Myosin VIII associates with microtubule ends and together with actin plays a role in guiding plant cell division
Figures
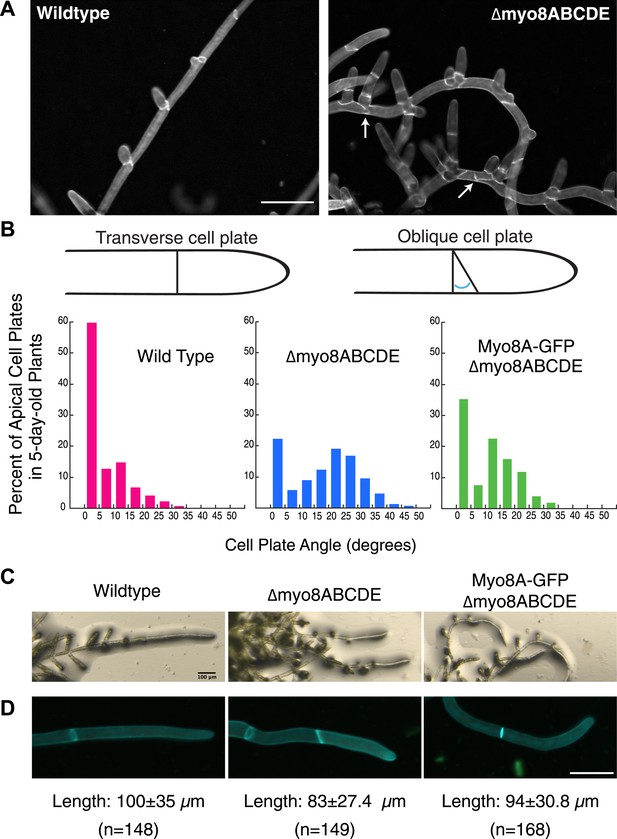
Cell plate defects in Δmyo8ABCDE can be restored by expression of Myo8A-GFP.
(A) 10-day-old wild type and myosin VIII null plants stained with calcofluor. Scale bar, 100 µm. Arrows indicate mis-positioned cell plates. (B) Histograms of cell plate angles of apical cells from 5-day-old plants regenerated from protoplasts. Images of apical cells were acquired as in Figure 1A and cell plate angles were measured manually using ImageJ. Number of cells analyzed: wild type (n = 151), Δmyo8ABCDE (n = 180), Myo8A-GFP in Δmyo8ABCDE (n = 167). All distributions are significantly different from each other (Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney Rank Sum Test, p < 0.001). (C) 8-day old plants regenerated from protoplasts were imaged with a stereo microscope. Scale bar, 100 µm. (D) Measurements of cell length were made on images of the apical cells from calcofluor stained 5 and 6-day old plants regenerated from protoplasts. Average apical cell lengths with standard deviation are indicated below each image. n indicates the number of cells measured. Scale bar, 50 µm.
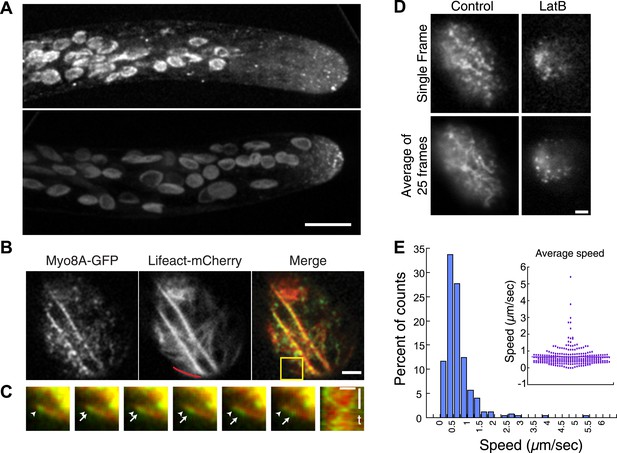
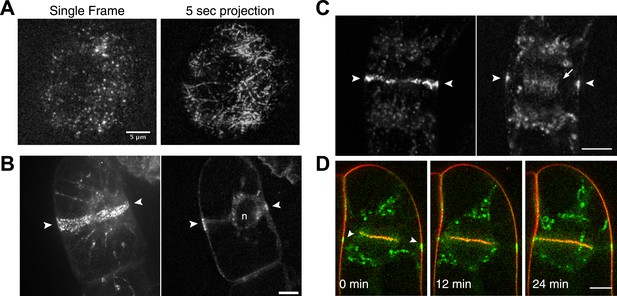
Myo8A moves on cortical actin filaments.
(A) Myo8A-GFP localizes to punctate structures throughout the cytosol as well as on the cell cortex. Images are maximum projections of z-stacks acquired with a spinning disc confocal. The punctate structures accumulate near the apex of the growing cell. Large globular structures are chloroplasts, which autofluorescence under these imaging conditions. Scale bar, 10 µm. (B) Images of Myo8A-GFP and Lifeact-mCherry in moss protonemata were simultaneously acquired with VAEM. In the merge Myo8A-GFP is green and Lifeact-mCherry is red. Scale bars, 2 µm. See also Video 1. Yellow box indicates the enlarged area shown in (C). Red line marks the trace for making the kymograph in (C). (C) An example of Myo8A-GFP particle moving along actin filaments. Six consecutive frames with 76 ms time interval are shown. Arrowhead indicates the starting position of a Myo8A-GFP particle, and arrows indicate the last position of that Myo8A-GFP. In the last frame, a new Myo8A-GFP particle binds to the same position indicated by the arrowhead. Linear movement of Myo8A-GFP is evident in kymograph. Scale bar, 1 µm. Scale bar in t, 1 s. (D) Moss protonemal cells expressing Myo8A-GFP, were treated with or without 25 µm Latrunculin B (LatB) and imaged with VAEM. In control samples, Myo8A-GFP linear trajectories are apparent in a frame average of 25 frames from approximately 2 s of real time, but absent in cells treated with LatB. Scale bars, 2 µm. See also Video 2. (E) Distribution of Myo8A-GFP velocities on actin filaments. Inset is a dot plot of the measured Myo8A-GFP velocities. Average velocity is 0.65 ± 0.57 µm/s; n = 249 events from seven cells.
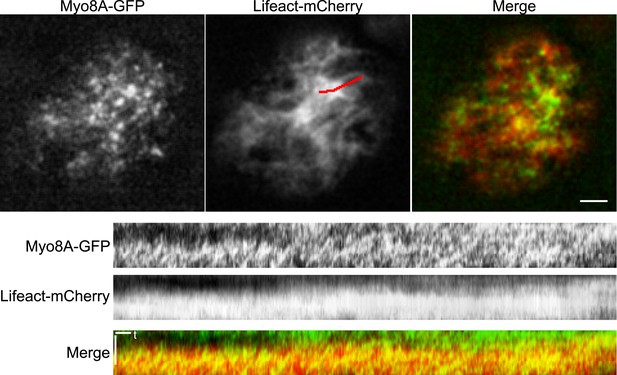
Myo8A moves on cortical actin filaments.
Images of Myo8A-GFP and Lifeact-mCherry in moss protonemata were simultaneously acquired with VAEM. In the merge Myo8A-GFP is green and Lifeact-mCherry is red. Scale bars, 2 µm. Scale bar in t, 1 s. Red line marks the trace for making the kymographs shown below.
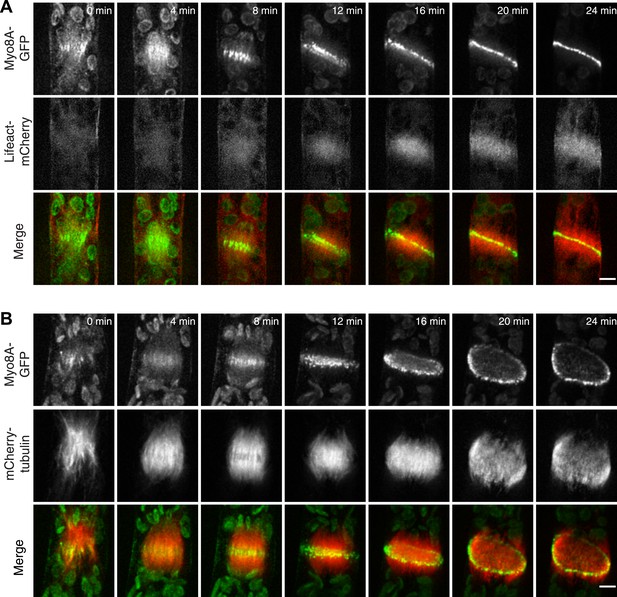
Myosin VIII localizes to the phragmoplast and cortical division site in moss.
A protonemal branching cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red). Images are maximum intensity projections of z-stacks from a spinning disc time-series acquisition. Before mitosis, Myo8A-GFP accumulates at the neck of the emerging cell (top, arrows). Myo8A-GFP accumulates at the spindle midzone (middle, arrow heads) and forms a ring at the edge of the phragmoplast that expands out to the cell cortex (bottom). Scale bar, 10 µm. See also Video 3.
Myo8A-GFP localizes to the cortical division site and the phragmoplast in moss.
Images from a 3D rotation of the spinning disc confocal images presented in Figure 3. Rotations along the plane of the phragmoplast equator show that in the early phragmoplast Myo8A-GFP is found throughout the phragmoplast midzone and the cell cortex. As the phragmoplast matures, Myo8A-GFP tightens into a ring along the leading edge of the phragmoplast.
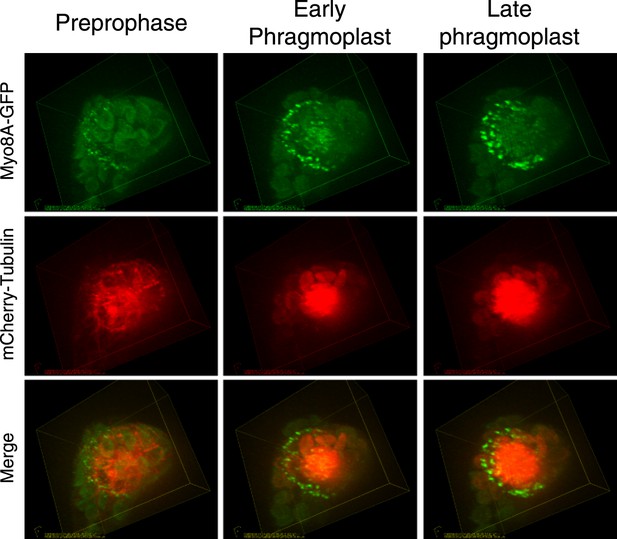
Myosin VIII localizes to the preprophase band, phragmoplast and cortical division site in tobacco BY-2 cells.
(A) Myo8A-GFP localizes to dynamic punctate cortical structures on the cell cortex of BY-2 cells. VAEM image of a single frame from a time-lapse acquisition is shown on the left. On the right is a maximum projection of frames from 5 s of real time. Linear trajectories are readily apparent in the maximum projection. See also Video 4. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B and C) Left, z-projection. Right, midplane. Tobacco BY-2 cell in preprophase (B) and cytokinesis (C) expressing moss Myo8A-GFP. Myo8A-GFP accumulates on the preprophase band (B, arrow heads). n denotes the nucleus. Myo8A-GFP remains at the cortical division site (C, arrow heads) and is at the phragmoplast midzone (C, arrow). (D) Images from a single focal plane of a dividing BY-2 cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and stained with FM4-64 (red) acquired over time. FM4-64 labels membrane added to the expanding cell plate (asterisk). Myo8A-GFP localizes to the phragmoplast midzone (arrow) and the cortical division site (arrow heads). See also Video 5. Images in (B–D) were acquired with a spinning disc confocal. (B–D) Scale bars, 10 µm.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Multiple sequence alignment of class VIII myosins from Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb), and Physcomitrella patens (Pp) generated with Clustal O. Nicotiana benthamiana sequences can be found on CyMobase. The following sequences can be found on Phytozome Physcomitrella patens v1.6: PpMyo8A (Pp1s228_18V6.1), PpMyo8C (Pp1s199_21V6.1). The following sequences can be found on NCBI: PpMyo8B (AEM05967), PpMyo8D (AEM05968), PpMyo8E (AEM05969), AtMyo8A (NP_194467), AtMyo8B (NP_175453), AtMyo8C (NP_001078755), AtMyo8D (NP_188630).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03498.012
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Table shows the amino acid sequence comparison between Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb) and Physcomitrella patens (Pp) class VIII myosins. Percent identity from Clusal O multiple sequence alignment is reported.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03498.013
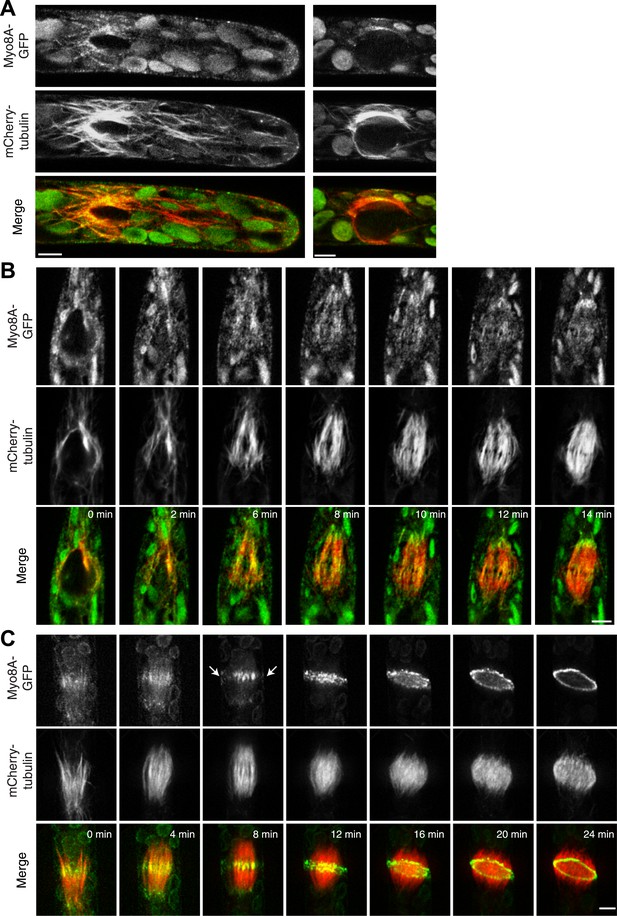
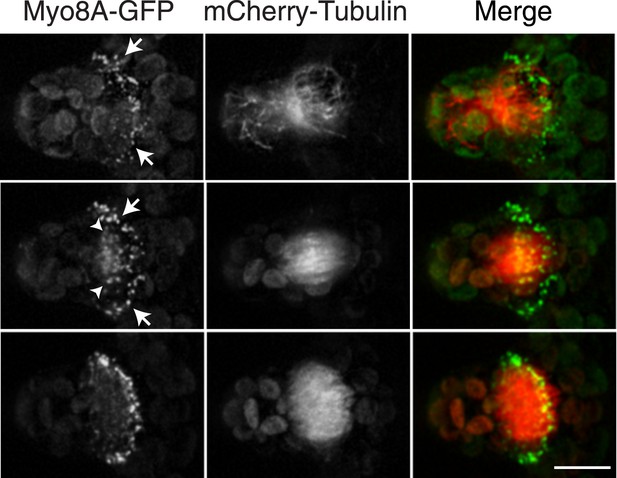
Myo8A-GFP localizes to the mitotic spindle and phragmoplast.
(A and B) Moss protonemal apical cells expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) imaged on a scanning confocal microscope. Images are single focal planes acquired over time. Scale bar, 5 µm. (A) Two examples of Myo8A-GFP associating with cytoplasmic microtubules surrounding the nucleus before mitosis. (B) Myo8A-GFP stays associated with microtubules throughout mitosis. See also Video 6. Scale bar, 5 µm. (C) Myo8A-GFP accumulates in the midzone. Arrows indicate cortical accumulation. Images were acquired with a spinning disc confocal microscope and are maximum projections of z-stacks acquired over time. See also Video 7. Scale bar, 5 µm. In all cases, large globular structures are chloroplasts that auto-fluoresce in the GFP channel.
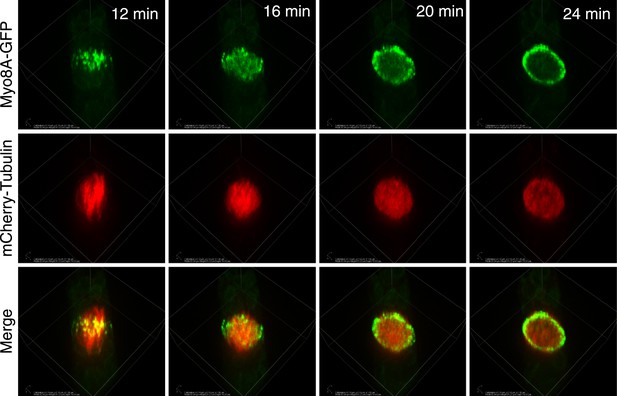
Myo8A-GFP localization in the phragmoplast.
Images from a 3D rotation of the spinning disc confocal images presented in Figure 5C. Rotations along the plane of the phragmoplast equator show that in the early phragmoplast Myo8A-GFP is found throughout the phragmoplast midzone and the cell cortex. As the phragmoplast matures, Myo8A-GFP tightens into a ring along the leading edge of the phragmoplast.
Myo8A-GFP localizes to the mitotic spindle and phragmoplast independent of actin.
Moss protonemal apical cells imaged on a spinning disc confocal microscope. All images are maximum projections of z-stacks acquired over time. (A) Cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and Lifeact-mCherry (red). (B) Cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) treated with 25 µm LatB. See also Video 8. Scale bars, 5 µm. In all cases, large globular structures are chloroplasts that auto-fluoresce in the GFP channel.

Dose response of latrunculin B in apical protonemal moss cells.
VAEM images of protonemal apical cells expressing lifeact-mRuby2 were acquired with increasing concentrations of LatB. At 25 µM, the concentration used for all drug treatments, it is no longer possible to observe actin filaments (n = 25 cells).
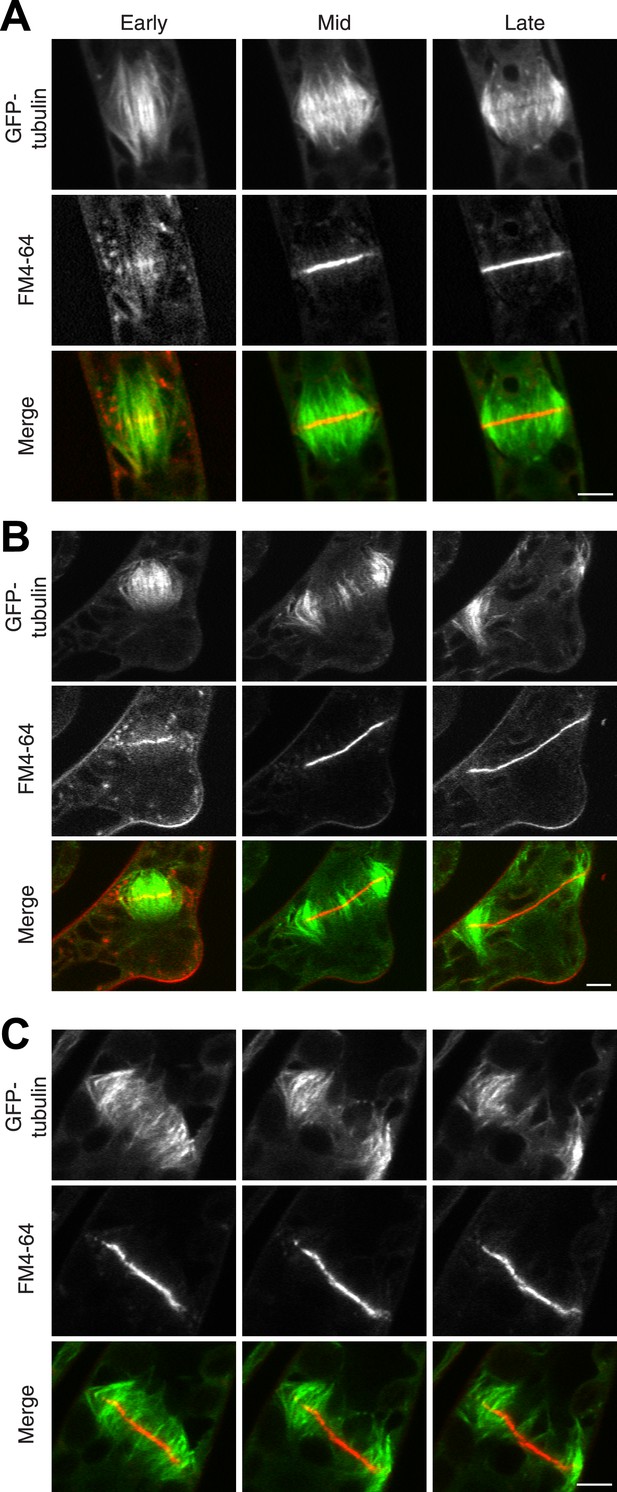
Actin is required for Myo8 function in cytokinesis. Phragmoplasts from wild type.
(A) Δmyo8ABCDE (B) and wild type treated with 25 µM LatB (C) expressing GFP-tubulin (green) and stained with FM4-64 (red). Cells were imaged on a scanning confocal microscope. For LatB treatment, wild type plants were treated with 25 µM LatB for 2 hr, then stained with FM4-64 and imaged in the presence of 25 µM LatB. Images are single focal planes taken from a time series. Scale bars, 5 µm. See also Video 9 (for A), Video 10 (for B), and Video 11 (for C).
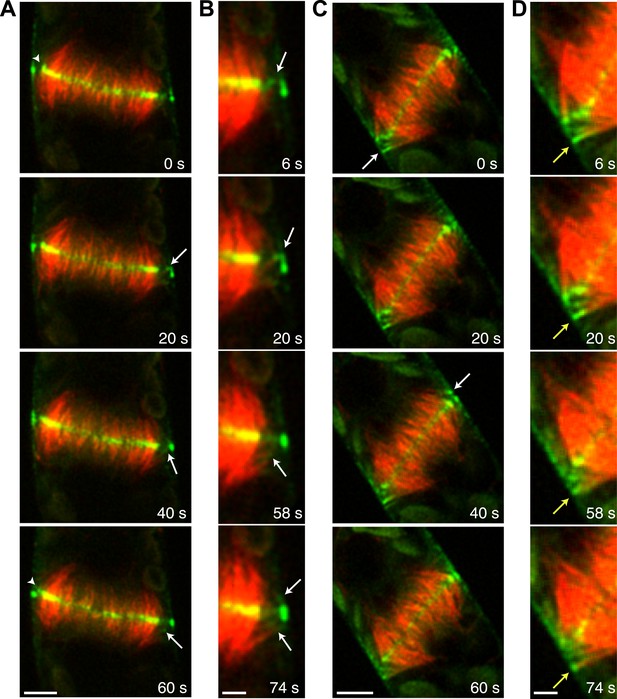
Myo8A-GFP associates with the ends of phragmoplast microtubules.
Images of a protonemal apical cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) were acquired with a spinning disc confocal microscope. Images are a single focal plane from a time series. Arrows indicate enrichment of Myo8A-GFP at the ends of peripheral microtubules. Arrow heads indicate where peripheral microtubules are incorporated into the phragmoplast midzone. (A) In a control cell, peripheral microtubules focus at the phragmoplast midzone. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) Zoom-in of the phragmoplast periphery from the control cell. Peripheral microtubules with Myo8A-GFP are evident in this area. In the presence of actin, peripheral microtubules are incorporated into the phragmoplast midzone rapidly. Scale bar, 2 µm. (C) In a cell treated with 25 µM LatB, peripheral microtubules are no longer focused at the midzone. Scale bar, 5 µm. (D) Zoom-in of the phragmoplast periphery in the LatB treated cell. Peripheral microtubules stay associated with the cell cortex for more than a minute. Scale bar, 2 µm. See also Video 12.
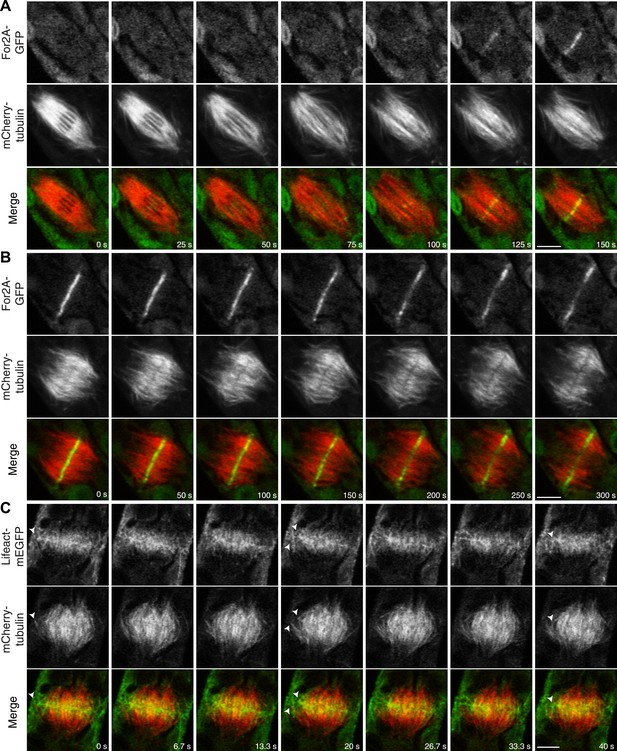
Actin is polymerized on the phragmoplast edge.
Single focal plane images acquired with a laser scanning confocal microscope. (A and B) Protonemal apical cell expressing For2A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red). (A) In metaphase through anaphase (A, t = 0–75 s), For2A-GFP is not associated with the spindle. See also Video 13. (B) For2A-GFP is enriched at the phragmoplast midzone and remains on the edge of the phragmoplast throughout cytokinesis. See also Video 14. (C) Protonemal cell expressing Lifeact-mEGFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red). Microtubules intersect actin filaments between the leading edge of the phragmoplast and the cell cortex (arrow heads). See also Video 15. Scale bars, 5 µm.
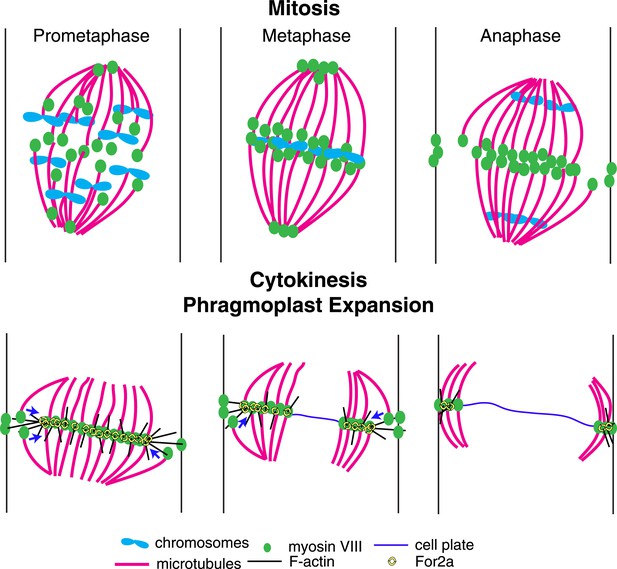
A model for myosin VIII function in phragmoplast guidance.
In prometaphase, myosin VIII localizes to plus ends throughout the mitotic spindle. In metaphase, myosin VIII accumulates at the spindle midzone and on the poles. During anaphase, myosin VIII is observed on peripheral microtubules and at the cell cortex. As the phragmoplast forms, the midzone myosin VIII accumulation tightens into a thin band on the phragmoplast edge. For2A is at the phragmoplast midzone. Actin filaments are generated between the phragmoplast and cortical myosin VIII. Peripheral microtubules with plus-end associated myosin VIII translocate on actin filaments and are incorporated into the expanding phragmoplast.
Videos
Myo8A moves on cortical actin filaments (see Figure 2B).
Myo8A-GFP (green) and Lifeact-mCherry (red) were simultaneously imaged with VAEM (acquired at 13 fps). Video is playing at 15 fps. Scale bar, 2 µm.
Myo8A motility at the cell cortex depends on actin (see Figure 2D).
Moss protonemal cells expressing Myo8A-GFP were imaged with VAEM continuously at 12.233 fps. Video is playing at 25 fps. Scale bar, 2 µm. Bottom panels show the same time series with a 25 frame rolling average.
Myo8A-GFP marks the future site of cell division in moss branching cells (see Figure 3).
Moss branch cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) was imaged with a spinning disc confocal microscope. Images are maximum projections of a z-stack acquired every minute. Video is playing at 4 fps. Scale bar, 10 µm.
Myo8A-GFP localizes to dynamic punctate cortical structures on the cell cortex of BY-2 cells (see Figure 4A).
BY-2 cells expressing Myo8A-GFP were imaged with VAEM (acquired at 11.3 fps). Video is playing at 11.3 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.
Myo8A-GFP localizes to the phragmoplast and cortical division site in tobacco BY-2 cells (see Figure 4D).
BY-2 cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) stained with FM4-64 (red) was imaged with spinning disc confocal microscope. Images are a single focal plane acquired every minute. Video is playing at 3 fps. Scale bar, 10 µm.
Myo8A-GFP localizes to the cytoplasmic microtubules around nucleus and remains on the spindle (see Figure 5B).
Moss apical cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) was imaged with a scanning confocal microscope. Images are a single focal plane acquired every minute. Video is playing at 4 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.
Myo8A-GFP associates with mitotic spindle and phragmoplast (see Figure 5C).
Moss apical cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) was imaged with a spinning disc confocal microscope. Images are maximum projections of a z-stack acquired every minute. Video is playing at 4 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.
Myo8A-GFP associates with the mitotic spindle and phragmoplast independent of actin (see Figure 6A,B).
Moss apical cells expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and lifeact-mCherry/mCherry tubulin (red) were imaged with a spinning disc confocal microscope. Images are maximum projections of a z-stack acquired every minute. Video is playing at 4 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm. Top, Myo8A-GFP and lifeact-mCherry in control cell. Bottom, Myo8A-GFP and mCherry-tubulin in LatB treated cell.
New membrane is deposited uniformly in a wild type dividing cell (see Figure 7A).
A wild type cell expressing GFP-tubulin was stained with FM4-64 and imaged in a single focal plane on a scanning confocal microscope. Video is playing at 10 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.
New membrane is deposited non-uniformly in a Δmyo8ABCDE dividing cell (see Figure 7B).
A Δmyo8ABCDE cell expressing GFP-tubulin was stained with FM4-64 and imaged in a single focal plane on a scanning confocal microscope. Video is playing at 10 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.
New membrane is deposited non-uniformly in a wild type dividing cell treated with LatB (see Figure 7C).
A wild type cell expressing GFP-tubulin was treated for two hours with 25 µM LatB and then stained with FM4-64 and imaged in 25 µM LatB. Images are from a single focal plane taken on a scanning confocal microscope. Video is playing at 10 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.
Peripheral microtubules require actin to be efficiently incorporated into the phragmoplast (see Figure 8).
Moss apical cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) were imaged with a spinning disc confocal microscope. Images are a single focal plane acquired every 2 s. Video is playing at 10 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm. Top, control. Bottom, LatB treated cell.
For2A-GFP does not associat with the mitotic spindle but is present in the phragmoplast (see Figure 9A).
Moss apical cell expressing For2A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) was imaged with a scanning confocal microscope. Images are a single focal plane acquired every 5 s. Video is playing at 5 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.
For2A-GFP remains at the edge of phragmoplast (see Figure 9B).
Moss apical cell expressing For2A-GFP (green) and mCherry-tubulin (red) was imaged with a scanning confocal microscope. Images are a single focal plane acquired every 5 s. Video is playing at 5 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.
Actin polymerizes between the edge of the phragmoplast and the cortical division site during cytokinesis (see Figure 9C).
Moss apical cell expressing Myo8A-GFP (green) and lifeact-mCherry (red) was imaged with a scanning confocal microscope. Images are a single focal plane acquired continuously at 3.75 fps. Video is playing at 75 fps. Scale bar, 5 µm.





