Ephrin-A/EphA specific co-adaptation as a novel mechanism in topographic axon guidance
Figures
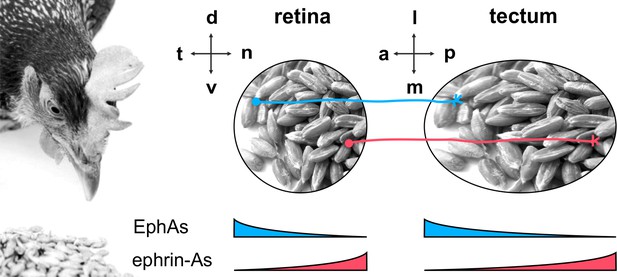
The retinotectal projection.
The topographic projection in the chicken visual system connects RGCs from the retina to the midbrain's optic tectum. The temporal/nasal (t/n) axis of the retina is mapped onto the anterior/posterior (a/p) axis of the tectum, whereas the retinal dorsal/ventral axis projects onto the lateral/medial axis of the tectum. Retinal GCs are guided to their tectal targets by repulsive signals from counter-gradient distributions of tectal ephrin-As (red; p>a) and EphAs (blue; a>p). Detection of these cues is mediated via retinal EphA and ephrin-A sensors, which are expressed in t>n and n>t gradients, respectively.
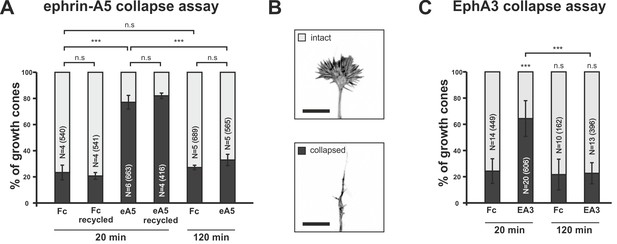
Growth cone desensitization towards soluble ephrin-A5 and EphA3.
(A) Temporal GCs initially collapse upon application of 250 ng/ml ephrin-A5-Fc (eA5 20 min: 77.1%), but recover their morphology within 120 min in the presence of the cue (eA5 120 min: 32.9% collapsed GCs). Ephrin-A5-Fc is still functional after incubation for 120 min, when re-used on a fresh culture (eA5 recycled 20 min: 81.5% collapsed). Fc controls demonstrate the specificity of the effect of ephrin-A5 (Fc 20 min: 23.3%; Fc recycled 20 min: 20.7%; Fc 120 min: 27.2%). (B) Representative intact and collapsed GC morphology (Phalloidin Alexa488). Scale bar: 10 µm. (C) Soluble EphA3-Fc triggers a collapse when administered at 15 µg/ml (EA3 20 min: 64.4% collapsed), whereas an equimolar concentration of Fc (4.2 µg/ml) does not (Fc 20 min: 24.3%). GCs desensitize towards EphA3-Fc within 120 min (EA3 120 min: 22.6%). Combined data from nasal and temporal GCs. N: number of independent experiments; number of analyzed GCs in brackets. Error bars represent standard deviations. T-test with n.s.: α ≥0.05, ***: α <0.001.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Original data underlying bar charts of Figure 2A, C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.005
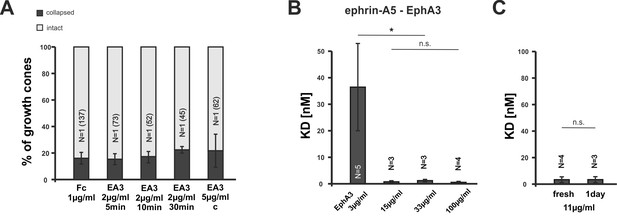
EphA3 collapse assays and ephrin-A5/EphA3 dissociation constants.
(A) Moderate concentrations of EphA3-Fc (EA3) do not trigger a collapse of nasal or temporal GCs, neither in dimeric nor in an antibody clustered form (Fc, 1 µg/ml, 20 min: 16.1% collapsed; EA3, 2 µg/ml, 5 min: 15.3%; 10 min: 17.3%; 30 min: 22.4%; EA3, 5 µg/ml antibody-clustered (C), 20 min: 21.7% collapsed). Antibody-induced clustering was achieved by preincubation of EphA3 with anti human Alexa Fluor488 goat IgG (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in a molar ratio of 2:1 (EphA3:AB) for 1 hr at room temperature. N: number of independent experiments; number of analyzed GCs in brackets. Error bars represent standard deviations. (B) Concentration-dependent binding of ephrin-A5 to EphA3 (see Materials and methods for details). Dissociation constants (KD) of ephrin-A5 and EphA3 decrease abruptly with increasing EphA3 concentrations, indicating a sharp increase in binding affinity, which is potentially due to the concentration-dependent formation of EphA3 clusters in solution. KDs ephrin-A5 binding to: EphA3 3 µg/ml: 36.68 nM; EphA3 15 µg/ml: 0.76 nM; EphA3 33 µg/ml: 1.23 nM; EphA3 100 µg/ml: 0.55 nM. (C) Potential EphA3 clusters are stable for at least one day in solution at a concentration of 11 µg/ml as indicated by a constant KD (fresh EphA3, 11 µg/ml: 3.37 nM; 1 day old EphA3, 11 µg/ml: 3.40 nM). (B, C) N: number of independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations. T-test with n.s.: α ≥0.05; *: α <0.05.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original data underlying bar charts of Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.007
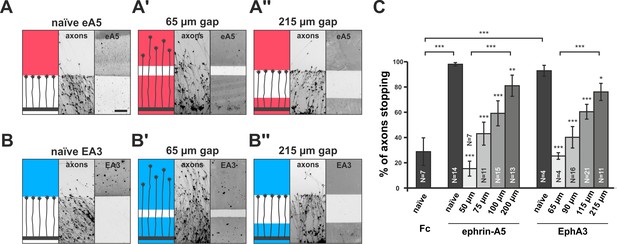
Growth cone adaptation towards substrate-bound ephrin-A5 and EphA3.
Subfigures in (A) and (B) each display a cartoon (left) illustrating the experimental setup consisting of explant (thick black strip), axons and printed guidance protein (colored field(s)), the inverted signal of fluorescent phalloidin-stained axonal actin (middle; explant not shown) and the underlying, antibody-labeled substrate (right) are shown in a detailed view of a representative microscopic image (scale: 100 µm). (A) Naïve temporal axons stop in front of a homogeneous field of ephrin-A5-Fc (eA5 15 µg/ml; red), but do not react to an identical boundary when initially grown on ephrin-A5 after a 65 µm wide gap (A'). Stopping behavior returns in axons having crossed a 215 µm wide, ephrin-free gap (A''). (B–B'') Nasal RGC axons show very similar behavior on EphA3-Fc (EA3 15 µg/ml, blue) gap substrates as described for ephrin-A5 gap assays. (C) Quantification of gap assays. Stop reactions were quantified as the percentage of fibers not entering the protein field after the gap. Fc naïve: 28.8% stopping. eA5 naïve: 98.0%, eA5 50 µm: 15.3%, eA5 75 µm: 43.0%, eA5 100 µm: 59.2%, eA5 200 µm: 81.0% stopping. EA3 naïve: 92.6%, EA3 65 µm: 25.0%, EA3 90 µm: 39.9%, EA3 115 µm: 60.1%, EA3 215 µm: 75.8% stopping. Ephrin-A5 gap assay patterns differ slightly from EphA3 patterns in gap width as a result of a modified stamp geometry. N: number of independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations. T-test with *: α <0.05, **: α <0.01, ***: α <0.001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Original data underlying bar chart of Figure 3C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.009
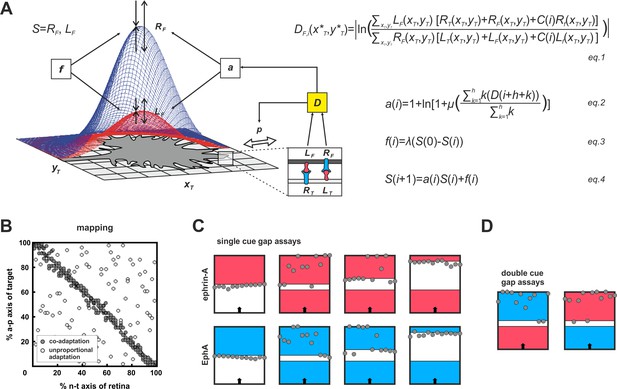
Modeling growth cone adaptation and topographic mapping.
(A) Fiber terminals are modeled as circular discs bearing Gaussian-shaped distributions of EphAs (RF, blue) and ephrin-As (LF, red), according to their retinal origin, moving on a rectangular target field of unit squares (xT, yT), carrying target-derived guidance cues (LT and RT). Fiber–target and fiber–fiber (cis and trans) interactions and the resulting forward and reverse signals integrate into a guidance potential, D (equation1), which determines the probability, p, of a change in position (only fiber–target interactions are illustrated in the inset). Additionally, D is used to calculate an adaptation coefficient, a (equation2), which simultaneously modulates RF and LF (collectively called S; equation4) through 'co-adaptation'. A resetting force, f (equation3), counteracts a. For mathematical detail see 'Material and methods'. (B) Mapping plots of simulations with 200 fiber terminals using different implementations of adaptation. The anterior-posterior (a-p) position of a terminal on the target is plotted as a function of naso-temporal (n-t) origin (perfect topography is indicated by all terminals targeting the main diagonal). Terminals that are enabled to regulate sensors independently from each other by canonical adaptation are widely scattered across the target field (white circles), whereas co-adapted terminals (regulating both sensors concomitantly) find their topographically correct target positions (gray circles). In the basic model, the potential minimum is at a position where fiber and target ephrin/Eph concentrations match. Therefore, canonical adaptation was implemented in terms of a tendency for GCs to independently match their forward and reverse sensor levels to the receptor and ligand levels, respectively, on the current target position. (C) After implementation of co-adaptation, naïve terminals stop in front of a field of high ephrin-A or EphA (LT = 4, red; RT = 4, blue), respectively, but ignore the same boundary in simulated gap assays with small gap size. In simulations with wider gaps, terminals stop again in front of the second field. Gap size = 20, 40, or 100 units respectively; n = 12; i = 2000; target field: 200 × 8. (D) Co-adaptation predicts that ephrin-A adapted terminals will ignore a field of high EphA after a small gap and vice versa. Gap size = 20; other parameters as in (C).
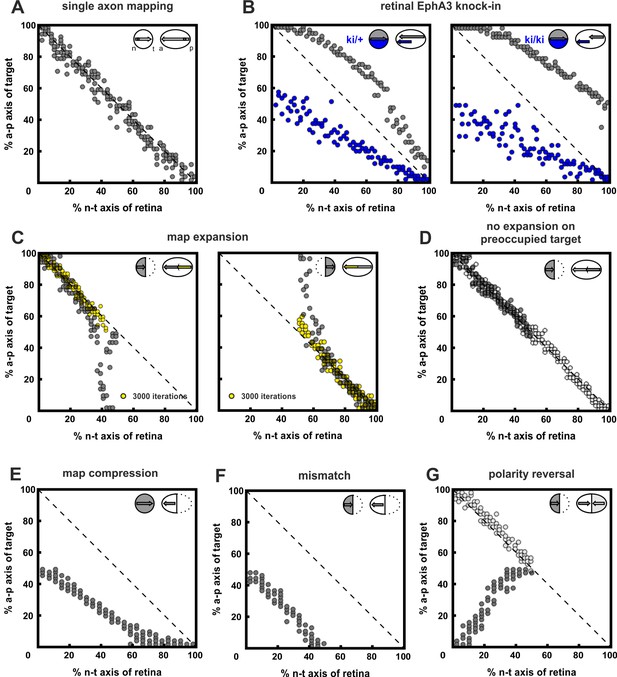
Inclusion of co-adaptation does not alter the explanatory power of the computational model.
For purposes of comparison, this figure, produced using the updated model that includes co-adaptation presented in this paper is structured in parallel to figure 7 in Gebhardt et al. (2012), which did not take adaptation into account. The results are highly similar, demonstrating that the inclusion of co-adaptation does not alter the performance of the original model. (A) 200 simulations of single fibers chosen randomly from the retinal field. Consistent with the experimental evidence in zebrafish, single fibers map topographically, as indicated by the accumulation of terminals on the main diagonal of the mapping plot. (B) EphA3 knock-in, Rki, in every second fiber (blue; ki/+: Rki = 2; ki/ki: Rki = 4; axonal ligand on knock-in fibers was reduced reciprocally to the axonal receptor). Consistent with the experiment, wild-type fibers (gray) are posteriorly displaced, with a more severe effect in homozygotes. (C) Map expansion. 100 fibers chosen from the nasal (n) or temporal (t) half of the retina reach their correct target (yellow) after 3000 iterations. After 30,000 iterations, fibers stably cover the whole tectum (gray). (D) No expansion occurs (gray) when a n half retina grows into a field containing the remnants of a previous full innervation (white). (E) Map compression. 200 fibers from a whole retina form a compressed topographic projection when growing into an anterior tectum half. (F) Mismatch. 100 n fibers form a half-projection, when growing into an anterior, non-matching, tectal half. (G) An additional n projection (gray) displays polarity reversal when growing into a tectal field still containing properly mapped n fibers (white) (n = 100; fiber–fiber interactions were put into effect earlier than usual, i.e., j = 2000 in C(i)).
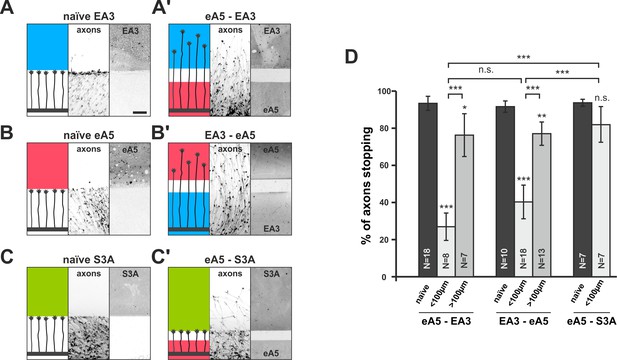
Co-adaptation of retinal growth cones in double-cue gap assays.
(A–C) Naïve axons stop in front of a homogeneous field of EphA3-Fc (A; EA3, blue; nasal axons), ephrin-A5-Fc (B; eA5, red; temporal axons), or Sema3A-Fc (C; S3A, green; temporal axons). Scale: 100 μm. (A'–C') Nasal, eA5-adapted GCs ignore a field of EA3 after a small gap (A') and, vice versa, temporal, EA3-adapted GCs ignore eA5 (B'). By contrast, temporal, eA5-adapted GCs are still strongly repelled by a field of S3A after a small gap, indicating specific co-adaptation of ephrin-A and EphA signals (C'). (D) Quantification of combined data of assays with 65 μm and 90 μm wide gaps grouped in ' < 100 μm' bars; 115 μm and 215 μm grouped in ' > 100 μm' bars. eA5-EA3: naïve: 93.4%, <100μm: 26.9%, >100μm: 76.3% stopping. EA3-eA5: naïve: 91.6%, <100μm: 40.3%, >100μm: 77.1% stopping. eA5-S3A: naïve: 93.7%, <100μm: 81.9% stopping. N: number of independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviations. T-test with n.s.: α ≥0.05, ***: α <0.001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Original data underlying bar chart of Figure 5D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.013
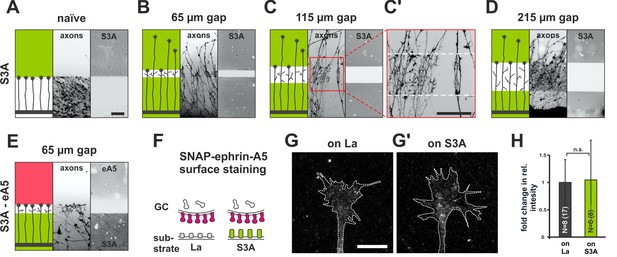
Growth cone adaptation towards Sema3A.
(A) Naïve axons stop in front of a homogeneous field of Sema3A-Fc (S3A, green), but predominantly ignore a similar field in gap assays with(B) 65 µm, (C) 115 µm and (D) 215 µm wide gaps. Axons strongly de-fasciculate and begin to branch in the Sema3A-free areas of the gap substrates, but not when growing on the protein fields (detail shown in C', white dotted lines indicate the position of the gap). The reason for this notable effect is currently unknown. Remarkably, the desensitization towards Sema3A in these assays is so strong that re-sensitization is not reached even after the largest gap-size available with our contact-printing stamps (215 µm). (E) S3A-eA5 double-cue gap assay. Sema3A-adapted GCs do not co-adapt towards ephrin-A5 and stop in front of an ephrin-A5 field after a 65 µm wide gap (cf. Figure 5B'). (F) SNAP-ephrin-A5 surface localization on Sema3A-adapted GCs. (G, G') Representative images of SNAP-ephrin-A5 surface-stained GCs growing on laminin or Sema3A, respectively (outline drawn in the actin channel indicated as a white, dotted line). (H) Quantification of SNAP-ephrin-A5 surface staining expressed as fold change in relative intensity compared to controls on laminin (on La: 1; on S3A: 1.07). N: number of independent experiments, number of analyzed GCs in brackets; error bars show standard deviations. T-test with n.s.: α ≥ 0.05. Scale (A–E): 100 µm, (G, G'): 10 µm.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original data underlying bar chart of Figure 5—figure supplement 1H.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.015
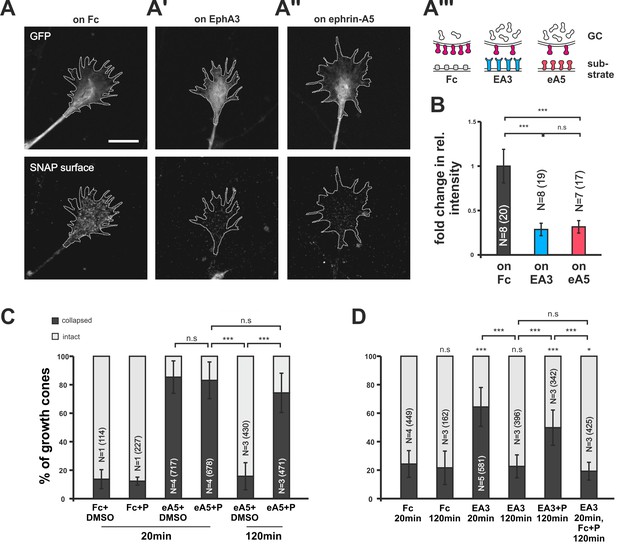
Endocytosis of guidance sensors upon growth cone desensitization.
(A) SNAP–ephrin-A5 surface signal is strongly reduced on GCs growing on either homogeneous EphA3-Fc (A') or ephrin-A5-Fc (A'') compared to controls (on Fc), indicating clearance of sensors from the surface upon co-adaptation. Outlines of GCs drawn in the GFP (transfection marker) channel are indicated as white, dotted lines. Scale: 10 µm. (A''') displays a cartoon of the experiment in (A–A'') with axonal SNAP surface labeled ephrin-A5 in magenta and with the corresponding guidance cues (Fc, gray; EA3, blue and eA5, red). (B) Quantification of SNAP–ephrin-A5 surface signal intensities. Relative signal intensity within the GC outline normalized to the control situation is given as fold change (on Fc: 1; on EA3: 0.29; on eA5: 0.32). (C) Effects of Pitstop2 on adaptation towards soluble ephrin-A5. Pitstop2 (P; carrier DMSO) prevents temporal GCs from desensitizing to 0.25 µg/ml ephrin-A5-Fc (eA5+DMSO 120 min: 15.8% collapsed; eA5+P 120 min: 74.3% collapsed). The initial response of GCs towards eA5 is unaltered in the presence of P (eA5+DMSO 20 min: 85.4% collapsed; eA5+P: 83.1% collapsed). Neither P itself, nor its carrier DMSO induces a collapse (Fc+DMSO 20 min: 13.6% collapsed; Fc+P 20 min: 7.5% collapsed). (D) Effects of Pitstop2 on adaptation towards soluble EphA3. Soluble EphA3-Fc (EA3; 15 µg/ml) triggers a collapse on nasal or temporal GCs (EA3 20 min: 64.4% collapsed; Fc [4.2 µg/ml] 20 min: 24.3% collapsed). GCs desensitize towards EA3 within 120 min (EA3 120 min: 22.6% collapsed), but not in the presence of 30 μM Pitstop2 (EA3+P 120 min: 49.8% collapsed). P does not impede GCs from recovering their morphology in general (EA3 20 min, then Fc+P 120 min: 19.3% collapsed). Combined data from nasal and temporal GCs. (B, C, D) N: number of independent experiments, number of analyzed GCs in brackets; error bars represent standard deviations. T-test with n.s.: α ≥0.05, *: α <0.05, ***: α <0.001.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Original data underlying the bar charts of Figure 6B—D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.017
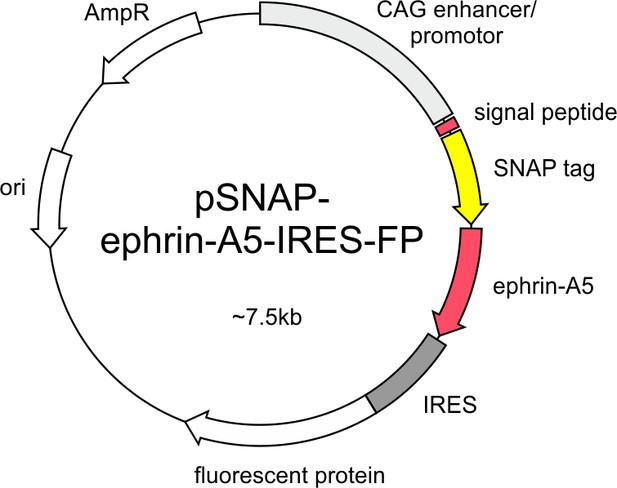
SNAP–ephrin-A5 expression constructs pSNAP–ephrin-A5–IRES-FP contains the coding sequence of a fusion protein consisting of the signal sequence of chick ephrin-A5 (60 bp), the SNAP-tag and full-length chick ephrin-A5 downstream of the CAG enhancer/promoter and upstream of an IRES-FP sequence.
The FP is EGFP in pSNAP–ephrin-A5–IRES-EGFP and dTomato in pSNAP–ephrin-A5–IRES–dTom.
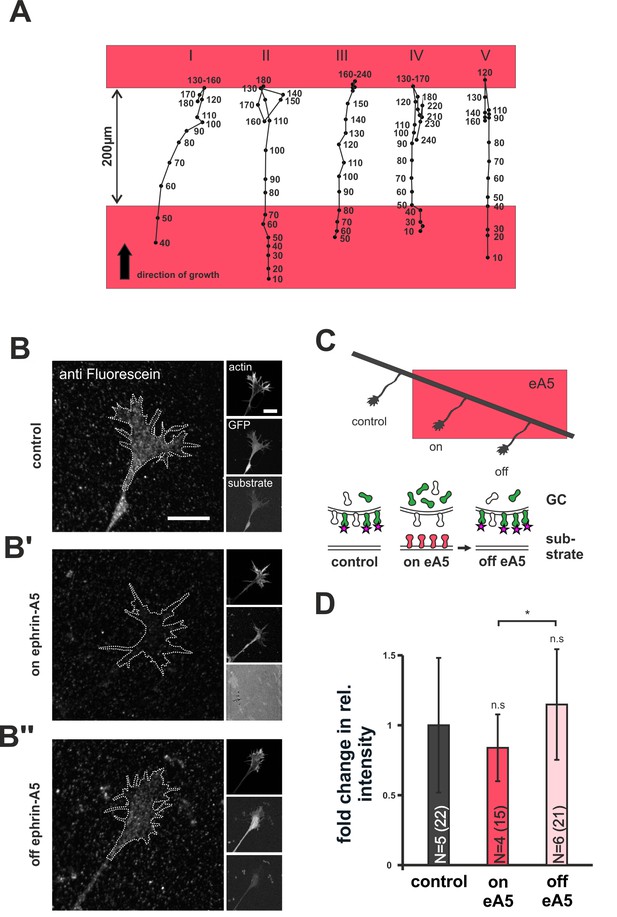
Dynamics of SNAP–ephrin-A5 during growth cone re-sensitization.
(A) Exemplary trajectories of five GCs (combined from N = 3 independent experiments) on ephrin-A5 gap patterns (red) in the presence of 40 µM AIM. Positions of GCs (black dots) were marked at the indicated time points (in minutes) after the addition of AIM. GCs stop and pause (I, III) or stop and retract (II, IV, V) upon reaching the second ephrin field, indicating full re-sensitization despite inhibition of local translation. (B–B'') SNAP–ephrin-A5 dynamics upon GC re-sensitization. Representative images of GCs, stained for formerly intracellular SNAP–ephrin-A5 that has been relocated to the membrane. Outlines of GCs drawn in the actin channel are indicated as white, dotted lines. Surface localization of ephrin-A5 (anti-fluorescein signal) is elevated in re-sensitizing GCs (B'', off ephrin-A5) compared to desensitized GCs (B', on ephrin-A5). Scale: 10 μm. (C) Experimental setup with retinal explant (black) on a field of ephrin-A5 (red) and cartoon of the experiment shown in (B–B'') with intracellular SNAP–ephrin-A5 (green), which is detected on the surface (magenta star). (D) Quantification of membrane-relocated SNAP–ephrin-A5 signals. Relative anti-fluorescein signal intensity within the GC outline normalized to the control is given as fold change. Control — 1; on eA5 — 0.85; off eA5 — 1.13. N: number of independent experiments, number of analyzed GCs in brackets; error bars represent standard deviations. T-test with n.s.: α ≥0.05, *: α <0.05.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Original data underlying the bar chart in Figure 7D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.020
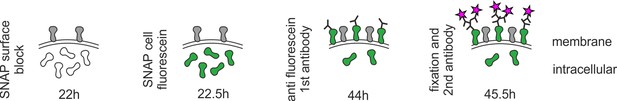
Staining procedure for recycled SNAP–ephrin-A5.
Extracellular SNAP–ephrin-A5 was blocked by SNAP surface block (gray), before the cell-permeant SNAP cell fluorescein was applied to the living cells (green). After washing, axons were allowed to grow for another 20–22 hr. Then, anti-fluorescein antibody was added to the living cells for 15 min, washed out and, subsequently, explants were fixed and stained for anti-fluorescein (magenta stars).
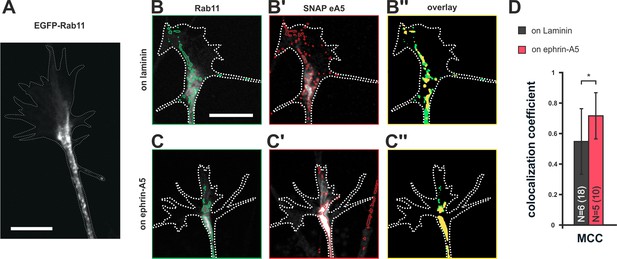
Colocalization of SNAP–ephrin-A5 and Rab11-positive endosomes.
(A) eGFP–Rab11 localization in a transfected RGC axon (outline drawn in the actin channel indicated as white, dotted line). Rab11-positive vesicular structures are predominantly observed in the axon shaft and the central domain of GCs and, to a lesser extent, are found to stretch into the more distal GC. (B–B'') Representative images of an eGFP–Rab11 (B) and a SNAP–ephrin-A5 (B') co-transfected GC on laminin substrate. Vesicular structures identified by automated image segmentation are indicated in green and red for each channel, respectively. (B'') Colocalization of SNAP–ephrin-A5 and eGFP–Rab11 within the Rab11-positive vesicles is shown as yellow areas. (C–C'') Example images of an eGFP–Rab11- (C) and a SNAP–ephrin-A5-transfected GC (C') growing on ephrin-A5-Fc. (C'') Colocalization of SNAP–ephrin-A5 and eGFP–Rab11 within the Rab11-positive vesicles (yellow areas) increases upon desensitization. (D) Manders' colocalization coefficient (MCC) as a measure of colocalization of SNAP–ephrin-A5 and eGFP–Rab11 within the Rab11-positive vesicles in naïve (on laminin: M2 = 0.55) and adapted (on ephrin-A5: M2 = 0.72) GCs, respectively. N: number of independent experiments, number of analyzed GCs in brackets; error bars indicate standard deviations. T-test with *: α <0.05. Scale: 10 μm.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Original data underlying the bar chart of Figure 8D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.023
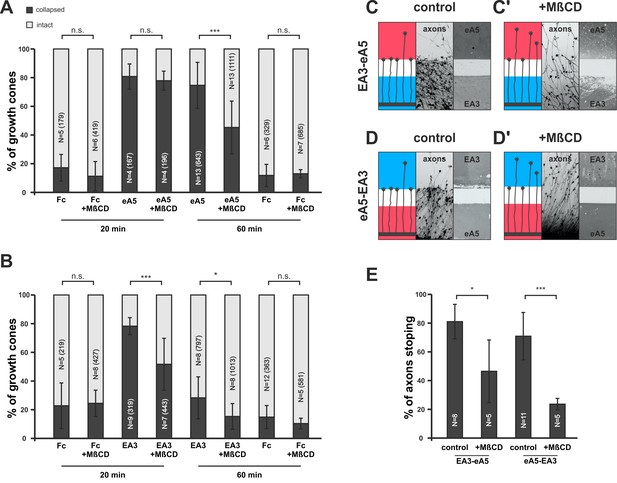
Disintegration of lipid microdomains induces co-adaptive growth cone desensitization.
(A) Ephrin-A5-Fc and (B) EphA3-Fc collapse assays. Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MβCD, 2 mg/ml)-treated GCs show enhanced desensitization (reduced collapse rates) when exposed to soluble ephrin-A5-Fc (0.25 μg/ml) or EphA3-Fc (15 μg/ml) compared to controls without MβCD. (A) GCs collapsed after 20 min incubation: Fc (0.25 μg/ml),16.7%; Fc+MβCD, 11.4%; eA5, 80.3%; and eA5+MβCD, 77.4%. GCs collapsed after after 60 min incubation: Fc, 12.1%; Fc+MβCD, 13.4%; eA5, 74.2%; and eA5+MβCD, 45.0%. (B) GCs collapsed after 20 min incubation: Fc (4.2 μg/ml), 22.8%; Fc+MβCD, 24.4%; EA3, 78.2%; and EA3+MβCD, 51.6%. GCs collapsed after 60 min incubation: Fc, 14.9%; Fc+MβCD, 10.4%; EA3, 28.3%; and EA3+MβCD, 14.5%. N: number of independent experiments, number of analyzed GCs in brackets; error bars show standard deviations. T-test with n.s.: α ≥0.05, *: α <0.05, ***: α <0.001. (C) EA3–eA5 and (D) eA5–EA3 double-cue gap assays. After 115 µm wide gaps, untreated GCs predominantly stop, whereas MβCD-treated GCs (C', D') ignore the protein field after the gap. (E) Quantification of double-cue gap assays: EA3–eA5, 80.7%; EA3–eA5+MβCD, 46.3% stopping; eA5–EA3, 70.9%; and eA5–EA3+MβCD, 23.6% stopping. N: number of independent experiments, error bars show standard deviations, T-test with *: α <0.05, ***: α <0.001.
-
Figure 9—source data 1
Original data underlying the bar charts in Figure 9A, B, E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.025
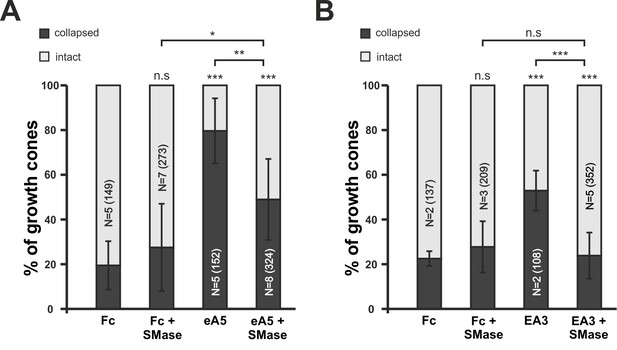
Disintegration of lipid microdomains by sphingomyelinase desensitizes growth cones towards soluble ephrin-A5 and EphA3.
(A) Ephrin-A5-Fc and (B) EphA3-Fc collapse assays. In accordance with MβCD experiments, Sphingomyelinase (SMase, 400mU/ml)-treated GCs show reduced collapse rates when exposed to soluble ephrin-A5-Fc (0.25 μg/ml) or EphA3-Fc (15 μg/ml) compared to controls without SMase. (A) Fc (0.25 μg/ml), 19.5%; Fc+SMase, 27.5%; eA5, 79.6%; and eA5+SMase, 50% collapsed. (B) Fc (4.2 μg/ml), 22.5%; Fc+SMase, 27.7%; EA3, 52.9%; and EA3+SMase, 23.8% collapsed after 20 min incubation. SMase was applied during a 30 min pre-incubation and thereafter together with Fc or ephrin-A5. N: number of independent experiments, number of analyzed GCs in brackets; error bars show standard deviations. T-test with n.s.: α ≥ 0.05, *: α < 0.05, **: α < 0.01, ***: α < 0.001.
-
Figure 9—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original data underlying the bar charts of Figure 9—figure supplement 1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25533.027
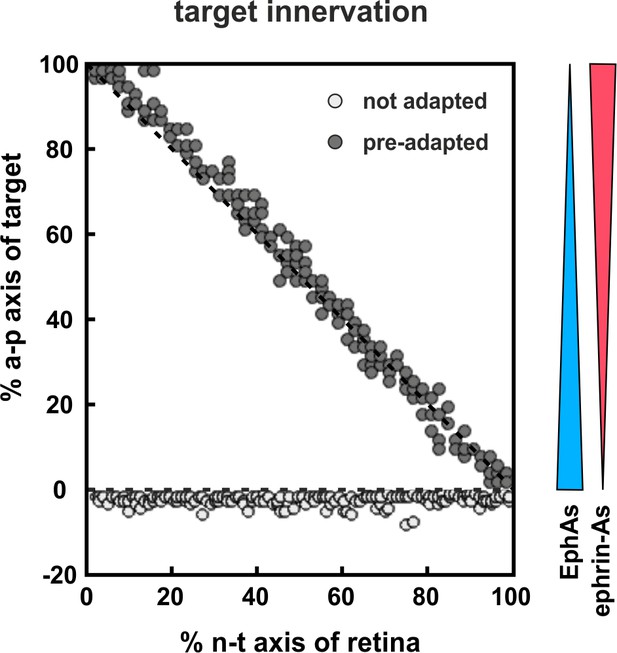
Modeling tectal innervation.
Co-adaptation enables fiber terminals to enter a tectal target field initially and allows correct mapping therein (gray circles), whereas non-adapted terminals (white circles) fail to enter a tectal target field in simulations with 200 GCs placed in front of the target. The graded distributions of EphAs (blue) and ephrin-As (red) on the target field are symbolized by the colored wedges. RF and LF of adapted terminals are initially deflected by a factor of 30.
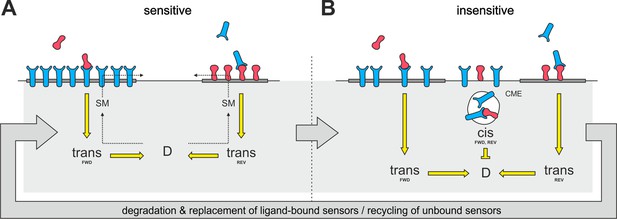
Proposed mechanism of co-adaptation.
(A) EphAs (blue) and ephrin-As (red), located in membrane lipid microdomains (dark gray), signal in trans due to external cues. Trans forward (FWD) and reverse (REV) signals integrate into the guidance potential, D, and elicit repulsion when not balanced. Trans signaling also promotes sphingomyelin (SM) synthesis, and when incorporated into the membrane, this phospholipid might proportionally solubilize EphAs and ephrin-As from their respective domains. (B) Dispersed, unbound sensors are destined for constitutive clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) and might increase cis signaling upon internalization, as anti-parallel orientation is favored in high-curvature membrane vesicles. Enhanced cis signals desensitize GCs to trans signals. Sensitivity returns with the recycling of unbound sensors, and degraded receptor/ligand complexes should constitutively be replaced through protein synthesis in the long run.





