Caenorhabditis elegans male sensory-motor neurons and dopaminergic support cells couple ejaculation and post-ejaculatory behaviors
Figures
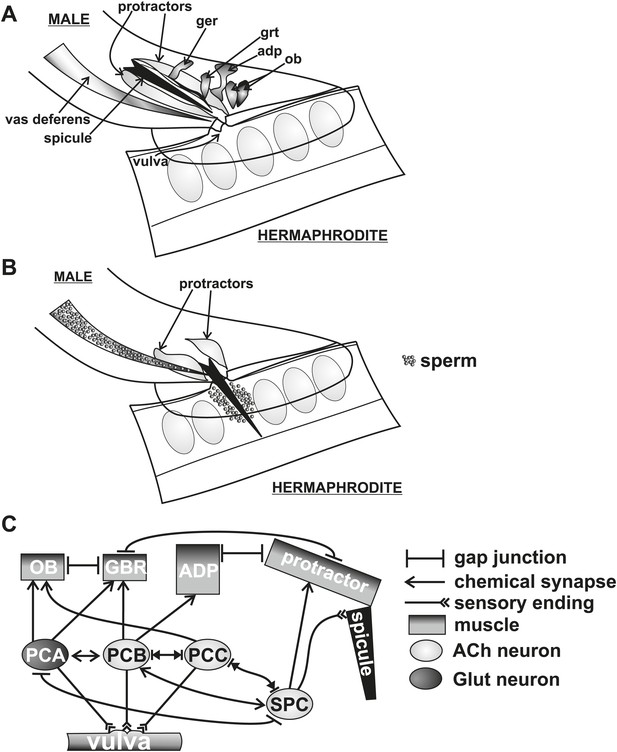
Conceptual diagram of structures and connectivity in the C. elegans male tail.
ger = gubernaculum erector muscle, grt = gubernaculum retractor muscle, adp = anal depressor muscle, ob = oblique muscle. (A) Diagram of the male tail positioned at the hermaphrodite vulva. The positions of the copulatory spicules and associated muscles are indicated. The oval structures in the hermaphrodite depict eggs. (B) Diagram of the male during spicule insertion and sperm release. (C) Abridged connectivity in the male tail, adapted from Jarrell et al. (2012).
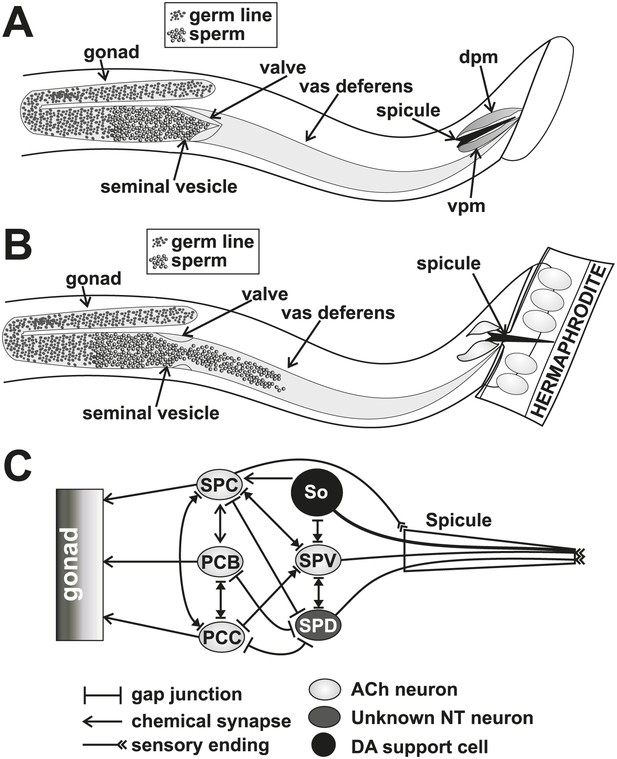
Conceptual diagrams of the structure and connectivity involved in ejaculation.
(A) Diagram of the males’ reproductive tract. dpm = dorsal protractor muscle, vpm = ventral protractor muscle. (B) Diagram of the initiation step of ejaculation. When the valve region separating the seminal vesicle from the vas deferens opens, sperm cells move toward the cloaca. (C) Connectivity of the spicule associated cells. Adapted from Jarrell et al. (2012).
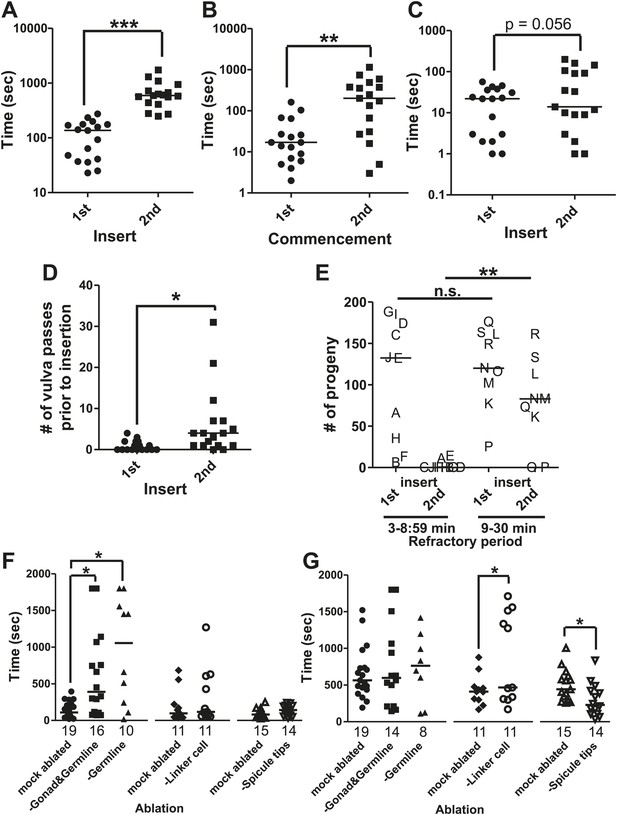
The refractory period is regulated by sperm release.
Line represents median. (A) 1st insert: the time required for a male to insert his copulatory spicules into the hermaphrodite vulva from the time he was placed with the hermaphrodites. 2nd insert: the time from 1st insert to finding a second hermaphrodite and repeating the mating process (refractory period). y-axis, the time it takes a male to insert his spicules, x-axis, insertion number. (B) Mating drive. 1st commencement: the time it takes the male to begin mating with a hermaphrodite after being placed on a mating lawn. 2nd commencement: the time from retraction to the next beginning of mating. (C) The total time the male spent at the vulva prior to insert. (D) The number of vulva passes prior to insertion. (A–D) n = 17. *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0001, paired t test. (E) The number of progeny sired following successive couplings. Males are grouped into two categories: males that re-copulated between 3 and 8:59 min following the 1st insertion and males that re-copulated between 9 and 30 min following the first insertion. The letters identify the same male for each insertion. x-axis indicates the insert as well as what refractory period group each male was placed in. y-axis is the number of progeny each male sired for the indicated insert. **p<0.05, Mann–Whitney test. (F and G) The first insert (F) and refractory period (G) for males with the indicated cell(s) removed. *p<0.05, Mann–Whitney test. n is indicated below the x-axis. The x-axis indicates the cells removed during the operation, and the y-axis indicates the time it took for males to insert their spicules into the hermaphrodite.
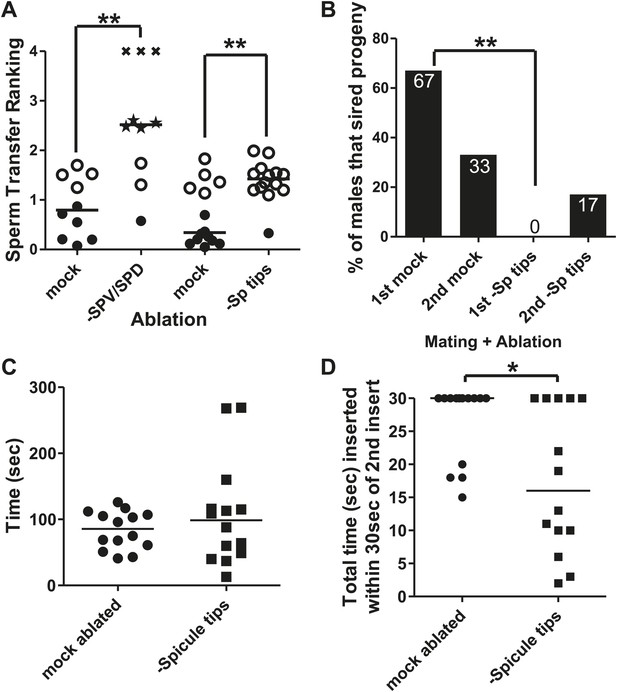
The spicule sensilla promote insertion behaviors.
(A) Sperm transfer ranking for males lacking the SPV and SPD sensory neurons and their age-matched controls. A male received a 0 if he ejaculated into the uterus, a 1 if he inserted but didn't ejaculate, a 2 if he ejaculated without inserting into the vulva, and a 3 if he was unable to ejaculate or insert. Additionally, each male was given up to 5 min to insert and transfer sperm. That time was divided by 300 s and added to the number he received for ejaculating, giving him a final ranking. Filled circles represent males that inserted and transferred sperm into the hermaphrodite. Open circles represent males that inserted but did not transfer sperm. Stars represent males that ectopically ejaculated. Xs represent males that neither inserted nor ejaculated within 5 min. Line indicates mean. **p<0.005, Mann–Whitney test. (B) Mating potency. The number on each column is the % of males that sired progeny. **p<0.005, Fisher's exact test. n = 12. (C) Time the males remained inserted the first time they mated. (D) Following the second intromission, spicule tips cut males often did not leave their spicules inserted very long. Reported here is the total amount of time the males’ spicules were inserted into the hermaphrodite for the first 30 s following the 2nd insert. *p<0.05, Mann–Whitney test. (C and D) n = 14.
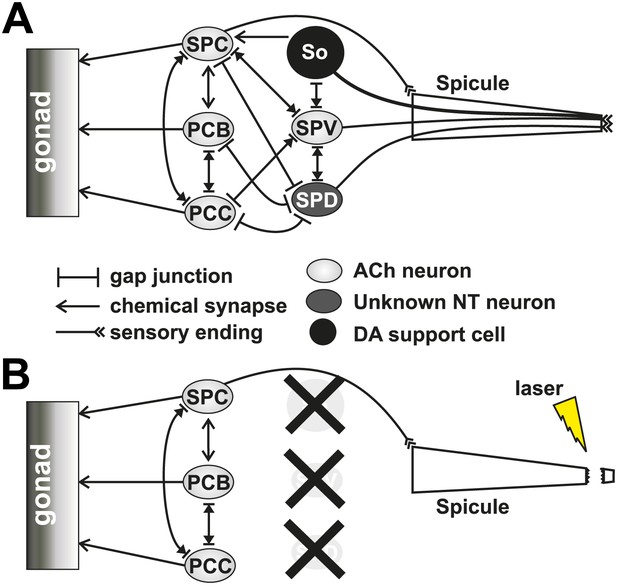
Cells affected by cutting off the spicule tips with a laser.
(A) Simplified diagram of the neuronal connectivity present in the spicule circuit in the male tail. (B) The same diagram as (A) representing what cells (with an ‘X’ over them) and connections are lost when the spicule tip is cut using a laser.
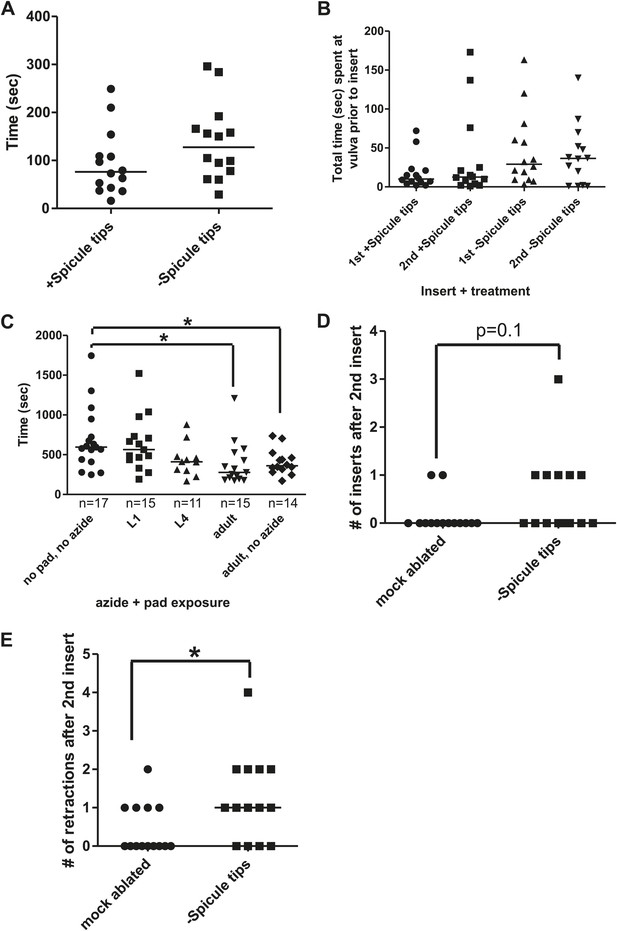
Spicule tips cut males display defects in mating.
(A) Mating drive in spicule tip cut males. The y-axis is the time it takes a virgin male to commence backing along a hermaphrodite cuticle. (B) Total time at vulva prior to insert in operated spicule tips cut males and intact males. (C) Effect of surgical environment on refractory period. The stage males are exposed to azide and/or an agar pad is given on the x-axis. The y-axis is the refractory period. *p<0.05, Mann–Whitney. For (A–C), line is the median. (D) The number of times a male successfully inserts his spicules in the 60 s following the 2nd insert. The median for both mock ablated and Spicule tips is 0. (E) The number of times a male retracts his spicules in the 60 s following the 2nd insert. *p<0.05, Mann–Whitney. For (A–C and E), line is the median.
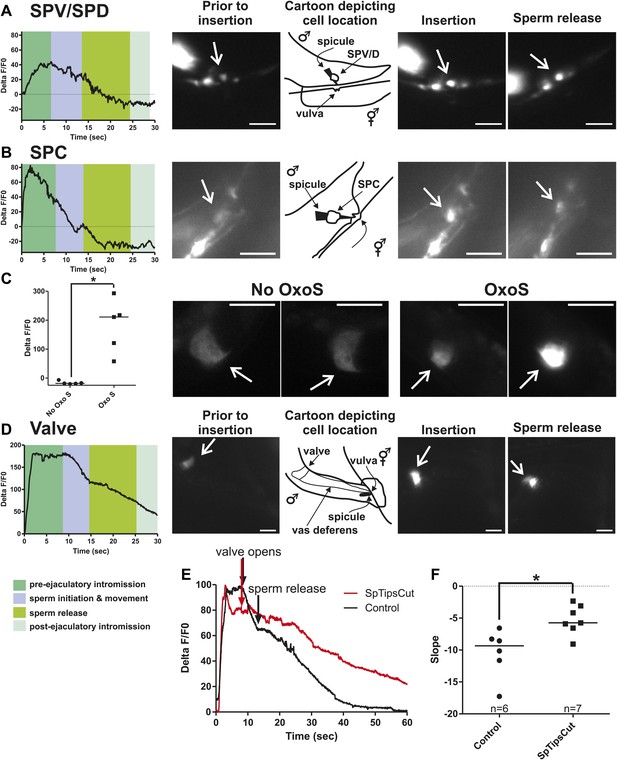
Ca2+ transients in SPV, SPD, SPC neurons, and gonad muscles during intromission and ejaculation.
(A, B, D). % ΔF/F0 trace including insertion and ejaculation. One representative recording is reported for each cell type. x-axis is time (seconds), y-axis is % ΔF/F0. The time of mating behaviors is indicated in color. Additional traces given in Figure 4—figure supplement 1 and Figure 4—figure supplement 3. (A) Trace of the SPV/SPD neurons, G-CaMP expressed from Pgpa-1. Scale bar = 20 µM. (B) Trace of the SPC neuron, G-CaMP expressed from Pgar-3B. Scale bar = 10 µM. (C) Graph of the largest calcium change (ΔF/F0) from time point 0. The pictures display fluorescence in the valve region at time 0 and 1 min later for males exposed and not exposed to OxoS. Males express G-CaMP in the gonadal valve from Ptry-5. *p value<0.05, Mann–Whitney test. Scale bar = 10 µM. (D and E) Traces of the valve region of the gonad, G-CaMP expressed from Ptry-5. Scale bar = 100 µM. SpTipsCut = spicule tips cut. (F) Slope of the line extrapolated from the highest Ca2+ transient plus 15 s. This time was chosen to include sperm release. *p value<0.05, Mann–Whitney test. Line represents median.
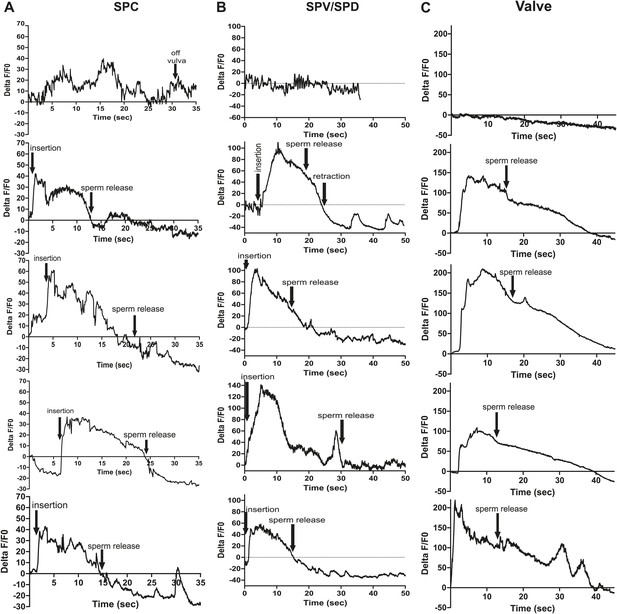
Ca2+ transient changes in cells that regulate ejaculation.
% ΔF/F0 trace for mating from insertion through sperm release and retraction, except for the first trace in each column which represents vulva prodding behavior. Arrows indicate when the behavior occurred. (A) Trace of SPC, G-CaMP expressed from Pgar-3B. (B) Trace of SPV/SPD, G-CaMP expressed from Pgpa-1. (C) Traces of the valve region of the gonad, G-CaMP expressed from Ptry-5.
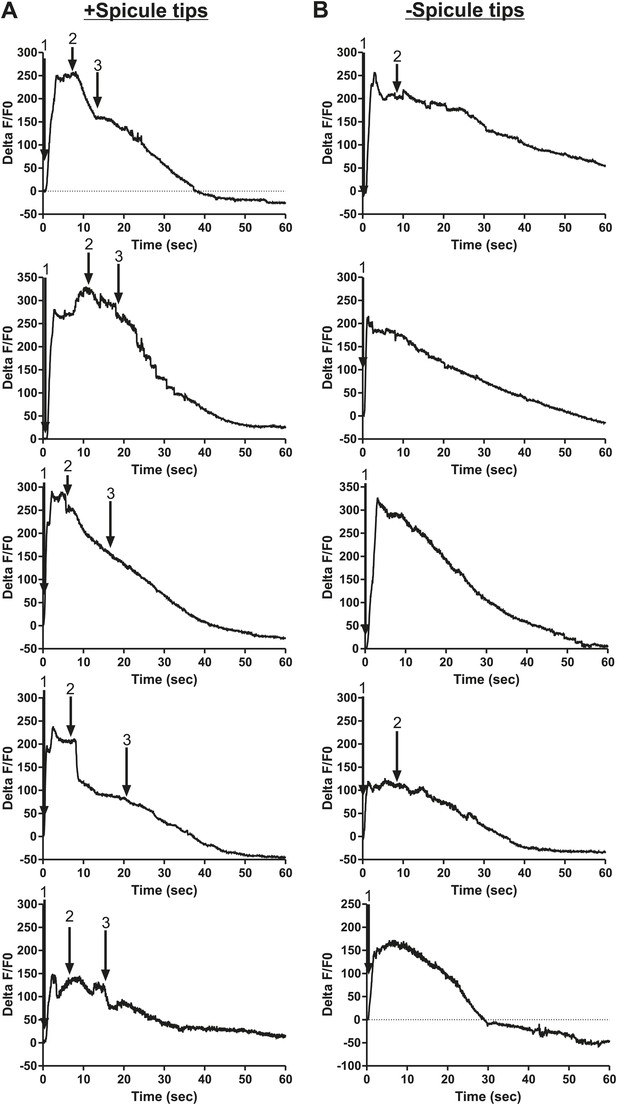
Removing the spicule sensilla impacts the Ca2+ changes in the gonadal valve.
% ΔF/F0 trace for mating from insertion (1) through valve opening (2) and sperm release (3). G-CaMP is expressed in the valve via Ptry-5. (A) Intact males and (B) spicule tip ablated males.
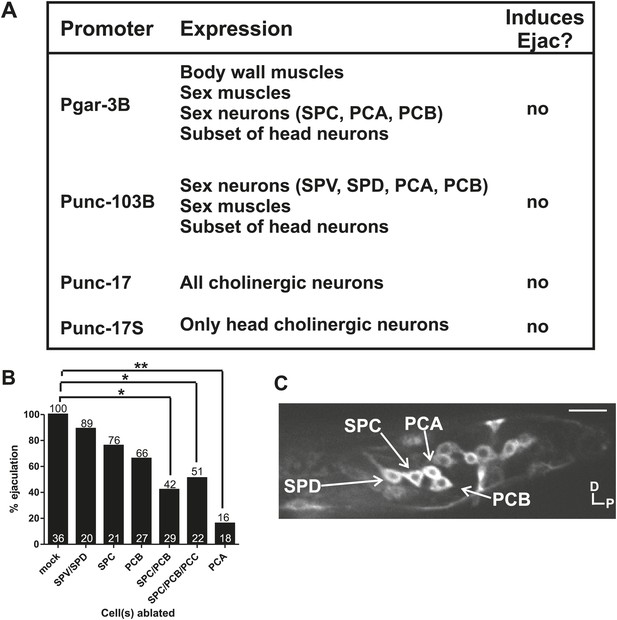
Cholinergic and glutamatergic neurons promote ejaculation.
(A) Chart of promoter, expression pattern, and ability of the promoter driving ChR2 to induce ectopic ejaculation (Ejac). (B) Graph of ectopic ejaculation in response to 475 nm wavelength light in rgIs6[Punc-17 small:ChR2, Punc-103B:ChR2, Pgar-3B:ChR2] males. x-axis indicates the cells ablated, y-axis is the percent of males that ectopically ejaculated in response to 475 nm wavelength light stimulation. n numbers are indicated at the bottom of each bar. *p<0.05, **p<0.005, Fisher's exact test. (C) Fluorescent, confocal image of a rgIs6[Punc-17 small:ChR2, Punc-103B:ChR2, Pgar-3B:ChR2] L4 male tail. Dorsal is up, posterior to the right. Cells important in mating behavior are indicated by the arrows. Scale bar = 10 µM.
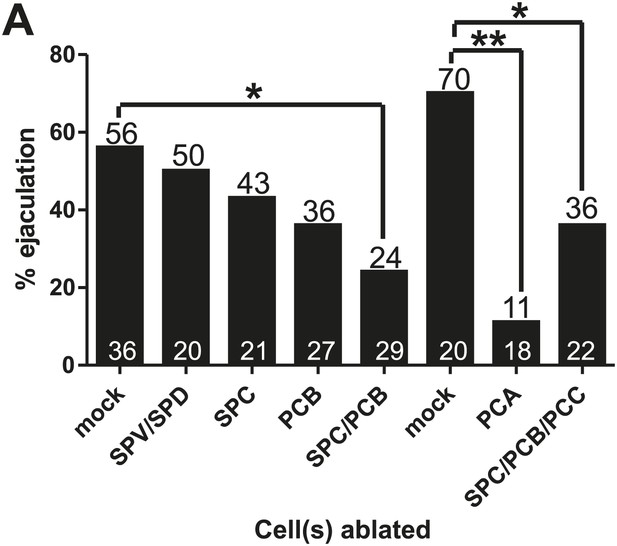
% of ChR2-expressing males that ejaculate in response to 475 wavelength light stimulation.
(A) Rate of ectopic ejaculation in response to 475 nm wavelength light exposure in males expressing ChR2 in the spicule and post cloacal sensilla. x-axis lists the cells ablated, y-axis is the % of males that ejaculated. *<0.05, **<0.005, Fisher's exact test. These numbers are normalized in Figure 4B.
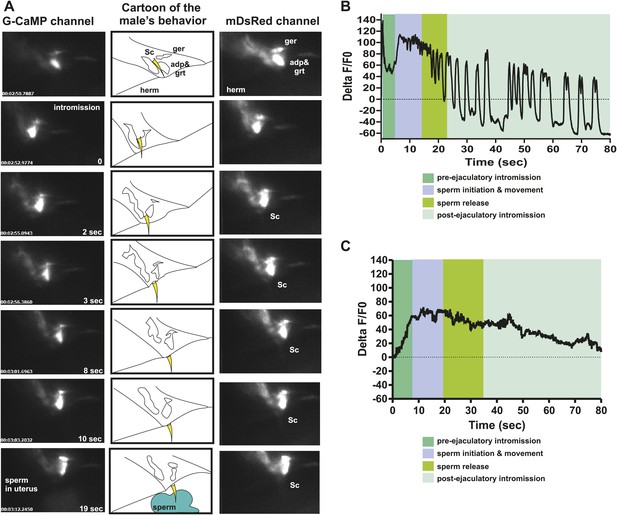
PCA contributes to the sex muscle-controlled spicule movement required for sperm to drain from the cloaca into the uterus.
(A) Images of sex muscle activity during intromission and ejaculation. Sc = spicule, ger = gubernaculum erector, adp = anal depressor, grt = gubernaculum retractor. The gubernaculum is located posteriorly to the spicule and assists in spicule movement. After insertion and prior to sperm release, the gubernaculum erector is required to adjust spicule position to allow sperm to drain into the hermaphrodite. The image on the left indicates G-CaMP fluorescence, the central image of diagram of male tail position at the hermaphrodite vulva, and the right image is mDsRed fluorescence. Time is indicated on the left image and spicule location on the right. (B) % ΔF/F0 in the anal depressor and the gubernaculum erector and retractor. G-CaMP expressed from Punc-103E. (C) % ΔF/F0 in the post cloacal sensilla PCA. G-CaMP expressed from Peat-4.
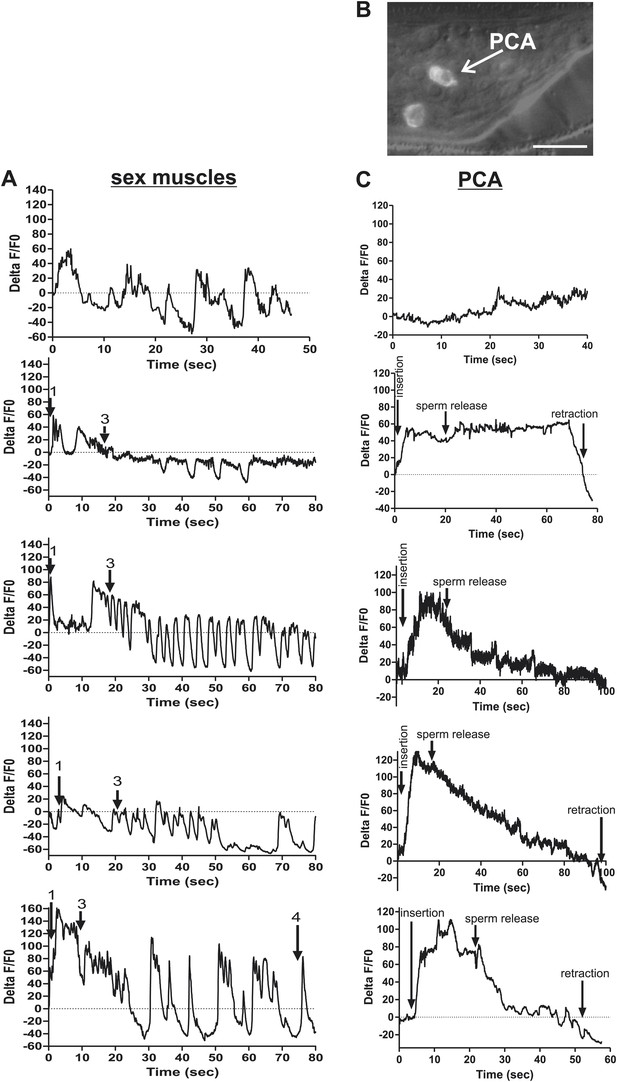
Ca2+ transient changes in sex muscles and the PCA neurons during ejaculation.
(A) Ca2+ transient changes in the muscles during mating. % ΔF/F0 trace for mating from insertion (1) through sperm release (3), and retraction (4). (A) G-CaMP is expressed in the sex muscles via Punc-103E. (B) Nomarski image overlaid with fluorescent image of Peat-4:YFP expression in the PCA post cloacal sensilla in the adult male tail. Scale bar = 10 µM. (C) %ΔF/F0 in PCA using Peat-4 to drive G-CaMP. (A and C) The first graph is extended prodding at the vulva, the other four include insertion and ejaculation.
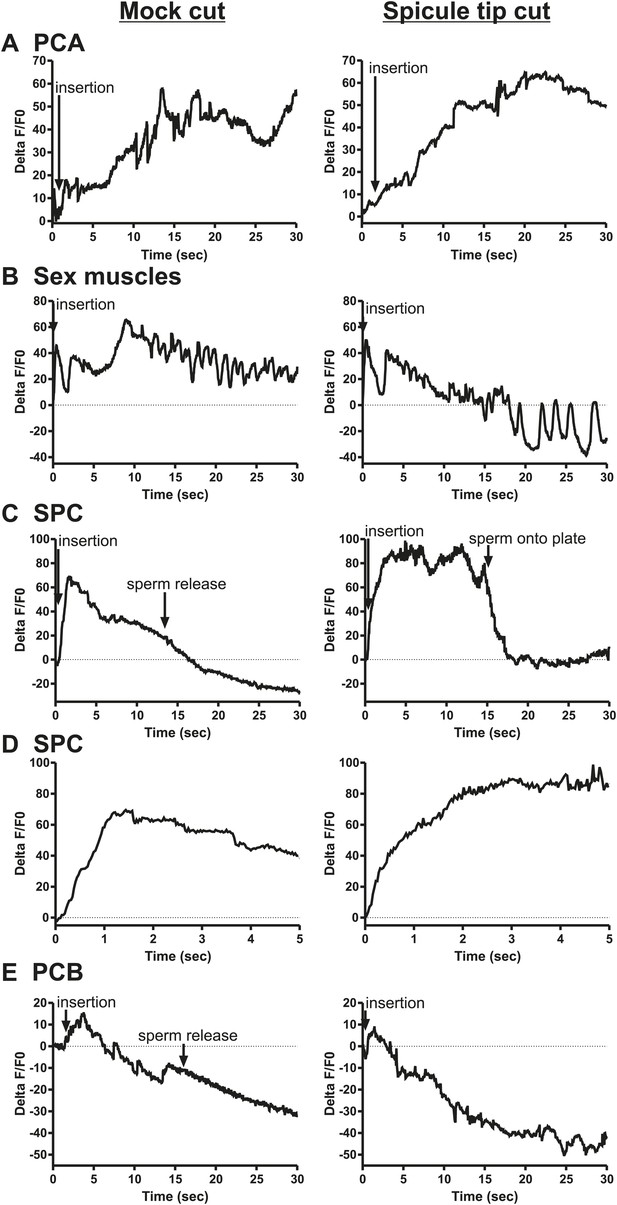
Calcium imaging in spicule tip cut males.
(A) % ΔF/F0 in the PCA. (B) % ΔF/F0 in the dorsal protractor, anal depressor, and gubernaculum erector and retractor. (C and D) % ΔF/F0 in the SPC. (E) % ΔF/F0 in the PCB.
Removing the spicule sensilla has no effect on the PCA neuron Ca2+ transients.
% ΔF/F0 for 30 s following insertion in PCA neurons. G-CaMP expressed in PCA using Peat-4. Males were either operated on by having their spicule tips removed (Spicule tips cut column) or exposed to the operating conditions (Spicule tips cut control column).
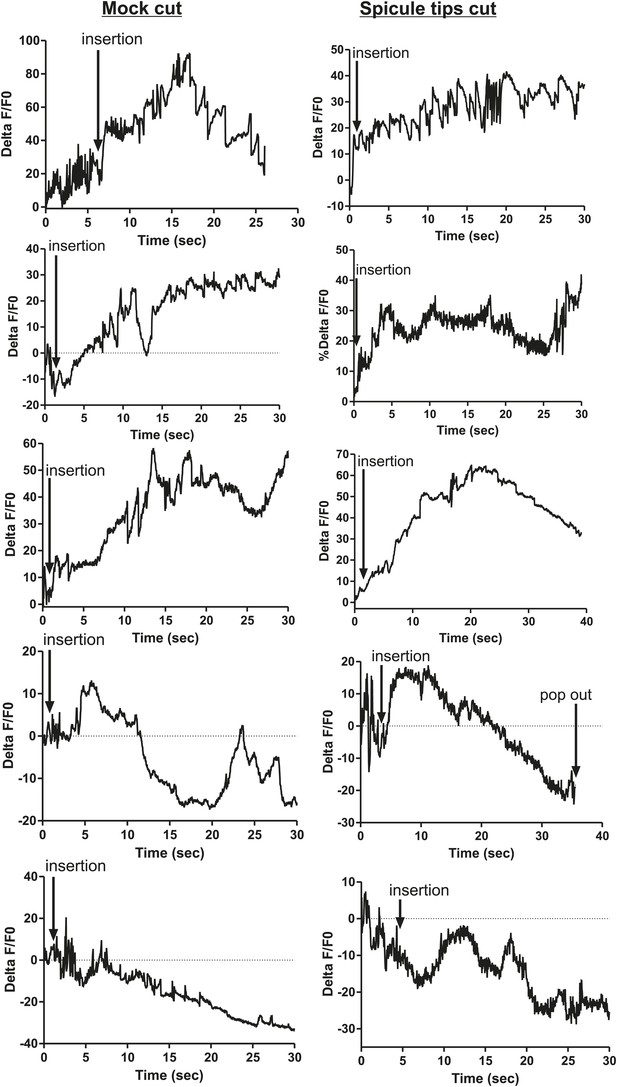
Removing the spicule sensilla has no effect on the sex muscle Ca2+ transients.
Calcium imaging in the dorsal sex muscles (dorsal protractor, gubernaculum erector and retractor, anal depressor) in spicule tip cut (right column) and non-cut controls (left column). G-CaMP expressed using Punc-103E. % ΔF/F0 from insertion through 30 s of intromission.
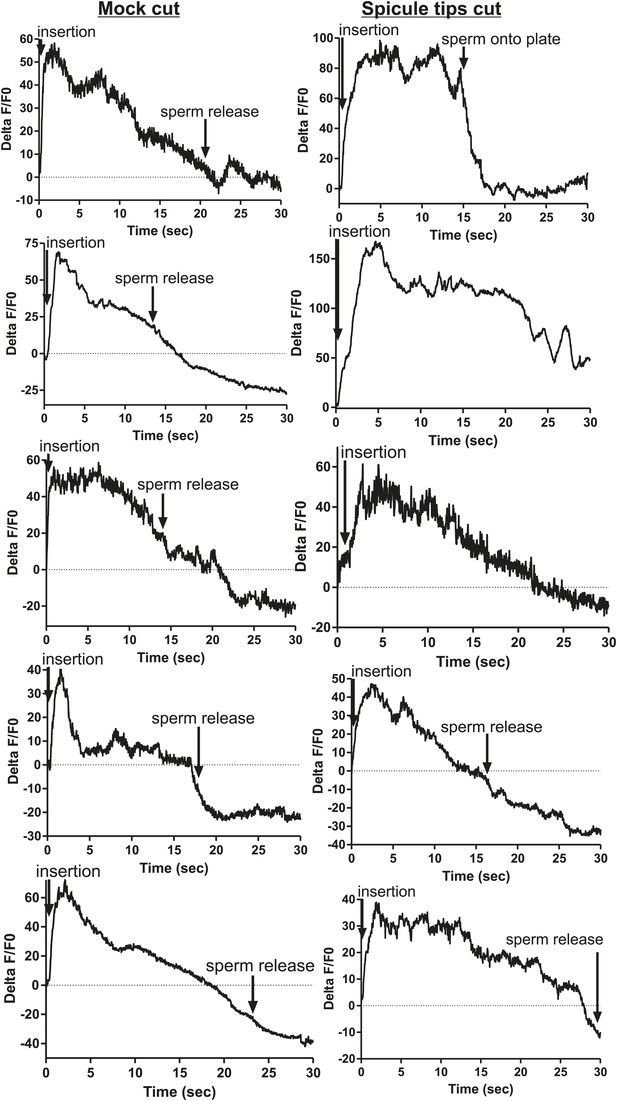
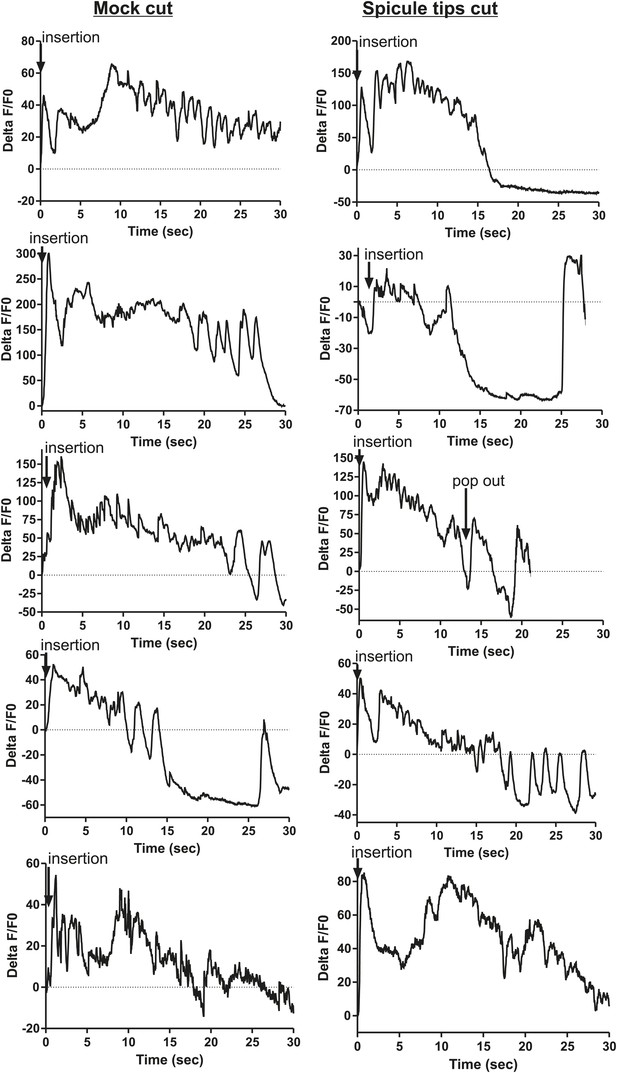
Ca2+ transients increase at a slower rate in the SPC neurons when the spicule sensilla are removed.
Calcium imaging in the SPC in spicule tips cut males (right column) and non-operated control males (left column). G-CaMP expressed from Pgar-3B. % ΔF/F0 reported from spicule insertion into hermaphrodite vulva through 30 s.
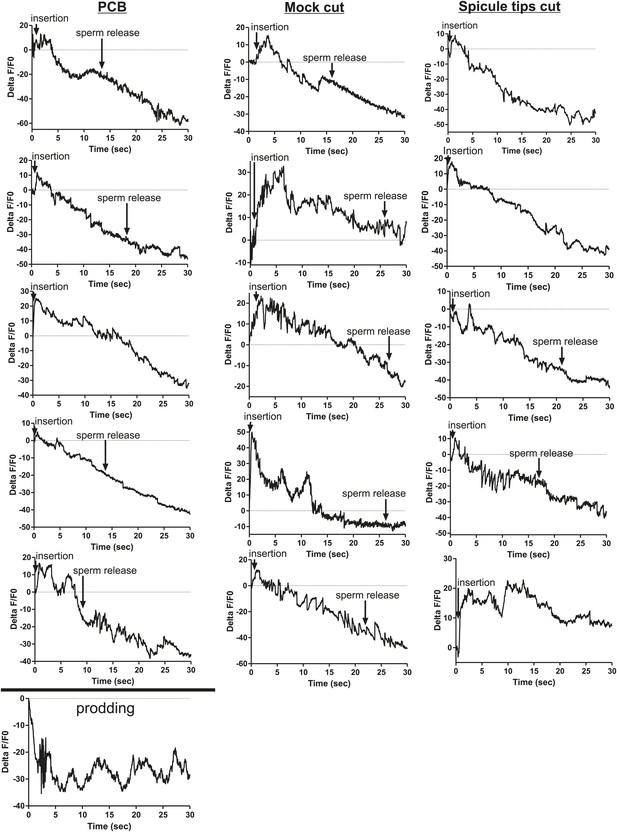
Removing the spicule sensilla has no effect on the PCB neuron Ca2+ transients.
Calcium imaging from Pdop-2:G-CaMP expressed in PCB. The first column shows the % ΔF/F0 for insertion and sperm release for five males. The final graph shows calcium imaging in the PCB while the male spicules are rhythmically prodding at the hermaphrodite vulva slit. The next two columns represent males that have been either surgically altered through removal of their spicule tips (Spicule tips cut) or males that have been placed under the operating conditions (Mock cut).
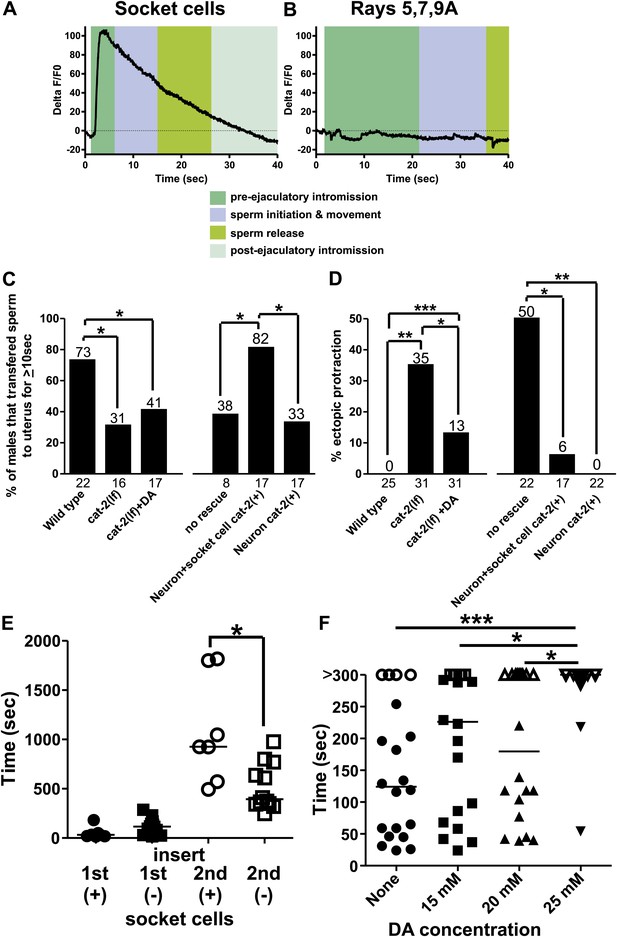
Socket cell dopamine (DA) promotes sperm release.
(A) % ΔF/F0 in the socket cells. G-CaMP is expressed from Pcat-2. (B) % ΔF/F0 in the dopaminergic rays 5,7,9A. G-CaMP is expressed from Pdat-1. (C) % of males that transferred sperm for ≥10 s into the uterus. (D) Ectopic protraction exhibited when males are placed with hermaphrodites. (C and D) cat-2(+) indicates in what cells cat-2 was rescued. *p value<0.05, **p value<0.005, ***p value<0.0001, Fisher's exact test. n values below the x-axis, percentages above the bars. (E) Time to 1st insert (1st) and refractory period (2nd) for cat-2(lf) rescued males. cat-2(+) is in all DA ray neurons. *p value<0.05, Mann–Whitney test. (F) The time required for virgin males to insert their spicules into a hermaphrodite. x-axis is the concentration of DA on which the males mated. y-axis is the amount of time (sec) the males took from being placed with hermaphrodites until they inserted their spicules into the uterus. Closed symbols indicate time from placement with hermaphrodites to insertion. Open symbols indicate the male did not insert within 5 min of being placed with hermaphrodites. Bars represent the median. *p value<0.05, **p value<0.005, ***p value<0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's correction.
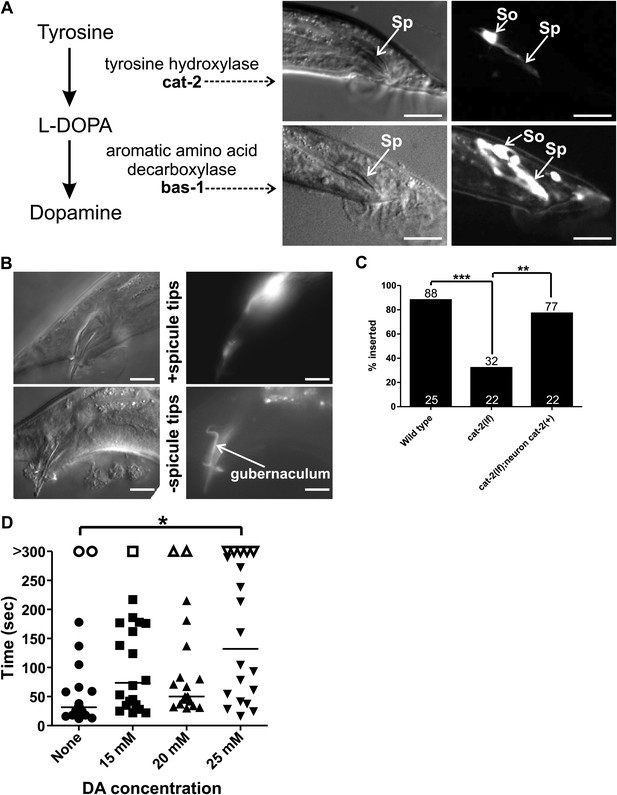
Socket cell DA regulates male mating.
(A) Dopamine synthesis pathway. Two DA synthesis genes, bas-1 and cat-2, are expressed in the male socket cells. Left images are DIC, right fluorescence. Sp = spicule, So = socket cells. Dorsal is up, anterior is to the left. Scale bar = 10 µM. (B) Images of a male expressing Pcat-2:YFP. Dorsal is up, anterior is to the right. Right, DIC images of the male tail. Left, fluorescent images of the male tail. Images of the spicule tips cut off are the same male 1 day later. Scale bar = 10 µM. (C) cat-2(lf) males insert at a low efficiency that is rescued by cat-2(+) in the ray neurons. Numbers above the bars are percentages, numbers at the x-axis indicate n. **p<0.005, ***p<0.0001, Fisher’s exact test. (D) Commencement times for males placed on the indicated concentrations of DA. Each dot represents one male and is a measurement of the time it took him, from the moment he was placed next to a 10 µM pad + hermaphrodites, to start backing along the hermaphrodite cuticle. n = 20 for each concentration. *p<0.05, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's correction.
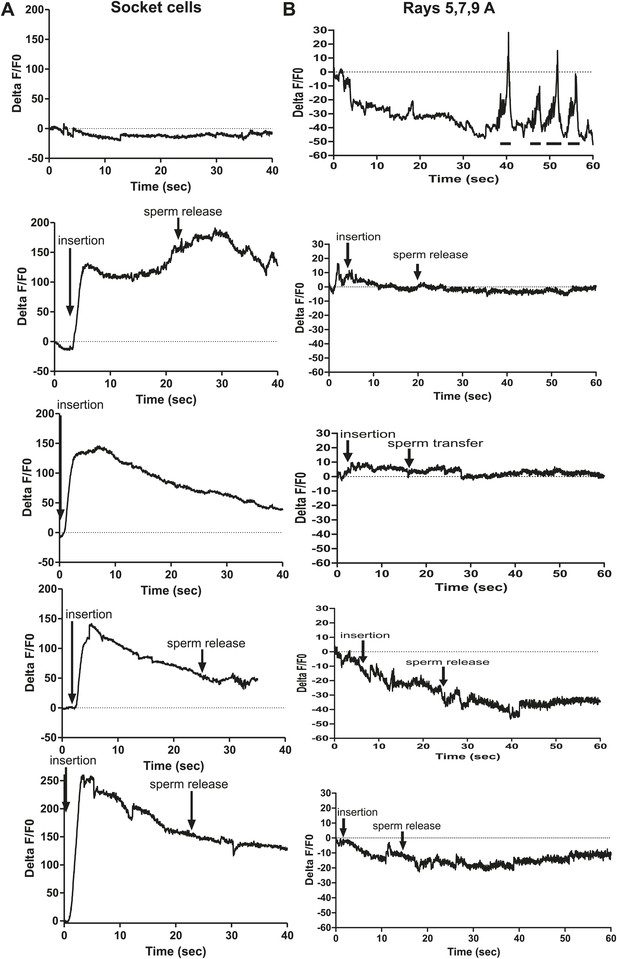
Ca2+ transients in the DA-expressing cells in the male tail.
(A and B) The first panel is the % ΔF/F0 in a male continuously prodding at the hermaphrodite vulva. All subsequent panels are % ΔF/F0 in males during insertion and sperm transfer into the uterus. (A) Ca2+ transient changes in the socket cells. G-CaMP was expressing using Pbas-1. (B) Ca2+ transient changes in the DA ray neurons 5,7,9A. G-CaMP was expressing using Pdat-1. The lines under the x-axis indicate where the male moved off the vulva.
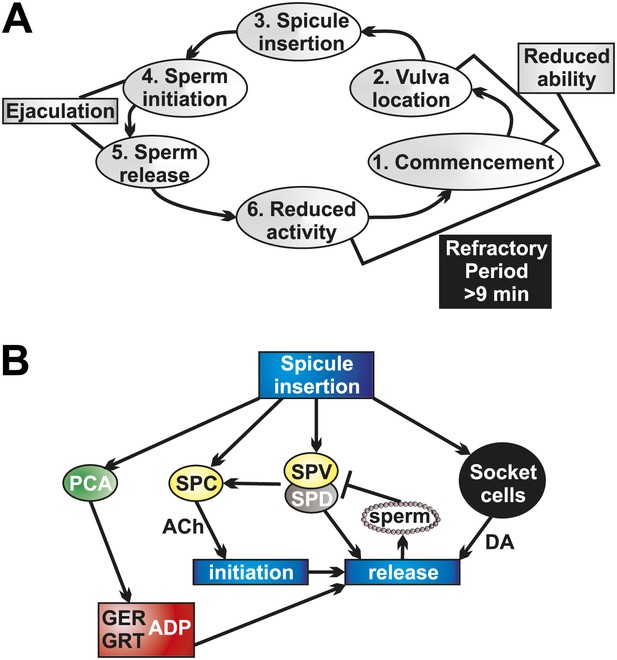
Socket cell DA and neuronal ACh regulate ejaculation and the refractory period.
(A) The steps of C. elegans male mating behavior. The order of the individual steps is given by the numbers. The refractory period is a period of reduced activity and mating ability following ejaculation. (B) Neurons, muscles, and support cells that are activated by spicule insertion. Mating behavior steps are represented by blue boxes. GER = gubernaculum erector muscle, GRT = gubernaculum retractor muscle, ADP = anal depressor muscle, DA = dopamine, ACh = acetylcholine. Glutamate is a possible PCA neurotransmitter.
Tables
Ca2+ transients following spicule insertion
| Cell | ↑Ca2+ insertion→peak (sec)* | Significance | Slope of initial Ca2+ increase (ΔF/F0%/sec) | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPC | 1.3 ± 0.52a | 45 ± 13 | ||
| Valve | 1.8 ± 0.79a | 60 ± 14 | ||
| SPV/SPD | 4.0 ± 1.0 | p<0.05 to ‘a’ | 21 ± 14 | p<0.05 to SPC and valve |
| PCA | 6.3 ± 0.56 | p<0.05 to ‘a’ | 15 ± 2.9 | p<0.05 to SPC and valve |
| Socket cells | 1.7 ± 0.36a | 94 ± 18 | p<0.005 to PCA | |
| Sex muscles 1st peak | 1.3 ± 1.7a | 155 ± 82 | p<0.005 to socket cells | |
| Sex muscles 2nd peak | 11 ± 3.9 | p<0.05 to sex muscles 1st peak | 46 ± 19† | p<0.0001 to sex muscles 1st peak |
| SPC control | 1.2 ± 0.30 | 60 ± 26 | ||
| SPC ablated | 2.2 ± 0.74 | p=0.022 to SPC control | 29 ± 12 | p=0.035 to SPC control |
-
Mean and standard deviation reported. For non-operated cell types, n = 5. Results of ANOVA: Newman–Keuls Multiple Comparison Test are shown. SPC–control and ablated, Mann–Whitney t test. SPC–control n = 6, SPC–ablated n = 7.
-
*
Time (sec) required for Ca2+ to increase from spicule insertion to Ca2+ peak.
-
†
Slope determined from where the Ca2+ begins to increase for a second time to Ca2+ peak following this second increase.
-
a
Peak times that are significantly different from the SPV/SPD and PCA cells.





