Streptomyces exploration is triggered by fungal interactions and volatile signals
Figures
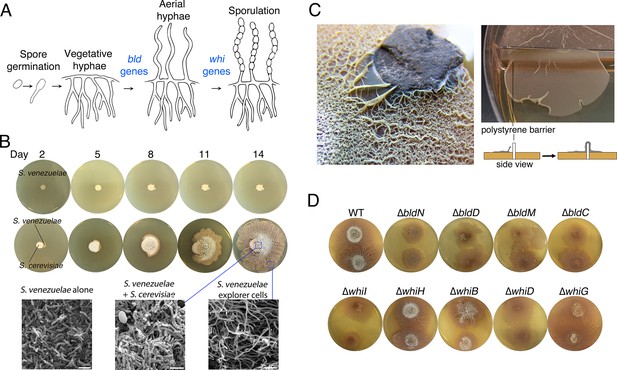
Physical association with yeast triggers Streptomyces exploratory behaviour.
(A) Developmental life cycle of Streptomyces. Germ tubes emerge from a single spore, and grow by apical tip extension and hyphal branching, forming a dense network of branching vegetative hyphae. In response to unknown signals, non-branching aerial hyphae coated in a hydrophobic sheath, escape into the air. Aerial hyphae differentiate into chains of dormant, stress-resistant non-motile spores. The bld gene products are required for the transition from vegetative growth to aerial hyphae formation, while the whi gene products are required for the differentiation of aerial hyphae into spore chains. (B) S. venezuelae grown alone (top row) and beside S. cerevisiae (middle row) on YPD (yeast extract-peptone-dextrose) medium over 14 days. Bottom panels: scanning electron micrographs of S. venezuelae grown alone (left), S. venezuelae on S. cerevisiae (middle), and S. venezuelae beside S. cerevisiae (right) for 14 days on YPD agar medium. White bars: 5 µm. (C) S. venezuelae explorer cells growing up a rock embedded in agar (left), and over a polystyrene barrier within a divided petri dish (right, and schematic below). (D) S. venezuelae wild type and developmental mutants grown beside S. cerevisiae on YPD agar medium for 14 days. Top: S. cerevisiae, together with wild type and ∆bld mutant strains (bld mutants cannot raise aerial hyphae and sporulate). Bottom: S. cerevisiae grown next to ∆whi mutant strains (whi mutants can raise aerial hyphae but fail to sporulate).
Explorer cells are hydrophilic.
S. venezuelae growing on top of S. cerevisiae cells raise hydrophobic aerial hyphae and spores. These structures effectively repel aqueous droplets (bromophenol blue dye dissolved in water). In contrast, explorer cells are hydrophilic, and application of aqueous droplets (as above) results in liquid dispersion.
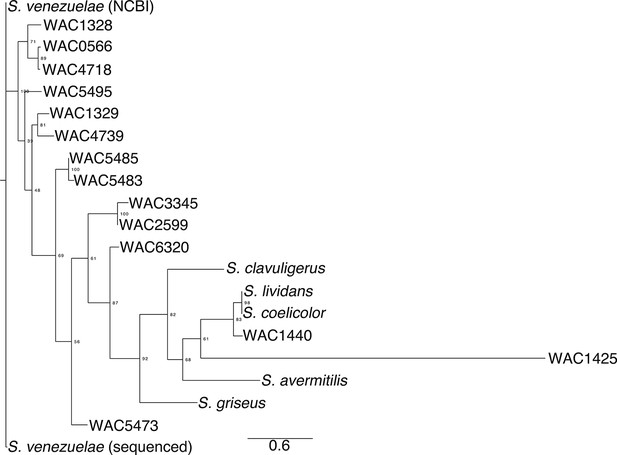

Phylogeny of exploratory streptomycetes.
The phylogeny was created using aligned rpoB sequences from wild Streptomyces isolates (WAC strains) that exhibited exploratory growth. For comparison, we included the non-spreading S. coelicolor, S. lividans, S. avermitilis, S. griseus and S. clavuligerus. A maximum likelihood tree was built using RaxML with a GTRGAMMA model of nucleotide substitution, with 500 bootstrap replicates to infer support values of nodes. Output was created using FigTree.
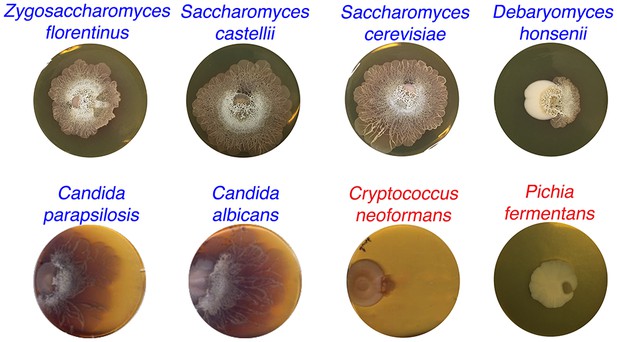
S. venezuelae grown beside diverse yeast strains.
S. venezuelae was grown beside the indicated yeast strains on YPD agar medium for 14 days. Z. florentinus, S. castellii, S. cerevisiae, D. honsenii, and P. fermentas are soil isolates, while C. parapsilosis, C. albicans and C. neoformans are laboratory strains. Yeast strains able to induce S. venezuelae exploratory growth are labelled in blue text, and yeast strains unable to induce S. venezuelae exploratory growth are shown in red.
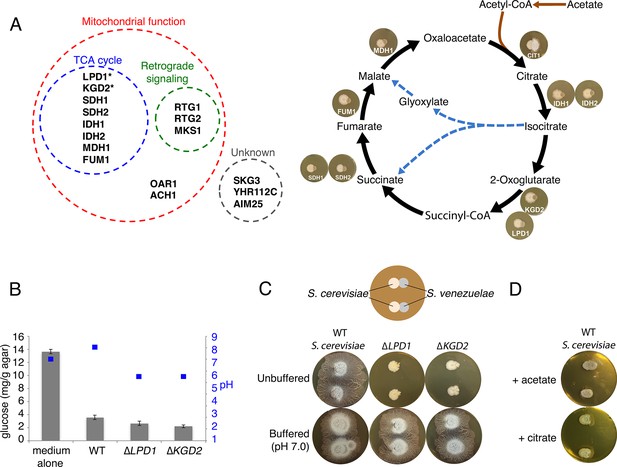
Yeast stimulates S. venezuelae exploratory growth by consuming glucose and inhibits it by acidifying the medium.
(A) S. cerevisiae mutants that fail to stimulate S. venezuelae exploratory growth. Left: functional grouping of the exploration-deficient S. cerevisiae mutations. Asterisks indicate genes also identified in C. albicans as affecting S. venezuelae exploratory growth. Right: Mutations in S. cerevisiae TCA cycle-associated genes affect exploration after citrate production. For each interaction, the indicated S. cerevisiae mutant was grown beside wild type S. venezuelae for seven days on YPD agar medium. (B) Glucose concentration and pH associated with wild type and mutant S. cerevisiae strains grown on YPD agar medium. Glucose concentrations (grey bars) and pH (blue squares) were measured from medium alone, and beneath wild type, ∆LPD1 or ∆KGD2 S. cerevisiae strains grown on YPD medium for seven days. All values represent the mean ± standard error for four replicates. (C) Top: schematic of the experimental set up, with S. cerevisiae grown to the left of S. venezuelae on YPD medium. Two replicates are grown on each agar plate. Bottom: wild type, ∆LPD1, and ∆KGD2 S. cerevisiae strains grown for 14 days beside wild type S. venezuelae on unbuffered YPD agar and YPD agar buffered to pH 7.0 with MOPS. (D) Wild type S. cerevisiae spotted beside wild type S. venezuelae and grown for 14 days on YPD agar medium plates supplemented with acetate or citrate, each buffered to pH 5.5.
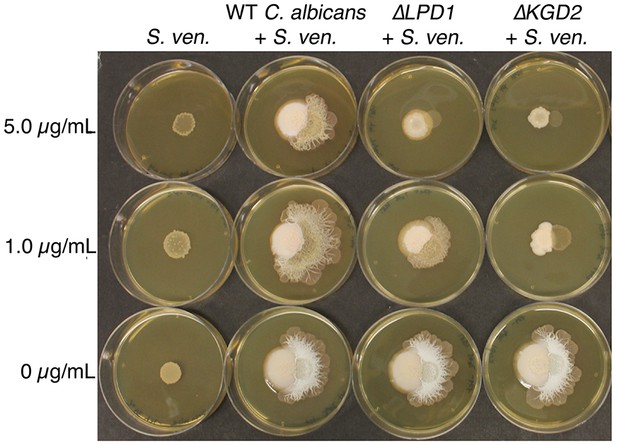
C. albicans gene mutations that affect S. venezuelae exploratory growth.
S. venezuelae (S. ven.) was inoculated alone or beside wild type (WT), ΔLPD1, or ΔKGD2 C. albicans strains on YPD agar for 10 days. C. albicans mutant strains were from the GRACE collection of tetracycline repressible deletion mutants. The indicated amount of tetracycline was added to YPD medium to induce the C. albicans gene deletion phenotype.
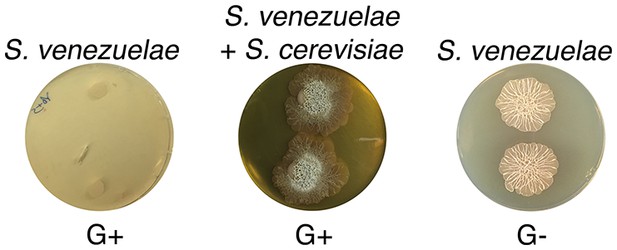
S. venezuelae grown alone on glucose-deficient medium exhibits similar exploratory growth to S. venezuelae growing next to yeast on glucose medium.
S. venezuelae was grown either alone or beside S. cerevisiae on G+ (glucose-containing) agar medium, and alone on G- (no glucose). Two replicates were spotted per plate, and plates were incubated for 10 days.
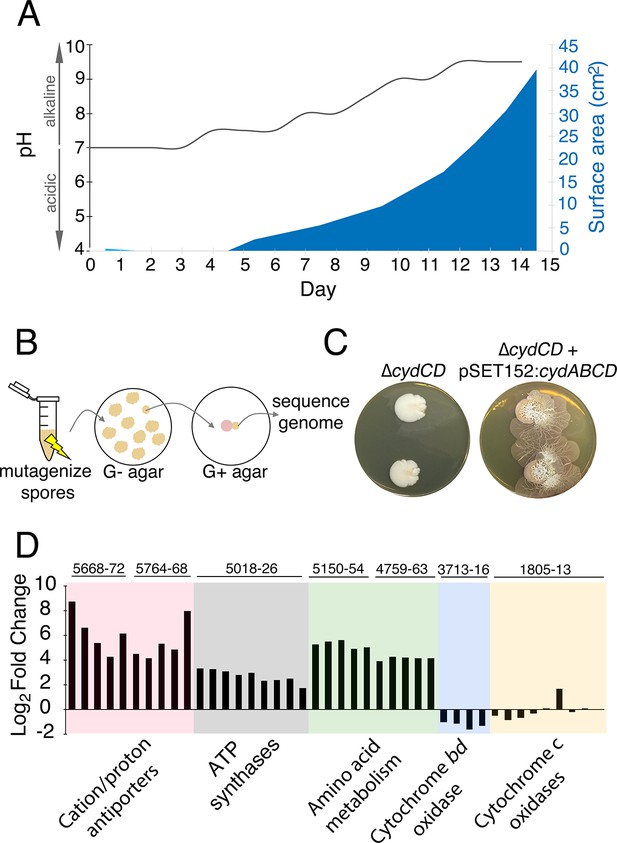
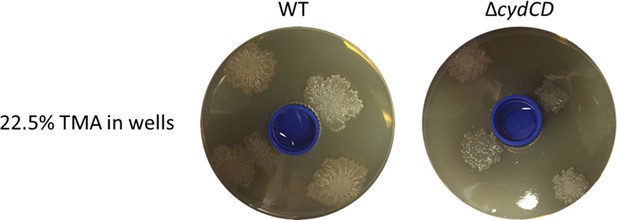
The alkaline stress response is associated with S. venezuelae exploratory behaviour.
(A) The surface area and medium pH associated with S. venezuelae explorer cells beside S. cerevisiae on YPD agar were measured and plotted every day for 14 days. (B) Schematic of the method used to identify genes required for S. venezuelae exploratory growth. S. venezuelae spores were subject to chemical mutagenesis, then screened on G- agar (no glucose, exploration-permissive without S. cerevisiae) for a lack of exploratory growth. Static colonies (beige) were grown beside S. cerevisiae (pink) on YPD medium to confirm a lack of exploratory growth. Genomic DNA was isolated from strains unable to initiate exploratory growth on G- agar, and when inoculated beside S. cerevisiae on YPD medium. Whole genome sequencing was performed to identify mutations responsible for the lack of exploratory growth. (C) Morphology of a mutant cytochrome bd oxidase S. venezuelae strain (∆cydCD) and the corresponding complemented strain grown on YPD agar for 14 days. (D) Transcript levels for alkaline stress-responsive genes in S. venezuelae explorer cells (grown beside S. cerevisiae on YPD medium), divided by levels for non-exploratory S. venezuelae cells (grown alone on YPD medium). Transcript levels were normalized and differential expression was log2-transformed. The associated sven gene numbers are shown above the bar graphs.

S. venezuelae grown alone raises the pH of glucose-deficient medium.
S. venezuelae was grown alone on G- (no glucose) or G+ (glucose-containing) agar medium containing the pH indicator bromothymol blue. Two replicates were inoculated on each plate, and these were grown for 14 days.
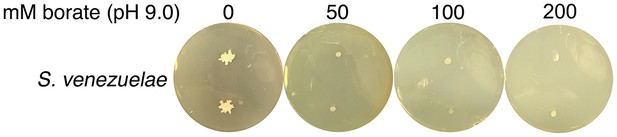
High pH alone does not stimulate S. venezuelae exploration.
S. venezuelae was grown alone on YPD agar medium buffered to pH 9.0 using 50, 100 or 200 mM borate. Two replicates were inoculated on each plate, and these were grown for 14 days.
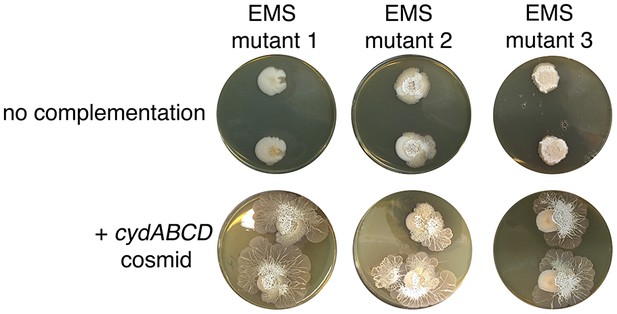
Complementation of explorer mutant phenotypes.
Top row: EMS (ethyl methanesulfonate) mutagenesis-derived S. venezuelae explorer mutants containing point mutations in the cydABCD operon, grown beside S. cerevisiae. Bottom row: Explorer mutants complemented with a cosmid carrying the wild type cydABCD operon. Two replicates were inoculated on each plate.
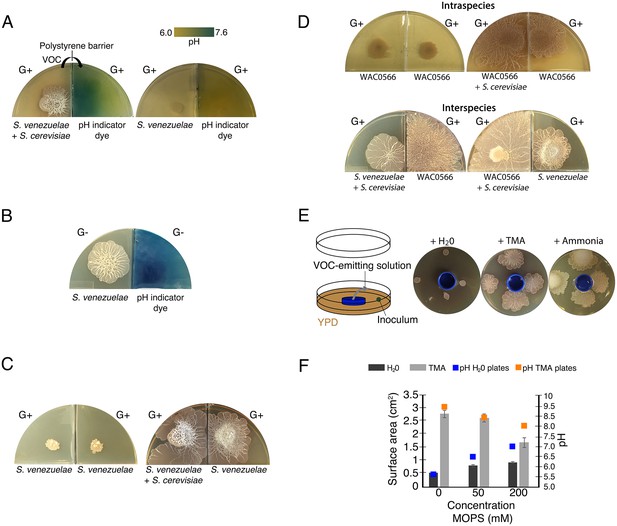
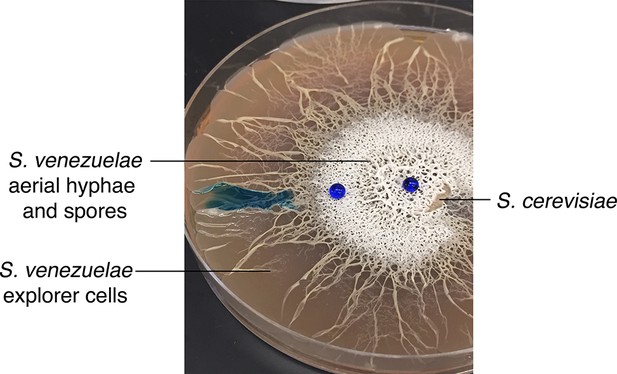
Volatile organic compounds released by S. venezuelae raise the medium pH and induce exploratory growth in physically separated Streptomyces.
(A) Effect of S. venezuelae explorer cells on pH of physically separated medium. Each compartment is separated by a polystyrene barrier. S. venezuelae and S. cerevisiae were grown in the left compartment of one plate (left), while S. venezuelae alone was grown in the left compartment of the other plate (right). After 10 days, bromothymol blue pH indicator dye was spread on the agar in the right compartment of each plate. Blue indicates VOC-induced alkalinity. (B) S. venezuelae was grown alone on YP (G- agar) in the left compartment, while the right compartment contained uninoculated YP (G-) agar. After seven days, the same pH indicator dye as in Figure 4A was spread over the agar in the right compartment. Blue represents a rise in pH above 7.6. (C) Left: S. venezuelae alone was inoculated in each compartment. Right: S. venezuelae was grown beside S. cerevisiae in the left compartment, and S. venezuelae alone was grown in the right compartment. All strains were grown on YPD (G+) agar medium for 10 days. (D) Top left: Wild Streptomyces isolate WAC0566 was grown alone in each compartment. Top right: WAC0566 was grown beside S. cerevisiae in the left compartment, and grown alone in the right compartment. Bottom left: S. venezuelae was grown beside S. cerevisiae in the left compartment, and WAC0566 was grown alone in the right compartment. Bottom right: WAC0566 was grown beside S. cerevisiae in the left compartment, while S. venezuelae was grown alone in the right compartment. All strains were cultured on YPD (G+) agar medium for 10 days. (E) Schematic of the plate-based assay used to assess the effects of volatile-emitting solutions (and controls) on nearby Streptomyces colonies. H2O, TMA, or ammonia solutions were placed in a blue plastic dish, and S. venezuelae was spotted around each dish on YPD medium. Plates were incubated at room temperature for seven days. (F) Surface area and pH of S. venezuelae colonies grown on YPD medium around small dishes containing H2O or TMA solutions, as shown in Figure 4E. S. venezuelae was grown at room temperature for seven days on either unbuffered YPD medium or YPD medium buffered to pH 7.0 using MOPS. All values represent the mean ± standard error for four replicates.
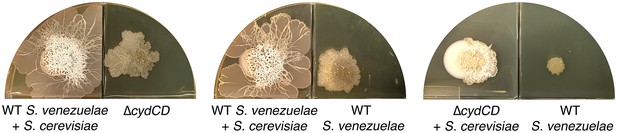
The S. venezuelae cydCD mutant strain can explore in response to volatile signals produced by neighbouring explorer cells.
Left: Wild type (WT) S. venezuelae was grown beside S. cerevisiae in the left compartment, and the S. venezuelae cydCD mutant strain was grown alone in the right compartment. Middle: Wild type S. venezuelae was grown beside S. cerevisia in the left compartment, and wild type S. venezuelae was grown alone in the right compartment. Right: The cydCD mutant was grown adjacent to S. cerevisiae in the left compartment (where it sporulated but did not spread), while wild type S. venezuelae was grown alone in the right compartment. All strains were grown on YPD (G+) agar medium for 10 days.
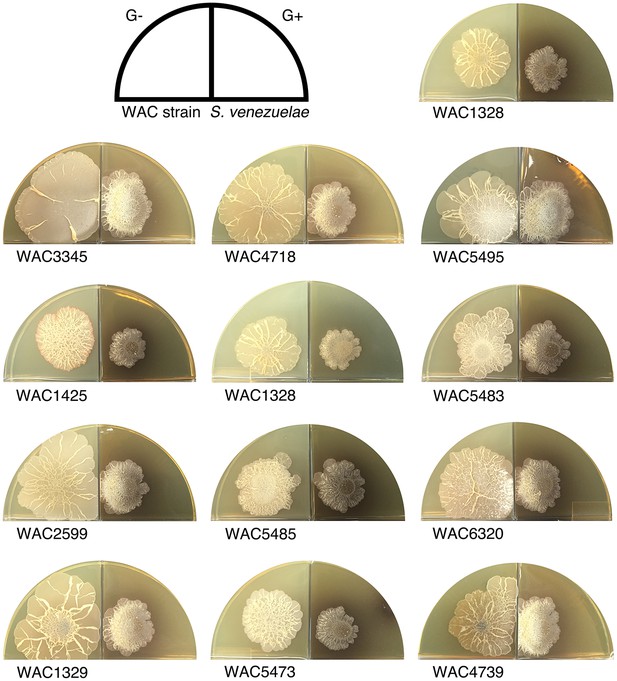

Wild explorer Streptomyces species promote exploration in S. venezuelae using volatile signals.
Using our two-quadrant assay, 13 independent wild Streptomyces isolates (WAC strains) were inoculated on G- agar, adjacent to S. venezuelae inoculated on G+ agar medium (where no exploration was observed on its own). Each WAC strain was able to promote S. venezuelae exploration through the release of a volatile compound.
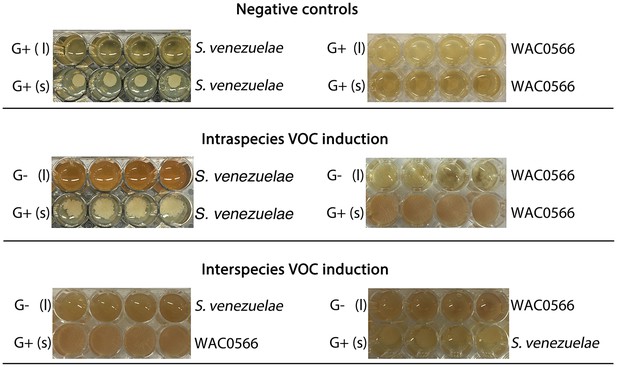
The VOC produced by S. venezuelae explorer cells can be produced by liquid-grown (G-) S. venezuelae and WAC0566 cultures.
All strains were grown in 48-well plates, with (l) indicating liquid cultures (top rows), and (s) indicating solid YPD agar (bottom rows). Liquid cultures were either G+ (glucose-containing) or G- (no glucose), while all solid medium was G+ (exploration repressive condition). Plates were grown shaking for three days. For all plates, we monitored exploration by strains growing on G+ agar (bottom rows), in response to VOCs produced by the liquid-grown cultures. The top panel shows S. venezuelae (left) and the wild Streptomyces strain WAC0566 (right) grown in G+ liquid (a condition where the VOC of interest is not expected to be produced). The middle panel shows the same strains, only grown in G- liquid (where the VOC was predicted to be produced). The bottom panel shows the test for interspecies VOC production/response, with S. venezuelae and WAC0566 grown in G- liquid, opposite WAC0566 and S. venezuelae, respectively.
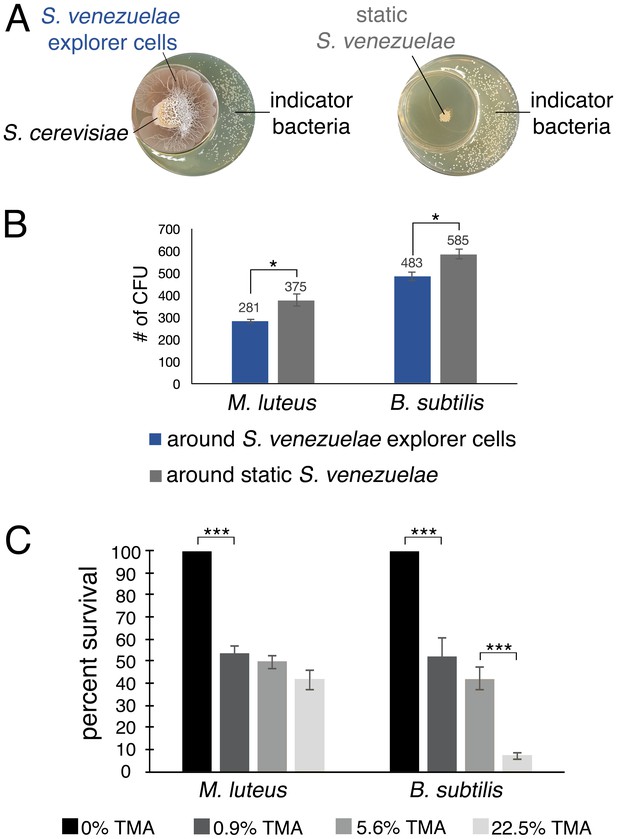
S. venezuelae VOCs inhibit the growth of other bacteria.
(A) S. venezuelae was grown beside S. cerevisiae (left) or alone (right) on YPD agar in a small dish placed within a larger dish containing YPD medium. After 10 days, an indicator strain (B. subtilis or M. luteus) was spread around the dish. (B) Quantification of B. subtilis and M. luteus colonies following growth adjacent to static or explorer S. venezuelae cultures. Values represent the mean ± standard error for three replicates. The asterisk (*) indicates p<0.05, as determined by a Student’s t-test. (C) Quantification of B. subtilis and M. luteus survival following incubation around small dishes containing TMA solutions at concentrations ranging from 0–22.5%. Plates were incubated at room temperature for two days. Percent survival indicates the OD600 of strains around wells containing 0.9%, 5.6%, or 22.5% TMA solutions compared to the OD600 of strains around wells containing H2O (100% survival). Values represent the mean ± standard error for three biological replicates, and each biological replicate is the average of four technical replicates. The asterisks (***) indicate p<0.005, as determined by a Student’s t-test.
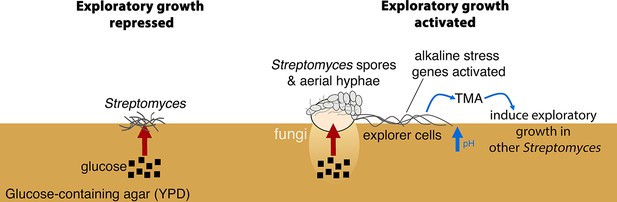
New model for Streptomyces development.
When S. venezuelae is grown alone on glucose-rich medium S. venezuelae exploratory growth is repressed (left). When S. venezuelae is grown beside S. cerevisiae or other yeast on glucose-rich medium (right), the yeast metabolizes glucose, relieving the repression of S. venezuelae exploration. S. venezuelae explorer cells produce the volatile pheromone TMA, which raises the pH of the medium from 7.0 to 9.5. Explorer cells activate alkaline stress genes to withstand the alkaline pH. TMA, and its associated medium alkalinisation, can induce exploratory growth in physically separated Streptomyces.
Videos
Leading edge of S. venezuelae explorer cells over a 17 hr time course.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21738.007Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary tables.
(a) VOCs identified using GC×GC-TOFMS. (b) Effects of media composition on S. venezuelae exploration when grown in the absence of yeast. (c) Oligonucleotides used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21738.021





