Childhood injury after a parental cancer diagnosis
Figures
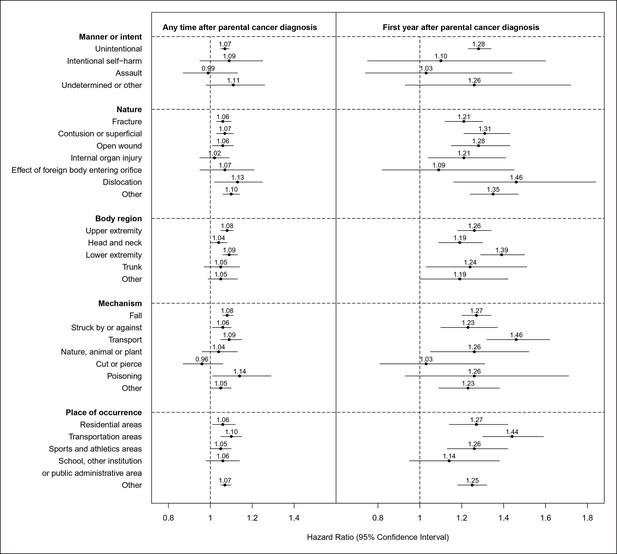
Hazard ratios for hospital contacts for injury among children with parental cancer compared to children without parental cancer, according to different characteristics of injury (Hazard ratios were adjusted for attained age, sex, number of siblings, gestational age, mode of delivery and birth weight of the child, paternal age at child's birth, maternal age at child's birth, maternal smoking during early pregnancy, and the highest educational level of the parents).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.08500.006Tables
Characteristics of the participating children and their parents.
| All children | Children with parental cancer | Children without parental cancer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | p |
| Characteristics of the children | ||||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 1,008,982 (51.4) | 40,527 (51.4) | 968,455 (51.4) | 0.72 |
| Female | 955,645 (48.6) | 38,288 (48.6) | 917,357 (48.6) | |
| No. of siblings and half siblings | ||||
| 0 | 189,556 (9.6) | 5,754 (7.3) | 183,802 (9.7) | |
| 1 | 784,911 (40.0) | 28,901 (36.7) | 756,010 (40.1) | <0.001 |
| 2 | 564,343 (28.7) | 23,291 (29.6) | 541,052 (28.7) | |
| ≥ 3 | 425,817 (21.7) | 20,869 (26.5) | 404,948 (21.5) | |
| Gestational age (weeks) | ||||
| < 35 | 42,376 (2.2) | 1,833 (2.3) | 40,543 (2.1) | |
| 35 - 36 | 70,999 (3.6) | 3,111 (3.9) | 67,888 (3.6) | |
| 37 - 38 | 363,508 (18.5) | 15,192 (19.3) | 348,316 (18.5) | |
| 39 - 40 | 973,949 (49.6) | 38,169 (48.4) | 935,780 (49.6) | <0.001 |
| 41 - 42 | 456,222 (23.2) | 18,333 (23.3) | 437,889 (23.2) | |
| ≥ 43 | 12,898 (0.7) | 528 (0.7) | 12,370 (0.7) | |
| Missing | 44,675 (2.3) | 1,649 (2.1) | 43,026 (2.3) | |
| Mode of delivery | ||||
| Caesarean section | 237,822 (12.1) | 10,300 (13.1) | 227,522 (12.1) | |
| Vaginal delivery | 1,684,729 (85.8) | 66,971 (85.0) | 1,617,758 (85.8) | <0.001 |
| Missing | 42,076 (2.1) | 1,544 (2.0) | 40,532 (2.1) | |
| Birth weight (g) | ||||
| < 2500 | 78,412 (4.0) | 3,455 (4.4) | 74,957 (4.0) | |
| 2500-2999 | 207,951 (10.6) | 8,361 (10.6) | 199,590 (10.6) | |
| 3000-3499 | 604,528 (30.8) | 23,466 (29.8) | 581,062 (30.8) | |
| 3500-3999 | 665,343 (33.9) | 26,714 (33.9) | 638,629 (33.9) | <0.001 |
| 4000-4499 | 290,798 (14.8) | 12,039 (15.3) | 278,759 (14.8) | |
| ≥ 4500 | 68,620 (3.5) | 2,980 (3.8) | 65,640 (3.5) | |
| Missing | 48,975 (2.5) | 1,800 (2.3) | 47,175 (2.5) | |
| Maternal smoking in early pregnancy | ||||
| No | 1,421,392 (72.4) | 55,388 (70.3) | 1,366,004 (72.4) | |
| Yes | 383,760 (19.5) | 17,036 (21.6) | 366,724 (19.5) | <0.001 |
| Missing | 159,475 (8.1) | 6,391 (8.1) | 153,084 (8.1) | |
| Characteristics of the parents | ||||
| Paternal age at child's birth (years) | ||||
| < 20 | 11,942 (0.6) | 166 (0.2) | 11,776 (0.6) | |
| 20-24 | 199,251 (10.1) | 4,232 (5.4) | 195,019 (10.3) | |
| 25-29 | 584,302 (29.7) | 16,318 (20.7) | 567,984 (30.1) | <0.001 |
| 30-34 | 628,352 (32.0) | 23,309 (29.6) | 605,043 (32.1) | |
| ≥ 35 | 540,780 (27.5) | 34,790 (44.1) | 505,990 (26.8) | |
| Maternal age at child's birth (years) | ||||
| < 20 | 47,255 (2.4) | 840 (1.1) | 46,415 (2.5) | |
| 20-24 | 395,011 (20.1) | 9,283 (11.8) | 385,728 (20.5) | |
| 25-29 | 713,827 (36.3) | 23,318 (29.6) | 690,509 (36.6) | <0.001 |
| 30-34 | 547,990 (27.9) | 25,787 (32.7) | 522,203 (27.7) | |
| ≥ 35 | 260,544 (13.3) | 19,587 (24.9) | 240,957 (12.8) | |
| Highest educational level | ||||
| Primary school or lower | 98,230 (5.0) | 4,144 (5.3) | 94,086 (5.0) | |
| Secondary education | 987,431 (50.3) | 36,105 (45.8) | 951,326 (50.5) | |
| Tertiary education | 844,523 (43.0) | 36,812 (46.7) | 807,711 (42.8) | <0.001 |
| Postgraduate education | 34,063 (1.7) | 1,748 (2.2) | 32,315 (1.7) | |
| Missing | 380 (0.0) | 6 (0.0) | 374 (0.0) |
Hazard ratios for hospital contact for injury among children with parental cancer compared to children without parental cancer.
| Any Time After Parental Cancer Diagnosis | First Year After Parental Cancer Diagnosis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | No. of Children With a Hospital Contact for Injury | Person-years | HR (95%CI) * | p (Wald Test) | No. of Children With a Hospital Contact for Injury | Person-years | HR (95%CI) * | p (Wald Test) |
| No parental cancer | 548,488 | 11,879,075 | 1 | 548,488 | 11,879,075 | 1 | ||
| Parental cancer | 15,377 | 298,302 | 1.07 (1.05-1.09) | 2,674 | 44,600 | 1.27 (1.22-1.33) | ||
| Time since cancer diagnosis | ||||||||
| ≤ 1 year | 2,674 | 44,600 | 1.27 (1.22-1.33) | — | — | — | ||
| >1 and ≤3 years | 3,850 | 74,087 | 1.10 (1.07-1.14) | <0.001 | — | — | — | |
| > 3 years | 8,853 | 179,615 | 1.01 (0.99-1.03) | — | — | — | ||
| Sex of the cancer parent | ||||||||
| Male | 6,554 | 126,277 | 1.08 (1.05-1.11) | 0.48 | 1,166 | 18,917 | 1.32 (1.24-1.40) | 0.13 |
| Female | 8,823 | 172,026 | 1.06 (1.04-1.09) | 1,508 | 25,683 | 1.24 (1.18-1.31) | ||
| Tobacco-related cancer † | ||||||||
| No | 12,008 | 233,848 | 1.07 (1.05-1.09) | 0.72 | 2,142 | 35,080 | 1.29 (1.24-1.35) | 0.13 |
| Yes | 3,369 | 64,454 | 1.08 (1.04-1.12) | 532 | 9,520 | 1.20 (1.10-1.31) | ||
| Alcohol-related cancer ‡ | ||||||||
| No | 10,464 | 201,389 | 1.08 (1.05-1.10) | 0.30 | 1,745 | 28,525 | 1.30 (1.24-1.37) | 0.16 |
| Yes | 4,913 | 96,913 | 1.06 (1.02-1.09) | 929 | 16,076 | 1.23 (1.15-1.31) | ||
| Predicted 5-year relative survival rate | ||||||||
| < 20% § | 931 | 18,845 | 1.02 (0.95-1.10) | 160 | 3,041 | 1.15 (0.98-1.35) | ||
| 20-80% | 7,112 | 136,080 | 1.08 (1.06-1.11) | 0.21 | 1,243 | 20,736 | 1.27 (1.19-1.35) | 0.38 |
| ≥ 80% ¶ | 7,334 | 143,377 | 1.06 (1.04-1.09) | 1,271 | 20,824 | 1.30 (1.23-1.38) | ||
| Parental psychiatric comorbidity after cancer diagnosis ‖ | ||||||||
| No | 14,630 | 285,621 | 1.06 (1.05-1.08) | 0.001 | 2,611 | 43,663 | 1.27 (1.22-1.32) | 0.45 |
| Yes | 747 | 12,681 | 1.21 (1.12-1.31) | 63 | 938 | 1.41 (1.08-1.85) | ||
-
HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval
-
*Adjusted for attained age, sex, number of siblings, gestational age, mode of delivery and birth weight of the child, paternal age at child's birth, maternal age at child's birth, maternal smoking during early pregnancy, and the highest educational level of the parents.
-
†Tobacco-related cancers include cancers in lung, oesophagus, larynx, pharynx, mouth, lip, salivary glands, tongue, stomach, urinary bladder, kidney, uterine cervix, colon and pancreas.
-
‡Alcohol-related cancers include cancers in liver, oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, oesophagus, colorectum and breast.
-
§Including cancers in esophagus, liver, gall bladder, biliary tract, pancreas, lung and stomach.
-
¶Including cancers in lip, breast, corpus uteri, testis, skin, thyroid and other endocrine glands, and Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
-
‖Including depression, anxiety disorders, stress reaction and adjustment disorder.
Hazard ratios for hospital contact for injury among children with parental cancer compared to children without parental cancer, according to sex, age and number of full and half siblings of the child.
| No Parental Cancer | Any Time After Parental Cancer Diagnosis | First Year After Parental Cancer Diagnosis | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics of the Child | No. of Children With a Hospital Contact for Injury | Person-years | HR (95%CI) | No. of Children With a Hospital Contact for Injury | Person-years | HR(95%CI) | p for interaction | No. of Children With a Hospital Contact for Injury | Person-years | HR (95%CI) | p for interaction |
| Sex* | |||||||||||
| Male | 313,806 | 5,966,451 | 1 | 9,088 | 150,070 | 1.11 (1.08-1.13) | < 0.001 | 1,594 | 22,747 | 1.30 (1.24-1.37) | 0.17 |
| Female | 234,682 | 5,912,624 | 1 | 6,289 | 148,233 | 1.02 (0.99-1.05) | 1,080 | 21,854 | 1.23 (1.16-1.31) | ||
| Age (years)† | |||||||||||
| < 3 | 35,157 | 876,761 | 1 | 103 | 2,106 | 1.21 (0.99-1.47) | 57 | 1,155 | 1.25 (0.96-1.63) | ||
| 3-5 | 55,452 | 1,508,188 | 1 | 439 | 11,775 | 1.07 (0.97-1.18) | 131 | 3,181 | 1.19 (1.00-1.42)§ | ||
| 6-11 | 197,984 | 4,625,786 | 1 | 4,085 | 88,106 | 1.08 (1.05-1.12) | 0.60 | 756 | 14,435 | 1.24 (1.15-1.34) | 0.72 |
| 12-15 | 134,995 | 2,500,216 | 1 | 4,698 | 83,199 | 1.08 (1.04-1.11) | 777 | 11,429 | 1.27 (1.18-1.37) | ||
| ≥ 15 | 124,900 | 2,368,124 | 1 | 6,052 | 113,116 | 1.06 (1.03-1.09) | 953 | 14,400 | 1.32 (1.23-1.41) | ||
| No. of full and half siblings‡ | |||||||||||
| 0 | 56,174 | 1,346,435 | 1 | 1,143 | 24,301 | 1.05 (0.98-1.11) | 208 | 3,759 | 1.30 (1.13-1.50) | ||
| 1 | 229,145 | 4,982,310 | 1 | 5,806 | 113,772 | 1.06 (1.04-1.09) | 0.13 | 987 | 16,907 | 1.24 (1.16-1.32) | 0.74 |
| 2 | 151,985 | 3,242,395 | 1 | 4,356 | 85,386 | 1.05 (1.02-1.09) | 782 | 12,748 | 1.28 (1.19-1.38) | ||
| ≥ 3 | 111,184 | 2,307,935 | 1 | 4,072 | 74,843 | 1.11 (1.07-1.15) | 697 | 11,187 | 1.31 (1.21-1.41) | ||
-
HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval
-
*Adjusted for attained age and sex of the child, interaction between sex of the child and cancer of the parents, number of siblings, gestational age, mode of delivery and birth weight of the child, paternal age at child's birth, maternal age at child's birth, maternal smoking during early pregnancy, and the highest educational level of the parents.
-
†Adjusted for attained age of the child, interaction between attained age of the child and cancer of the parents, sex, number of siblings, gestational age, mode of delivery and birth weight of the child, paternal age at child's birth, maternal age at child's birth, maternal smoking during early pregnancy, and the highest educational level of the parents.
-
‡Adjusted for attained age, sex and number of siblings of the child, interaction between number of siblings of the child and cancer of the parents, gestational age, mode of delivery and birth weight of the child, paternal age at child's birth, maternal age at child's birth, maternal smoking during early pregnancy, and the highest educational level of the parents
-
§p = 0.054
Hazard ratios for hospital contact for injury among children with parental cancer compared to children without parental cancer, according to the number of previous hospital contact for injury of the child
| Characteristics | No. of Children With a Hospital Contact for Injury | Person-years | HR (95%CI) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| No contact | |||
| No parental cancer | 548,488 | 11,879,075 | 1 |
| Parental cancer | 15,377 | 298,302 | 1.07 (1.05-1.09) |
| One contact | |||
| No parental cancer | 228,560 | 1,542,926 | 1 |
| Parental cancer | 5,981 | 31,308 | 1.24 (1.20-1.28) |
| Two contacts | |||
| No parental cancer | 107,833 | 454,049 | 1 |
| Parental cancer | 2,796 | 9,130 | 1.26 (1.20-1.32) |
| Three contacts | |||
| No parental cancer | 53,784 | 176,237 | 1 |
| Parental cancer | 1,377 | 3,691 | 1.21 (1.13-1.31) |
| Four contacts | |||
| No parental cancer | 28,126 | 74,499 | 1 |
| Parental cancer | 722 | 1,600 | 1.19 (1.07-1.33) |
-
HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval
-
*Adjusted for attained age, sex, number of siblings, gestational age, mode of delivery and birth weight of the child, paternal age at child's birth, maternal age at child's birth, maternal smoking during early pregnancy, and the highest educational level of the parents
Swedish revisions of the international classification of diseases (ICD) for psychiatric comorbidity of the cancer parents.
| ICD 8 (1969-1986) | ICD 9 (1987-1996) | ICD-10 (1997-presesnt) | |
| Depression | 296.2, 298.0, 300.4 | 296B, 300E, 311 | F32-F39 |
| Anxiety disorders | 300 except 300.3, 300.4 | 300 except 300D, 300E | F40, F41, F44, F45, F48 |
| Stress reaction and adjustment disorder | 307 | 308, 309 | F43 |
Additional files
-
Reporting standards
Standard used to collect data: The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.08500.009





