A comprehensive search for calcium binding sites critical for TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel activity
Figures
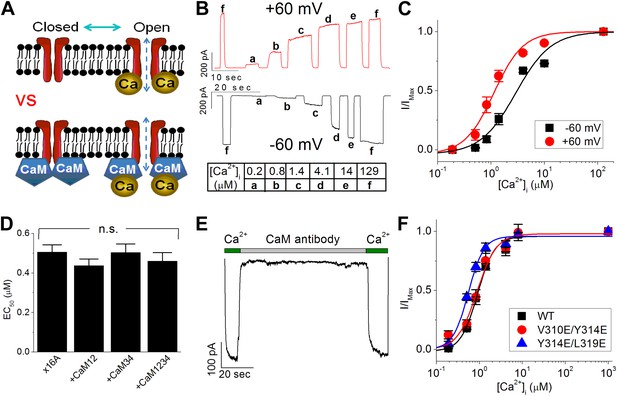
Calmodulin (CaM) is not responsible for the calcium-dependent activation of TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channels (CaCC).
(A) Two competing models to explain TMEM16A calcium sensitivity have been proposed. It is unclear whether calcium directly binds to TMEM16A-CaCCs (upper panel) or whether CaM is required to mediate the calcium sensitivity of the channel (lower panel). (B) Representative current traces of wildtype mouse TMEM16A-CaCC (mTMEM16A) recorded at +60 mV and −60 mV in response to various intracellular calcium concentrations using an inside-out patch clamp configuration. Table indicates the concentration of calcium used. (C) Calcium dose–response of mTMEM16A channel at +60 mV and −60 mV. The smooth curves represent fits to the Hill equation (‘Materials and methods’). (D) Loss-of-function CaM mutants (CaM12, CaM34, CaM1234) did not reduce the apparent calcium sensitivity of the endogenous TMEM16A (x16A) channel in Xenopus oocytes. n.s.: non-significant. (E) Application of monoclonal anti-CaM antibody CaM85 (2 μg/ml) to the cytosolic face of inside-out patches had no effect on the calcium sensitivity of endogenous Xenopus TMEM16A-CaCC. (F) Mutating residues reported by Vocke et al. (2013) to be in the CaM binding domain of mTMEM16A did not affect apparent TMEM16A-CaCC calcium sensitivity.
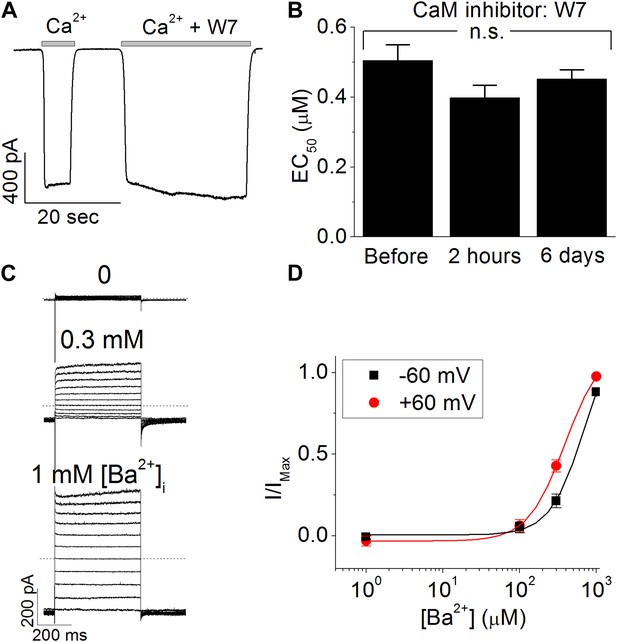
Calmodulin (CaM) is not involved in the calcium-dependent activation of TMEM16A-CaCC.
(A) Acute application of 50 µM W7, a CaM antagonist, to the cytosolic face of the inside-out patches failed to inhibit endogenous Xenopus TMEM16A-CaCC currents. (B) Chronic incubation of Xenopus oocytes with W7 did not reduce the apparent calcium sensitivity of endogenous Xenopus TMEM16A-CaCC. (C and D) Barium, a divalent cation that is incapable of binding CaM, can robustly activate mouse TMEM16A-CaCC. (C) CaCC currents were recorded with voltage steps in +20 mV increments from −80 mV to +120 mV in isotonic 140 mM NaCl solutions. Both holding and repolarizing potentials were −80 mV. Dotted lines indicate the zero current level. (D) Barium dose–response curves of wildtype mTMEM16A channel at +60 mV and −60 mV. Smooth curve represent fits to the Hill equation.
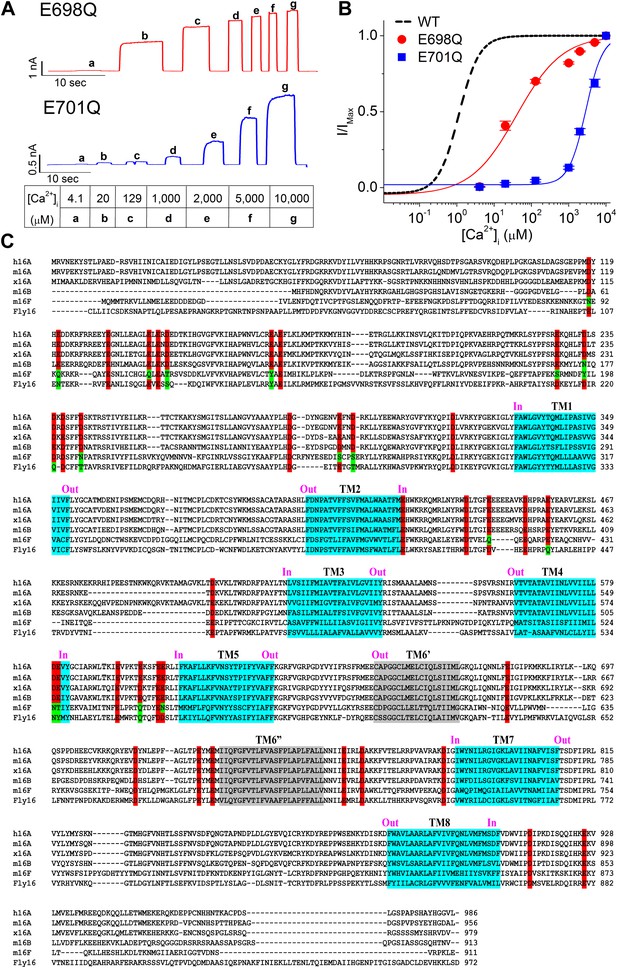
Screen for potential calcium-binding residues in TMEM16A-CaCC.
(A and B) Quantification of the apparent calcium sensitivity of E698Q and E701Q (Yu et al., 2012) mutant TMEM16A channels. (A) Representative current traces of E698Q and E701Q mutants in response to intracellular solutions with different calcium concentrations recorded at +60 mV. Table indicates the concentration of calcium used. (B) Calcium dose–response curves of the mTMEM16A channels at +60 mV. Smooth curves represent fits to the Hill equation. (C) Sequence alignment of the calcium-activated TMEM16 channels. h16A, m16A, x16A, m16B, m16F and Fly16 are the human TMEM16A (Uniprot ID #Q5XXA6), mouse TMEM16A (Uniprot ID #Q8BHY3-2), Xenopus TMEM16A (Uniprot ID #B5SVV6), mouse TMEM16B (Uniprot ID #Q8CFW1), mouse TMEM16F (Uniprot ID #Q6P9J9) and Drosophila TMEM16 channels (Uniprot ID #Q86P24), respectively. Highly conserved acidic residues that are potentially exposed to the cytoplasm are highlighted in red. Some residues with conserved oxygen-containing side chains in m16F and Fly16 are highlighted in green. Putative transmembrane (TM) segments are highlighted in cyan. The controversial TM6 segments are highlighted in gray and labeled as TM6′ and TM6″, respectively. ‘In’ and ‘Out’ indicate the intracellular and extracellular side of the membrane, respectively.
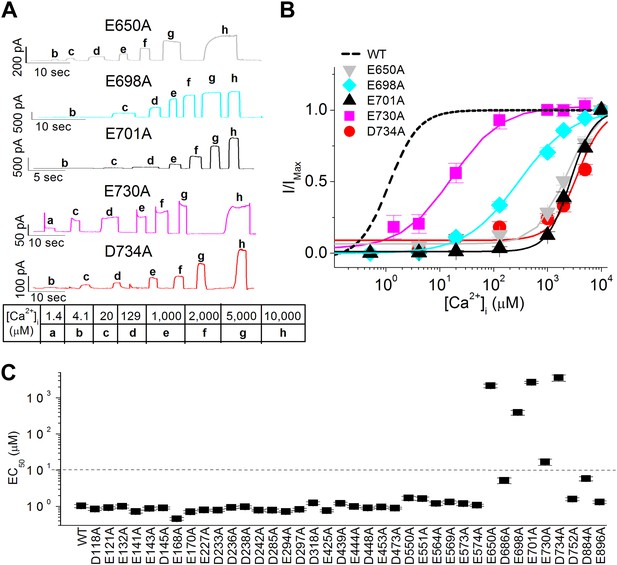
Systematic alanine scan of highly conserved intracellular acidic residues identified five mutations that dramatically reduced the apparent calcium sensitivity of TMEM16A-CaCC.
(A) Representative current traces of the E650A, E698A, E701A, E730A and D734A mutant channels in response to different intracellular calcium solutions recorded at +60 mV. Table indicates the concentration of calcium used. (B) Calcium dose–response curves of these mutant mTMEM16A channels at +60 mV. Smooth curves represent fits to the Hill equation. (C) Summary of apparent calcium sensitivity (EC50s) of all alanine mutants tested. Dotted line indicates a 10-fold increase in EC50 compared to wildtype channels.
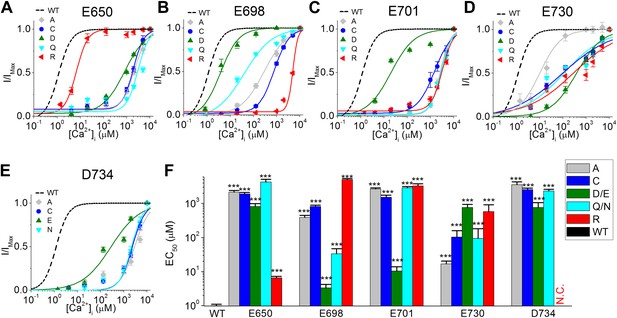
The effects of different amino acid side chains on the calcium sensitivity of mutant TMEM16A-CaCC channels indicate that E698, E701, E730 and D734 might be directly involved in binding calcium.
(A–E) Calcium dose–response curves of (A) E650, (B) E698, (C) E701, (D), E730, and (E) D734 mutant mTMEM16A channels at +60 mV. Smooth curves represent fits to the Hill equation. Maximum activity was constrained to 1 for these fittings. (F) Summary of apparent calcium sensitivity (EC50s) of mTMEM16A mutants. N.C.: no obvious CaCC current recorded. ***p<0.001.
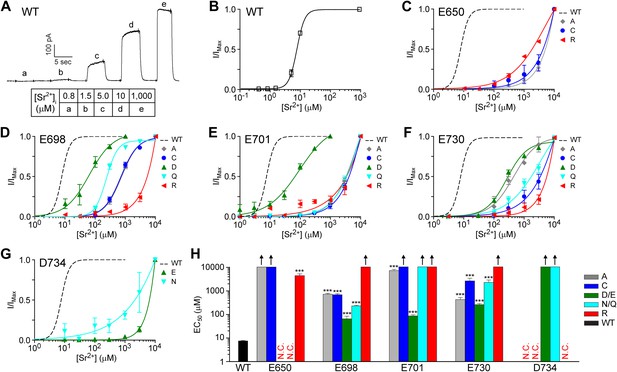
TMEM16A channel sensitivity to strontium ions is disrupted by mutations of the identified calcium-binding sites.
(A) Representative current trace of wildtype mTMEM16A in response to different intracellular strontium solutions recorded at +60 mV. Table indicates the concentration of strontium used. (B) Strontium dose–response curve of wildtype mTMEM16A channels at +60 mV. (C–G) Strontium dose–response curves of the (C) E650, (D) E698, (E) E701, (F) E730, and (G) D734 mutant mTMEM16A channels at +60 mV. Smooth curves represent fits to the Hill equation. (H) Summary of apparent strontium sensitivity (EC50s) of mTMEM16A mutants. N.C.: no obvious CaCC current recorded. Upward arrows: estimated strontium EC50 >10 mM and cannot be reported with confidence. ***p<0.001.
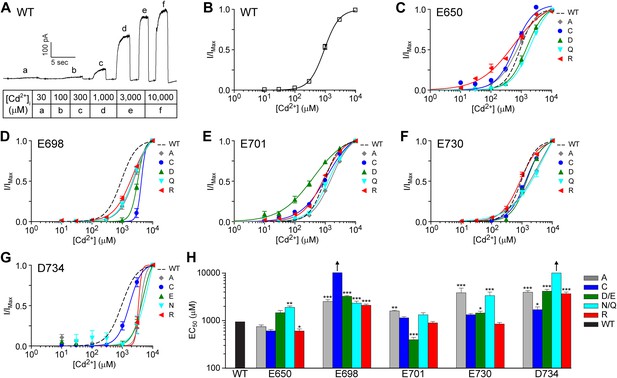
TMEM16A channel sensitivity to cadmium ions is disrupted by mutations at the identified calcium-binding sites.
(A) Representative current trace of wildtype mTMEM16A in response to different intracellular cadmium solutions recorded at +60 mV. Table indicates the concentration of cadmium used. (B) Cadmium dose–response curve of wildtype mTMEM16A channels at +60 mV. (C–G) Cadmium dose–response curves of the (C) E650, (D) E698, (E) E701, (F) E730, and (G) D734 mutant mTMEM16A channels at +60 mV. Smooth curves represent fits to the Hill equation. (H) Summary of apparent cadmium sensitivity (EC50s) of mTMEM16A mutants. Upward arrows: estimated cadmium EC50 >10 mM and cannot be reported with confidence. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
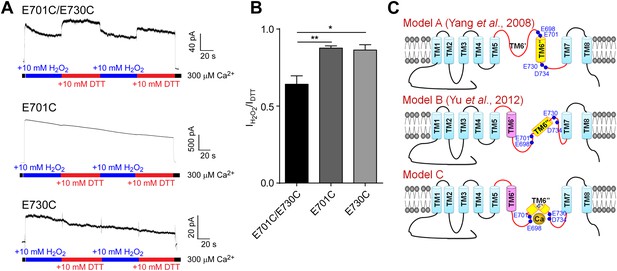
Cysteine crosslinking suggests that the calcium-binding residues in TMEM16A-CaCC form a metal ion binding pocket that is exposed to the cytoplasm.
(A) Representative traces of E701C/E730C, E701C, and E730C mTMEM16A mutants recorded under reducing (DTT) and oxidizing (H2O2) conditions. (B) Comparison of currents recorded in oxidizing conditions of mutants shown in A. When activated for long periods of time, TMEM16A-CaCCs exhibit a persistent decrease in activity, as previously described (Vocke et al., 2013). Current amplitudes were measured 60 s after the onset of perfusion and are normalized to currents recorded in reducing conditions. ***p<0.001. (C) Schematic illustrating the position of the putative calcium binding residues (E698, E701, E730 and D734) based on two previous membrane topological models (Model A and B) (Yang et al., 2008b; Yu et al., 2012) and our experimental data (Model C).
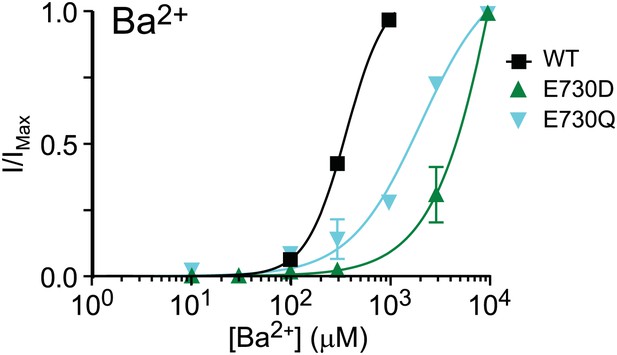
Barium dose-response curve of wildtype and mutant mTMEM16A channels at +60 mV. E730D and E730Q were the only mutants that produced appreciable activity out of the channels tested.
The pattern of bariumdependentactivation is not similar to that of cadmium-dependent activation.





