Functional diversity of excitatory commissural interneurons in adult zebrafish
Figures
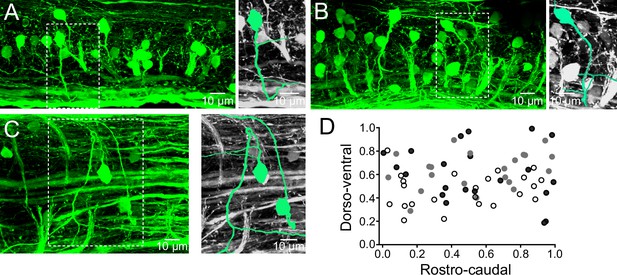
Distribution of V0v interneurons in the spinal cord.
(A,B) Lateral views of a spinal segment from two different preparations showing the distribution of GFP-expressing V0v interneurons. Images are the maximum intensity projections from 164 and 193 optical sections respectively. Most V0v interneurons project ventrally before crossing the midline as indicated in expansions (right panels). (C) Dorsal view of the spinal cord showing two V0v interneurons and their crossing axonal projections (neurons are colored and expanded in the right panels for clarification). The image is the maximum intensity projections from 90 optical sections (D) Graph showing the dorso-ventral and rostro-caudal distribution of V0v interneurons within one hemisegment. Data are from three different preparations (black, grey and open circles). The ventral edge is defined as 0 and the dorsal edge as 1. V0v interneurons are evenly distributed along the rostro-caudal axis, with an average of 21 ± 6 neurons per hemisegment (mean ± SEM).
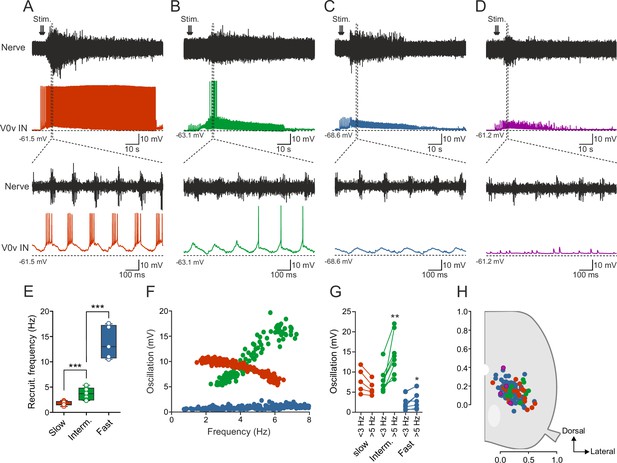
Activity of V0v interneurons during locomotion.
Slow (red), intermediate (green), fast (light blue) and non-patterned (purple) V0v interneurons show different activity patterns during locomotion. (A) Recording from a V0v interneuron that was active already at a slow swimming frequency and remained recruited at high frequencies. (B) Recording from a V0v interneuron that was not active at slow swimming frequencies and became recruited only at intermediate and high frequencies. (C) Recording from a V0v interneuron that only displayed subthreshold membrane potential oscillations that did not reach the firing threshold at slow and intermediate swimming frequencies. (D) Recording from a V0v interneuron whose activity was non-patterned by swimming activity. (E) Recruitment frequency was significantly different between the three subtypes of V0v interneurons with patterned membrane potential oscillations during swimming activity (one-way ANOVA, F(2, 28) = 123.3, p<0.0001; followed by Tukey’s procedure as post hoc; graph displays means and SEM; n = 17 from 16 preparations, 9 from 8 preparations and 5 from 5 preparations for slow, intermediate and fast, respectively). (F) The amplitude of the membrane potential oscillations of the three (slow, intermediate and fast) rhythmically active V0v interneurons varied with swimming frequency. (G) The membrane oscillation amplitude increased significantly between slow (<3 Hz) and intermediate (>5 Hz) swimming frequencies for the V0v interneurons recruited at intermediate and fast swimming frequencies (Student’s paired t-test; p=0.035 for slow, p=0.0029 for intermediate, p=0.018 for fast; n = 5 from 5 preparations, 8 from 8 preparations, and 9 from 7 preparations for slow, intermediate and fast, respectively). (H) There is no topographic organization of the somata of the different V0v interneurons in the spinal motor column. There was no significant difference (one-way ANOVA, F(3, 115) = 2.129, p>0.05) between the soma size of the different sub-classes (slow: 40.4 ± 1.5; intermediate: 44.5 ± 3.0; fast: 41.8 ± 1.2; and unpatterned: 53.3 ± 9.9).
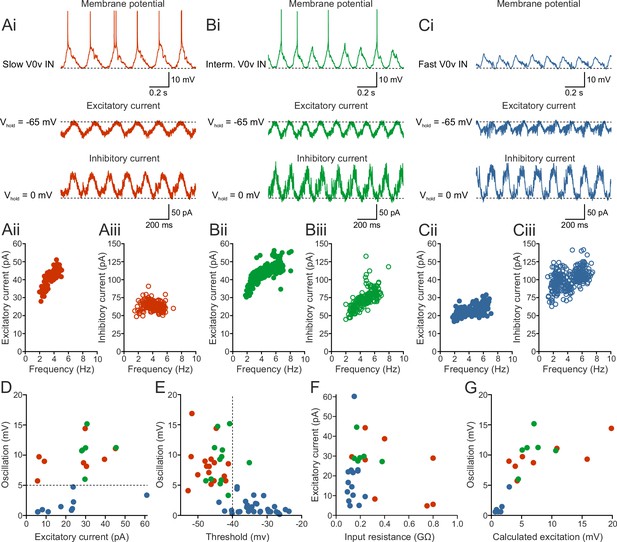
Recruitment order is determined by synaptic input and intrinsic properties.
(Ai–Ci) The patterned activity of the V0v interneurons was mediated by rhythmic and alternating excitatory and inhibitory currents. (Aii–Ciii) Both the excitatory and inhibitory current amplitude was dependent on the swim frequency, but did not vary significantly between the three V0v interneuron subtypes for excitatory currents (one-way ANOVA F(2,26) = 2.13, p>0.05; Tukey’s procedure as post hoc; n = 8 from 8 preparations, 6 from 5 and 15 from 15 preparations for slow, intermediate and fast respectively) and only between intermediate and fast for the inhibitory currents (one-way ANOVA F(2,24) = 5.21, p<0.05; Tukey’s procedure as post hoc; n = 8 from 8 preparations, 6 from 5 preparations, and 13 from 13 preparations for slow, intermediate and fast, respectively). (D) There was no correlation between the amplitude of the membrane potential oscillations and the excitatory currents. Slow/intermediate neurons (red and green) differed significantly from fast neurons (blue) in oscillation amplitude (Student’s t-test; p<0.0001; n = 14 and 10 for slow/intermediate and fast neurons, respectively). Slow/intermediate neurons always had oscillation amplitudes above 5 mV and fast always below 5 mV (as indicated by the dashed line). (E) There was a correlation between the amplitude of the membrane potential oscillations and the firing thresholds of the different V0v interneurons. Firing thresholds of slow/intermediate (red and green) neurons were significantly different from those of fast (blue) neurons (Student’s t-test; p<0.0001; n = 26 and 28 for slow/intermediate and fast neurons, respectively). Most slow/intermediate neurons had a firing threshold below −40 mV and most fast neurons a firing threshold above −40 mV (indicated by the dashed line). (F) There was no correlation between the amplitude of the excitatory current and the input resistance of the different V0v interneurons. (G) The amplitude of the membrane potential oscillations was strongly correlated with the calculated excitatory drive received by the different V0v interneurons (linear regression, R2 = 0.52).
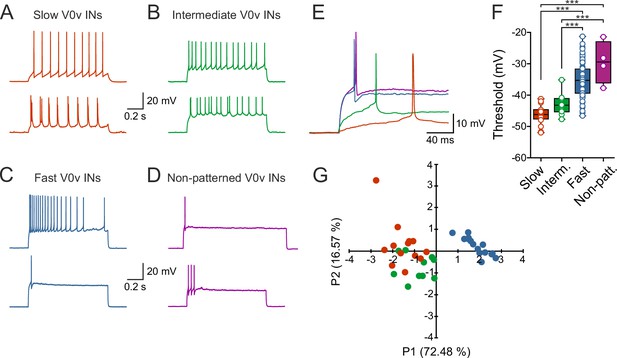
V0v interneuron sub-classes display distinct intrinsic properties.
(A–D) Examples of two different neurons from each group firing in response to an injected subthreshold current step (A) The V0v interneurons active already at slow swimming frequencies were either tonically firing or fired in bursts in response to current injections. (B) The V0v recruited at intermediate frequencies also displayed tonic firing or bursting in response to current injections. (C) The fast V0v interneurons always displayed strong adaptation. (D) The V0v interneurons with non-patterned changes in the membrane potential fired only a few action potentials and displayed strong adaptive properties. (E) The different V0v interneurons had different thresholds for firing action potentials in response to injected current. (F) The firing thresholds were significantly different from each other and correlated strongly with the recruitment order as a function of swimming frequency (one-way ANOVA F(3,104) = 33.8, p<0.0001; Tukey’s procedure as post hoc; n = 19 from 17 preparations, 11 from 11 preparations, 74 from 58 preparations, and 4 from 4 preparations for slow, intermediate, fast and non-patterned respectively). (G) A principal component analysis revealed that the V0v interneurons with patterned membrane potential oscillations could be separated from each other with those active at slow and intermediate frequencies showing partial overlap. The percentage of the total variance explained by PC1 and PC2 were 72.48 and 16.57, respectively. The percentage contribution of the different variables to PC1 and PC2, respectively, was: input resistance 20.4 and 44.9; action potential threshold 26.5 and 4.1; membrane oscillation amplitude in current clamp 21.5 and 48.6; minimum recruitment frequency 31.6 and 2.3 (n = 13 neurons from 13 preparations, 10 neurons from 9 preparations, and 15 neurons from 13 preparations for slow, intermediate and fast, respectively).
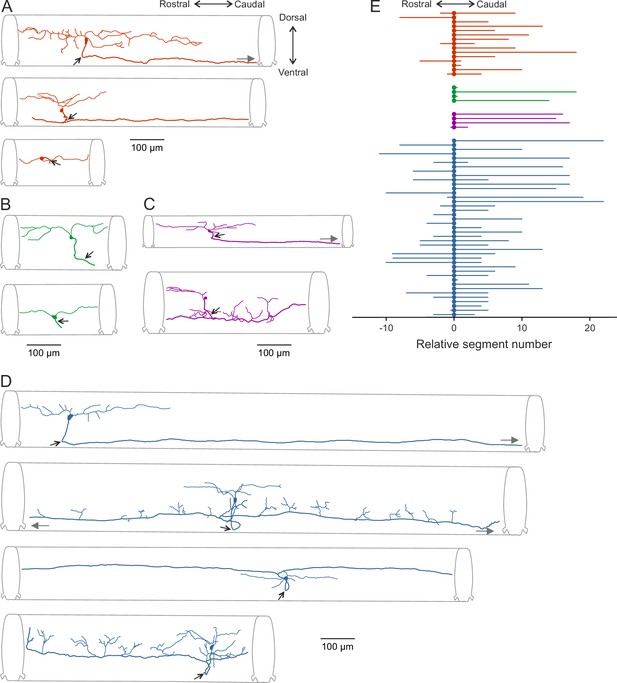
Morphological diversity of V0v interneurons.
(A–D) Examples of dye-labeled V0v interneurons. (A) Slow, (B) intermediate, (C) non-patterned, (D) fast. The morphologies of the different V0v interneurons show heterogeneity in terms of their axonal and dendritic projections. Small, black arrows indicate where the axon crosses to the contralateral side; grey, filled grey arrows indicate that the axon projects further than illustrated (E) Graph showing the range of the axonal projections of the different neurobiotin-labeled V0v interneurons.





