Methylation of RNA polymerase II non-consensus Lysine residues marks early transcription in mammalian cells
Figures
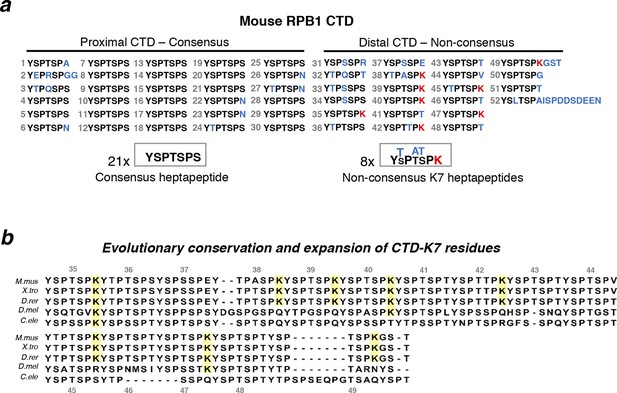
Structure and evolutionary conservation of the C-terminal domain of RPB1.
(a) Mouse RPB1 CTD is composed of 52 heptapeptide repeats with consensus amino-acid sequence YSPTSPS, which is represented 21 times at the most proximal CTD region. Non-consensus amino acids are enriched for at the distal region. Most abundant non-consensus residues are lysines, all found at heptad position 7 (K7; represented in red). Other non-consensus residues are represented in blue. (b) Amino-acid sequence alignment of the most distal part of the CTD containing K7 residues across different species: Mus musculus (M. mus); Xenopus tropicalis (X. tro); Danio rerio (D. rer); Drosophila melanogaster (D. mel); and, Caenorhabditis elegans (C. ele). Conservation of CTD K7 residues is highlighted in yellow. CTD repeat numbering was done according to the mouse CTD sequence between repeats 35 and 49, and aligned to the other species CTDs from the position of the repeat containing the first lysine in each organism. RPB1, RNA polymerase II large subunit; CTD, C-terminal domain.
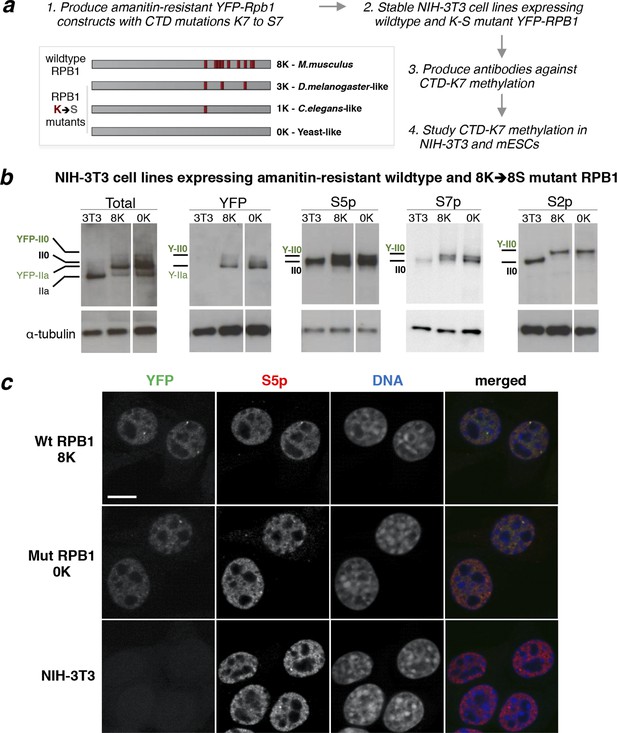
Mutation of CTD-K7 to -S7 residues does not interfere with RPB1 stability, phosphorylation or subcellular localization.
(a) Outline of strategy used to generate mouse cell lines bearing K7-to-S7 mutations and study CTD-K7 methylation. Red bars represent CTD repeats with K7 residues. The nomenclature of the cell lines is indicative of the number of K7 residues retained in each α-amanitin-resistant Rpb1 constructs. (b) Expression and phosphorylation levels of RPB1 in cell lines expressing wild-type and mutant YFP-Rpb1 construct. Levels of total RPB1, YFP, S5p, S7p and S2p were analyzed by western blotting in total cell extracts from NIH-3T3 (3T3) and from NIH-3T3 cell lines expressing wild-type (8K) and mutant (0K) RPB1. Hypo- (IIa) and hyperphosphorylated (II0) isoforms of YFP-Rpb1 constructs migrate slower than wild-type construct detected in 3T3 due to the YFP tag (Y-IIa and Y-II0 respectively). Total RPB1 was detected with an antibody to the N-terminus of RPB1. α-tubulin was used as loading control. For each blot/antibody, samples were run in the same gel, and re-ordered to improve clarity. Complete western blots are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. (c) Whole-cell detection of RPB1 expression in wild-type (8K), mutant (0K) and untransfected NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Expression and distribution of total RNAPII (YFP, green) is similar in 8K and 0K cell lines. Immunofluorescence of S5p (pseudo-colored red) shows similar pattern and distribution in the three cell lines. DNA (pseudo-colored blue) was counterstained with TOTO-3. Scale bar, 10 µm. CTD, C-terminal domain; RPB1, RNA polymerase II large subunit; YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.
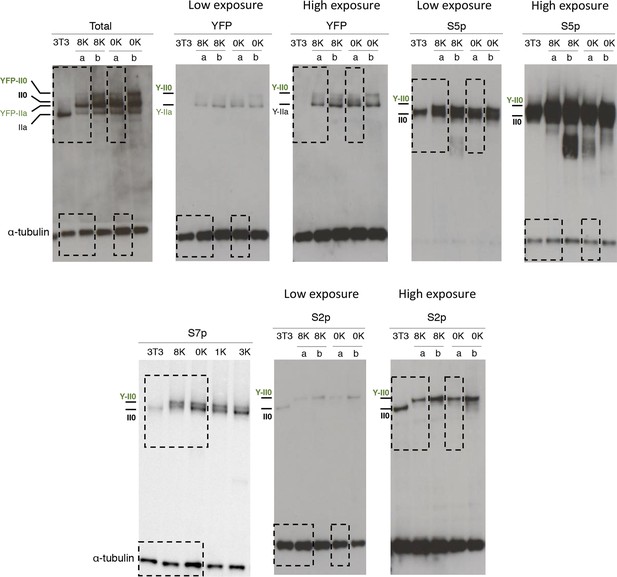
Complete western blots used in Figure 2a.
Sections shown in Figure 2a are highlighted with dashed boxes. High and low exposure blots are shown for YFP, S5p, and S2p. For total RPB1, YFP, S5p and S2p, two different cell lines (a and b) stably expressing the 8K and 0K constructs were analyzed, but only one of each was selected for Figure 2a (8K-a and 0K-a) and used in further analyses. Total RPB1 was detected with an antibody to the N-terminus of RPB1. RPB1, RNA polymerase II large subunit; YFP, yellow flourescent protein.
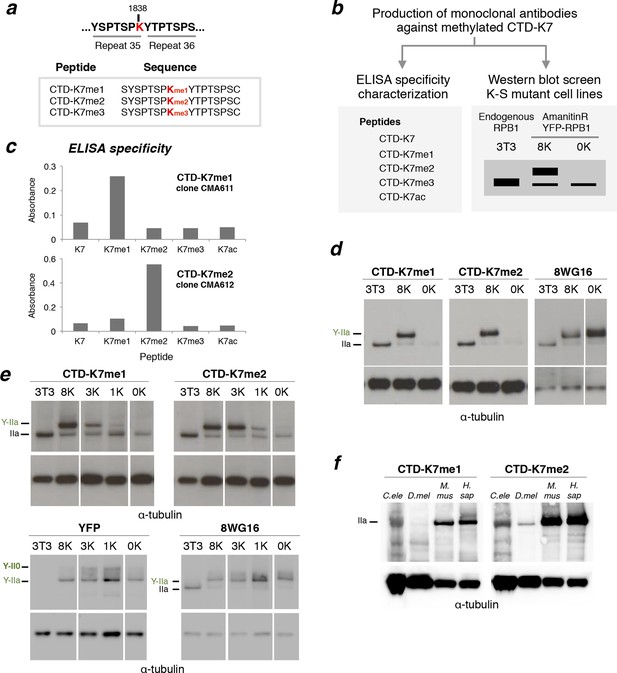
RPB1 is mono- and di-methylated at CTD-K7 residues.
(a) Amino-acid sequence of CTD-K7-methyl peptides used for immunization, designed based on the sequence of mouse CTD repeats 35 and 36. (b) Schematic representation of strategy used for production and screening of specific CTD-K7-methyl antibodies. Antibody clones that specifically recognize K7 or its modifications should bind strongly to the wild-type band, the 8K slower-migrating band, but not to the mutant 0K band. (c) Specificity of CTD-K7 methyl antibodies was assessed by ELISA using unmodified (K7), mono- (K7me1), di- (K7me2), tri-methylated (K7me3) and acetylated (K7ac) CTD peptides (Table 1). Clones CMA611 and CMA612 are specific for K7me1 and K7me2, respectively. (d) K7me1 and K7me2 mark hypophosphorylated RPB1 in mouse cells with migration similar to forms detected using 8WG16 antibody. Western blotting was performed using total protein extracts from NIH-3T3 (3T3), and from NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing wild-type 8K (8K) or mutant 0K (0K). K7me1 and K7me2 are detected in 3T3 and 8K, but not in 0K cell lines. CTD methylation migrates at the level of hypophosphorylated RNAPII (IIa and Y-IIa). Low levels of methylation of endogenous RPB1 is also detected in 8K and 0K cell lines, due to expression from endogenous Rpb1 locus. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. For 8WG16 blot, samples were run in the same gel, and re-ordered to improve clarity. Original western blots are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1a. (e) CTD K7 residues are mono- and di-methylated in 3T3 cells at levels that increase with K7 number. K7me1 and K7me2 were detected by western blotting using whole-cell extracts from 3T3 lines expressing 8K, 3K, 1K or 0K Rpb1 constructs; untransfected 3T3 cell extracts were used as an additional control. RPB1 levels were measured by immunoblotting of YFP and using 8WG16 antibody with specificity for unmodified S2. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. Samples were run in the same gel, and re-ordered to improve clarity. Original western blots are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1c. (f) K7me2 and K7me1 are detected in invertebrates, mouse and human cells. Western blotting of K7me1 and K7me2 was performed using C. elegans whole worm extract (C. ele), D. melanogaster embryo extract (D. mel), total cell extracts from NIH-3T3 cells (M. mus) and from human HEK-293T cells (H. sap). α-Tubulin was used as loading control. RPB1, RNA polymerase II large subunit; YFP, yellow flourescent protein. Original western blots are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1d.
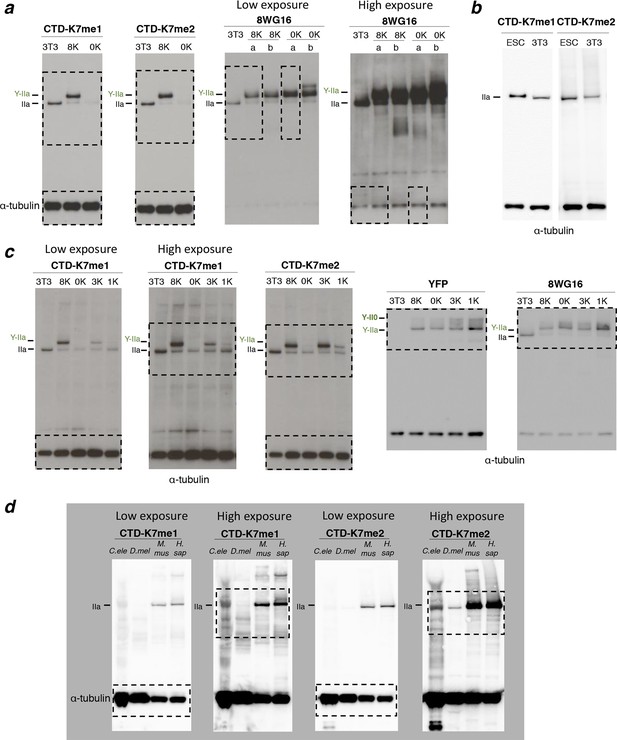
Complete western blots used in Figure 3a, 3e and 3f, and detection of CTD methylation in mouse ES cells.
(a) Complete western blot used in Figure 3d. Sections shown in Figure 3d are highlighted with dashed boxes. In the case of 8WG16, two different cell lines (a and b) that stably express each of the 8K and 0K constructs were analyzed but only one is shown in Figure 3d (8K-a and 0K-a). (b) Detection of CTD K7me1 and K7me2 in mouse ES cells at hypophosphorylated RPB1 (IIa) confirms the association of CTD-K7 methylation with the lower migrating RPB1 form. (c) Complete western blot used in Figure 3e. Sections used are highlighted with dashed boxes. Lower and higher exposures of western blots are displayed for K7me1. (d) Complete western blot used in Figure 3f. Low and high exposure versions are displayed and sections used are highlighted with dashed boxes. α-tubulin is used as reference; extracts were obtained from different extraction protocols and protein quantification was not possible for all samples. CTD, C-terminal domain; ES, embryonic stem; RPB1, RNA polymerase II large subunit.
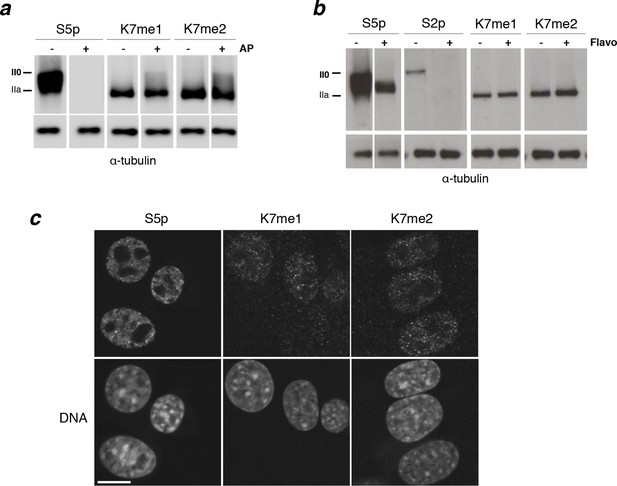
Interplay between K7me1 and K7me2 with RPB1 phosphorylation.
(a) CTD K7me1 and K7me2 mark hypophosphorylated and intermediately phosphorylated Rpb1 forms, but not the hyperphosphorylated (II0) form. Western blotting using the indicated antibodies was performed after treatment of nitrocellulose membranes in the presence (+) or absence (–) of alkaline phosphatase (AP). Hypo- (IIa) and hyperphosphorylated (II0) RPB1 forms are indicated. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. Lanes were re-ordered to improve clarity. Original western blots are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1a. (b) K7me1 and K7me2 abundance is insensitive to CDK9 inhibition with inhibitor flavopiridol. Mouse ES cells were treated with flavopiridol (10 µM, 1 hr), before western blotting using antibodies specific for S5p, S2p, K7me1 or K7me2. Hypo- (IIa) and hyperphosphorylated (II0) RPB1 forms are indicated. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. Lanes were re-ordered to improve clarity. Original western blots are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1b. (c) K7me1 and K7me2 are localized in the nucleoplasm with a more restricted distribution than S5p. Whole-cell immunofluorescence of S5p, K7me1 and K7me2 was performed using mouse NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Nucleic acids were counterstained with TOTO-3. Scale bar, 10 µm. RPB1, RNA polymerase II large subunit.
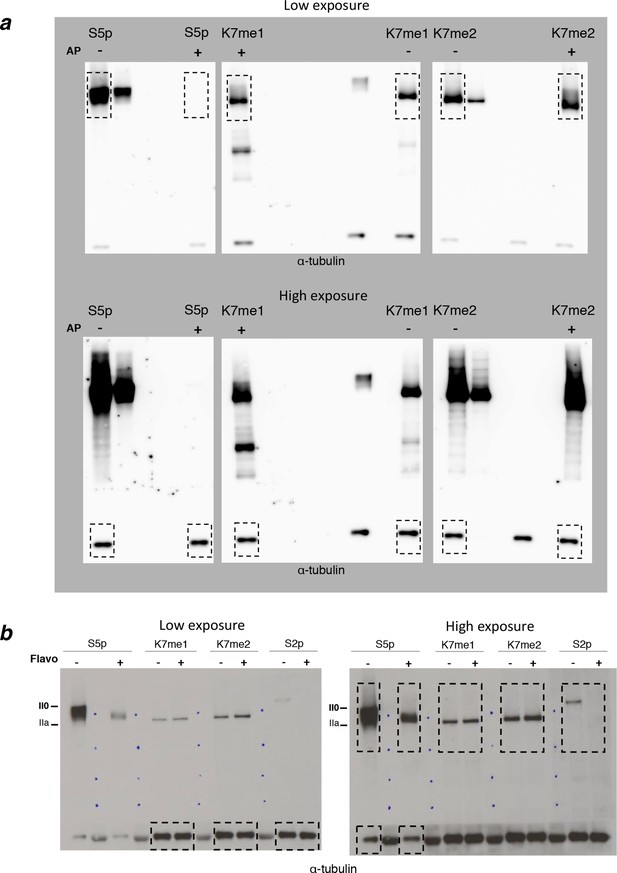
Complete western blots used in Figure 4a and 4b.
(a) Complete western blot used in Figure 4a. Used sections are highlighted with dashed boxes and low and higher exposure blot versions are displayed. Sections of the membrane treated with alkaline phosphatase and the respective untreated controls are indicated. (b) Complete western blot used in Figure 4b. Used sections are highlighted with dashed boxes and low and higher exposure blot versions are displayed.
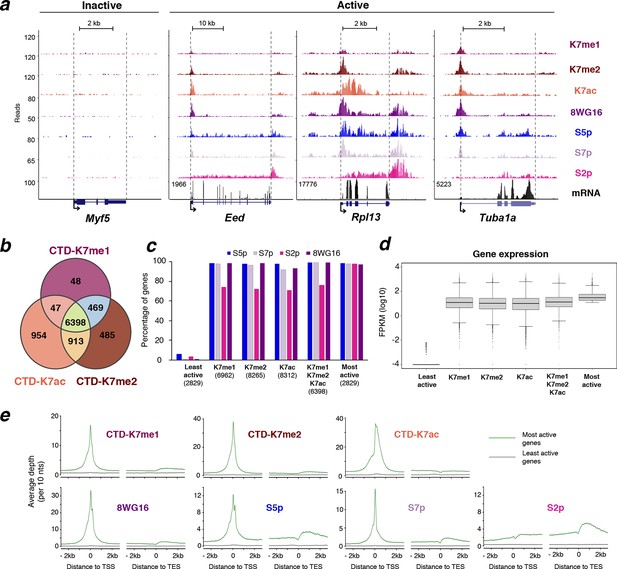
K7me1 and K7me2 mark promoters of expressed genes.
(a) K7me1 and K7me2 are enriched at promoters of active genes. ChIP-seq profiles for K7me1, K7me2, K7ac, 8WG16, S5p, S7p and S2p, and mRNA-seq profiles are represented for the inactive gene Myf5, and active genes Eed, Rpll13 and Tuba1a. Images were obtained from UCSC Genome Browser using mean as windowing function. (b) Methylation and acetylation of CTD-K7 residues coincides at most genes. Gene promoters positive for K7me1 (6962), K7me2 (8265) and K7ac (8312) were identified using a peak finder approach (see Materials and methods). The overlap between the three CTD-K7 modifications is represented using a Venn diagram. (c) CTD-K7 methylation and acetylation extensively co-occur with other CTD modifications. The percentages of genes positive for S5p, S7p, S2p and unmodified S2 are represented for each group of genes positive for K7me1, K7me2 and K7ac individually or simultaneously. Least and most active genes (bottom and top 15% expressed genes, respectively) are represented for comparison. Numbers of genes are indicated below each group of genes. (d) CTD-K7 methylation and acetylation are associated with active genes genome-wide. mRNA levels are similar at genes positive for K7me1, K7me2 and/or K7ac. Least and most active genes are represented for comparison. A pseudocount of 10-4 was added to FPKM prior to logarithmic transformation. (e) K7me1, K7me2 and K7ac are strongly enriched around the TSS of most active genes. ChIP-seq average enrichment profiles of K7me1, K7me2, K7ac, unmodified S2 (8WG16), S5p, S7p and S2p, for the most active (green) and least active (gray) genes represented over 5 kb window centered on the TSS and TES. Genes positive for H3K27me3 and/or H2Aub1 were excluded, to minimize confounding effects due to polycomb repression, which is abundant in mouse ES cells (Brookes et al., 2012). CTD, C-terminal domain; ES, embryonic stem; FPKM, Fragments Per Kilobase of exon per Million mapped reads; mRNA, messenger RNA; TES, transcription end sites; TSS, transcription start sites.
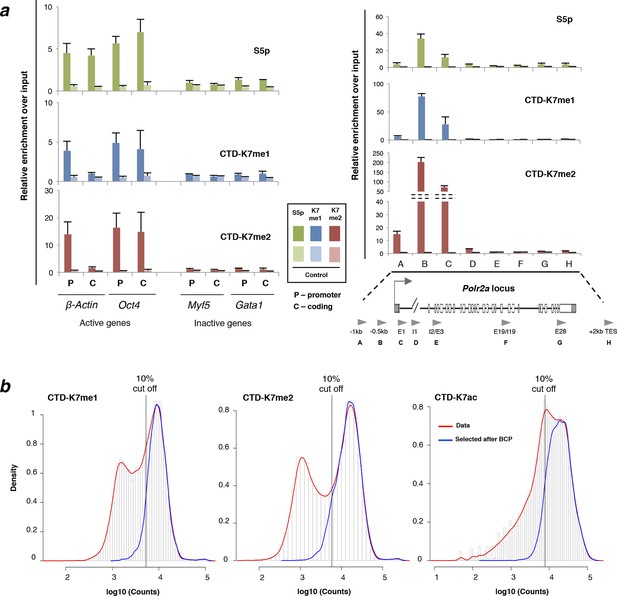
CTD-K7 mono- and di-methylation are enriched at promoters of active genes.
(a) Abundance and distribution of K7me1, K7me2, and S5p was assessed by ChIP followed by qPCR at promoters and coding regions of active (β-Actin, Oct4, Nanog and Polr2a) and inactive (Gata1 and Myf5) genes using fixed chromatin from mouse ES cells. Mean and standard deviations are presented from 2–3 independent ChIP experiments, Background levels were measured using a non-specific control antibody against digoxigenin (Control). ChIP enrichment levels are expressed relative to input DNA using the same amount of DNA in the qPCR. (b) Distribution of ChIP-seq signal at gene promoters for CTD-K7me1, K7me2 and K7ac. Histograms for the distribution of signal at ± 2 kb windows centered at all gene promoters (red lines) or at gene promoters classified as positive according to their positive overlap with genomic regions identified by BCP analysis (blue lines). Vertical lines mark the 10% cut off. CTD-K7ac data was published in (Schroeder et al., 2013). BCP, Bayesian change-point; ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing; CTD, C-terminal domain; qPCR, quantitative polymerasechain reaction.
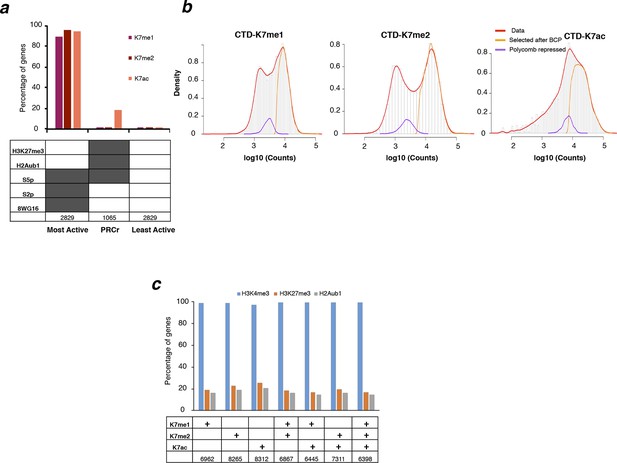
RNAPII CTD is mono- and di-methylated exclusively at active genes and not at Polycomb repressed genes.
(a) Percentage of genes positive for K7me1, K7me2 and K7ac in three different classes of genes: active, polycomb repressed (PRCr) and inactive. Active genes are positive for S5p, S7p, S2p and 8WG16, and are negative for H3K27me3 and H2Aub1; PRCr genes are positive for H3K27me3, H2Aub1 and S5p and negative for S2p and 8WG16; inactive genes are negative for H3K27me3, H2Aub1, S5p, S2p and 8WG16. Number of genes for each group is indicated. (b) Distribution of ChIP-seq signal at gene promoters for CTD-K7me1, K7me2 and K7ac. Histograms for the distribution of signal at ± 1 kb windows centered at all gene promoters (red line), or at gene promoters classified as positive according to their overlap with the enriched regions identified by BCP (see Materials and methods; orange line), or at PRCr genes (purple line) classified as described in (a). Overlapping genes are excluded to avoid confounding effects. (c) Percentage of genes positive for H3K4me3, H3K27me3 and H2Aub1 for different groups of genes classified according to the presence of K7me1, K7me2 and/or K7ac shows a preferential association of CTD-K7 methylation and acetylation with H3K4me3. The number of genes for each group is indicated. BCP, Bayesian change-point; CTD, C-terminal domain; ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing; PRCr, polycomb repressed.

Exploring the relationship between different CTD modifications using correlation and linear regression analyses.
(a) Matrix of Spearman’s correlation coefficients between the levels of K7me1, K7me2, K7ac, 8WG16, S5p, S7p, S2p (2 kb window after TES), mRNA and mock ChIP control ordered according to increasing correlation with mRNA. This correlation analysis was performed with the group of active genes (n = 1564) positive for S5p, S7p and S2p, with expression level of FPKM >1, and negative for H3K27me3 and H2Aub1, also excluding overlapping genes and genes whose maximum RNAPII peak (8WG16) is >50 bp away from the annotated TSS. Figure 6—figure supplement 1 represents the full group of active genes, including genes with maximum 8WG16 peak deviated from TSS >50 bp. (b) The partial correlations between K7me2 and S2p is zero or becomes negative after removing the contribution of other intervening modifications. Schematic summarizes the dependencies between K7me2 and other CTD modifications relative to S2p (TES); the respective correlations are represented on top. Partial correlations between K7me2 and S2p after removing the effect of the other CTD modifications are indicated in red (*** P-value < 1×10-9; n.s., non-significant). (c) Levels of S7p and K7ac independently contribute to S2 phosphorylation. The partial correlations between S7p and S2p when controlling for K7ac (top) and between K7ac and S2p when controlling for S7p (bottom) remain positive (indicated in red; *** P-value < 1x10-9). (d) Exhaustive stepwise regression analysis for prediction of S2p levels at the TES using K7me1, K7me2, 8WG16, S5p, S7p, K7ac and CpG. The five best models using 1– 5 predictors are shown. Positive and negative coefficients are represented by black and red squares, respectively; the values of adjusted R2 and Akaike information criterion (AIC) are indicated for each model (* P-value ≤ 0.05; ** P-value ≤ 0.01; *** P-value ≤ 0.001; n.s., non-significant). ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; CTD, C-terminal domain; FPKM, Fragments Per Kilobase of exon per Million mapped reads; mRNA, messenger RNA; TES, transcript end sites; TSS, transcription start sites.
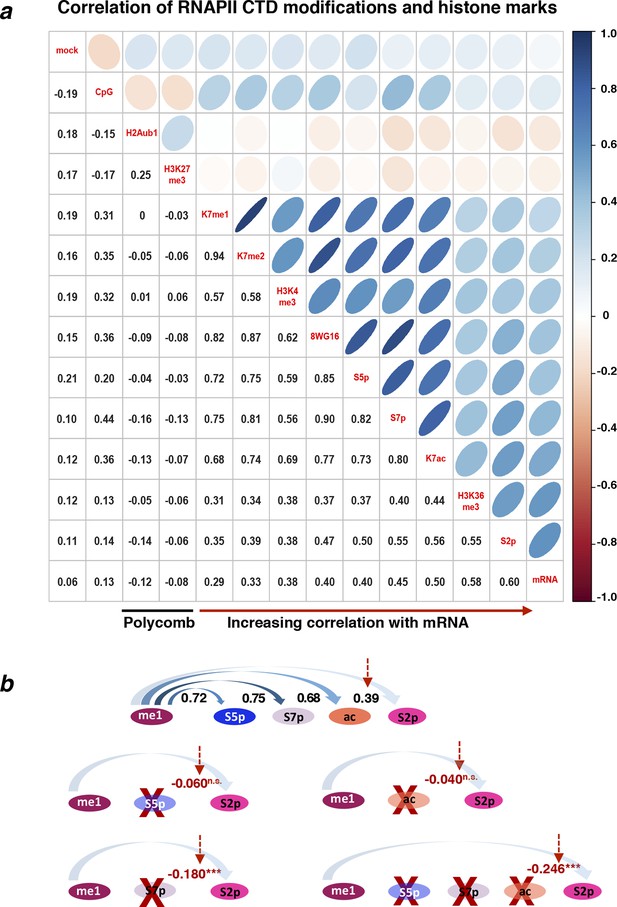
Correlations between different RNAPII CTD modifications and histone marks for all active genes.
(a) Matrix of Spearman’s correlation coefficients between the levels of several histone and CTD modifications, mRNA, CpG and mock control. The correlations present in Figure 6a were expanded here to a larger group of active genes (n = 4271) defined as positive for S5p, S7p, and S2p, negative for repressive histone marks H3K27me3 and H2Aub1 and with FPKM >1. The correlation matrix is organized according to increasing correlation with mRNA. (b) Schematic of the temporal/spatial order of CTD modifications relative to K7me1 with the respective correlations represented on top. Partial correlations between K7me1 and S2p controlling for the indicated CTD modifications are indicated in red (*** P-value < 1x10–12; n.s., non-significant). CTD, C-terminal domain; FPKM, Fragments Per Kilobase of exon per Million mapped reads; mRNA, messenger RNA.
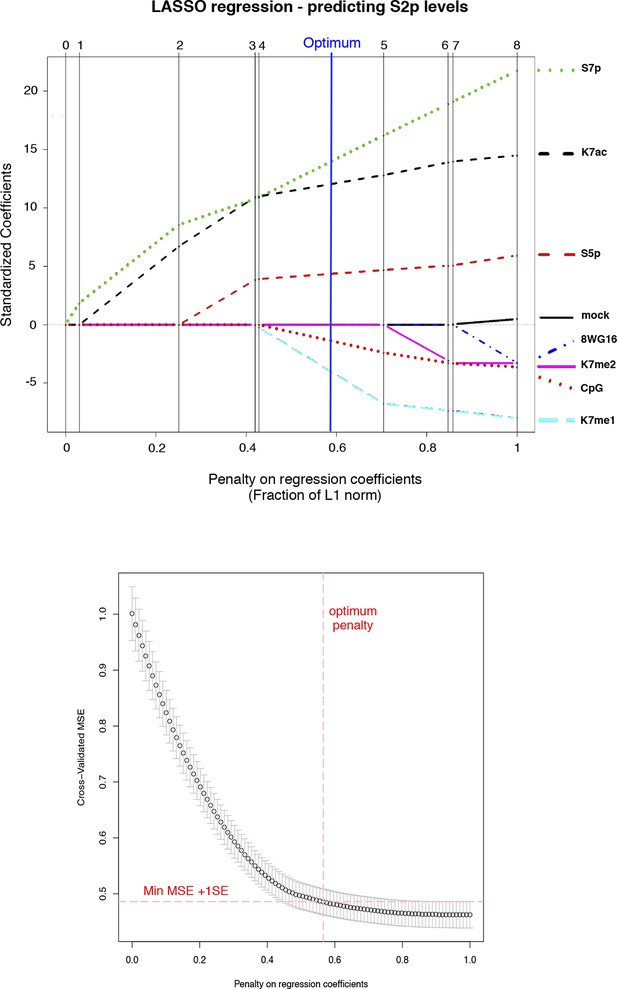
CTD K7me1 and K7me2 negatively contribute for the prediction of S2p levels.
Typical LASSO regression models to predict S2p levels select K7me1 or K7me2 as negative predictor variables at the optimum penalty (blue line, top graph). LASSO regression employs the L1 norm to penalize (shrink) regression coefficients towards zero in order to prevent over-fitting due to co-linearity between predictor variables. Here, we used 8WG16, S5p, S7p, K7me1, K7me2, K7ac and CpG as input predictors and employed 10-fold cross-validation (bottom graph) to select the most parsimonious model within 1 SE of the minimum MSE, represented by the red dashed lines. CTD, C-terminal domain; LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; MSE, mean standard error; SE, standard error.
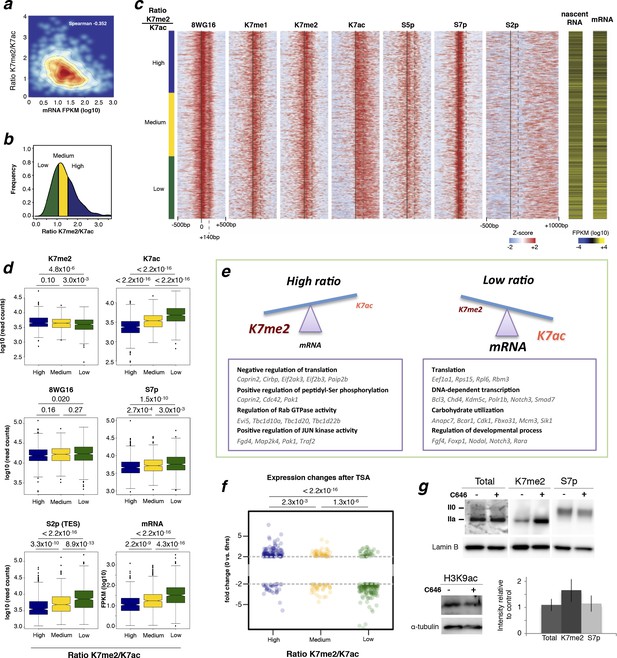
CTD-K7 methylation and acetylation have different distributions at the promoters of active genes and their levels are associated with gene expression.
(a) K7me2/K7ac ratio correlates negatively with mRNA expression. (b) Distribution of K7me2/K7ac ratios, and their division into three quantiles: low (green), medium (yellow) and high (blue) ratios. (c) Heatmaps showing ChIP-seq density for a group of active genes (n = 1564 genes, defined as in Figure 6a) using ± 500 bp windows centered on promoters, except for S2p, using window -500 to +1000 bp; z-scores per gene are represented. Genes were ordered according to K7me2/K7ac ratios, from highest to lowest. Gene expression (both nascent and mature RNA; FPKM) is represented for comparison. (d) Unmodified S2 (8WG16), K7me2, K7ac, S7p, S2p (TES) and gene expression (mRNA) levels are represented for the three quantiles of K7me2/K7ac ratio. A Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to calculate significant differences between the K7me2/K7ac quantiles and the respective p-values are represented. (e) Schematic representation of the relation between K7me2 and K7ac levels with mRNA expression. Examples of Gene Ontology (GO) terms and respective genes associated with high and low K7me2/K7ac ratios are represented. (f) Amount of fold change after 6 hr treatment with the histone deacetylase inhibitor TSA is represented for the three quantiles of K7me2/K7ac ratio. Fisher’s exact test was used to calculate significant differences between the K7me2/K7ac quantiles and the respective P-values are represented. Only genes with a minimum fold change of 2-fold change at 6 hr TSA treatment are shown. Dashed line: 2-fold change. (g) Inhibition of P300 promotes an increase in global levels of CTD-K7me2. Mouse ES cells were treated with P300 inhibitor C646 (30 µM, 3 hr), before western blotting with antibodies specific for total RNAPII, K7me2 and S7p (top panel) and H3K9 acetylation (bottom left panel). Hypo- (IIa) and hyperphosphorylated (II0) RPB1 forms are indicated. Lamin B and α-tubulin were used as loading control. Original western blots are shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 4. Relative quantification of western blot signal intensity (bottom right panel). Signal intensity of total RNAPII, K7me2 and S7p for control and C646 treated samples was normalized to the corresponding Lamin B signal. The levels of total RNAPII, K7me2 and S7p after P300 inhibition are represented relative to the signal from control (DMSO only) cells. Bars represent average values with standard deviation from two biological replicates and two to four technical replicates. CTD, C-terminal domain; ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; ES, embryonic stem; FPKM, Fragments Per Kilobase of exon per Million mapped reads; mRNA, messenger RNA; TSA, Trichostatin A.
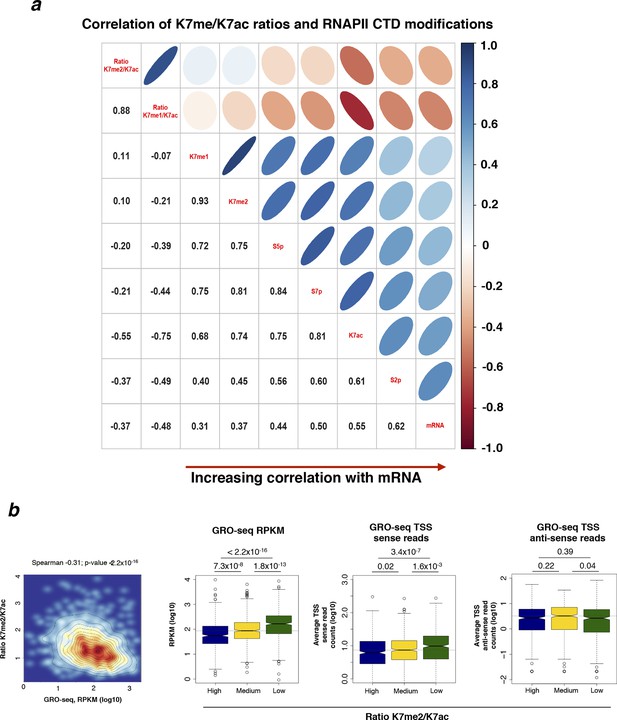
CTD methylation / acetylation ratio negatively correlates with S2p and RNA production.
(a) CTD K7 methylation / acetylation ratio negatively correlates with S2p (TES) and mRNA. Matrix of Spearman’s correlation coefficients between ratios K7me1/K7ac and K7me2/K7ac and K7me1, K7me2, S5p, S7p, K7ac, S2p (2 kb window after TES) and mRNA ordered according to increasing correlation with mRNA. The group of active genes (n = 1564) was defined in Figure 6a. (b) Higher levels of sense nascent transcripts are detected with decreasing K7me2/K7ac ratios; anti-sense TSS reads are similar across K7 ratio quantiles, except for a small decrease in the low ratio, high expression quantile. Published GRO-seq data obtained in mouse ES cells (Jonkers et al. 2014) were analysed to determine RPKM and read counts from –500 to +1000 bp relative to TSS. CTD, C-terminal domain; ES, embryonic stem; GRO-seq, globalrun-on sequencing; mRNA, messenger RNA; TES, transcription end sites; TSS, transcription start sites.
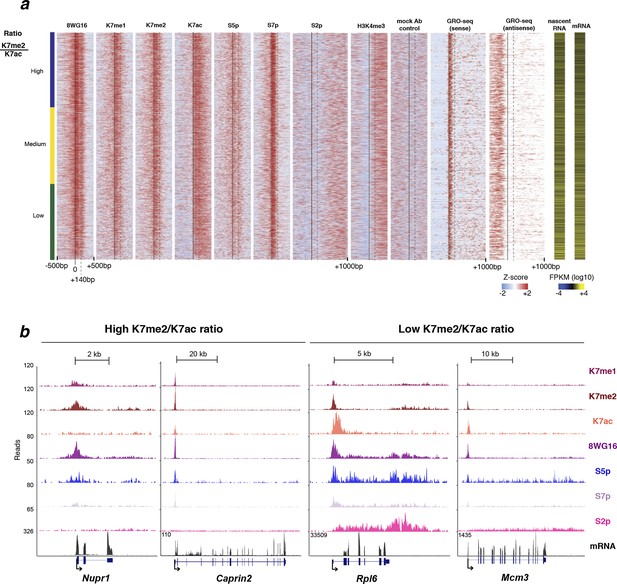
Distribution of different RPB1 modifications around the promoter of active genes.
(a) Heatmaps of ChIP-seq density using a ± 500 bp window centered around the TSS (unless stated otherwise) of active genes defined as positive for S5p, S7p and S2p, as negative for H3K27me3 and H2Aub1 and with FPKM >1 (n = 4271); z-scores per gene are represented. Genes were ordered from highest to lowest K7me2/K7ac ratio, and individual heatmaps are represented for different RPB1 modifications, histone modification H3K4me3 and no antibody control. Gene expression is represented for comparison [both nascent (GRO-seq signal and RPKM values) and mature RNA]. (b) Examples of active genes associated with high and low K7me2/K7ac ratio. Single gene ChIP-seq profiles for RPB1 modifications and mRNA expression for genes associated with high K7me2/K7ac ratio (Nupr1; ratio 5.7 and Caprin2; ratio 2.8) and low K7me2/K7ac ratio (Rpl6; ratio 0.5 and Mcm3; ratio 0.8). Single gene ChIP-seq images were obtained from UCSC genome browser. ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing; GRO-seq, global run-on sequencing; RPB1, RNA polymerase II large subunit; RPKM, reads per kilobase per million of reads mapped; TSS, transcription start sites.
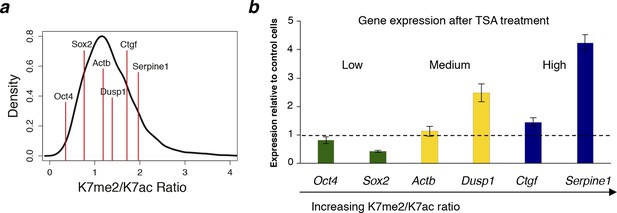
Genes with higher K7me2/K7ac ratio are up-regulated after TSA treatment.
(a) Range of K7me2/K7ac ratios for genes used in expression analysis after Trichostatin A (TSA) treatment. (b) Total RNA levels were analysed by quantitative RT-PCR after treatment of ES cells with TSA (50 nM, 3 hr) or vehicle DMSO (control cells). Expression relative to control cells is represented and genes are ordered according to K7me2/K7ac ratio. Total RNA levels were measured using primers for the 5´end of each gene and normalized for Actb mRNA levels. Mean and standard deviations from 3 independent TSA treatments are represented. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; ES, embryonic stem; RT-PCR, reversetranscription polymerase chain reaction.
Complete western blots used in Figure 7g.
Sections shown in Figure 7g are highlighted with dashed boxes. High and low exposure blots are shown for K7me2. In the H3K9ac western blot, the sections shown with increasing exposure time correspond to the area blotted for H3K9ac. Total RPB1 was detected with an antibody to the N-terminus of RPB1. RPB1, RNA polymerase II large subunit.
P300 inhibition promotes a small increase in global levels of CTD-K7me2.
Mouse ES cells were treated with P300 inhibitor C646 (30 μM, 3h), before western blotting with antibodies specific for total RPB1, K7me1, K7me2 and S7p. Hypo- (IIa) and hyperphosphorylated (II0) RPB1 forms are indicated. Loading control: Lamin B.
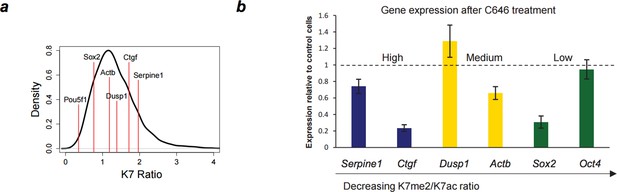
Down-regulation of gene expression after P300 inhibition.
(A) Range of K7me2/K7ac ratios for genes used in expression analysis after C646 treatment. (B) Total RNA levels were measured by quantitative RT-PCR after treatment of ES cells with C646 (30 μM, 3h) or vehicle DMSO (control cells). Expression relative to control cells is represented and genes are ordered according to K7me2/K7ac ratio. Total RNA levels were measured using primers for the 5´end of each gene and normalized for Actb mRNA levels. Mean and standard deviations from 3 independent TSA treatments are represented.
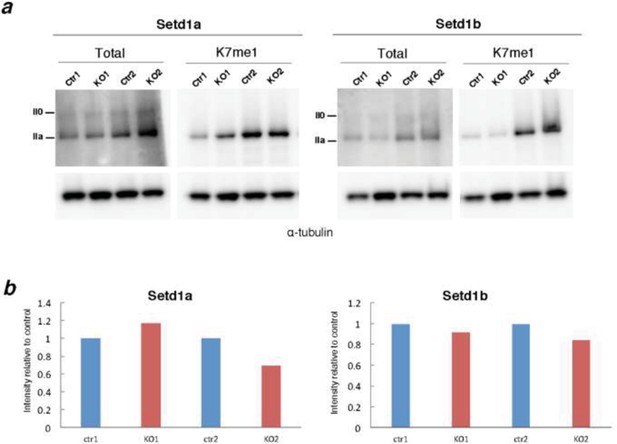
Screen of CTD-K7 methylase activity in conditional KO mouse ES cells for H3K4 methyltransferases.
(A) Western blotting was performed using protein extracts from mouse ES cells with conditional knockout for H3K4 methylase Setd1a or Setd1b for total RPB1 and K7me1 in 2 biological replicates. Hypo- (IIa) and hyper-phosphorylated (II0) RPB1 forms are indicated. α-tubulin was used as loading control. (B) Signal intensities for total RPB1 and K7me1 (control and KO samples) were normalized to the corresponding α-tubulin signal to correct for variability in loading. Levels of K7me1 were normalized to the total amount of RPB1 and intensity relative to control cells is represented for the 2 replicates.
Tables
RPB1 CTD peptides. CTD peptides with unmodified, mono-, di-, tri-methyl and acetyl K7 residues were used in ELISA assays to characterize the specificity of the CTD methyl antibodies produced in this study.
| Peptide sequence | Modification |
|---|---|
| SYSPTSPKYTPTSPSC | Unmodified |
| SYSPTSPKme1YTPTSPSC | K7 monomethyl |
| SYSPTSPKme2YTPTSPSC | K7 dimethyl |
| SYSPTSPKme3YTPTSPSC | K7 trimethyl |
| SYSPTSPKacYTPTSPSC | K7 acetyl |
-
CTD, C-terminal domain; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
List of Antibodies used in this study. Full description of the antibodies and the amounts or concentrations used in this study for WB, ChIP or IF.
| Amount/dilution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Raised in (isotype) | Clone | Stock | WB | ChIP | IF | Source |
| S5p | Mouse (IgG) | CTD4H8 (MMS-128P) | 1 mg/ml | 1/200,000 | 10 µl (10 µg) | 1/3000 | Covance |
| S7p | Rat (IgG) | 4E12 | - | 1/10 | - | - | Kind gift from Dirk Eick |
| S2p | Mouse (IgM) | H5 (MMS-129R) | 1–3 mg/ml | 1/500 | - | - | Covance |
| Unphospho-S2 | Mouse (IgG) | 8WG16 (MMS-126R) | 1–3 mg/ml | 1/200 | - | - | Covance |
| N-terminus (Total RPB1) | Rabbit (IgG) | H224 (sc-9001x) | 200 µg/ml | 1/200 | - | - | Santa Cruz Biotechnology |
| K7me1 | Mouse (IgG) | CMA611 | 10 mg/ml | 1/1000 | 5 µl (50 µg) | 1/200 | This study |
| K7me2 | Mouse (IgG) | CMA612 | 10 mg/ml | 1/1000 | 5 µl (50 µg) | 1/200 | This study |
| H3K9ac | Rabbit serum | 39585 | - | 1/1000 | - | - | Active Motif |
| Lamin B | Goat (IgG) | C-20 Sc-6216 | 200 µg/ml | 1/500 | - | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | |
| α-tubulin | Mouse (IgG) | T6074 | 2 mg/ml | 1/10,000 | - | - | Sigma |
| GFP | Rabbit (IgG) | A11122 | 2 mg/ml | 1/1000 | - | - | Life Technologies |
| Digoxigenin | Mouse (IgG) | 200–002-156 | 1.2 mg/ml | - | 10 µl (12 µg) | - | Jackson ImmunoResearch |
-
ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; IF, immunofluorescence; WB, western blotting.
List of PCR primers used in this study. Primer sequences (F, forward; R, reverse) are represented (5´to 3´orientation) for promoter and coding regions of active and inactive genes. Primers designed for the Polr2a locus (scheme in Figure 5—figure supplement 1a) cover the promoter region (–1 and –0.5 kb), exons (E1 and E28), intron (I1), exon-intron boundaries (I2/E3 and E19/I19) and downstream of TES (+2 kb TES).
| Gene | Primer sequence | Gene | Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChIP primers β-actin (promoter) F | GCAGGCCTAGTAACCGAGACA | Gene expression primers β-actin 5´F | CCACCCGCGAGCACA |
| β-actin (promoter) R | AGTTTTGGCGATGGGTGCT | β-actin 5´R | CCGGCGTCCCTGCTTAC |
| β-actin (coding) F | TCCTGGCCTCACTGTCCAC | β-actin Exon1 F | TCTTTGCAGCTCCTTCGTTG |
| β-actin (coding) R | GTCCGCCTAGAAGCACTTGC | β-actin Exon2 R | ACGATGGAGGGGAATACAGC |
| Oct4 (promoter) F | GGCTCTCCAGAGGATGGCTGAG | Oct4 5´F | TGAGCCGTCTTTCCACCA |
| Oct4 (promoter) R | TCGGATGCCCCATCGCA | Oct4 5´R | TGAGCCTGGTCCGATTCC |
| Oct4 (coding) F | CCTGCAGAAGGAGCTAGAACA | Sox2 5´F | AGGGCTGGGAGAAAGAAGAG |
| Oct4 (coding) R | TGTGGAGAAGCAGCTCCTAAG | Sox2 5´R | ATCTGGCGGAGAATAGTTGG |
| Myf5 (promoter) F | GGAGATCCGTGCGTTAAGAATCC | Serpine1 5´F | CCCCGAGAGCTTTGTGAAG |
| Myf5 (promoter) R | CGGTAGCAAGACATTAAAGTTCCGTA | Serpine1 5´R | AAGGTGCCTTGTGATTGGCT |
| Myf5 (coding) F | GATTGCTTGTCCAGCATTGT | Dusp1 5´F | CGGTGAAGCCAGATTAGGAG |
| Myf5 (coding) R | AGTGATCATCGGGAGAGAGTT | Dusp1 5´R | AGGAGCGACAATCCAACAAC |
| Gata1 (promoter) F | AGAGGAGGGAGAAGGTGAGTG | Ctgf 5´F | GACTCAGCCAGATCCACTCC |
| Gata1 (promoter) R | AGCCACCTTAGTGGTATGACG | Ctgf 5´R | GTGCAGAGGCGACGAGAG |
| Gata1 (coding) F | TGGATTTTCCTGGTCTAGGG | ||
| Gata1 (coding) R | GTAGGCCTCAGCTTCTCTGTAGTA | ||
| Polr2a (-1 kb) F | CCGTAAAGCTATTAGAGCACAGG | ||
| Polr2a (-1 kb) R | ATGCATAAGGCAGGCAAGAT | ||
| Polr2a (-0.5 kb) F | GTAACCTCTGCCGTTCAGGA | ||
| Polr2a (-0.5 kb) R | TTTCTCCCTTTCCGGAGATT | ||
| Polr2a (E1) F | CAGGCTTTTTGTAGCGAGGT | ||
| Polr2a (E1) R | GACTCAGGACTCCGAACTGC | ||
| Polr2a (I1) F | CAGAGGGCTCTTTGAATTGG | ||
| Polr2a (I1) R | GCATCAGATCCCCTTCATGT | ||
| Polr2a (I2/E3) F | GCCCTCTTCTGGAGTGTCTG | ||
| Polr2a (I2/E3) R | AGGAAGCCCACATGAAACAC | ||
| Polr2a (E19/I19) F | CCAAGTTCAACCAAGCCATT | ||
| Polr2a (E19/I19) R | TCTTAACCGCTGAGCCATCT | ||
| Polr2a (E28) F | TCTCCCACTTCTCCTGGCTA | ||
| Polr2a (E28) R | CCGAGGTTGTCTGACCCTAA | ||
| Polr2a (+2 kb TES) F | GAGGGGCAGACACTACCAAA | ||
| Polr2a (+2 kb TES) R | AAAAGGCCAAAGGCAAAGAT |
Description of ChIP-seq and messenger RNA datasets used in this study. Full description of the ChIP-seq datasets produced or re-analysed in this study. NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) Sample reference is indicated for published datasets.
| ChIP-seq dataset | Dataset origin | Antibody clone | Mapped reads (millions) | ES cell line |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPB1-K7me1 (GSM1874007) | This study | CMA611 (this study) | 64 | ESC OS25 |
| RPB1-K7me2 (GSM1874008) | This study | CMA612 (this study) | 69 | ESC OS25 |
| RPB1-K7ac (SRR1028808) | Schröder et al. (2013) | AcRPB1 (Schröder et al., 2013) | 85 | ESC |
| Input (SRR1028807) | Schröder et al. (2013) | - | 21 | ESC |
| RPB1-S5p (GSM850467) | Brookes et al. (2012) | CTD4H8 (MMS-128P, Covance) | 22 | ESC OS25 |
| RPB1-S7p (GSM850468) | Brookes et al. (2012) | 4E12 (Chapman et al., 2007) | 11 | ESC OS25 |
| RPB1-S2p (GSM850470) | Brookes et al. (2012) | H5 (MMS-129R, Covance) | 33 | ESC OS25 |
| Unphospho-S2 (8WG16) (GSM850469) | Brookes et al. (2012) | 8WG16 (MMS-126R, Covance) | 24 | ESC OS25 |
| Mock IP (GSM850473) | Brookes et al. (2012) | - | 12 | ESC OS25 |
| H3K4me3 (GSM307618) | Mikkelsen et al. (2007) | ab8580 (Abcam) | 9 | ESC V6.5 |
| H3K36me3 (GSM850472) | Brookes et al. (2012) | 13C9 (Rechtsteiner et al., 2010) | 23 | ESC OS25 |
| H2Aub1 (GSM850471) | Brookes et al. (2012) | E6C5 (Upstate) | 18 | ESC OS25 |
| H3K27me3 (GSM307619) | Mikkelsen et al. (2007) | 07–449 (Upstate) | 8 | ESC V6.5 |
| RNA datasets | Dataset origin | Mapped reads (millions) | Cell line | |
| mRNA-seq (GSM850476) | Brookes et al. (2012) | 74 | ESC OS25 | |
| GRO-seq (GSE48895) | Jonkers et al. (2014) | 25 | ESC V6.5 (“untreated”) | |
-
ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing; ES, embryonic stem; GRO-seq, global run-on sequencing.





