Position- and Hippo signaling-dependent plasticity during lineage segregation in the early mouse embryo
Figures
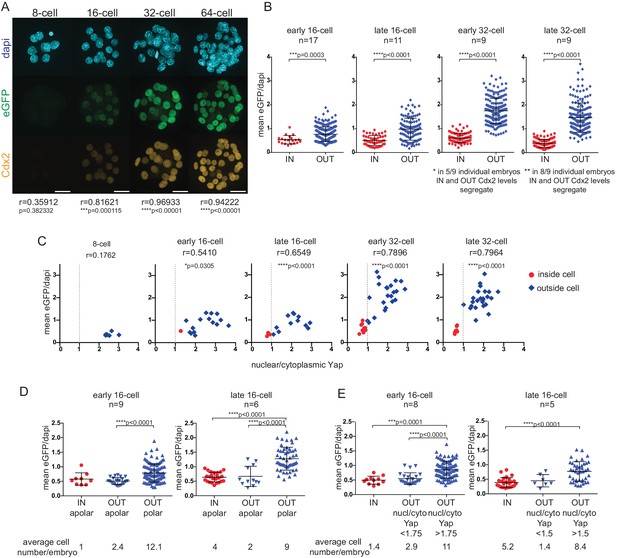
Cdx2-eGFP is an early marker of the developing TE lineage, governed by Hippo signaling differences from the early 16 cell stage.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining against Cdx2 and eGFP in Cdx2-eGFP heterozygous embryos at different stages. Representative images of 10 8 cell, 39 16 cell, 35 32 cell and 11 64 cell embryos stained and imaged in two independent experiments. Scale bar: 25 μm. Correlation between eGFP and endogenous Cdx2 signals was calculated by measuring fluorescence intensities in individual cell nuclei and performing Pearson’s correlation (r indicates coefficient). p-values are also given for each embryonic stage. (B) Mean fluorescence intensity of eGFP (Y-axis) in individual inside and outside cell nuclei of different stage Cdx2-eGFP embryos. Position was determined by co-staining embryos with phalloidin (F-actin) and cells with any surface membrane exposure were classified as outside. n indicates number of embryos. * and ** note how eGFP/Dapi measurements segregate in individual embryos. Statistical significance was calculated by Mann-Whitney test and significant p-values are indicated. Error bars: s.d. of mean. (C) Mean eGFP intensity relative to nuclear/cytoplasmic Yap ratio in individual inside (red) and outside (blue) cells in Cdx2-eGFP embryos at different stages. Representative measurements from 5 8 cell, 8 early 16 cell, 5 late 16 cell, 5 early 32 cell and 4 late 32 cell embryos are shown. All embryos were stained and imaged in one experiment. Correlation was calculated using Pearson’s correlation (r indicates correlation coefficient) and p-value is given. (D–E) Mean fluorescenceintensity of eGFP (Y-axis) in single cells in different cell populations, in early and late 16 cell stage Cdx2-eGFP embryos. (D) Inside apolar, outside apolar and outside polar cell populations. (E) Inside cells, outside cells with low nuclear/cytoplasmic Yap ratio and outside cells with high nuclear/cytoplasmic Yap ratio. Polarity was determined by phospho-ezrin staining. n indicates number of embryos analyzed. Statistical significance was calculated by Kruskal-Wallis test and significant p-values are indicated. Error bars: s.d. of mean. Cells in M-phase are not included.
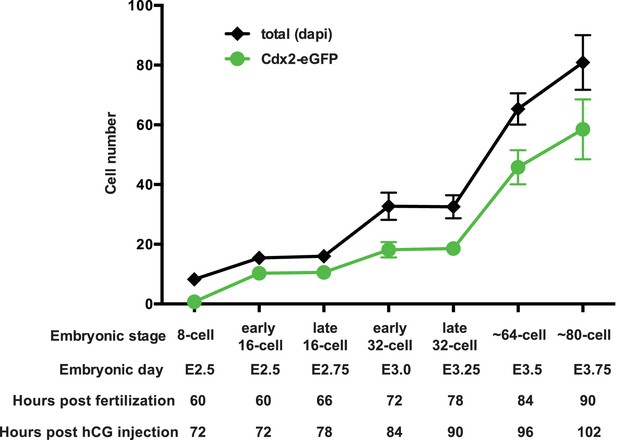
Developmental staging of Cdx2-eGFP embryos.
Cdx2-eGFP embryos were always staged based on cell number, which we determined in live embryos based on the number of Cdx2-eGFP positive cells present. An additional layer of ‘early’ and ‘late’ sub-staging was included, which refers to the time of embryo isolation. For example ‘early 16 cell’ embryos were harvested at E2.5 – a time point when the population of embryos are between 8 and 16 cell stages – but only 16 cell embryos were used (embryos with average of 12 visible Cdx2-eGFP positive cells). Or ‘late 16 cell’ embryos were harvested at E2.75 -when embryos are between 16- and 32 cells - however only strictly 16 cell embryos (embryos with average of 12 visible Cdx2-eGFP positive cells) were used from this time point. We established criteria for staging using the number of Cdx2-eGFP positive cells in live embryos. Graph above shows average number of Cdx2-eGFP positive cells in live staged embryos at each stage (8 cell n = 10, early 16 cell n = 14, late 16 cell n = 19, early 32 cell n = 21, late 32 cell n = 24, ~64 cell n = 11 and ~80 cell n = 14). A subset of staged embryos were fixed and total cell numbers were determined by Dapi staining (8 cell n = 10, early 16 cell n = 14, late 16 cell n = 15, early 32 cell n = 21, late 32 cell n = 24, ~64 cell n = 11 and ~80 cell n = 11). Error bars indicate standard deviation of mean. Using this guide, only carefully staged embryos were used at each time point for all experiments in the study.
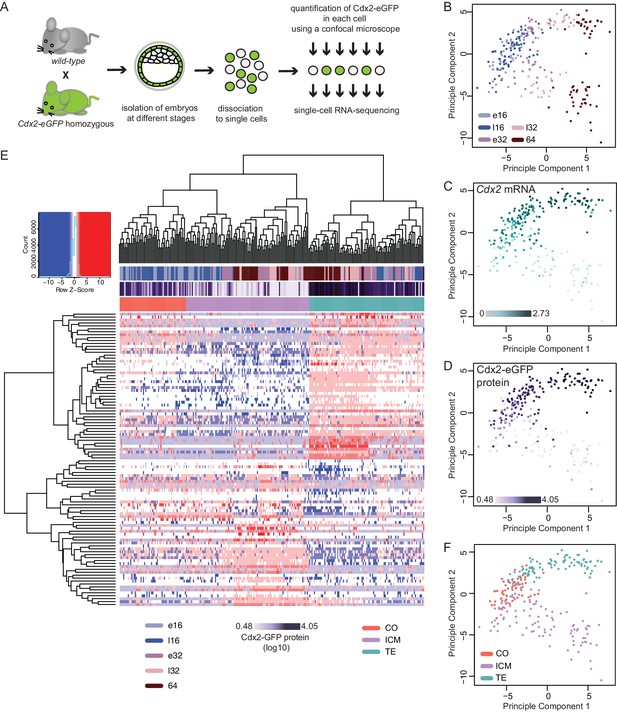
Single–cell RNA sequencing reveals gradual emergence of ICM and TE lineages.
(A) Experimental outline for harvesting single cells for RNA sequencing. (B–D) Principal component analysis using top 100 variable genes across all cells, where each cell is annotated for (B) developmental time (C) corresponding expression level (log10 RPKM) of Cdx2 mRNA (D) corresponding Cdx2-eGFP protein (measured prior to RNA sequencing). (E) Heatmap showing log10 RPKM expression level of early 32 cell lineage signature genes in all 262 cells. Cells were annotated for developmental time, corresponding Cdx2-eGFP values and lineage identity, assigned based on Spearman’s rank correlation clustering. (F) Principal component analysis using top 100 variable genes across all cells, showing TE, ICM and co-expressing (CO) lineage assignment of cells.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Excel file of differentially expressed genes from SCDE analysis between ‘Cdx2-low’ and ‘Cdx2-high’ cell populations (based on PCA groupings) at the early 32 cell stage.
Top 50 ‘Cdx2-low’ genes and top 50 ‘Cdx2-high’ genes used as ICM- and TE-specific gene signature, respectively.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22906.006
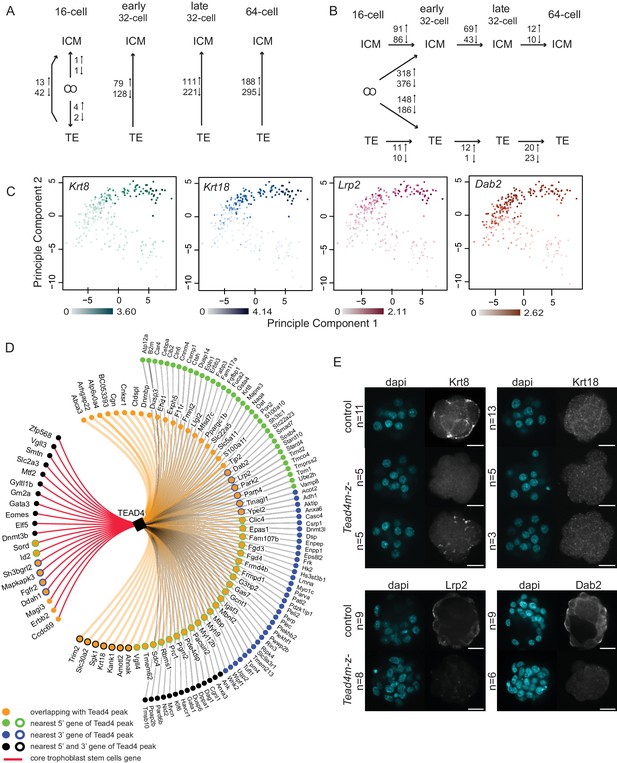
Different gene expression dynamics during development of ICM and TE lineages.
(A–B) Summary of the number of genes differentially expressed from SCDE analysis (A) between lineages within each developmental time point and (B) between developmental time points within each lineage. Due to the low number of ICM and TE cells at the early and late 16 cell stages, these time points were pooled. (C) Principal component analysis using top 100 variable genes across all cells, annotated for the expression level (log10 RPKM) of early TE-associated genes Krt8, Krt18, Lrp2 and Dab2. (D) TE-specific genes identified by single-cell RNA sequencing associated with at least one Tead4 binding site in trophoblast stem cells (Home et al., 2012). Gene association with Tead4 binding sites was defined as in Home et al. – genes overlapping with Tead4 peaks and genes nearest to Tead4 peaks in 5’ and 3’ directions are considered. Core trophoblast genes (Ralston et al., 2010) are also shown (red line). (E) Representative immunofluorescence stainings of control (Tead4m-z+) and Tead4 maternal/zygotic mutant (Tead4m-z-) embryos for Krt8 and Krt18 (16 cell stage embryos) and Lrp2 and Dab2 (32 to 64 cell stage embryos; Lrp2 and Dab2 were not detected in earlier stage embryos). n indicates total number of embryos analyzed. Scale bar: 25 μm.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Excel file of differentially expressed genes from SCDE analysis between lineages within each developmental time point.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22906.008
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Excel file of differentially expressed genes from SCDE analysis between developmental time points within each lineage.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22906.009
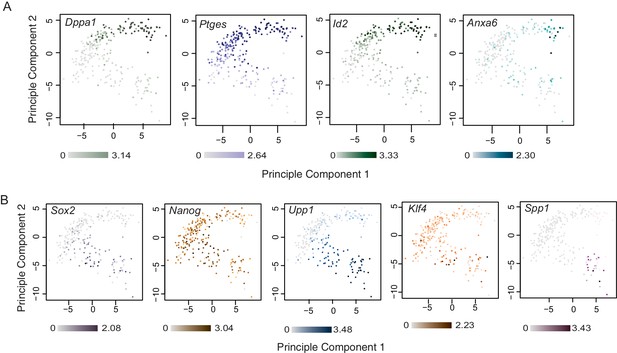
Examples of lineage and stage specific gene expression patterns identified by single-cell RNA sequencing.
Principal component analysis using top 100 variable genes across all cells, annotated for the expression level (log10 RPKM) of (A) TE-associated genes Dppa1, Ptges, Id2 and Anxa6 and (B) ICM-associated genes Sox2, Nanog, Upp1, Klf4 and Spp1. Sox2, Nanog, Upp1 were upregulated between 16 cell/early 32 cell stage ICM, Klf4 was upregulated between early 32 cell/late 32 cell stage ICM and Spp1 was upregulated between late 32 cell/64 cell stage ICM. Dppa1, Ptges, Id2 were upregulated in as early as the 16 cell stage TE and Anxa6 was upregulated between late 32 cell/64 cell stage TE.
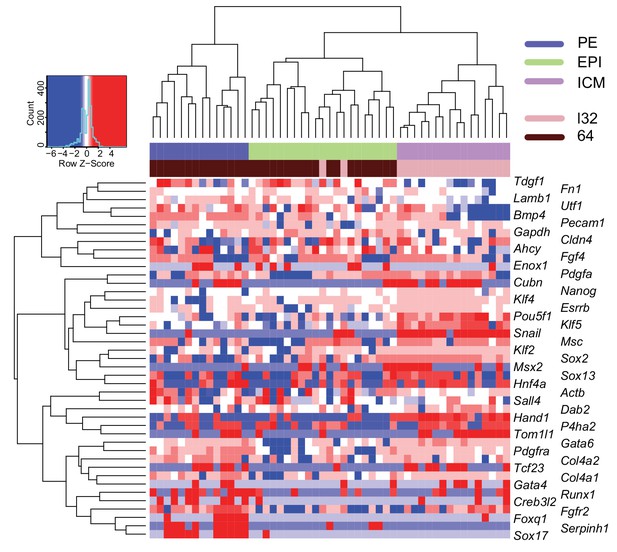
ICM commitment coincides with initiation of epiblast and primitive endoderm segregation.
Heatmap showing the expression level (log10 RPKM) of epiblast (EPI) and primitive endoderm (PE) markers for 64 cell ICM (33 cells) and late 32 cell ICM (18 cells). A panel of known EPI and PE lineage markers were used as input (Guo et al., 2010; Ohnishi et al., 2014). Lineage identities (ICM, EPI and PE) were assigned to cells based on groupings by Spearman’s rank correlation clustering.
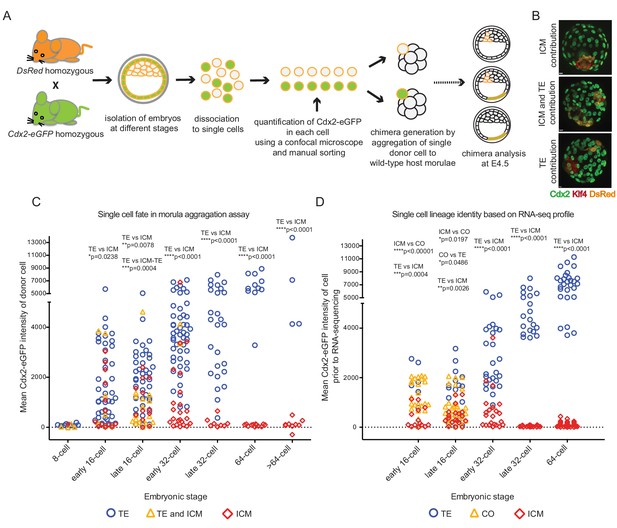
Individual cells with different Cdx2-eGFP levels aggregated to host morulae show gradual and differential loss of developmental potential over time.
(A) Experimental outline of morula aggregation assay. (B) Examples of chimeras with TE, ICM and TE and ICM contributions, analyzed at E4.5 by immunofluorescence staining. (C) Plot showing all aggregation chimera results. Each data point represents a single donor cell isolated from different stage embryos (X axis) with the level of mean Cdx2-eGFP measured in each cell before aggregation (Y axis). Donor cells are color coded for the lineage their progeny contributed to in the chimera. Statistically significant differences in Cdx2-eGFP intensities between different contributions (ICM vs TE and TE vs ICM-TE) were calculated using Mann-Whitney test and significant p-values are indicated. (D) Plot showing lineage identities assigned to single cells based on RNA sequencing profiles. Each data point represents a single cell isolated from different stage embryos (X axis) with the level of mean Cdx2-eGFP measured in each cell before sequencing (Y axis). Cells are color coded according to their lineage profiles. Statistically significant differences in Cdx2-eGFP intensities between different lineage groups (ICM vs TE, TE vs CO and ICM vs CO) were calculated using Mann-Whitney test and significant p-values are indicated.
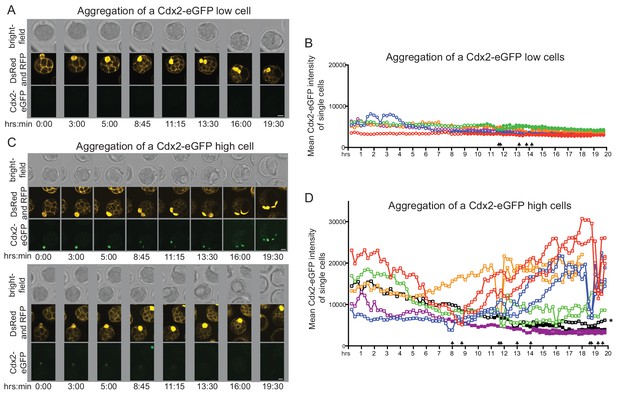
Live imaging chimera formation following single early 32 cell stage donor cell aggregation to host morula.
(A–B) Single plane snapshots from live imaging movies of chimera formation with (A) Cdx2-eGFP low and (B) Cdx2-eGFP high donor cells. To aid scoring of inside and outside positions in chimeras, wild-type host embryos were microinjected with membrane-localized RFP mRNA at the 2 cell stage. Single donor cells were isolated from early 32 cell stage embryos and were identified by the ubiquitous DsRed label. In order to allow imaging on a flat glass surface, donor cells in these experiments were microinjected under the zona pellucida of the host. Time scale indicates hours and minutes after aggregation. Scale bar: 20 μm. (C–D) Quantification of Cdx2-eGFP during chimera formation with (C) Cdx2-eGFP low and (D) Cdx2-eGFP high donor cells and their progeny throughout live imaging movies. Clear symbol indicates outside position of donor cell or its progeny, filled symbol indicates full internalization. Arrows indicate when donor cell or its progeny undergo mitosis. Position of daughter cell marker by * could not be determined as it was in a portion of the embryo that protruded though the hole made in the zona pellucida during donor cell injection.
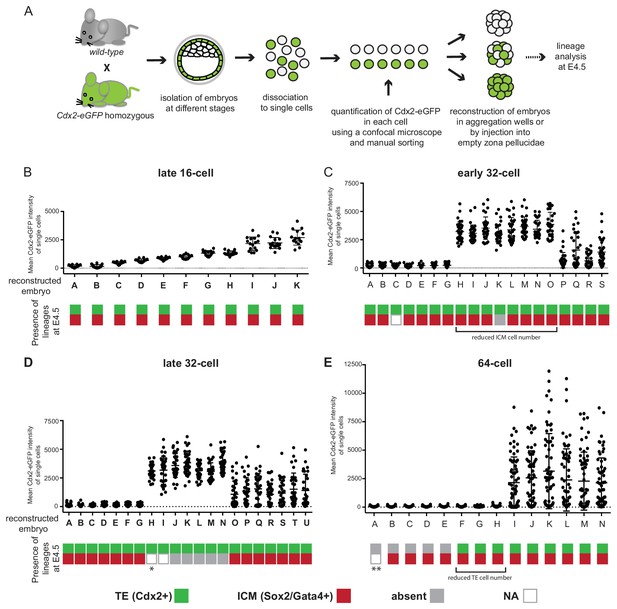
Embryos reconstructed entirely from Cdx2-eGFP low or high cells loose their potential to recapitulate ICM and TE lineages at different times.
(A) Experimental outline to reconstruct embryos entirely of Cdx2-eGFP low, high or random cells. (B–E) Plots showing embryo reconstructions from single cells isolated from (B) late 16 cell, (C) early 32 cell, (D) late 32 cell and (E) 64 cell stages. Each embryo (X axis, labeled with letters) was reconstructed from Cdx2-eGFP-quantified (Y axis) single cells. Color-coding below indicates the presence of Cdx2 positive TE (green) and Sox2 or Gata4 positive ICM (red) cells in reconstructed embryos at E4.5. Grey indicates the absence of a lineage; white (N/A) indicates the embryo was lost during immunofluorescence staining, thus information is only available of the TE lineage from the live Cdx2-eGFP marker before fixation. * embryo visually only consisting of trophoblast vesicles. ** embryo morphology like B-E embryos, likely contains both Gata4 and Sox2 positive cells.
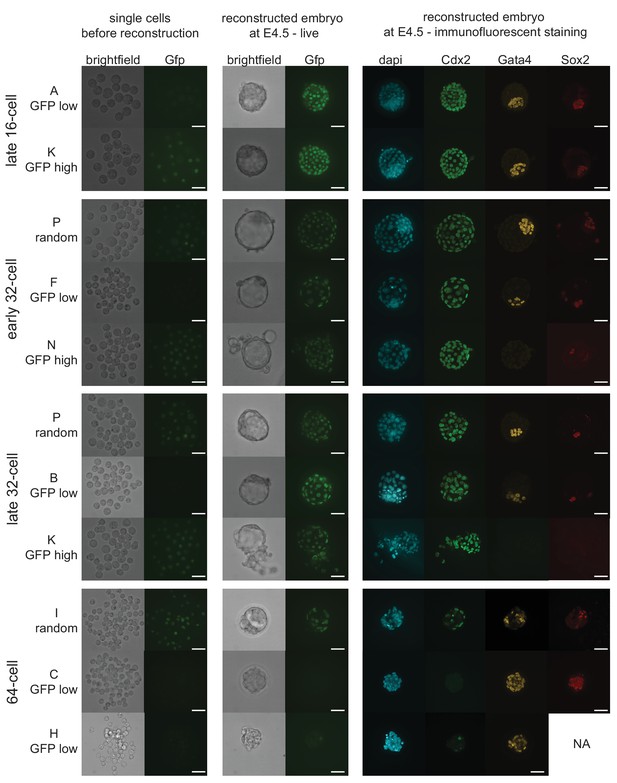
Representative images of embryo reconstructions from single cells at different stages.
Single cells used to reconstruct embryos (left panel) are either Cdx2-eGFP low, high or randomly mixed. Reconstructed embryos live at embryonic day 4.5 (E4.5) (middle panel). Immunofluorescence staining for lineage markers in reconstructed embryos at E4.5 (right panel). Scale bar: 40 µm.
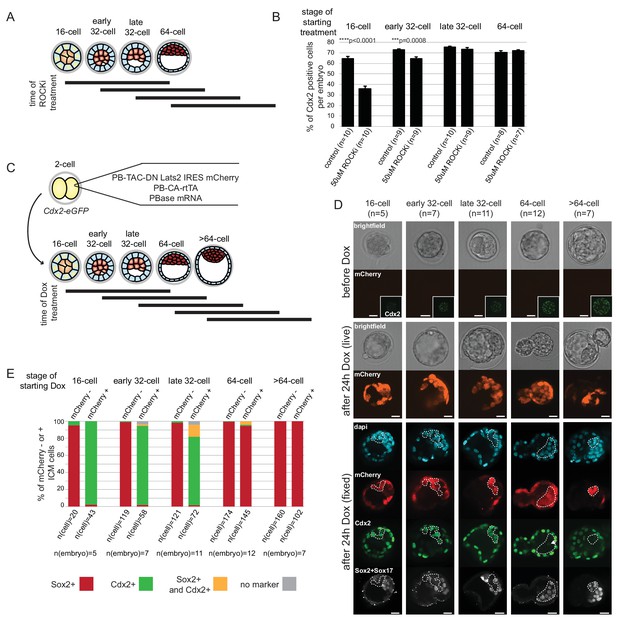
ICM and TE progenitors show loss of responsiveness to Hippo signaling manipulation at the same time as they loose responsiveness to positional changes.
(A) Overview of Hippo signaling activation time course. Each bar represents 24 hr of 50 µM ROCKi treatment. (B) Percent of Cdx2 positive cells per embryo cultured for 24 hr in control or ROCKi conditions. Label on top indicates the stage embryos started treatment. n indicates number of embryos analyzed. Statistical significance was calculated using t-test and significant p-values are indicated. Error bars: s.d. of mean. (C) Strategy for inducible Hippo signaling inactivation. Mostly mosaic Dox-inducible DN Lats2-IRES-mCherry transgenic embryos were generated. Each bar represents 24 hr of Dox treatment. (D) Dox-inducible DN Lats2-IRES-mCherry transgenic embryos were imaged before Dox treatment (top panel) and the same embryo was imaged following 24 hr of Dox live (middle panel) and fixed/stained for lineage markers (bottom panel). A representative embryo is shown for each stage. Live mCherry is shown as an extended focus image, immunofluorescence stainings shown as single plane images. mCherry positive ICMs in mosaic transgenic embryos are circled with a dotted line. Arrow points to a rare ICM cell in a 64 cell stage-induced embryo with weak Cdx2 expression, which also co-expressed an ICM marker. Scale bar: 25 µm. n indicates number of transgenic embryos analyzed. (E) All mCherry negative (non-transgenic control) and mCherry positive (DN Lats2-mCherry transgenic) ICM cells were scored in mosaic embryos for presence or absence of lineage markers following 24 hr of Dox treatment by immunofluorescence staining. Cells with different lineage marker expression are shown as percent of all mCherry negative or mCherry positive ICM cells analyzed. n(cell) indicates number of cells analyzed at each stage and n(embryo) indicates number of embryos cells were pooled from. Chi-squared test was used to test whether cell fate was affected by DN Lats2-mCherry expression. 16 cell p-value=8.48491E-18; early 32 cell p-value=5.50841E-34; late 32 cell p-value=6.32116E-35; 64 cell p-value=0.004103716; >64 cell p-value=0.588416983.
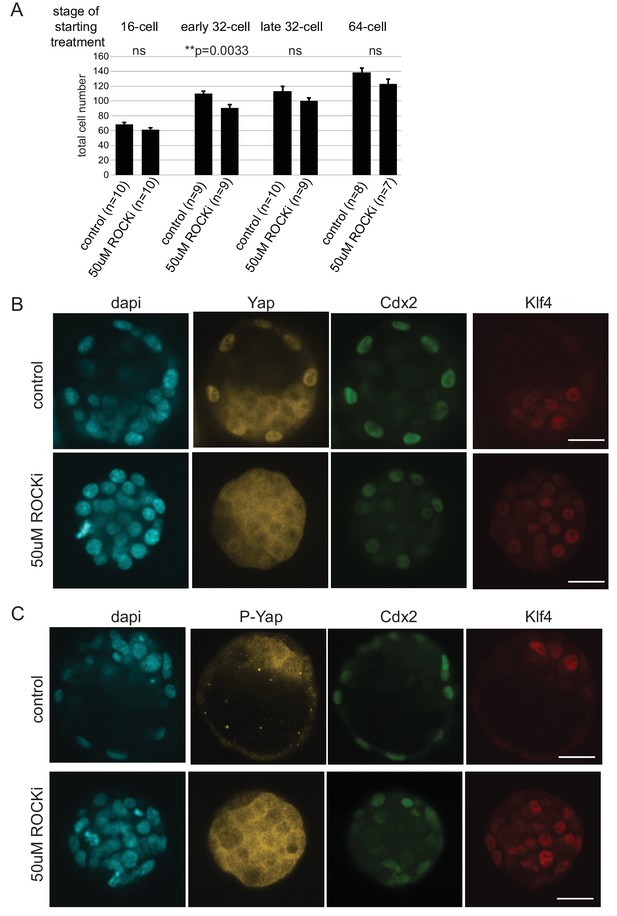
Effect of ROCKi treatment on cell number and Hippo signaling.
(A) Total cell numbers in control and 50 µM ROCKi treated embryos at different stages. n indicates number of embryos analyzed. Statistical significance was calculated using t-test and significant p-values are indicated. Error bars: s.d. of mean. (B) Immunofourescence staining of control and 50 µM ROCKi treated embryos for TE marker (Cdx2), ICM marker (Klf4) and Yap. 24 hr treatment was started at the 16 cell stage. A total of 4 control and 4 ROCKi-treated embryos were imaged in one experiment. Scale bar: 25 µm. (C) Immunofourescence staining of control and 50 µM ROCKi treated embryos for TE marker (Cdx2), ICM marker (Klf4) and phospho-Yap (form of Yap sequestered into the cytoplasm due to active Hippo signaling). 24 hr treatment was started at the 16 cell stage. A total of 4 control and 3 ROCKi-treated embryos were imaged in one experiment. Scale bar: 25 µm.
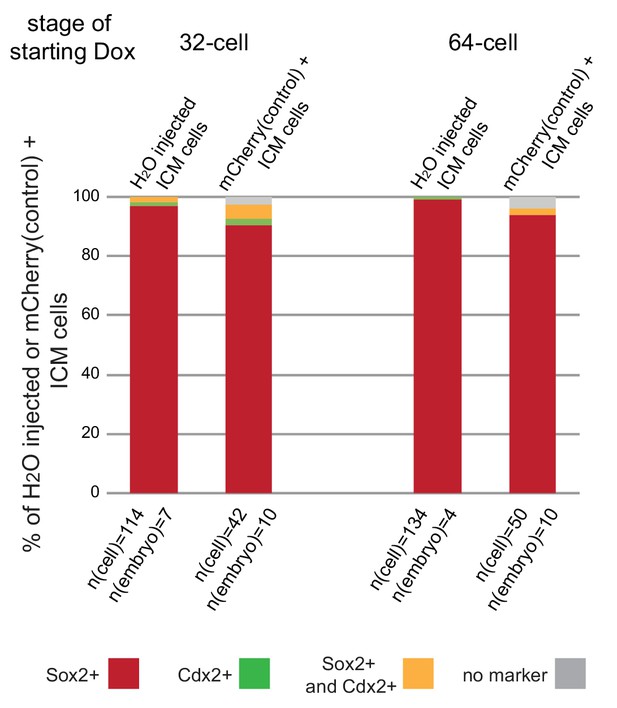
Expression of mCherry only does not influence cell fate in the embryo.
2 cell stage embryos were injected with H2O (wild-type control) or a cocktail of PB-TAC-mCherry-IRES-mCherry, PB-CAG-rtTA and PBase mRNA (mCherry control). Embryos were treated with Dox for 24 hours starting at the 32 or 64 cell stages. Following Dox treatment cell fate of ICM cells was analyzed by immunofluorescence staining for lineage markers. Cell fates shown as percent of all H2O injected ICM cells (in H2O injected embryos) or all mCherry positive ICM cells (in mCherry control embryos). n(cell) indicates number of cells analyzed at each stage and n(embryo) indicates number of embryos cells were pooled from. Chi-squared test was used to test whether cell fate was affected by mCherry expression. 32 cell p-value= 0.139370244, 64 cell p-value= 0.07551351.
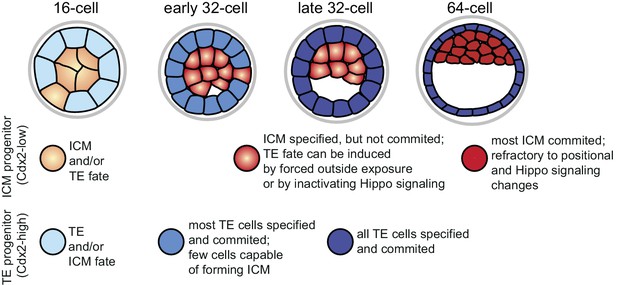
Graphical summary of specification and commitment of ICM and TE progenitors.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22906.022Videos
Live imaging a single Cdx2-eGFP low donor cell from a 32 cell stage embryo aggregating with a host morula - donor cell moves in and contributes to the ICM.
Related to Figure 4.
Live imaging a single Cdx2-eGFP high donor cell from a 32 cell stage embryo aggregating with a host morula – donor cell stays on the surface and contributes to the TE.
Related to Figure 4.
Live imaging a single Cdx2-eGFP high donor cell from a 32 cell stage embryo aggregating with a host morula - donor cell moves in and contributes to the ICM.
Related to Figure 4.





