Connexin26 hemichannels with a mutation that causes KID syndrome in humans lack sensitivity to CO2
Figures
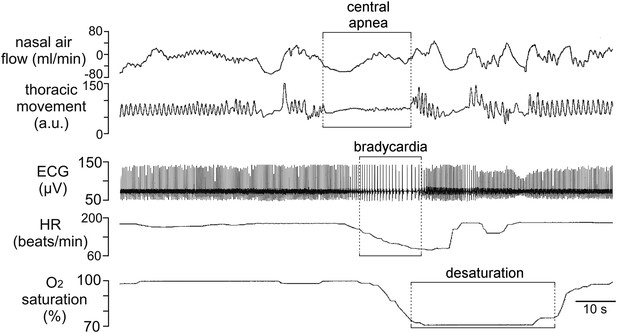
Incidence of central sleep apnea in a patient with Cx26A88V.
Recording of cardiorespiratory activity during sleep from an infant at a post-menstrual age of 40 weeks diagnosed with KID syndrome. Traces of nasal air flow, thoracic movement, electrocardiogram (ECG), heart rate (HR) and arterial O2 saturation show that this patient exhibited a prolonged period during which no effort was made to breathe and this was followed by pronounced bradycardia and arterial O2 desaturation, all of which are characteristic of central sleep apnea. Unfortunately, at 2 months of age this patient died from overwhelming sepsis.
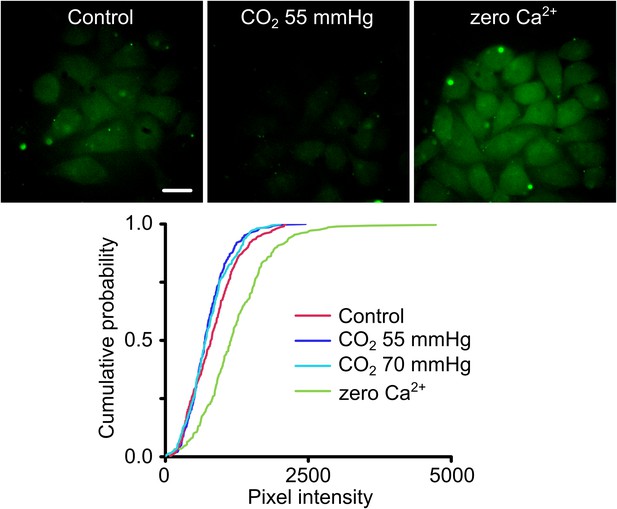
Cx26A88V hemichannels are no longer sensitive to CO2.
(Top) Images of HeLa cells expressing Cx26A88V under control, hypercapnic and zero Ca2+ conditions. The cells were exposed to 200 µM carboxyfluorescein (CBF) for 5 min under each condition before being washed. Some low background loading of CBF is seen under control conditions. In presence of CO2 no loading is seen. The positive control of removal of extracellular Ca2+ causes robust dye loading demonstrating the presence of functional hemichannels. (Bottom) Cumulative probability distributions of pixel intensity of HeLa cells expressing Cx26A88V under control, hypercapnia (two levels of PCO2) and zero Ca2+. Only the removal of extracellular Ca2+ causes dye loading as shown by the rightward shift of the curve to higher pixel intensities (p = 0.004, Mann Whitney U test compared to control). These distributions show all of the measurements made (minimum 40 cells each from five independent repetitions).
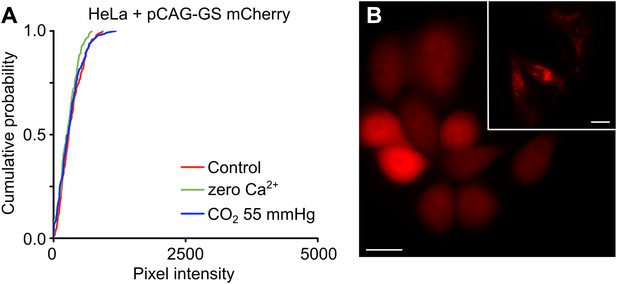
HeLa cells transfected with the empty pCAG-GS mCherry vector show no sensitivity to CO2 and do not dye load when exposed to zero Ca2+ aCSF.
(A) Cumulative probability distributions of pixel intensity for HeLa cells transfected with pCAG-GS mCherry under control, hypercapnia and zero Ca2+ conditions. The cells were exposed to 200 µM CBF for 5 min under each condition before being washed. The graphs show all of the measurements from 4 independent repetitions for each condition. (B) When transfected with pCAG-GS mCherry, the HeLa cells exhibit diffuse red fluorescence from expression of the mCherry. This contrasts with the punctate fluorescence seen flowing transfection with pCAG-GS Cx26-mCherry (inset). Scale bars 20 µm.
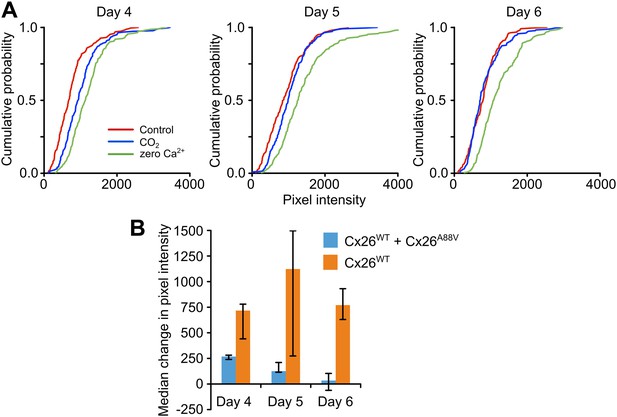
Cx26A88V hemichannels act in a dominant negative manner to remove CO2 sensitivity from Cx26WT.
(A) Cumulative probability distributions for CO2-dependent dye loading in HeLa cells that stably express Cx26WT, which have been transfected with Cx26A88V. 4 days after transfection with Cx26A88V the cells still exhibit significant sensitivity to 55 mmHg PCO2 stimulus (p = 0.048 CO2 compared to control, Mann Whitney U test). 5 and 6 days after transfection the CO2 sensitivity of the HeLa cells was abolished. On all 3 days, the positive control of zero Ca2+ caused dye loading, demonstrating the presence of functional hemichannels. The graphs show all of the measurements made from 5 independent repetitions of the experiment. (B) Comparison of the sensitivity to CO2 of HeLa cells stably expressing Cx26WT which have been transfected with Cx26A88V (Cx26WT + Cx26A88V, n = 5) with those that have not (Cx26WT, n = 7). In the absence of transfection, the Cx26WT-expresssing HeLa cells retain sensitivity to CO2 on all 3 days. By contrast Cx26A88V causes significantly depressed CO2 sensitivity 4 days after transfection (p = 0.001), and loss of sensitivity on days 5 (p = 0.024) and 6 (p = 0.001). Comparisons of Cx26WT with Cx26WT + Cx26A88V via Mann Whitney U test, and False Discovery Rate procedure for multiple comparisons (Curran-Everett, 2000). Error bars upper and lower quartiles.





