Hippocampal neurogenesis enhancers promote forgetting of remote fear memory after hippocampal reactivation by retrieval
Figures
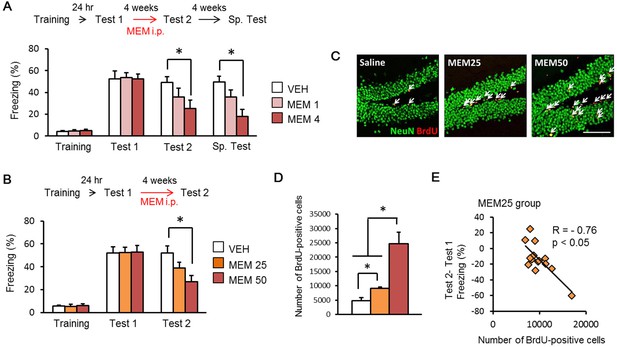
Memantine (MEM) treatment enhanced forgetting of contextual fear memory through the increase in adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
(A) MEM treatment enhanced forgetting of contextual fear memory in a manner dependent on the number of MEM treatments. [VEH = vehicle-treated group, n = 10; MEM (1), n = 10; MEM (4), n = 10]. (B) MEM treatment enhanced forgetting of contextual fear memory in a dose-dependent manner (VEH group, n = 12; MEM25 group, n = 14; MEM50 group, n = 13). (C) Representative immunohistochemically stained BrdU-positive cells (red) and NeuN-positive cells (green) at 24 hr after Test 2. Scale bar = 100 µm. (D) The number of BrdU-positive cells in the dentate gyrus (DG) (VEH, n = 3; MEM25, n = 14; MEM50, n = 3). (E) Correlation between the number of BrdU-positive cells and the differences of freezing scores before and after the MEM treatments (MEM25 = 25 mg/kg body weight; MEM50 = 50 mg/kg body weight) in contextual fear conditioning tasks (n = 14). i.p. = intraperitoneal injection. *p<0.05. The results of the statistical analyses are presented in Figure 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Summary of statistical analyses with F values.
The asterisks indicate a significant difference.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17464.003
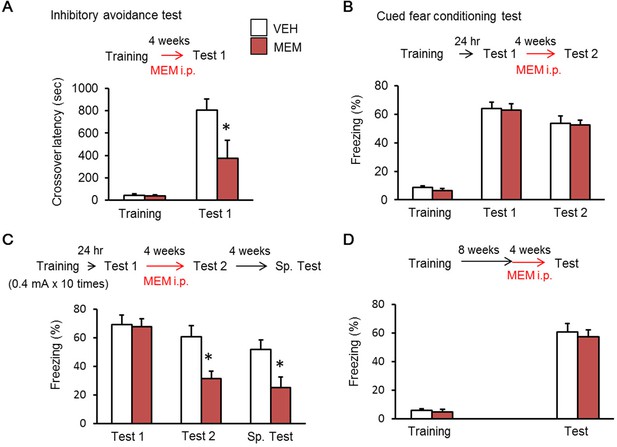
Memantine (MEM) treatment enhanced forgetting of hippocampus-dependent fear memory.
(A) MEM treatment enhanced forgetting of hippocampus-dependent inhibitory avoidance memory [vehicle treated group (VEH), n = 11; MEM group, n = 10]. (B) MEM-treated mice showed normal amygdala-dependent memory (VEH, n = 12; MEM, n = 12). (C) MEM treatment affects strong fear memory (VEH, n = 8; MEM, n = 9). (D) Remote fear memory formed eight weeks after MEM treatment did not enhance forgetting (VEH, n = 10; MEM, n = 10). (A) and (C), *p<0.05, compared with the saline group. i.p. = intraperitoneal. The results of the statistical analyses are presented in Figure 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Summary of statistical analyses with F values.
The asterisks indicate a significant difference.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17464.005
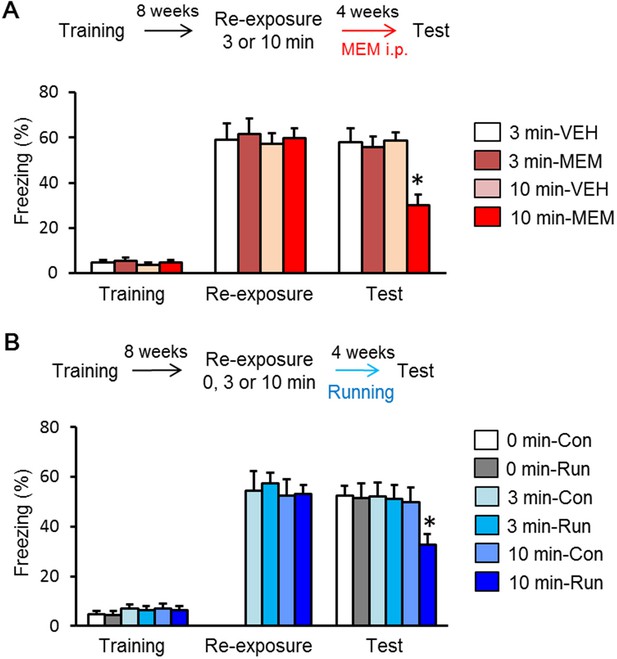
Enhancement of adult hippocampal neurogenesis after long-period recall enhanced forgetting of remote fear memory.
(A) Memantine (MEM) treatment enhanced forgetting of remote fear memory after 10 min re-exposure (3 min vehicle treatment group (VEH), n = 10; 3 min MEM-treated group, n = 10; 10 min VEH, n = 12; 10 min MEM, n = 13). (B) Running after 10 min re-exposure enhanced forgetting of remote fear memory [No Run (Con), 0 min, n = 12; Run, 0 min, n = 9; No Run, 3 min, n = 12; Run, 3 min, n = 11; No Run, 10 min, n = 12; Run, 10 min, n = 11]. *p<0.05, compared with other groups in the test. The results of the statistical analyses are presented in Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Summary of statistical analyses with F values.
The asterisks indicate a significant difference.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17464.007
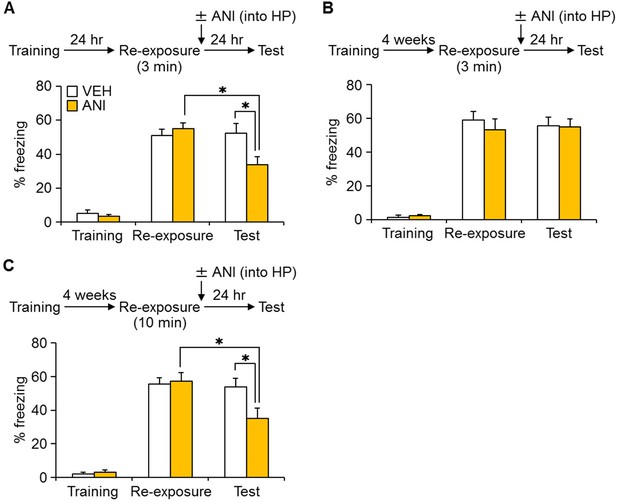
Inhibition of protein synthesis in the hippocampus (HP) blocked reconsolidation of remote fear memory.
(A) Three min re-exposure to the context 24 hr after training [vehicle-treated group (VEH), n = 10; anisomycin (ANI), n = 15]. (B) Three min re-exposure to the context four weeks after training (VEH, n = 8; ANI, n = 8). (C) Ten min re-exposure to the context four weeks after training (VEH, n = 11; ANI, n = 11). Error bars, SEM. *p<0.05. The results of the statistical analyses are presented in Figure 4—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Summary of statistical analyses with F values.
The asterisks indicate a significant difference.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17464.009
The cannula tip placement in the hippocampus.
(A–C) The cannula tip placement form mice infused with each drug as illustrated in Figure 4A (A), Figure 4B (B), and Figure 4C (C). Schematic drawings of coronal sections from all micro-infused animals (hippocampus, 1.94 mm posterior to the bregma). Only mice with needle tips within the boundaries of the hippocampus were included in the data analyses. ANI = anisomycin; VEH = vehicle.
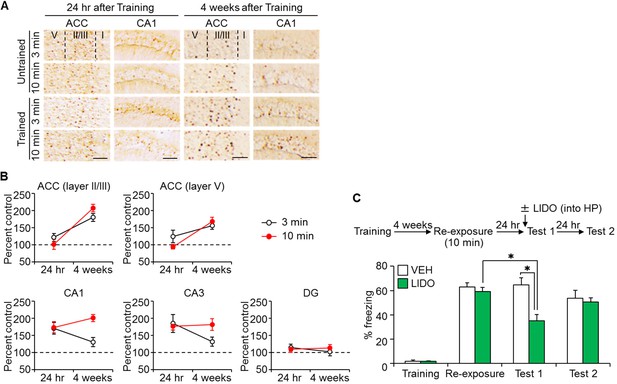
Long-time retrieval of remote fear memory reactivated the hippocampus (HP).
(A) Representative immunohistochemical staining of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and CA1 c-fos-positive cells from the indicated group. Scale bars = 100 μm. Two groups were trained with a foot shock (trained group) and the remaining two groups did not receive a foot shock (untrained group). Twenty-four hr (recent memory) or four weeks (remote memory) after the training, mice were placed back in the training context for 3 or 10 min for short or long memory recall, respectively (re-exposure). (B) The c-fos expression in the ACC (layers II/III, and V) and the hippocampus [CA1, CA3, and the dentate gyrus (DG) regions]. N = 10 for each group. The c-fos expression in the trained groups was expressed as a percentage relative to the untrained groups. (C) Ten min re-exposure to the context four weeks after training [vehicle-treated group (VEH), n = 11, lidocaine-treated group (LIDO), n = 11]. Error bars, SEM. *p<0.05. The results of the statistical analyses are presented in Figure 5—source data 1.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Summary of statistical analyses with F values.
The asterisks indicate a significant difference.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17464.012
The cannula tip placement in the hippocampus.
The cannula tip placement form mice infused with each drug as illustrated in Figure 5C. Schematic drawings of coronal sections from all micro-infused animals (hippocampus, 1.94 mm posterior to the bregma). Only mice with needle tips within the boundaries of the hippocampus were included in the data analyses. LIDO = lidocaine; VEH = vehicle.





