The conserved ATPase PCH-2 controls the number and distribution of crossovers by antagonizing their formation in Caenorhabditis elegans
Figures
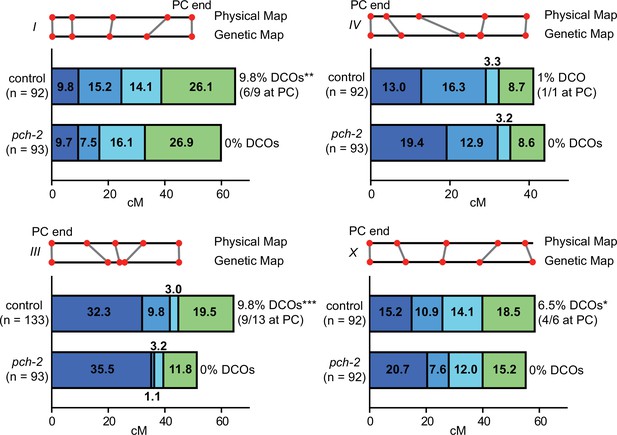
PCH-2 controls the number and distribution of crossovers in similar patterns on multiple chromosomes.
Genetic analysis of meiotic recombination in wildtype and pch-2 mutants. DCO indicates double crossovers. Physical and genetic maps of chromosomes I, III, IV and the X chromosome are depicted to scale. Genetic distance is shown in centimorgans. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Numerical data depicted in Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102409/elife-102409-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
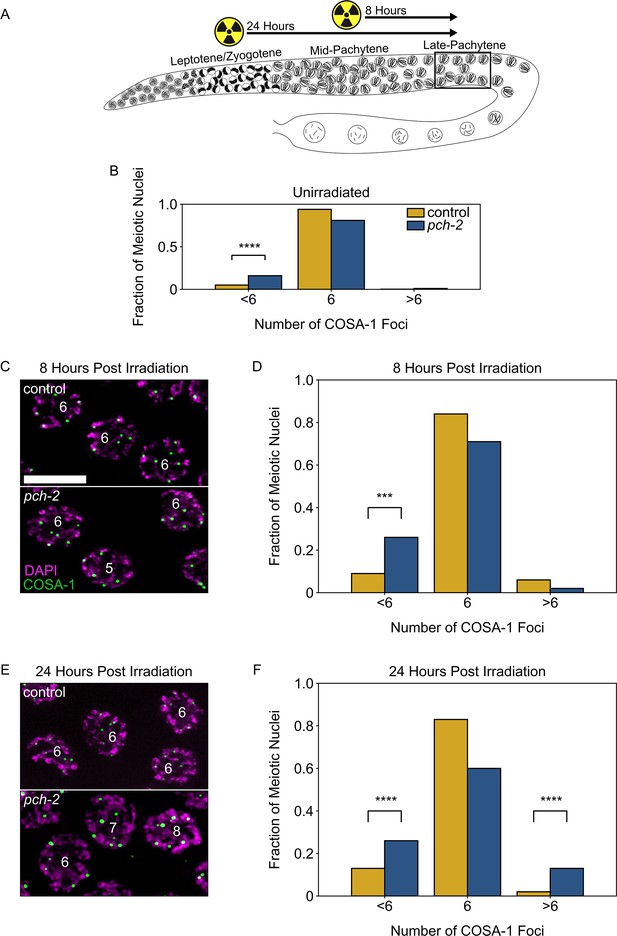
PCH-2 prevents exogenous double strand breaks from becoming crossovers in early meiotic prophase.
(A) Illustration of the irradiation experiments in control and pch-2 mutants. Box indicates late pachytene, the area where GFP::COSA-1 foci are analyzed. (B) Fraction of meiotic nuclei with less than six, six, or greater than six GFP::COSA-1 foci in control animals (yellow, n = 446) and pch-2 mutants (blue, n = 552). (C) Meiotic nuclei in control animals and pch-2 mutants 8 hours post irradiation stained for DAPI (magenta) and GFP::COSA-1 (green). Scale bar is 4 um. (D) Fraction of meiotic nuclei with less than six, six, or greater than six GFP::COSA-1 foci in control animals (yellow, n = 143) and pch-2 mutants (blue, n = 125) 8 hours post irradiation. (E) Meiotic nuclei in control animals and pch-2 mutants 24 hours post irradiation with DAPI (magenta) and GFP::COSA-1 (green). (F) Fraction of meiotic nuclei with less than six, six, or greater than six GFP::COSA-1 foci in control animals (n = 179) and pch-2 mutants (n = 378) 24 hours post irradiation. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Numerical data depicted in Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102409/elife-102409-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
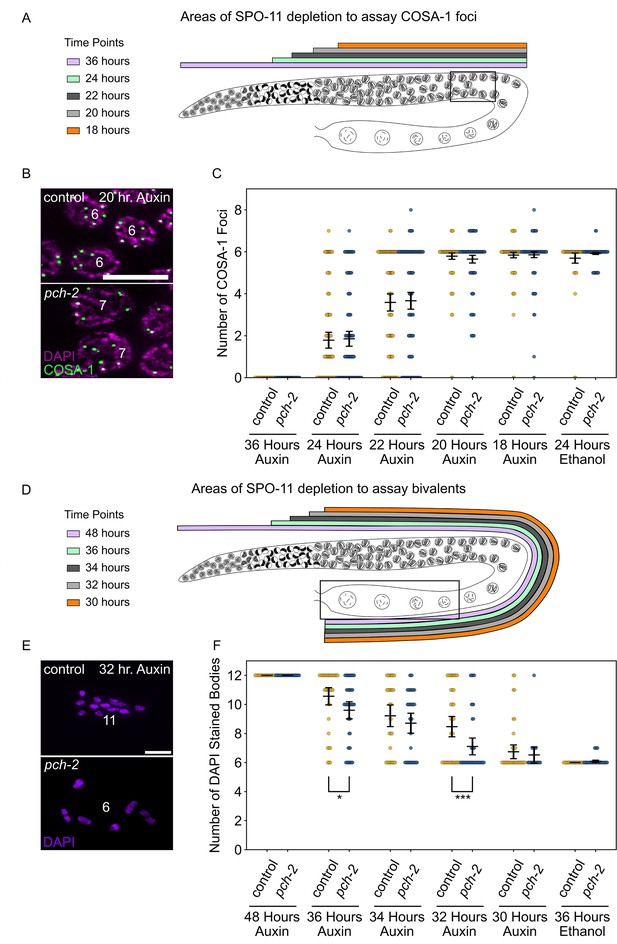
PCH-2 prevents SPO-11-induced double-strand breaks from becoming crossovers in early meiotic prophase.
(A) Illustration of the SPO-11 depletion experiment to assay GFP::COSA-1 in control animals and pch-2 mutants at different timepoints of auxin treatment. Each timepoint indicates when SPO-11 is depleted in the germline with auxin-induced degradation. Box indicates late pachytene, the area where GFP::COSA-1 foci are analyzed. (B) Representative images of meiotic nuclei in control animals and pch-2 mutants treated with auxin for 20 hours, stained for DAPI (magenta) and GFP::COSA-1 (green). Scale bar is 5 um. (C) Number of GFP::COSA-1 foci in meiotic nuclei at different timepoints of auxin treatment in control (blue) and pch-2 mutants (yellow). Error bars represent SEM. N values are as follows: 36 hours on auxin, control (78 nuclei), and pch-2 (83 nuclei); 24 hours on auxin, control (132 nuclei), and pch-2 (155 nuclei); 22 hours on auxin, control (152 nuclei), and pch-2 (168 nuclei); 20 hours on auxin, control (139 nuclei), and pch-2 (157 nuclei); 18 hours on auxin, control (154 nuclei), and pch-2 (154 nuclei); and 24 hours on ethanol, control (86 nuclei), and pch-2 (143 nuclei). (D) Illustration of the SPO-11 depletion experiment to assay bivalents in control animals and pch-2 mutants at different timepoints of auxin treatment. Each timepoint indicates when SPO-11 is depleted in the germline with auxin-induced degradation. Box indicates diakinesis, where DAPI-stained bodies are analyzed. (E) Oocytes from control animals and pch-2 mutants stained for DAPI (magenta). Scale bar is 4 um. (F) Number of DAPI-stained bodies in meiotic nuclei at different timepoints of auxin treatment in control animals and pch-2 mutants. N values are as follows: 48 hours on auxin, control (47 nuclei), and pch-2 (43 nuclei); 36 hours on auxin, control (46 nuclei), and pch-2 (50 nuclei); 34 hours on auxin, control (41 nuclei), and pch-2 (41 nuclei); 32 hours on auxin, control (51 nuclei), and pch-2 (47 nuclei); 30 hours on auxin, control (46 nuclei), and pch-2 (21 nuclei); and 36 hours on ethanol, control (52 nuclei), and pch-2 (48 nuclei). Error bars represent SEM and *<0.05, ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Numerical data depicted in Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102409/elife-102409-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
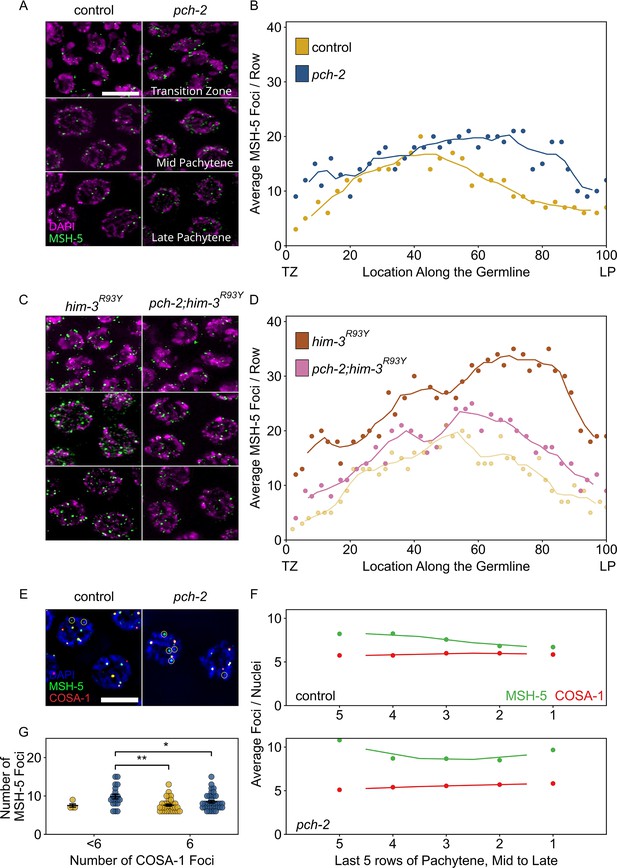
PCH-2 is required for timely loading and removal of MSH-5 on meiotic chromosomes through its regulation of HIM-3.
(A) Representative images of nuclei in different stages of meiotic prophase in control animals and pch-2 mutants stained for DAPI (magenta) and GFP::MSH-5 (green) Scale bar is 5 um. (B) Scatter plot showing average GFP::MSH-5 foci per row of germline nuclei in control animals (yellow, 163 nuclei) and pch-2 mutants (blue, 195 nuclei) from the transition zone (TZ) to late pachytene (LP), normalized to 100. The line represents a rolling average of four rows. (C) Representative images of nuclei in different stages of meiotic prophase in him-3R93Y mutants (left) and pch-2;him-3R93Y double mutants (right), stained for DAPI (magenta) and GFP::MSH-5 (green). (D) Scatter plot showing average GFP::MSH-5 foci per row in him-3R93Y (brown, 183 nuclei) and pch-2;him-3R93Y mutants (pink, 163 nuclei) from the TZ to LP, normalized to 100. The line represents a rolling average of four rows. Similar data is provided for a control germline (opaque yellow, 236 nuclei) for comparison. (E) Representative images of meiotic nuclei in control animals and pch-2 mutants stained for DAPI (blue), GFP::MSH-5 (green), and OLLAS::COSA-1 (red). Yellow circles indicate GFP::MSH-5 without OLLAS::COSA-1. Scale bar is 4 um. (F) Scatter plot showing average GFP::MSH-5 (green) and OLLAS::COSA-1 (red) foci per row in the last five rows of the germline in control animals (36 nuclei) and pch-2 mutants (45 nuclei). The line represents a rolling average of two rows. (G) Swarm plot showing number of GFP::MSH-5 foci in control (yellow, 14 nuclei) and pch-2 mutant (blue, 29 nuclei) nuclei with less than six OLLAS::COSA-1 foci (left) and six OLLAS::COSA-1 foci (right). Error bars represent SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Numerical data depicted in Figure 4 and Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102409/elife-102409-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx

PCH-2 does not regulate GFP::MSH-5 loading and removal through HTP-3.
(A) Representative images of nuclei in different stages of meiotic prophase in htp-3H96Y and pch-2; htp-3H96Y mutants stained for DAPI (magenta) and GFP::MSH-5 (green). Scale bar in all images is 5 um. (B) Scatter plot showing average GFP::MSH-5 foci per row of germline nuclei in htp-3H96Y (blue, 132 nuclei) and pch-2; htp-3H96Y (green, 161 nuclei) mutants from the transition zone to late pachytene, normalized to 100. The line represents a rolling average of four rows. Similar data is provided for a control germline (opaque yellow, 163 nuclei) for comparison.
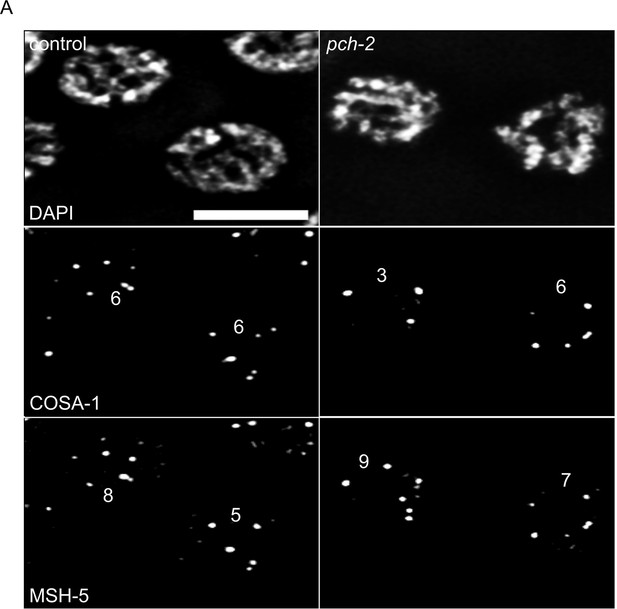
pch-2 meiotic nuclei with elevated numbers of GFP::MSH-5 foci show defects in crossover assurance.
(A) Gray scale images of control and pch-2 mutant nuclei stained for DAPI, GFP::MSH-5 and OLLAS::COSA-1. Scale bar in image is 4 um.
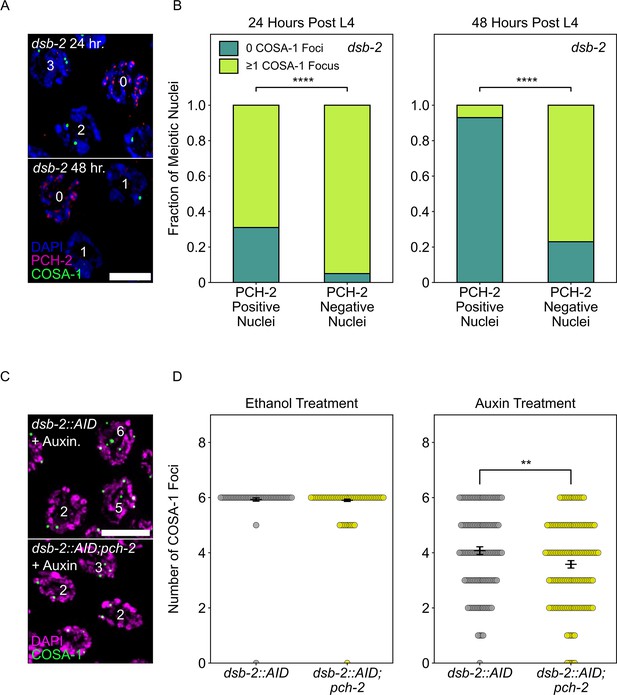
PCH-2 is removed when crossovers are designated.
(A) Representative images of meiotic nuclei in dsb-2 animals 24 hours post L4 and 48 hours post L4 stained for DAPI (magenta), PCH-2 (red), and GFP::COSA-1 (green). Scale bar is 4 um. (B) Stacked histograms showing percentage of PCH-2 positive (n = 43 at 24 hours, n = 42 at 48 hours) and negative (n = 194 at 24 hours, n = 130 at 48 hours) nuclei with (lime) and without (dark green) GFP::COSA-1 foci in dsb-2 mutants at 24 hours post L4 and 48 hours post L4. (C) Representative images of meiotic nuclei in dsb-2::AID and dsb-2::AID;pch-2 mutants treated with auxin and stained for DAPI (magenta) and GFP::COSA-1 (green). Scale bar is 5 um. (D) Swarm plot showing the number of GFP::COSA-1 foci in dsb-2::AID (gray) and dsb-2::AID;pch-2 (lemon) mutants when treated with ethanol or auxin. N values are as follows: dsb-2::AID (101 nuclei) and dsb-2::AID;pch-2 (154 nuclei) on ethanol, dsb-2::AID (136 nuclei) and dsb-2::AID;pch-2 (131 nuclei) on auxin. Error bars represent the SEM. **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Numerical data depicted in Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102409/elife-102409-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
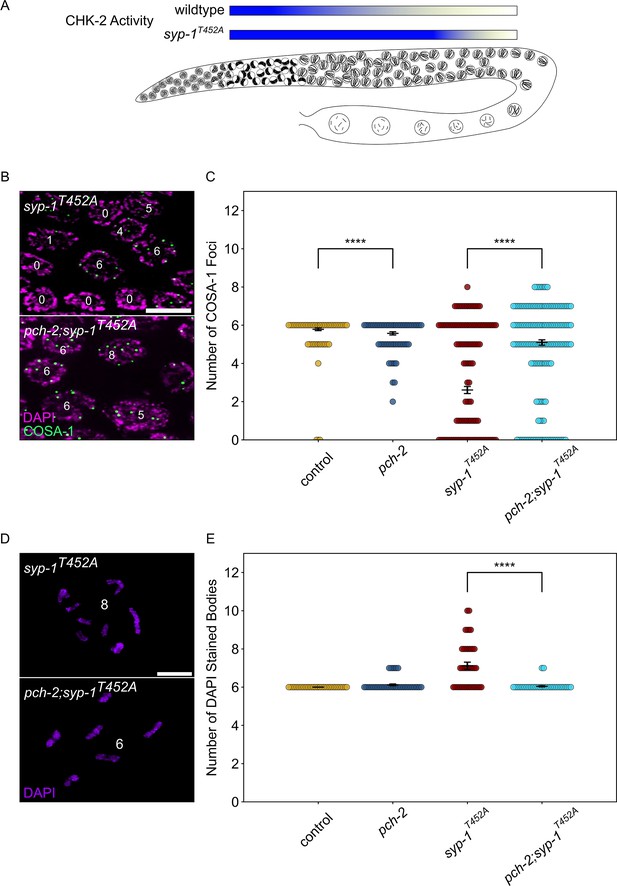
PCH-2 and high CHK-2 activity control the fate of early double-strand breaks.
(A) Illustration of CHK-2 activity in wildtype and syp-1T452A germlines. (B) Representative images of meiotic nuclei late pachytene in syp-1T452A and pch-2;syp-1T452A mutants stained for DAPI (magenta) and GFP::COSA-1 (green). Scale bar is 5 um. (C) Swarm plot showing number of GFP::COSA-1 foci in control animals (blue), pch-2 (yellow), syp-1T452A (maroon), and pch-2;syp-1T452A (light blue) mutants. Error bars represent SEM. (D) Oocytes from syp-1T452A and pch-2;syp-1T452A mutant worms stained for DAPI (magenta). Scale bar is 4 um. (D) Swarm plot showing number of DAPI-stained bodies in control animals (blue, n = 154), pch-2 (yellow, n = 89), syp-1T452A (maroon, n = 247), and pch-2;syp-1T452A (light blue, n = 242) mutants. Error bars represent SEM. ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Numerical data depicted in Figure 6, Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102409/elife-102409-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
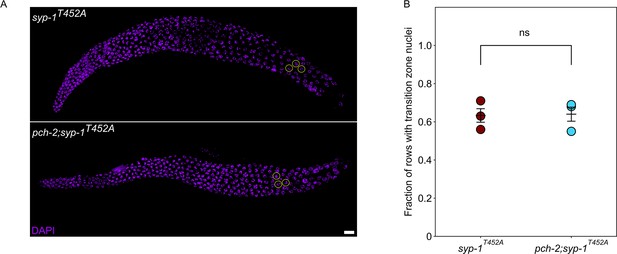
syp-1T452A and pch-2;syp-1T452A mutants display a similar defect in meiotic progression.
(A) Representative images of syp-1T452A and pch-2;syp-1T452A mutant germlines. Encircled nuclei indicate transition zone nuclei. Scale bar indicates 10 um. (B) Quantification of fraction of rows of transition zone nuclei in three germlines in syp-1T452A (maroon) and pch-2;syp-1T452A (light blue) mutants.
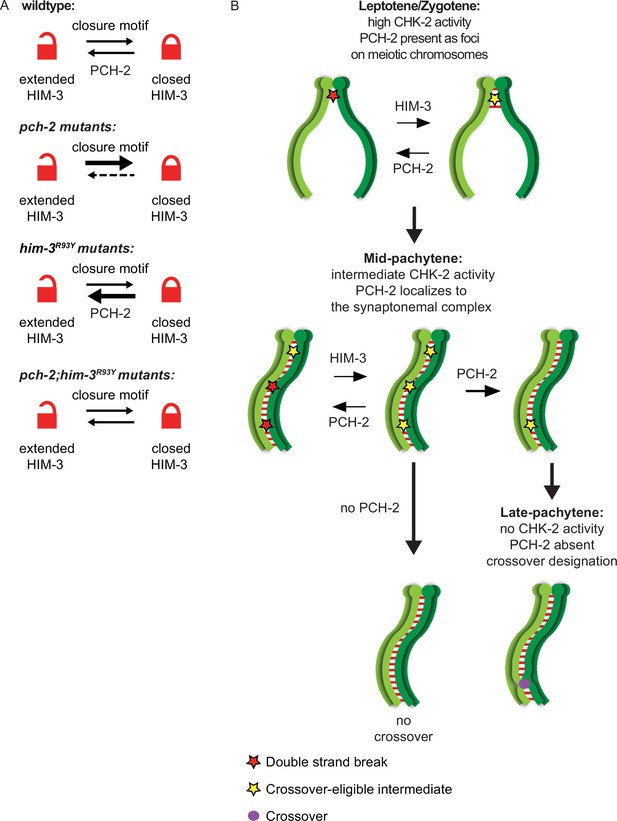
PCH-2 remodels HIM-3 to disassemble crossover-eligible intermediates, controlling crossover distribution and number.
(A) Model for how pch-2 and him-3R93Y mutations genetically interact to affect the progression of meiotic recombination. HIM-3 adopts the closed conformation upon binding an interacting protein with a closure motif and its conversion to the extended conformation is facilitated by PCH-2’s remodeling of its HORMA domain. (B) Model for how PCH-2 and HIM-3 progressively implement meiotic recombination during different stages of meiotic prophase.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) used for recombination assay.
SNPs, primers, enzymes used for restriction digests, and expected fragment sizes used for the recombination assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102409/elife-102409-supp1-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102409/elife-102409-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





