The dyskerin ribonucleoprotein complex as an OCT4/SOX2 coactivator in embryonic stem cells
Figures
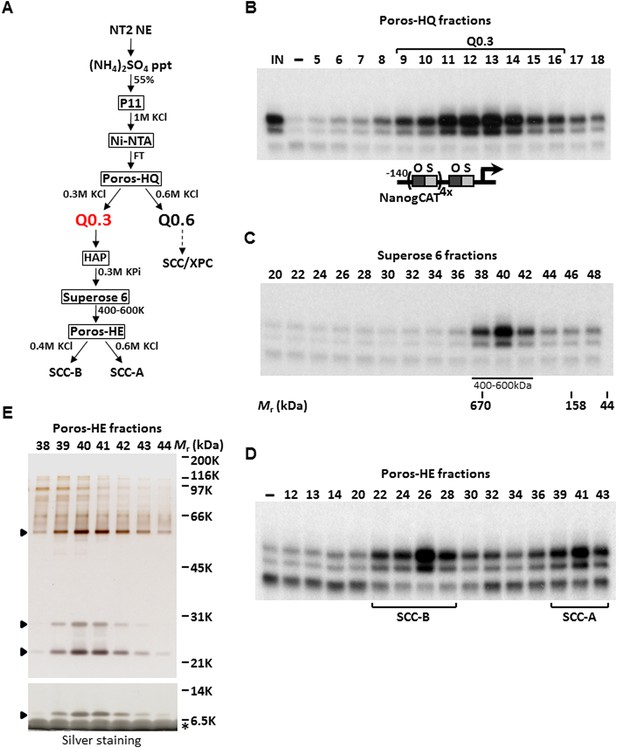
Purification of Stem Cell Coactivator-A (SCC-A) required for OCT4/SOX2-dependent activation of the Nanog gene.
(A) Chromatography scheme for purification of Q0.3 from NT2 nuclear extracts (NT2 NE). NT2 NE is first subjected to ammonium sulfate precipitation (55% saturation) followed by a series of chromatographic columns including cation exchangers phosphocellulose (P11), heparin (Poros-HE), the anion exchanger Poros-HQ, hydroxyapatite (HAP), and gel filtration medium Superose 6. (B) Input (IN, Ni-NTA flowthrough), buffer control (−) and fractions containing Q0.3 eluted from a Poros-HQ anion exchanger (fraction number indicated) are assayed in the presence of OCT4, SOX2, and recombinant XPC complex in in vitro transcription assays. (C) Q0.3 appears to migrate as a single activity. Superose 6 fractions are assayed as in (B). Mobilities of peak activity (400–600 K) and gel filtration protein standards are shown at bottom. (D) Q0.3 is composed of two distinct coactivator activities, SCC-A and SCC-B. Transcription reactions contain buffer control (−), Poros-HE fractions and are assayed as in (B). SCC-A activity elutes in fractions 39–43. (E) Silver-stained 10% Bis-Tris polyacrylamide gel of the active SCC-A fractions. Filled arrowheads indicate polypeptides that co-migrate with SCC-A activity. The bottom panel shows the same fractions separated on a 12% SDS-PAGE gel to show the smallest subunit of SCC-A. Insulin added to Poros-HE fractions as a protein stabilizer is indicated by asterisk.
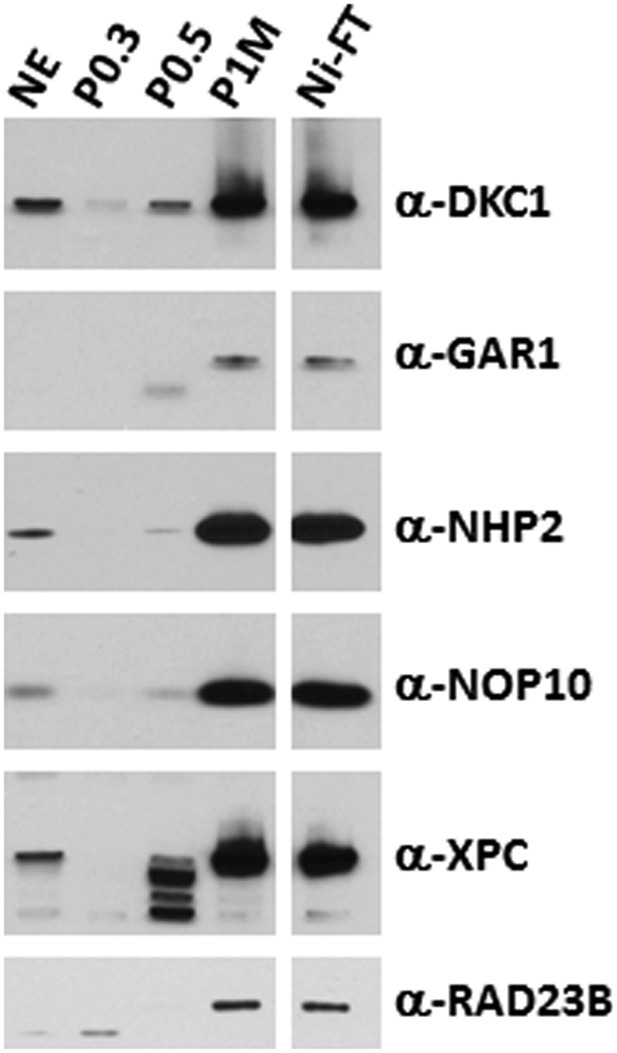
The DKC1 and the XPC coactivator complexes are highly enriched in the transcriptionally active phosphocellulose 1 M KCl (P1M) and Ni-NTA flowthrough (Ni-FT) fractions.
Comparative western blot analysis of NT2 nuclear extract (NE), phosphocellulose 0.3 M, 0.5 M, 1 M KCl fractions (P0.3, P0.5, P1M, respectively), and Ni-NTA flowthrough (Ni-FT) using antibodies against DKC1, GAR1, NHP2, NOP10, XPC, and RAD23B. Each lane contains 5 μg of protein as determined by Bradford protein assay (Bio-Rad).
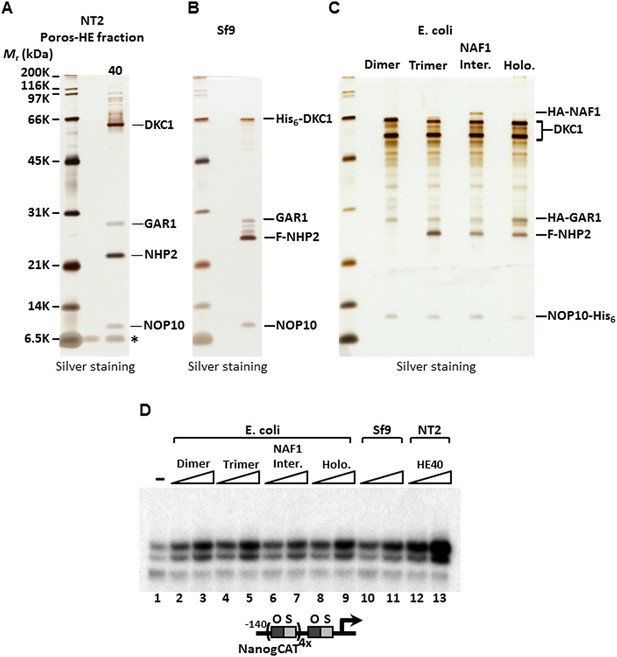
SCC-A is the dyskerin (DKC1) complex.
(A) Silver stained SDS-PAGE gel of Poros-HE peak activity fraction in Figure 1E with protein identities determined by mass spectrometry analysis. (B) Silver stained SDS-PAGE gel of recombinant DKC1 complex reconstituted in insect Sf9 cells infected with baculoviruses expressing His6-tagged DKC1, untagged GAR1, FLAG-tagged NHP2, and untagged NOP10. (C) Silver stained SDS-PAGE gel of recombinant partial and holo DKC1 as well as NAF1-containing intermediate complexes reconstituted in E. coli cells expressing various epitope-tagged subunits and untagged DKC1 as denoted. A prominent partial fragment of DKC1 co-purifies extensively with the full length DKC1 complexes. (D) Recombinant DKC1 complexes enhance OCT4/SOX2-activated transcription of Nanog. Buffer control (−), bacterial DKC1-NOP10 heterodimer (lanes 2 and 3), DKC1-NHP2-NOP10 trimer (lanes 4 and 5), NAF1-DKC1-NHP2-NOP10 intermediate (lanes 6 and 7), and holo DKC1-GAR1-NHP2-NOP10 (lanes 8 and 9), recombinant holo DKC1 complex purified from Sf9 cells (lanes 10 and 11), and endogenous holo-complex from NT2 (Poros-HE peak activity fraction 40, lanes 12 and 13) are assayed over a twofold concentration range. Transcription reactions contain OCT4, SOX2, recombinant XPC complex, and a Poros-HE fraction containing SCC-B.
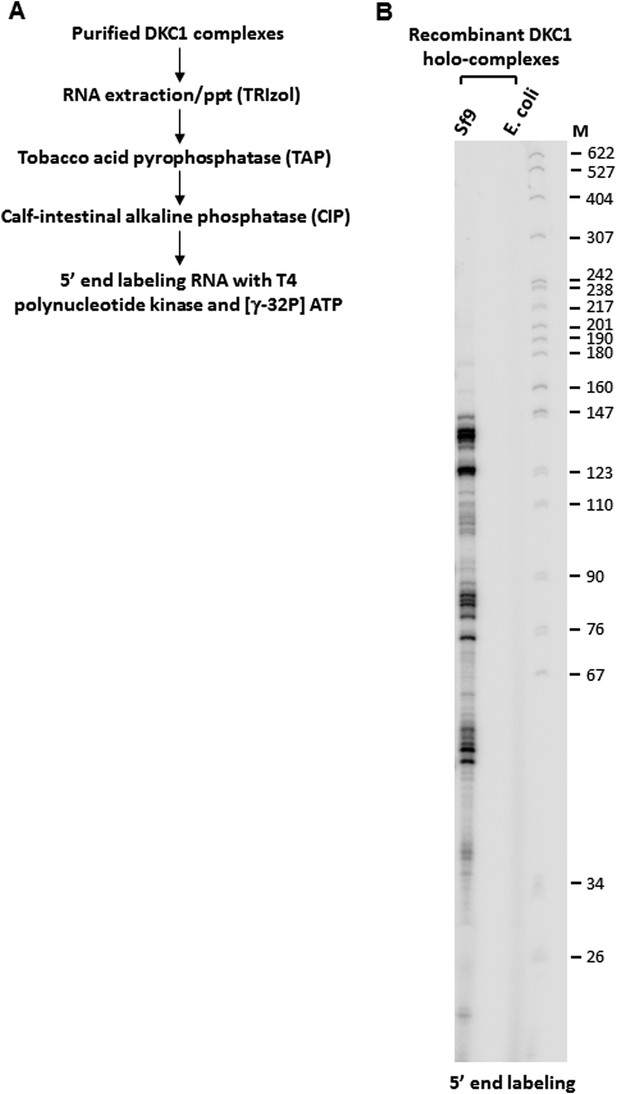
5’ end radiolabeling of RNAs co-purified from recombinant DKC1 complexes.
(A) Schematics of RNA labeling procedure. RNAs are treated with tobacco acid pyrophosphatase (TAP) to remove 5′ cap and dephosphorylated with APex heat-labile alkaline phosphatase before being radiolabeled by T4 polynucleotide kinase (T4 PNK). (B) Recombinant DKC1 complexes reconstituted in E. coli lack detectable co-purifying RNAs. 5′ end radiolabeled RNAs from DKC1 complexes purified from Sf9 and E. coli cells are separated on a 6% urea-polyacrylamide gel. Size markers (M) are in nucleotides.
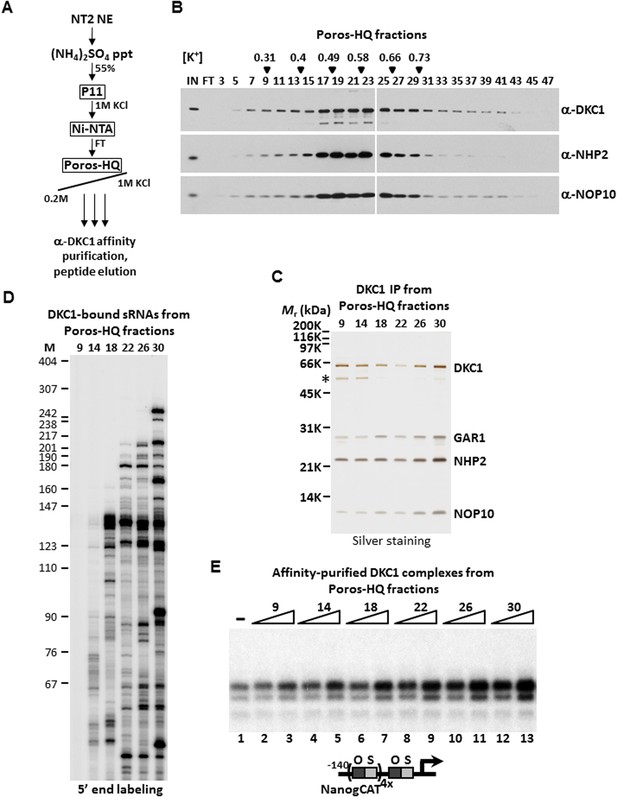
DKC1-associated small RNAs modulate transcriptional coactivator activity.
(A) Purification scheme of endogenous DKC1 ribonucleoprotein complexes (RNPs). A partially purified fraction (Ni-FT) containing the bulk of the DKC1 RNPs in NT2 cells (See Figure 1—figure supplement 1) is fractionated over a Poros-HQ anion exchange column followed by affinity purification using a monoclonal antibody against DKC1 and peptide elution. (B) Extensive heterogeneity of the endogenous DKC1 RNPs from NT2 cells. Western blotting of input (IN), flowthrough (FT), and various salt-eluted Poros-HQ fractions using antibodies against DKC1, NHP2, and NOP10. Filled inverted triangles indicate fraction numbers used for affinity purification. Salt concentrations ([K+] in M) of selected fractions are indicated. (C) Silver stained SDS-PAGE gel of the DKC1 RNPs affinity-purified from indicated Poros-HQ fractions. A proteolytic fragment of DKC1 is denoted by asterisk. (D) 5′ end labeling of RNAs isolated from affinity-purified DKC1 RNPs from indicated Poros-HQ fractions. Radiolabeled RNAs were separated on a 6% denaturing urea-polyacrylamide gel. Size markers are in nucleotides. (E) Buffer control (−) or affinity-purified DKC1 RNPs from salt-eluted Poros-HQ fractions over a threefold concentration range are assayed using in vitro transcription. Reactions contain OCT4, SOX2, recombinant XPC complex, a Poros-HE fraction containing SCC-B.
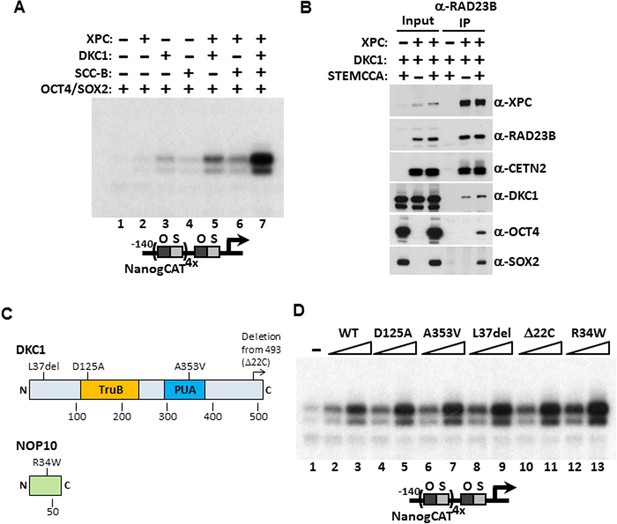
Mechanism of Coactivation by the DKC1 Complex.
(A) Co-dependent activation of Nanog transcription by the XPC complex, the DKC1 complex, and SCC-B. Recombinant XPC and DKC1 complexes purified from Sf9 cells, and SCC-B purified from bacteria were added individually (lanes 2–4), or in various combinations (lanes 5–7) to in vitro transcription reactions containing OCT4 and SOX2. Strongest synergistic activation is observed when all three coactivators are present in the transcription reaction (lane 7). (B) DKC1 interacts with the XPC complex independent of OCT4 and SOX2 in vivo. Control (−), plasmids expressing mouse XPC complex (XPC), mouse DKC1 complex (DKC1), and STEMCCA were co-transfected into 293T cells. Cell lysates are immunoprecipitated with anti-RAD23B antibody. Input extracts (2%) and RAD23B-bound proteins were analyzed by western blotting. (C) Schematic diagrams showing the two structural domains in DKC1 (TruB and PUA) and mutations in DKC1 and NOP10 selected for functional analyses in (D). All mutations except D125A are identified in patients with dyskeratosis congenita (DC). (D) Wild type, pseudouridine synthase inactive (D125A), and DC mutant DKC1 complexes (Dkc1 A353V, Dkc1 L37del, Dkc1 Δ22C, and Nop10 R34W) are reconstituted in Sf9 cells and assayed over a threefold concentration range in in vitro transcription reactions containing OCT4, SOX2, recombinant XPC complex, and SCC-B.
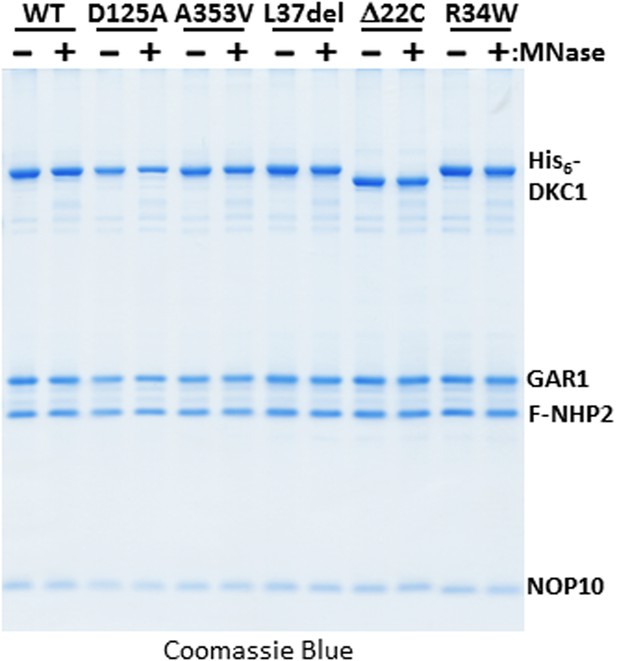
Micrococcal nuclease (MNase)-treated recombinant DKC1 complexes remain structurally intact.
Recombinant wild-type (WT) and various mutant DKC1 complexes are mock treated (−) or digested extensively with MNase (+), and washed extensively to remove any dissociated RNAs prior to FLAG peptide elution. Eluted protein complexes are analyzed by Coomassie Blue staining.
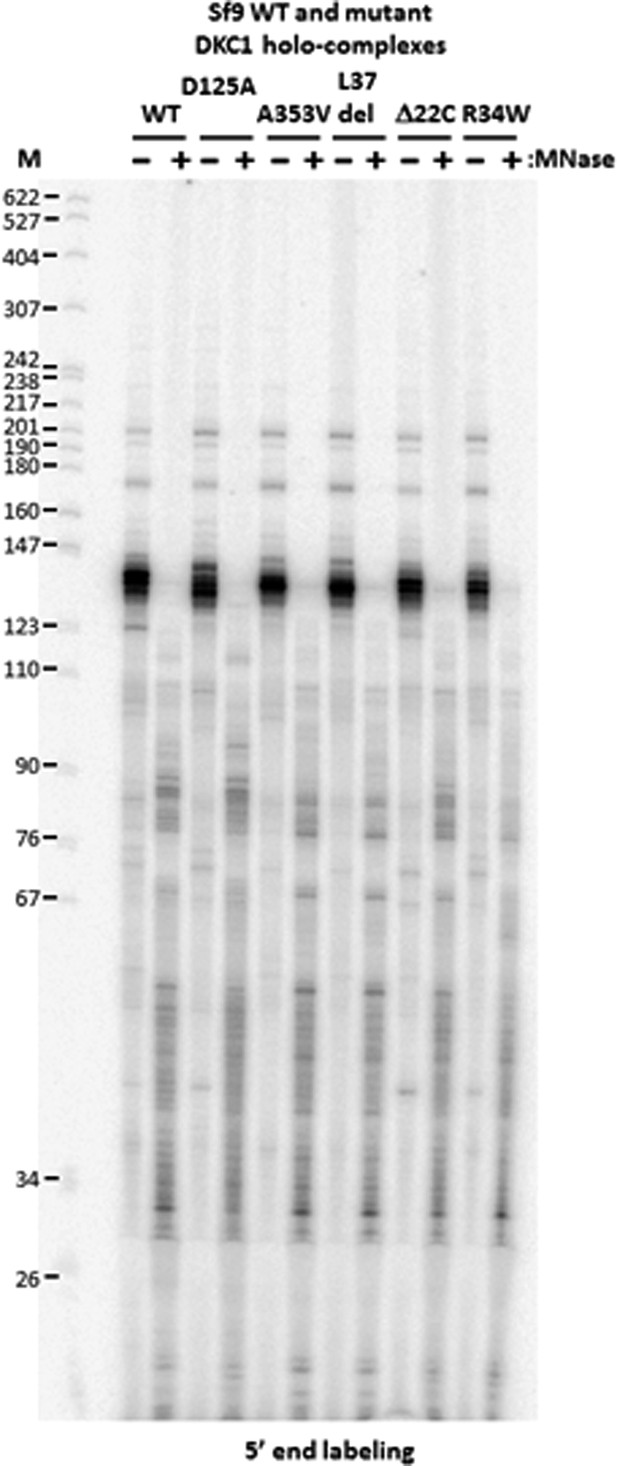
DKC1-associated RNAs in recombinant DKC1 complexes are resistant to extensive MNase digestion.
RNAs co-purified from mock and MNase-treated recombinant DKC1 complexes in Figure 4—figure supplement 1 are 5′ end radiolabeled and separated on a 6% urea-polyacrylamide gel as described in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Note that the prominently labeled 130–140 nucleotide (nt)-long RNA clusters are resistant to complete nuclease digestion. It appears that these RNAs are cut on average once by MNase to generate two new smaller clusters (80–90 nt and 30–55 nt) that remain stably associated with the DKC1 complexes. Increasing the amount of MNase and/or nuclease digestion time did not change the patterns or disrupt the integrity of the protein complexes (data not shown).
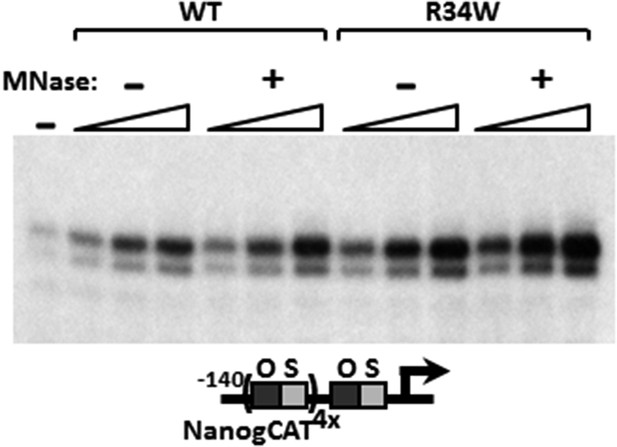
MNase digestion moderately increases DKC1 coactivator activity.
Mock (−) or MNase-treated (+) WT and Nop10 R34W DKC1 complexes are assayed in in vitro transcription reactions (over a fourfold concentration range) supplemented with OCT4, SOX2, recombinant XPC complex and SCC-B.
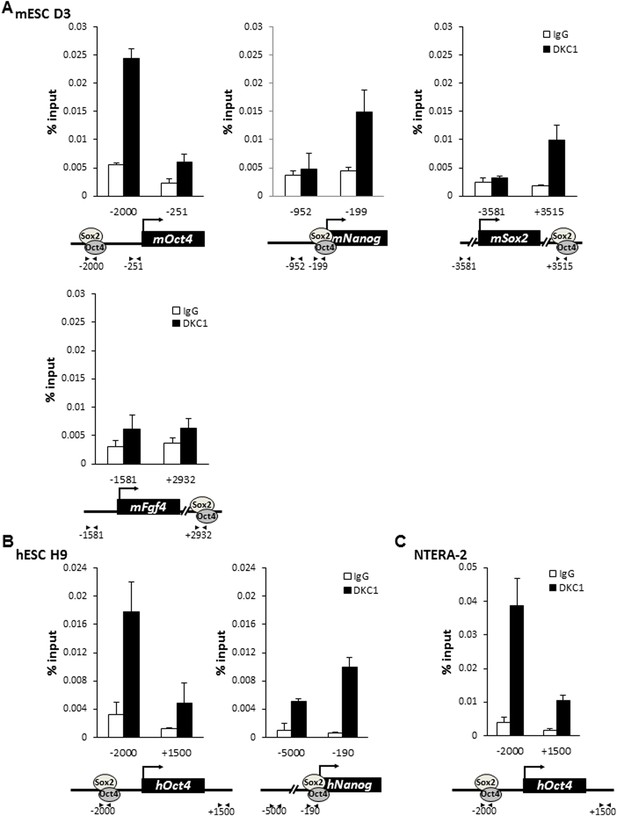
The DKC1 complex is recruited to regulatory regions of key pluripotency genes in mouse and human ES cells.
(A) Co-occupancy of DKC1, OCT4, and SOX2 on enhancers of Oct4, Nanog, Sox2, but not Fgf4, in mouse ES cell line D3. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of DKC1 occupancy on control and enhancer regions of the Oct4, Nanog, Sox2, and Fgf4 gene loci. Representative data (n = 3) showing the enrichment of DKC1 (black bars) compared to control IgGs (white bars) are analyzed by qPCR and expressed as percentage of input chromatin. Schematic diagrams of OCT4/SOX2 binding sites of each gene and the relative positions of the amplicons used to detect enriched ChIP fragments are shown at the bottom. Error bars represent standard deviation, n = 3. Primer sequences can be found in Supplementary file 1. (B) DKC1 is recruited to regulatory regions of Oct4 and Nanog in human ES cell line H9. Representative ChIP data (n = 3) are analyzed as described in (A). Error bars represent standard deviation, n = 3. (C) DKC1 is enriched on Oct4 promoter in human embryonal carcinoma cell line NT2. Representative ChIP data (n = 3) are analyzed as described in (A). Error bars represent standard deviation, n = 3.
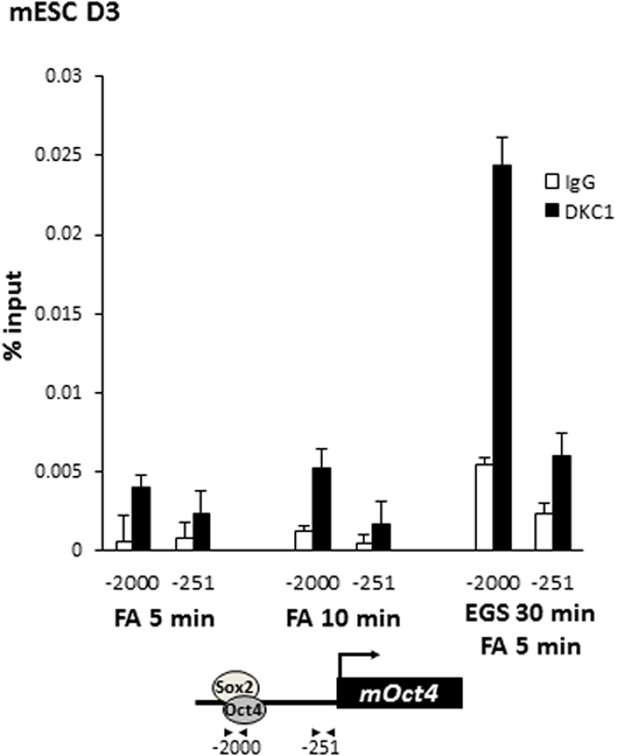
Crosslinking DKC1 to chromatin requires protein–protein crosslinker ethylene glycol bis[succinimidylsuccinate] (EGS) in addition to formaldehyde (FA).
Mouse ES cell line D3 is crosslinked with FA for 5 min (left), 10 min (middle), or with EGS for 30 min followed by FA for 5 min (right). ChIP analysis of DKC1 occupancy on control (−251) and enhancer (−2000) regions of the Oct4 gene locus. Enrichment of DKC1 (black bars) compared to control IgGs (white bars) are analyzed by qPCR and expressed as percentage of input chromatin. Schematic diagrams of OCT4/SOX2 binding sites of each gene and the relative positions of the amplicons used to detect enriched ChIP fragments are shown at the bottom. Error bars represent standard deviation, n = 3.
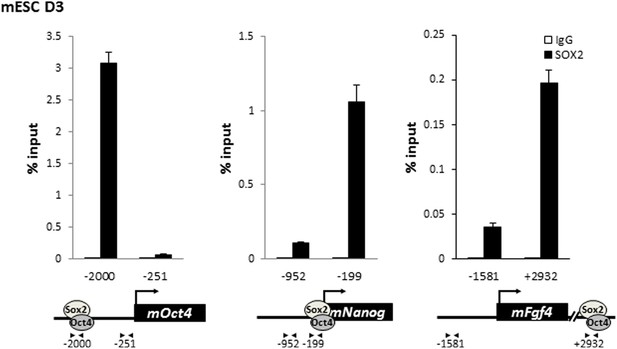
SOX2 is enriched on the regulatory regions of Oct4, Nanog, and Fgf4 in mouse ES cells.
Mouse ES cell line D3 is crosslinked with EGS and FA. Enrichment of SOX2 compared to control IgGs is analyzed as described in Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
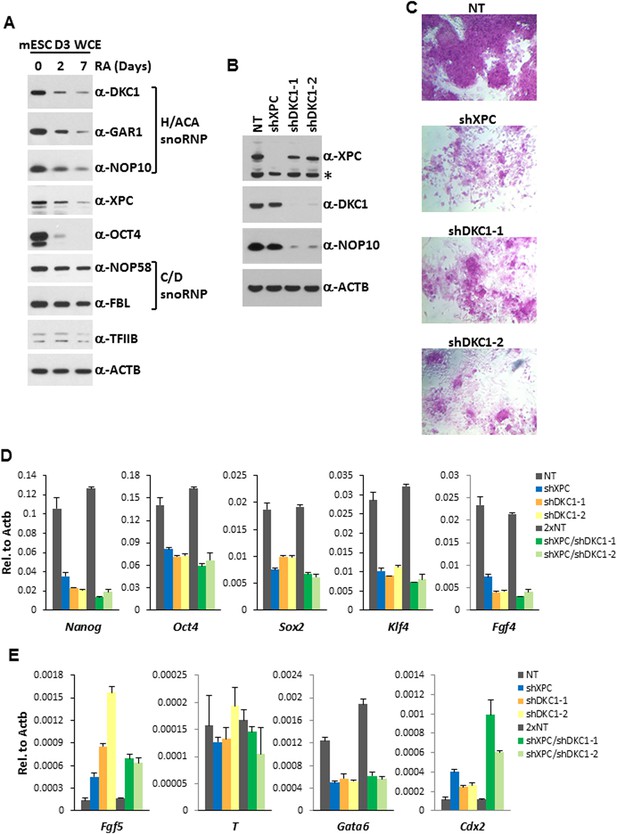
The DKC1 complex is required for stem cell maintenance.
(A) Downregulation of the DKC1 complex upon retinoic acid (RA)-induced differentiation of mouse ES cell line D3. Western blot analyses of whole cell extracts prepared from D3 cells (mESC D3 WCE) collected at indicated days post LIF withdrawal and RA treatment using antibodies against the DKC1 complex (DKC1, GAR1, and NOP10), XPC, OCT4, the NOP58/fibrillarin (FBL) complex, TFIIB, and β-actin as loading control. (B) shRNA-mediated knockdown of the DKC1 complex in mouse ES cells. Whole cell extracts of mouse D3 cells infected with control non-target (NT) lentiviruses or with lentiviruses targeting XPC (shXPC) or DKC1 (shDKC1-1 and shDKC1-2) are analyzed by western blotting. MOI = 25. Asterisk denotes non-specific signals. (C) ES cell colony morphology and alkaline phosphatase (AP) activity are maintained in control non-target shRNA infected D3 cells (NT), but are compromised in XPC (shXPC) and DKC1 depleted cells using two independent shRNAs (shDKC1-1 and shDKC1-2). (D) DKC1 and/or XPC depletion in ES cells compromised pluripotency gene expression. Quantification of Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and Fgf4 mRNA levels in single and double knockdown of XPC and DKC1 in D3 cells are analyzed by qPCR and normalized to β-actin (Actb). For double knockdown experiments, a cumulative MOI = 50 is used. Data from representative experiments are shown. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3). (E) DKC1 and/or XPC depletion in ES cells induces spontaneous differentiation towards primitive ectoderm and trophectoderm. Quantification of mRNA levels of primitive ectoderm marker Fgf5, mesoderm marker T, primitive endoderm marker Gata6, and extraembryonic trophectoderm marker Cdx2 in single and double knockdown of XPC and DKC1 in D3 cells are analyzed as in (D). Primer sequences can be found in Supplementary file 1.
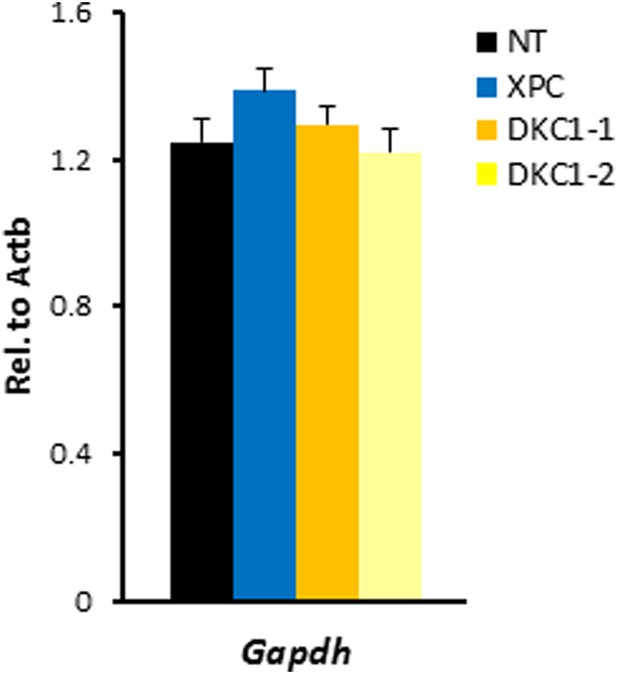
shRNA-mediated knockdown of DKC1 in mouse ES cells does not compromise housekeeping gene expression.
Quantification of housekeeping gene Gapdh mRNA levels in control (NT), XPC, and DKC1 knockdown D3 cells are analyzed as in (D). Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3).
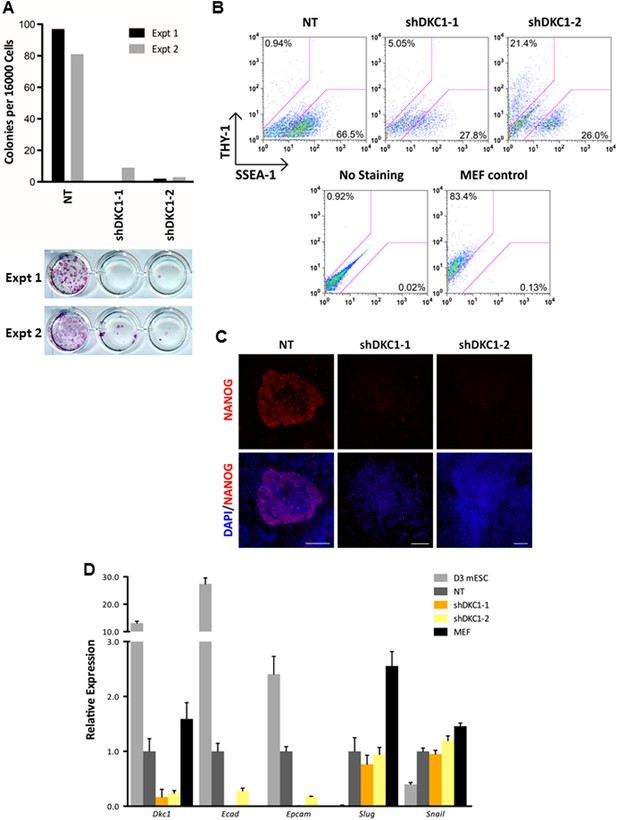
The DKC1 complex is required for mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) during somatic cell reprogramming.
(A) Depletion of DKC1 blocks somatic cell reprogramming. CF-1 mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) are infected with lentiviruses expressing OCT4, KLF4, SOX2, and c-MYC (STEMCCA) and reverse tetracycline-controlled transactivator (rtTA) together with control non-target shRNA (NT) or two independent shRNAs targeting DKC1 (shDKC1-1 and shDKC1-2). Infected MEFs are plated onto gelatin coated 24-well plates (Experiment 1) or 24-well plates containing mitomycin-treated feeder MEFs (Experiment 2); cellular reprogramming is initiated by the addition of doxycycline (dox). Cells are stained for AP activity and counted after 14 days (11 days with dox followed by 3 days without dox) post induction (dpi). (B) Single cell suspensions of 14 dpi CF-1 MEFs as described in (A) are stained with anti-mouse SSEA-1 and anti-THY-1 antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Representative confocal images of NANOG stained colonies 17 dpi (14 days with dox followed by 3 days without dox) as described in (A). The same acquisition settings—excitation laser intensity, gain, and exposure time—were used for all NANOG images. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) DKC1-depleted MEFs are arrested at the MET during iPS cell generation. Somatic cell reprogramming of CF-1 MEFs is performed as in (A). Cells were collected at 14 dpi (11 days with dox followed by 3 days without dox). mRNA levels of Dkc1, epithelial markers Ecad (also known as Cdh1) and Epcam, and mesenchymal markers Slug and Snail are compared with that of uninduced MEFs and mouse ES cell line D3 by qPCR. Values are normalized to expression levels in control non-target knockdown samples. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3). Primer sequences can be found in Supplementary file 1.
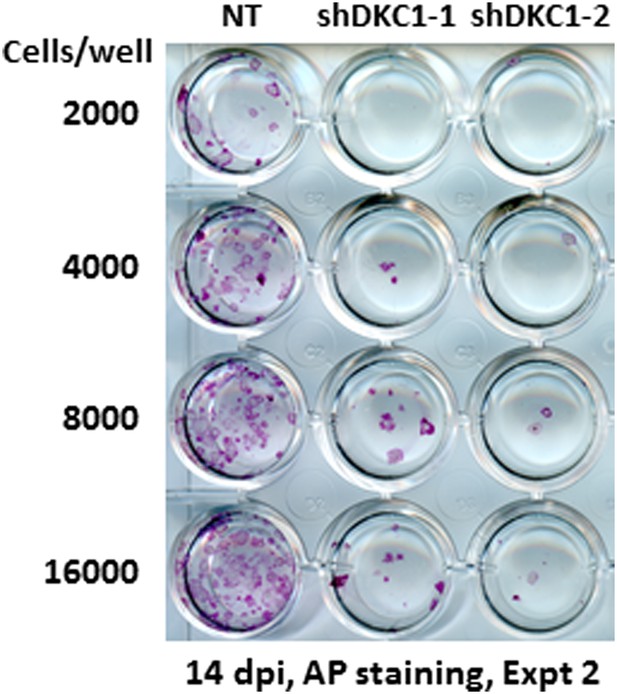
Somatic cell reprogramming is blocked by DKC1 depletion.
Induced MEFs depleted of DKC1 by two independent shRNAs (shDKC1-1 and shDKC1-2) as described in Figure 7A are plated along with MEFs infected with control non-target lentiviruses onto 24-well plates at indicated cell numbers on feeders. AP-positive colonies are stained 14 days post induction (dpi) (11 days with dox followed by 3 days without dox).
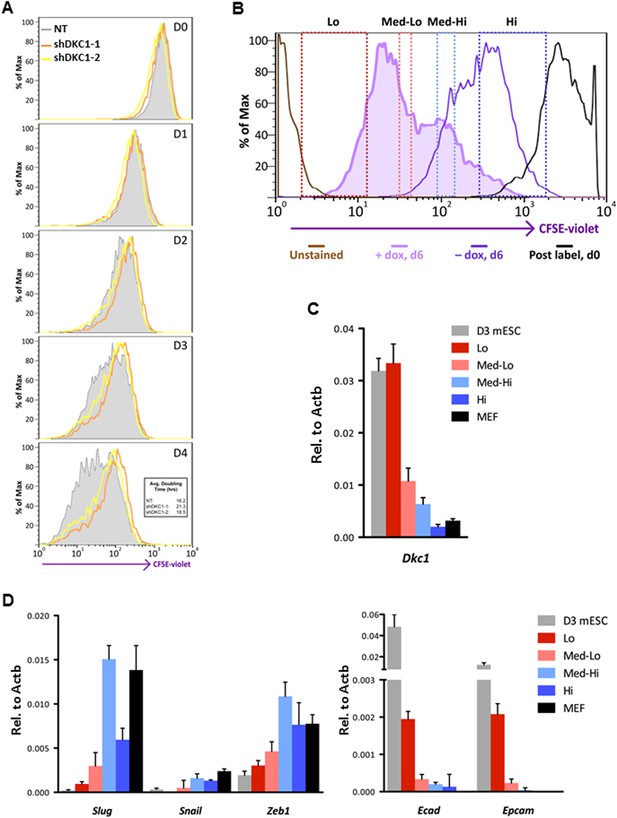
Fast cycling somatic cell state conducive to iPS cell generation requires DKC1.
(A) MEFs depleted of DKC1 by two independent shRNAs (shDKC1-1 and shDKC1-2), along with MEFs infected with control non-target lentiviruses, were analyzed using the CellTrace CFSE Proliferation Assay (Life Technologies). The doubling time for each population was calculated using the mean fluorescence intensity of each timepoint over 96 hr. (B) Induced MEFs (light purple) are treated with dox for 4 days, labeled with CFSE, and continuously cultured in the presence of dox for an additional 48 hr prior to FACS. Populations for ultrafast (Lo), fast (Med-Lo), medium slow (Med-Hi), and slow (Hi) cycling dox-induced MEFs are sorted based on CFSE intensity and denoted by dashed boxes. CFSE-intensity of MEFs immediately after labeling (black), unlabeled MEFs (brown), and uninduced MEFs 48 hr post-labeling (dark purple) are shown and used as controls. (C) mRNA levels of Dkc1 and Oct4 in sorted MEF populations (Lo-Hi) are compared to D3 ES cells and uninduced MEFs by qPCR. Results are normalized to Actb. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3). (D) Ultrafast (CFSE-Lo) cycling MEFs undergo early MET. mRNA levels of mesenchymal genes (Slug, Snail, and Zeb1; left), and epithelial genes (Ecad and Epcam; right) in sorted CFSE-labeled cell populations are compared to D3 ES cells and uninduced MEFs by qPCR. Data are analyzed as in (C). Primer sequences can be found in Supplementary file 1.
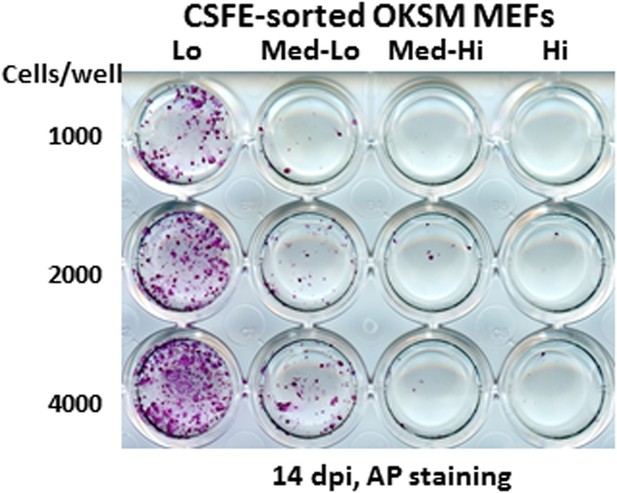
Ultrafast cycling MEF population contains the bulk of reprogramming activity.
Sorted MEF populations (CFSE-Lo, Med-Lo, Med-Hi, and Hi) in Figure 7B are plated on feeders in 24-well plates at indicated cell numbers. AP-positive colonies are stained as described in Figure 7A.
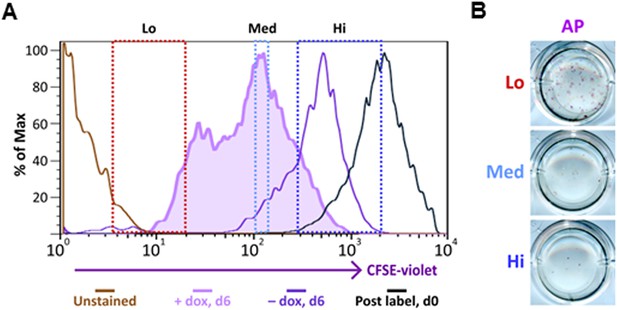
Ultrafast cycling somatic cell state can be induced in secondary OKSM MEFs.
(A) Labeling and sorting of CFSE-labeled MEFs carrying an integrated dox-inducible transgene expressing OCT4, KLF4, SOX2, and c-MYC (OKSM MEFs) are performed and analyzed as described in Figure 8B. (B) Sorted OKSM MEF popuations (CFSE-Lo, Med, and Hi) in (A) are plated onto 24-well plate. Cells are stained for AP activity after 14 days dpi (11 days with dox followed by 3 days without dox).
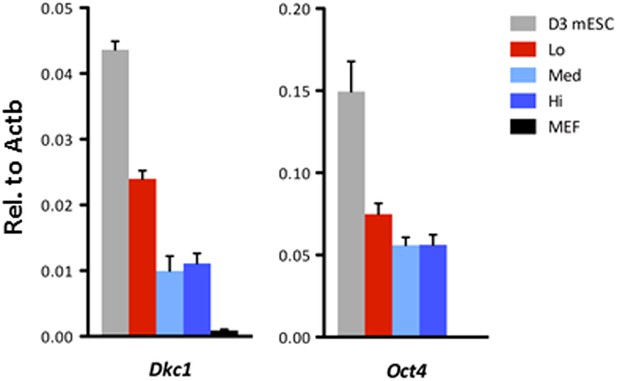
Ultrafast cycling OKSM MEFs have elevated Dkc1 levels.
Dkc1 expression is upregulated in the ultrafast cycling MEFs upon OKSM expression. mRNA levels of Dkc1 and Oct4 in sorted MEF populations described in (C) are compared to D3 ES cells and uninduced MEFs by qPCR. Results are normalized to Actb. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3). Primer sequences can be found in Supplementary file 1.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Primer sequences.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03573.023





