Translational control of nociception via 4E-binding protein 1
Figures
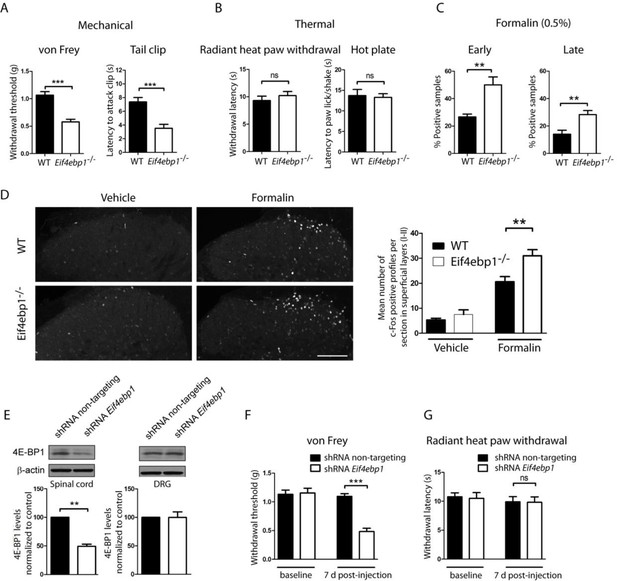
Eif4ebp1-/- mice exhibit mechanical hypersensitivity and increased formalin response.
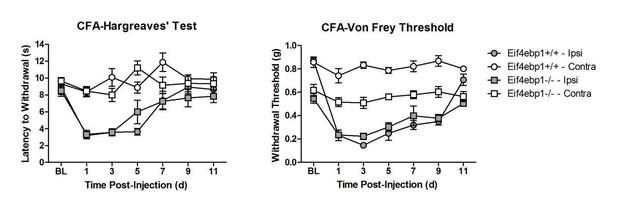
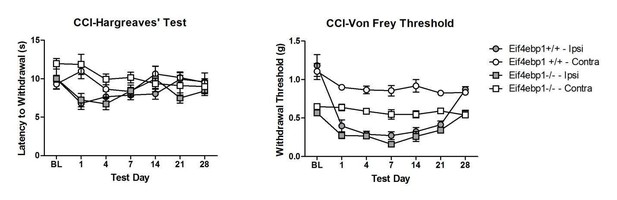
Mechanical pain sensitivity is increased in Eif4ebp1-/- mice as evident by decreased von Frey thresholds (A, n=8/genotype) and shortened latencies to attack tail clip (A, n=8/genotype), whereas thermal sensitivity is not altered (B, n=8/genotype). (C) Eif4ebp1-/- mice show more nocifensive (licking/shaking) behavior of the injected hind paw than their wild-type (WT) littermates in the formalin test (0.5%, 20 μl, n=8/genotype). Changes in paw weight, indicative of formalin-induced inflammation, were not different in Eif4ebp1-/- mice (not shown). (D) Intraplantar injection of formalin (0.5%, 20 μl) induced an enhanced upregulation of c-Fos (2 h post injection) in superficial layers (I-II) of the lumbar spinal cord of Eif4ebp1-/- as compared to WT mice (n=3 mice/group, 10 sections/mouse). (E) Western blot analysis of lysates prepared from the dorsal horn of the lumbar spinal cord and L3/L4 DRGs seven days post intraparenchymal dorsal horn injection of lentiviruses expressing shRNA against Eif4ebp1 as compared to non-targeting (scrambled) shRNA (n=3/condition). Mice injected with shRNA against Eif4ebp1 exhibit a reduction in von Frey threshold 7 days post injection (F, n=9/condition), whereas thermal sensitivity is not altered (G, n=9/condition). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns–not significant by Student’s t-test or t-test following repeated measures ANOVA. Scale bar: 100 μm. See also figure supplement 1 and 2.
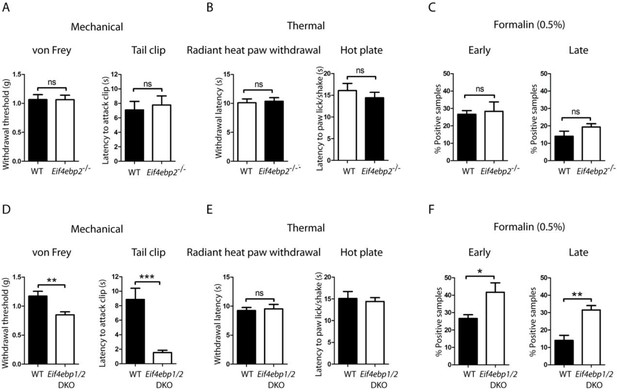
Eif4ebp1/2 DKO mice, but not Eif4ebp2-/-, mice exhibit mechanical hypersensitivity and enhanced formalin responding.
Mechanical and thermal pain sensitivities are not altered in Eif4ebp2-/- mice as evident by data from von Frey and tail clip assays (A, n=9/genotype), and radiant heat paw-withdrawal and hot-plate tests (B, n=9/genotype). (C) Eif4ebp2-/- mice show no difference in nocifensive (licking/shaking) behavior as compared to wild-type littermates in the formalin test (0.5%, 20 μm, n=8/genotype). (D-F) Eif4ebp1/2 DKO mice show mechanical hypersensitivity (D, n=7/genotype) and enhanced pain behavior in the formalin test (F, n=7/genotype), but no alterations in thermal sensitivity (E, n=8/genotype). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns–not significant by Student’s t-test.
No gross alterations in the dorsal horn of the Eif4ebp1-/- mice.
To assess the possibility of spinal cord reorganization in Eif4ebp1-/- mice, we performed immunostaining of NeuN (A), Substance P (SP, B), calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP, C), isolectin B4 (IB4, D), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, E), and 5HT3A receptor (HTR3A, F) in lumbar spinal cord sections. No gross alterations were identified in Eif4ebp1-/- mice with any marker (n=3 mice per genotype, 12 sections/marker). (G) Western blot analysis of lysates prepare d from DRG and dorsal horn for 4E-BP1 and 4E-BP2. Scale bar 150 μm.
Distribution of lentivirus-driven eGFP expression.
Lentiviruses expressing eGFP were microinjected (intraparenchymal injection (IPI)) directly into the dorsal horn of the lumbar spinal cord. Seven days later the spinal cord was extracted and immunostained for a neuronal marker NeuN. A representative lumbar spinal cord low magnification micrographs (upper panels) and confocal high magnification images (lower panels, NeuN red, eGFP green). Scale bar 150 μm.
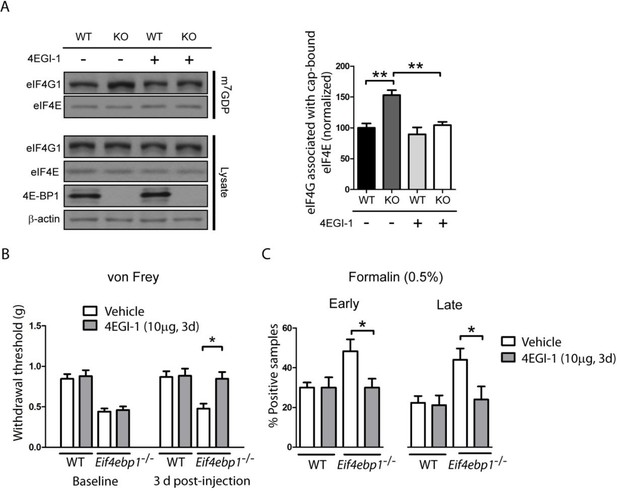
Increased levels of eIF4F complex in Eif4ebp1-/- mice cause mechanical hypersensitivity and increased formalin response.
(A) Left, Immunoblot analysis of cap column pull-down proteins prepared from the spinal cord of Eif4ebp1-/- and wild-type mice (WT) treated with 4EGI-1 (10 μg, i.t. once a day for 3 days) or vehicle. Right, quantification of eIF4G1 in cap column pull-down material (n=4/genotype/drug). (B) Chronic 4EGI-1 treatment rescues mechanical hypersensitivity of Eif4ebp1-/- mice. von Frey threshold was measured prior to (baseline) and after 4EGI-1 chronic treatment (10 μg, i.t., once a day for 3 days, n=8/genotype/drug). (C) Chronic 4EGI-1 treatment normalizes the enhanced nocifensive (licking/shaking) behavior of Eif4ebp1-/- mice during the early (0–10 min post-formalin, 0.5%) and late phases (10–60 min post-formalin) of the formalin test (n=8/genotype/drug). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p< 0.01 by Student’s t-test following two-way (genotype x drug) ANOVA (in A, C) or following two-between (genotype, drug), one-within (repeated measures) ANOVA (in B).
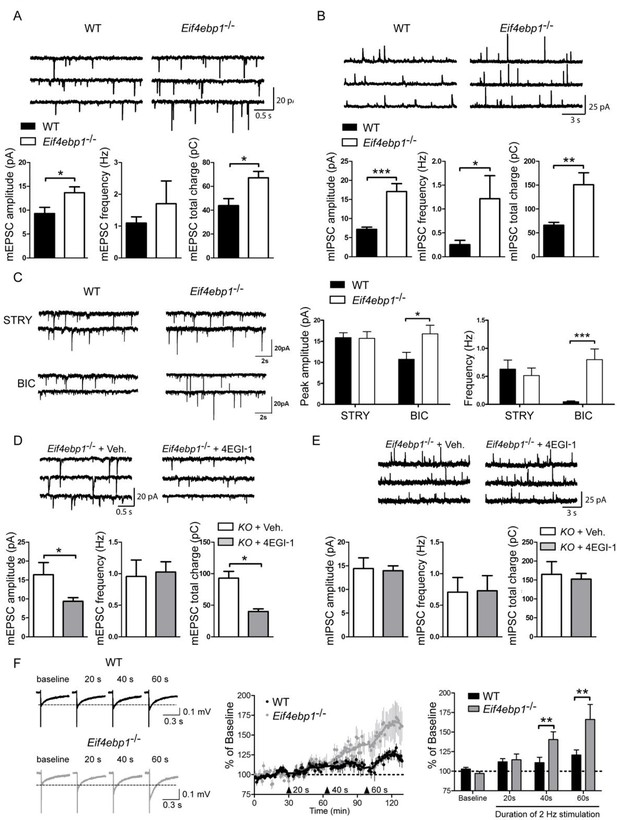
Excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmissions are increased in the spinal cord of Eif4ebp1-/- mice.
Representative traces (top) of mEPSCs (A) and mIPSCs (B) from lamina II neurons in acute lumbar spinal cord slices from Eif4ebp1-/- and wild-type mice (WT). Bar graphs (bottom) show mEPSC (A) and mIPSC (B) amplitude, frequency and synaptic total charge transfer (A: n=8 WT; n=7 Eif4ebp1-/-; B: n=9 WT; n=7 Eif4ebp1-/-). (C) To isolate GABAA or glycinergic mIPSCs, strychnine (STRY, glycine receptor antagonist, 1 μM) or bicuculline (BIC, GABAA receptor antagonist, 10 μM) were used, respectively. Left: representative traces of mIPSC in the presence of strychnine or bicuculline from Eif4ebp1-/- and WT slices. Right: bar graphs showing mIPSC amplitude and frequency in the presence of strychnine (n=7 WT; n=8 Eif4ebp1-/-) or bicuculline (n=9 WT; n=8 Eif4ebp1-/-). Eif4ebp1-/- mice were treated with 4EGI-1 (10 μg, daily for 3 days, i.t.) or vehicle, and the mEPSCs (D) and mIPSCs (E) were recorded from lamina II neurons (n=7 vehicle; n=11 4EGI-1). (F) Synaptic potentiation was elicited by stimulation of the dorsal root (2 Hz) for 20, 40 and 60 s and recording fEPSPs 125 μm from the dorsal surface of the spinal cord. Synaptic potentiation is induced in Eif4ebp1-/-, but not WT spinal cord preparation, by 40 s stimulation. Left: representative traces of fEPSPs, evoked by stimulation for the indicated length of time. Right: bar graph showing the summary of synaptic potentiation during the last 5 min prior to stimulation (n=7 WT; n=8 Eif4ebp1-/-). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by Student’s t-test (A, B, D, E), or by Student’s t-test following two-way ANOVA (genotype x drug in C; genotype x duration in F).
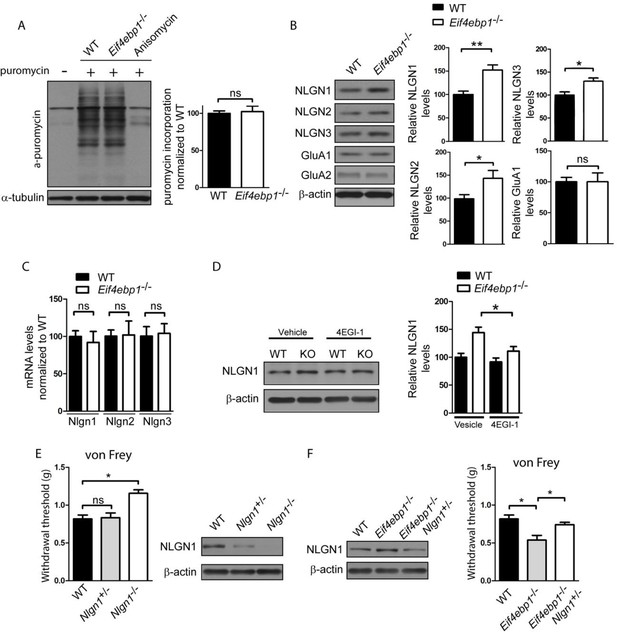
Enhanced expression of neuroligin 1 contributes to mechanical hypersensitivity of Eif4ebp1-/- mice.
(A) General translation is not altered in Eif4ebp1-/- mice as assessed by puromycin incorporation (n=3/genotype). (B) Protein expression of neuroligin (NLGN) 1, 2 and 3 is increased in synaptosomes prepared from the dorsal horn of the lumbar spinal cord of Eif4ebp1-/- mice (n=5/genotype), whereas their mRNA levels are not changed (C). (D) Wild-type (WT) and Eif4ebp1-/- mice were treated with 4EGI-1 (10 μg, daily for 3 days, i.t.) or vehicle, and the protein levels of neuroligin 1 were measured in lysates prepared from the dorsal horn of the lumbar spinal cord using western blot analysis (n=5/condition). (E) Nlgn1-/- mice exhibit elevated von Frey thresholds, whereas Nlgn1+/- mice show no alteration in mechanical sensitivity (n=10 WT and Nlgn1-/-; n=15 Nlgn1+/-). (F) Deletion of one allele of Nlgn1 in Eif4ebp1 knockout mice (Eif4ebp1-/- / Nlgn1+/-) normalizes neuroligin 1 protein levels in the dorsal horn of the lumbar spinal cord of Eif4ebp1-/- mice (left) and partially attenuates mechanical allodynia of Eif4ebp1-/- mice (right, n=10 wild-type, n=7 Eif4ebp1-/-, n=14 Eif4ebp1-/- / Nlgn1+/-). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns–not significant, by Student’s t-test (A–C), Bonferroni post-hoc test following two-between (genotype, condition) one-within (repeated measures) ANOVA (E), or Bonferroni post-hoc test following one-way ANOVA (F).
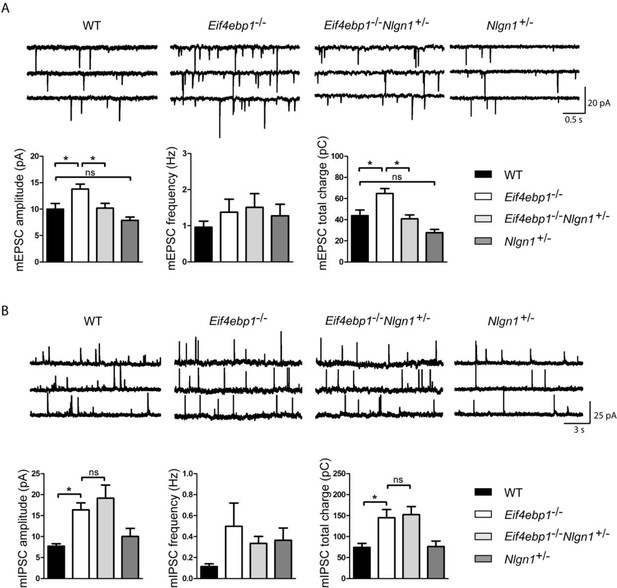
Reduction of neuroligin 1 levels in Eif4ebp1-/- mice normalizes the enhanced excitatory synaptic transmission. mEPSCs
(A) and mIPSCs (B) were recorded from lamina II spinal neurons of wild-type (WT), Eif4ebp1-/-, Eif4ebp1-/-/Nlgn1+/- and Nlgn1+/- mice. Top: representative traces of recordings from the four genotypes. Bottom: bar graph showing mEPSC (A) and mIPSC (B) amplitude, frequency and synaptic total charge transfer (n=11 WT; n=9 Eif4ebp1-/-; n=10 Eif4ebp1-/-/ Nlgn1+/-; n=7 Nlgn1+/-). The increase in mEPSC amplitude and total charge in Eif4ebp1-/- mice is rescued following deletion of one Nlgn1 allele, whereas mIPSCs are not affected. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 by Bonferroni post-hoc test following one-way ANOVA. See also figure supplement 1.
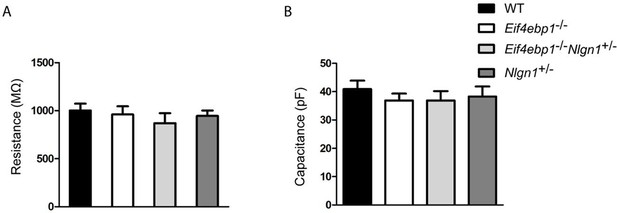
Input resistance and membrane capacitance are not altered in lamina II spinal neurons from Eif4ebp1-/-, Eif4ebp1-/-/Nlgn1+/- and Nlgn1+/- mice.
Input resistance (A) and membrane capacitance (B) of lamina II spinal neurons from wild-type (WT) (n=11), Eif4ebp1-/- (n=9), Eif4ebp1-/-/Nlgn1+/- (n=10) and Nlgn1+/- mice (n=7). No differences were found in either input resistance (p>0.05, Bonferroni’s post-hoc test following one-way ANOVA) or membrane capacitance (p>0.05, Bonferroni’s post-hoc test following one-way ANOVA). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.