A sequential multi-target Mps1 phosphorylation cascade promotes spindle checkpoint signaling
Figures
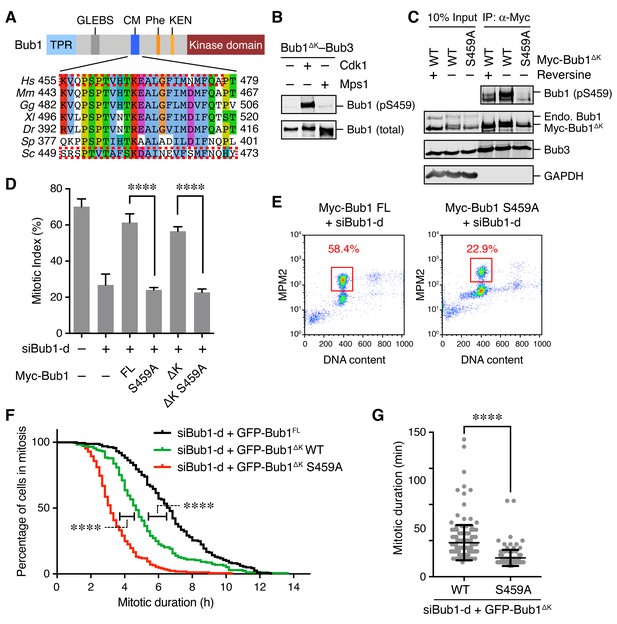
Phosphorylation of Bub1 S459 is critical for spindle checkpoint activation.
(A) Domains and motifs of Bub1 and sequence alignment of its conserved motif (CM). TPR, tetratricopeptide repeat; GLEBS, Gle2-binding sequence; Phe, phenylalanine-containing motif, also known as ‘ABBA’ motif; KEN, lysine-glutamate-asparagine motif. Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Gg, Gallus gallus; Xl, Xenopus laevis; Dr, Danio rerio; Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The boxed regions in scBub1 and hsBub1 were synthesized as phospho-peptides and used in this study. (B) Recombinant Bub1ΔK–Bub3 complex was incubated with Cdk1–Cyclin B1 (Cdk1) or Mps1 in the presence of ATP. The kinase reactions were blotted with indicated antibodies. (C) HeLa cells stably expressing Myc-Bub1ΔK wild-type (WT) or S459A mutant were treated with nocodazole and MG132 in the presence or absence of reversine. Myc-Bub1 was immunoprecipitated and blotted with indicated antibodies. Endo., endogenous. (D) Flow cytometry of HeLa Tet-On cells stably expressing indicated siRNA-resistant Myc-Bub1 transgenes that were transfected with siBub1-d and treated with taxol. Mitotic indices were calculated as percentages of MPM2+ 4N cells in flow cytometry, and then plotted. FL, full-length. △K, mutant with the kinase domain truncated. Error bars, s.d. (n = 4 independent experiments). ****p<0.0001; Student’s t-test. (E) Representative flow cytometry plots of cells in (D). (F) HeLa Tet-On cells stably expressing indicated GFP-Bub1 transgenes were transfected with siBub1-d, treated with taxol, and imaged with time lapse microscopy. Cumulative percentages of cells remaining in mitosis were plotted against mitotic duration. Data from three independent experiments were combined. n (FL) = 161; n (△K)=173; n (△K S459A)=169. ****p<0.0001; Log-rank test. (G) Mitotic durations of cells stably expressing GFP-Bub1ΔK WT or S459A that were depleted of endogenous Bub1 and not treated with microtubule poisons. Data from three independent experiments were combined. Each dot represents one cell. n (WT) = 170; n (S459A)=157. ****p<0.0001; Student’s t-test.
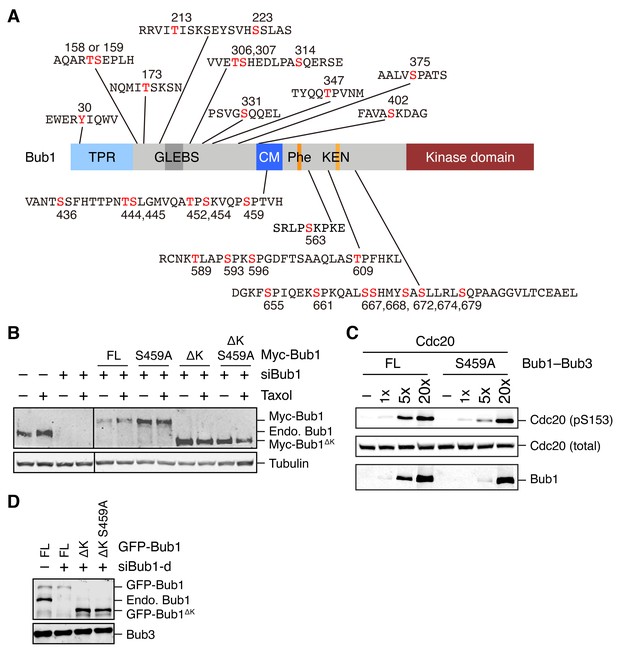
Identification of mitotic phosphorylation sites in human Bub1 and characterization of the Bub1 S459A mutant.
(A) Domain structure of human Bub1 and a summary of all 30 phosphorylation sites identified by mass spectrometry. Phosphorylated residues are denoted in red. (B) Lysates of cells in Figure 1D were blotted with anti-Bub1 and anti-Tubulin antibodies. (C) Recombinant Cdc20 was incubated with varying doses of recombinant Bub1–Bub3 full-length (FL) or S459A in the presence of ATP. The kinase reactions were resolved on SDS-PAGE and blotted with the indicated antibodies. (D) Lysates of cells in Figure 1F and G were blotted with anti-Bub1 and anti-Bub3 antibodies.
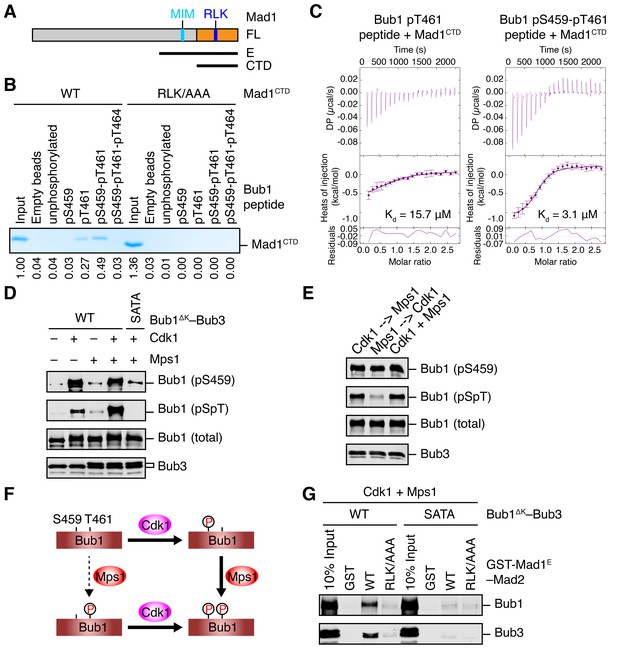
Sequential phosphorylation of human Bub1 by Cdk1 and Mps1 enhances its binding to Mad1.
(A) Domains and motifs of Mad1. Schematic domain structures and tested fragments of Mad1 protein. CTD, C-terminal domain; MIM, Mad2-interacting motif; RLK, the arginine-leucine-lysine motif. The E fragment of Mad1 containing both MIM and CTD was used to make the Mad1–Mad2 complex in this study. (B) In vitro pull-down of Mad1CTD using empty beads or beads conjugated to the indicated Bub1 peptides. Proteins bound on beads were separated on SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie blue staining. Relative band intensities were quantified and indicated below the gel. (C) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) assays of binding between the C-terminal domain (CTD) of human Mad1 and the human Bub1 peptides containing either phospho-T461 alone or both phospho-S459 and phospho-T461. Kd, dissociation constant. (D) In vitro kinase assays of recombinant Bub1ΔK–Bub3 WT or S459A/T461A (SATA) treated with Cdk1 or Mps1 or both. The kinase reactions were resolved on SDS-PAGE and blotted with indicated antibodies. pSpT, a phospho-specific antibody recognizing both phospho-S459 and phospho-T461. (E) In vitro kinase assays similar to (D), except that the kinases were added in the indicated orders. In lanes 1 and 2, Cdk1 or Mps1 was first incubated with the substrate for 30 min before being inhibited by RO3306 or reversine, respectively. (F) Schematic drawing of the sequential phosphorylation of Bub1 at S459 and T461 by Cdk1 and Mps1. (G) Bub1ΔK–Bub3 WT and SATA were first phosphorylated by both Cdk1 and Mps1, and then assayed for binding to GST-Mad1E–Mad2 beads. The bound proteins were blotted with the indicated antibodies.
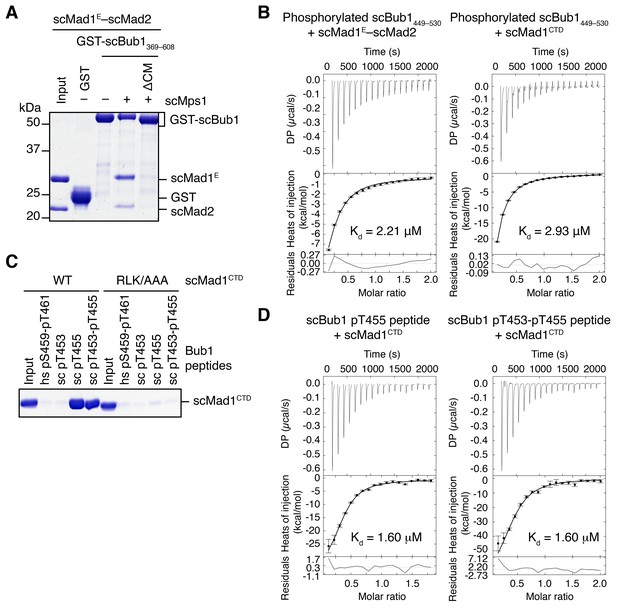
Binding of scBub1 phosphorylated at T455 by Mps1 to scMad1 CTD.
(A) In vitro pull-down of the scMad1E–scMad2 complex with beads bound to GST or the indicated GST-scBub1 fragments, which were expressed alone or co-expressed with the kinase domain of scMps1. Proteins bound to the beads were analyzed with SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. (B) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) assay of binding between Mps1-phosphorylated scBub1449–530 and the scMad1E–scMad2 complex or the C-terminal domain (CTD) of scMad1. Kd, dissociation constant. (C) In vitro pull-down of scMad1CTD WT and RLK/AAA with beads conjugated to the indicated scBub1 peptides. The phosphorylated residues of Bub1 peptides were denoted. hs, Homo sapiens. (D) ITC assays of binding between the C-terminal domain (CTD) of scMad1 and the scBub1 peptides containing either phospho-T455 alone or both phospho-T453 and phospho-T455. Kd, dissociation constant.
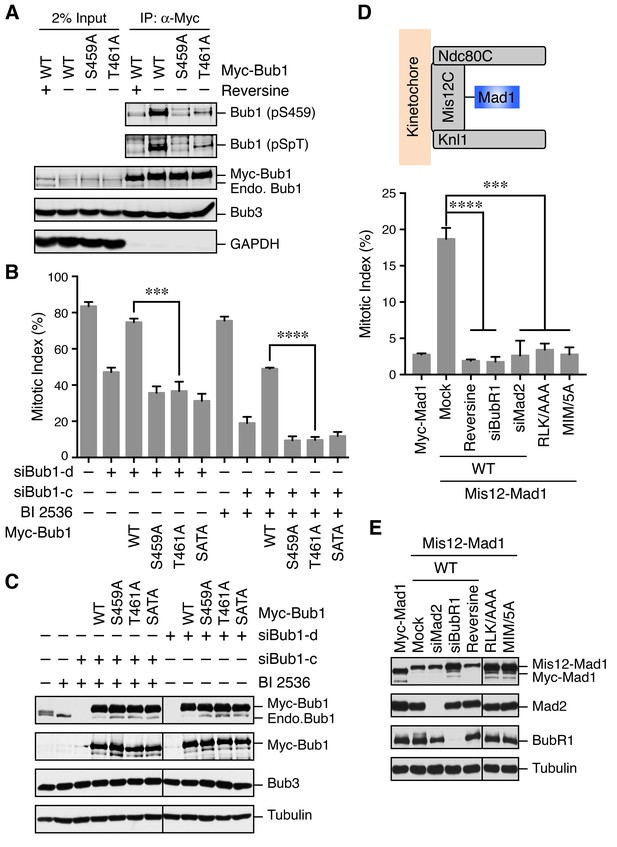
The Bub1–Mad1 interaction is crucial for checkpoint activation in human cells.
(A) HeLa cells expressing Myc-Bub1 transgenes were treated with nocodazole and MG132 in the presence or absence of reversine. Myc-Bub1 proteins were immunoprecipitated and blotted with the indicated antibodies. (B) Mitotic indices of cells expressing Bub1 transgenes that were transfected with the indicated Bub1 siRNA and treated with nocodazole in the presence or absence of the Plk1 inhibitor BI2536. Error bars, s.d. (n = 3 independent experiments). ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; Student’s t-test. (C) Lysates of cells in (B) were blotted with the indicated antibodies. Endo., endogenous. (D) Mitotic indices of cells expressing the indicated Mis12–Mad1 fusion proteins that were treated with reversine or siRNAs against BubR1 or Mad2. MIM/5A, Mad1 mutant with its MIM (541KVLHM545) changed to five alanines. Error bars, s.d. (n = 3 independent experiments). ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; Student’s t-test. (E) Lysates of cells in (D) were blotted with the indicated antibodies.
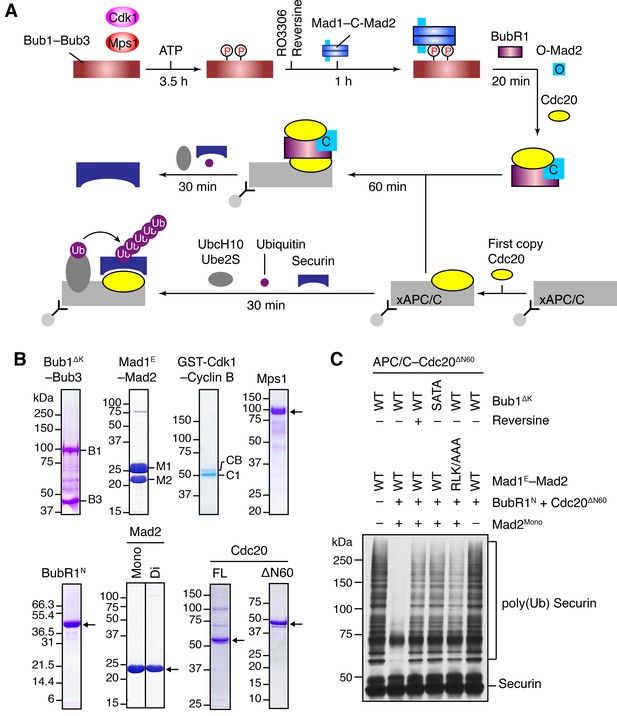
The Bub1–Mad1 complex promotes APC/CCdc20 inhibition by MCC components.
(A) Flow charts of the in vitro reconstitution of Mps1-stimulated APC/C inhibition by MCC components. The incubation times of each reaction step are indicated. All processes were performed at room temperature. Molecules are not drawn to scale. xAPC/C, the APC/C complex isolated from Xenopus egg extract by immunoprecipitation. Ub, ubiquitin. (B) A collection of recombinant proteins used for the in vitro reconstitution. Relevant protein bands were labeled or indicated by arrows. B1, Bub1ΔK; B3, Bub3; M1, Mad1E; M2, Mad2; CB, Cyclin B1; C1, GST-Cdk1; Mono, monomeric Mad2; Di, dimeric Mad2; FL, full-length. (C) The ubiquitination reactions as depicted in (A) were resolved on SDS-PAGE and blotted with the anti-Myc antibody that detected Myc-Securin. The slow-migrating species represented the poly-ubiquitinated forms of Securin. For the reversine sample, the inhibitor was added to the kinase reaction containing Mps1 and Bub1ΔK–Bub3 prior to ATP addition.
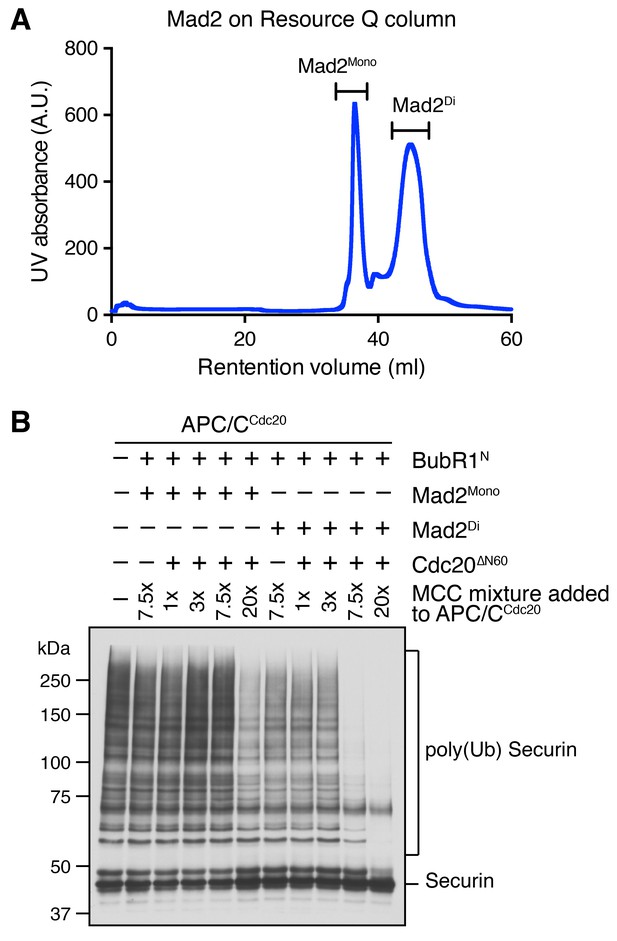
Characterization of monomeric and dimeric Mad2 in the APC/CCdc20 inhibition assay.
(A) UV trace of recombinant purified Mad2 fractionated on a Resource Q column. The first peak belongs to the Mad2 monomer (Mad2Mono), whereas the second peak contains the Mad2 dimer (Mad2Di). (B) Spontaneous MCC assembly with Mad2Mono or Mad2Di and the subsequent inhibition of APC/CCdc20. Experiments were performed as depicted in Figure 4A, except that the Bub1 phosphorylation and Bub1–Mad1 binding steps were omitted. Varying amounts of the MCC mixture were added to APC/CCdc20. The ubiquitination reaction mixtures were resolved on SDS-PAGE and blotted with the anti-Myc antibody that detected Myc-Securin. The slow-migrating species represented the poly-ubiquitinated forms of Securin.
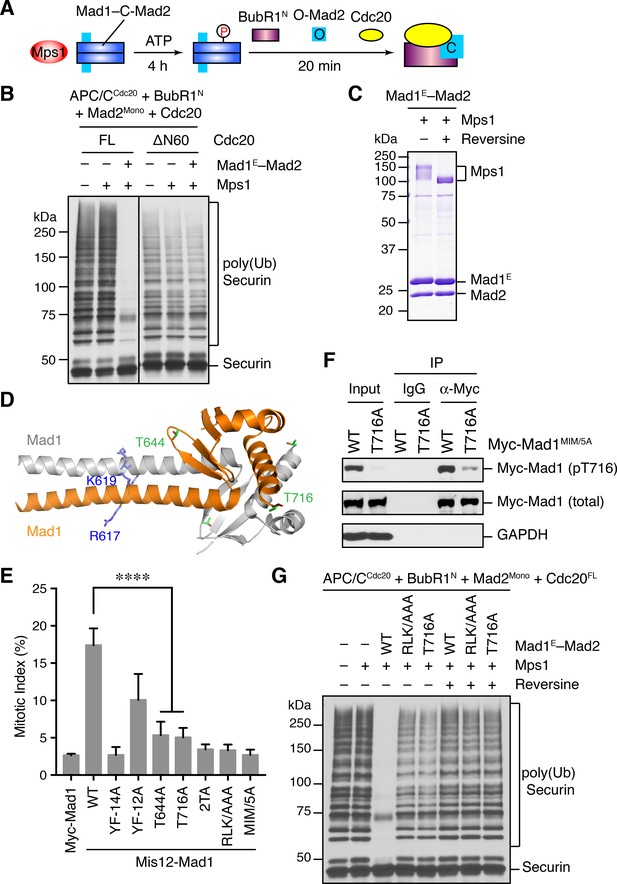
Phosphorylation of Mad1 T716 by Mps1 promotes MCC assembly and checkpoint signaling.
(A) Schematic drawing of the assay examining MCC assembly facilitated by Mps1-phosphorylated Mad1–C-Mad2. (B) MCC assembly and APC/C inhibition were performed as depicted in (A). The ubiquitination reaction mixtures were resolved on SDS-PAGE and blotted with the anti-Myc antibody that detected Myc-Securin. The slow-migrating species represented the poly-ubiquitinated forms of Securin. FL, full-length. Cdc20ΔN60 lacks residues 1–60. (C) Recombinant human Mad1E–Mad2 complex was incubated with Mps1 in the presence or absence of reversine. The reactions were resolved on SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie. Note that Mps1 underwent autophosphorylation in the absence of reversine. (D) Cartoon drawing of the crystal structure of human Mad1CTD (PDB ID: 4DZO) with the RLK motif, T644, and T716 shown in sticks. (E) Mitotic indices of HeLa cells expressing the indicated Mis12–Mad1 fusion proteins. Error bars, s.d. (n = 5 independent experiments). ****p<0.0001; Student’s t-test. (F) HeLa cells expressing Myc-Mad1 MIM/5A or MIM/5A;T716A were synchronized with thymidine and released into nocodazole-containing medium. MIM/5A, mutant with the Mad2 Interacting Motif replaced by alanine. Because overexpression of Mad1 inactivates the spindle checkpoint, we used Mad1 MIM/5A to prevent cells from escaping nocodazole-mediated mitotic arrest. Myc-Mad1 proteins were immunoprecipitated and blotted with indicated antibodies. (G) The MCC mixtures were prepared as depicted in (A) with the indicated Mad1E proteins, and then applied to the APC/C-dependent ubiquitination assay. The ubiquitination reaction mixtures were resolved on SDS-PAGE and blotted with the anti-Myc antibody that detected Myc-Securin. The slow-migrating species represented the poly-ubiquitinated forms of Securin. In reactions containing reversine, reversine was added prior to the addition of ATP.
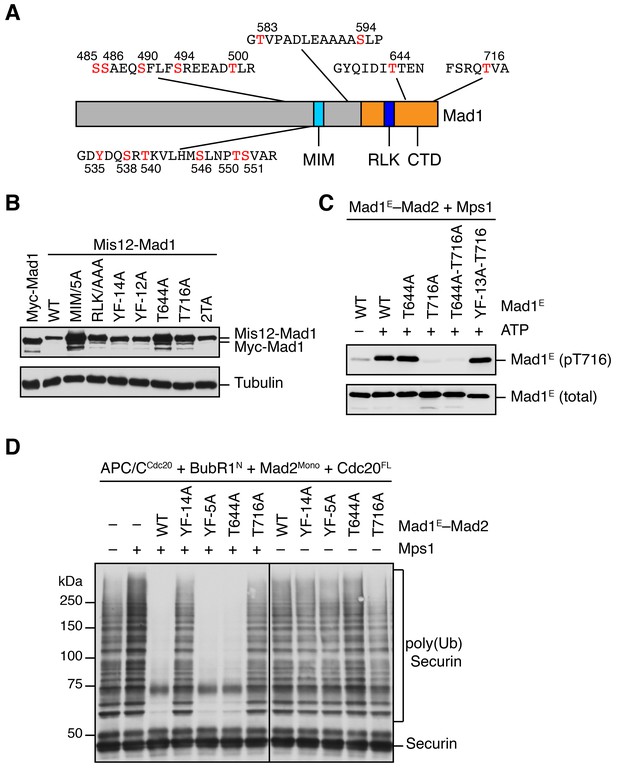
Characterization of Mad1 phosphorylation and its function in APC/C inhibition by MCC components.
(A) Summary of all 15 Mps1-phosphorylation sites of Mad1E identified by mass spectrometry. Phosphorylated residues are depicted in red. (B) Lysates of cells in Figure 5E were blotted with anti-Mad1 and anti-Tubulin antibodies. (C) In vitro kinase assays of recombinant Mad1E–Mad2 WT or indicated mutants treated with Mps1 in the absence or presence of ATP. YF-13A-T716, Mad1 mutant with all phosphorylation sites except T716 mutated to phenylalanine or alanine. The kinase reactions were resolved on SDS-PAGE and blotted with indicated antibodies. pT716, a phospho-specific antibody recognizing phospho-T716 of Mad1. (D) The MCC mixtures were prepared as depicted in Figure 5A with the indicated Mad1E proteins, and then applied to the APC/C ubiquitination assay. The ubiquitination reaction mixtures were resolved on SDS-PAGE and blotted with the anti-Myc antibody that detected Myc-Securin. The slow-migrating species represented the poly-ubiquitinated Securin. YF-5A, Y535F/S538A/T540/S546A/T550A/S551A; YF-14A, mutant with all Mps1 phosphorylation sites of Mad1E mutated to phenylalanine or alanine.
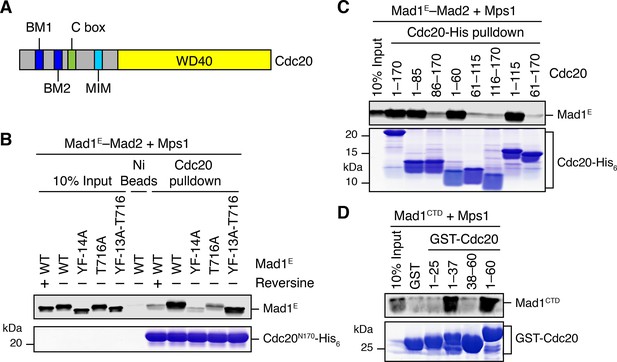
Phosphorylation of Mad1 T716 promotes its binding to Cdc20.
(A) Domains and motifs of Cdc20. C box, a conserved APC/C-binding motif; MIM, Mad2-interacting motif; BM1, basic motif 1 (27RWQRK31); BM2, basic motif 2 (54RTPGRTPGK62). (B) In vitro pull-down of the indicated Mad1E–Mad2 complexes (which had been pre-treated with the kinase domain of Mps1) by Ni2+ beads bound to Cdc20N170-His6. The bait protein was stained with Coomassie, and the prey proteins bound to beads were blotted with the anti-Mad1 antibody. (C) In vitro pull-down of the Mad1E–Mad2 complex (which had been pre-treated with the kinase domain of Mps1) by Ni2+ beads bound to the indicated Cdc20-His6 proteins. The bait proteins were stained with Coomassie, and the prey proteins bound to beads were blotted with the anti-Mad1 antibody. (D) In vitro pull-down of Mad1CTD (which had been pre-treated with the kinase domain of Mps1) by beads bound to the indicated GST-Cdc20 fragments. The bait proteins were stained with Coomassie, and the prey proteins bound to beads were blotted with the anti-Mad1 antibody.
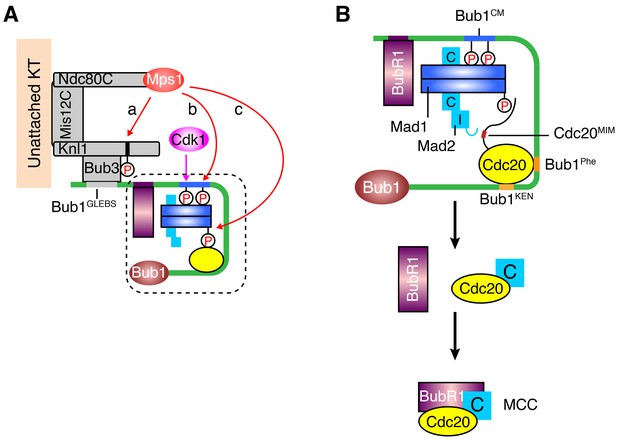
A sequential multi-target phosphorylation cascade by Mps1 promotes the assembly and activation of the Bub1–Mad1 scaffold.
(A) Mps1 recognizes unattached kinetochores (KT) through its direct binding to the Ndc80 complex (Ndc80C). At kinetochores, Mps1 first phosphorylates Knl1 at multiple MELT motifs to recruit the Bub1–Bub3 complex (a). After Cdk1 phosphorylates Bub1 S459, Mps1 then phosphorylates Bub1 T461 (b). The doubly phosphorylated Bub1 conserved motif (CM) binds to and recruits the Mad1–C-Mad2 core complex. Mps1 then phosphorylates Mad1 at T716, and this phosphorylation enables Mad1 binding to Cdc20 (c). (B) The boxed region in (A) is magnified and shown with more molecular details here. The Mad1–C-Mad2 core complex bound to phosphorylated Bub1 CM can further recruit O-Mad2 and convert it to I-Mad2. The WD40 domain of Cdc20 is anchored to the Phe and KEN boxes of Bub1, whereas the N-terminal basic tail of Cdc20 is bound by the phosphorylated Mad1 CTD. This bipartite Cdc20-binding mode positions the MIM of Cdc20 close to I-Mad2, promoting the formation of the C-Mad2–Cdc20 complex. This binary complex can further bind to BubR1 (bound to Bub1 or from cytosol) to form MCC.





