Epidemiology and burden of multidrug-resistant bacterial infection in a developing country
Figures
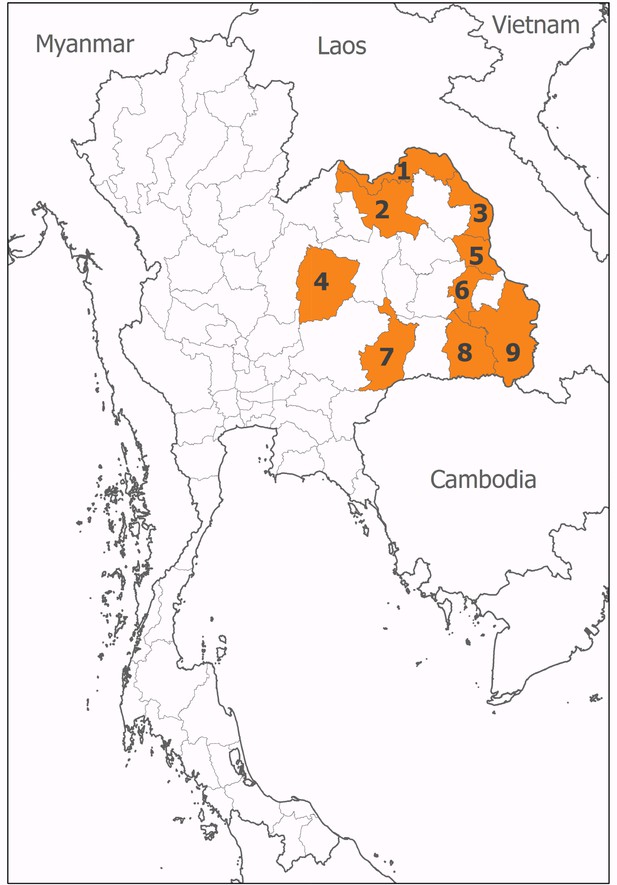
Location of participating hospitals.
These were situated in (1) Nong Khai, (2) Udon Thani, (3) Nakhon Phanom, (4) Chaiyaphum, (5) Mukdahan, (6) Yasothon, (7) Burirum, (8) Sisaket, and (9) Ubon Ratchathani provinces.
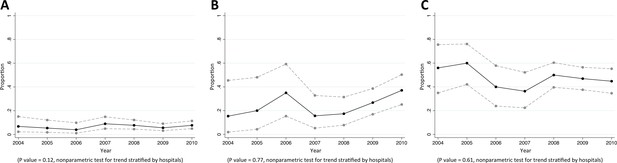
Trends in proportions of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia being caused by MRSA in Northeast Thailand.
(A) community-acquired, (B) healthcare-associated and (C) hospital-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia.
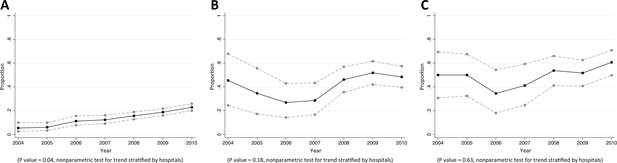
Trends in proportions of Escherichia coli bacteraemia being caused by E. coli non-susceptible to extended-spectrum cephalosporins in Northeast Thailand.
(A) community-acquired, (B) healthcare-associated and (C) hospital-acquired E. coli bacteraemia.
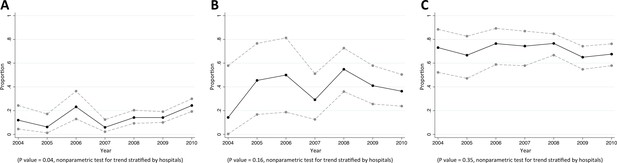
Trends in proportions of Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteraemia being caused by K. pneumoniae non-susceptible to extended-spectrum cephalosporins in Northeast Thailand.
(A) community-acquired, (B) healthcare-associated and (C) hospital-acquired K. pneumoniae bacteraemia.
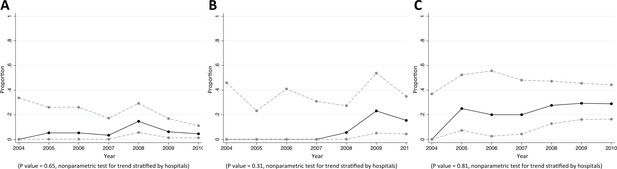
Trends in proportions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteraemia being caused by P. aeruginosa non-susceptible to carbapenem in Northeast Thailand.
(A) community-acquired, (B) healthcare-associated and (C) hospital-acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteraemia.
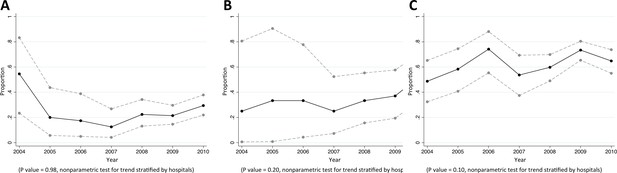
Trends in proportions of Acinetobacter spp bacteraemia being caused by Acinetobacter spp non-susceptible to carbapenem in Northeast Thailand.
(A) community-acquired, (B) healthcare-associated and (C) hospital-acquired Acinetobacter spp bacteraemia.
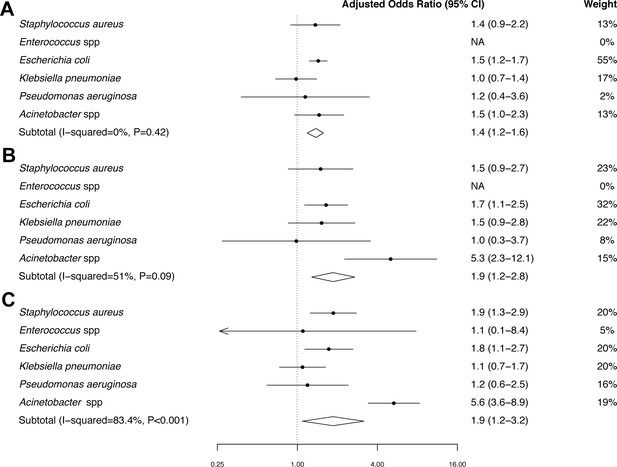
Forest plot of mortality in patients with MDR bacteraemia compared with non-MDR bacteraemia in Northeast Thailand.
(A) Community-acquired bacteraemia. (B) Healthcare-associated bacteraemia. (C) Hospital-acquired bacteraemia.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Mortality in patients with MDR and non-MDR bacteraemia in Northeast Thailand.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18082.017
Tables
Proportions of bacteraemias being caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) variants of those bacteria.
| Pathogens | Community-acquired bacteraemia (CAB) | Healthcare-associated bacteraemia (HCAB) | Hospital-acquired bacteraemia (HAB) | p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDR Staphylococcus aureus | 94/1176 (8%) | 73/259 (28%) | 222/446 (50%) | <0.001 |
| MDR Enterococcus spp | 0/176 (0%) | 0/49 (0%) | 4/117 (3%) | 0.02 |
| MDR Escherichia coli | 1177/3382 (35%) | 288/494 (58%) | 252/403 (63%) | <0.001 |
| MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae | 146/1010 (14%) | 71/196 (36%) | 301/455 (66%) | <0.001 |
| MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 13/286 (5%) | 10/103 (10%) | 45/179 (25%) | <0.001 |
| MDR Acinetobacter spp | 125/449 (28%) | 58/115 (50%) | 374/501 (75%) | <0.001 |
-
NOTE: CAB was defined as the isolation of a pathogenic bacterium from blood taken in the first 2 days of admission and without a hospital stay in the 30 days prior to admission. HCAB was defined as the isolation of a pathogenic bacterium from blood taken in the first 2 days of admission and with a hospital stay within 30 days prior to the admission. HAB was defined as the isolation of a pathogenic bacterium from blood taken after the first 2 days of admission.
Antibiogram of S. aureus causing bacteraemia in Northeast Thailand.
| Antibiotic category | Antibiotic agents | CAB (n = 1176 patients) | HCAB (n = 259 patients) | HAB (n = 446 patients) | p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 24/484 (5%) | 16/84 (19%) | 66/151 (44%) | <0.001 |
| Ansamycins | Rifampin | 2/129 (2%) | 1/19 (5%) | 0/38 (0%) | 0.37 |
| Anti-MRSA cephalosporins | Ceftaroline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Cefamycins | Oxacillin * | 80/1145 (7%) | 67/247 (27%) | 210/441 (48%) | <0.001 |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 3/45 (7%) | 2/8 (25%) | 4/10 (40%) | 0.01 |
| Moxifloxacin | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Folate pathway inhibitors | Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole | 99/1139 (9%) | 57/251 (23%) | 185/438 (42%) | <0.001 |
| Fucidanes | Fusidic acid | 33/618 (5%) | 4/170 (2%) | 12/291 (4%) | 0.26 |
| Glycopeptides | Vancomycin † | 4/833 (0.5%) | 0/190 (0%) | 2/357 (1%) | 0.86 |
| Teicoplanin | 2/66 (3%) | 1/17 (6%) | 0/17 (0%) | 0.72 | |
| Telavancin | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Glycylcyclines | Tigecycline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Lincosamides | Clindamycin | 118/1147 (10%) | 77/251 (31%) | 202/438 (46%) | <0.001 |
| Lipopeptides | Daptomycin | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | 138/1116 (12%) | 76/240 (32%) | 222/429 (52%) | <0.001 |
| Oxazolidinones | Linezolid | 0/81 (0%) | 0/16 (0%) | 0/32 (0%) | - |
| Phenicols | Chloramphenicol | 6/86 (7%) | 4/24 (17%) | 2/14 (14%) | 0.21 |
| Phosphonic acids | Fosfomycin | 14/361 (4%) | 10/66 (15%) | 24/141 (17%) | <0.001 |
| Streptogramins | Quinupristin-dalfopristin | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Doxycycline | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Minocycline | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| MDR | 94/1176 (8%) | 73/259 (28%) | 222/446 (50%) | <0.001 |
-
NOTE: Data are number of isolates demonstrating non-susceptible to the antimicrobial over the total number of isolates tested (%). CAB = Community-acquired bacteraemia, HCAB = Healthcare-associated bacteraemia, HAB = Hospital-acquired bacteraemia, and NA = Not available. The first isolate of each patient was used. MDR (one or more of these have to apply): (i) an MRSA is always considered MDR by virtue of being an MRSA (ii) non-susceptible to ≥1 agent in ≥3 antimicrobial categories.
-
* Defined by using a 30 μg cefoxitin disc and an inhibition zone diameter of <21 mm.
-
† Defined by using a 30 μg vancomycin disc and an inhibition zone diameter of <15 mm.
Antibiogram of Enterococcus spp. causing bacteraemia in Northeast Thailand.
| Antibiotic category | Antibiotic agents | CAB (n = 176 patients) | HCAB (n = 49 patients) | HAB (n = 117 patients) | p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin (high level) | 35/153 (23%) | 24/45 (53%) | 63/101 (62%) | <0.001 |
| Streptomycin | Streptomycin (high level) | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Carbapenems* | Imipenem | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Meropenem | 1/1 (100%) | NA | 3/5 (60%) | >0.99 | |
| Doripenem | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 37/44 (84%) | 9/10 (90%) | 31/37 (84%) | >0.99 |
| Levofloxacin | 5/18 (28%) | 1/6 (17%) | 11/15 (73%) | 0.01 | |
| Moxifloxacin | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Glycopeptides | Vancomycin | 9/176 (5%) | 0/49 (0%) | 6/113 (5%) | 0.27 |
| Teicoplanin | 0/11 (0%) | 0/4 (0%) | 0/10 (0%) | - | |
| Glycylcyclines | Tigecycline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Lipopeptides | Daptomycin | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Oxazolidinones | Linezolid | 0/8 (0%) | 0/2 (0%) | 0/4 (0%) | - |
| Penicillins | Ampicillin | 20/134 (15%) | 6/37 (16%) | 34/81 (42%) | <0.001 |
| Streptogramins* | Quinupristin-dalfopristin | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Tetracycline | Doxycycline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Minocycline | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| MDR | 0/176 (0%) | 0/49 (0%) | 4/117 (3%) | 0.02 |
-
NOTE: Data are number of isolates demonstrating non-susceptible to the antimicrobial over the total number of isolates tested (%). CAB = Community-acquired bacteraemia, HCAB = Healthcare-associated bacteraemia, HAB = Hospital-acquired bacteraemia, and NA = Not available. The first isolate of each patient was used. MDR: non-susceptible to ≥1 agent in ≥3 antimicrobial categories.
-
*Intrinsic resistance in E. faecium against carbapenems and in E. faecalis against streptogramins. When a species has intrinsic resistance to an antimicrobial category, that category is removed prior to applying the criteria for the MDR definition and is not counted when calculating the number of categories to which the bacterial isolate is non-susceptible.
Antibiogram of E. coli causing bacteraemia in Northeast Thailand.
| Antibiotic category | Antibiotic agents | CAB (n = 3382 patients) | HCAB (n = 494 patients) | HAB (n = 403 patients) | p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 559/3346 (17%) | 166/484 (34%) | 178/398 (45%) | <0.001 |
| Tobramycin | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Amikacin | 72/2685 (3%) | 26/397 (7%) | 32/326 (10%) | <0.001 | |
| Netilmicin | 68/1394 (5%) | 25/259 (10%) | 42/254 (17%) | <0.001 | |
| Anti-MRSA cephalosporins | Ceftaroline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Antipseudomonal penicillins + β lactamase inhibitors | Ticarcillin-clauvanic acid | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 23/511 (5%) | 10/103 (10%) | 15/89 (17%) | <0.001 | |
| Carbapenems | Ertapenem | 4/1325 (<1%) | 1/235 (<1%) | 4/205 (2%) | 0.02 |
| Imipenem | 3/2449 (<1%) | 0/386 (0%) | 3/344 (1%) | 0.04 | |
| Meropenem | 0/1988 (0%) | 1/314 (<1%) | 1/244 (<1%) | 0.05 | |
| Non-extended spectrum cephalosporins | Cefazolin | 468/1095 (43%) | 115/174 (66%) | 80/102 (78%) | <0.001 |
| Cefuroxime | 219/1438 (15%) | 96/226 (42%) | 102/202 (50%) | <0.001 | |
| Extended-spectrum cephalosporins | Cefotaxime | 501/3076 (16%) | 199/455 (44%) | 185/361 (51%) | <0.001 |
| Ceftazidime | 392/3020 (13%) | 165/446 (37%) | 164/351 (47%) | <0.001 | |
| Cefepime | 30/293 (10%) | 12/42 (29%) | 18/53 (34%) | <0.001 | |
| Cephamycins | Cefoxitin | 36/1200 (3%) | 16/215 (7%) | 16/195 (8%) | <0.001 |
| Cefotetan | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 728/3000 (24%) | 221/452 (49%) | 171/384 (45%) | <0.001 |
| Folate pathway inhibitors | Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole | 1738/3007 (58%) | 294/442 (67%) | 225/350 (64%) | <0.001 |
| Glycylcyclines | Tigecycline | 0/7 (0%) | NA | 0/1 (0%) | - |
| Monobactams | Aztreonam | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Penicillins | Ampicillin | 2246/2843 (79%) | 371/420 (88%) | 301/342 (88%) | <0.001 |
| Penicillins + β lactamase inhibitors | Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid | 790/3074 (26%) | 191/463 (41%) | 158/373 (42%) | <0.001 |
| Ampicillin-sulbactam | 83/296 (28%) | 18/48 (38%) | 12/25 (48%) | 0.06 | |
| Phenicols | Chloramphenicol | 14/63 (22%) | 1/4 (25%) | 3/5 (60%) | 0.14 |
| Phosphonic acids | Fosfomycin | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Polymyxins | Colistin* | 2/34 (6%) | 0/6 (0%) | 1/6 (17%) | 0.61 |
| MDR | 1177/3382 (35%) | 288/494 (58%) | 252/403 (63%) | <0.001 |
-
NOTE: Data are number of isolates demonstrating non-susceptible to the antimicrobial over the total number of isolates tested (%). CAB = Community-acquired bacteraemia, HCAB = Healthcare-associated bacteraemia, HAB = Hospital-acquired bacteraemia, and NA = Not available. The first isolate of each patient was used. MDR: non-susceptible to ≥1 agent in ≥3 antimicrobial categories.
-
*Defined by using an inhibition zone of <11 mm.
Antibiogram of K. pneumoniae causing bacteraemia in Northeast Thailand.
| Antibiotic category | Antibiotic agents | CAB (n = 1010 patients) | HCAB (n = 196 patients) | HAB (n = 455 patients) | p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 94/999 (9%) | 53/193 (27%) | 265/444 (60%) | <0.001 |
| Tobramycin | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Amikacin | 17/815 (2%) | 12/157 (8%) | 109/398 (27%) | <0.001 | |
| Netilmicin | 20/450 (4%) | 23/112 (21%) | 124/320 (39%) | <0.001 | |
| Anti-MRSA cephalosporins | Ceftaroline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Antipseudomonal penicillins + β lactamase inhibitors | Ticarcillin-clauvanic acid | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 24/166 (14%) | 14/32 (44%) | 73/121 (60%) | <0.001 | |
| Carbapenems | Ertapenem | 2/432 (0%) | 1/100 (1%) | 5/264 (2%) | 0.17 |
| Imipenem | 1/778 (0%) | 1/164 (1%) | 2/408 (0%) | 0.24 | |
| Meropenem | 0/583 (0%) | 1/113 (1%) | 2/317 (1%) | 0.10 | |
| Non-extended spectrum cephalosporins | Cefazolin | 76/319 (24%) | 30/60 (50%) | 101/127 (80%) | <0.001 |
| Cefuroxime | 81/478 (17%) | 35/98 (36%) | 161/231 (70%) | <0.001 | |
| Extended-spectrum cephalosporins | Cefotaxime | 146/902 (16%) | 71/173 (41%) | 298/424 (70%) | <0.001 |
| Ceftazidime | 124/927 (13%) | 63/176 (36%) | 295/430 (69%) | <0.001 | |
| Cefepime | 5/100 (5%) | 8/22 (36%) | 25/51 (49%) | <0.001 | |
| Cephamycins | Cefoxitin | 15/396 (4%) | 10/95 (11%) | 14/230 (6%) | 0.03 |
| Cefotetan | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 143/894 (16%) | 66/176 (38%) | 187/430 (43%) | <0.001 |
| Folate pathway inhibitors | Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole | 198/876 (23%) | 69/171 (40%) | 219/407 (54%) | <0.001 |
| Glycylcyclines | Tigecycline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Monobactams | Aztreonam | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Penicillins + β lactamase inhibitors | Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid | 131/945 (14%) | 68/183 (37%) | 291/443 (66%) | <0.001 |
| Ampicillin-sulbactam | 20/105 (19%) | 9/17 (53%) | 23/38 (61%) | <0.001 | |
| Phenicols | Chloramphenicol | 4/19 (21%) | 0/2 (0%) | 0/3 (0%) | >0.99 |
| Phosphonic acids | Fosfomycin | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Polymyxins | Colistin * | 0/6 (0%) | 0/2 (0%) | 0/5 (0%) | - |
| MDR | 146/1010 (14%) | 71/196 (36%) | 301/455 (66%) | <0.001 |
-
NOTE: Data are number of isolates demonstrating non-susceptible to the antimicrobial over the total number of isolates tested (%). CAB = Community-acquired bacteraemia, HCAB = Healthcare-associated bacteraemia, HAB = Hospital-acquired bacteraemia, and NA = Not available. The first isolate of each patient was used. MDR: non-susceptible to ≥1 agent in ≥3 antimicrobial categories.
-
* Defined by using an inhibition zone of <11 mm.
Antibiogram of P. aeruginosa causing bacteraemia in Northeast Thailand.
| Antibiotic category | Antibiotic agents | CAB (n = 286 patients) | HCAB (n = 103 patients) | HAB (n = 179 patients) | p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 29/235 (12%) | 13/88 (15%) | 60/140 (43%) | <0.001 |
| Tobramycin | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Amikacin | 27/284 (10%) | 13/100 (13%) | 48/177 (27%) | <0.001 | |
| Netilmicin | 8/155 (5%) | 5/67 (7%) | 34/120 (28%) | <0.001 | |
| Antipseudomonal carbapenems | Imipenem | 14/238 (6%) | 6/86 (7%) | 37/154 (24%) | <0.001 |
| Meropenem | 9/163 (6%) | 8/73 (11%) | 24/125 (19%) | 0.001 | |
| Doripenem | 2/17 (12%) | 0/3 (0%) | 2/2 (100%) | 0.04 | |
| Antipseudomonal cephalosporins | Ceftazidime | 29/280 (10%) | 16/103 (16%) | 68/179 (38%) | <0.001 |
| Cefepime | 2/36 (6%) | 2/18 (11%) | 10/28 (36%) | 0.01 | |
| Antipseudomonal fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 24/275 (9%) | 12/101 (12%) | 39/169 (23%) | <0.001 |
| Levofloxacin | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) | 1/1 (100%) | >0.99 | |
| Antipseudomonal penicillins + β lactamase inhibitors | Ticarcillin-clauvanic acid | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 8/85 (9%) | 6/38 (16%) | 8/46 (17%) | 0.37 | |
| Monobactams | Aztreonam | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Phosphonic acids | Fosfomycin | 1/1 (100%) | NA | NA | - |
| Polymyxins | Colistin | 0/7 (0%) | 0/3 (0%) | 1/7 (14%) | >0.99 |
| Polymyxin B | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| MDR | 13/286 (5%) | 10/103 (10%) | 45/179 (25%) | <0.001 |
-
NOTE: Data are number of isolates demonstrating non-susceptible to the antimicrobial over the total number of isolates tested (%). CAB = Community-acquired bacteraemia, HCAB = Healthcare-associated bacteraemia, HAB = Hospital-acquired bacteraemia, and NA = Not available. The first isolate of each patient was used. MDR: non-susceptible to ≥1 agent in ≥3 antimicrobial categories.
Antibiogram of Acinetobacter spp. causing bacteraemia in Northeast Thailand.
| Antibiotic category | Antibiotic agents | CAB (n = 449 patients) | HCAB (n = 115 patients) | HAB (n = 501 patients) | p values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 112/390 (29%) | 45/105 (43%) | 310/455 (68%) | <0.001 |
| Tobramycin | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Amikacin | 123/442 (28%) | 45/112 (40%) | 310/495 (63%) | <0.001 | |
| Netilmicin | 44/203 (22%) | 24/64 (38%) | 224/381 (59%) | <0.001 | |
| Antipseudomonal carbapenems | Imipenem | 87/397 (22%) | 37/102 (36%) | 293/459 (64%) | <0.001 |
| Meropenem | 65/284 (23%) | 32/81 (40%) | 229/348 (66%) | <0.001 | |
| Doripenem | 16/45 (36%) | 9/10 (90%) | 6/7 (86%) | 0.001 | |
| Antipseudomonal fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 84/413 (20%) | 53/106 (50%) | 322/481 (67%) | <0.001 |
| Levofloxacin | 2/5 (40%) | 2/2 (100%) | 8/9 (89%) | 0.11 | |
| Antipseudomonal penicillins + β lactamase inhibitors | Ticarcillin- clauvanic acid | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 22/98 (22%) | 13/28 (46%) | 74/106 (70%) | <0.001 | |
| Extended-spectrum cephalosporins | Cefotaxime | 242/291 (83%) | 89/94 (95%) | 407/420 (97%) | <0.001 |
| Ceftazidime | 133/448 (30%) | 61/114 (54%) | 377/500 (75%) | <0.001 | |
| Cefepime | 18/53 (34%) | 10/22 (45%) | 95/133 (71%) | <0.001 | |
| Folate pathway inhibitor | Trimethopri-sulphamethoxazole | 119/356 (33%) | 55/99 (56%) | 333/435 (77%) | <0.001 |
| Penicillins + β lactamase inhibitors | Ampicillin-sulbactam | 43/134 (32%) | 16/29 (55%) | 79/115 (69%) | <0.001 |
| Polymyxins | Colistin * | 2/16 (13%) | 0/14 (0%) | 0/33 (0%) | 0.11 |
| Polymyxin B | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | NA | NA | NA | - |
| Doxycycline | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| Minocycline | NA | NA | NA | - | |
| MDR | 125/449 (28%) | 58/115 (50%) | 374/501 (75%) | <0.001 |
-
NOTE: Data are number of isolates demonstrating non-susceptible to the antimicrobial over the total number of isolates tested (%). CAB = Community-acquired bacteraemia, HCAB = Healthcare-associated bacteraemia, HAB = Hospital-acquired bacteraemia, and NA = Not available. The first isolate of each patient was used. MDR: non-susceptible to ≥1 agent in ≥3 antimicrobial categories.
-
* Defined by using an inhibition zone of <11 mm.
Estimates of mortality attributable to multidrug-resistance (MDR) in hospital-acquired infection (HAI) in Thailand.
| Pathogens | No of patients* | Estimated mortality (%)† | Estimated mortality if the infections were caused by non-MDR organisms (%)†, ‡ | Estimated excess mortality caused by MDR (%)†, ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDR Staphylococcus aureus | 18,725 | 8262 (44%) | 5463 (29%) | 2799 (15%) |
| MDR Escherichia coli | 11,116 | 2163 (19%) | 1566 (14%) | 597 (5%) |
| MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae | 15,239 | 5267 (35%) | 4979 (33%) | 288 (2%) |
| MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 6118 | 3966 (65%) | 3696 (60%) | 270 (4%) |
| MDR Acinetobacter spp | 36,553 | 25,551 (70%) | 10,383 (28%) | 15,168 (41%) |
| Total | 87,751 | 45,209 (52%) | 26,087 (30%) | 19,122 (22%) |
-
*Cumulative incidence of antimicrobial resistant HAI in Thailand 2010 estimated by Pumart et al. (2012).
-
†All parameters used to estimate the mortality and excess mortality are shown in Supplementary file 2.
-
‡Excess mortality caused by MDR (mortality attributable to MDR) was defined as the difference in mortality of patients with MDR infection and their mortality if they were infected with non-MDR infections.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Factors associated with 30-day mortality of bacteraemia patients.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18082.019
-
Supplementary file 2
Parameters used to estimate mortality attributable to multidrug-resistance in Thailand.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18082.020





