The Drosophila formin Fhos is a primary mediator of sarcomeric thin-filament array assembly
Figures
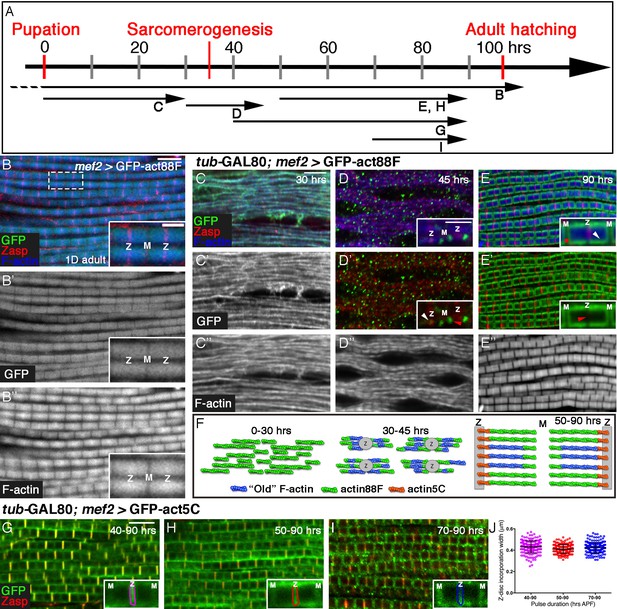
Four distinct modes of GFP-actin monomer incorporation contribute to formation of IFM thin-filament arrays.
(A) Scheme of IFM development intervals used for unrestricted and temporally restricted expression of GFP-actin88F (B–E”) or GFP-actin5C (G–I). (B–B”) Induction of GFP-actin88F expression (green, gray) with mef2-Gal4 throughout fly development results in full monomer incorporation into the thin-filament arrays (phalloidin- blue, gray), as monitored in IFMs of young (1–3 days old) adults. Z-discs are indicated by anti-Zasp52 (red). The designations 'Z' and M' are used throughout to mark the Z-disc (array barbed-end) and H-zone/M line (array pointed end) regions of the sarcomere. (C–E’’) Incorporation patterns of GFP-actin88F (green, gray) following temporally restricted expression pulses using the mef2-GAL4 driver and the GAL80ts/TARGET system. Microfilaments are visualized with phalloidin (blue, gray). Z-discs are indicated by anti-Zasp52 (red). (C–C”) 0–30 hrs APF. Initial uniform incorporation. (D–D”) 30–45 hrs APF. 'Patched' incorporation of monomers. This mode occurs mainly at array ends (insets in D and D’), in proximity to the future Z-disc (Z, white arrow) or towards the opposite boundary of the nascent arrays (M, red arrow). (E–E’’) 50–90 hr APF. Monomer incorporation into a 'frame' generated by peripheral 'thickening' (white arrowhead in panel E inset) and pointed-end growth (M and red asterisk in panel E inset). Red arrowhead (panel E’ inset) points to an absence of incorporated monomers at the barbed-end boundary (Z) of the arrays. (F) Schematic representations of the incorporation process. Blue filaments denote previously incorporated ('old') actin, while green (88F) and orange (5C) marks monomers newly incorporated during the indicated pulse. An initial period (0–30 hr APF) of extensive actin polymerization and the establishment of nascent thin-filament arrays are followed by an interim period (30–45 hr APF) of 'patchy' incorporation during which individual, uniform sarcomeric units are defined. The second half of pupal development is devoted to array growth via pointed-end elongation and recruitment of circumferential filaments, as well as turnover at array barbed ends. (G–I) Incorporation patterns of GFP-actin5C (green) following temporally restricted expression pulses using the GAL80ts/TARGET system. Z-discs are indicated by anti-Zasp52 (red). Restricted expression 'windows' corresponded to 40–90 (G), 50–90 (H) and 70–90 (I) hrs APF. Insets show the GFP-actin5C incorporation patterns in single sarcomeres, in which the prominent Z-disc associated stripe is outlined (Z, Z-disc region; M, M-line region). (J) Quantification reveals a constant width of the GFP-actin5C incorporation stripe overlying the Z-disc region despite the different pulse durations, n = 200 (50 sarcomeres each from 4 different flies). Scale bars correspond to 5 μm in all main panels, 2 μm in the insets.
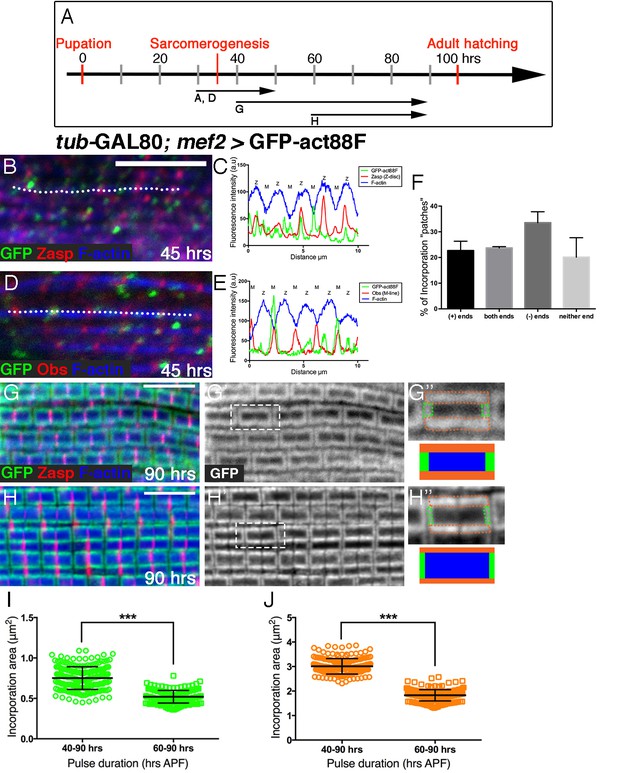
Peripheral growth of the nascent arrays is continuous.
(A) Scheme of IFM development intervals used for temporally restricted expression of GFP-actin88F. (B,D) Incorporation patterns of GFP-actin88F (green) following temporally restricted expression pulses at 30–45 hrs APF. Thin filament array ends are marked by Zasp52 (red) for the barbed ends and Obscurin (red) for the pointed end; microfilaments are visualized with phalloidin (blue). (C,E) Representative intensity profiles along the white dashed line in (B,D), shows the positions of 'patch' incorporation events in nascent sarcomeres. (F) The distribution of 'patch' incorporation events across the thin filament arrays, broken up into four categories. Data obtained from 50 sarcomeres in 5 different pupae (n=250). (G–J) Incorporation patterns of GFP-actin88F (green, gray) following temporally restricted expression pulses at 40–90 hrs APF (G–G’’) and 60–90 hrs APF (H–H’’), using the mef2-GAL4 driver and the GAL80ts/TARGET system. Z-discs are indicated by anti-Zasp52 (red) and microfilaments are visualized with phalloidin (blue). Incorporation “frames” are outlined and schematized (G”,H”) to show relative frame sizes following the two expression pulses and to distinguish between the array 'core' (blue), elongation from pointed-ends (green) and radial thickening (orange). Scale bars in all panels correspond to 5 μm. (I,J) Quantifications show significant (~40%, p<0.0001) differences between the long and short expression pulses in both the elongation (I) and radial (J) incorporation areas, indicative of continuous growth in both modes, n=200 (50 sarcomeres each from 4 different flies). P values determined by Mann-Whitney test.
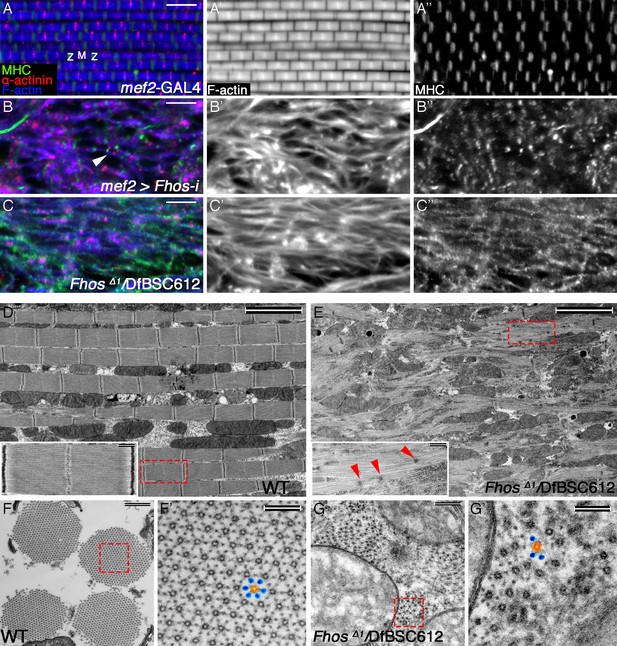
The formin Fhos is essential for organization and growth of thin filament arrays.
(A–C”) Confocal images of IFMs dissected from 1 day old flies or pharate adults and stained with anti- α-actinin (red) to mark Z-disc structures, phalloidin (blue, gray) to visualize microfilaments and anti-MHC (green, gray) to visualize myosin. (A–A”) mef2-GAL4 control. Z and M mark the Z-disc and M-line of a single sarcomere. (B–B”) mef2-GAL4>UAS-fhos RNAi (knockdown of all fhos isoforms). Myofibril and sarcomere structure and organization are defective, but sporadic, undersized sarcomeric units can be observed (white arrowhead in B). (C–C’’) fhosΔ1/Df(3L)BSC612 (fhos null). Deletion of the fhos locus results in full impairment of myofibril and sarcomeric organization. (D–E) TEM micrographs of longitudinal sections of IFMs dissected from control 1 day old flies (D) and fhos null (fhosΔ1/Df(3L)BSC612) pharate adults (E). Distinction in the overall myofibril organization is readily apparent, with fhos null IFMs lacking typical myofibril and sarcomeric individualization. The insets contrast the stereotypic, highly-ordered structure of the control sarcomeric units (inset D) with the poor organization of arrays within fhos null myofibrils and their failure to form individual sarcomeres (inset E). Red arrowheads in (E) point to dispersed, rudimentary Z-discs. (F–G’) TEM micrographs of transverse sections of IFMs dissected from control 1 day old flies (F,F’) and fhos null (fhosΔ1/Df(3L)BSC612) pharate adults (G,G’). Primed panels are magnifications of the dashed squares in panels (F) and (G). In contrast to the highly ordered hexagonal lattice of thick (orange) and thin filaments (blue) in control myofibrils (F’), fhos null myobrils lack a defined spatial organization (G’). Scale bars: 5 μm (A-E), 500 nm (insets in D,E, and F,G), 100 nm (F’,G’).
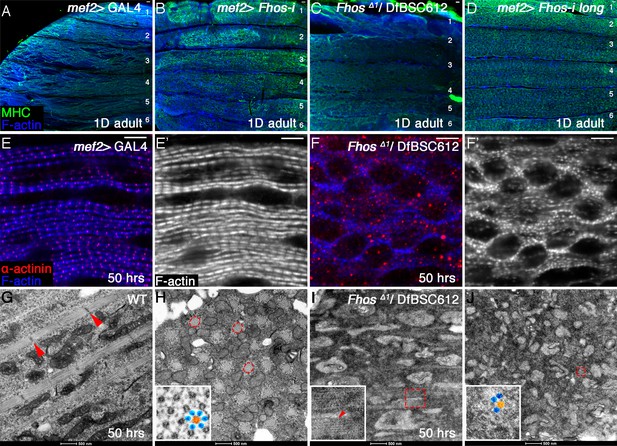
Fhos function is required during the early stages of sarcomerogenesis.
(A–D) Low magnification images of hemithoraces from 1 day old or pharate adults, dissected from a control (mef2-GAL4) fly (A), a fhos knockdown fly (all isoforms) (B), a fhos null fly (fhosΔ1/Df(3L)BSC612) (C) and a fhos knockdown fly (long isoforms only) (D), and stained with anti-MHC (green) and phalloidin (blue). No significant differences in muscle fiber size, number or overall morphology are observed. (E–F’) Higher magnification views of IFMs dissected from control (E,E”) or fhos null (F,F’) pupae at 50 hr APF, and stained with the Z-disc marker anti-α-actinin (red) and phalloidin (blue, gray). The fhos null IFMs display a severely defective organization of myofibrils and sarcomeres. (G–J) TEM views of longitudinal (G,I) or cross (H,J) sectioned material from IFMs dissected from control (G,H) or fhos null (I,J) pupae at 50 hr APF. Control myofibrils run parallel to each other (G) and contain regularly-spaced Z-discs (red arrowheads in G) and nascent filament arrays, displaying an ordered, hexagonal lattice organization (H, dashed circles and inset (thick [orange] and thin filaments [blue]). Only sporadic myofibrils bearing short, weakly-organized filament arrays are found within the fhos null muscle fibers (I, J, dashed squares and insets). Scale bars: 50 μm (A–D), 5 μm (E–F’), 500 nm (G and J).
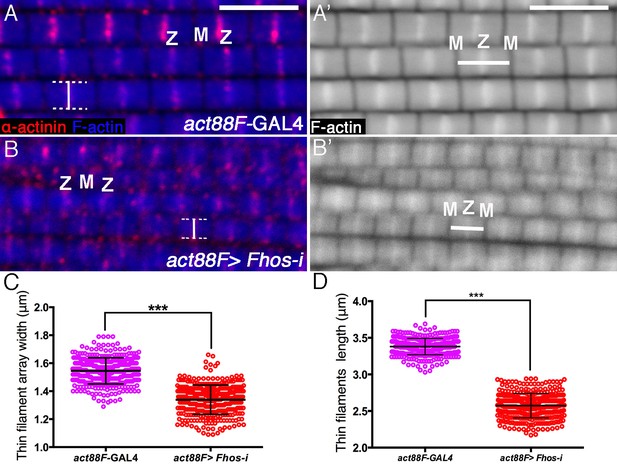
Fhos is required for proper sizing of thin-filament arrays.
(A–B’) Confocal images of IFMs dissected from young adult flies and stained with anti-α-actinin (red) to mark Z-disc structures and phalloidin (blue, gray) to visualize microfilaments. (A–A’) act88F-GAL4 control. (B–B’) act88F-GAL4>UAS-fhos RNAi (knockdown of fhos initiating at mid-pupal stages). Z and M mark the Z-disc and M-line of a single sarcomere. Vertical bars (A,B) mark the width of a single sarcomere, while horizontal bars (A’,B’) mark the length of a single thin-filament array. (C–D) Quantification of the average width and length of thin-filament arrays in control (act88F-GAL4) and fhos knockdown IFMs dissected from young (1 day old) flies. The data represent the measurements of 50 sarcomeres each from 7 flies (n = 350) for each genotype. Following fhos knockdown arrays are significantly thinner (~15%, p<0.0001) (C) and shorter (~30%, p<0.0001) P values determined by Mann-Whitney test for width and length measurements. Scale bars in all panels correspond to 5 μm.
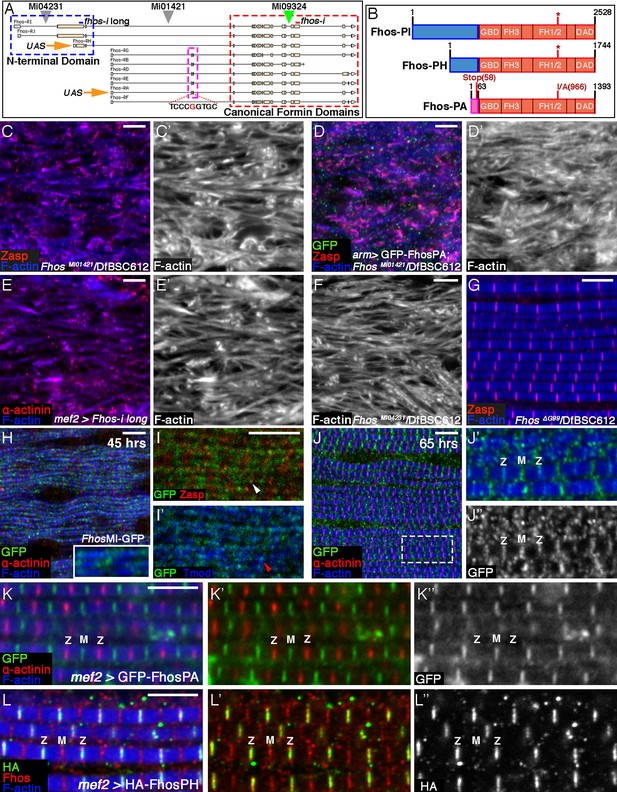
Localization of Fhos at the Z-disc is essential for its function.
(A) Map of the Fhos genomic locus and transcripts (after Flybase, (Attrill et al., 2016). Shown are the nine known fhos transcripts (designated Fhos-RA--Fhos-RI), which are divided into two groups (RA-RG and RH-RI). The two groups share a nearly identical set of 3’ exons (red dashed rectangle), which encode a conventional FHOD-family formin, but are expressed via distinct regulatory regions, and possess distinct sets of 5’ exons, including 5’ coding exons (blue and purple dashed rectangles) that encode different N-terminal domains. The two transcript variants, RH and RA, used to generate, respectively, the long and short transgenic UAS-Fhos constructs are indicated by orange arrows. The insertion positions of three MiMIC elements, MI04231 (inserted downstream of long isoform initiation sites), MI01421 (inserted downstream of all transcript initiation sites), and MI09324 (used to produce the Fhos-GFP 'protein trap') are indicated by inverted triangles. Positions of two dsRNA target sequences used, one common to all fhos isoforms (red bar) and the other specific to the long forms (blue bar) are shown above the transcript map. The CRISPR/Cas9-generated deletion of the guanine residue at position 99 of the short isoform transcript and its adjacent sequence are indicated. (B) Schematic representation of three representative Fhos protein isoforms. The canonical formin domains common to all forms are colored red, while the alternative N-terminal domains are in blue (long forms) and purple (short form). Canonical domains indicated include the GTPase binding domain (GBD), formin homology (FH) domains 1/2 and 3, and the diaphanous autoregulatory domain (DAD). The positions of the I966A point mutation in the FH2 domain and the premature stop codon, generate by the frameshift mutation ΔG99 in the Fhos-PA N-terminal domain are indicated. (C–D’) Zasp (red) and phalloidin (blue and gray) stainings demonstrate the severe, null-like disruption of myofibril and sarcomere microfilament organization in hemizygous FhosMI01421/Df(3L)BSC612 pharate adult flies (C,C’), similar to that observed in fhosΔ1 hemizygotes. No rescue is observed following expression of UAS-GFP-Fhos-PA (green) driven by arm-Gal4 in this background (D,D’). (E–F) α-actinin (red) and phalloidin (blue and gray) stainings demonstrate the severe, null-like phenotypes following specific RNAi mediated knockdown of the Fhos long-isoforms (E,E’) and in hemizygous FhosMI04231/Df(3L)BSC612 (F) pharate adult flies. (G) Zasp (red) and phalloidin (blue) stainings demonstrate normal myofibril and sarcomeric structure of Fhos ΔG99/Df(3L)BSC612 hemizygotes, in which the short Fhos isoforms are not expressed. (H–L’’) Fhos localization in myofibrils, as monitored at two distinct pupal developmental time points, 45 hr APF (H–I’), and 65 hr APF (J–J’’), via a GFP 'exon trap' engineered at the insertion site of the MiMIC transposon MI09324 (green triangle in A). The GFP-tagged Fhos proteins (all isoforms) generated in this manner are visualized with anti-GFP (green or gray), Z-discs are visualized with anti-α-actinin or anti-Zasp (red), thin filament pointed ends visualized by anti-Tmod (blue) and microfilaments with phalloidin (blue). The diffuse/punctate initial localization of Fhos-GFP overlying broad portions of the growing myofibrils (H), in some cases shows an adjacent localization to the nascent Z-disc (I white arrowhead) or to array pointed ends (I’ red arrowhead). The initial punctate localization gives way to a striated pattern restricted to the vicinities of both the barbed (Z) and pointed (M) ends of the thin-filament arrays (J–J’’). (K–K”) Localization of the short isoform of Fhos in IFMs from a young adult fly, visualized by expression of UAS-GFP-Fhos-PA using the mef2-GAL4 driver (anti-GFP, green or gray). Z-discs are visualized with anti-α-actinin (red), and microfilaments with phalloidin (blue). GFP-Fhos-PA localizes to the vicinity of the pointed ends of the arrays (M). (L–L”) Localization of the long isoforms of Fhos in IFMs from a young adult fly, visualized with anti-HA (green and gray), following expression of UAS-HA-Fhos-PH using the mef2-GAL4 driver. Fhos-PH-PA localizes to the vicinity of the barbed ends of the arrays (Z), where it overlaps with the general Fhos distribution to both the barbed and pointed ends (M) of the arrays (visualized with anti-Fhos [red]). Microfilaments visualized with phalloidin (blue). Scale bars in all panels correspond to 5 μm.
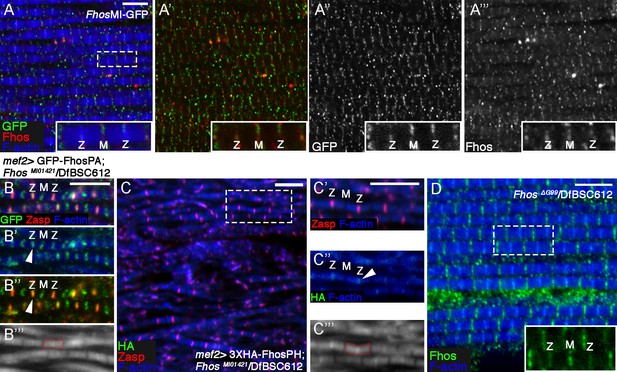
Fhos localization at the Z-disc is essential for its function.
(A–A’’’) Fhos localization in IFM myofibrils from young adult flies. Shown are myofibrils from a fly in which GFP was inserted into the Fhos locus (see text and Figure 3A). Fhos localization was monitored by anti-GFP (green or gray) and anti-Fhos (red or gray) and microfilaments are visualized with phalloidin (blue). Both methods demonstrate enrichment of Fhos in the vicinities of the pointed (M) and barbed (Z) ends of the thin-filament arrays. (B–B’’’) Sporadic rescue of the disrupted myofibril and sarcomere organization of null hemizygous FhosMI01421/Df(3L)BSC612 young (1 day old) flies following mef2-Gal4 driven expression of UAS-GFP-Fhos-PA (green). Z-discs are marked by anti-Zasp52 (red) and microfilaments are visualized with phalloidin (blue or gray). Formation of sarcomeres is always accompanied by localization of GFP-Fhos-PA not only to the pointed (M) but also to the barbed (Z) ends of the thin-filament arrays. (C–C’’’) Partial rescue of null hemizygous FhosMI01421/Df(3L)BSC612 young (1 day old) flies following mef2-Gal4 driven expression of UAS-3XHA-Fhos-PH (green), a long isoform that localizes strictly to the Z-disc region. Z-discs are marked by anti-Zasp52 (red) and microfilaments are visualized with phalloidin (blue or gray). (D) The properly ordered arrays from a hemizygous Fhos ΔG99/Df(3L)BSC612 fly- expressing only the long isoforms- show Fhos localization (visualized with anti-Fhos, green) near both the pointed (M) and barbed (Z) ends of the thin-filament arrays; microfilaments are visualized with phalloidin (blue). The dashed rectangle in (A,C,D) corresponds to the magnified inset. Scale bars in all panels correspond to 5 μm.
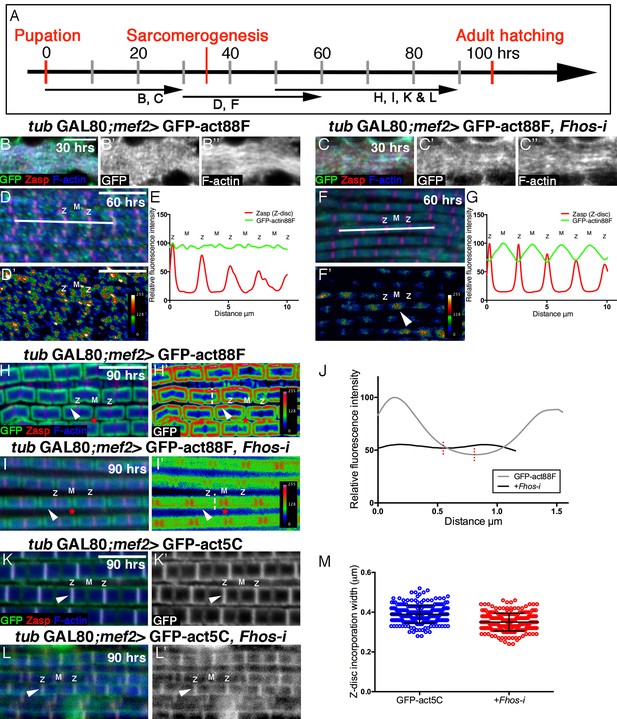
Fhos is required for the 'patchy' actin monomer incorporation and radial expansion aspects of thin-filament array growth.
(A) Scheme of IFM development intervals used for temporally restricted expression of GFP-actin88F (B–J) or GFP-actin5C (K–M’) in wildtype (B–B”,D,D’,H,H’,K,K’) or Fhos knockdown (C–C”,F,F’,I,I’,L,L’) IFMs. (B-I’) GFP-actin88F (green, gray) expression between 0–30 (B–C’), 30–60 (D-G) and 50–90 (H-I’) hr APF. Z-discs are visualized with anti-Zasp52 (red) and microfilaments with phalloidin (blue, gray). (B–C’) The general and uniform incorporation of monomers into microfilaments characteristic of the initial phase of sarcomere formation (B–B”) is not affected in fhos knockdown myofibrils (C–C”). (D–G) The dispersed and 'spotty' wildtype incorporation pattern during the interim (30–60 hr APF) phase (D) is replaced by a pointed-end centered pattern in fhos knockdown myofibrils (F). These pattern distinctions are further demonstrated by heat maps of the GFP-actin88F distribution (D’,F’) and quantification of GFP intensity (E,G) derived from 10 μm profiles covering approximately four sarcomeric units (white lines in D and F; data were acquired for 15 profiles from 7 different pupae for each genotype [n = 105]). (H–I’) The incorporation 'frames'normally generated by late GFP-actin88F expression pulses (H,H’) lack peripheral incorporation (arrowheads) following fhos knockdown (I,I’), but these abnormally thin myofibrils retain proper incorporation at array 'pointed' ends (red asterisks). The lack of incorporation 'frames' is also demonstrated by heat maps (H’,I’), and the quantification of GFP intensity (J; data were acquired for 100 profiles from 4 different flies for each genotype [n = 400]) along vertical profiles (white dashed line H’,I’), which show the loss of peripheral incorporation and thinner sarcomeres (red dashed lines in J). (K-M) GFP-actin5C (green, gray) expression between 50–90 hr APF. Z-discs are visualized with anti-Zasp52 (red) and microfilaments with phalloidin (blue). GFP-actin5C induction in parallel to fhos knockdown showed normal Z-disc associated turnover (arrowheads). (M) Quantification of Z-disc incorporation band width (data were acquired for 50 Z-discs from 4 different flies for each genotype [n = 200]). Scale bars in all panels correspond to 5 μm.
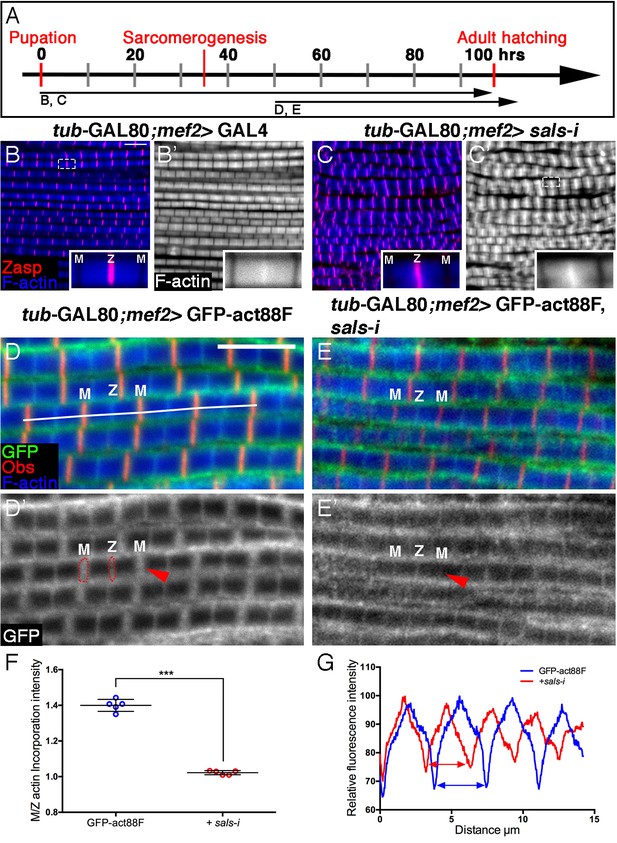
Sals is required for 'pointed-end' thin-filament growth.
(A) Scheme of IFM development intervals used for temporally restricted expression of sals RNAi and GFP-actin88F. (B–C’) IFMs dissected from control (mef2-GAL4) 1 day old flies (B,B’) and sals knockdown pharate adults (C,C’), in which RNAi expression was initiated at 0 hr APF. Z-discs are visualized with anti-Zasp52 (red) and microfilaments with phalloidin (blue or gray). sals knockdown results in sarcomere shortening and 'pointed' end abnormalities (insets in B’ and C’; for quantification see Figure 5—figure supplement 1D). (D–E’) IFMs dissected from young (1–2 day old) flies in which GFP-actin88F expression (anti-GFP, green, gray) was initiated at 50 hr APF on its own (D,D’) or together with sals RNAi (E,E’). M lines are visualized with anti-Obscurin (red) and microfilaments with phalloidin (blue). (F) The GFP-actin88F incorporation band at the 'pointed' ends is significantly decreased following sals knockdown, as shown by the M/Z intensity ratio (p<0.0001, P values determined by Mann-Whitney test), while the addition of peripheral microfilaments is unaffected. (G) Quantification of phalloidin intensities derived from 13 μm profiles (white line in D). sals RNAi myofibrils (red line) exhibit shorter sarcomeric units compared to control (blue line). Scale bars in all panels correspond to 5 μm.
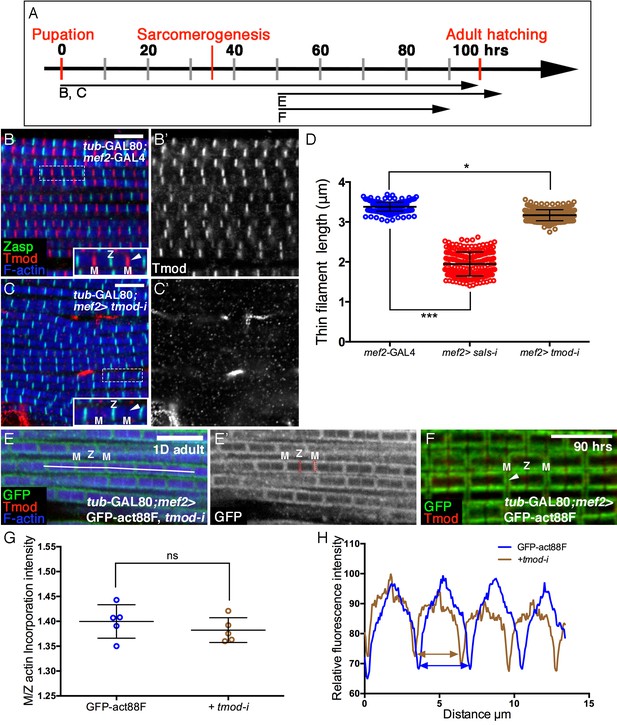
Involvement of Tmod in nascent thin filament array elongation.
(A) Scheme of IFM developmental intervals used for temporally restricted expression of tmod RNAi and GFP-actin88F. (B–C’) IFMs dissected from control (mef2-GAL4) (B,B’) and tmod knockdown (C,C’) 1 day old flies, in which RNAi expression was initiated at 0 hr APF. Anti-Tmod (red) visualized array pointed ends, Z-discs are visualized with anti-Zasp52 (green) and microfilaments with phalloidin (blue or gray). tmod knockdown results in mild significant sarcomere shortening (~10%, p<0.01), which is, however, considerably milder than shortening following sals knockdown (~40%, p<0.0001). The data for sals and tmod knockdown represent measurements of 50 sarcomeres each from 5 flies (n = 250). The P values determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for array length measurements. (E,E’) IFMs dissected from young (1–2 day old) flies in which GFP-actin88F expression (anti-GFP, green, gray) was initiated at 50 hr APF together with tmod RNAi. Pointed ends are visualized with anti-Tmod (red) and microfilaments with phalloidin (blue). The GFP-actin88F incorporation pattern remains intact following tmod knockdown: (G) The M/Z ratio of incorporation band intensity is not significantly changed (p>0.01, P values determined by Mann-Whitney test) and quantification of phalloidin intensity (H) derived from 13 μm profiles (white line in E), indicates only slight shortening of the arrays. (F) Interestingly, IFMs dissected from a 90 hr APF pupa exhibit a complete absence of Tmod staining (red) at the vicinity of pointed ends. Scale bars in all panels correspond to 5 μm.
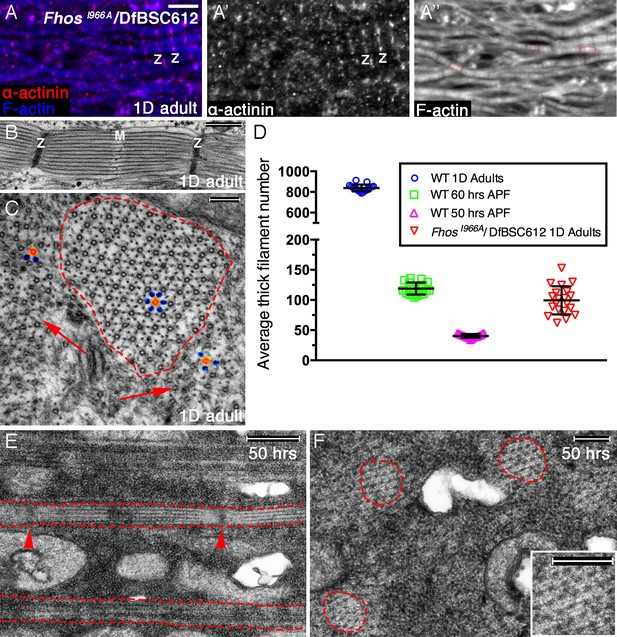
Early Fhos function does not require barbed-end activities.
(A–A’’) IFM myofibrils from a FhosI966A/Df(3L)BSC612 1 day old adult fly. Z-discs are marked by anti-α-actinin (red or gray) and microfilaments are visualized with phalloidin (blue or gray). The thin myofibrils display organized arrays of repeated sarcomeric units (red outlines in A’’). (B–F) TEM analysis of IFM myofibrils from FhosI966A/Df(3L)BSC612 flies. (B,C) One day old adult flies. A longitudinal section (B) shows a stereotypic sarcomeric unit displaying clear Z-disc (Z) and M line (M) structures. A cross section (C) shows an individual sarcomeric unit (red dashed circle) harboring a well-formed lattice of thick and thin filaments. Arrows point to accumulations of nearby filaments, which could serve as a source for radial growth, but have not been recruited. The degree of lattice organization within and outside the sarcomere can be appreciated from the spatial arrangement of representative thick (orange) and thin (blue) filaments. (D) Quantification of sarcomere size in wildtype and FhosI966A/Df(3L)BSC612 pupae and adult flies at the indicated ages, based on the number of thick filament units in TEM cross-sections (n = 20 for each background). (E,F) 50 hr APF pupae. Longitudinal (E) and cross (F) sections show myofibril individualization (red dashed lines in E) and formation of nascent sarcomeric units (red dashed circles in F) with defined Z-disc borders (red arrowheads in E; see also Figure 2—figure supplement 1G,H). Scale bars correspond to 5 μm (A), 100 nm (B), 500 nm (C,F) and 200 nm (E).
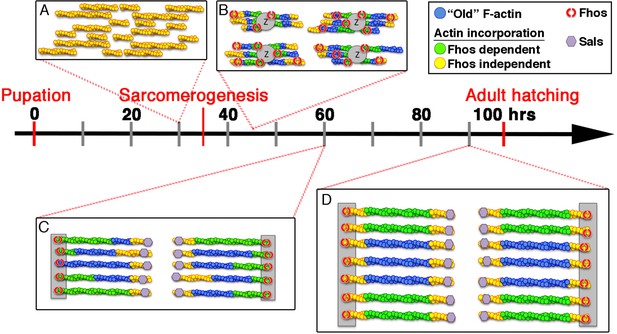
Model of IFM thin-filament array assembly and the roles of Fhos and Sals.
Four distinct stages of thin-filament array assembly and maturation are represented in correlation to pupal developmental stages. (A) Extensive filament polymerization (0–30 hr APF), which takes place in a Fhos-independent manner. (B) Organization of nascent sarcomeres and patched actin incorporation (30–45 hr APF). Fhos localizes to the nascent arrays, and is required for their organization into discrete structural units. (C,D) Growth and maturation of nascent sarcomeres (45 hr APF- eclosion). Fhos localizes to the vicinity of the Z-discs, and is essential for radial growth of the thin-filament arrays, possibly via peripheral filament recruitment. Two additional actin incorporation modes are executed in a Fhos independent manner. Z-disc associated monomer turnover, and 'pointed' end elongation, which is mediated primarily by Sals.





