Dopamine neurons learn relative chosen value from probabilistic rewards
Figures
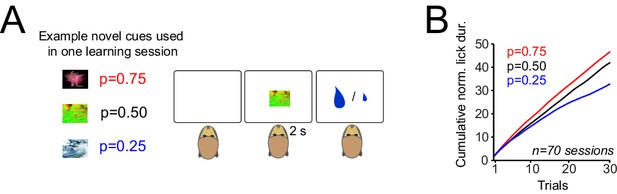
Monkeys rapidly learn the value of cues that predict rewards with different probabilities.
(A) Pavlovian task. Left: example of novel visual cues (fractal images) presented to monkeys. In each trial, animals were presented with a visual cue and received a large (0.4 ml) or small (0.1 ml) drop of juice reward 2s after cue onset. Specific cues predicted the large reward with probabilities of p=0.25, p=0.5 and p=0.75, together with small reward at 1–p. In each session of the experiment (lasting 90–120 trials), three novel cues were differentially associated with the three tested reward probabilities. Over consecutive trials, cues with different reward probabilities were presented to animals pseudorandomly. Trials were separated by inter-trial intervals of 2–5 s. Animals had no specific behavioural requirements throughout this task. (B) Monkeys’ lick responses during Pavlovian learning. The lick responses were measured from cue onset to onset of reward delivery.
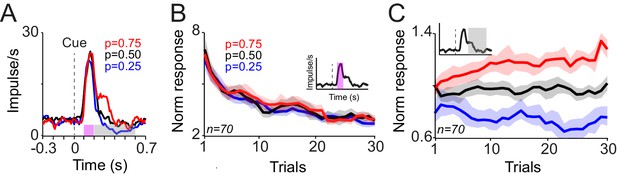
Responses of dopamine neurons acquire predictive value from the frequency of rewards.
(A) Peri-stimulus time histograms (PSTHs) of a dopamine neuron in response to novel cues predicting rewards with different probabilities. Pink (0.1–0.2 s after cue onset) and grey (0.2–0.6 s after cue onset) horizontal bars indicate analysis windows used in B and C, respectively. (B) Decrease of neuronal population responses, measured at 0.1–0.2 s after cue onset (pink inset), over consecutive learning trials. Error bars show standard error of mean (s.e.m.) across neurons (n = 70, pooled from monkeys A and B). (C) Differentiation of neuronal population responses, measured at 0.2–0.6 s after cue onset (grey inset), over consecutive learning trials. The following figure supplement is available for Figure 2:
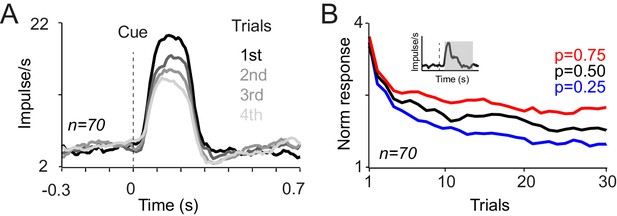
Compound novelty-value responses of dopamine neurons to novel cues associated with different probabilistic rewards.
(A) PSTHs of dopamine population responses to novel reward predicting cues. Neuronal responses in the first, second, third and fourth trials are plotted separately. (B) Neuronal population responses to cues (measured 0.1–0.6 s after the cue onset) over consecutive learning trials. The grey zone shows the analysis window, comprising both novelty and value responses.
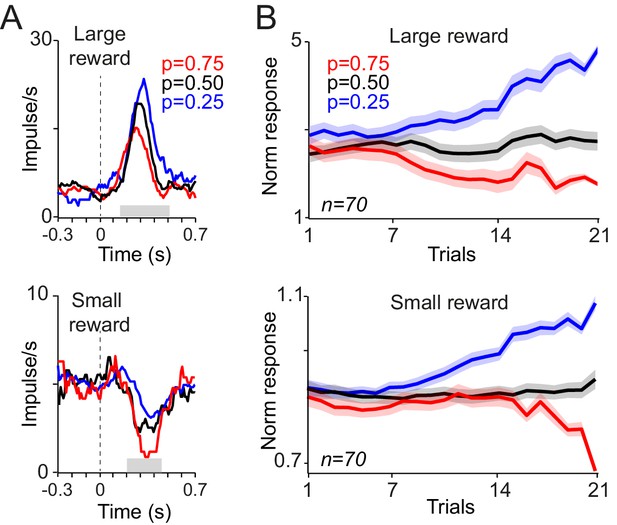
Responses of dopamine neurons to reward delivery develop over trials to reflect the learned value of probabilistic cues.
(A) PSTHs of example dopamine neurons in response to delivery of large and small juice rewards (top, bottom). Probabilities indicated in colour refer to the occurrence of the large reward in gambles containing one large and one small reward (0.4 ml and 0.1 ml, respectively). (B) Neuronal population responses to large and small juice rewards over consecutive learning trials. Responses were measured in analysis windows indicated by corresponding grey horizontal bars in A (top: 0.15–0.5 s, bottom: 0.2–0.45 s after reward onset).
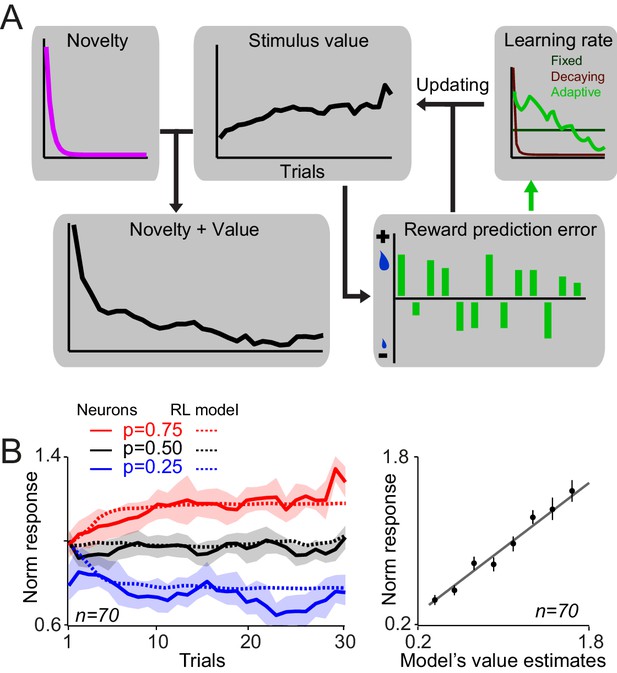
A reinforcementlearning model with a novelty term and an adaptive learning rate account for dopamine responses during learning.
(A) Schematic of RL models fitted on neuronal responses. In each trial, the model updates the value of stimulus based on the experienced reward prediction error. Six variants of RL models were tested (three different learning rates, each with or without novelty term). In brief, we optimized the free parameters of each model so that it minimized the difference between dopamine responses to cues (measured 0.1–0.6 s after the cue, thus including both novelty and value component) and model’s estimates of novelty + value. We then examined the relation between value-driven neuronal responses and value estimates of the superior model and also the relation between novelty-driven neuronal responses and novelty estimates of the superior model. For details of model implementation and fitting procedure see Materials and methods. (B) Left: Value estimates of the superior model (i.e. the model with a novelty term and adaptive learning rate) overlaid on neuronal population responses measured 0.2–0.6s after the cue onset,(from Figure 2C). For details of parameter estimation and model comparison see Supplementary file 1. Right: Regression of dopamine responses to cues (dopamine value responses, i.e. 0.2–0.6 s after the cue onset) onto value estimates of the superior RL model. See Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for regression of dopamine novelty signals onto novelty-driven model’s estimates.
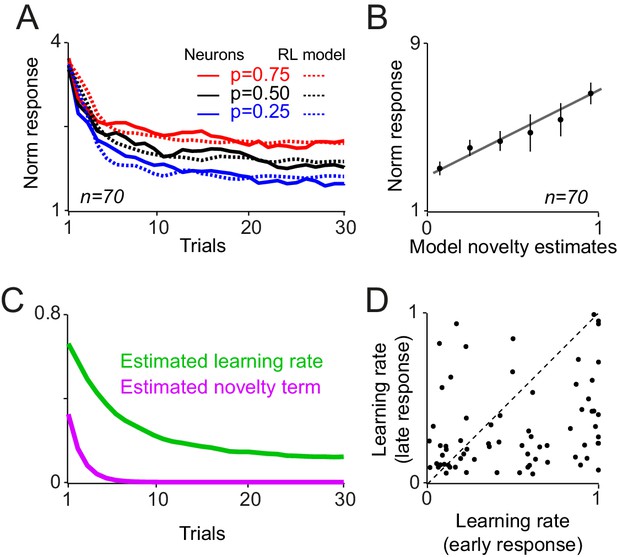
A reinforcement learning model with a novelty term and an adaptive learning rate account for dopamine responses during learning.
(A) Novelty + value estimates of the superior model (i.e. the model with a novelty term and adaptive learning rate) overlaid on neuronal population responses measured 0.1–0.6s after the cue onset (from Figure 2—figure supplement 1B). (B) Regression of dopamine novelty signals (measured 0.1–0.2 s after the cue onset) onto novelty-driven estimates of the superior model. (C) Average of estimated learning rate and estimated novelty term of the superior model. (D) Scatter plot of session-by-session estimated learning rates of early and late components of dopamine responses to cues. For this analysis, the model with fixed learning rate that included novelty term was rearranged so that its novelty term followed an error-driven learning (see Methods and materials). Each dot corresponds to a session.
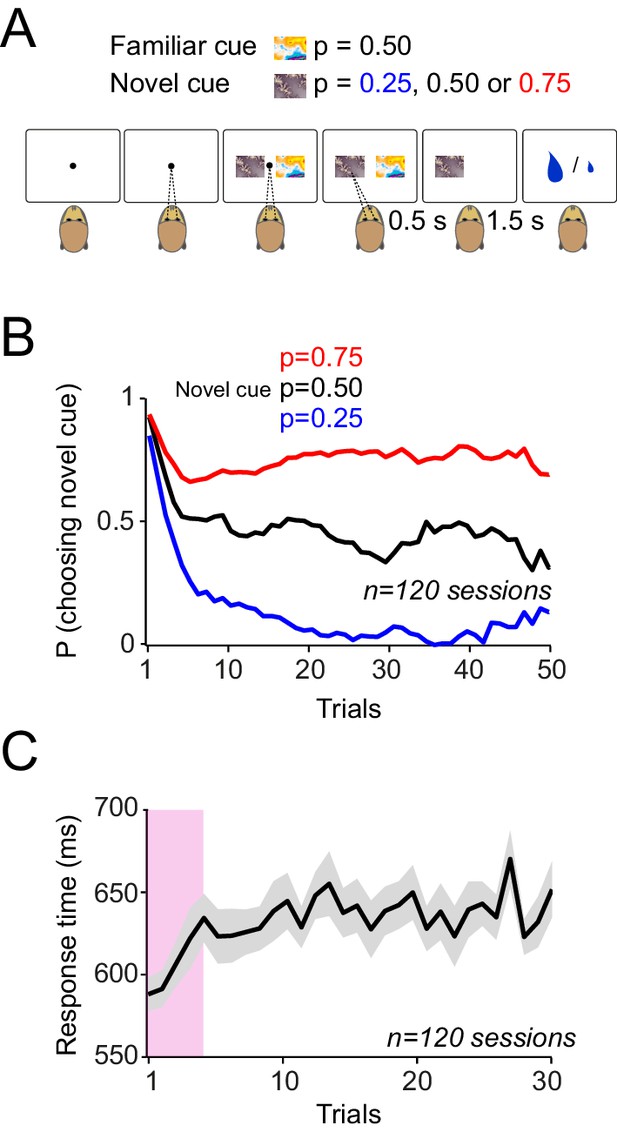
Monkeys rapidly learn to make meaningful choices among probabilistic reward predicting cues.
(A) Choice task. In each trial, after successful central fixation for 0.5 s, the animal was offered a choice between two cues, the familiar cue and the novel cue. The animal indicated its choice by a saccade towards one of the cues. The animal was allowed to saccade as soon as it wanted. The animal had to keep its gaze on the chosen cue for 0.5 s to confirm its choice. Reward was delivered 1.5 s after the choice confirmation. The animals had extensive prior experience with one of the cues (familiar cue predicting 50% chance of getting 0.4 ml and 50% chance of receiving 0.1 ml). The alternative cue was a novel cue with the reward probability unknown to the animal. The novel cues were associated with reward probabilities of 0.25, 0.50 or 0.75 of receiving the large (0.4 ml) reward and 0.1 ml otherwise. After a block (of typically 50 trials) the novel cue was replaced with another novel cue. Trials were separated with inter-trial interval of 2–5 s. Failure to maintain the central fixation or early breaking of fixation on the chosen option resulted in 6 s time-out. (B) Monkeys’ choice behaviour. At the onset of each learning session, both animals chose the novel cue over the familiar cue for 4–5 trials. Afterwards, animals preferentially chose the cue that predicted reward with higher probability. (C) Saccadic choice response times. Both monkeys showed significantly faster reaction times (defined as the interval between the cue onset and the time the animal’s saccade acquired the chosen option) in the first 4–5 trials of each learning block. Error bars are s.e.m across behavioural sessions.
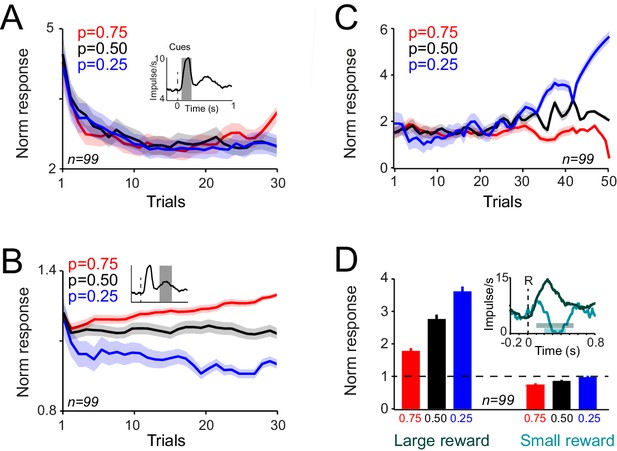
Dopamine responses to cues differentiate as monkeys learn the value of novel cues in the choice task.
(A) Neuronal population responses to cues over consecutive trials of the choice task, measured during 0.1–0.2 s after the cue onset (Dopamine novelty responses, see inset). Only trials in which animal chose the novel cue were shown in all panels of this figure. (B) Neuronal population responses to cues over consecutive trials of the choice task, measured during 0.4–0.65 s after the cue onset (Dopamine value responses, see inset). See Figure 6—figure supplement 1 for more detailed analysis of time course of the neuronal activity. (C) Population dopamine responses to the large reward over trials in which the novel cue was chosen and large reward was delivered. (D) Population dopamine responses to the reward delivery in trials in which the novel cue was chosen. Each bar demonstrates the mean neuronal response averaged across later (30th to last trial) of each session. Bars on the left represent neuronal activity in response the large reward (0.4 ml). Bars on the right represent neuronal activity in response to the small reward (0.1 ml). Inset illustrates PSTHs of an example neuron in response to small and large rewards. Horizontal bars in the inset indicate the temporal window used for computing bar plots (large rewards: 0.1–0.55 s after the reward onset, small rewards: 0.2–0.45 s after the reward onset). Error bars represent s.e.m across neurons (n = 99, pooled from monkeys A and B).
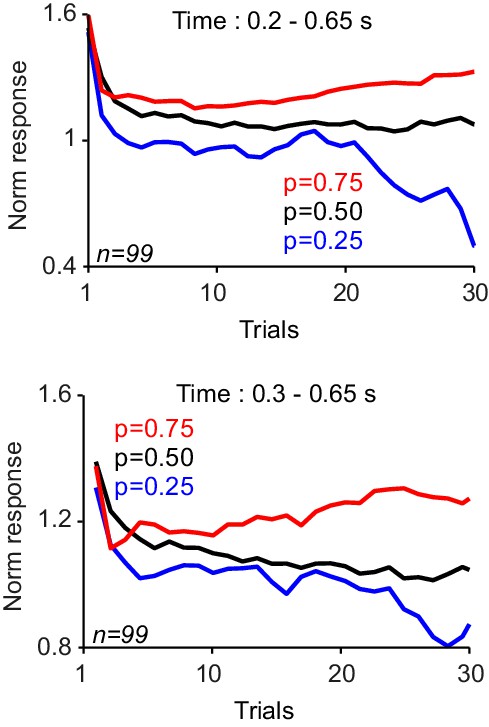
Neuronal responses to cue in the choice task.
The responses were averaged in the time window indicated in each panel. In each panel, only trials in which animal chose the novel cue were shown. Responses very early after cue onset only reflect the novelty of stimuli (Figure 6A). However, later component of dopamine response reflected both novelty signals as well as learned values. Finally the very late part of neuronal responses reflected only learned values (Figure 6B).
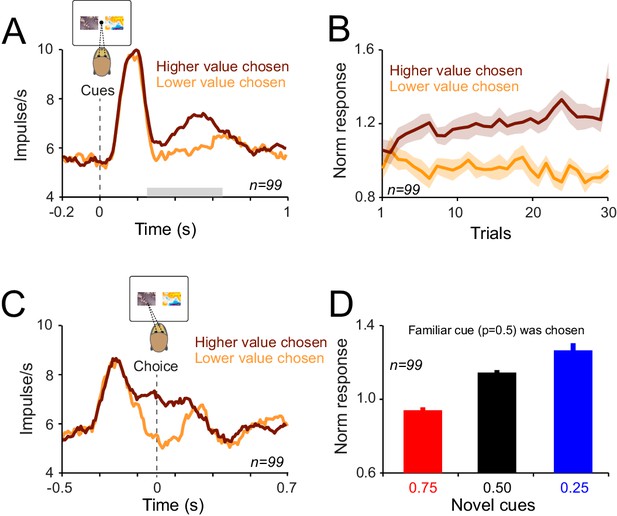
During learning dopamine neurons acquire choice-sensitive responses which emerge prior to response initiation.
(A) Population dopamine PSTHs to cues in the choice task. Grey horizontal bar indicates the temporal window used for statistical analysis. In all plots, all trials of learning blocks are included. Note that the results would be similar after excluding initial trials of each learning session. (B) Population dopamine responses to cues (0.4–0.65 s after the cue onset) over consecutive choice trials. Trials are separated based on animal’s choice. (C) Population dopamine PSTHs aligned to the saccade initiation (i.e. the time on which animal terminated the central fixation to make a saccade towards one of the cues). Dopamine choice-sensitive responses appeared ~130 ms prior to saccade initiation. (D) Averaged neuronal population responses to cues in trials in which animals chose the familiar cue. Despite the fact that animal had extensive experience with the familiar cue (and hence accurate estimate of its value), neuronal responses showed dependency on the value of the unchosen cue. See Figure 7—figure supplement 1 for the time course of this effect over consecutive trials of learning.
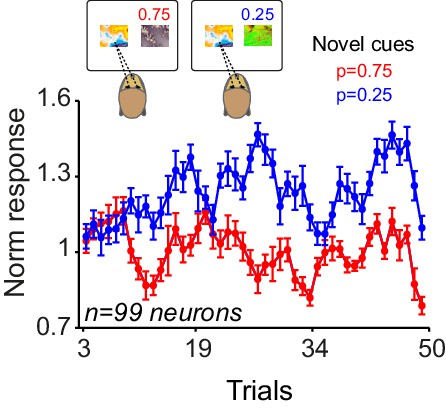
Population dopamine responses to cues over trials in which animals chose the familiar cue over the novel cues.
After nine choice trials, neuronal responses showed dependency to the value of the unchosen cue. Responses to cues at first and second trials are not shown because in these trials animals almost never chose the familiar cue (see Figure 5B).
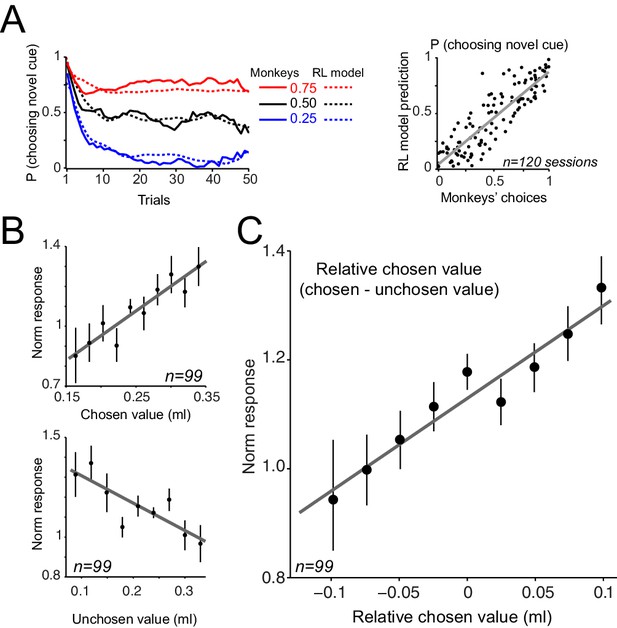
Dopamine neurons encode relative chosen values.
(A) Left: Animals choices were simulated using standard reinforcement learning (RL) models (see Figure 8—figure supplements 1 and 2 and Materials and methods). Dotted lines show the performance of the model in predicting monkeys’ choices. Solid lines show monkeys’ choice behaviour (identical to Figure 5B). The parameters of the RL model were separately optimized for each behavioural session (Supplementary file 2). Right: The RL model’s session-by-session probability of choosing the novel cue, estimated using model’s optimized parameters, versus monkeys’ session-by-session probability of choosing the novel cue. (B) Upper panel: Regression of neuronal population responses to cues onto trial-by-trial chosen values estimated from the RL model fitted on monkeys’ choice data. Lower panel: Regression of neuronal population responses to cues onto trial-by-trial unchosen values estimated from the RL model fitted on the choice data. (C) Regression of neuronal population responses to cues onto trial-by-trial relative chosen values (i.e. chosen value – unchosen value) estimated from the RL model fitted on the choice data. Importantly, the chosen and unchosen value variables were not, on average, strongly correlated (r = −0.039, Pearson’s correlation), and we excluded from this analysis sessions in which the absolute value of the correlation coefficient between the chosen and unchosen variables was larger than 0.25. In B and C, the neuronal responses were measured 0.4–0.65 s after cue onset (i.e. dopamine value signals) and are regressed against value estimates of the superior model. In explaining the neuronal responses, relative chosen value outperformed other variables in all six models tested. See Figure 8—figure supplement 2B for regression of responses measured 0.1–0.2 s after cue onset (i.e dopamine novelty responses) onto model-driven novelty estimates. Regression of whole neuronal responses (0.1–0.65 s after the cue onset) against value estimates of the RL model further confirmed relative chosen value as the best explanatory variables (R2 = 0.57, 0.61 and 0.83 for unchosen, chosen and relative chosen values). In all plots, all trials of learning blocks are included (regression results are similar after excluding initial (i.e. 5) trials of each session).
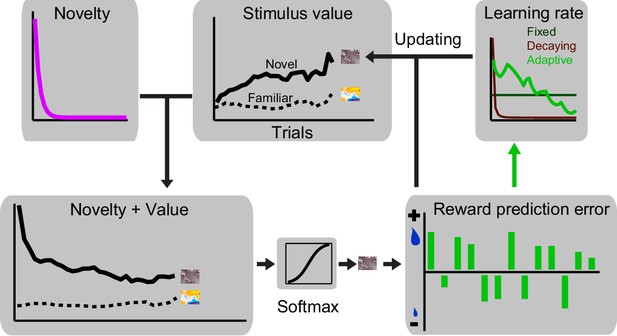
Schematic of the RL model used for simulating monkeys’ choice behaviour.
In each trial, the model makes a choice by comparing values associated with familiar and novel cues (for models with novelty term: value vs novelty + value associated with familiar and novel cues are compared). Upon receiving the outcome, the model computes a prediction error, i.e. the difference between received outcome and prior expectation, which is used to update the value of chosen option. We fit six variations of RL models on monkeys’ choices, differing in their learning rate parameter and in having/not having a novelty term. See Materials and methods and Supplementary file 2 for details of the model implementation.
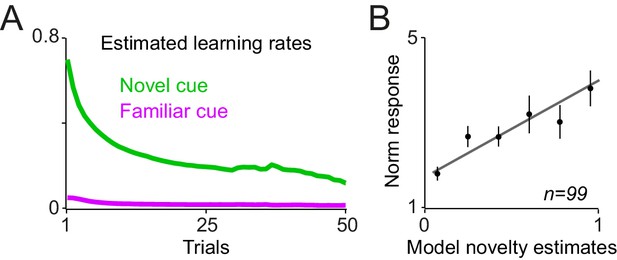
Estimated learning rates of the RL model and regression of dopamine novelty responses to model-driven novelty estimates.
(A) Average estimated learning rates of the superior model for familiar and novel cues. (B) Regression of neuronal population responses measured 0.1–0.2 s after the cue onset onto novelty estimates of the superior model.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Estimated parameters for six RL models fitted on dopamine responses in the Pavlovian task.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18044.017
-
Supplementary file 2
Estimated parameters for six RL models fitted on monkeys’ choices.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18044.018





