The RNF168 paralog RNF169 defines a new class of ubiquitylated histone reader involved in the response to DNA damage
Figures
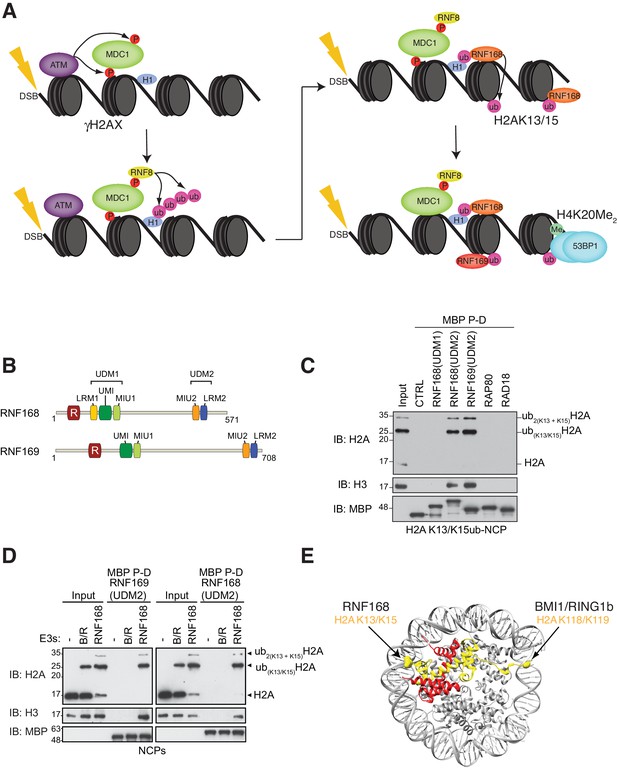
RNF168 and RNF169 bind RNF168-ubiquitylated NCPs.
(A) Schematic of RNF8-mediated DNA DSB repair pathway. ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated, MDC1: mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1, BRCT: breast cancer 1 C-terminal, H1: linker histone H1, RNF: ring finger proteins, 53BP1: p53 binding protein 1, Ub: ubiquitin, P: phosphate group, Me: methyl group. (B) Domain architecture of RNF168(1-571) and RNF169(1-708). Domains and motifs are indicated. R: RING domain, MIU: motif interacting with ubiquitin, UIM: ubiquitin-interacting motif, UMI: UIM-, MIU-related ubiquitin binding motif, LRM: LR motif. (C) MBP pull-down assays of RNF168-ubiquitylated nucleosome core particles (H2AK13/K15ub-NCP) with the indicated MBP fusion proteins (RNF168-UDM1(110–201), RNF168-UDM2(374–571), RNF169-UDM2(662–708), RAP80(60-124) and RAD18(201-240)). Input: 5% of the amount of ubiquitylated NCPs used in the pull-down. The migration of molecular mass markers (kDa) is indicated on the left. (D) Pull-down assays of NCPs ubiquitylated with the indicated E3s by either MBP–RNF169(UDM2) (left) or MBP–RNF168(UDM2) (right). A reaction without E3 (-) acts as a negative control. B/R: BMI1/RING1b. (E) Structure of the nucleosome (PDB: 2PYO [Clapier et al., 2008b]). One copy of H2A and H2B is labeled in yellow and in red, respectively. Lysines that are ubiquitylated by RNF168 (H2A K13/K15) and BMI1/RING1B (H2A K118/K119) are indicated in space filling representation.
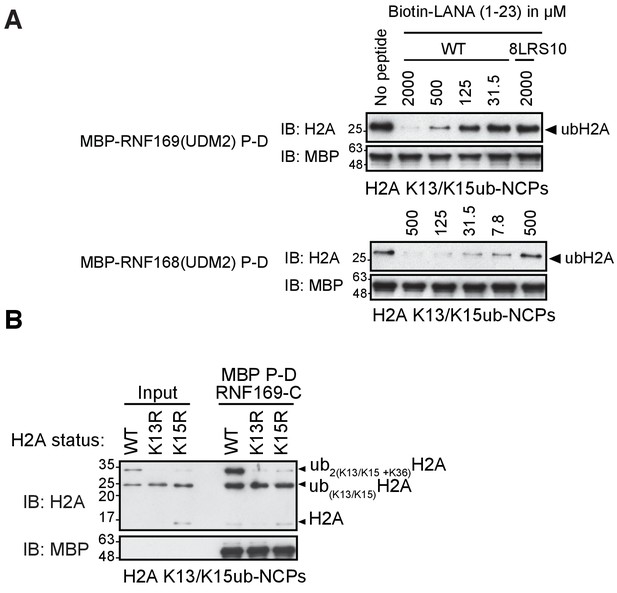
RNF169(UDM2) binds with higher affinity than RNF168 and does not discriminate between H2AK13 and K15 ubiquitylation.
(A) Pull-down assays of NCP ubiquitylated by RNF168 using either MBP-RNF169(UDM2) or MBP-RNF168(UDM2) in the presence of varying concentrations of the acidic patch interacting KSHV LANA peptide. In addition, the 8LRS10 mutant (mut: L8A R9A and S10A) that does not bind to the NCP is added in one case (concentration of the LANA peptide in μM). (B) Pull-down assay of NCPs conjugated to ubiquitin with MBP-RNF169(UDM2). H2A mutants K15R and K13R were used to catalytically produce monoubiquitylated H2AK13-ub and H2AK15-ub, respectively. Catalytic ubiquitylation of K13R and K15R species by RNF168 produces a small amount of diubiquitylated H2A with the second ubiquitin conjugated to position K36, as indicated on the gel (Wilson et al., 2016). Input: 5% of the amount of ubiquitylated NCPs used in pull-down; the migration of molecular mass markers (kDa) is indicated on the left.
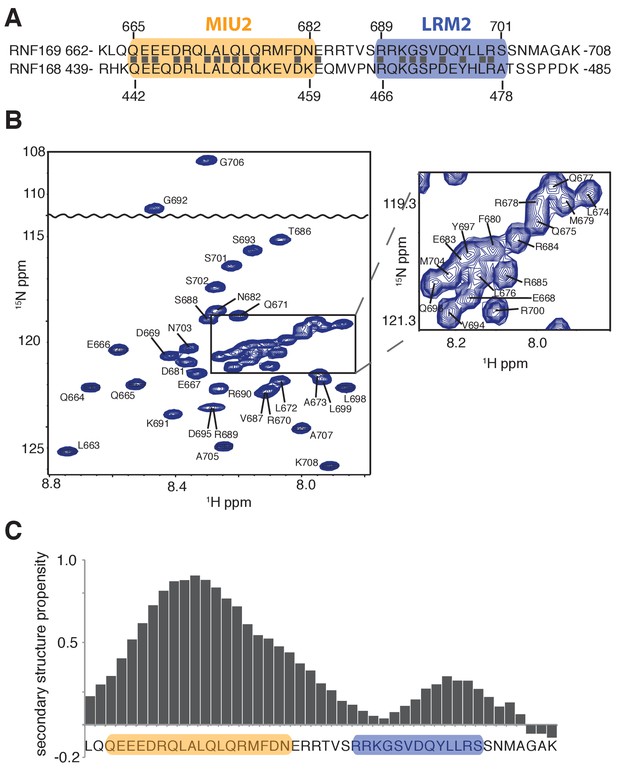
Solution NMR analysis of RNF169(UDM2) reveals a flexible LRM2.
(A) Primary sequence of MIU2 (orange) and LRM2 (blue) modules of both RNF169 and RNF168. Conserved residues are indicated with vertical bars. (B) Assigned 1H-15N HSQC spectrum of 15N,13C-labeled RNF169(UDM2). Data collected at 11.7 T, 35°C. (C) Output from SSP program (Marsh et al., 2006) using RNF169(UDM2) backbone chemical shifts as input. Corresponding primary sequence of RNF169(662-708) displayed along horizontal axis, with MIU2 (orange) and LRM2 (blue) regions highlighted. Positive and negative SSP values indicate α-helical and β-strand secondary structure propensities, respectively.
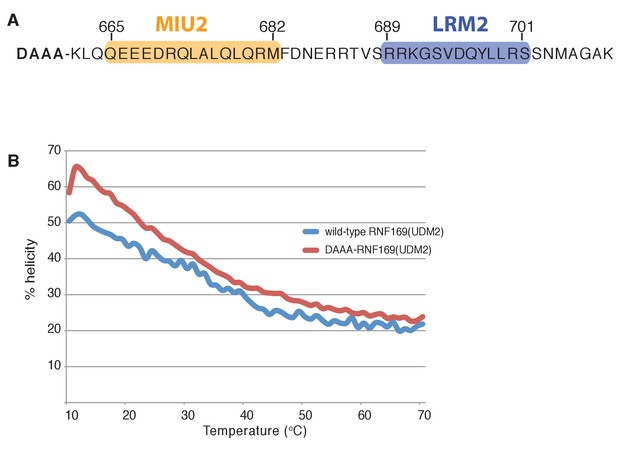
Modified RNF169(UDM2) construct exhibits higher thermo stability.
(A) Primary sequence of the modified RNF169(UDM2) construct used for NMR experiments at 45°C; addition of four N-terminal residues shown in bold. (B) Temperature melt of wild-type RNF169(UDM2) and the N-terminal extended variant using circular dichroism spectroscopy. Helical percentage calculated as described in Materials and Methods.
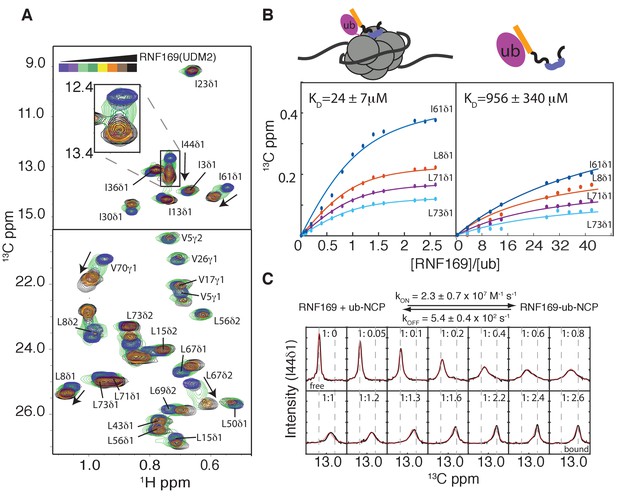
Thermodynamics and kinetics of the RNF169(UDM2)-H2AK13C ub-NCP interaction.
(A) Selected regions of 1H-13C HMQC spectra of ILV-methyl labeled ubiquitin in H2AK13Cub-NCPs with increasing amounts of unlabeled RNF169(UDM2). Arrows indicate direction of peak movement. Data collected at 14.1 T, 45°C. (B) Chemical shift derived binding curves for selected residues in ILV-methyl labeled ubiquitin in H2AK13Cub-NCPs (left panel) and free ILV-methyl labeled ubiquitin (right panel) upon addition of unlabeled RNF169(UDM2) (circles), with best fits (solid lines) shown. Ratio of RNF169(UDM2) to ubiquitin indicated on horizontal axis. (C) Fitted line shapes for I44δ1 (extracted from 1H-13C correlation spectra by taking traces along the 13C-dimension). Experimental data in black, with simulated line shapes in red. Ratio of ubiquitin to RNF169(UDM2) indicated in each panel and vertical grey dashed lines denote the resonance positions of I44δ1 in the absence (free) and presence (bound) of saturating amounts of RNF169(UDM2). The extracted kinetic parameters for the RNF169, ub-NCP binding reaction are shown above the traces.
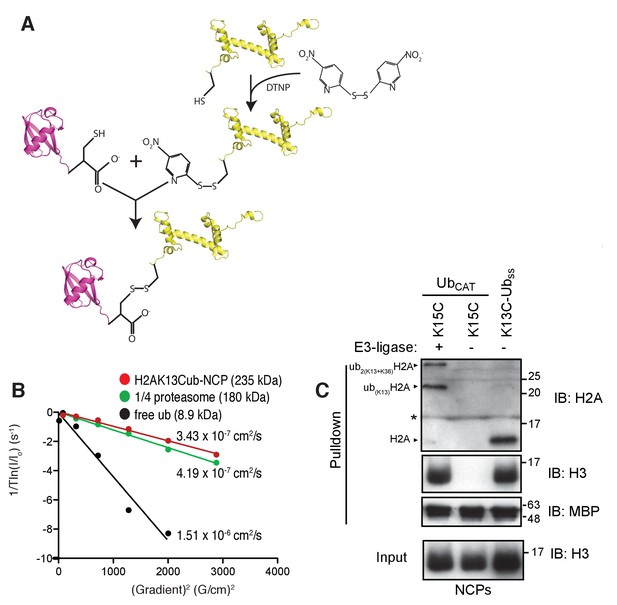
Preparation and validation of disulfide linked H2AK13Cub-NCPs.
(A) Schematic outlining the chemical activation of H2AK13C and conjugation with ubG76C. (B) NMR derived diffusion constants for free ubiquitin (black), H2AK13Cub-NCP (red) and ¼ proteasome (green). Plot of 1/Tln(I/Io) as a function of squared gradient strength (circles), where T is the diffusion time (100 ms for ubiquitin, 250 ms for NCP and ¼ proteasome) and I, Io are the intensities in the presence and absence of encoding gradients, with best fits (lines) and calculated diffusion constants indicated. (C) Pull-down assays of NCPs ubiquitylated by RNF168 (ubCAT) or prepared through the disulfide directed approach (K13C-Ubss). MBP-RNF169(UDM2) was used in the pull-down. One pull-down in the absence of RNF168 (- E3-ligase) is used as a negative control. The gel was run in the presence of a reducing agent (dithiothreitol) so the H2AK13C-Ubss linkage is reduced to H2AK13C. Antibody against the acidic patch of H2A was used to detect H2A from Drosophila. Catalytic ubiquitylation of K15C species by RNF168 produces a small amount of diubiquitylated H2A with the second ubiquitin conjugated to position K36, as indicated on the gel (Wilson et al., 2016). The * indicates an artifact from the gel. Input: 5% of the amount of ubiquitylated NCPs used in pull-down. The migration of molecular mass markers (kDa) is indicated on the right.
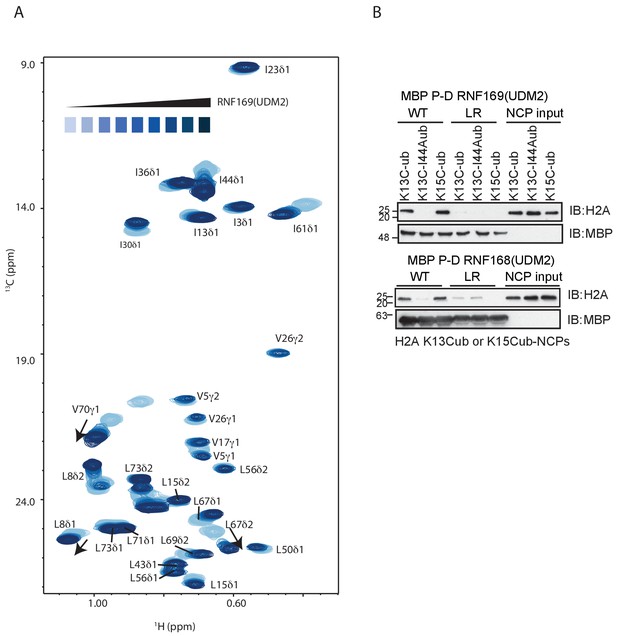
RNF169(UDM2) binds ubiquitin through its canonical hydorphobic face in both the free and NCP-bound context.
(A) Overlay of 1H-13C HMQC spectra of ILV-methyl labeled ubiquitin with increasing amounts of RNF169(UDM2), as indicated. Data recorded at 11.7 T, 45°C. Final RNF169(UDM2) to ubiquitin ratio of 42:1. (B) Pull-down assay of NCPs conjugated to wild-type or I44A ubiquitin with MBP-RNF169(UDM2) (top panel) or MBP-RNF168(UDM2) (bottom panel). Ub-NCP binding-deficient RNF169(L699A/R700A) and RNF168(L476A/R477A) mutants, denoted by LR, were used as negative controls. Input: 5% of the amount of ubiquitylated NCPs used in pull-down; the migration of molecular mass markers (kDa) is indicated on the left.
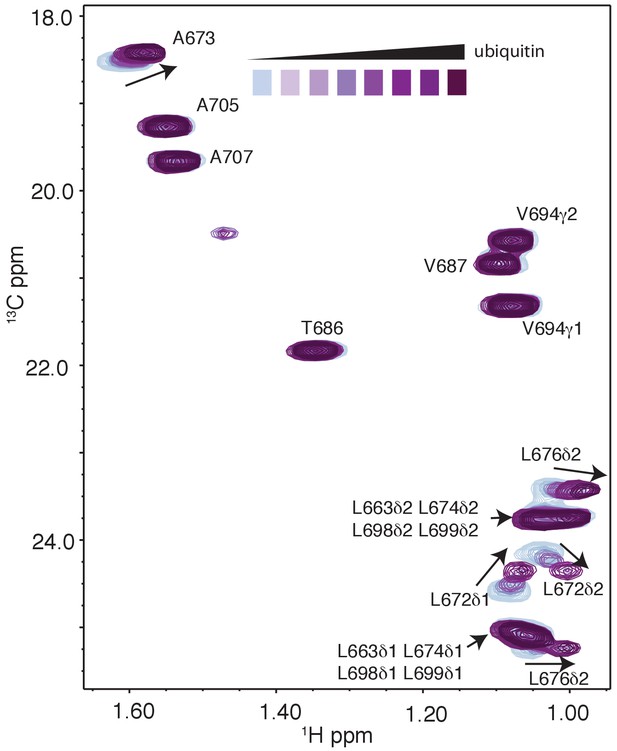
Selected regions of CT-1H-13C HSQC spectra of 15N,13C wild-type RNF169(UDM2) with increasing amounts of unlabeled ubiquitin.
Arrows indicate direction of peak movement. Data collected at 11.7 T, 35°C.
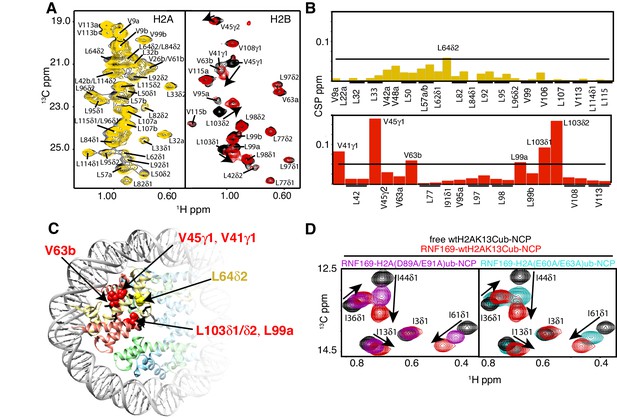
NMR and mutagenesis identify the nucleosome acidic patch as the binding interface for RNF169(UDM2).
(A) Superimposed 1H-13C HMQC spectra of ILV-methyl labeled H2A (left panel) and ILV-methyl labeled H2B (right panel) in the context of the H2AK13Cub-NCP without (black) and with (yellow, left; red, right) wild-type RNF169(UDM2), respectively. RNF169(UDM2) was added at 2.5-fold excess relative to ubiquitin. Arrows indicate peak movement. Data collected at 14.1 T, 45°C. (B) Chemical shift perturbations (CSPs) in ILV-methyl labeled H2A (yellow, top panel) and ILV methyl-labeled H2B (red, bottom panel) H2AK13Cub-NCPs. Residues with CSP values 1σ above the average are indicated (black line). CSPs were calculated as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Location of residues with significant CSPs in H2A (yellow) and H2B (red) shown in space filling representation and indicated with arrows on nucleosome crystal structure (2PYO) (Clapier et al., 2008a). Acidic patch residues are shown in stick representation and coloured black. H2A: light yellow, H2B: salmon, H3: light blue and H4: light green. (D) Selected isoleucine regions of 1H-13C HMQC spectra of free (black) and 2.5-fold excess RNF169(UDM2) bound (red) ILV-methyl labeled ub H2AK13Cub-NCP. Spectra of acidic patch mutant NCPs, H2AK13C(D89A/E91A)ub-NCP (purple, left panel) and H2AK13C(E60A/E63A)ub-NCP (teal, right panel), with 5-fold excess RNF169(UDM2) to ubiquitin are overlaid and highlight the resulting binding deficiency. All data are recorded at 14.1 T, 45°C.
Overlay of 1H-13C HMQC spectra of ILV-methyl labeled H3 H2AK13Cub-NCPs with (red) and without (black) RNF169(UDM2).
No significant CSPs are observed. Data recorded at 14.1 T, 45°C.
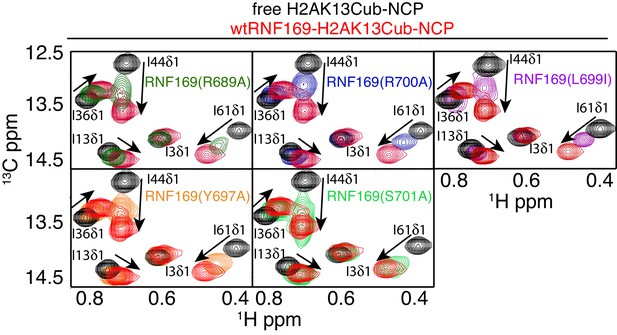
R689 and L699/R700 are critical to the formation of the complex.
Isoleucine region of 1H-13C HMQC spectra of ILV-methyl labeled ub H2AK13C-ubNCP without (black) and with (red) wild-type RNF169(UDM2) and the indicted RNF169(UDM2) LRM2 mutants. The ratio of wild-type or mutant RNF169(UDM2) to ubiquitin was 2.5:1 in all cases.
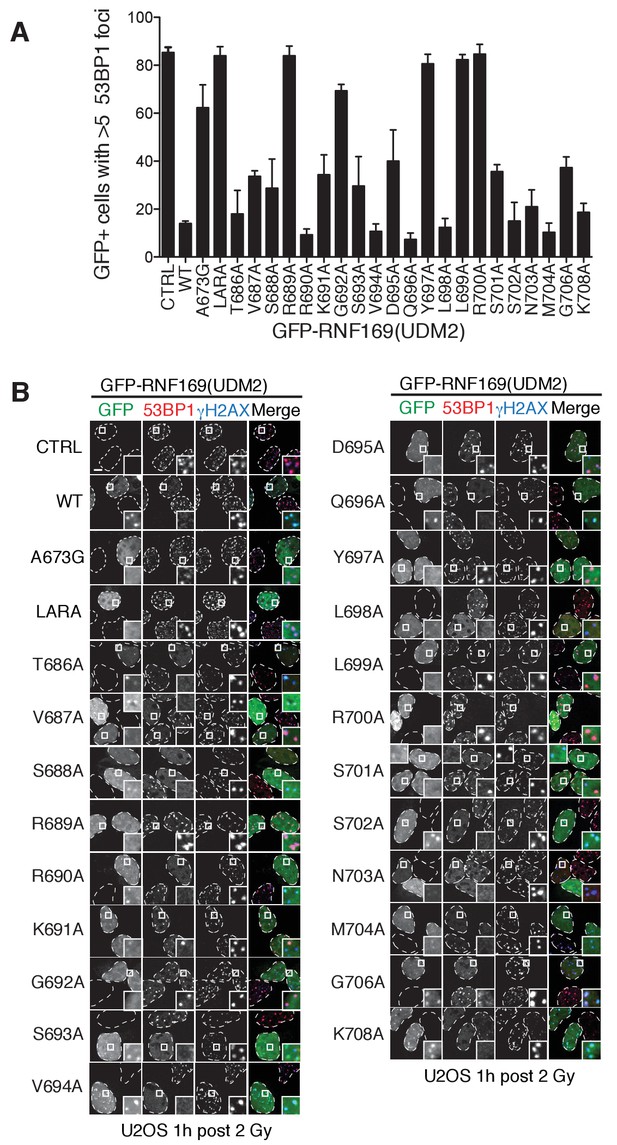
Alanine scanning of LRM2 reveals criticial residues in RNF169(UDM2)-ubNCP interaction.
(A) Quantification of 53BP1 foci in U2OS cells transfected with GFP-RNF169(UDM2) wild-type or mutant, as indicated along the horizontal axis. CTRL: untransfected cells, LARA: L699A/R700A. Error bars represent the mean ±1 standard deviation for n = 3. Cells were irradiated (2 Gy) and processed for 53BP1 and γ-H2AX immunofluorescence as well as GFP imaging 1 hr after irradiation. (B) Corresponding micrographs of the experiments presented in (A). Dash lines outline nucleus of the cells and scale bar represents 5 µm.
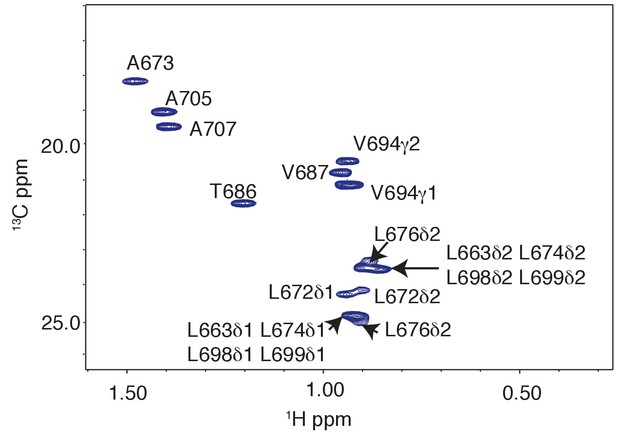
Methyl resonances of LRM2 region are overlapped in 1H-13C CT-HSQC of 15N,13C wild-type RNF169(UDM2).
Significant resonance overlap of leucine residues is observed. Data recorded at 11.7 T, 35°C.
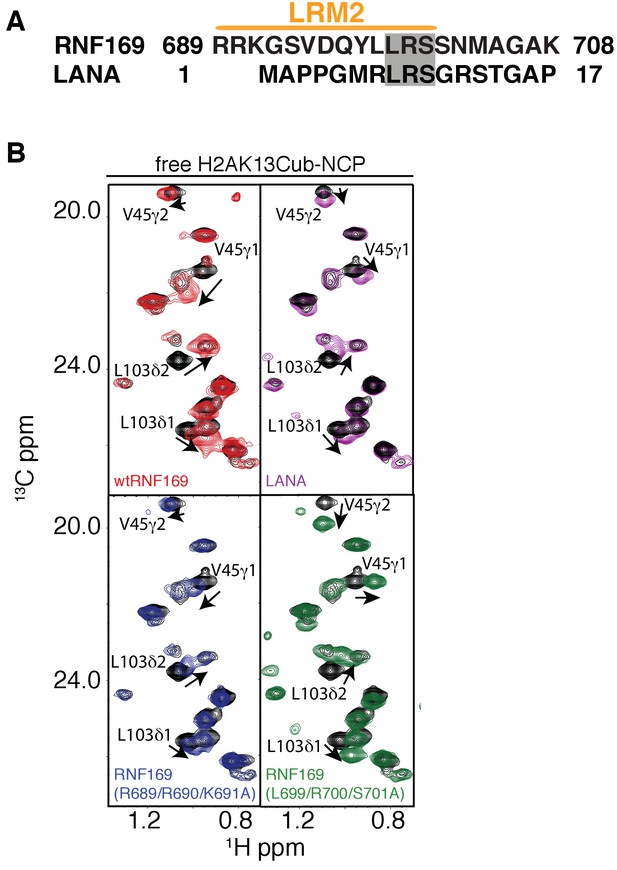
NMR reveals a similar acidic patch binding mode for R689 and R700 of RNF169(LRM2) and LANA(1-23).
(A) Alignment of the primary sequences of RNF169(UDM2) and the LANA peptide. Common residues that have been shown to be relevant for NCP binding are shaded in gray. (B) Selected regions of 1H-13C HMQC spectra of free ILV-methyl labeled H2B in the context of H2AK13Cub-NCPs in black, overlaid with corresponding spectral regions as recorded on ILV-methyl labeled H2B H2AK13Cub-NCP samples with RNF169(UDM2) (red), with the LANA peptide (purple), with RNF169(R689/R690/K691A)(UDM2) (blue) and with RNF169(L699/R700/S701A)(UDM2) (green). Residues with significant CSPs are labeled, and the ratio of RNF169(UDM2) or LANA to ubiquitin was 5:1. All spectra were recorded at 14.1 T, 45°C.
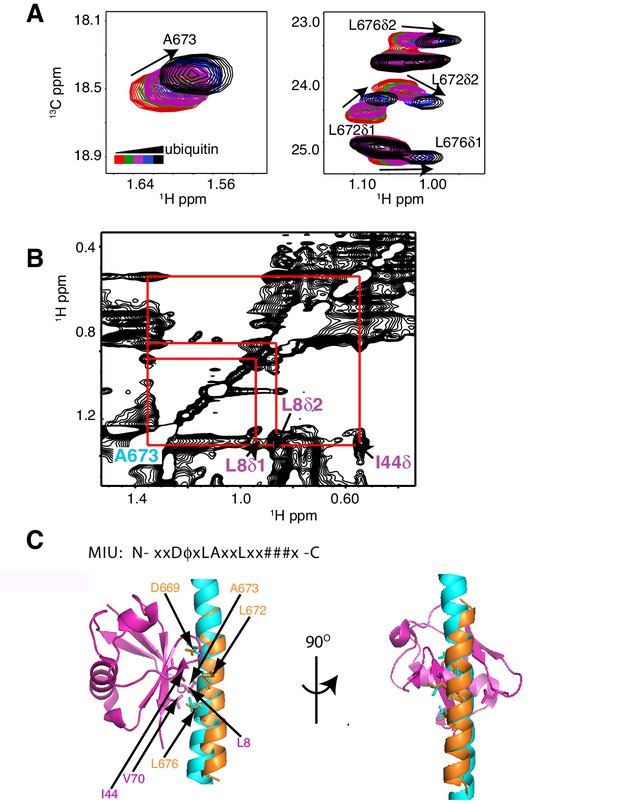
The RNF169 MIU2-ubiquitin interaction involves the canonical binding surface of ubiquitin and a central alanine in the MIU2.
(A) Overlaid regions of 1H-13C CT-HSQC spectra of 13C-labeled RNF169(UDM2) upon addition of increasing amounts of free ubiquitin. Residues with significant chemical shift changes are labeled. Data recorded at 11.7 T, 35°C. (B) Selected region of 1H-1H NOESY spectrum of ILV-methyl labeled ubiquitin and 13C-labeled RNF169(UDM2) at 1:8 molar ratio (200 ms mixing time). Cross peaks between A673 of RNF169(UDM2) and I44δ1, L8δ1/δ2 of ubiquitin are indicated. Data recorded at 14.1 T, 20°C. (C) Signature MIU primary sequence; x: any amino acid type, φ: large hydrophobic and #: acidic. Structural model of RNF169(MIU2)-ubiquitin from HADDOCK docking calculations, aligned for comparison with crystal structure of the Rabex(MIU)-ubiquitin complex (2C7N (Penengo et al., 2006)). Signature MIU residues within RNF169(MIU2) and Rabex and hydrophobic patch residues are shown in stick representation. Ubiquitin: magenta, RNF169(MIU2): orange, Rabex(MIU): cyan.
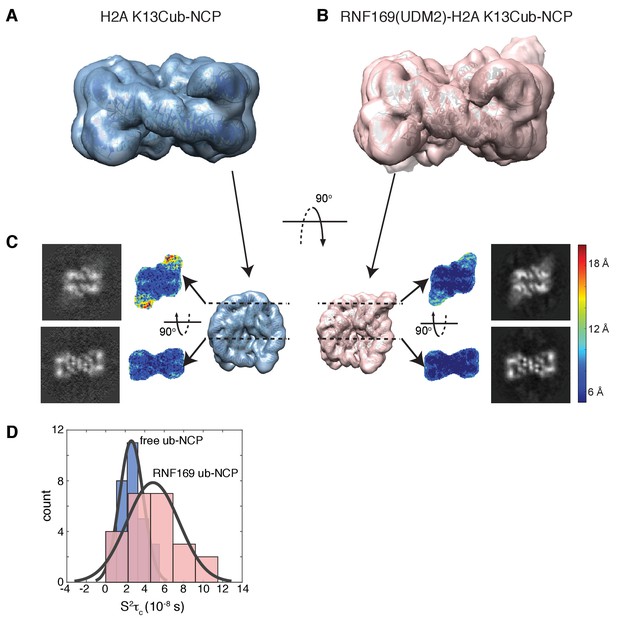
Ubiquitin is highly dynamic in the absence of RNF169(UDM2).
(A) H2AK13Cub-NCP cryo-EM map at 8.1 Å resolution and (B) RNF169(UDM2) bound H2AK13Cub-NCP cryo-EM map at 6.6 Å resolution including the drosophila NCP crystal structure (2PYO) (Clapier et al., 2008a) fit within the map as a rigid body using UCSF chimera. (C) Indicated equivalent lateral slices through free H2AK13Cub-NCP (left panels) and RNF169(UDM2) bound H2AK13Cub-NCP maps (right panels), showing the raw map density and colored according to local resolution estimates (Kucukelbir et al., 2014). (D) Histogram comparison of S2τC values obtained for ILV-methyl labeled ubiquitin in free (blue) and RNF169(UDM2) bound H2AK13Cub-NCPs (pink) fit to a normal distribution.
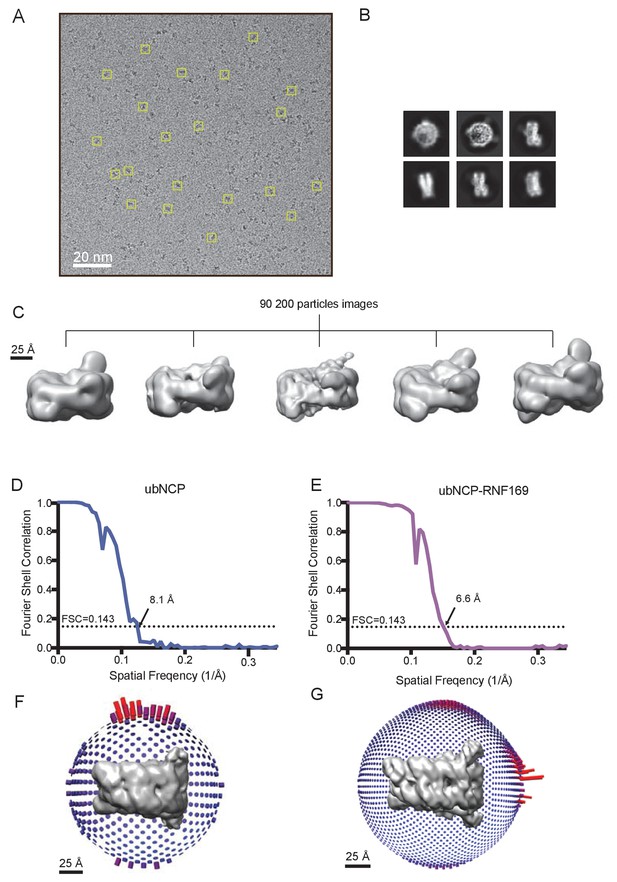
Cryo-EM data and processing.
(A) Representative cryo-EM micrographs. Several individual particle projections are boxed. (B) Examples of 2D class average images from cryo-EM of the RNF169(UDM2)-ubNCP complex. (C) 3D classification of the 90 200 selected particle images obtained after 2D classification. All classes show varying detail, location and volume of density for the covalently attached ubiquitin. The most populated high-resolution class was refined with C2 symmetry to yield the final RNF169(UDM2)-ubNCP map. (D) Fourier shell correlation curve after a gold-standard map refinement of the ubNCP structure obtained during preliminary complex optimization, corrected for the effects of map masking. (E) Fourier shell correlation curve after a gold-standard map refinement of the final RNF169(UDM2)-ubNCP structure, corrected for the effects of map masking. (F) Euler angle distribution plot of all particle images used for the symmetrized ubNCP map. Bar length and color (blue low, red high) corresponds to number of particle images contributing to each view. (G) Euler angle distribution plot of all particle images used for the symmetrized RNF169(UDM2)-ubNCP map. Bar length and color (blue low, red high) corresponds to number of particle images contributed to each view.
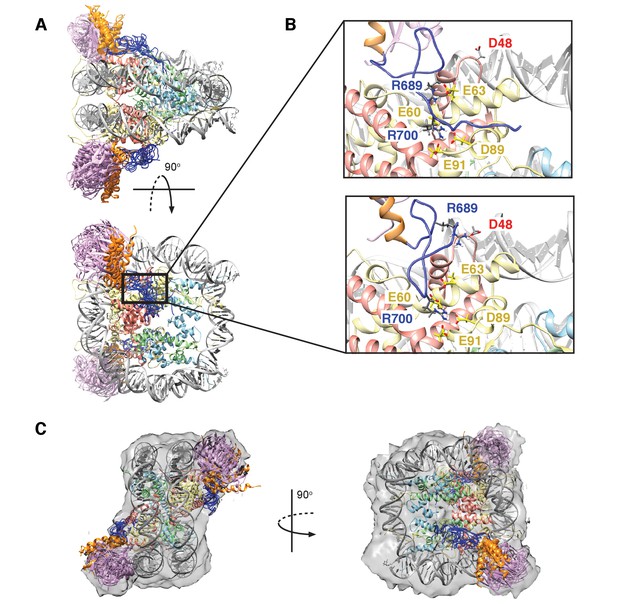
Structural model of the RNF169(UDM2)-ubNCP complex.
(A) Alignment of ten representative members of the RNF169(UDM2)-ubNCP structural ensemble obtained from replica-averaged MD simulations constrained by CSPs and mutagenesis data. Histones H2A and H2B were used to align the structures with only one copy of the histones and DNA shown for simplicity. Ubiquitin: magenta, RNF169(662-682)(MIU2): orange, RNF169(683-708)(LRM2): blue, H2A: yellow, H2B: salmon, H3: light blue, H4: light green, DNA: gray. (B) Enlarged view focusing on specific contacts between R689 and R700 and the nucleosome acidic patch in two separate structures. (C) Two viewpoints of ten aligned members of the RNF169(UDM2) ub-NCP structural ensemble fit into the RNF169(UDM2) bound H2AK13Cub-NCP cryo-EM map. Molecular graphics images were produced using the UCSF Chimera package(Pettersen et al., 2004).
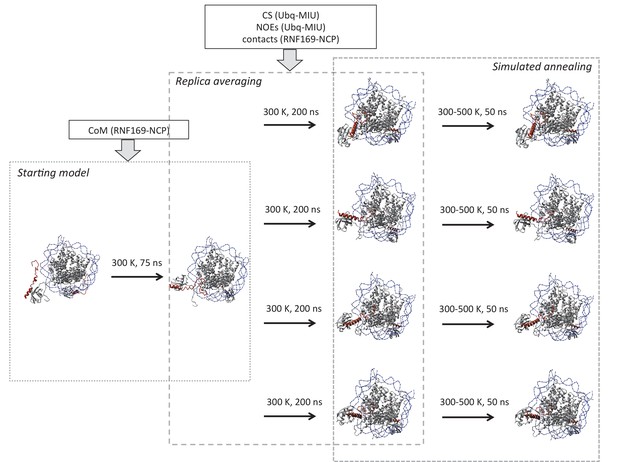
Schematic outline of replica-averaged MD protocol used.
Restraints used in each stage are indicated in boxes; COM: centre of mass, CS: chemical shifts, NOEs: Nuclear Overhauser effects, contacts: CSPs and mutagenesis restraints. Temperature and timescale of each step is indicated above arrows. Explicit details can be found in Materials and Methods.
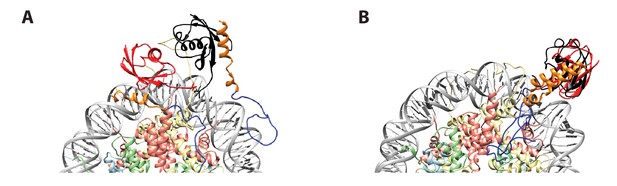
Initial position of ub in RNF(UDM2)-ubNCP starting structures does not influence the final ub orientation.
(A) Alignment of RNF(UDM2)-ubNCP starting conformations for replica-averaged MD simulations. Histones H2A and H2B were used to align the structures with only one copy of the histones and DNA shown for simplicity. The starting position of ubiquitin used in a pair of simulations is shown in black and red. RNF169(662-682)(MIU2): orange, RNF169(683-708)(LRM2): blue, H2A: light yellow, H2B: salmon, H3: light blue, H4: light green, DNA: gray. (B) Alignment of RNF(UDM2)-ubNCP final conformations from replica-averaged MD simulations, as in A.





