Hippocampome.org: a knowledge base of neuron types in the rodent hippocampus
Figures
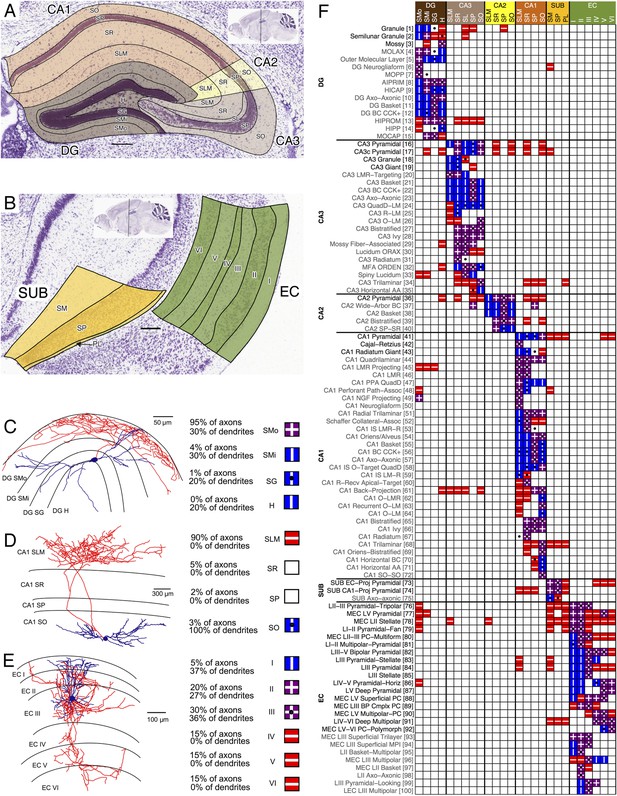
Defining neuron types with anatomical parcels and morphological patterns.
(A, B) Nissl staining of a P56 mouse (coronal sections 74 and 85 from the Allen Brain Atlas) overlaid by color-coded parcels (in accord with Temporal-Lobe.com) of (A) the hippocampus proper and (B) the rest of the hippocampal formation. See main text for abbreviations. (C–E) Example morphological reconstructions from NeuroMorpho.Org (left) with red axons and blue dendrites; their estimated axonal and dendritic breakdown by layers (middle); and Hippocampome.org representation (right) with blue square and vertical line (|) indicating dendritic presence, red square and horizontal line (−) indicating axonal presence, purple square and cross (+) indicating both axonal and dendritic presence, and a black dot (•) indicating soma location. (C) Dentate gyrus (DG) Outer Molecular Layer cell with axons in SMo and dendrites in all layers (NMO_00179; [Mott et al., 1997]). (D) CA1 O-LM cell with axons in SLM and dendrites in SO (NMO_02347; [Cossart et al., 2003]). (E) MEC LII Pyramidal-Multiform cell with axons in layers II–VI and dendrites in layers I-III (NMO_07252; (Quilichini et al., 2010]). (F) Axon and dendrite locations for 100 representative neuron types (glutamatergic: black; GABAergic: gray; full matrix: hippocampome.org/morphology or hippocampome.org/php/images/morphology/Morphology_Matrix.jpg).
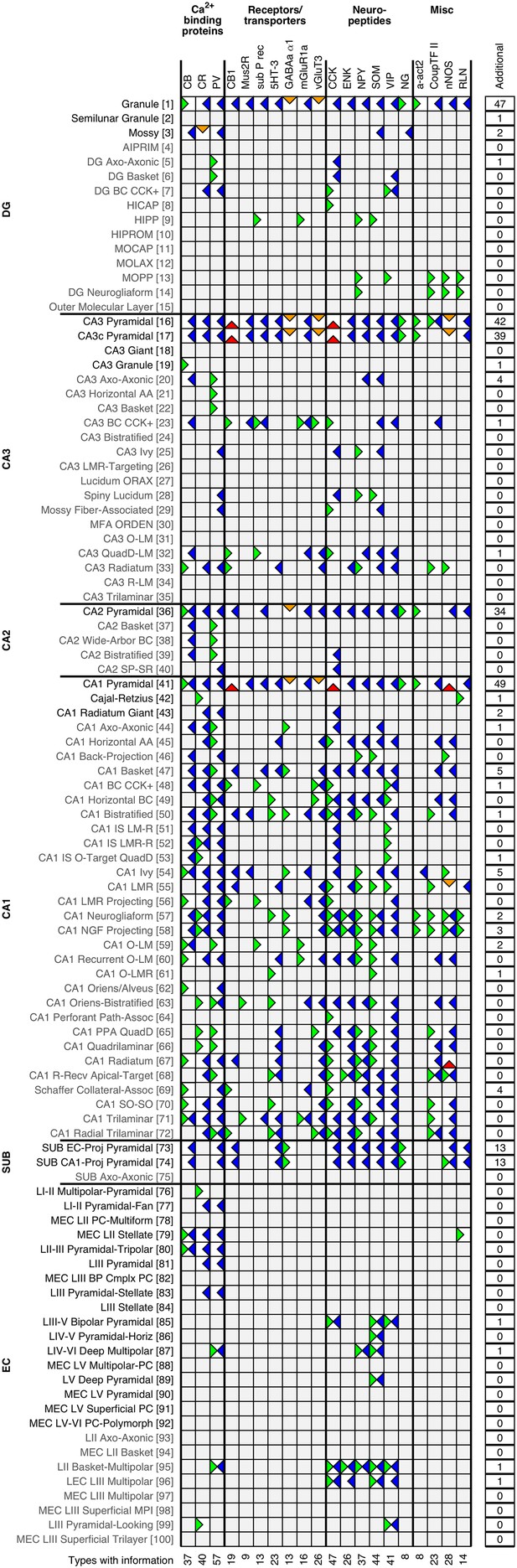
Expression of 20 common biomarkers for 100 representative neuron types (full matrix: hippocampome.org/markers or hippocampome.org/php/images/marker/Marker_Matrix.jpg; complete list of abbreviations: hippocampome.org/help).
Positive expression: left green flags; negative expression: right blue; mixed expression (possible subtypes): left/right green blue; mixed expression (different experimental protocols, species, or sub-cellular localization): top orange; unresolved mixed expression: bottom red; empty gray boxes indicate that morphologically linkable information was not found. The right summary column reports the number of additional biomarkers with known expression for each neuron type. Bottom values are counts of neuron types with available information for each biomarker.
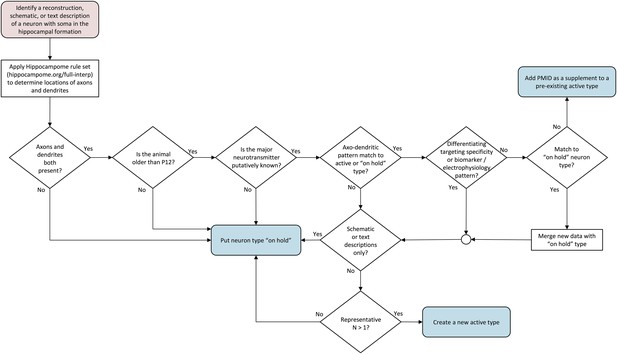
Flow chart of inclusion criteria for neuron types.
Beginning with a reconstruction, schematic, or text description of a neuron morphology, the flow chart ends with either a new ‘on hold’ neuron type, supplemental information for an existing active neuron type, or a new active neuron type. Intermediate decision points evaluate the presence of both axons and dendrites, the determination of the main neurotransmitter, the uniqueness of the new type, and whether information is sufficient to create a new active type.
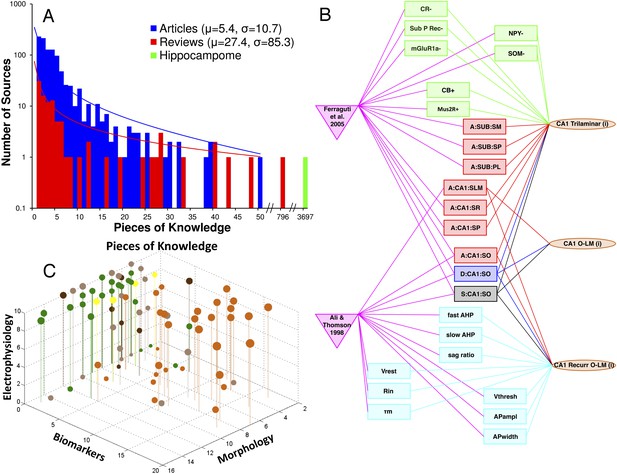
Quantifying knowledge in Hippocampome.org about morphology, biomarkers, and electrophysiology of hippocampal neuron types.
(A) Histograms comparing the sum of pieces of knowledge (PoK) in relevant journal articles or book chapters, in reviews, and in Hippocampome.org. (B) Interconnected knowledge graph of neuron type properties mined from two typical journal articles. (C) Balloon plot of collated knowledge for a majority of GABAergic neuron types. The balloon size indicates the sum of PoK for that type across all three dimensions; balloon color denotes the subregion (as in Figure 1). Note the dearth of biomarker information in entorhinal cortex (EC) and the uneven distribution of data between CA3 and CA1.
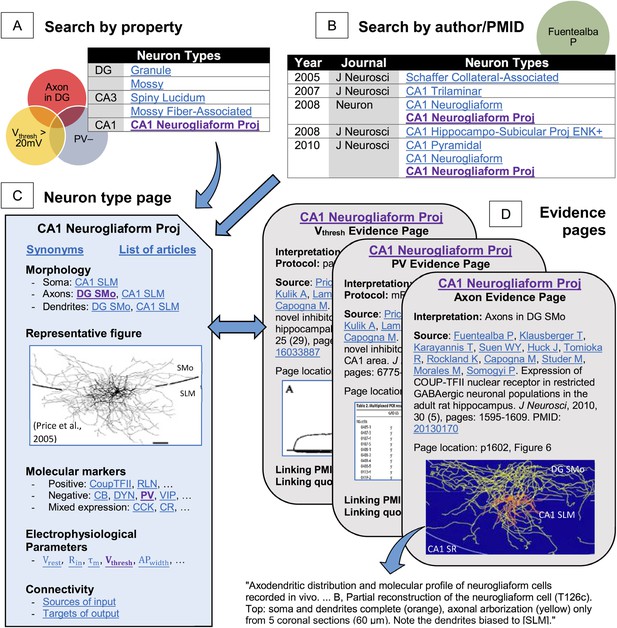
Hippocampome.org enables searching neuron types by neurotransmitter; axon, dendrite, and soma locations; molecular expression; electrophysiological parameters; and input/output connectivity.
(A) Sample query for parvalbumin-negative neuron types with axons in DG and firing threshold >20 mV. (B) The knowledge base may also be queried for a specific PubMed ID or author name (e.g., ‘Fuentealba P’). (C, D) Returned results link to (C) neuron type summary pages (Figure 1A from Price et al., 2005, J. Neurosci. 25:6775–6786 [permission to reuse granted by SfN]) and (D) evidence from published figures, tables, and text quotes supporting all reported properties (Figure 6B from Fuentealba et al., 2010, J. Neurosci. 30:1595–1609; Table 2 and Figure 3A from Price et al., 2005, J. Neurosci. 25:6775–6786 [permission to reuse granted by SfN]).
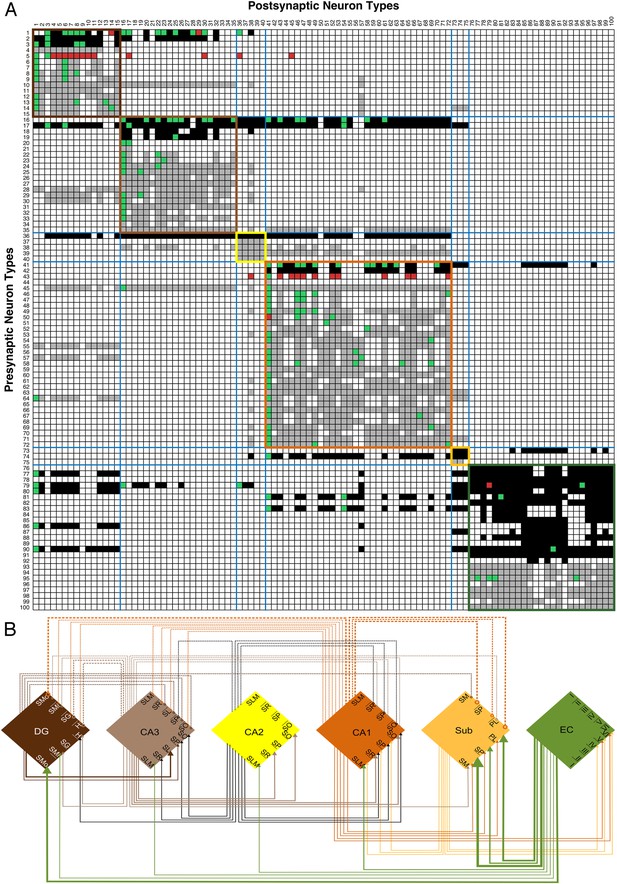
Neuron type connectivity (area color coding and numbering as in Figure 1).
(A) Known and potential connections for 100 neuron types (full matrix: hippocampome.org/connectivity or hippocampome.org/php/images/connectivity/Connectivity_Matrix.jpg), with pre-synaptic types in rows and post-synaptic types in columns. Black squares indicate potential glutamatergic connections and gray squares GABAergic. Pairs of neuron types with experimentally established and refuted synapses are shown using green and red squares, respectively. Colored boundaries demarcate intra-area connections. (B) Regional pathways with 33 glutamatergic connections (full lines ending in arrows) and 20 GABAergic connections (dashed lines ending in open circles); line thickness represents the numbers of connected neuron types between areas.
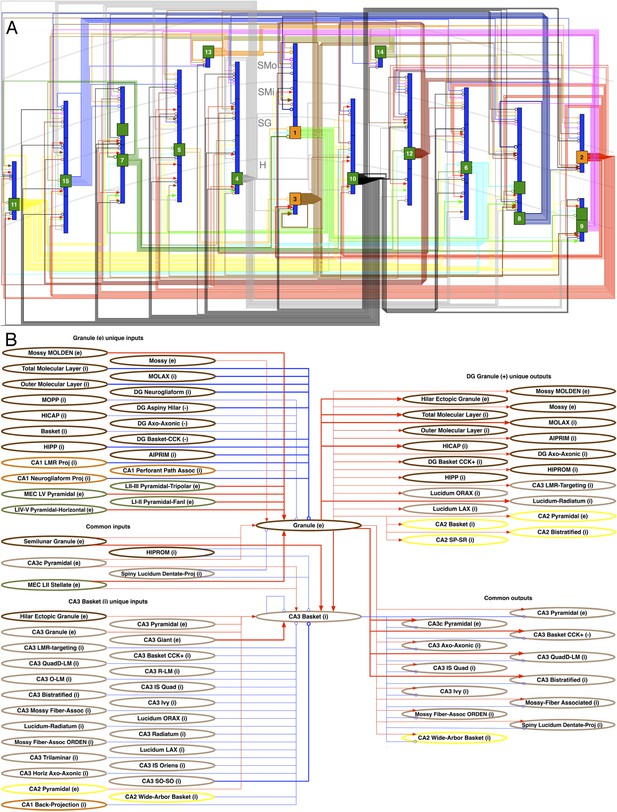
Neuron type circuitry.
(A) Circuit diagram of selected neuron types in DG (full diagram: hippocampome.org/php/images/connectivity/DG_Circuit_Diagram.jpg or hippocampome.org/php/images/connectivity/DG_Circuit_Diagram.graffle.zip). Axonal connections from pre-synaptic somata (orange glutamatergic, green GABAergic) to post-synaptic somata or dendrites (blue) have unique line colors for each pre-synaptic type for clarity. Lines ending in arrows and open circles indicate, respectively, glutamatergic and GABAergic connections; 22 known (thick lines) and 231 potential (thin) connections are depicted. 1: Granule. 2: Semilunar Granule. 3: Mossy. 4: AIPRIM. 5: Axo-axonic. 6: Basket. 7: Basket CCK+. 8: HICAP. 9: HIPP. 10: HIPROM. 11: MOCAP. 12: MOLAX. 13: MOPP. 14: Neurogliaform. 15: Outer Molecular Layer. (B) Pre- and post-synaptic connections for DG Granule and CA3 Basket cells. Red lines ending in arrows indicate glutamatergic connections, and blue lines ending in open circles indicate GABAergic connections. Thick and thin lines indicate, respectively, known and potential connections. Neuron types are color coded by area of origin (as in Figure 1).
Tables
Electrophysiological properties for 50 representative neuron types (full table: hippocampome.org/electrophysiology or hippocampome.org/php/images/electrophysiology/Electrophysiology_Table.jpg)
| Vrest (mV) | Rin (MΩ) | τm (ms) | Vthresh (mV) | fAHP (mV) | APampl (mV) | APwidth (ms) | maxFR (Hz) | sAHP (mV) | Sag ratio | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG (8) | Granule | −75 ± 2(16) ∈ 5 | 228 ± 79.1(31) ∈ 5 | 26.9 ± 6.7(31) ∈ 5 | 35 ∈ 5 | 11.7 ± 1.1(16) ∈ 3 | 91 ∈ 5 | 0.87 ± 0.06(16) ∈ 2 | 72 ± 8(16) | 0.6 ± 0.4(16) ∈ 3 | 0.97 ± 0.01(16) ∈ 3 |
| Mossy | −62 ± 1(9) | 199 ± 19(9) | 41 ± 3(8) | 23.7 | 6.2 ± 0.9(9) | 62.5 | 0.78 ± 0.04(9) | 50 ± 6(9) | 2.8 ± 0.7(9) | 0.81 ± 0.03(9) | |
| AIPRIM | −64 ± 2(4) | 363 ± 62(4) | 30 ± 6(4) | 16 | 12.3 ± 2.3(4) | [76, 77.9] | 0.5 ± 0.02(4) | 81 ± 9(4) | 9 ± 2.7(4) | 0.8 ± 0.04(4) | |
| DG Axo-axonic | −65.1 ± 3.9(14)e | 73.9 ± 23.8(14)e | 7.7 ± 3.8(14)e | 13r ∈ 2 | 7r ∈ 2 | 78r ∈ 2 | 0.42r ∈ 2 | 85r | 4.5r ∈ 2 | – | |
| DG Basket | −62 ± 3(3) | 43 ± 5(3) ∈ 3 | 10 ± 1(3) ∈ 2 | [17.6, 19.0] ∈ 3 | 20 ± 2.3(3) ∈ 2 | [71.6, 73.6] ∈ 2 | 0.25 ± 0.04(3) ∈ 2 | 230 ± 15(3) ∈ 2 | 2.3 ± 0.2(3) | 0.97 ± 0.02(3) ∈ 2 | |
| HIPROM | −65 ± 6(3) | 371 ± 47(3) | 35 | [25.1, 27.3] | 13.1 ± 3.0(3) | 80.8 | 0.72 ± 0.08(3) | 69 ± 4(3) | 3.1 ± 1.0(3) | 0.82 ± 0.02(3) | |
| MOLAX | −54.5 ± 1.9(13) ∈ 2 | 198.2 ± 23.8(13) ∈ 2 | 18.4 ± 1.1(13) | 15.2 ∈ 2 | 11 ∈ 2 | [43.2, 44.4] ∈ 2 | [1.26, 1.64] | 50 | 3.5mr ∈ 2 | – | |
| Total Molecular Layer | −54.5 ± 1.9(13) | 198.2 ± 23.8(13) | 18.4 ± 1.1(13) | 15.2 | 11 | [43.2, 44.4] | [1.26, 1.64] | 50 | 4.5 | – | |
| CA3 (8) | CA3 Pyramidal | −60.5 ± 5.4(43) ∈ 8 | 126 ± 8(35) ∈ 8 | 61 ± 24(36) ∈ 7 | 13 ∈ 5 | 10.2 ± 0.5(43) ∈ 3 | 97.6 ± 1.9(43) ∈ 4 | 1 ± 0.1(43) ∈ 4 | 40 ± 20.8(3) | 7.5m ∈ 3 | 1.01 ± 0.01(7) ∈ 4 |
| CA3 Giant | −57 ± 1.2(28)r | 595 ± 224(28)r | 67 ± 23(28)r | 22r | 14r | 76 ± 7.5(28)r | 1.1 ± 0.1(28)r | >50 ± 3(13) | 7.1r | 0.68r | |
| CA3 Granule | −78 ± 0.5(15) | 139 ± 11(15) | 17.1 ± 1.8(15) | 27.4 | 7.95 | 104.3 | [0.821, 1.072] | >100 | 1.75 | 0.99 | |
| CA3 Basket | −58.5 ± 2.8(6)mr | 122.9 ± 26.7(6)mr | 11.2 ± 2.9(6)mr | 25.6mr | 35mr | 77.1mr | 0.54 ± 0.1(8)mr | 33.6 ± 6.4(6)mr | 3mr | 0.93mr | |
| Lucidum ORAX | −61 ± 6(9) ∈ 2 | 284 ± 180(9) ∈ 2 | 42 ± 17(8) ∈ 2 | 16.3 ∈ 2 | 15 ± 6.6(9) ∈ 2 | 77.7 ∈ 2 | 0.53 ± 0.2(9) ∈ 2 | 75 ± 28.3(8) ∈ 2 | 6.6 ± 3.9(9) ∈ 2 | 0.9 ± 0.1(8) ∈ 2 | |
| MFA ORDEN | −57 ± 5(13) | 225 ± 93(13) | 29.1 ± 14.6(13) | 20 | 13.1 ± 1.9(13) | 74 | 0.72 ± 0.15(13) | 73 ± 16(13) | 6.5 | – | |
| CA3 O-LM | −60 ± 12(15)mr | 315.1 ± 161.1(15)mr | 33.3 ± 5.4(15)mr | [16, 37]mr | 34.8mr | 109mr | 0.84 ± 0.2(15)mr | 182 ± 161.1(15)mr | 1.3mr | 0.79 ± 0.1(10)mr | |
| CA3 Trilaminar | −61.2 ± 13(8)mr | 167.3 ± 59.1(8)mr | 16.9 ± 8.8(8)mr | 12mr | 30mr | [69, 99]mr | 0.57 ± 0(8)mr | 101.5 ± 62.2(8)mr | 0.1mr | 0.88mr | |
| CA2 (4) | CA2 Basket | −71.2 ± 4(6)e | 77 ± 19.3(6)e | 8.2 ± 3.2(6)e | [17, 27]e | 22 ± 5.1(6)e | 62.7 ± 9(6)e | 0.5 ± 0.1(6)e | >180e | 3e | 0.99e |
| CA2 Wide-arbor BC | −74.9 ± 5.6(10)e | 111.8 ± 36.7(10)e | 12.6 ± 4.2(10)e | [26, 34]e | 19.5 ± 9(10)e | 65.5 ± 7.1(10)e | 0.6 ± 0.1(10)e | >125e | 7e | 0.55e | |
| CA2 Bistratified | −72.7 ± 1.1(3)e | 83.3 ± 16.7(3)e | 13.7 ± 10(3)e | [42, 56]e | 14.4 ± 11.8(3)e | 65.2 ± 7.8(3)e | 0.4 ± 0.1(3)e | – | 3.2e | 0.99e | |
| CA2 SP-SR | −71 ± 4.5(8)e | 82.6 ± 24.4(8)e | 12.7 ± 3.8(8)e | 19e | 11.5e | 67e | 0.5 ± 0.1(8)e | >160e | 3.3e | 0.86e | |
| CA1 (16) | CA1 Pyramidal | −62.4 ± 2.4(21) ∈ 7 | 65.6 ± 4.4(20) ∈ 7 | 22.4 ± 1.5(20) ∈ 6 | 16.6 ∈ 7 | 6.8 ∈ 2 | 90 ∈ 4 | 1 ∈ 3 | >32 | 1.7 ∈ 3 | 0.74 ∈ 3 |
| CA1 Radiatum Giant | −66 ± 3.6(16) ∈ 2 | 56 ± 14(25) ∈ 2 | 50 ± 7.9(7)r ∈ 2 | 31 ∈ 2 | 8 ∈ 2 | 70 ∈ 2 | 1.9 ± 0.2(7)r | >26 | 8.3r ∈ 2 | 0.86 ∈ 2 | |
| CA1 Horizontal AA | −57 ± 5(15)m | [186, 252]r | [16, 32]r | 25m | [6.0, 13.7]r | [71.4, 90.2]r | [0.7, 1.1]r | 87r ∈ 2 | 6.1m | 0.74m | |
| CA1 Basket | −57 ± 5(15)m ∈ 2 | 116 ± 63(15)m ∈ 2 | 13 ± 8(15)m ∈ 2 | 19 ∈ 3 | 10 ∈ 3 | 62 ∈ 3 | 0.54 ± 0.11(15)m ∈ 2 | >60 | 2e ∈ 3 | 0.84 ± 0.06(15)m | |
| CA1 BC CCK+ | −61.4 ± 3.2(5) | 281.68 ± 79.7(5) | 25.07 ± 5.6(5) | 21.5 ∈ 3 | 15.17 ± 3.4(5) ∈ 3 | 76.92 ± 11.7(5) ∈ 3 | 0.84 ± 0.1(5) | >30 | 7 ∈ 2 | 0.825 | |
| CA1 Horizontal BC | −55.4 ± 9.5(17) ∈ 2 | [116, 199] ∈ 2 | [15.4, 25.5] ∈ 2 | 24 ∈ 2 | 11 ∈ 2 | 130 ∈ 2 | 0.77 ± 0.10(18)m ∈ 2 | >50m | 4.8m ∈ 2 | 0.6 ∈ 2 | |
| CA1 Ivy | −71 | 72.8 ± 53.6(5) | 7.6 ± 4.1(5) | 30.1 | 13.6 ± 3.8(5) | 44 | 0.8 ± 0.2(5) | – | 3 | 0.98 | |
| CA1 LMR | −53.1 ± 4.0(48)r ∈ 3 | 352 ± 107(49)r ∈ 3 | 32.9 ± 12.7(11)r ∈ 3 | 13.2r ∈ 3 | 21.5r ∈ 3 | 86.9 ± 11.0(49)r ∈ 3 | 1.3r ∈ 3 | – | 0.2r ∈ 4 | 0.92 ± 0.11(15)r ∈ 3 | |
| CA1 Neurogliaform | −63.1 ± 5.6(33) ∈ 2 | 215.3 ± 92.8(32) ∈ 2 | 12.43 ± 4.59(32) ∈ 2 | 32.4 ∈ 2 | 20.4 ± 4.1(34) ∈ 2 | 73 ∈ 2 | 0.9 ± 0.18(26) ∈ 2 | 52.8 ± 31.0(26) | 9 ∈ 2 | 0.99 ∈ 2 | |
| CA1 NGF Projecting | −63.1 ± 5.6(33) | 215.3 ± 92.8(32) | 12.43 ± 4.59(32) | 32.4 | 20.4 ± 4.1(34) | 73 | 0.9 ± 0.18(26) | 52.8 ± 31.0(26) | 9 | 0.99 | |
| CA1 Recurrent O-LM | [−85, −65]e | 70 ± 13.72(8)e | 12.8 ± 1.5(8)e | 25e | 16.1 ± 10.7(8)e | 58.75 ± 7.2(8)e | 0.6 ± 0.3(8)e | >150e | 5e | 0.71e | |
| CA1 PPA QuadD | −64 ± 7(23)m | 216 ± 124(23)m | 46 ± 18(23)m | 27m | 22 ± 3(23)m | 61 ± 7(23)m | 0.77 ± 0.12(23)m | >40m | 1.3m | 0.79 ± 0.09(23)m | |
| Schaffer Collateral-Assoc | −55.8 ± 2.8(10)e ∈ 2 | 96.3 ± 36.0(10)e ∈ 2 | 16.2 ± 8.9(10)e ∈ 2 | 11e ∈ 2 | 11.4 ± 2.8(10)e ∈ 2 | 70.8 ± 8.0(10)e ∈ 2 | 0.74 ± 0.1(10)e ∈ 2 | >100 | 5.5e ∈ 2 | 0.86e | |
| CA1 SO–SO | −59 ± 10(19)m ∈ 2 | 401 ± 212(19)m | 38 ± 13(19)m | 24m ∈ 2 | 15 ± 4(19)m ∈ 2 | 48 ± 10(19)m ∈ 2 | 1.12 ± 0.14(19)m | >160m | 4.8m ∈ 2 | 0.69m ∈ 2 | |
| CA1 Trilaminar | −64 ± 7(23)m | 216 ± 124(23)m | 46 ± 18(23)m | 27m | 22 ± 3(23)m | 61 ± 7(23)m | 0.77 ± 0.12(23)m | >130m | 4.7m | 0.79m | |
| CA1 Radial Trilaminar | −57 ± 5(15)m | 116 ± 63(15)m | 13 ± 8(15)m | 29m ∈ 3 | 25 ± 4(15)m ∈ 3 | 48 ± 8(15)m ∈ 3 | 0.54 ± 0.11(15)m | >120m | 0.82m ∈ 3 | 0.89m | |
| EC (14) | LI-II Multipolar-Pyramidal | [−70, −56] | 430 ± 121.7(37) | 25 ± 15.2(37) | [8.1, 23.1] | [3.7, 7.3] | 77.5 ± 15.2(37) | 1.22 ± 0.4(37) | >50 | 4.7 | 0.78 ± 0.06(37) |
| LI-II Pyramidal-Fan | [−62, −59] ∈ 2 | 400 ± 98(96) ∈ 2 | 15.8 ± 14.2(96) ∈ 2 | [7.5, 8.4] ∈ 2 | [7.1, 7.3] ∈ 2 | 69 ± 19.6(96) ∈ 2 | 1.25 ± 0.49(96) ∈ 2 | >40 | [0, 6] ∈ 2 | 0.66 ± 0.05(96) ∈ 2 | |
| MEC LII PC-Multiform | [−70, −56] | 430 ± 121.7(37) | 25 ± 15.2(37) | [8.1, 23.1] | [3.7, 7.3] | 77.5 ± 15.2(37) | 1.22 ± 0.4(37) | >25 | 4.7 | 0.78 ± 0.06(37) | |
| MEC LII Oblique Pyramidal | [−62, −59] | 400 ± 98(96) | 15.8 ± 14.2(96) | [7.5, 8.4] | [7.1, 7.3] | 69 ± 19.6(96) | 1.25 ± 0.49(96) | >40 | [0, 6] | 0.66 ± 0.05(96) | |
| MEC LII Stellate | [−62, −59] ∈ 2 | 30.2 ± 12.5(112)e ∈ 2 | 8.9 ± 1.9(112)e ∈ 2 | [7.5, 8.4] ∈ 2 | [7.1, 7.3] ∈ 2 | 69 ± 19.6(96) ∈ 2 | 1.25 ± 0.49(96) ∈ 2 | >40 | [0, 6] | 0.66 ± 0.05(96) ∈ 2 | |
| LII-III Pyramidal-Tripolar | [−70, −56] ∈ 2 | 400 ± 98(96) ∈ 2 | 15.8 ± 14.2(96) ∈ 2 | [8.1, 23.1] ∈ 2 | [3.7, 7.3] ∈ 2 | 69 ± 19.6(96) ∈ 2 | 1.25 ± 0.49(96) ∈ 2 | >40 | 4.7 ∈ 2 | 0.66 ± 0.05(96) ∈ 2 | |
| LEC LIII Multipolar Principal | [−68, −65] | 450 ± 78(27) | 29 ± 12.5(27) | [21.17, 26.03] | [10.23, 11.04] | 70 ± 15.6(27) | 1.38 ± 0.26(27) | >25 | 4.06 | 0.9 ± 0.1(27) | |
| LEC LIII Complex Pyramidal | [−68, −65] | 450 ± 78(27) | 29 ± 12.5(27) | [21.17,26.03] | [10.23,11.04] | 70 ± 15.6(27) | 1.38 ± 0.26(27) | >25 | 4.06 | 0.9 ± 0.1(27) | |
| LIII Pyramidal-Stellate | [−68, −65] ∈ 2 | 450 ± 78(27) ∈ 2 | 29 ± 12.5(27) ∈ 2 | [21.17, 26.03] ∈ 2 | [10.23, 11.04] ∈ 2 | 70 ± 15.6(27) ∈ 2 | 1.38 ± 0.26(27) ∈ 2 | [85, 105]e ∈ 2 | 4.06 ∈ 2 | 0.9 ± 0.1(27) | |
| LIII-V Bipolar Pyramidal | [−69, −67] | 490 ± 79(28) | 36 ± 16(28) | [18.2, 21.8] | [5.6, 8.7] | 70 ± 15.9(28) | 1.48 ± 0.2(28) | >29 | [2, 7] | 0.86 ± 0.11(28) | |
| LIV-VI Deep Multipolar | −59.8 ± 6.8(8) ∈ 4 | 272.3 ± 105.8(8) ∈ 4 | 26.6 ± 6.5(8) ∈ 4 | 36 ∈ 4 | 15 ∈ 4 | 75 ∈ 4 | 1.39 ± 0.6(8) ∈ 4 | >70 | 4.4 ∈ 4 | 0.9 ∈ 3 | |
| LV Deep Pyramidal | −65.02 ± 3.8(38)e ∈ 2 | 75.67 ± 28.72(38)e ∈ 2 | 12.83 ± 3.65(38)e ∈ 2 | 22.14e ∈ 2 | 17.44 ± 2.64(38)e ∈ 2 | 64.96 ± 6.53(38)e ∈ 2 | 1.53 ± 0.28(38)e ∈ 2 | >70 | 0.1e ∈ 2 | 0.88e ∈ 2 | |
| MEC LV-VI PC-Polymorph | −63 | 480 ± 94(14) | 41 ± 19(14) | [26.7, 28.7] | [7.1, 9.1] | 73 ± 8 (14) | 2.1 ± 0.8(14) | >33 | 1.6 | 0.91 ± 0.09(14) | |
| LEC LVI Multipolar-PC | −64 | 450 ± 90(13) | 26 ± 14(13) | [26.8, 29.0] | [6.0, 8.8] | 74 ± 14 (13) | 1.7 ± 0.4(13) | >10 | 1.2 | 0.9 ± 0.1(13) |
-
Values are mean values ± standard deviations or [range]; parentheses indicate the number of data points (default = 1; 2 for ranges). Values of maxFR reported as relative lower limits (e.g., >30 Hz) are measured from limited spike trains. The data are selected from a set (∈) of available values based on experimental conditions and number of measurements. Preferred conditions (rat/body temperature/patch clamp) are not indicated; otherwise, m = mice, r = room temperature, e = microelectrodes.





