towards the pial surface in Gsk3-deleted neurons when compared to control basal dendrite orientation. (n = 3, n = 3 CKO; 15 control and 15 Gsk3-deleted neurons quantified). (E) Apical dendrite dendrogram indicates polarization and length of processes. Control apical dendrites project pially (90°). Numerous small apical branches form near the soma and project laterally (orange arrows). Gsk3-deleted neurons also project pially-directed apical dendrites. However, Apical branches have a pially-directed orientation, resulting in abnormal morphology (orange arrows, also see C').
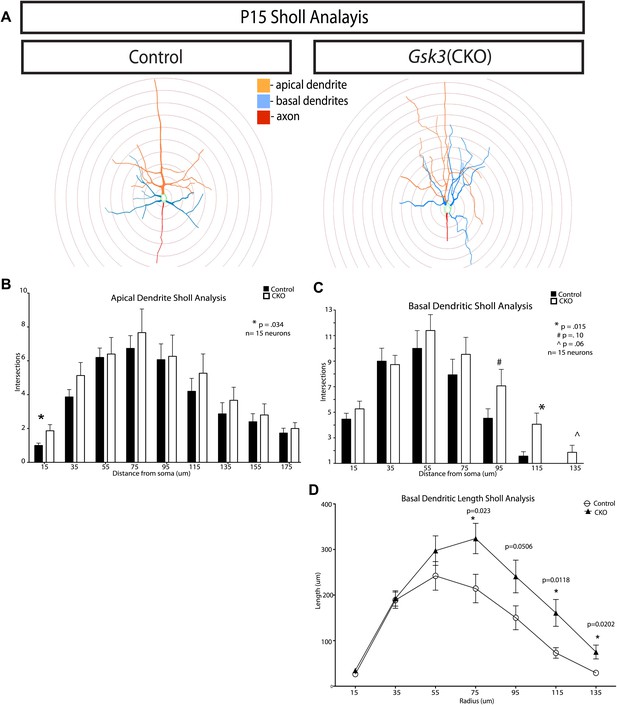
Quantification of dendritic branching at P15 in control and Gsk3-deleted neurons.
(A) Representitive images of control and Gsk3-deleted neurons used for Sholl analysis with specific processes pseudocolored for identification. (B) Apical dendrite Sholl analysis of Gsk3-deleted neurons shows significantly increased branching close to the soma. p=0.034. Additionally, Gsk3-deleted neurons display a trend toward increased branching in areas further from the soma. (C) Basal dendrite Sholl analysis of Gsk3-deleted neurons shows significantly increased branching in basal dendrites in areas furthest away from the soma (p=0.015). (D) Basal dendrite sholl analysis of dendritic lengths reveals altered morphology of Gsk3-deleted neurons. Gsk3-deleted neurons have increased lengths of basal dendrites in areas beginning 75 μm away from the soma. p=0.023, p=0.0118, and p=0.0202.
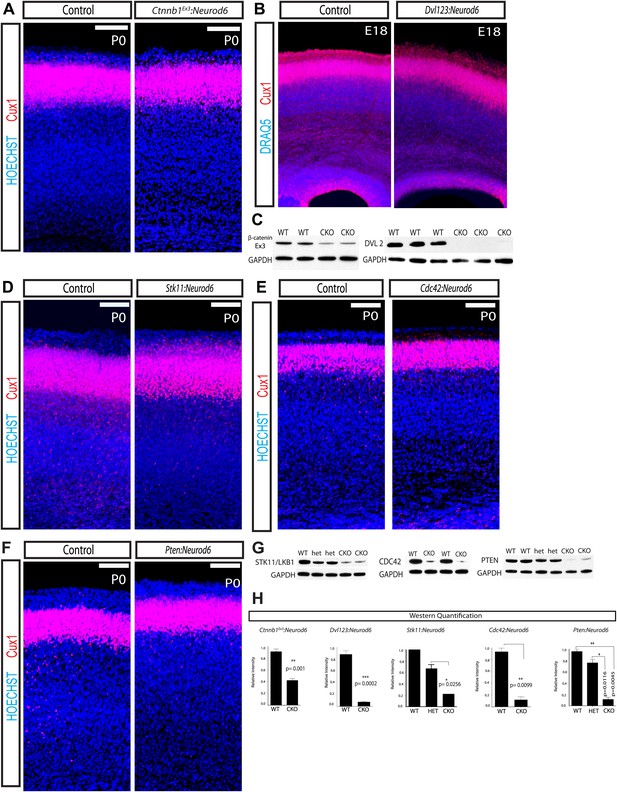
Lamination in other signaling mutants.
(A) P0 representative coronal sections of control (heterozygous for floxed allele) and Ctnnb1Ex3:Neurod6 mutants stained for Cux1 (red) and Hoechst (blue). (n = 5) Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) E18 Coronal sections of control and Dvl123:Neurod6 showing Cux-1 (red) and DRAQ5 (blue) staining. Cux-1 neurons reach layer 2/3 in both controls and Dvl123:Neurod6 triple mutants. (n = 3). (C) Western blot verification of protein deletion after recombination of floxed alleles with Neurod6-Cre. Ctnnb1Ex3:NeuroD6 (n = 3 WT, n = 3 CKO), Dvl123:NeuroD6 (n = 3 WT, n = 3 CKO). GAPDH was probed as a loading control. (D–F) P0 representative coronal sections of control (heterozygous for floxed allele) and indicated mutant lines stained for Cux1 and Hoechst. Scale bars are 100 μm, at least n = 5 per line. (G) Western blot verification of protein deletion in mutant lines. GAPDH was probed as a loading control. N's refer to numbers of mutants and paired controls. Stk11:Neurod6 (n = 2), Cdc42:Neurod6 (n = 2), Pten:Neurod6 (n = 3). (H) P0 Western Blot quantification of Ctnnb1Ex3:Neurod6, Dvl123:Neurod6, Stk11:Neurod6, Pten:Neurod6 and Cdc42:Neurod6 lines.
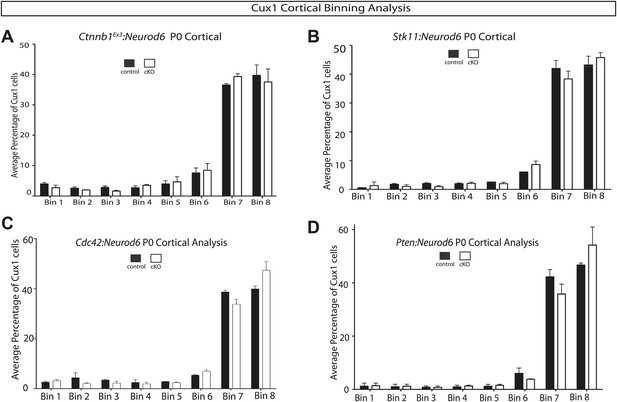
Quantification of lamination in other signaling mutants.
(A–D) P0 quantification of Cux1 expressing neurons using 8 Bin quantification in conditional mutants and control shown in Figure 6. (A) Ctnnb1Ex3:Neurod6, (B) Stk11:Neurod6, (C) Cdc42:Neurod6, (D) Pten:Neurod6. (n = 2 het control mice, n = 2 CKO mice per line). Between 2000 and 3000 Cux1 neurons were scored in each of the control pairs and each of the mutant pairs.
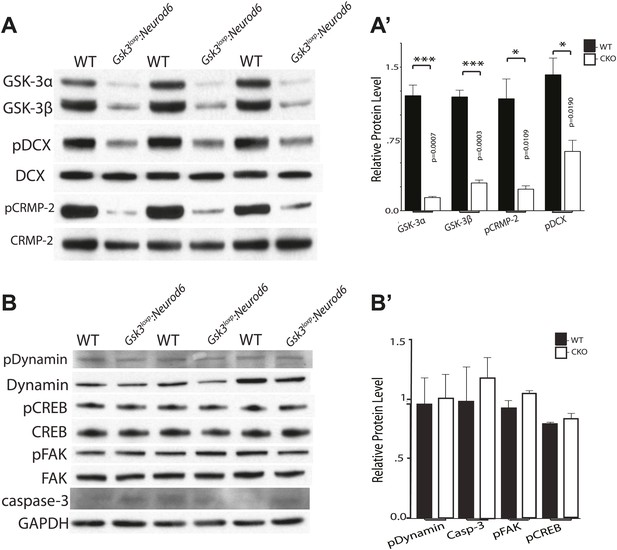
Phosphorylation status of GSK-3 substrates.
(A–A') Western blots of P0 cortical lysates from Gsk3loxp:Neurod6 mutants and wild-type controls performed in triplicate. Levels of GSK-3 proteins and phospho-target proteins are shown. Strong reductions in phosphorylation of doublecortin on ser327/Thr321 and CRMP-2 on Thr514 are evident. (A') Quantification of relative densities from A. p values shown in figure (n = 3, unpaired t-test) (B–B') Western blots of cortical lysates at P0 showing levels of other GSK-3 targets. No changes were observed in phosphorylation of dynamin, pCREB, or pFAK. No change was observed in cleaved caspase-3. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B') Quantification of relative protein densities (n = 3, unpaired t-test).
Videos
Live cell imaging of radially migrating neurons in a cortical slice preparation.
Control neurons electroporated at E15.5 migrate towards the pial surface after 3 days ex vivo. Neurons are imaged using time-lapse microscopy with images taken every 45 min for a 20-hr session.
Gsk3-deleted neurons fail to migrate in cortical slice preparation.
Gsk3a−/−Gsk3bloxp/loxp mice electroporated at E15.5 with Neurod1-cre and Z/EG have an elongated multipolar stage and do not migrate towards the pial surface. Images were taken every 45 min over a 20-hr imaging session.





