MiniCORVET is a Vps8-containing early endosomal tether in Drosophila
Figures
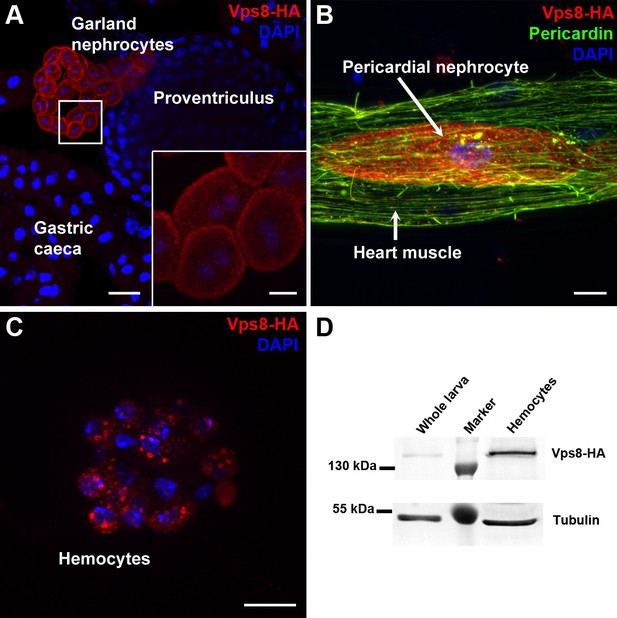
Vps8 is highly expressed in nephrocytes and hemocytes.
(A–C) These panels show various tissues of larvae expressing a Vps8-HA reporter under the control of genomic vps8 promoter sequences. (A) Low magnification image of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Note the prominent expression of the reporter in garland nephrocytes. Inset shows garland cells at higher magnification. (B) Part of the heart tube stained with anti-Pericardin and anti-HA. The reporter is detected exclusively in pericardial nephrocytes, heart muscle cells lack reporter signal. (C) Vps8-HA expression in hemocytes. (D) Western blot showing lysates of whole larvae and isolated hemocytes demonstrates the high expression of Vps8-HA in hemocytes. Bars: (A): 40 µm, inset, (B,C): 10 µm.
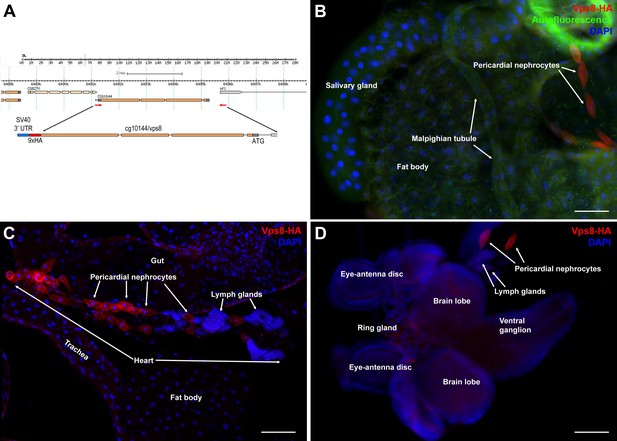
Vps8 is highly expressed in larval nephrocytes and hemocytes.
(A) In the map of the cg10144/vps8 locus, red arrows indicate the primers used to amplify genomic vps8 sequences that were used to generate the vps8-HA transgene (shown enlarged). This construct contains 824 base pairs upstream of the Vps8 transcription start site (including part of the first exon of the neighboring gene sfl), the entire Vps8 transcription unit including exons and introns, but lacks the stop codon and 3' UTR of Vps8. These sequences are replaced by a 9xHA coding sequence followed by a stop codon, and the SV40 small t intron and polyadenylation site (a widely used genetic element in Drosophila expression vectors). This genomic promoter-driven Vps8-HA construct was inserted randomly into the fly genome. We recovered two stable insertions, one integrated onto the X and another one onto the 3rd chromosome. The protein expression pattern (and localization) from these two transgenic insertions are indistinguishable. We show the X chromosomal insertion throughout the paper, because it was easier to carry out genetic rescue experiments with that (note that the Vps8 gene is located on the 3rd chromosome). (B–D) These panels show various larval tissues expressing the Vps8-HA reporter. Note the prominent expression of this reporter in pericardial nephrocytes, while fat body, salivary gland and Malpighian tubule cells show very low or undetectable signal. In panel (B), autofluorescence (green channel) of the tissues was also captured to help the recognition of the indicated organs. Bars: 100 µm.
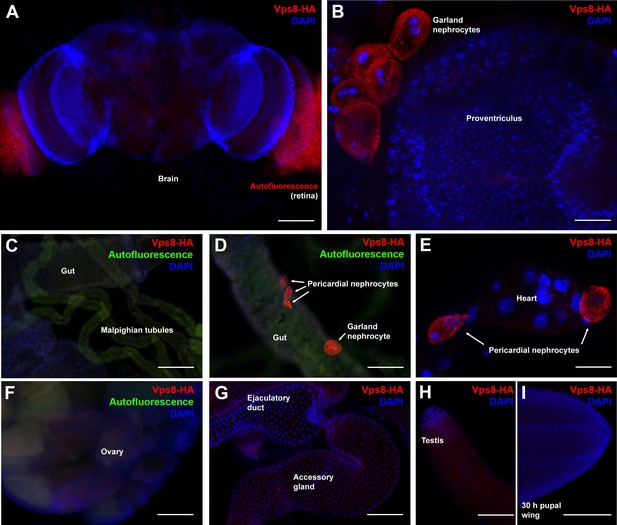
Vps8 expression in various adult and pupal tissues.
(A–H) These panels show various adult tissues expressing the Vps8-HA reporter. (I) This panel shows a 30 hr pupal wing from an animal expressing the Vps8-HA reporter. The reporter is strongly expressed in adult garland (B,D) and pericardial nephrocytes (D,E). In contrast, adult brain, proventriculus, various parts of the gut, Malpighian tubules, heart, ovary, ejaculatory duct and its accessory gland, testis and pupal wings shown in panels (A–I) produce very weak or undetectable signal. Note that the retina in panel A shows some red autofluorescence that is also seen in unstained samples. In panels (C, D, and F), green autofluorescence of the tissues was also captured to help the recognition of the indicated organs. Note that the nephrocytes shown in panel D were detached from their original location, and this way made it possible to determine that the intensity of the reporter signal is similar in the two nephrocyte subtypes. Bars: (A, C, D, F–I): 100 µm, (B, E): 25 μm.
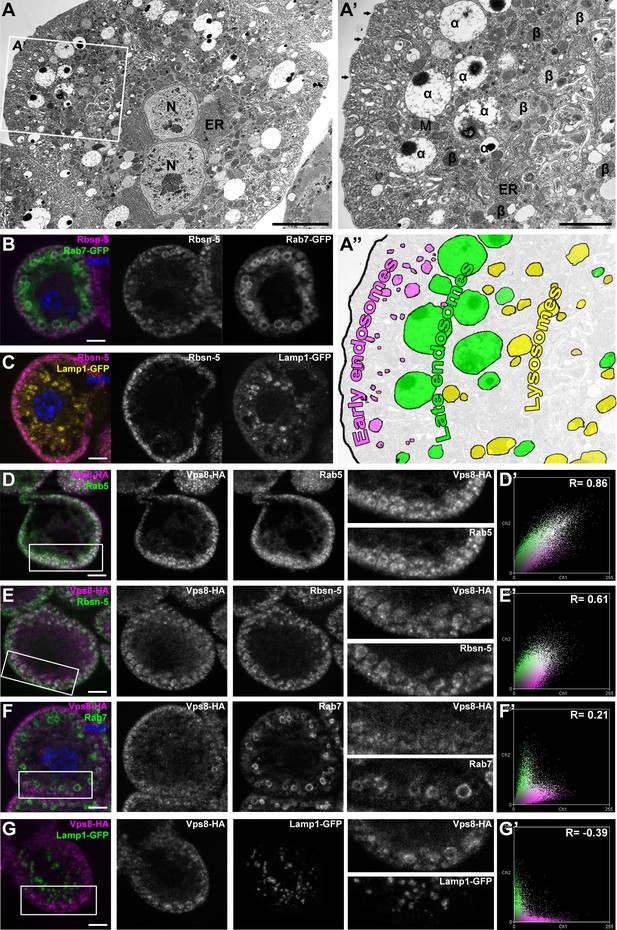
Vps8 localizes to early endosomes in nephrocytes.
(A–C) These panels illustrate the general structure of garland nephrocytes. (A) Ultrastructure of a wild type garland nephrocyte. (B–C) Fluorescent images of garland cells expressing the late endosomal marker Rab7-GFP (green on B) or lysosomal Lamp1-GFP (yellow on C), both co-labeled with the early endosome specific anti-Rbsn-5 (magenta on both images. (A,A’,A’’) Garland nephrocytes are enlarged binucleate (N) cells surrounded by a basal membrane (arrows on A’), and contain numerous vesicles. Outermost the peripheral early endosomal layer is seen, which corresponds to the Rbsn-5 vesicle population in fluorescent images. Under this layer, enlarged electron-lucent vesicles are found that often contain a dense core. These are the α-vacuoles, which correspond to the Rab7-positive late endosomal layer. Beta-vacuoles are seen at the perinuclear region, and correspond to the Lamp1-positive lysosome layer. M: mitochondrion, ER: endoplasmic reticulum (D–G) Vps8-HA colocalizes with endogenous Rab5 (D) and Rbsn-5 (E), but not with Rab7 (F) or with Lamp1-GFP (G). Scatter plots show the intensity correlation profiles of Vps8-HA (magenta) with these endosomal and lysosomal markers (green) (D–G’). Pearson correlation coefficients shown at the top of these panels indicate the strong colocalization of Vps8-HA with Rab5 or Rbsn-5, only incidental colocalization with Rab7, and mutually exclusive localization with Lamp1-GFP. Bars: (A–G): 5 µm, (A’‘’): 2 µm.
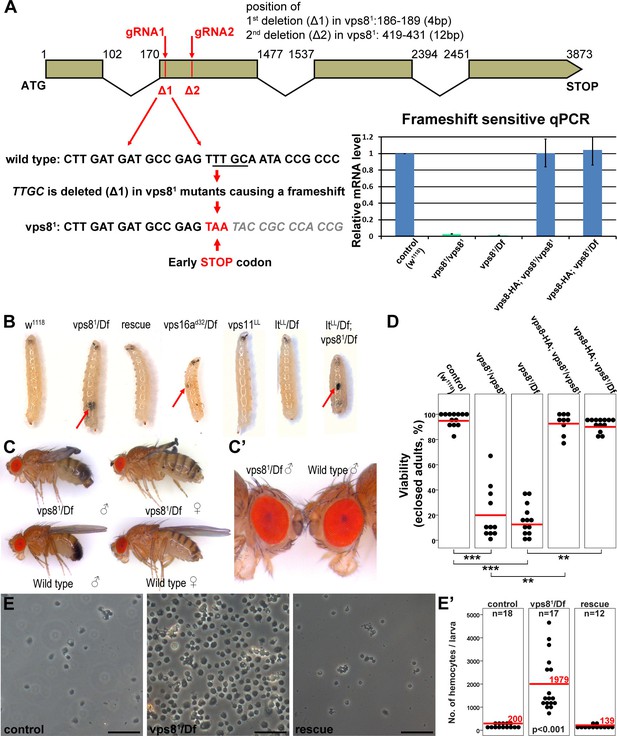
Generation of a vps8 null mutant.
(A) Map of the vps8/cg10144 locus. CRISPR/Cas9-induced deletions in vps81 mutants are indicated with red lines. The sequence of the region containing the first microdeletion and the resulting early stop codon is indicated. The chart shows the results of qPCR analyses from animals of the indicated genotypes. Frameshift-sensitive primers were used to reveal that the amount of wild type vps8 transcript in mutants is negligible. The vps8 mRNA level is restored in mutants carrying the vps8-HA rescue transgene. (B) Photographs of larvae carrying mutations in various CORVET or HOPS subunit genes. Mutants of vps8, vps16a and double mutants lacking both vps8 and lt develop melanotic tumors (red arrows) in their body cavity. (C,C’) Photographs of adult vps81 mutant and control flies. Except for the wing spreading defects, the overall body structure of mutants is similar to wild type (C), including compound eye structure and pigmentation (shown enlarged in C’). (D) Dot plots show the percentage of adults that manage to eclose from the pupal case in the indicated genotypes. Each data point represents one experiment. The average number of eclosing mutant adults is decreased to 20% (vps81/vps81) and 16% (vps81/Df), and viability is restored by the vps8-HA transgene. Red lines represent the mean, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (E) Images of isolated hemocytes demonstrate that circulating hemocyte number is 10-fold higher in vps8 mutants than in controls or mutants expressing the Vps8-HA rescue transgene. (E’) shows the quantification of hemocyte data, with red lines and numbers representing mean hemocyte numbers. Bars: 50 µm in (E).
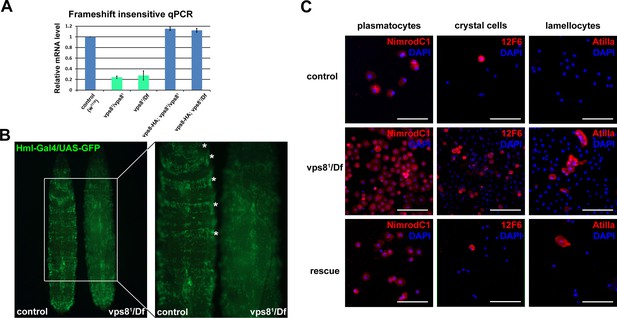
Loss of Vps8 results in ectopic immune activation.
(A) This chart shows the results of qPCR analyses from animals of the indicated genotypes, using primers that are not sensitive to the presence of frameshift mutations in vps8 mutants. The mRNA level is remarkably decreased in mutants, and it is restored by the Vps8-HA transgene. (B) The sessile hematopoetic compartment is visualized by blood cell specific expression of GFP in a wild type and a vps8 mutant larva. In contrast to the wild type situation, cells are detached from the body wall and the sessile tissue is disorganized in mutants, which likely contributes to the elevated number of circulating hemocytes. (C) Hemocytes stained by different hemocyte subtype-specific antibodies. Most of the hemocytes are plasmatocytes in controls and rescued animals. The en masse appearance of circulating crystal cells and lamellocytes in mutants indicates immune activation. Bars in (C): 50 μm.
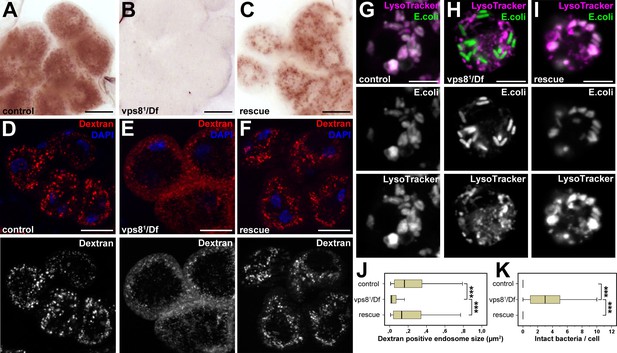
Loss of Vps8 impairs endocytic trafficking in garland nephrocytes and hemocytes.
(A–C) Garland cells take up silver nitrate from the hemolymph and store it in vesicles, which are visible as brown dots. Compared to control or rescue animals, garland nephrocytes from vps8 mutants contain almost no detectable silver inclusions. (D–F) Vps8 mutant garland cells can take up fluorescent dextran but fail to incorporate it into large endosomes (5 min pulse, no chase). (G–I) Vps8 mutant hemocytes take up FITC labeled bacteria but fail to acidify these endocytic vacuoles. (J,K) Quantification of data from panels (D–F) and (G–I). The medians of data are indicated as vertical black lines within the boxes. Bars show the upper and lower quartiles, ***p<0.001. Bars: (A–F): 20 µm, (G–I): 5 µm.
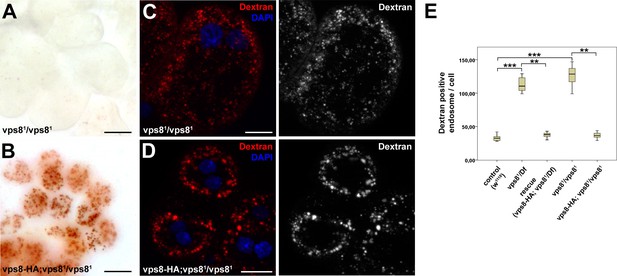
Loss of Vps8 impairs endocytic trafficking in garland nephrocytes and hemocytes.
(A,B) Garland nephrocytes from homozygous vps81 mutants contain practically no detectable silver inclusions (similar to vps81/Df animals shown in Figure 4B), and this effect can be rescued by the vps8-HA transgene. (C,D) The fluorescent dextran uptake phenotype of homozygous vps81 mutant garland nephrocytes is similar to vps81/Df cells shown in Figure 4E. The phenotype can be rescued with the vps8-HA transgene. (E) Quantification of the number of dextran positive endosomes/cell from panels (C,D) and Figure 4D–F. The medians of data are indicated as vertical black lines within the boxes. Bars show the upper and lower quartiles, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Bars: (A,B): 20 µm, (C,D): 10 µm.
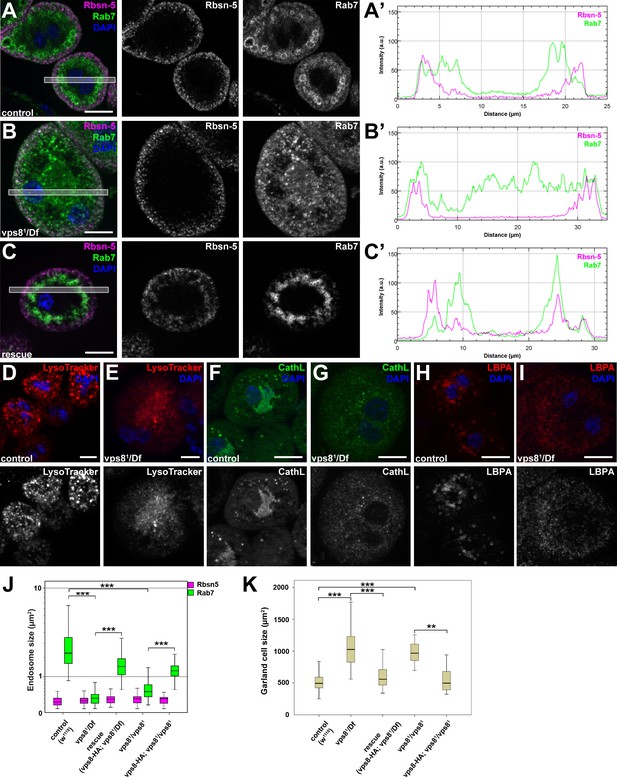
The biogenesis of late endosomes and lysosomes is impaired in vps8 mutant garland nephrocytes.
(A–C) Late endosomes are fragmented in garland nephrocytes lacking Vps8, unlike early endosomes. In wild type control or rescued cells, a layer of Rab7-positive endosomes (green) is found under the peripheral Rbsn-5 positive endosomes (magenta). In contrast, small granular Rab7 structures fill the whole cytoplasm of vps8 mutants, while the Rbsn-5 pattern remains unchanged in these cells. Panels (A’–C’) show the plot profiles of the framed areas in composite images. (D,E) LysoTracker-, (F,G) Cathepsin L- (H,I) and LBPA-positive lysosomal structures are fragmented in vps8 mutant nephrocytes. (J) Quantification of data from panels (A–C) and from Figure 5—figure supplement 1. (K) Vps8 mutant nephrocytes are significantly larger than control or rescued cells. The medians of data are indicated as horizontal black lines within the boxes. Bars show the upper and lower quartiles, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Bars: 10 µm. Please see Figure 5—figure supplements 1,2 for additional data.
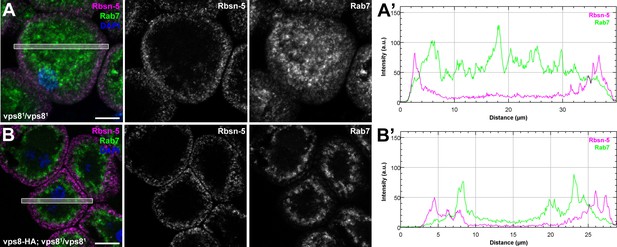
The biogenesis of late endosomes is impaired in homozygous vps8 mutant garland nephrocytes.
(A) Rab7 positive late endosomes are fragmented in homozygous vps81 mutant garland nephrocytes, similar to vps81/Df cells shown in Figure 5B. (B) Late endosome defects of vps81 homozygotes are rescued by the vps8-HA transgene. Bars: 10 µm. Panels (A’) and (B’) show the plot profiles of the framed areas in composite images.
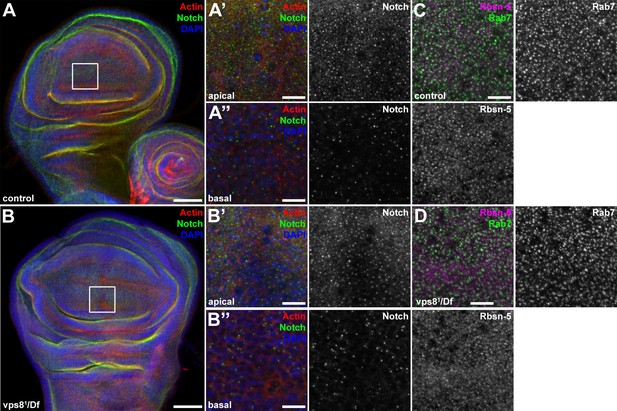
The endosomal compartment of larval wing disc cells is normal in vps8 mutant larvae.
(A,B) Larval wing discs stained with cortical actin phalloidin and extracellular domain-specific anti-Notch. Wing disc structure and the pattern of endosomal Notch are similar in control (A) and vps8 mutant (B) animals. Panels (A’, B’) and (A’’, B’’) show high magnification images of the framed areas in (A) and (B), respectively, and are taken from the apical and basal regions of the columnar cell layer. (C,D) High magnification images showing the apical regions of the columnar cell layer at the wing pouch region of the discs, stained with anti-Rbsn-5 and anti-Rab7. The pattern and distribution of both early and late endosomes are similar in controls (C) and vps8 mutants (D). Bars: (A, B): 50 µm, (A’–B’’), (C,D): 10 µm.
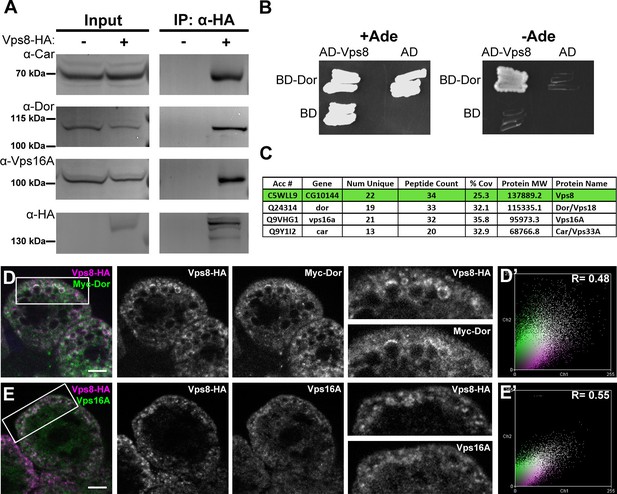
Vps8 forms a miniCORVET complex with the class C Vps proteins Dor/Vps18, Car/Vps33A and Vps16A.
(A) Endogenous Car, Dor and Vps16A proteins coprecipitate with Vps8-HA. (B) Vps8 interacts with Dor in yeast two-hybrid experiments. Yeast colony growth on synthetic medium lacking Ade indicates a direct interaction between the two proteins. AD: Gal4 activation domain-containing vector, BD: Gal4 DNA binding domain-containing vector. (C) Summary of the mass spectrometry (MS) data from Vps8-HA immunoprecipitates. 3 Vps proteins (Dor, Car, Vps16A) coprecipitated with the bait (Vps8-HA, highlighted with green background) with high peptide count, suggesting that these 4 proteins form a stable complex. Please see Supplementary file 2 for additional proteomic data. (D,E) Vps8-HA colocalizes with myc-tagged Dor (D) or endogenous Vps16A (E). (D’, E’) Scatter plots display the intensity correlation profiles of Vps8-HA (magenta) with either myc-Dor or Vps16A (green), with Pearson correlation coefficients shown at the top. Bars: 5 µm.
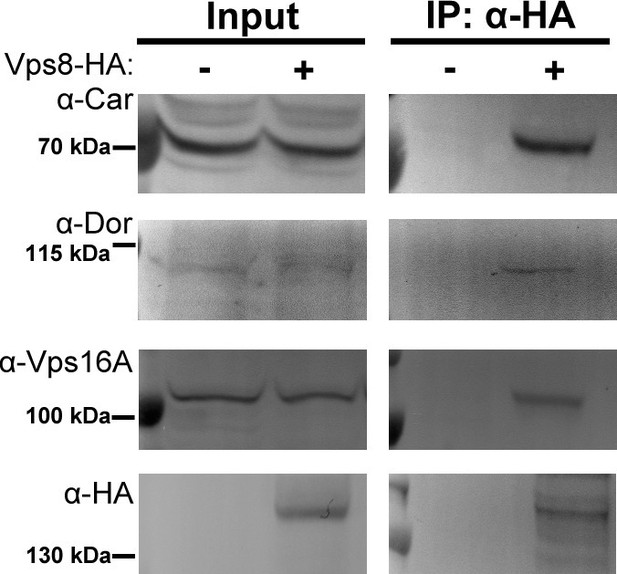
Vps8 coprecipitates the class C Vps proteins Dor/Vps18, Car/Vps33A and Vps16A from larval lysates.
Endogenous Car, Dor and Vps16A proteins coprecipitate with Vps8-HA from larval lysates, similar to adult samples shown in Figure 6A.
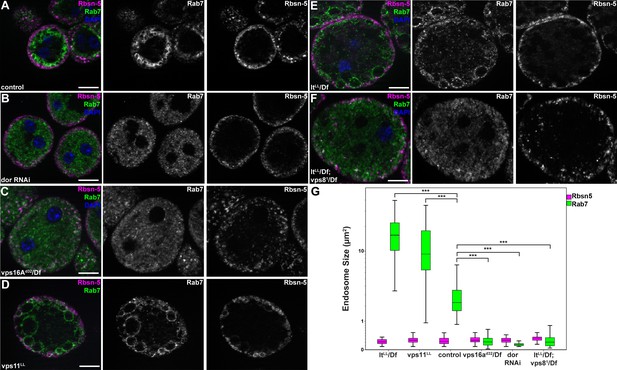
MiniCORVET promotes endosomal fusion upstream of HOPS.
Garland nephrocytes lacking the miniCORVET subunits Dor/Vps18 (B) or Vps16A (C) have fragmented Rab7-positive late endosomes compared to controls (A), whilst the early endosomal Rbsn-5 signal remains unchanged. In contrast, cells lacking Vps11 (D) or the HOPS specific subunit Lt/Vps41 (E) have enlarged Rab7-positive vesicles. (F) Double mutants for vps8 and lt display a phenotype similar to vps8 mutants, as Rab7-positive late endosomes appear as small dots filling the cytoplasm. (G) Quantification of data from panels (A–F). The median of data is indicated as a horizontal black line within the boxes. Bars show the upper and lower quartiles, ***p<0.001. Bars: 10 µm. Please see Figure 7—figure supplement 1. for additional data.
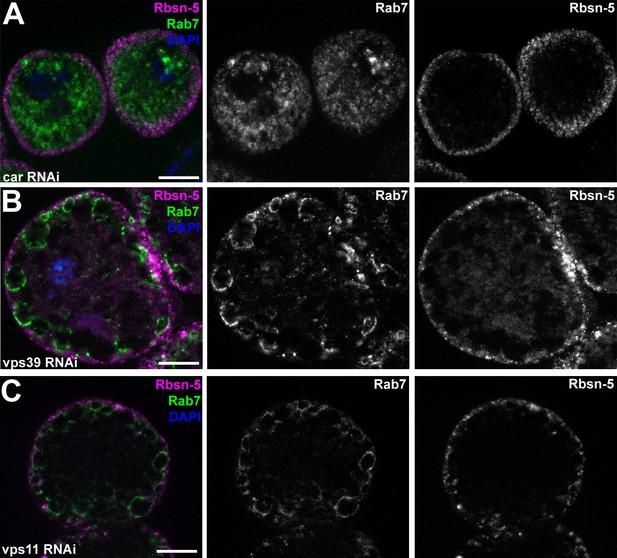
Additional miniCORVET and HOPS mutant nephrocyte data.
(A–C) Garland cells stained with anti-Rbsn-5 and Rab7. Knockdown of car (A) leads to fragmentation of late endosomes. In contrast, RNAi silencing of vps39 (B) or vps11 (C) results in the enlargement of late endosomes. Note that the phenotype of vps11 RNAi cells is identical to vps11 mutants shown in (Figure 7D. (D–L) Bars: 10 µm.
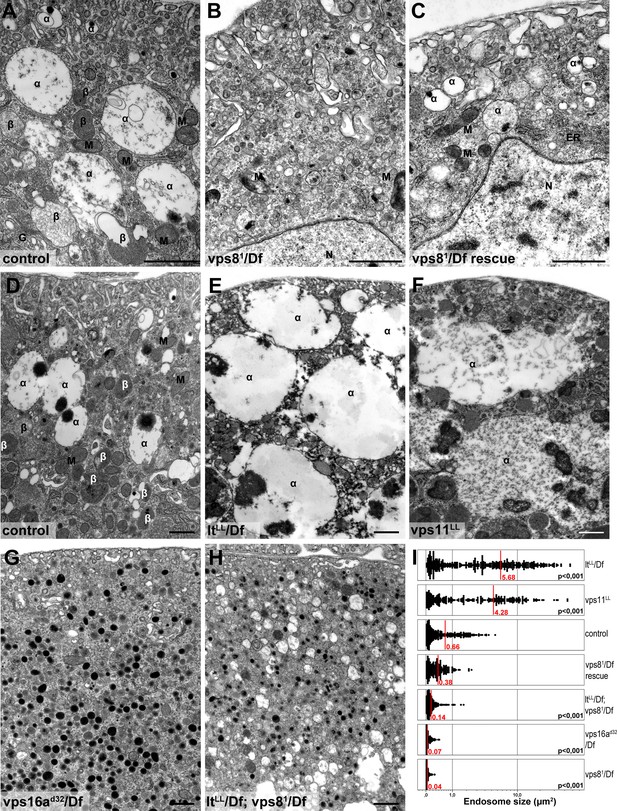
Loss of miniCORVET leads to fragmentation of endosomes, unlike HOPS defects.
Vps81 mutant (B) garland nephrocytes lack normal sized α-vacuoles and only small vesicles can be found, unlike in control (A,D) or rescued (C) cells. In contrast, nephrocytes lacking either the HOPS specific subunit Lt/Vps41 (E) or Vps11 (F) contain enlarged α-vacuoles, which often have multiple cores. The simultaneous loss of both miniCORVET and HOPS function in vps16A single (G) or lt and vps8 double mutant cells (H) also results in fragmented, small α-vacuoles similar to vps8 single mutants. Note that these nephrocytes also contain numerous small electron-dense organelles, which may represent a Golgi-derived pre-lysosomal compartment. N: nucleus, M: mitochondria, ER: endoplasmic reticulum. (I) Quantification of data from panels (A–G). The size of each endosome is represented as a single punctum on the dot plots. Red lines and numbers show the mean endosome area in µm2. Bars: 1 µm. Please see Figure 8—figure supplement 1. for additional data.
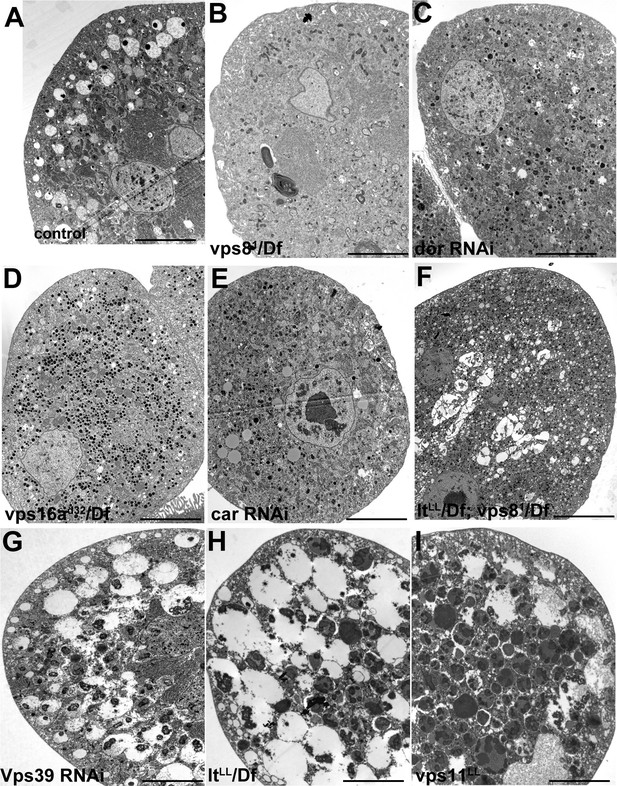
Additional miniCORVET and HOPS mutant nephrocyte data.
Low magnification ultrastructural images of garland nephrocytes. Large α-vacuoles containing a single dense core that are clearly visible in control cells (A) are absent from cells lacking miniCORVET (B–F). In cells that retain miniCORVET function but lack HOPS, α-vacuoles are greatly enlarged, and aberrant α-vacuoles with darker lumen accumulate in the perinuclear region (G–I). The simultaneous lack of both miniCORVET and HOPS function (C–F) leads to the appearance of numerous small electron-dense primary lysosome-like granules. Bars: 5 µm.
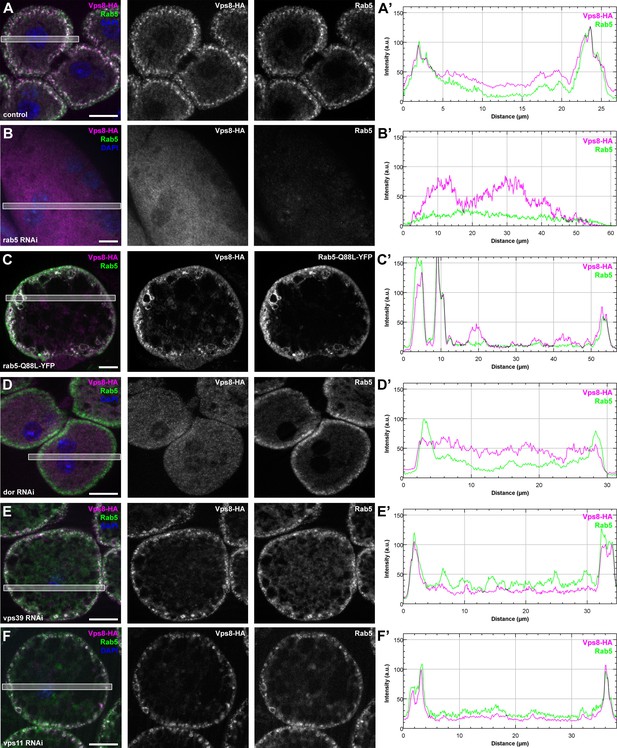
Vps8 localization to early endosomes depends on Rab5 and miniCORVET subunits, but not the HOPS complex.
(A–F) Images from garland nephrocytes expressing Vps8-HA in different genetic backgrounds (as indicated) were stained with anti-HA (magenta) and anti-Rab5 (green). Plot profiles of the framed areas are shown in panels (A’–F’). Vps8-HA and Rab5 colocalize at the periphery of control cells (A). In the absence of Rab5, Vps8-HA is dispersed in the cytoplasm. Note the absence of Rab5 signal, which indicates efficient RNAi knockdown. (B). The colocalization of Vps8-HA with Rab5 is maintained on enlarged early endosomes in cells expressing the constitutively active form of Rab5 (C). Rab5-positive early endosomes are present at the periphery of nephrocytes in the absence of Dor, but Vps8-HA is no longer found on these structures (D). In contrast with this, loss of either Vps39 (E) or Vps11 (F) does not affect the localization of Vps8-HA to Rab5-positive early endosomes. Bars: 10 µm. Please see Figure 9—figure supplement 1. for additional data.
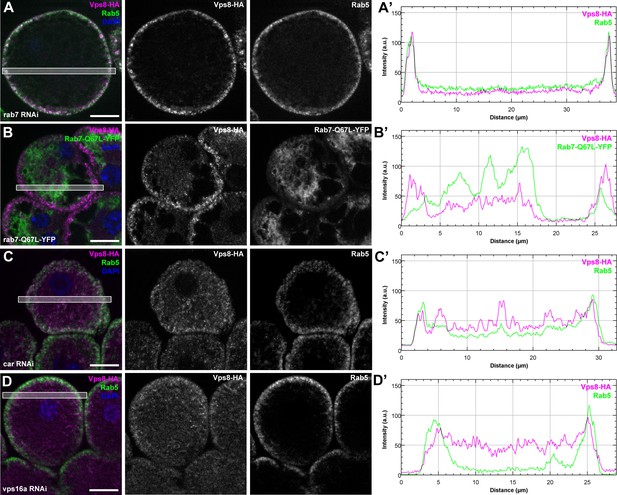
The early endosomal localization of Vps8 is independent of Rab7 and requires Car/Vps33A and Vps16A.
All images show garland nephrocytes expressing Vps8-HA in different genetic backgrounds, stained with anti-HA (magenta) and anti-Rab5 or GFP (green). Panels (A’–D’) show the plot profiles of the framed areas in composite images, with Vps8-HA signal in magenta and Rab5 (A’, C’, D’) or Rab7-Q67L-YFP (B’) in green. (A) Vps8-HA sustains its early endosomal localization in garland nephrocytes undergoing Rab7 RNAi. (B) Vps8-HA remains associated with peripheral Rab5-positive vesicles in garland cells expressing a constitutively active form of Rab7. (C, D) Rab5-positive early endosomes are present in the periphery of cells undergoing RNAi silencing of car (C) or vps16A (D), but Vps8-HA is dispersed throughout the cytoplasm. Bars 10 µm.
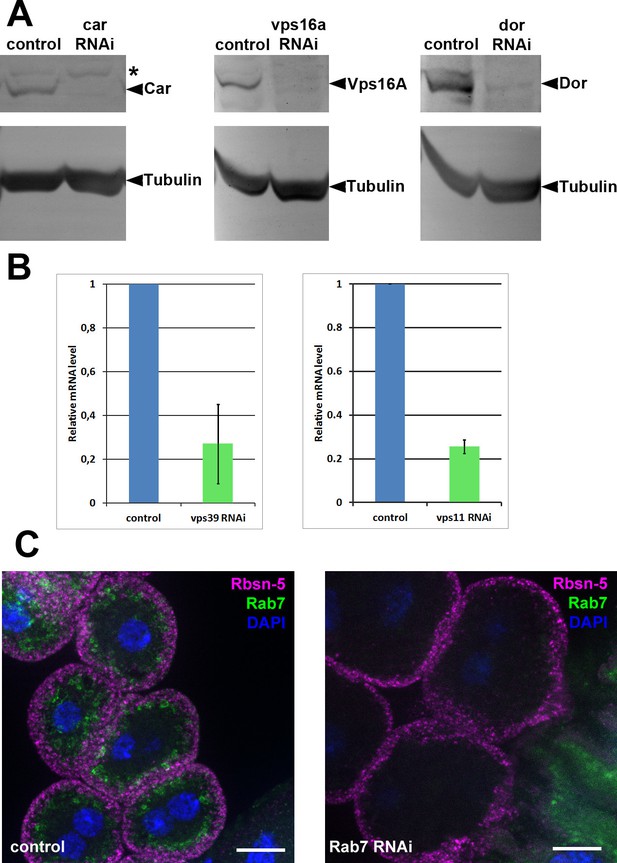
Validation of knockdown efficiencies for RNAi lines used in this study.
(A) Western blots from larvae ubiquitously expressing car, vps16a or dor RNAi (driven by tub-Gal4). In all three cases, the corresponding protein product practically disappears from the blots in RNAi samples. Asterisk marks a non-specific band in the left panel. (B) Charts showing mRNA levels in animals ubiquitously expressing vps11 or vps39 RNAi, driven by tub-Gal4 (vps11 RNAi) or actin-Gal4 (vps39 RNAi). (C) The Rab7 signal disappears in garland cells expressing rab7 RNAi, indicating efficient knockdown. Note that Rab7 is still detected in the gastric caeca, seen in the bottom right corner of the right panel, because rab7 RNAi is not expressed in that tissue. Bars: 10 µm.
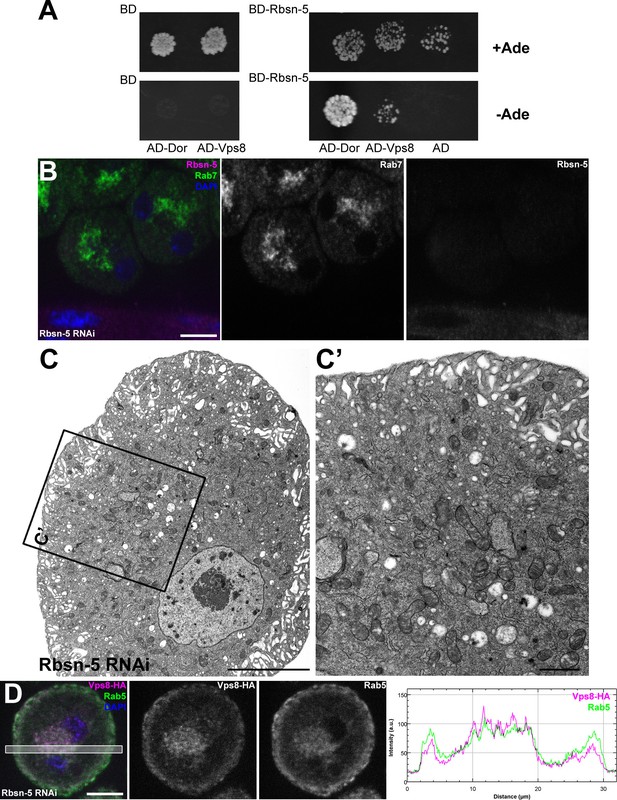
Rbsn-5 binds to Dor/Vps18 and is also required for early endosomal fusions.
(A) Rbsn-5 directly binds to Dor, based on prominent growth of yeast colonies on synthetic medium lacking Ade in yeast two hybrid experiments. (B) Rab7-positive late endosomes are fragmented in cells undergoing Rbsn-5 RNAi. Note the absence of Rbsn-5 signal in nephrocytes but not in the gut that is visible in the bottom part of this panel, indicating efficient knockdown. (C) Endosomes are fragmented in Rbsn-5 RNAi garland cells, based on the lack of large α-vacuoles in ultrastructural images. (D) In the absence of Rbsn-5, Rab5-positive early endosomes are fragmented and accumulate in the perinuclear region of garland nephrocytes, and the plot profile of the framed area is also shown. Note that Vps8-HA remains associated with these early endosomes. Bars: (B,D): 10 µm, (C,C’): 5 and 1 µm, respectively.
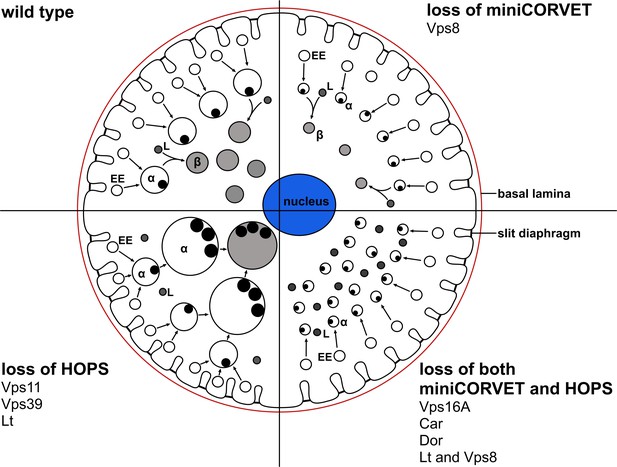
A cartoon illustrating garland nephrocytes in wild type, miniCORVET and/or HOPS loss-of-function animals.
In control cells, fusion of early endosomes leads to formation of large electron lucent late endosomes (α-vacuoles) that contain a single core. These vacuoles mature into degradative endolysosomes (β-vacuoles), possibly by fusing with primary lysosomes. In cells lacking Vps8 (and as a result miniCORVET function), α-vacuoles remain small and fragmented due to insufficient early endosomal fusion events. In cells lacking HOPS function due to loss of Lt, Vps39 or Vps11, late endosomes fail to mature into degradative lysosomes. Note that α-vacuoles enlarge into enormous vacuoles containing multiple dense cores in these cells, likely because of the continuous input from early endosomal fusions that are supported by the tethers miniCORVET and Rbsn-5. Nephrocytes lacking both miniCORVET and HOPS function (due to loss of the shared subunits Vps16A, Car, Dor, or the double mutation of Vps8 and Lt) contain fragmented late endosomes as in the case of Vps8 mutants, and accumulate small dense granules (possibly Golgi-derived vesicles transporting lysosomal cargo). EE: early endosome, L: primary lysosome.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Nucleotide sequence of the wild type vps8/CG10144 gene (from the translational start codon to the stop codon) and the deletions present in the vps81 allele.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.14226.024
-
Supplementary file 2
Detailed Vps8-HA proteomic data.
The table contains all peptides/proteins identified in the precipitate from Vps8-HA animals, which were absent in controls. Acc#: UNIPROT accession number. Num Unique: number of unique peptides identified for the listed protein.% Cov: The percentage indicates the sequence coverage by the identified peptides. MW: molecular weight in Daltons. Both% Cov and MW were calculated from the genomic sequence listed in the database that may differ from the mature protein. DROME: Drosophila melanogaster.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.14226.025
-
Supplementary file 3
Genotype of animals used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.14226.026
-
Supplementary file 4
Additional table showing statistical tests, N values and p-values.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.14226.027





