Fluctuations of the transcription factor ATML1 generate the pattern of giant cells in the Arabidopsis sepal
Figures
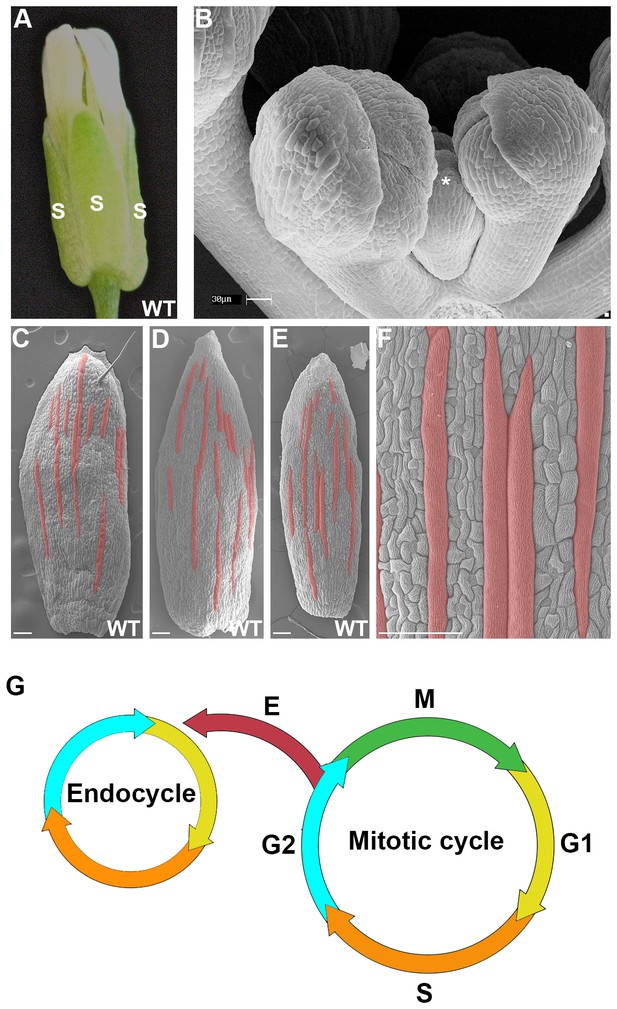
The scattered pattern of giant epidermal cells.
(A) An image of a wild-type (WT) Arabidopsis thaliana flower. The sepals (s) are the outermost leaf-like floral organs. (B) SEM image of developing sepals on young flower buds. The three flowers in the middle are in approximately the same orientation and stages as the live imaged sepals. Live images typically start with sepals at the youngest stage shown, exemplified by the center flower (*). (C–F) SEM images of mature wild-type sepals. Each sepal exhibits variations in the arrangement of giant cells. Giant cells are false colored in red using Photoshop. Magnified view of E shown in F. Scale bars in B, 30 µm and in C–F, 100 µm. (G) A cell cycle diagram depicting the mitotic cell cycle and the endoreduplication cycle (endocycle). During the mitotic cycle, a new 2C cell will enter Gap 1 (G1). In G1, the cell will increase its size in preparation for DNA synthesis (S), where it will then become 4C. After S phase, the cell will enter Gap2 (G2), where it will continue to grow in size and produce more protein in preparation for mitosis (M). Completion of mitosis will result in the formation of two 2C daughter cells, which will then re-enter the mitotic cycle. Alternatively a cell may endocycle (E), where a cell will go through G1, S, G2 but bypass M to form a polyploid cell. Note that giant cells are 8C and higher polyploid epidermal cells that form through endoreduplication.
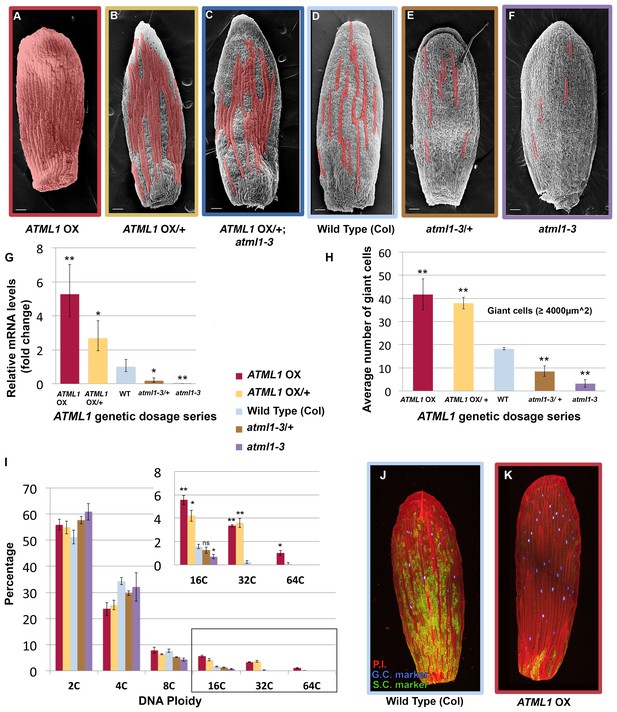
ATML1 levels influence the quantity of giant cells that form on the sepal.
(A–F) SEM images of sepals from an ATML1 genetic dosage series. Giant cells are false colored in red. (A) ATML1 overexpression line that is homozygous for the pPDF1::FLAG-ATML transgene. (B) ATML1 overexpression line that is hemizygous for the pPDF1::FLAG-ATML1 transgene. (C) ATML1 overexpression line hemizygous for the pPDF1::FLAG-ATML1 transgene crossed into a atml1–3 mutant background. (D) Wild type. (E) atml1–3/+ heterozygous mutant. (F) atml1–3 homozygous mutant. (G) qPCR on inflorescences from dosage series verifying that ATML1 mRNA levels vary between lines as expected. Fold change is calculated as the average of three biological replicates. Error bars represent the extended standard deviation. (H) Quantification of the average number of giant cells per sepal in ATML1 dosage series using semi-automated image processing. Giant cells are defined as cells with an area larger than 4000 µm2. Error bars represent the standard error of mean, n = 3 sepals per genotype, with each pooled genotype having >1000 cells analyzed. (I) Ploidy of epidermal cells in sepals of the ATML1 dosage series determined by flow cytometry. Inset shows percentage of high ploidy nuclei. Average of 3 biological replicates with >40,000 nuclei analyzed per replicate; error bars represent standard error of mean. Note that epidermal cells include a large number of 2C and 4C cells on the back (adaxial) side of the sepal in all genotypes, which are not affected by ATML1 overexpression. (J–K) Confocal maximum intensity projection image of a wild-type (J) and ATML1 overexpression (K) sepal expressing the giant (3xvenus, nuclear localized, blue) and small cell (GFP, ER localized, green) molecular markers. Cell walls are stained with propidium iodide (PI, red). In the ATML1 overexpression sepal (K), the giant cell marker is expressed in almost every cell and the small cell marker is extremely reduced. Note: Margin cells at the edges of the sepals are distinct cell types that are not affected by ATML1. Scale bars in A–F, 100 µm. T-tests were performed between genetically altered dosage series and wild-type sepals. p-value ≤ 0.05 marked with *, p-value ≤ 0.01 marked with **, and non-significant denoted by ns.
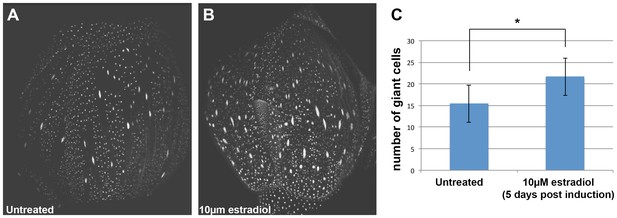
ATML1 estradiol inducible transgenic plants form ectopic giant cells five days after application of 10 µM estradiol.
(A) A confocal image of an untreated ATML1 estradiol-inducible stage 10 flower expressing an ATML1 transcriptional marker (proATML1-nls-3XGFP). Note that ATML1 transcriptional reporter is only expressed in the outermost epidermal layer. The front sepal contains approximately 17 giant cells. (B) A confocal denoised image of a 10 µM estradiol treated ATML1 estradiol-inducible stage 10 flower expressing the ATML1 transcriptional marker. Note that now the transcriptional reporter is being expressed in multiple cell layers, suggesting that ATML1 was successfully induced. The front sepal contains approximately 30 giant cells. (C) Quantification of the number of giant cells for untreated (n = 7) versus 10 µM estradiol treated (n = 7) stage 8–10 sepals. On average, estradiol treated sepals form more giant cells than their untreated counterparts. T-tests were performed between untreated and estradiol treated sepals. p-value ≤ 0.05 marked with *. Inflorescences were treated with estradiol on days 1–3 and then imaged on day 5. Associated with Figure 2.
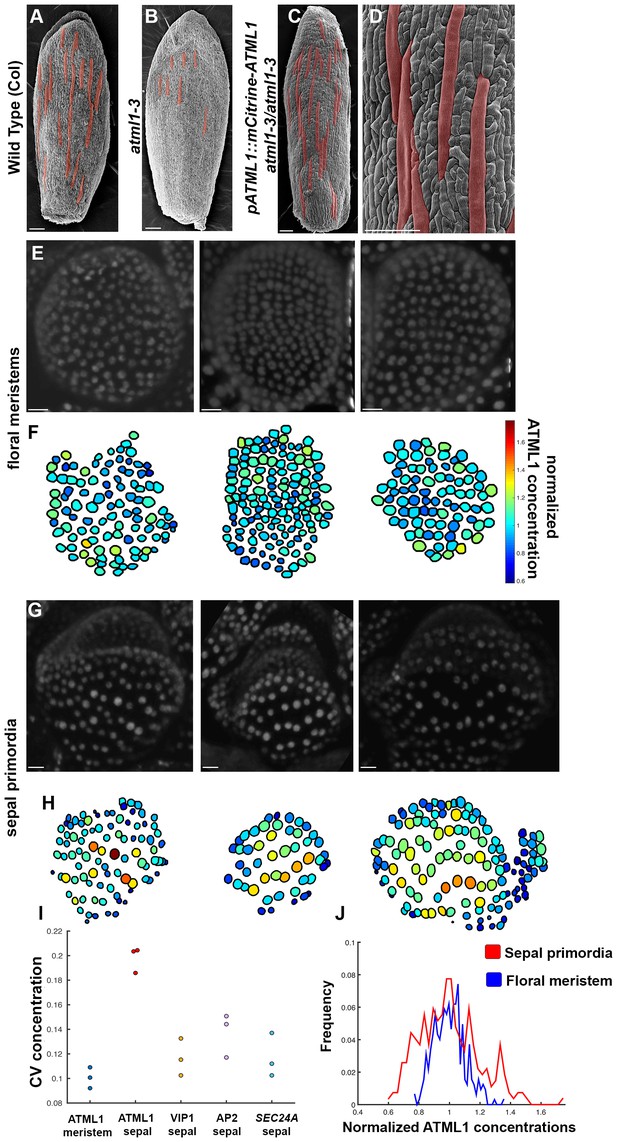
mCitrine-ATML1 expression is variable from cell to cell in the sepal but uniform in the meristem.
(A) SEM image of a wild-type (Col) sepal. (B) SEM image of an atml1–3 mutant sepal. Note that atml1 mutants exhibit a lack-of-giant-cell phenotype. (C–D) SEM images showing that the pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 transgene rescues the lack-of-giant-cell phenotype normally exhibited by the atml1–3 mutant. Additionally, both the number and spacing pattern of giant cells appear similar to wild type (A). Giant cells in (A–D) are false colored red. (E) Confocal denoised images of three floral meristems expressing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white). (F) Heat maps of mean normalized concentration levels of mCitrine-ATML1 expression in the floral meristems. (G) Confocal denoised images of three young sepal primordia expressing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white) (right most sepal is shown later in Figure 4—figure supplement 2 as time 0 hrs of the 3rd mCitrine-ATML1 reporter sepal). (H) Heat maps of mean normalized concentration levels of mCitrine-ATML1 expression in the young sepal primordia. (I) Dot plot of the coefficients of variation (CV) of normalized fluorescent protein concentration in each sample. The CV of mCitrine-ATML1 in nuclei of young developing sepals is higher than in nuclei of floral meristems. The high CV is specific to mCitrine-ATML1 as VIP1-mCitrine (pVIP1::VIP1-mCitrine), AP2-2XYpet (pAP2::AP2-2XYpet) and a SEC24A transcriptional reporter (SEC24::H2B-mGFP) have lower CVs in young sepals. n = 3 for each genotype. (J) Histograms of normalized mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations for sepals (from H; red) and meristems (from F; blue). Both histograms show a unimodal distribution, however the distribution of ATML1 concentrations in single cells is broader in the sepal than in the meristem. Scale bars in A–D 100 µm; E and G, 10 µm. The number of cells analyzed for mCitrine-ATML1 meristems from left to right: n = 102, 136 and 82. The number of cells analyzed for each mCitrine-ATML1 sepal primodium in order from left to right: n = 91, 48 and 142. Denoised images and corresponding heat maps for pSEC24A::H2B-GFP, VIP1-mCitrine and AP2-2XYpet sepals are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
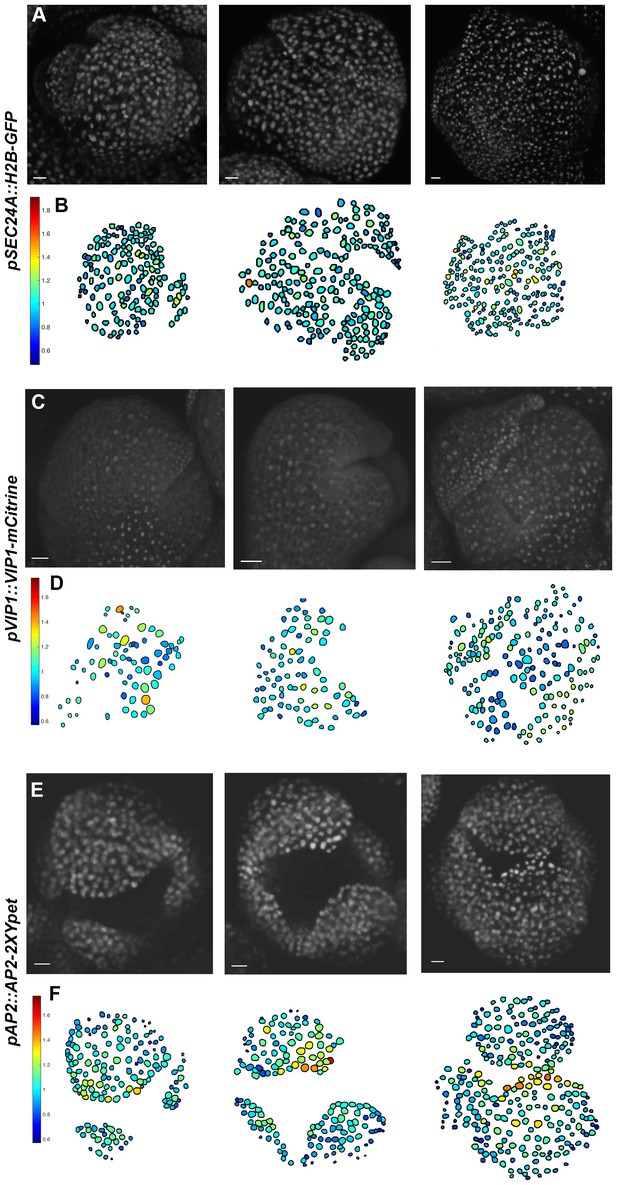
The transcriptional reporter SEC24A:: H2B-GFP and the fusion proteins VIP1-mCitrine, and AP2-2XYpet are uniformly expressed in the developing sepal.
(A) Confocal denoised images of three developing sepals expressing pSEC24A::H2B-GFP. (B) Heat maps of normalized mean concentration levels of pSEC24A::H2B-GFP expression in the developing flowers. (C) Confocal denoised images of three developing sepals expressing pVIP1::VIP1-mCitrine. (D) Heat maps of normalized mean concentration levels of pVIP1::VIP1-mCitrine expression in the developing flowers. (E) Confocal denoised images of three developing sepals expressing pAP2::AP2-2XYpet. (F) Heat maps of normalized mean concentration levels of pAP2::AP2-2XYpet expression in the developing flowers. Scalebars: A, 10 µm; C, 20 µm; E, 20 µm. pSEC24A::H2b-GFP, pVIP1::VIP1-mCitrine and pAP2::AP2-2XYpet are ubiquitously expressed in multiple cell layers. To make all three genotypes comparable to mCitrine-ATML1 flowers, only nuclei in the epidermal cell layer were used for the analysis. The number of cells analyzed for each pSEC24A::H2B-GFP sepal primordium from left to right: n = 145, 215 and 232. The number of cells analyzed for each VIP1-mCitrine sepal primordium from left to right: n = 73, 80 and 180. The number of cells analyzed for each AP2-2XYpet sepal primordium from left to right: n = 152, 160 and 262. To make all three genotypes comparable to mCitrine-ATML1 flowers, only nuclei in the epidermal cell layer were used for the analysis. Associated with Figure 3.
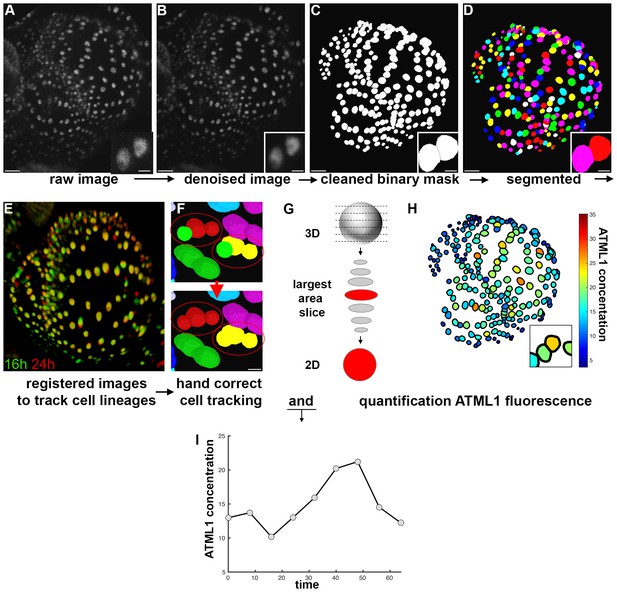
Image analysis pipeline to quantify fluorescent fusion protein concentration.
(A) Raw confocal image of developing sepal expressing mCitrine-ATML1 (sepal also presented in Figure 4). (B) Denoised confocal images using PureDenoise ImageJ software. (C) Binary mask created in MorphoGraphX. (D) Segmented image created in Costanza. (E) 3D projection of registered pairs of consecutive sepal confocal acquisitions (16 hr in green and 24 hr in red). (F) Manual correction of incorrectly tracked nuclei in MorphoGraphX. Top panel shows two examples where ALT did not correctly track one of two daughter cells. Bottom panel shows that nuclei can be manually corrected in MorphoGraphX. (G) Schematic of quantification process. A MATLAB module detects the confocal z-stack slice with largest area for each nucleus. Then, fluorescence concentration is quantified (total fluorescence divided by area) using the raw intensity z-stack. (H) Heat map of the fluorescence concentration for each nucleus on the sepal. (I) Example of ATML1 fluorescence concentration in one nucleus tracked through time.
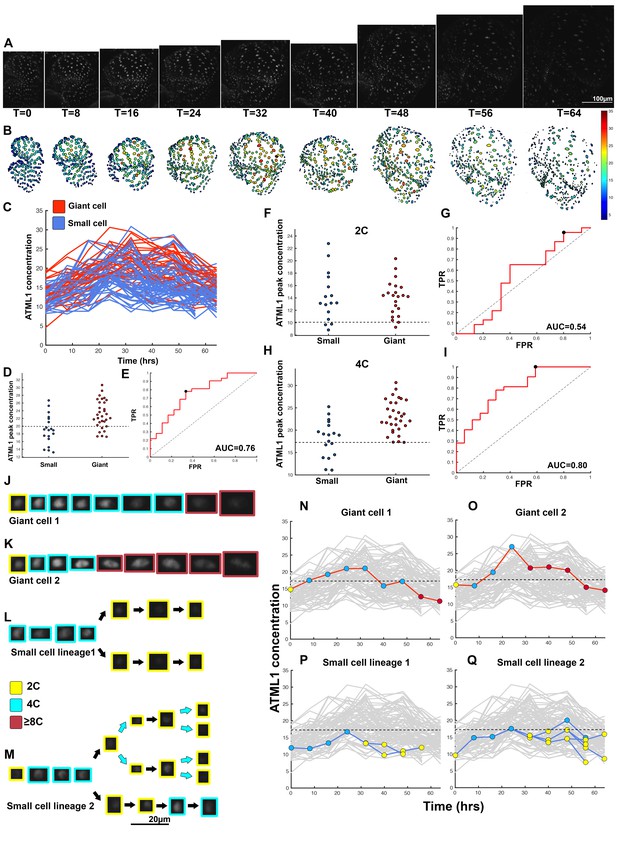
ATML1 fluctuates in sepal epidermal cells to initiate giant cell patterning.
(A) Raw images of pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 64 hr. (B) Heat map showing corresponding mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C) mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations tracked over time in cells that became giant (red) and cells that divided to stay small (blue). (D) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels in each lineage preceding endoreduplication or mitotic division (Materials and methods). The concentration threshold that best separates giant cells from small cells is shown as a dashed line. (E) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (red) for (D). The ratio of correctly and incorrectly classified cells (i.e. the true positive rate (TPR) and false positive rate (FPR)) is calculated for a varying threshold value, providing a characteristic curve. The area under the curve (AUC) provides a measure of accuracy for predicting cell fate based on ATML1 concentration (1 being perfect and 0.5 no better than random classification). The AUC is 0.76. The black dot marks the optimal concentration threshold where the difference between TPR and FPR is maximal. (F–I) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentrations and ROC analysis for G1 (2C) or G2 (4C) phases of the cell cycle preceding endoreduplication or mitotic division. (F) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels and optimal concentration thresholds separating giant cells from small cells at G1. (G) ROC curve for (F). (H) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels and optimal concentration thresholds separating giant cells from small cells at G2. (I) ROC curve for (H). For (G) AUC = 0.52 (not predictive) and for (I) AUC = 0.8 (predictive of cell fate). (J–M) Single cell lineages tracked through time (64 hr). Each denoised nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C, and red = 8C and higher. (J–K) giant cell and (L–M) small cell lineages. (N–Q) Tracked mCitrine-ATML1 concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineages in (J–M). The ploidy at each point corresponds to the color of the dot, as above. mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations for all other cell lineages are plotted in grey for context. Note that giant cells in N and O cross the threshold while they are in G2 (4C) of the cell cycle, while in Q, mCitrine-ATML1 crosses the threshold in 2C at t = 48 hr but then the cell goes onto divide. Additionally, the fate of the cell that crosses the threshold in 4C at t = 48 hr remains unknown. A total of 110 lineages were analyzed (n = 646 cells). This flower is shown in Video 1. Three similar replicate flowers are shown in the Figure 4—figure supplements 1, 2 and 3.
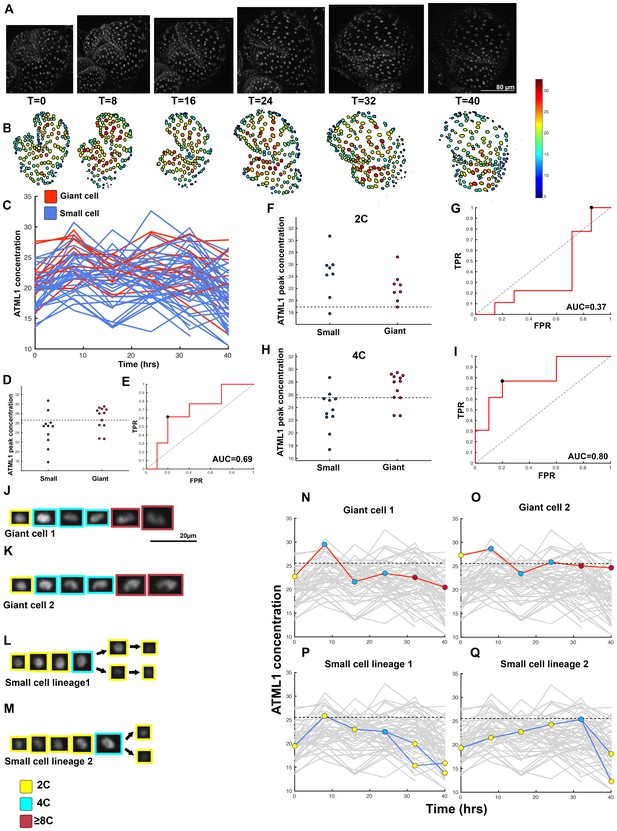
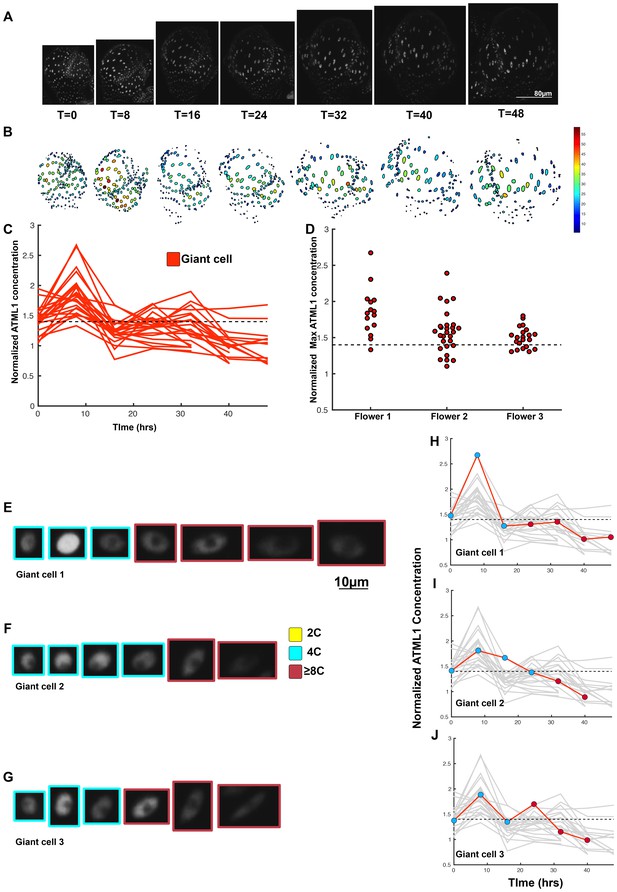
Second flower that demonstrates ATML1 fluctuates in sepal epidermal cells to initiate giant cell patterning.
(A) Raw images of pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 40 hr. (B) Heat maps showing corresponding mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C) mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations tracked over time in cells that became giant (red) and cells that divided to stay small (blue). (D) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels in each lineage preceding endoreduplication or mitotic division with a predictive concentration threshold (dashed line) derived from the ROC analysis. (E) ROC curve for (D) identifying a predictive threshold. AUC is 0.69. The black dot marks the optimal concentration threshold where the difference between TPR and FPR is maximal. (F–I) A threshold in G2 stage of the cell cycle is predictive whereas a threshold in G1 is not. (F) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels and optimal concentration thresholds separating giant cells from small cells at G1. (G) ROC curve for (F). (H) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels and optimal concentration thresholds separating giant cells from small cells at G2. (I) ROC curve for (H). For (G) AUC = 0.37 (not predictive) and for (I) AUC = 0.8 (predictive of cell fate). (J–M) Single cell lineages tracked through time (40 hr). Each nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C, and red = 8C and higher. (J–K) giant cell and (L–M) small cell lineages. (N–Q) Tracked mCitrine-ATML1 concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineages in (J–M). Note that in (P) a 2C cell passes the giant cell threshold but then divides at t = 8 hr. Additionally in (Q) a 4C cell approaches the giant cell threshold but then divides at t = 32 hr. A total of 80 lineages analyzed (n = 413 cells). Associated with Figure 4 and Video 2.
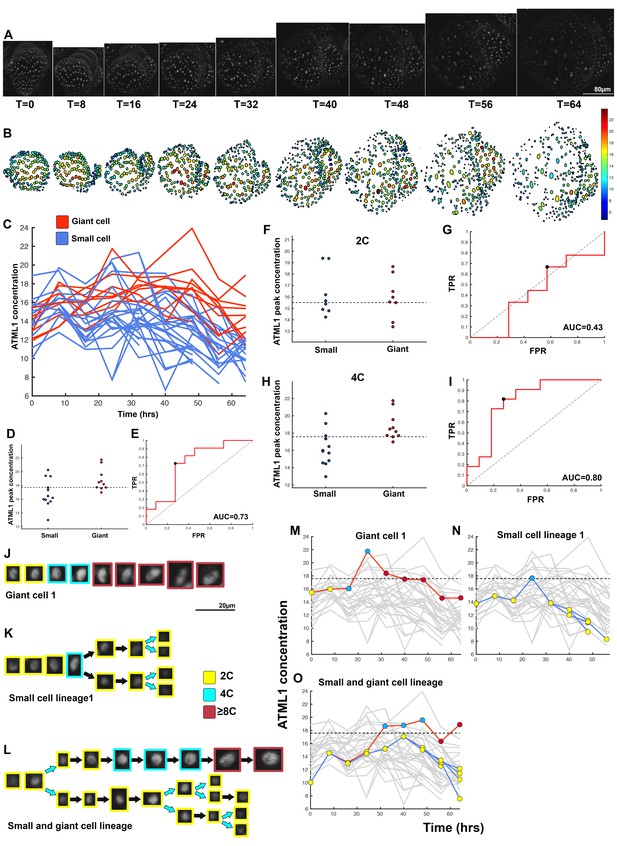
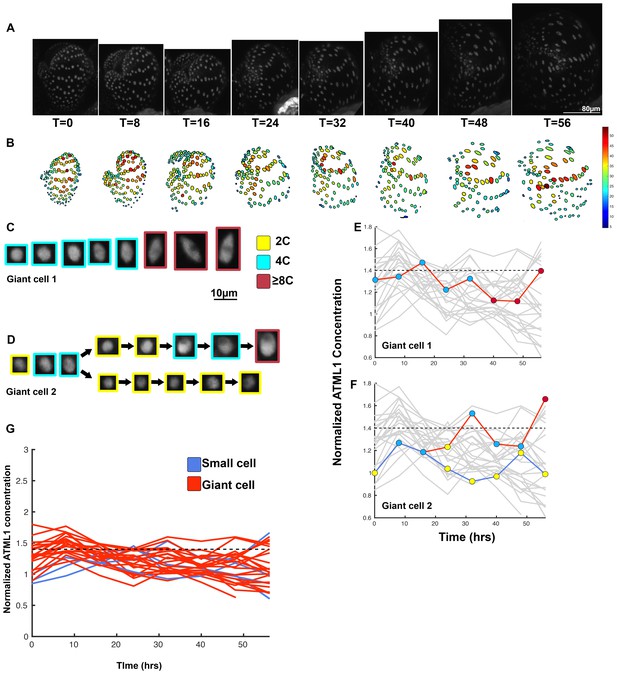
Third flower that demonstrates ATML1 fluctuates in sepal epidermal cells to initiate giant cell patterning.
(A) Raw images of pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 64 hr. (B) Heat map showing corresponding mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C) mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations tracked over time in cells that became giant (red) and cells that divided to stay small (blue). (D) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels in each lineage preceding endoreduplication or mitotic division with a predictive concentration threshold (dashed line) derived from the ROC analysis. (E) ROC curve identifying a predictive threshold. AUC is 0.73. The black dot marks the optimal concentration threshold where the difference between TPR and FPR is maximal. (F–I) A threshold in G2 stage of the cell cycle is predictive whereas a threshold in G1 is not. (F) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels and optimal concentration thresholds separating giant cells from small cells at G1. (G) ROC curve for (F). (H) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels and optimal concentration thresholds separating giant cells from small cells at G2. (I) ROC curve for (H). For (G) AUC = 0.43 (not predictive) and for (I) AUC = 0.8 (predictive of cell fate). (J–L) Single cell lineages tracked through time (64 hr). Each nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C, and red = 8C and higher. (J) Giant cell, (K) small cell, and (L) small cell and giant cell lineages. (M–O) Tracked mCitrine-ATML1 concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineages in (J–L). Note that in (N) a 4C cell approaches the giant cell threshold but then divides at t = 24 hr. Additionally, in (O) two daughter cells go on to have different cell fates. A total of 50 lineages analyzed (n = 195 cells). Associated with Figure 4 and Video 3.
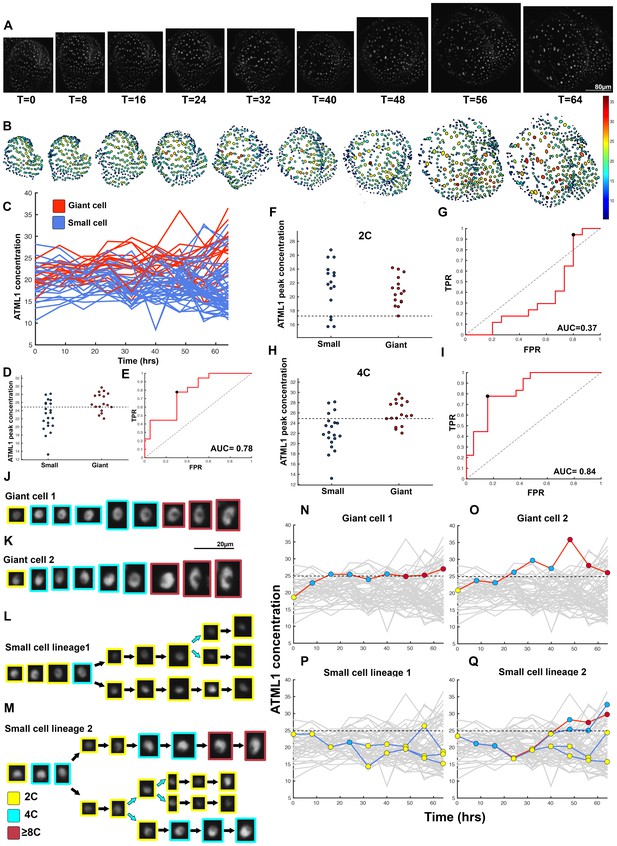
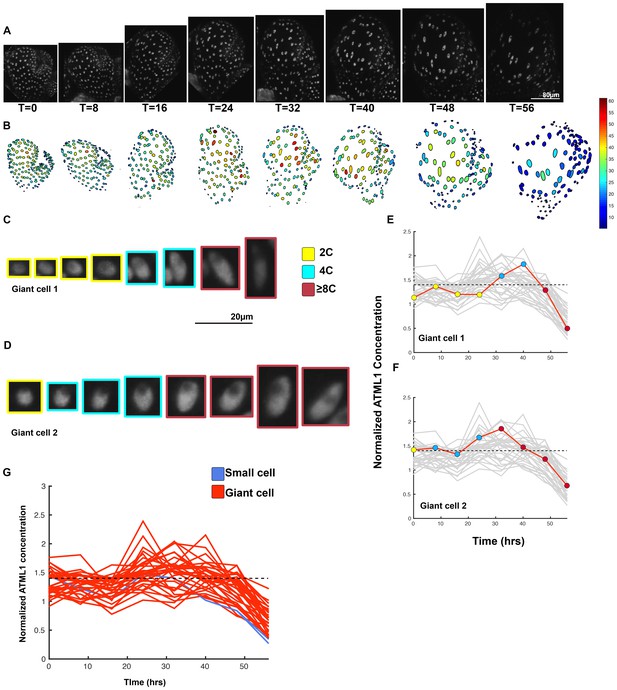
Fourth flower that demonstrates ATML1 fluctuates in sepal epidermal cells to initiate giant cell patterning.
(A) Raw images of pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 64 hr. (B) Heat map showing corresponding mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C) mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations tracked over time in cells that became giant (red) and cells that divided to stay small (blue). (D) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels in each lineage preceding endoreduplication or mitotic division with a predictive concentration threshold (dashed line) derived from the ROC analysis. (E) ROC curve identifying a predictive threshold. AUC is 0.78. The black dot marks the optimal concentration threshold where the difference between TPR and FPR is maximal. (F–I) A threshold in G2 stage of the cell cycle is predictive whereas a threshold in G1 is not. (F) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels and optimal concentration thresholds separating giant cells from small cells at G1. (G) ROC curve for (F). (H) mCitrine-ATML1 peak concentration levels and optimal concentration thresholds separating giant cells from small cells at G2. (I) ROC curve for (H). For (G) AUC = 0.37 (not predictive) and for (I) AUC = 0.84 (predictive of cell fate). (J–M) Single cell lineages tracked through time (64 hr). Each nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C, and red = 8C and higher. (J–K) giant cell and (L–M) small cell lineages. (N–Q) Tracked mCitrine-ATML1 concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineages in (J–M). Note that in (Q) two daughter cells go on to have different cell fates. A total of 80 lineages analyzed (n = 436 cells). Associated with Figure 4 and Video 4.
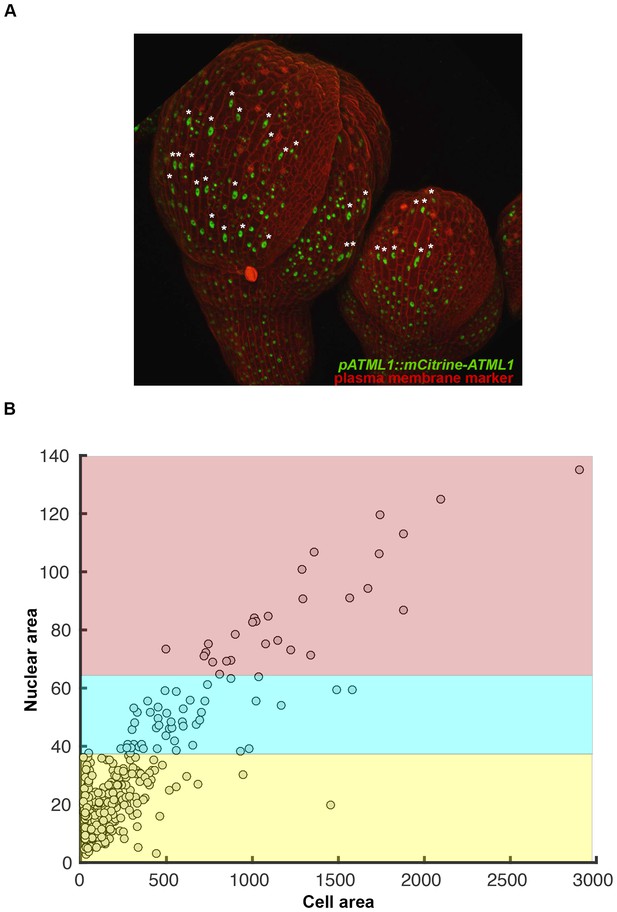
Giant cells can be identified by their large, elongated, endoreduplicating nuclei.
(A) Confocal image of two sepals expressing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (Green) in the nucleus and the plasma membrane marker pML1:mCherry-RCI2A (Red). Asterisks mark giant endoreduplicating cells. Note that endoreduplicated nuclei exhibit an elongated shape. (B) Nuclear area and cell area were quantified from (A) and show a linear correlation (R2 = 0.87). Red, blue and yellow correspond to respective ploidy classifications based on an area threshold (Box 2). Associated with Figure 4.
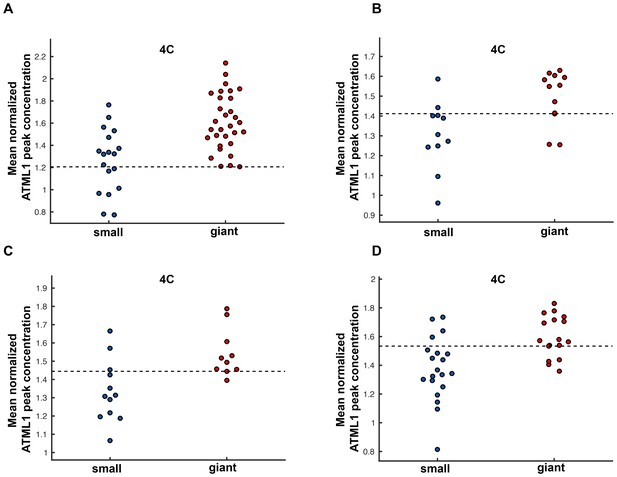
Mean normalized mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations for all four pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1;atml1–3 flowers.
(A) mCitrine-ATML1 flower number 1 (shown in Figure 4). Flower has an inferred normalized ATML1 concentration peak threshold of 1.21. (B) mCitrine flower number 2 (shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1). Flower has an inferred normalized ATML1 concentration peak threshold of 1.41. (C) mCitrine-ATML1 flower number 3 (shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Flower has an inferred normalized ATML1 concentration peak threshold of 1.45. (D) mCitrine-ATML1 flower number 4 (shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 3). Flower has an inferred normalized ATML1 concentration peak threshold of 1.55. The average normalized ATML1 concentration peak threshold for all four flowers is 1.4. This threshold value was established as the common threshold. Associated with Figure 4.
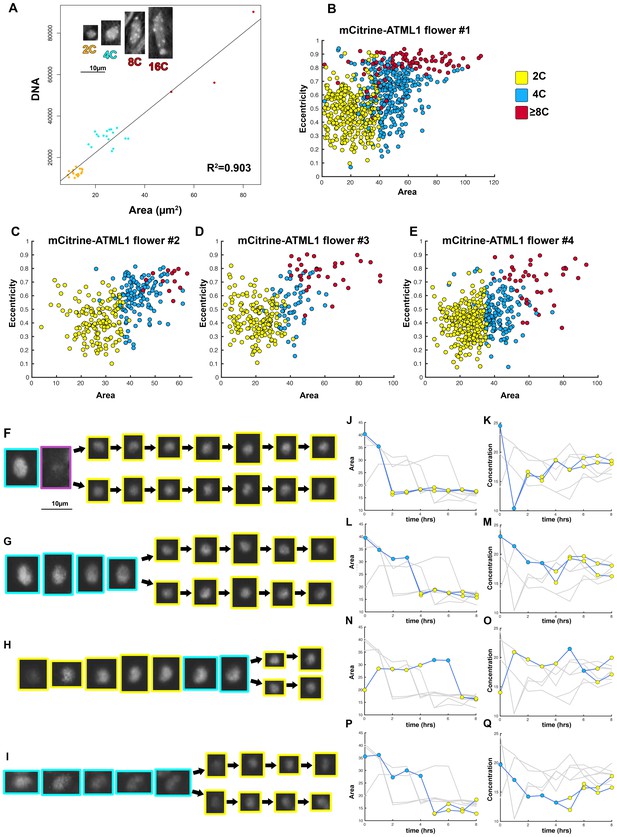
Nuclear area was used to determine cell cycle stage.
(A) DAPI stained wild-type sepal nuclei show that DNA content and nuclear area are linearly correlated (R2 = 0.903). 2C nuclei are colored yellow, 4C nuclei are colored blue, and 8C/16C nuclei are colored red. One representative confocal image of each classified nucleus is inset on the top left of the graph. Scalebar = 10 µm2. N = 38 nuclei were analyzed. (B–E) Area versus eccentricity of different ploidies classified from an area threshold using pATML1::mcitrine-ATML1;atml1–3 flowers. 2C cells in yellow are <35 µm2 in area. 4C cells are in blue and are ≥35 µm2 in area with an eccentricity of ≤0.7. Endoreduplicating cells (≥8C) are >35 µm2 with an eccentricity of >0.7. In a few instances, a giant cell was poorly segmented and received a low area. These cells were manually corrected. (B) Flower 1; a total of n = 646 cells were analyzed (C) Flower 2; a total of n = 413 cells were analyzed. (D) Flower 3; a total of n = 195 cells were analyzed. (E) Flower 4; a total of n = 436 cells were analyzed. (F–I) Nuclei that undergo a mitotic division from a one-hour interval live imaging series, showing the size change from 4C to 2C after division. (J, L, N, P) Traces of nuclear areas over time corresponding to (F–I). Note that nuclei have an area of approximately 35 µm2 before dividing. Immediately upon division, nuclei have an area of approximately 15 µm2. (K, M, O, Q) mCitrine-ATML1 concentration of nuclei in (F–I). Note that mCitrine-ATML1 concentration seemingly fluctuates, independently of nuclear area.
A threshold-based mechanism is consistent with increased giant cell formation in ATML1 overexpression lines.
(A) Raw images of pPDF1::GFP-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing overexpression sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 48 hr. (B) Heat map showing corresponding GFP-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C) normalized GFP-ATML1 concentrations tracked over time. Note that all cells tracked become giant. (D) Normalized GFP-ATML1 peak concentration levels in each lineage preceding endoreduplication for all three pPDF1::GFP-ATML1 flowers. Dashed line represents the common normalized threshold derived from pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1;atml1–3 flowers (Figure 4—figure supplement 5). Note that almost all nuclei reach high concentrations of GFP-ATML1 above the threshold before endoreduplicating. (E–G) Single giant cells tracked through time (48 hr). Each denoised nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C, and red = 8C and higher. (H–J) Tracked normalized GFP-ATML1 concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineages in (E–F). The ploidy at each point corresponds to the color of the dot, as above. GFP-ATML1 concentrations for all other cell lineages are plotted in grey for context. Note that the giant cells cross the threshold while they are in G2 (4C) of the cell cycle. A total of 23 lineages were analyzed (n = 129 cells). This flower is shown in Video 5. Two similar replicate flowers are shown in the Figure 5—figure supplements 1 and 2.
Second flower demonstrating that a threshold-based mechanism is consistent with increased giant cell formation in ATML1 overexpression lines.
(A) Raw images of pPDF1::GFP-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing overexpression sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 56 hr. (B) Heat maps showing corresponding GFP-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C–D) Single giant cells tracked through time (56 hr). Each denoised nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C, and red = 8C and higher. Note that the giant cells cross the threshold while they are in G2 (4C) of the cell cycle. Moreover, in (D) the cell does not pass the threshold and instead divides. In the next cell cycle one of the two daughter cells passes the threshold in 4C and starts to endoreduplicate. (E–F) Tracked GFP-ATML1 normalized concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineages in (C–D). The ploidy at each point corresponds to the color of the dot, as above. GFP-ATML1 concentrations in all cell lineages are plotted in grey for context. Note that the giant cells cross the threshold while they are in G2 (4C) of the cell cycle. Moreover, in (D) the cell does not pass the threshold and instead divides. In the next cell cycle one of the two daughter cells passes the threshold in 4C and starts to endoreduplicate (G) Normalized GFP-ATML1 concentrations tracked over time. Note that most cells tracked are red and become giant and a few small cells area tracked in blue. Dashed line represents the common normalized threshold derived from pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1;atml1–3 flowers (Figure 4—figure supplement 5). A total of 28 lineages were tracked (n = 198 cells). Associated with Figure 5 and Video 6.
Third flower demonstrating that a threshold-based mechanism is consistent with increased giant cell formation in ATML1 overexpression lines.
(A) Raw images of pPDF1::GFP-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing overexpression sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 56 hr. (B) Heat maps showing corresponding GFP-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C–D) Single giant cells tracked through time (56 hr). Each denoised nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C, and red = 8C and higher. Note that the giant cells cross the threshold while they are in G2 (4C) of the cell cycle. (E–F) Tracked GFP-ATML1 normalized concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineages in (C–D). The ploidy at each point corresponds to the color of the dot, as above. GFP-ATML1 concentrations in all cell lineages are plotted in grey for context. Note that the giant cells cross the threshold while they are in G2 (4C) of the cell cycle. (G) Normalized GFP-ATML1 concentrations tracked over time. Note that most cells tracked become giant (red) and a few small cells are tracked in blue. Dashed line represents the common normalized threshold derived from pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1;atml1–3 flowers (Figure 4—figure supplement 5). A total of 33 lineages were tracked (n = 257 cells). Associated with Figure 5 and Video 7.
The dynamics of ATML1 fluctuations are independent of endoreduplication.
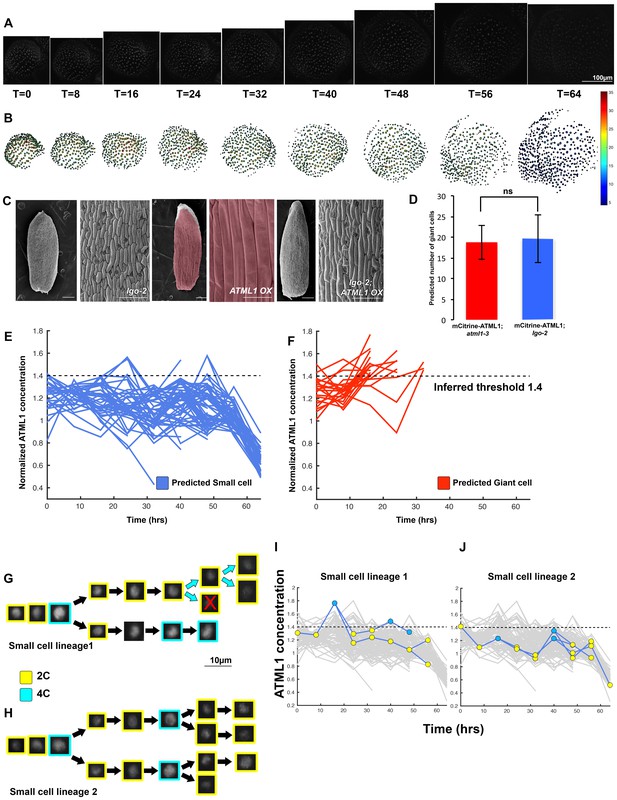
(A) Raw images of pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing lgo mutant sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 64 hr. (B) Heat maps showing corresponding mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C) Genetic epistasis analysis between lgo-2 mutant and ATML1 overexpression line (pPDF1::FLAG-ATML1). Plants homozygous for both the lgo mutation and the overexpression transgene do not form giant cells, demonstrating that LGO acts genetically downstream of ATML1 to promote endoreduplication. (D) Quantification of the average number of giant cells in four pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; atml1–3 sepals (ncells = 75, four sepals) compared to the number of giant cells predicted to form by applying the common threshold to ATML1 concentrations observed in pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; lgo sepals (ncells = 59, three sepals). Error bars = standard error of mean. Approximately the same number of cells would be expected to become giant cells in lgo sepals as in wild type, except that they fail to endoreduplicate. A T-test performed between the two populations yielded a non-significant (ns) p-value of 0.9 (E) Traces of mCitrine-ATML1 normalized concentrations of cells that do not reach the inferred threshold in G2 of the cell cycle and are predicted to remain small (nsmall = 70). (F) Traces of mCitrine-ATML1 normalized concentrations of cells that reach the inferred threshold during G2 of the cell cycle and are predicted to become giant (ngiant = 25). The trace ends when the cell is predicted to become giant. In (E–F) the dashed line represents the common normalized threshold derived from pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1;atml1–3 flowers (Figure 4—figure supplement 5). (G–H) Single small cell lineages tracked through time (64 hr). Each nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C. The cell marked with X is lost from our tracking. (I–J) Tracked mCitrine-ATML1 concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineages in (G–H). Cells that cross the mCitrine-ATML1 threshold fail to endoreduplicate and instead divide. A total of 149 lineages were analyzed (n = 495 cells). This flower is shown in Video 8. Two similar replicate flowers are shown in the Figure 6—figure supplements 1 and 2.
Second flower showing that dynamic fluctuations of ATML1 are independent of endoreduplication.
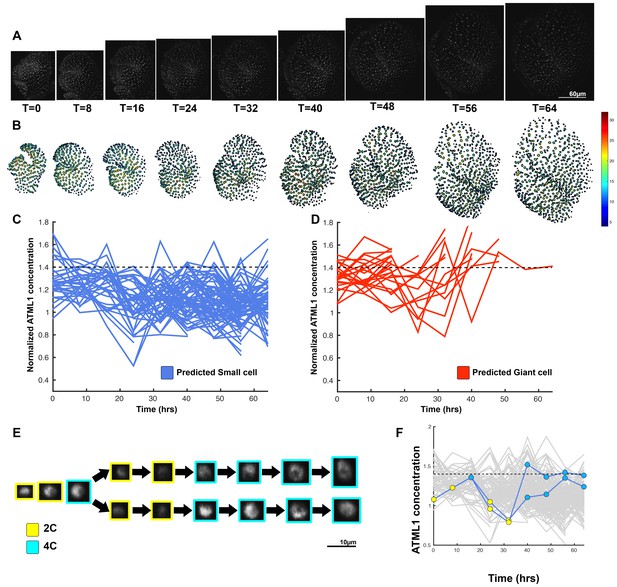
(A) Raw images of pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing lgo mutant sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 64 hr. (B) Heat map showing corresponding mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C) Traces of cells that do not reach the inferred threshold (1.4) in G2 of the cell cycle and are predicted to remain small, nsmall = 87. (D) Cell traces of cells that reach the inferred threshold (1.4) during G2 of the cell cycle that are predicted to become giant. ngiant = 26. The trace ends when the cell is predicted to become giant. (E) Single small cell lineage tracked through time (64 hr). Each nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C. (F) Tracked mCitrine-ATML1 concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineage in (E). A total of 196 lineages were tracked (n = 756 cells). Associated with Figure 6 and Video 9.
Third flower showing that dynamic fluctuations of ATML1 are independent of endoreduplication.
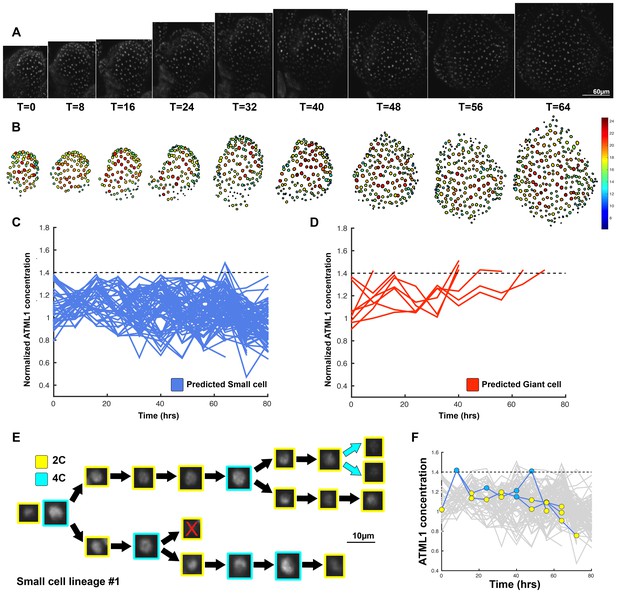
(A) Raw images of pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (white) from a live imaging series of a developing lgo mutant sepal. Images were taken every 8 hr for 64 hr. Labels below the snapshots display the time after the time course was initiated, in hour units. (B) Heat map showing corresponding mCitrine-ATML1 concentrations (total fluorescence divided by area) at each time point from (A). (C) Traces of cells that do not reach the inferred threshold (1.4) in G2 of the cell cycle and are predicted to remain small. nsmall=128. (D) Cell traces of cells that reach the inferred threshold (1.4) during G2 of the cell cycle that are predicted to become giant. ngiant = 8. The trace ends when the cell is predicted to become giant. (E) Single small cell lineage tracked through time (64 hr). Each nucleus image is outlined in a color associated with its ploidy: yellow = 2C, blue = 4C. The cell with the X is lost from our tracking. (F) Tracked mCitrine-ATML1 concentration levels corresponding to the single cell lineage in (E). A total of 151 lineages were tracked (n = 619 cells). Associated with Figure 6 and Video 10.
A plausible stochastic model for giant cell patterning.
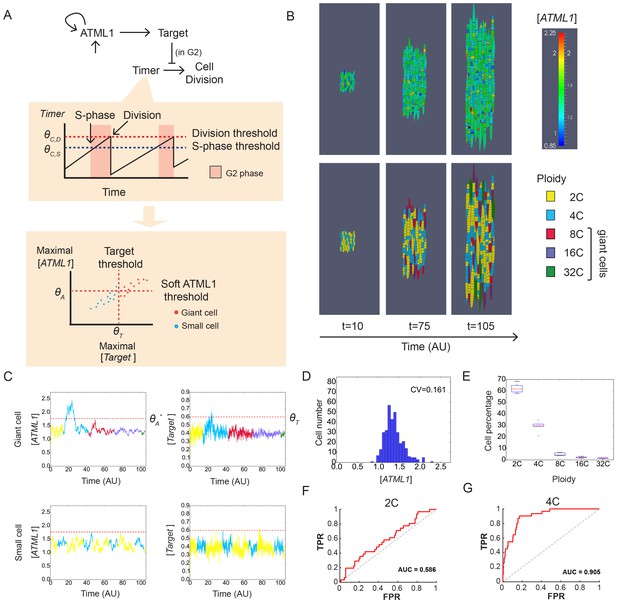
(A) Schematic diagram of the computational model for giant cell patterning. Top panel shows the proposed ATML1 model network in which ATML1 can prevent cell division and instead drive entry into endoreduplication and giant cell specification. Middle panel shows a cartoon of the cell cycle timer time course. When the timer exceeds a first threshold level ΘC,S, cells enter into the G2 phase and increase their ploidy to 4C. When the timer reaches a second threshold level, ΘC,D, cells divide, unless their target levels have surpassed the threshold ΘT sometime during G2 phase. Bottom panel shows a scatter plot cartoon illustrating how a ‘hard threshold’ in the target levels results in a ‘soft threshold’ in ATML1. We refer to a hard threshold when levels right above or below the threshold will result in two different outcomes. If the target perfectly followed the dynamics of ATML1, its upstream regulator, and obeyed a deterministic dynamics, all cells that cross the target threshold ΘT would also cross a corresponding hard ATML1 threshold. Hence, a hard threshold in the target would be effectively encoded as a hard threshold on its upstream regulator ATML1. In contrast, in our model, the target has a finite degradation rate, and stochastic dynamics, so that it is not a perfect follower of ATML1 dynamics; thus, a hard threshold in target levels (vertical red dashed line) results in a soft threshold in ATML1 (horizontal red dashed line). A cell close to the ATML1 soft threshold may or may not pass the target threshold and endoreduplicate to become a giant cell. Dots in the bottom panel is a cartoon of the ATML1 maxima of simulated cell lineages, with red dots indicating cells that become giant, while blue dots represent mitotically dividing small cells. (B) Simulation snapshots of the in silico growing sepal showing (top) ATML1 concentrations and (bottom) cell ploidies (Video 11). (C) Time courses of ATML1 (left) and its target (right) for a cell committing to the giant fate (top) and a small dividing cell (bottom). Colors of the time traces represent the cell ploidy. Color code for the ploidies is the same as in panel B. Red dashed lines represent the predicted soft ATML1 threshold ΘA*, and the ΘT hard threshold imposed in the target (Materials and methods). (D) Histogram at a final simulation time point showing ATML1 concentration levels. (E) Boxplot showing the percentage of cell ploidies in a simulated tissue for five simulations with different random initial ATML1, target and timer levels. (F–G) ROC analysis of the ATML1 concentration maxima for the simulated lineages at (F) 2C and (G) 4C, showing that the ATML1 maximal levels at 2C is not predictive, in agreement with experimental data (Figure 4F–I; Figure 4—figure supplements 1–3F–I). Parameter values are described in Table 1.
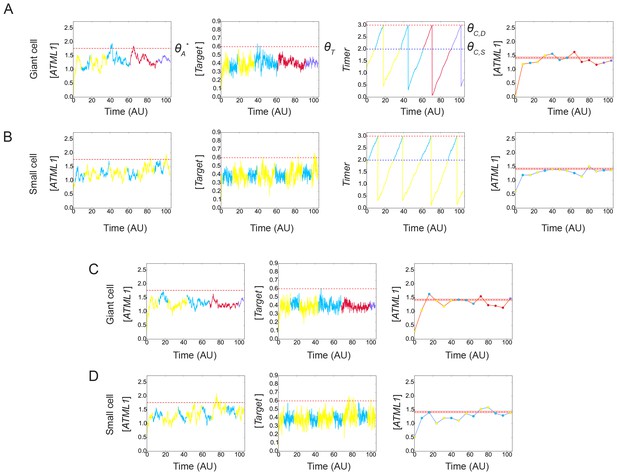
Simulation results showing different stochastic time courses.
Time courses for cells committing to the (A and C) giant fate and (B and D) small cell fate of ATML1 (left), its target (middle left for A and B; middle for C and D) and the timer (middle right for A and B). Colors of the time traces represent the cell ploidy, as in Figure 7. Right panels in show the ATML1 time courses as in the left panel but with less time resolution, which we refer to as coarse-grained time courses. Such coarse-grained time courses are shown to emulate an experimental time courses. Dot colors in the coarse-grained time course panels represent the ploidy, following the color code in Figure 7B, while the line color refers in this case to the cell type at the end of the simulation, being orange for giant cells and blue for the small dividing cells. Horizontal red lines in the ATML1 panels represent the predicted soft threshold ΘA* and the red shaded region is a measure of its error (Materials and methods). The other horizontal lines in the target and timer variables show the different thresholds set in the simulations. Coarse-grained time courses show we may lose some ATML1 peaks due to the lower time resolution, and this might slightly decrease the levels of the predicted threshold with respect to the threshold predicted from traces with higher time resolution. Cells with ATML1 levels reaching the predicted soft threshold in G2 are likely to have the corresponding downstream target levels above the target threshold, driving endoreduplication (see A). However, ATML1 may even cross the predicted soft threshold, and still not drive giant cell endoreduplication, if the target does not cross its own threshold (see C middle and right). On the other side, cells being close to but not reaching the ATML1 threshold might endoreduplicate, provided that the target crosses its corresponding threshold (C left, middle). Parameter values are described in Table 1. Associated with Figure 7.
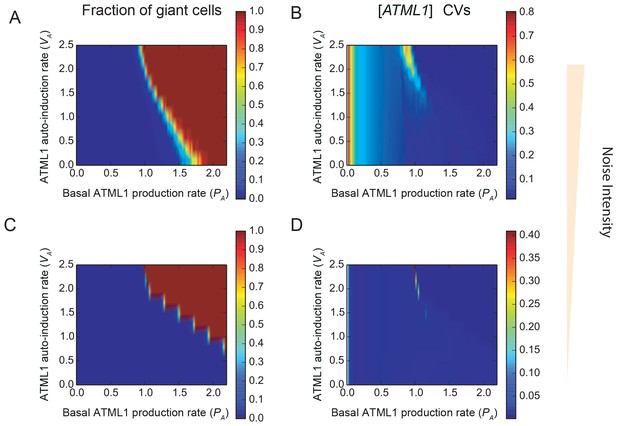
Stochastic fluctuations are essential for generating the giant cell patterning.
Phase diagrams across the parameter space of basal ATML1 production rates and ATML1 auto-induction rates showing (A and C) the fraction of giant cells in the tissue and (B and D) the CVs of the ATML1 concentration in the tissue at (A–B) higher (E0 = 15) and (C–D) lower (E0 = 1500) noise intensities. Note that the noise intensity is inversely proportional to the characteristic cell size E0. At higher basal ATML1 production rates, all cells cross the ATML1 soft threshold and endoreduplicate to become giant (fraction of giant cells = 1, colored dark red on the heat map). Conversely, at lower basal ATML1 production rates, all cells divide to remain small (fraction of giant cells = 0, colored dark blue on the heat map). For a certain range of basal ATML1 production rates, dynamic stochastic fluctuations create a salt-and-pepper pattern of giant cells interspersed between mitotically dividing cells (rainbow region of the parameter space). At lower noise intensities, no pattern emerges in a wide visible region of the studied parameter space, and the modeled sepal has either just non-giant or giant cells. A few parameter values might still drive a salt-and-pepper pattern at low noise intensities, provided that the initial conditions are sufficiently noisy. Parameter values are described in Table 1. Associated with Figure 7.
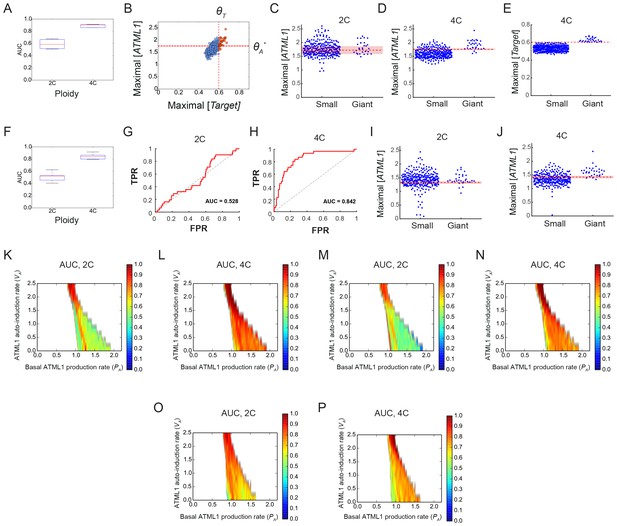
Classification analysis of the simulated data shows that a weak feedback or no feedback in ATML1 reproduces the experimental observations.
Analysis for (A–D) full and (F–J) coarse grained simulated time courses show we get equivalent AUC values and similar ATML1 soft thresholds. (A and F) AUC values of 5 simulations with different random initial conditions. (B) Scatter plot showing the maximal ATML1 levels and the corresponding target levels at 4C for (red) giant and (blue) small dividing cells. Dashed vertical and horizontal lines show the imposed hard threshold for the target (ΘT) and the predicted soft threshold for ATML1 (ΘA*) (Materials and methods). This plot shows that a hard threshold in the target results in a soft threshold in ATML1: above the soft threshold ΘA*, we find cells having higher and lower maximal target levels than the target threshold ΘT, becoming giant cells or remaining as small cells, respectively. (C–D, I–J) Spread plots showing the maxima of the ATML1 at 2C and 4C and the predicted ATML1 threshold ΘA*. (E) Spread plot of the maximal target values at 4C and the predicted target threshold ΘT*. Notice that the predicted hard threshold for the target ΘT* accurately matches the assigned target threshold ΘT (see panel B). (G–H) ROC curves for the coarse-grained time course (see Figure 7F–G for the equivalent ROC curves computed with the simulated time resolution of 0.1). (K–N) ROC analysis performed on simulated data with (K–L) higher and (M–N) lower time resolution in the parameter space show equivalent AUC trends. This analysis show that cells can be classified with respect to its maximal ATML1 levels at 4C but not in 2C in a wide region of the parameter space, namely, when there is no feedback, or when there is weak feedback. This is in agreement with the analysis of the experimental data. In contrast, with higher feedback strengths, maximal ATML1 levels in both 2C and 4C become predictive of giant cell fate, which does not correspond to our experimental data. The ROC analysis has been performed just in the parameter region where simulations lead to a pattern of giant and dividing cells, i.e., where the fraction of giant cells in the tissue being between 0 and 1. ROC analysis in higher (K–L) and lower (M–N) time resolution time courses give equivalent results. (O–P) ROC analysis in the parameter space for a model where the target can induce endoreduplication throughout the whole cell cycle and not just in G2. The time resolution for the ROC analysis and threshold determination was 0.1 AU for A–E panels, eight for F– J and M–N panels, and 0.5 for K–L and O–P panels. Parameter values are described in Table 1. Associated with Figure 7.
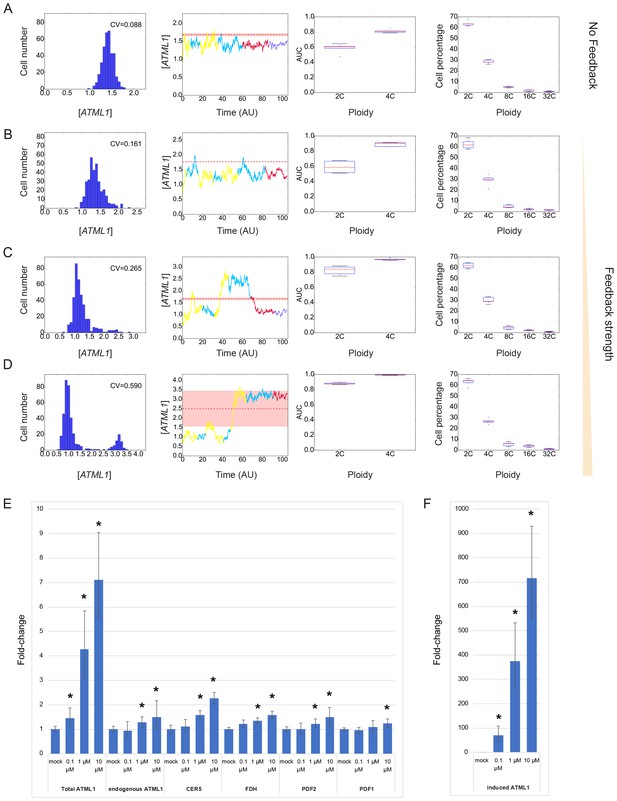
Theoretical and experimental study of the ATML1 auto-induction strength.
(A–D) Simulation results of the model with different ATML1 auto-induction strengths show different qualitative behaviors. Simulations with different feedback strengths and different ATML1 basal production rates that lead to similar percentages of giant cells in the tissue (7 to 9%) are shown. Histograms of ATML1 concentrations (left), ATML1 time traces for cells becoming giant cells (middle left), ROC analysis (middle right) and percentages of cells with the different ploidies. Boxplots are obtained from five simulations with different initial conditions (middle right and right panels). The stronger is the feedback, the higher is the CV for the ATML1 concentrations. No feedback or a weak feedback give rise to a unimodal distribution of ATML1 concentrations (A–C), while a stronger feedback can give rise to a bimodal distribution (D). For no feedback (A) or weaker feedback (B), small and fast fluctuations drive the singling out of cells for endoreduplication. Stronger feedback strengths make larger fluctuations appear, whose time-scales are larger (C–D). This makes the ATML1 peak levels at 2C equivalent to 4C levels. In these cases, the AUC values are also high at 2C, which does not correspond to the experimental data. Similar fractions of giant cells are produced by all four induction strengths (A–D). Color codes of the time traces are as in Figure 7—figure supplement 1. The red lines and shaded bands in the time traces represent the predicted ATML1 soft threshold ΘA* and its error, respectively (Materials and methods). Feedback auto-induction strengths and basal production rates for the different panels are (A) VA = 0, PA = 1.41, (B) VA = 1.25, PA = 1.14, (C) VA = 1.75, PA = 1.01 and (D) VA = 2.5, PA = 0.88, respectively. Left and right panels in (B) are also shown in Figure 7, and the AUCs panel in (B) is shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 3. Other parameter values are described in Table 1. (E–F) QPCR results testing feedback strength of ATML1 induction on endogenous ATML1 48 hr after application of 10 µM, 1 µM or 0.1 µM estradiol (inducing agent) compared to mock treated inflorescences. Endogenous ATML1 transcript levels increase approximately 1.5-fold within 48 hr after ATML1 is induced with 10 µM estradiol as compared to mock-treated plants. To put this fold change in context, we examined the 10 µM estradiol induction of other genes downstream of ATML1 including CER5 (2.3-fold), FDH (1.6-fold), PDF2 (1.5-fold) and PDF1 (1.2-fold). Note that these downstream genes are induced with very similar fold changes as the endogenous ATML1. CER5, FDH, and PDF1 do not encode transcription factors and therefore cannot act in a feedback loop. This suggests that the feedback of ATML1 on itself is not activating ATML1 further than other targets at the 48 hr time point. The transgene was induced about 700-fold by 10 µM estradiol (F). Induction with 0.1 µM or 1 µM estradiol produced intermediate levels of induction and activation of downstream genes, also consistent with a weak positive feedback loop. Wilcoxon 1-tailed tests were performed between the corresponding mock treated and estradiol treated plants. p-value ≤ 0.05 marked with *. Associated with Figure 7.
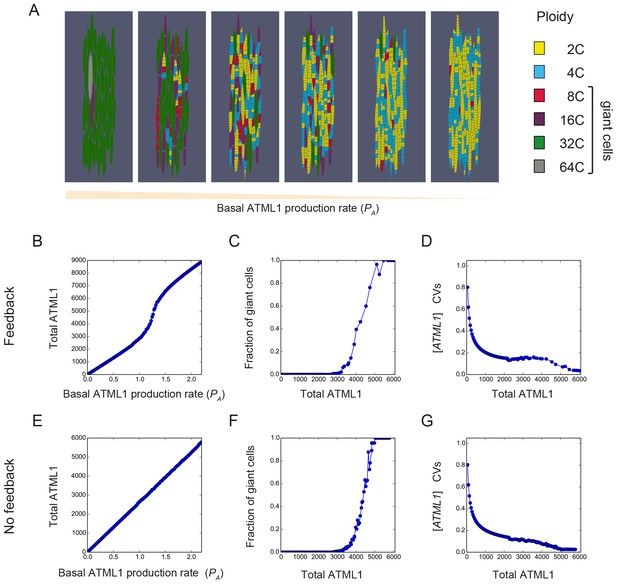
The model recapitulates ATML1 dosage dependency.
(A) Snapshots showing the resulting patterns of giant cells (8C, 16C, 32C and 64C cells) and small cells (2C and 4C cells) at the final time point of the simulations when the basal ATML1 production rate is modified. Values chosen for the ATML1 basal production rate from the parameter exploration shown in panels B-G are, from left to right: PA = 1.58, PA = 1.25, PA = 1.17, PA = 1.14, PA = 1.01 and PA = 0.99. (B–G) Simulation results for different basal ATML1 production rates for (B–D) a model with a weak auto-induction ATML1 feedback loop (VA = 1.25) and for (E–G) a model with no feedback (VA = 0). (B and E) Total amount of ATML1 in the tissue. The total ATML1 amount is the sum of the area of each cell multiplied by the ATML1 concentration in that cell. The feedback drives a sharper increase of ATML1 amount for a certain range of basal ATML1 production rates. (C and F) Fraction of giant cells (8C, 16C, 32C and 64C cells) in the tissue with respect to the total amount of ATML1. The gradual increase of the fraction of cells with respect to the total ATML1 amount in the tissue is qualitatively consistent with the different phenotypes shown in Figure 2. The model with feedback has a slightly more gradual increase in fraction of giant cells with respect to the total amount of ATML1. (D and G) CVs of the ATML1 concentrations in the tissue. In the cases of having a weak feedback or not having a feedback, there is a plateau of CV values for intermediate ATML1 total amounts in the tissue. Stronger feedback levels will lead to non-monotonic CVs with respect to the total amount of ATML1 (see Figure 7—figure supplement 2B). Other parameter values are described in Table 1.
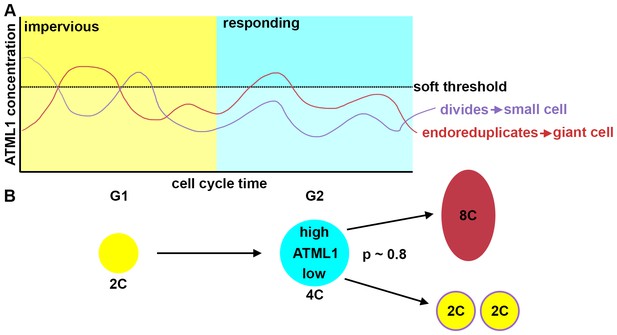
Fluctuations of ATML1 around a soft threshold pattern giant cells and small cells in the sepal.
ATML1 fluctuates in every young sepal epidermal cell. However, cells only respond to high levels of ATML1 during G2 phase of the cell cycle. (A) Schematic showing that in G1, cells are impervious to high concentrations of ATML1. In G2, cells can respond to ATML1 to become a giant cell if levels surpass a soft threshold. If a cell does not receive a high enough level then the cell will divide. (B) Schematic demonstrating a cell progression from 2C (G1 phase of the cell cycle) to 4C (G2 stage of the cell cycle). The cell will then either become an 8C cell, if it receives a high level of ATML1, or to divide to make two 2C cells if ATML1 levels are low. In the G2 phase, our inferred mCitrine-ATLML1 threshold level is about 80% accurate in predicting giant cells versus small identity correctly.
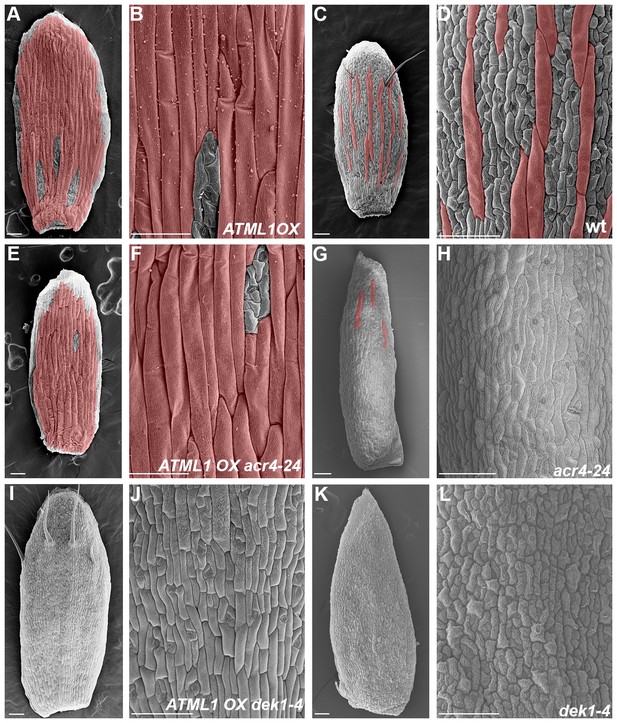
ACR4 and DEK1 act in the giant cell patterning pathway.
(A–B) SEM images of a sepal overexpressing (OX) ATML1 under the PDF1 promoter (pPDF1::FLAG-ATML1). (C–D) SEM images of a wild-type sepal. (E–F) SEM images of sepal homozygous for both ATML1 OX transgene and acr4 mutation. (G–H) SEM images of acr4–2 mutant sepal. Note that the number of giant cells is severely reduced. (I–J) SEM images of a sepal homozygous for both ATML1 OX transgene and dek1–4 mutation. Sepal contains no giant cells. (K–L) SEM image of dek1–4 mutant sepal. Note that no giant cells form. All giant cells are false colored red. Scalebars in A–L, 100 µm. Associated with Figure 9.
Videos
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; atm1l-3 sepal shown in Figure 4.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr until giant cells form.
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; atm1l-3 sepal shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr until giant cells form.
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; atm1l-3 sepal shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 2.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr until giant cells form.
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; atm1l-3 sepal shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 3.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr until giant cells form.
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; atml1–3 sepal.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every hour to capture the size (area) of nuclei before and after division. Associated with Box 2.
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; atml1–3 sepal.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every hour to capture the size (area) of nuclei before and after division. Associated with Box 2.
A movie of a developing pPDF1::GFP-ATML1 sepal shown in Figure 5.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr until giant cells form.
A movie of a developing pPDF1::GFP-ATML1 sepal shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr until giant cells form.
A movie of a developing pPDF1::GFP-ATML1 sepal shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 2.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr until giant cells form.
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; lgo sepal shown in Figure 6.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr throughout development.
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; lgo sepal shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr throughout development.
A movie of a developing pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1; lgo sepal shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 2.
The sepal primordium was live imaged every 8 hr throughout development.
Simulation results showing ATML1, target, timer levels and cell ploidies throughout time in a growing tissue.
Cells that cannot divide, increase their ploidy, becoming giant cells. The time resolution of the displayed movie (0.5) is lower than the actual simulation time step (0.1), so fluctuations in ATML1 and in the target may be missed. Color scales in the ATML1 and target variables have been truncated for the sake of better visualizing the fluctuations. Parameter values are described in Table 1.
Tables
Main parameter values used for simulations in Figures 7 and 8 and Figure 7—supplements 1–4. We omit time and concentration units, since all are considered arbitrary.
Parameter | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
PA | ATML1 basal production rate | 1.14 |
VA | ATML1 auto-induction rate | 1.25 |
KA | ATML1 concentration for half ATML1 auto-induction maximal rate | 1.9 |
nA | Hill coefficient for ATML1 auto-induction | 5 |
GA | ATML1 degradation rate | 1 |
VT | Target maximal production rate | 10 |
KT | ATML1 concentration for half ATML1-mediated target maximal production rate | 2 |
nT | Hill coefficient for ATML1-mediated target induction | 1 |
GT | Target degradation rate | 10 |
ΘT | Target threshold for inhibiting mitosis | 0.6 |
ΘC,S | Timer threshold for synthesis | 2 |
ΘC,D | Timer threshold for timer resetting | 3 |
PC | Timer basal production rate | 0.1 |
E0 | Characteristic effective volume | 15 |
Exponential radial growth rate | 0.007 | |
Exponential added growth rate to the vertical direction | 0.012 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
A zip file containing both Raw data and selected lineages for pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (mCitrine-ATML1), PDF1::GFP-ATML1 (PDF1), and lgo-2;pATML1::mCitrine-ATML1 (lgo) flowers.
See readme files within the different folders for further information. All raw image confocal tif files and example image processing files may be downloaded from: http://dx.doi.org/10.7946/P29G6M
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.19131.046
-
Source code 1
MATLAB code for all image quantification and analysis, as well as receiver operator characteristics (ROC) analysis as described in the Materials and methods section.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.19131.047
-
Source code 2
Code for simulating ATML1 dynamics in a growing tissue.
Scripts for the analysis and representation of the simulation results are also provided. See readme files within the different folders for further information.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.19131.048





