Plasmodium P36 determines host cell receptor usage during sporozoite invasion
Figures
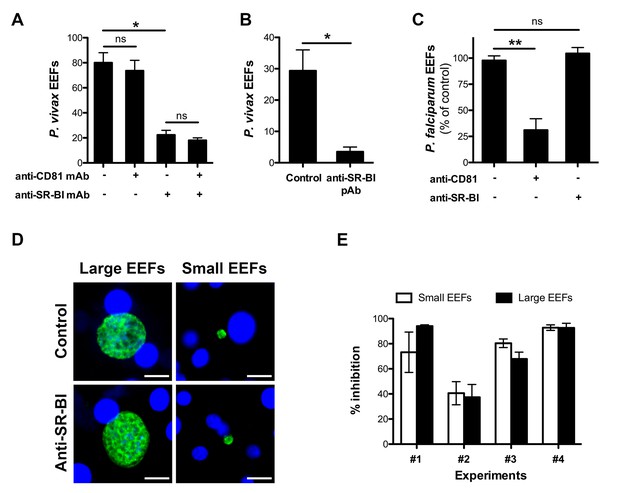
Anti-SR-BI antibodies inhibit P. vivax but not P. falciparum sporozoite infection.
(A) Primary human hepatocyte cultures were incubated with P. vivax sporozoites in the presence of anti-CD81 and/or anti-SR-BI mAbs at 20 μg/ml, and the number of EEF-infected cells was determined 5 days post-infection after labeling of the parasites with anti-HSP70 antibodies. (B) Primary human hepatocytes were incubated with P. vivax sporozoites in the presence or absence of anti-SR-BI polyclonal rabbit serum (diluted 1/100), and the number of EEFs was determined at day 5 by immunofluorescence. (C) Primary human hepatocyte cultures were incubated with P. falciparum sporozoites in the presence of anti-CD81 mAb (20 μg/ml) and/or anti-SR-BI polyclonal rabbit serum (diluted 1/100), and the number of EEF-infected cells was determined 5 days post-infection after labeling of the parasites with anti-HSP70 antibodies. Results from three independent experiments are shown and expressed as the percentage of control (mean ±SD). (D) Immunofluorescence analysis of P. vivax EEFs at day 5 post-infection of primary human hepatocytes. Parasites were labeled with anti-HSP70 antibodies (green), and nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). Large EEFs and small EEFs were observed in both control and anti-SR-BI antibody-treated cultures. Scale bars, 10 μm. (E) Inhibitory activity of anti-SR-BI antibodies on small EEFs (white histograms) and large EEFs (black histograms). The results from four independent experiments are shown, and are expressed as the percentage of inhibition observed with anti-SR-BI antibodies as compared to the control.
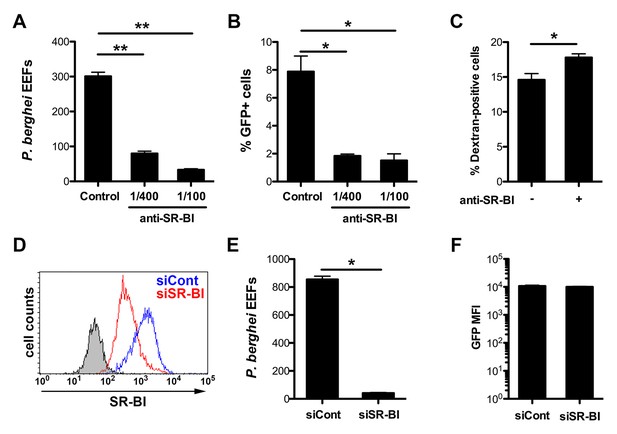
Infection of human HepG2 cells by P. berghei sporozoites depends on SR-BI.
(A) HepG2 cells were incubated with P. berghei sporozoites for 3 hr in the absence (Control) or presence of increasing concentrations of rabbit polyclonal SR-BI antisera. Infected cultures were further incubated for 24 hr before quantification of EEFs-infected cells by fluorescence microscopy. (B) HepG2 cell cultures were infected with PbGFP sporozoites as in A, and the number of invaded cells (GFP+) was quantified by FACS 3 hr post-infection. (C) HepG2 cells were incubated for 3 hr with PbGFP sporozoites and rhodamine-labeled dextran, in the presence or absence of anti-SR-BI antibodies. The percentage of traversed (dextran-positive) cells was then determined by FACS. (D) HepG2 cells transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting SR-BI (siSR-BI, red histogram) or with a control siRNA (siCont, blue histogram) were stained with anti-SR-BI antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. The negative staining control is in grey. (E) P. berghei EEF number in HepG2 cells transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting SR-BI (siSR-BI) or a control siRNA (siCont). (F) HepG2 cells transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting SR-BI (siSR-BI) or a control siRNA (siCont) were infected with PbGFP sporozoites and incubated for 24 hr, before measurement of the mean fluorescence intensity (GFP MFI) of infected (GFP-positive) cells by FACS.
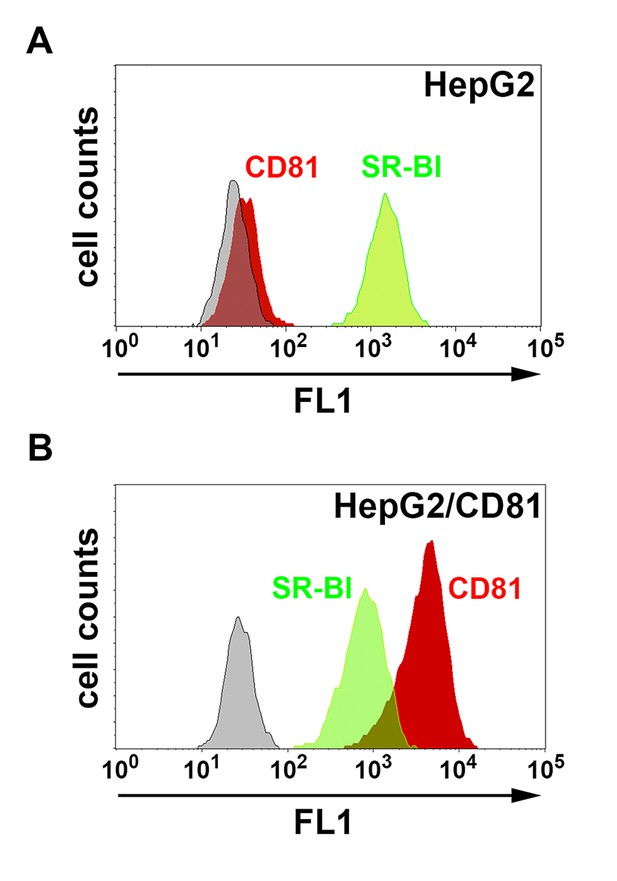
CD81 and SR-BI surface expression in HepG2 and HepG2/CD81 cells.
HepG2 (A) and HepG2/CD81 cells (B) were stained with anti-CD81 (red histograms) or anti-SR-BI (green histograms) antibodies and analyzed by FACS.
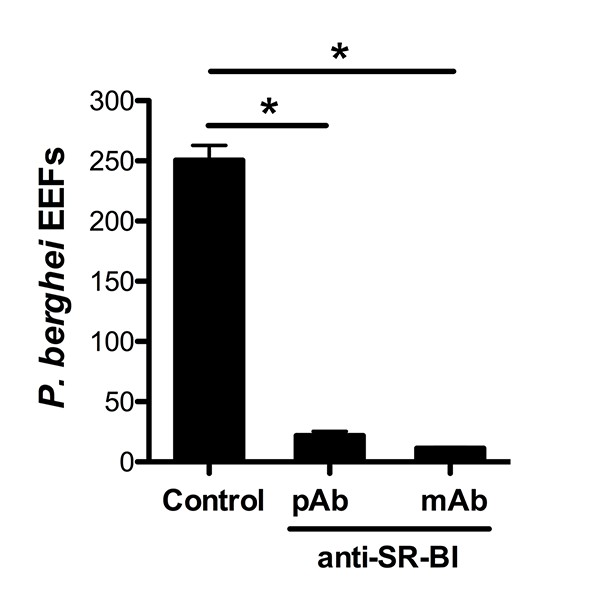
Anti-SR-BI antibodies neutralize P. berghei infection of HepG2 cells.
Effect of anti-SR-BI rat polyclonal antibodies (pAb) and mouse mAb on P. berghei EEF numbers in HepG2 cells.
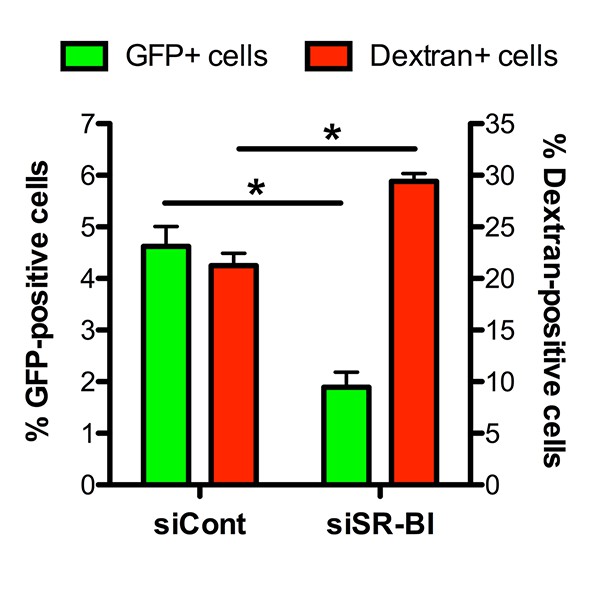
Effect of SR-BI silencing on sporozoite cell traversal and invasion.
HepG2 cells transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting SR-BI (siSR-BI) or a control siRNA (siCont) were incubated for 3 hr with PbGFP sporozoites and rhodamine-labeled dextran, and the percentage of invaded cells (GFP-positive, green bars) and traversed cells (dextran-positive, red bars) was determined by FACS.
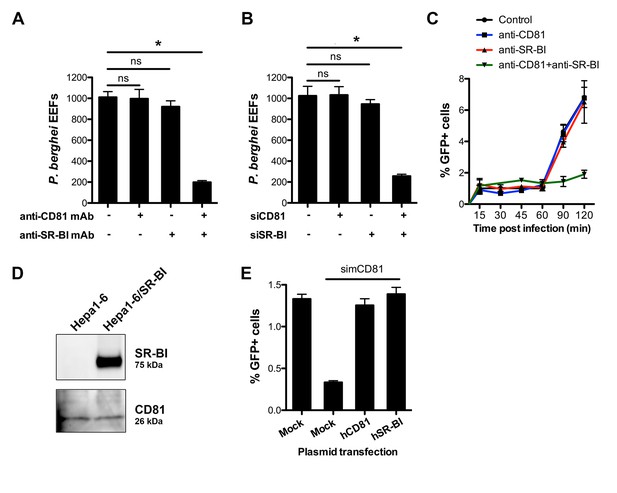
CD81 and SR-BI define alternative entry routes for P. berghei sporozoites.
(A) HepG2/CD81 cells were incubated with P. berghei sporozoites in the presence or absence of anti-human CD81 and/or SR-BI mAbs, and the number of EEFs-infected cells was determined by fluorescence microscopy 24 hr post-infection. (B) P. berghei EEF numbers in HepG2/CD81 cells transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting CD81 (siCD81) and/or SR-BI (siSR-BI). (C) HepG2/CD81 cells were incubated with PbGFP sporozoites for 15–120 min, in the presence or absence of anti-CD81 and/or anti-SR-BI antibodies, then trypsinized and directly analyzed by FACS to quantify invaded (GFP-positive) cells. (D) Protein extracts from Hepa1-6 cells and Hepa1-6 cells transiently transfected with a human SR-BI expression plasmid were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies recognizing mouse and human SR-BI (Abcam) or mouse CD81 (MT81). (E) Hepa1-6 cells were transfected first with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting endogenous mouse CD81 (simCD81), then with plasmids encoding human CD81 (hCD81) or SR-BI (hSR-BI). Cells were then incubated with PbGFP sporozoites, and the number of infected (GFP-positive) cells was determined 24 hr post-infection by FACS.
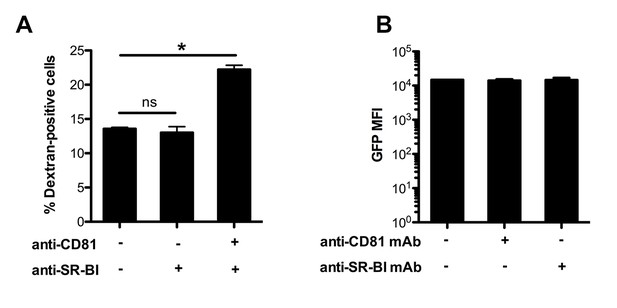
Effect of anti-CD81 and anti-SR-BI antibodies on P. berghei sporozoite cell traversal and intracellular development.
(A) HepG2/CD81 cells were incubated for 3 hr with PbGFP sporozoites and rhodamine-labeled dextran, in the presence or absence of anti-CD81 and/or SR-BI antibodies. The percentage of traversed (dextran-positive) cells was then determined by FACS. (B) HepG2/CD81 cells were infected with PbGFP sporozoites in the presence or absence of anti-CD81 or anti-SR-BI antibodies, and incubated for 24 hr before measurement of the MFI of infected (GFP-positive) cells by FACS.
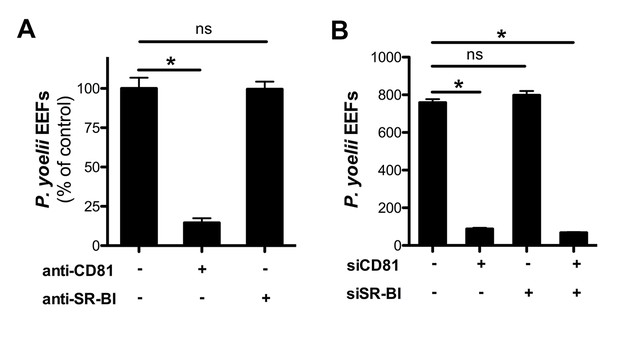
Infection of HepG2/CD81 cells by P. yoelii sporozoites depends on CD81 but not SR-BI.
(A) HepG2/CD81 cells were incubated with P. yoelii sporozoites in the presence of anti-CD81 mAb (20 μg/ml) or anti-SR-BI polyclonal rabbit serum (diluted 1/100), and the number of EEF-infected cells was determined 24 hr post-infection by fluorescence microscopy. Results from three independent experiments are shown and expressed as the percentage of control (mean ± SD). (B) P. yoelii EEF numbers in HepG2/CD81 cells transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting CD81 (siCD81) and/or SR-BI (siSR-BI).
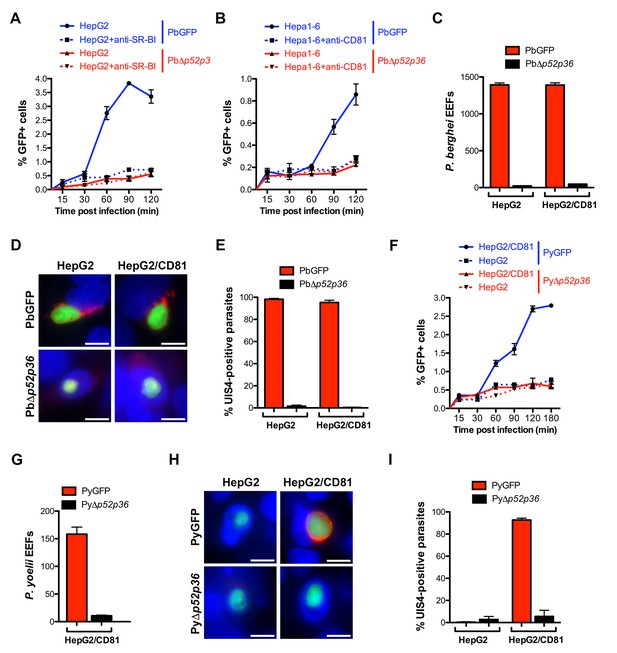
The 6-cys proteins P52 and P36 are required for productive host cell invasion.
(A–B) HepG2 (A) or Hepa1-6 cells (B) were incubated with PbGFP (blue lines) or PbΔp52/p36 sporozoites (red lines) for 15–120 min, in the presence (dotted lines) or absence (solid lines) of anti-SR-BI (A) or anti-CD81 (B) antibodies. Cells were then trypsinized and directly analyzed by FACS to quantify invaded (GFP-positive) cells. (C) HepG2 and HepG2/CD81 cells were infected with PbGFP or PbΔp52/p36 sporozoites and the number of EEFs was determined 28 hr post-infection by fluorescence microscopy. (D) HepG2 and HepG2/CD81 cells infected with PbGFP or PbΔp52/p36 sporozoites were fixed at 28 hr post-infection, stained with anti-UIS4 antibodies (red) and the nuclear stain Hoechst 33342 (blue), and examined by fluorescence microscopy. Parasites were detected based on GFP expression (green). Scale bars, 10 μm. (E) Quantification of UIS4 expression in HepG2 and HepG2/CD81 cells infected with PbGFP (red) or PbΔp52/p36 (black). (F) HepG2 (dotted lines) and HepG2/CD81 cells (solid lines) were incubated with PyGFP (blue lines) or PyΔp52/p36 sporozoites (red lines) for 15–180 min, trypsinized, and directly analyzed by FACS to quantify invaded (GFP-positive) cells. (G) HepG2/CD81 cells were infected with PyGFP or PyΔp52/p36 sporozoites and the number of EEFs was determined 24 hr post-infection by fluorescence microscopy. (H) HepG2 and HepG2/CD81 cells infected with PyGFP or PyΔp52/p36 sporozoites were fixed at 24 hr post-infection, stained with anti-UIS4 antibodies (red) and the nuclear stain Hoechst 33342 (blue), and examined by fluorescence microscopy. Parasites were detected based on GFP expression (green). Scale bars, 10 μm. (I) Quantification of UIS4 expression in HepG2 and HepG2/CD81 cells infected with PyGFP (red) or PyΔp52/p36 (black).
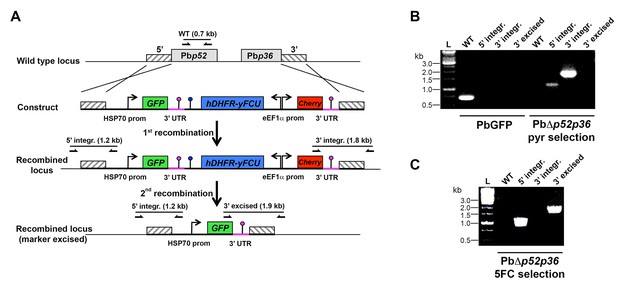
Targeted gene deletion of p52 and p36 in P. berghei.
(A) Replacement strategy to generate PbΔp52p36 parasites. The wild-type (WT) genomic locus of P. berghei p52/p36 was targeted with a GOMO-GFP replacement plasmid containing a 5’ and a 3’ homologous sequence inserted on each side of the plasmid GFP/hDHFR-yFCU/mCherry triple cassette. Upon double crossover recombination, the adjacent p52 and p36 genes are replaced by the plasmid cassettes. Subsequent recombination between the two identical PbDHFR/TS 3’ UTR sequences (pink lollipops) results in excision of hDHFR-yFCU and mCherry. Genotyping primers and expected PCR fragments are indicated by arrows and lines, respectively. (B–C) PCR analysis of genomic DNA isolated from control PbGFP and PbΔp52p36 parasites recovered after positive selection with pyrimethamine (B) and after negative selection with 5-fluorocytosine (C). Confirmation of the predicted recombination events was achieved with primer combinations specific for 5’ integration (5’ integr.), 3’ integration (3’ integr.) or 3’ integration followed by marker excision (3’ excised). Primers used for genotyping are indicated in the Materials and methods. The absence of amplification with primer combinations specific for the WT locus (WT) and the non-excised integrated construct (3’ integration) confirms that the final populations contain only PbΔp52p36 drug-selectable marker-free P. berghei parasites.
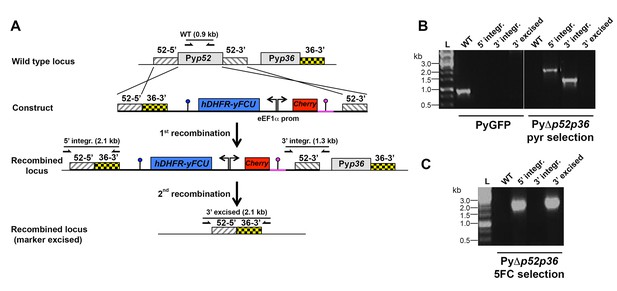
Targeted gene deletion of p52 and p36 in P. yoelii.
(A) Replacement strategy to generate PyΔp52p36 parasites. The wild-type (WT) genomic locus of P. yoelii p52/p36 in the PyGFP parental line was targeted with a GOMO replacement plasmid containing a 5’ and a 3’ homologous sequence from pyp52 inserted on each side of a hDHFR-yFCU/mCherry double cassette. An additional 3’ homologous sequence from pyp36 (36–3’) was inserted immediately downstream of the 5’ homologous sequence from pyp52 (52–5’). Upon double crossover recombination, pyp52 is replaced by the plasmid cassettes. Subsequent recombination between the two identical 36–3' sequences results in excision of hDHFR-yFCU, mCherry and pyp36. Genotyping primers and expected PCR fragments are indicated by arrows and lines, respectively. (B–C) PCR analysis of genomic DNA isolated from parental PyGFP and PyΔp52p36 parasites recovered after positive selection with pyrimethamine (B) and after negative selection with 5-fluorocytosine (C). Confirmation of the predicted recombination events was achieved with primer combinations specific for 5’ integration (5’ integr.), 3’ integration (3’ integr.) or 3’ integration followed by marker excision (3’ excised). Primers used for genotyping are indicated in Materials and methods. The absence of amplification with primer combinations specific for the WT locus (WT) and the non-excised integrated construct (3’ integration) confirms that the final populations contain only PyΔp52p36 drug-selectable marker-free P. yoelii parasites.
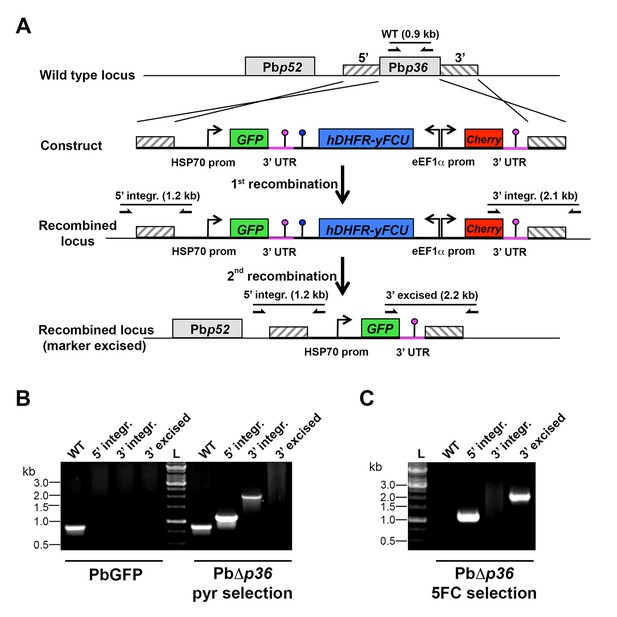
Targeted gene deletion of p36 in P. berghei.
(A) Replacement strategy to generate PbΔp36 parasites. The wild-type (WT) genomic locus of P. berghei p36 was targeted with a GOMO-GFP replacement plasmid containing a 5’ and a 3’ homologous sequence inserted on each side of the plasmid GFP/hDHFR-yFCU/mCherry triple cassette. Upon double crossover recombination, the p36 gene is replaced by the plasmid cassettes. Subsequent recombination between the two identical PbDHFR/TS 3’ UTR sequences (pink lollipops) results in excision of hDHFR-yFCU and mCherry. Genotyping primers and expected PCR fragments are indicated by arrows and lines, respectively. (B–C) PCR analysis of genomic DNA isolated from control PbGFP and PbΔp36 parasites recovered after positive selection with pyrimethamine (B) and after negative selection with 5-fluorocytosine (C). Confirmation of the predicted recombination events was achieved with primer combinations specific for 5’ integration (5’ integr.), 3’ integration (3’ integr.) or 3’ integration followed by marker excision (3’ excised). Primers used for genotyping are indicated in the Materials and methods. The absence of amplification with primer combinations specific for the WT locus (WT) and the non-excised integrated construct (3’ integration) confirms that the final populations contain only PbΔp36 drug-selectable marker-free P. berghei parasites.
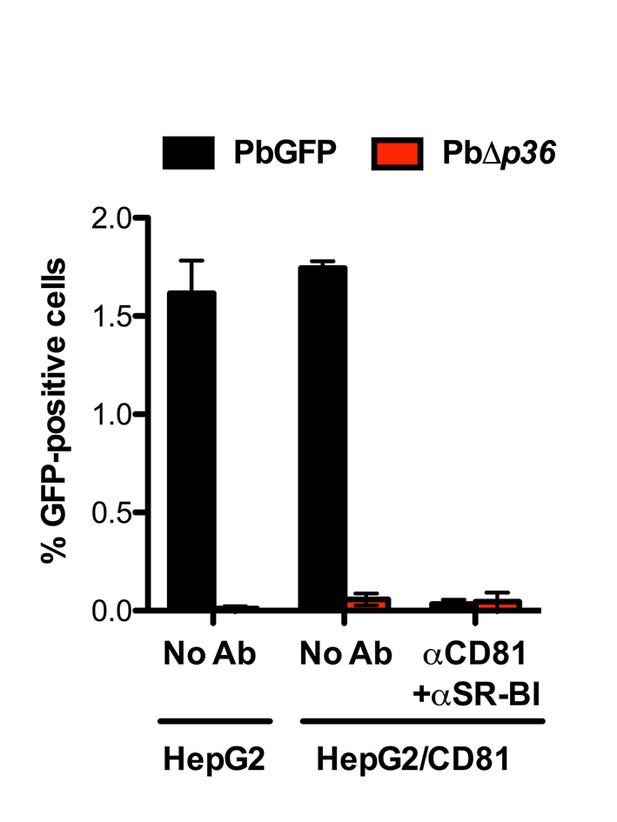
P36 is required for P. berghei sporozoite entry via both SR-BI- and CD81-dependent routes.
HepG2 and HepG2/CD81 cells were incubated with PbGFP or PbΔp36 sporozoites in the presence or absence of anti-CD81 and anti-SR-BI antibodies, and the percentage of infected (GFP-positive) cells was determined 24 hr post-infection by FACS.
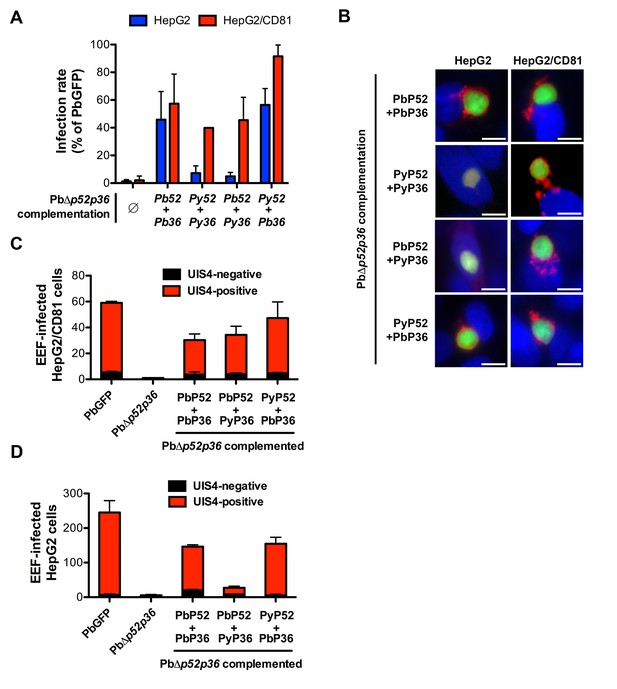
P36 mediates CD81-independent entry in P. berghei sporozoites.
(A) HepG2 (blue histograms) or HepG2/CD81 cells (red histograms) were incubated with sporozoites from PbΔp52/p36 parasites genetically complemented with P. berghei and/or P. yoelii P52 and P36, and analysed by FACS or fluorescence microscopy to determine the number of GFP-positive cells 24 hr post-infection. Results from three independent experiments are shown and are expressed as the percentage of infection in comparison to control PbGFP-infected cultures (mean ±SD). (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of UIS4 expression in HepG2 or HepG2/CD81 cells infected with genetically complemented PbΔp52/p36 sporozoites. Cells were fixed with PFA 28 hr post-infection, permeabilized, and stained with anti-UIS4 antibodies (red) and the nuclear stain Hoechst 33342 (blue). Parasites were detected based on GFP expression (green). Scale bars, 10 μm. (C–D) HepG2/CD81 (C) and HepG2 (D) cells were infected with PbGFP, PbΔp52/p36 and complemented PbΔp52/p36 sporozoites. The numbers of UIS4-positive (red histograms) and UIS4-negative (black histograms) EEFs were determined by fluorescence microscopy 24 hr post-infection.
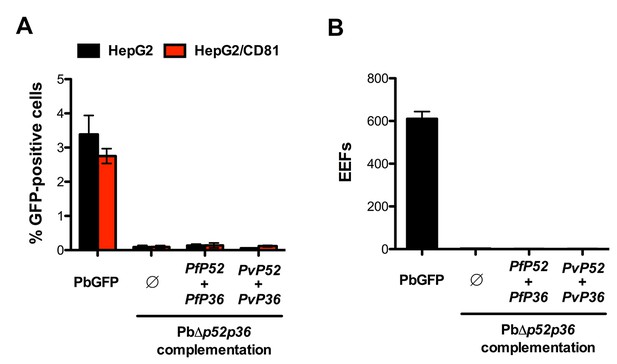
Genetic complementation with p52 and p36 from P. falciparum or P. vivax does not restore sporozoite infectivity in PbΔp52p36 parasites.
(A) HepG2 and HepG2/CD81 cells were incubated with PbGFP, PbΔp52p36 and PbΔp52p36 complemented with p52 and p36 from P. falciparum or P. vivax. The percentage of infected (GFP-positive) cells 24 hr post-infection was determined by FACS. (B) Primary human hepatocytes were incubated with PbGFP, PbΔp52p36 and PbΔp52p36 complemented with p52 and p36 from P. falciparum or P. vivax. The number of EEFs was determined 24 hr post-infection by fluorescence microscopy.
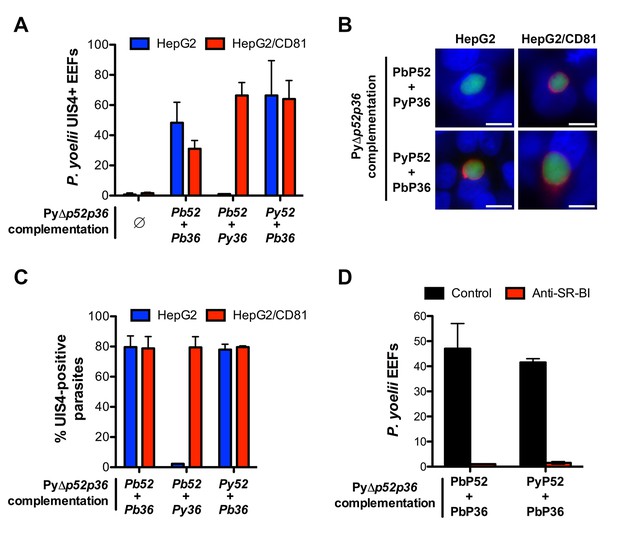
Transgenic P. yoelii sporozoites expressing PbP36 can infect CD81-null cells via SR-BI.
(A) HepG2 (blue) and HepG2/CD81 cells (red) were incubated with genetically complemented PyΔp52/p36 sporozoites, and fixed 24 hr post-infection. The number of UIS4-positive vacuoles was then determined by immunofluorescence. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of UIS4 expression in HepG2 or HepG2/CD81 cells infected with sporozoites of PyΔp52/p36 parasites genetically complemented with P52 and P36 from P. berghei or P. yoelii. Cells were fixed with PFA, permeabilized, and stained with anti-UIS4 antibodies (red) and the nuclear stain Hoechst 33342 (blue). Parasites were detected based on GFP expression (green). Scale bars, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of UIS4 expression in HepG2 (blue) and HepG2/CD81 cells (red) infected with genetically complemented PyΔp52/p36 sporozoites and processed as in B for immunofluorescence. (D) HepG2 cells were incubated with PyΔp52/p36 sporozoites complemented with PbP36 and either PbP52 or PyP52, in the presence or absence of anti-SR-BI antibodies. Infected cultures were fixed 24 hr post-infection, and the number of EEFs was then determined by fluorescence microscopy.
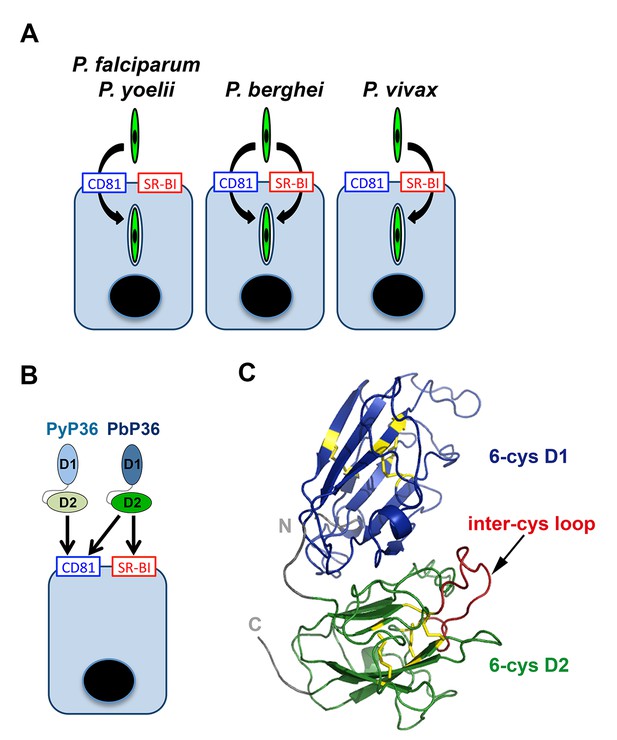
Model of host cell entry pathways for Plasmodium sporozoites.
(A) Host cell membrane proteins CD81 and SR-BI define two independent entry routes for Plasmodium sporozoites. P. falciparum and P. yoelii sporozoites require CD81 for infection, whereas P. vivax sporozoites infect hepatocytes using SR-BI. P. berghei sporozoites can enter cells alternatively via CD81 or SR-BI. (B) The 6-cysteine domain protein P36 determines host cell receptor usage during P. yoelii and P. berghei sporozoite invasion. Whilst PyP36 supports only CD81-dependent sporozoite entry, PbP36 mediates sporozoite invasion through both CD81- and SR-BI-dependent pathways. (C) Model of the 3D structure of P. berghei P36, established based on the crystal structure of PfP12 (2YMO). In the ribbon diagram, the tandem 6-cysteine domains are shown in blue (D1) and green (D2), respectively, and the cysteine residues and disulphide bonds in yellow. The loop located between the third and fourth cysteine residues of the D2 domain (inter-cys loop) is indicated in red.
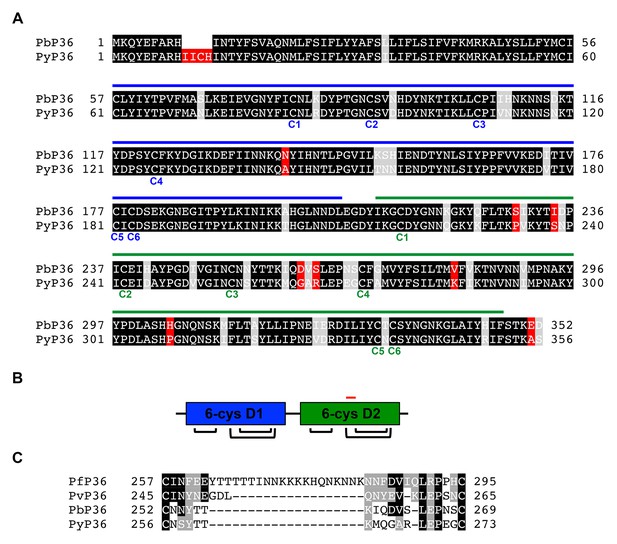
P36 protein sequence analysis.
(A) Alignment of P. berghei and P. yoelii P36 protein sequences. Identical, similar and different amino acids are shaded in black, grey and red, respectively. The tandem 6-cys domains D1 and D2 are indicated with blue and green lines, respectively, above the protein sequences. The six cysteine residues of each domain are indicated below the protein sequences. (B) Schematic representation of the tandem D1 and D2 6-cys domains of P36, showing the disulfide bond arrangement. The position of the ‘inter-cys loop’, located between the third and fourth cysteine residues of D2, is indicated as a red line. (C) Alignment of P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. berghei and P. yoelii inter-cys loop sequences. Identical and similar amino acids are shaded in black and grey, respectively.





