High-frequency stimulation-induced peptide release synchronizes arcuate kisspeptin neurons and excites GnRH neurons
Figures
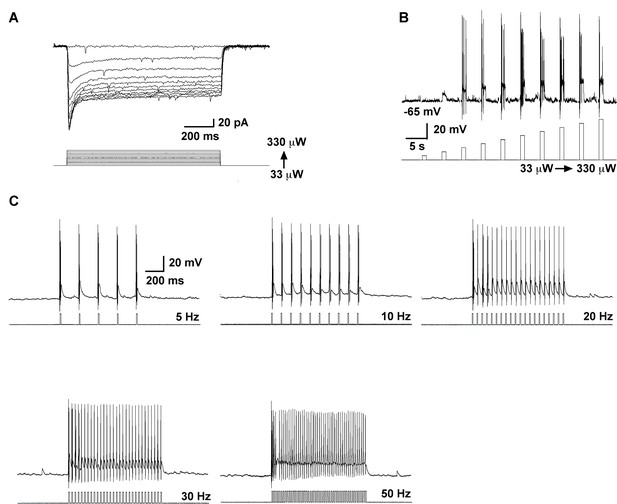
High fidelity response to light (470 nm) stimulation of ARH Kiss1 ChR2-expressing neurons.
(A–B) Examples of evoked inward currents in voltage-clamp (A) and depolarization in current-clamp (B) with varied light intensity (33–330 µW). (C) Trains of light pulses (0.9 mW, 10 ms pulse-width) at various frequencies and the resulting action potentials in the same neuron from A and B.
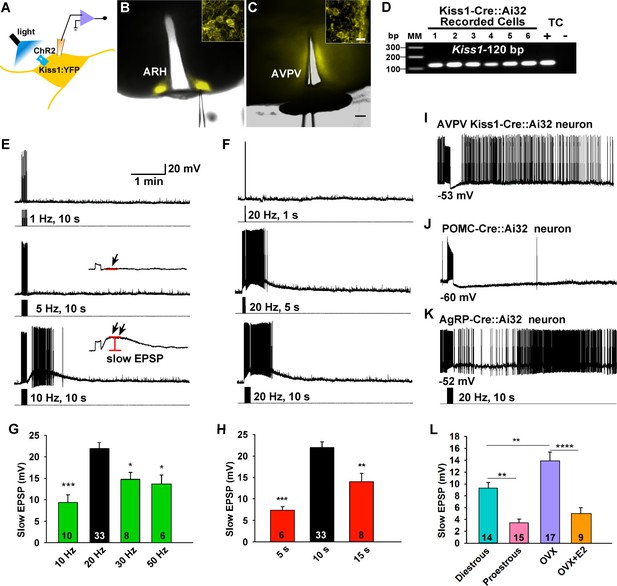
Slow excitatory postsynaptic potential (slow EPSP) is frequency and duration dependent.
(A) Illustration of experimental approach. (B–C), Overlay of epifluorescence (YFP) and differential interference contrast (DIC) images during whole-cell recording (pipette tip can be seen) from Kiss1 neurons in ARH (B) and AVPV (C) brain slices from a Kiss1-Cre::Ai32 mouse (scale bar = 200 µm). (B,C) Insets show high power magnification of labeled cells in each area (scale bar = 10 µm). ARH, hypothalamic arcuate nucleus; AVPV, anteroventral periventricular nucleus. (D) Confirmation of Kiss1 expression in YFP-expressing neurons from Kiss1-Cre::Ai32. Representative gel illustrating single-cell RT-PCR identification of Kiss1 mRNA following whole-cell recording in ChR2-YFP neurons. RNA extracted from the medial basal hypothalamic tissue control (TC) was included as positive (+, with RT) and negative (-, without RT) controls. MM, molecular marker. (E) Slow EPSP induced by a 10-s photostimulation (light intensity 0.9 mW and pulse duration, 10 ms) with varied frequencies in the same neuron. The insets show the measurement of slow EPSP after low-pass filtering. 1–5 Hz photostimulation did not induce any post-stimulus depolarization (arrow, middle trace); but ≥10 Hz stimulation generated a significant post-stimulus depolarization (double arrow, lower trace). (F), Examples of synaptic responses induced by a train of stimuli (0.9 mW, 10 ms pulse-width) delivered at 20 Hz with varied duration in the same Kiss1ARH neuron. (G–H), Bar graphs summarizing slow EPSP responses induced by a train of stimulation at 10, 20, 30 and 50 Hz with duration of 10 s (G) and by a 20 Hz-stimulation delivered at 5, 10 and 15 s (H), current-clamped to -70 mV. The slow EPSP was larger when induced by 10-s and 20 Hz photostimulation (one-way ANOVA, effect of treatment, F(3, 53) = 9.912, p<0.0001 (G); F(2, 44) = 12.69, p<0.0001 (H); Newman-Keuls’s Multiple-comparison test, ***, **, * indicates p<0.005, 0.01 and 0.05, respectively. (I–K), Slow EPSP is unique to arcuate Kiss1 neurons. (I) Photostimulation induced auto-inhibition in AVPV Kiss1 neuron, (J) ARH POMC neuron and (K) AgRP neuron from Kiss1-Cre::Ai32, POMC-Cre::Ai32 and AgRP-Cre::Ai32 mice, respectively. (L) Light evoked slow EPSP in Kiss1ARH neurons was reduced by E2 treatment and varied during the ovulatory cycle. Bar graphs summarizing slow EPSP responses induced by 20 Hz, 10 s photostimulation in slices obtained from diestrous or proestrous females, or OVX females treated with either oil vehicle or E2 that had received injection of AAV-DIO-ChR2:YFP into ARH. Slow EPSP was larger in low estrogen states (one-way ANOVA, effect of treatment, F (3, 51) = 15.43, p<0.0001; Newman-Keuls’s Multiple-comparison test. ****, ** indicates p<0.001 and 0.01, respectively.
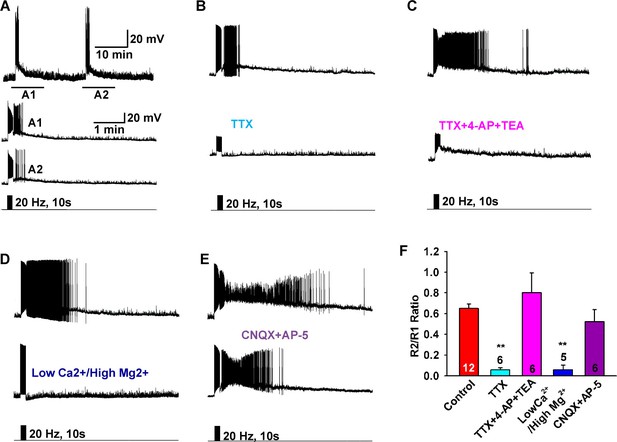
Slow EPSP is dependent on direct synaptic input from neighboring Kiss1 neurons.
(A) To reduce the variability between Kiss1 neurons from different animals, a response ratio (R2/R1) protocol was used in which the magnitude of second light response (A2) was compared to first response (A1). Representative traces showing that the R2/R1 ratio of two photostimuli is 0.65 in Kiss1ARH neurons. (B–E), Representative traces showing that the slow EPSP was abolished by perfusing TTX (B), and the TTX blockade was rescued by the addition of the K+ channel blockers 4-AP and TEA, suggesting a direct synaptic input from other Kiss1 neurons (C); the slow EPSP was abolished by perfusing low Ca2+/high Mg2+ (D); and the slow EPSP was unaffected by the ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists CNQX and AP5 (E). (F) Bar graphs summarizing the effects of drugs on the direct synaptic input (EPSP) to Kiss1 neurons. Comparisons between different treatments were performed using a one-way ANOVA analysis (F (4, 30) = 12.18, p<0.0001) with the Newman-Keuls’s post hoc test. ** indicates p<0.01 vs. control.
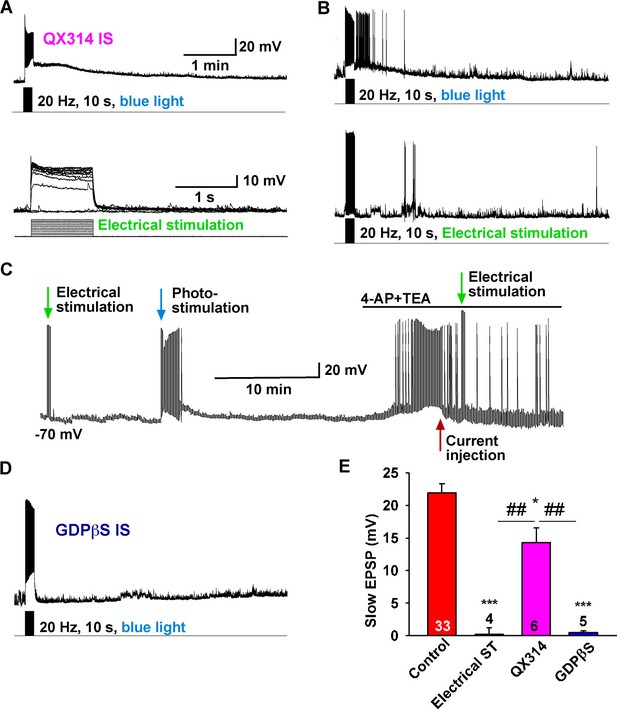
The slow EPSP is dependent upon G-protein activation.
(A) Intracellular dialysis with low concentrations of QX-314 (0.5 mM) in the internal solution (IS) blocked Na+ channels, but the slow EPSP induced by light stimulation was not blocked. (B) Slow EPSP induced by photostimulation (upper) was not mimicked by electrical stimulation (lower) at 20 Hz for 10 s in the same cell. (C) Electrical stimulation in the presence of 4-AP and TEA did not mimic the effects of photostimulation to induce a slow EPSP in Kiss1ARH neurons; a hyperpolarizing bias (current injection) was used to repolarize membrane potential to resting membrane potential when the 4-AP/TEA response reached the maximal depolarization. (D) Intracellular dialysis with GDPβS (2 mM) blocked the slow EPSP, demonstrating that the slow EPSP was mediated by G protein-coupled receptors. (E) Bar graphs summarizing the effects of Na+ channel and G-protein blockers and electrical stimulation on the slow EPSP in Kiss1 neurons. Comparisons between different treatments were performed using a one-way ANOVA analysis (F (3, 44) = 22.39, p<0.0001) with the Newman-Keuls’s post hoc test. *** and * indicates p<0.005 and p<0.05 vs. control, respectively; ## indicates p<0.01, QX314 group vs electrical stimulation and GDPβS groups.
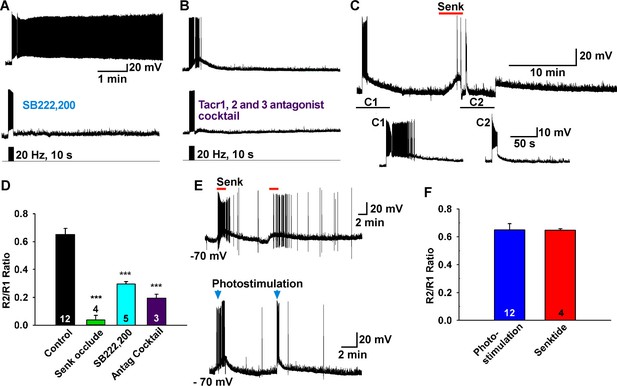
Tacr3 agonist mediates the slow EPSP.
(A–C) The slow EPSP was abrogated by an NKB receptor (Tacr3) antagonist SB222,200 (A) and the NKB receptor antagonist cocktail SDZ-NKT 343 (1 µM), GR94,800 (1 µM) and SB222,200 (3 µM) (Tacr1, 2 and 3 antagonists, respectively) (B). Furthermore, Tacr3 agonist senktide pretreatment completely occluded the slow EPSP (C), demonstrating that the slow EPSP was mediated by the Tacr3. A hyperpolarizing bias was used to repolarize the membrane potential to −70 mV when the senktide response reached the maximal depolarization (C2). (D) Bar graphs summarizing the effects of Tacr3 agonist and antagonists on the slow EPSP. Comparisons between different treatments were performed using a one-way ANOVA analysis (F(3, 20) = 31.6, p<0.0001) with the Newman-Keuls’s post hoc test. *** indicates p<0.005 vs. control. (E–F) Depolarization induced by senktide (250 nM) perfused on two separate occasions in a Kiss1ARH neuron. The R2/R1 ratio was 0.65 (E, upper trace), which was not different from the ratio from photostimulation (E, lower trace). (F) Bar graphs summarizing R2/R1 ratios (Un-paired t-test, t(14)= 0.0408, p = 0.9680).
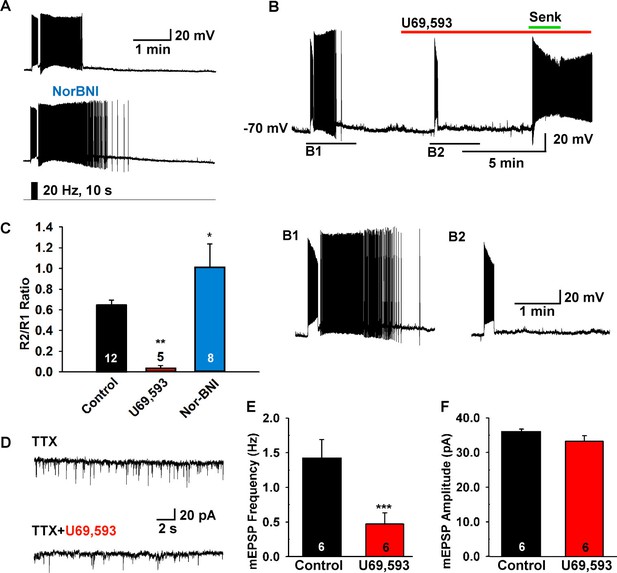
The κ-opioid receptor agonist blocks the slow EPSP.
(A–B) The κ-opioid receptor antagonist nor-BNI (1 μM) potentiated the slow EPSP (A) and the agonist U69,593 (1 µM) attenuated the slow EPSP (B2 versus B1). However, the Tacr3 agonist senktide is able to excite Kiss1ARH neurons in the presence of U69,593, indicative that the kappa-opioid effects are pre-synaptic to inhibit NKB release (B). (C) Bar graphs summarizing the effects of κ-opioid receptor agonist and antagonist on the slow EPSP. Comparisons between different treatments were performed using a one-way ANOVA analysis (F (2, 22) = 9.784, p = 0.0009) with the Newman-Keuls’s post hoc test. ** and * indicates p<0.01 and p<0.05 vs. control, respectively. (D–F) Effects of U69,593 on mEPSCs in Kiss1ARH neurons. Representative traces showing mEPSCs recorded at a holding potential of −60 mV under control conditions (TTX), and after TTX plus 1 µM U69,593. Summary data showing the effects of U69,593 on the frequency (E) and the amplitude (F) of mEPSCs in Kiss1ARH neurons (n = 6). Paired t-test, t(5) = 8.104, ***p<0.001 (E) and Paired t-test, t(5)=1.580, p = 0.1750 (F) compared to the control.
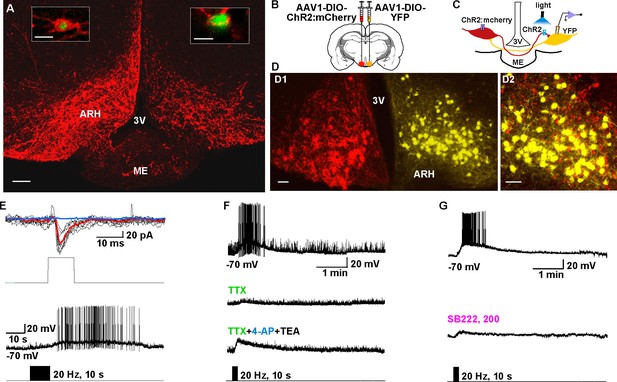
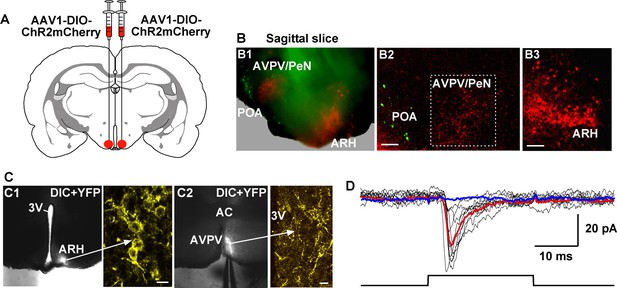
Kiss1ARH neurons send contralateral projections to Kiss1ARH neurons inducing circuit excitation.
(A) Confocal image of a coronal section through ARH from a Kiss1-Cre mouse following a unilateral ARH injection of AAV-DIO-ChR2:mCherry. Kiss1 neurons expressing ChR2-mCherry were observed on the injected left side, whereas only fibers were visible in the internal zone of the median eminence (ME) and in the contralateral ARH. (Scale bar = 100 μm). Insets on the ipsilateral and contralateral sides illustrate high power images of dual labeling of Kiss1-GFP and mCherry. On the ipsilateral side, a representative Kiss1-GFP neuron show co-expression of GFP and mCherry. (Scale bar = 10 μm). On the contralateral side, mCherry-positive fibers formed close contacts with a representative Kiss1-GFP neuron. (Scale bar = 10 μm). (B), Schematic of coronal sections through the ARH illustrating ChR2-mCherry and control YFP injections, in which one side of the ARH was injected with AAV-DIO-ChR2:mCherry and the contralateral side with AAV-DIO-YFP. (C) Illustration of the experimental approach. The whole-cell recorded neurons were YFP- expressing neurons. (D) Higher power images of a coronal section through the ARH from a Kiss1-Cre female showing the Kiss1 neurons expressing ChR2-mCherry (left side, red) (D1), versus AAV-DIO-YFP (right side, yellow) and overlay of epifluorescence (YFP and mCherry) images in YFP positive neuron area showing mCherry-expressing terminals (D2). Only mCherry expressing fibers were observed in the contralateral ARH (D2). Scale bars = 20 µm. ARH, hypothalamic arcuate nucleus; 3V, third ventricle. (E) Representative trace showing that photostimulation induced not only a fast glutamate response (upper traces) with a single 10 ms pulse, but also a slow EPSP (lower trace) with 20 Hz for 10 s photostimulation in the same cell. Red trace indicates averaged sweeps. Blue trace illustrates that the AMPA- and NMDA-mediated currents (EPSCs) were blocked with CNQX (10 μM) and D-AP5 (50 μM). (F) Representative traces showing that the slow EPSP was abolished by perfusing TTX, and the TTX blockade was rescued by the addition of non-selective K+ channel blockers 4-AP and TEA suggesting a direct input from other Kiss1 ChR2-expressing neurons. All Kiss1 neurons (n = 7) were rescued by the combination of K+ channel blockers. (G) Blue light stimulation induced a slow EPSP in a contralateral Kiss1ARH neuron (upper trace), which was antagonized by SB222,200 (3 µM) (lower trace).
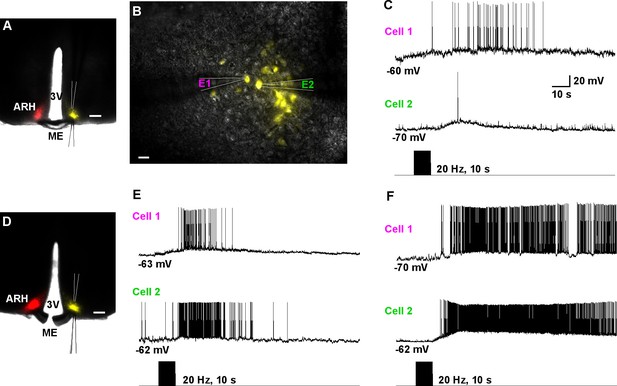
Dual patch recording reveal that high-frequency auto-excitation of ipsilateral Kiss1ARH neurons recruit contralateral Kiss1ARH neurons.
(A) Image of a coronal section through the ARH from Kiss1-Cre mouse that received dual injection of AAV-DIO-ChR2:mCherry (left side, red) and AAV-DIO-YFP (right side, yellow). Scale bar = 200 µm. (B) DIC and fluorescent image (YFP) of dual patch recording from Kiss1ARH neurons in the contralateral ARH; whole cell recordings were made with electrode 1 (E1) and electrode 2 (E2) in the current-clamp mode. Scale bar = 20 µm. (C) High-frequency photostimulation induced a simultaneous increase in firing and a slow EPSP in a pair of Kiss1ARH neurons (Cell 1 and Cell 2) recorded in the contralateral ARH. (D), Image of a coronal section through the ARH from Kiss1-Cre mouse that received dual injection of AAV-DIO-ChR2:mCherry (left side, red) and AAV-DIO-YFP (right side, yellow). In this slice, the ME was cut to disconnect the two sides. Scale bar = 200 µm. (E and F) Examples of synchronized activity obtained using dual patch recording from two pairs of Kiss1ARH neurons in the contralateral ARH (D). ARH, hypothalamic arcuate nucleus; ME, median eminence; 3V, third ventricle.
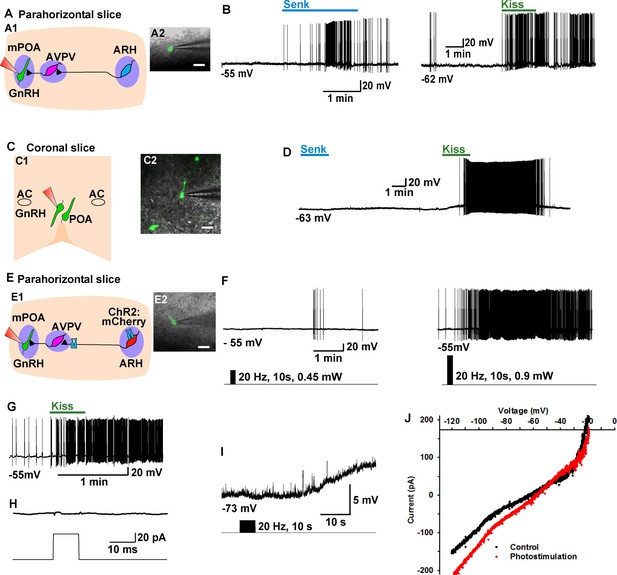
Tacr3 agonist senktide excites GnRH neurons indirectly through ARH Kiss1 neurons, and a slow EPSP in GnRH neurons is evoked with photoactivation of ChR2 Kiss1ARH neurons.
(A) Schematic drawing of the Kiss1ARH, Kiss1AVPV/PeN and GnRH neuronal circuit (A1) and a high power image (A2) of a parahorizontal slice from a GnRH-EGFP mouse illustrating whole-cell recording of GnRH neuron. Scale bar = 20 µM. (B) Representative traces showing that perfusing the slice with senktide (1 µM) induced depolarization and increased firing in a GnRH neuron (left), which was mimicked by perfusion with kisspeptin (10 nM, right). (C) Schematic drawing (C1) and highpower image (C2) of a coronal slice through the POA from a GnRH-EGFP mouse illustrating whole-cell recording of GnRH neuron. (D) Representative trace showing that perfusing the slice with senktide (1 µM) did not depolarize or increase firing of a GnRH neuron, but kisspeptin could excite the same POA GnRH neuron. E, Schematic drawing of the Kiss1ARH, Kiss1AVPV/PeN and GnRH neuronal circuit (E1) and a high power image (E2) of a parahorizontal slice from a bilateral arcuate AAV-DIO-ChR2:mCherry injected Kiss1-Cre::GnRH-EGFP mouse illustrating whole-cell recording of GnRH neuron. Scale bar, 20 µM (E2). (F–G) High-frequency photoactivation of ChR2-labeled ARH neurons with low (0.45 mW, left panel) and higher (0.9 mW, right panel) intensities evoked slow EPSPs and increased firing in the same GnRH neuron (F) which was mimicked by perfusion with kisspeptin (10 nM) (G) but low-frequency photostimulation (0.5 Hz) did not evoke a fast EPSC in this GnRH neuron (H). (I–J) High-frequency photoactivation of ChR2 evoked a slow EPSP (I) in another GnRH neuron, and the I-V relationship before and during the peak response from the same cell indicated that the reversal potential of the nonselective cation current was ~ -40 mV (J). AC, anterior commissure; ARH, hypothalamic arcuate nucleus; AVPV, anteroventral periventricular nucleus; mPOA, medial preoptic area.
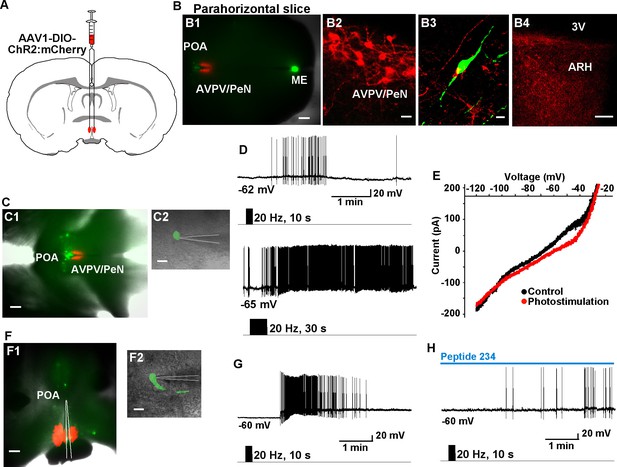
Photoactivation of Kiss1ARH fibers excites Kiss1AVPV/PeN neurons via glutamate release.
(A) Schematic drawing of a coronal section showing the bilateral viral injections in the ARH with AAV-DIO-ChR2:mCherry. (B) Sagittal brain slice (B1) and confocal images from the slice (B2, 3) of mouse bilaterally injected with a ChR2-mCherry-expressing viral vector into the ARH of Kiss1-Cre::GnRH-EGFP female mouse. Projections from Kiss1ARH neurons (B3) to the AVPV/PeN are illustrated (B2). Green neurons in the POA illustrate the location of GnRH neurons in the sagittal brain slice. Scale bars, 100 µm (B2, B3). (C) Overlay of epifluorescence (YFP) and differential interference contrast (DIC) images of a coronal arcuate slice showing injection site (C1) in a Kiss1-Cre:ChR2:YFP mouse (arrow points to high power image of labeled neurons in the ARH) and fiber-projections to the AVPV (C2; arrow points to labeled fibers in the AVPV area that are being photostimulated). Scale bars = 10 µm. (D) Example of light-evoked fast EPSCs in a Kiss1AVPV/PeN neuron (mean response: 33.2 ± 9.7 pA, n = 5). Red trace indicates averaged sweeps. Blue trace illustrates that the AMPA- and NMDA-mediated currents (EPSCs) were blocked with CNQX (10 μM) and D-AP5 (50 μM). Following recording, cells were harvested for scRT-PCR determination of Kiss1 mRNA expression. All recorded AVPV/PeN cells (n = 5) expressed Kiss1 mRNA (data not shown). ARH, hypothalamic arcuate nucleus; AVPV/PeN, anteroventral periventricular and periventricular preoptic nuclei; POA, preoptic area.
High-frequency photoactivation of Kiss1AVPV/PeN neurons excites GnRH neurons via kisspeptin release.
(A) Schematic drawing of coronal section showing bilateral viral injections in the AVPV with AAV-DIO-ChR2:mCherry. (B) Parahorizontal brain slice of mouse bilaterally injected with a ChR2-mCherry-expressing viral vector into the AVPV/PeN of Kiss1-Cre::GnRH-EGFP female mouse. Injection sites into AVPV/PeN are illustrated in low power (red, B1) and high power (B2). Kiss1AVPV/PeN neurons send projections rostrally to GnRH neurons (B3) and also caudally to the ARH (B4). Note that following AVPV/PeN injections, only mCherry fibers but no labeled cells were detected in the ARH. Scale bars, 200 µM (B1), 20 µm (B2), 10 µm (B3) and 50 µm (B4). (C), Low power (C1) and high power (C2) images of whole-cell recordings in an angled, parahorizontal slice from bilateral AVPV AAV-injected Kiss1-Cre::GnRH-GFP mouse. (D–E) High-frequency photoactivation of AVPV/PeN with durations of 10 s (upper) and 30 s (lower) evoked a slow EPSP (mean slow EPSP response following 30 s duration stimulation: 8.0 ± 2.9 mV, n = 4) and increased firing (D); typical I-V relationship for a kisspeptin-evoked response in GnRH neurons in the same cell (E). Scale bars, 200 µm (C1) and 20 µm (C2). (F), Coronal slice showing ChR2-mCherry expression in Kiss1AVPV/PeN neurons following bilateral viral injections in the AVPV/PeN area in a Kiss1-Cre::GnRH-EGFP mouse (F1). Scattered GnRH-EGFP neurons can be seen dorsal and lateral to the injection site, one of which is being recorded from (F1, low power; F2, high power). Scale bars, 200 µm (F1) and 20 µm (F2). (G) High-frequency photostimulation of Kiss1AVPV/PeN neurons causes a slow EPSP in a GnRH neuron that induces a high-frequency discharge. (H), High-frequency-induced depolarization/excitation of GnRH neurons is blocked (occluded) by the partial agonist peptide 234 (100 nM). ARH, hypothalamic arcuate nucleus; AVPV/PeN, anteroventral periventricular and periventricular preoptic nuclei; ME, median eminence; POA, preoptic area.
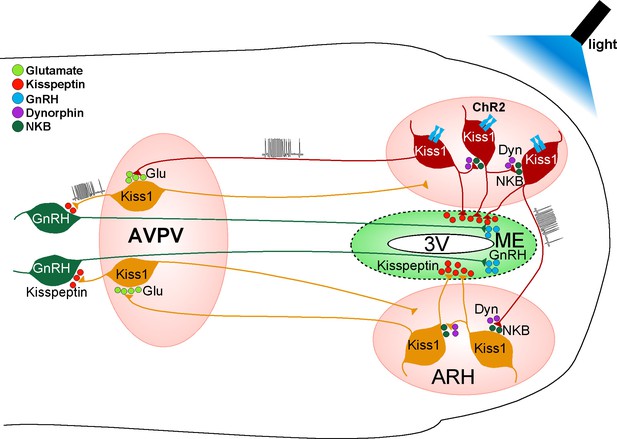
Proposed model by which activation of Kiss1 neurons governs GnRH neuronal excitability.
High-frequency photostimulation of Kiss1 neurons in the ARH releases NKB that depolarizes and recruits other Kiss1ARH neurons. Dynorphin is co-released and acts presynaptically to modulate (inhibit) the release of NKB. Together the two peptides govern the synchronous activity of Kiss1ARH neurons and promote kisspeptin release that stimulates GnRH release in the median eminence (ME). Kiss1ARH neurons also communicate with the Kiss1AVPV/PeN neurons via the fast neurotransmitter glutamate, which stimulates burst-firing of Kiss1AVPV/PeN neurons. Activation of these rostral Kiss1 neurons releases kisspeptin to robustly excite GnRH neurons via activation of the GPR54 signaling cascade, thereby stimulating the release of GnRH at the time of the preovulatory surge. Kisspeptin, GPR54, NKB, Tacr3 and GnRH are all required for normal fertility.





