Simultaneous activation of parallel sensory pathways promotes a grooming sequence in Drosophila
Figures
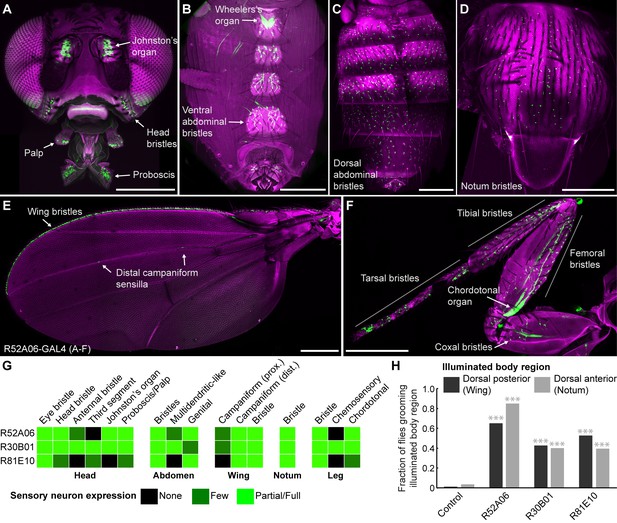
GAL4 lines expressing in sensory neurons whose activation elicits grooming.
(A–E) Peripheral expression pattern of R52A06-GAL4 expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP). Confocal maximum projections are shown. Sensory neurons are in green and autofluorescence from the cuticle is in magenta. Body parts shown are: (A) head, (B) ventral abdomen, (C) dorsal abdomen, (D) notum, (E) wing, and (F) prothoracic leg. Labeled arrows indicate specific sensory classes. In (C) and (D) all GFP positive cells are bristle mechanosensory neurons. Scale bars, 250 μm. (G) Summary table of the expression patterns of R52A06-, R30B01-, and R81E10-GAL4 in sensory neurons on each indicated body part. (H) Grooming responses to optogenetic activation of sensory neurons targeted by different GAL4 lines expressing ChR2. An optical fiber connected to an LED was used to direct light to the dorsal surface of the anterior or posterior body (Figure 1—figure supplement 2). The fraction of flies that showed a grooming response to the blue light-illuminated body region is plotted (n ≥ 40 trials for each body part). Grey shades and labels indicate the region that was illuminated. Chi-squared test, Asterisks: p<0.0001. See Video 1 and Video 2 for representative examples.
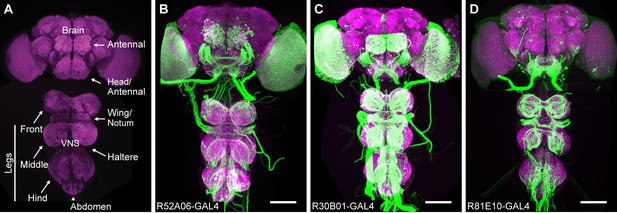
Anatomy of sensory GAL4 lines.
(A) Sensory neurons project their axons (afferents) to specific regions of the central nervous system (CNS) depending on which body part they are from. The neuropile of the CNS visualized with anti-Bruchpilot (magenta). A confocal image maximum projection is shown. (B–D) Three different GAL4 lines expressing GFP in afferent projections from the different body parts. GFP was visualized with anti-GFP antibodies (green). Scale bar, 100 μm. GAL4 lines shown are R52A06-GAL4 (B), R30B01-GAL4 (C), and R81E10-GAL4 (D).
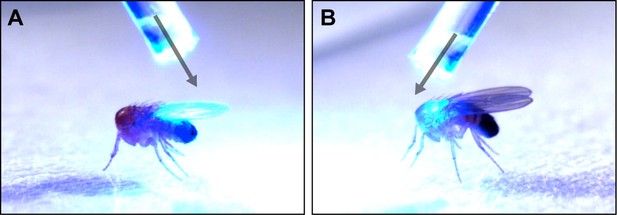
Optogenetic illumination of sensory neurons on different body regions.
(A–B) A fiber optic probe that was connected to a blue light LED was used to direct light to specific body regions. Images show illumination of the posterior (A) or anterior (B) dorsal surfaces of decapitated flies. See Video 1 and Video 2 for representative examples.
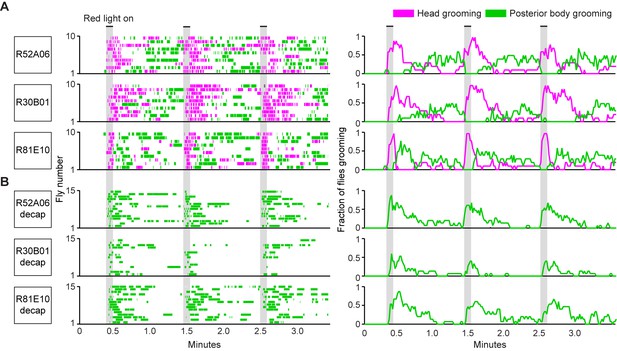
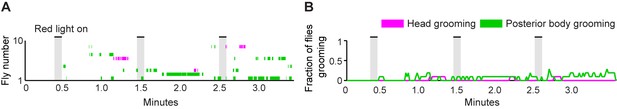
Simultaneous optogenetic activation of body sensory neurons elicits sequential grooming.
(A–B) Head (magenta) or posterior body grooming movements (green) elicited with red light-illumination of R52A06-, R30B01-, and R81E10-GAL4 flies expressing CsChrimson. The movements are mutually exclusive. Ethograms of ten individual flies are stacked for each line (left). Histograms show the fraction of flies that were performing specific grooming movements within one-second time bins (right). Gray bars indicate five second presentations of red light. (A) Grooming movements performed by intact flies. (B) Grooming movements performed by decapitated flies. See Video 3, Video 4, and Video 5 for representative examples. Red light illumination of control flies did not elicit grooming (Figure 2—figure supplement 1).
Illumination of control flies does not elicit grooming.
(A) Ethograms showing head (magenta) or posterior body grooming (green) with red light-illumination of control flies. Ethograms of individual flies are stacked on top of each other. (B) Histogram shows the fraction of flies that were performing each grooming movement within one-second time bins. Gray bars indicate a five second presentation of red light. This is the control for the experiment shown in Figure 2.
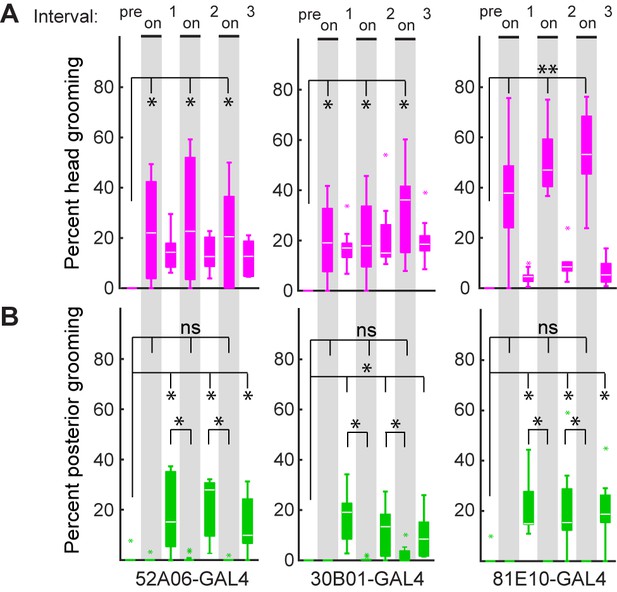
Simultaneous optogenetic activation of body sensory neurons elicits a prioritized head grooming response.
(A–B) Box plots show the percent time flies spent performing head (A) or posterior grooming (B) with optogentic activation of neurons targeted by 52A06-, 30B01-, and 81E10-GAL4 (from experiment shown in Figure 2A). Plotted time bins include the period before the optogenetic stimulus (pre), the three optogenetic stimuli (on), and the three post stimulus rest periods (1-3). Bottom and top of the boxes indicate the first and third quartiles respectively; the white line specifies median; whiskers show the upper and lower 1.5 IQR; magenta and green asterisks indicate data outliers (n = 10 for each box). Black asterisks show *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Friedman test followed by post-hoc Wilcoxon signed rank test for pairwise comparisons with Bonferroni-Holm correction for multiple comparisons.
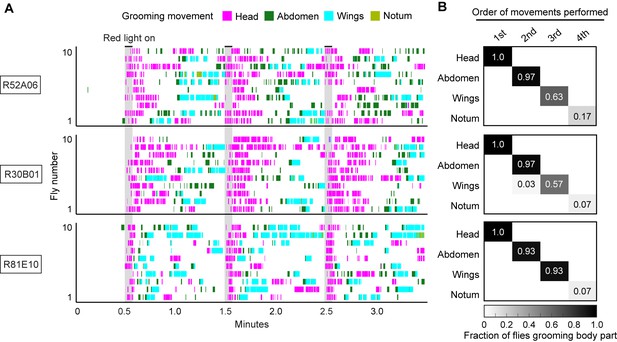
Simultaneous optogenetic activation of body sensory neurons elicits a grooming sequence.
(A) Ethograms showing different grooming movements elicited with red light-illumination of R52A06-, R30B01-, or R81E10-GAL4 flies expressing CsChrimson. Ethograms of ten individual flies are stacked for each GAL4 line. Gray bars indicate five-second presentations of a red light stimulus. Colors indicating the grooming movements are shown above the ethograms. The same ethograms with binned head and posterior grooming movements are shown in Figure 2A. (B) Grids show the fraction of flies performing a specific grooming movement as their first, second, third, or fourth novel movement from the onset of the red light stimulation until the beginning of the next red light stimulus. The fraction of flies performing notum grooming is low because most flies did not perform that grooming movement. Notum grooming was similarly rare with dust induced grooming (Seeds et al., 2014).
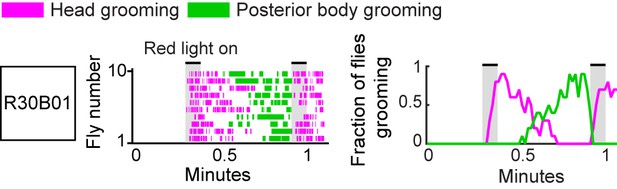
Simultaneous optogenetic activation of body sensory neurons elicits eye grooming and terminates ongoing posterior grooming.
Head (magenta) or posterior body grooming (green) elicited with red light-illumination of R30B01-GAL4 flies expressing CsChrimson. Only flies that performed posterior body grooming at the moment of the second stimulus are plotted. Ethograms of ten individual flies are stacked (left). Histograms show the fraction of flies that were performing specific grooming movements within one-second time bins (right). Gray bars indicate five-second presentations of red light. Intervals between the optogenetic stimulations are 30 s, compared to 60 s in Figure 2.
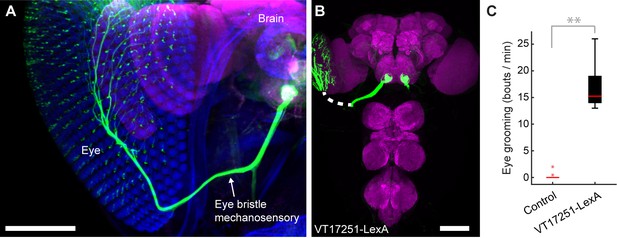
Interommatidial bristle mechanosensory neurons elicit eye grooming.
(A–B) The expression pattern of VT17251-LexA in eye bristle mechanosensory neurons. The neurons were stained with anti-GFP (green) and the brain neuropile is stained with anti-Bruchpilot (magenta). Both images are maximum intensity projections. Scale bars, 100 μm. (A) Expression pattern shown in the semi-intact head. The eye and head cuticle is shown in blue. (B) Expression pattern in the CNS. White dashed line indicates the trajectory of eye bristle mechanosensory neuron axons found from the more intact preparations in (A). (C) Eye grooming bout rate with optogentic activation of neurons targeted by VT17251-LexA. Bottom and top of the boxes indicate the first and third quartiles respectively; median is the red line; whiskers show the upper and lower 1.5 IQR; red dots are data outliers (n = 10 for each box; asterisks show p<0.001, Kruskal-Wallis and post hoc Mann-Whitney U pairwise test).
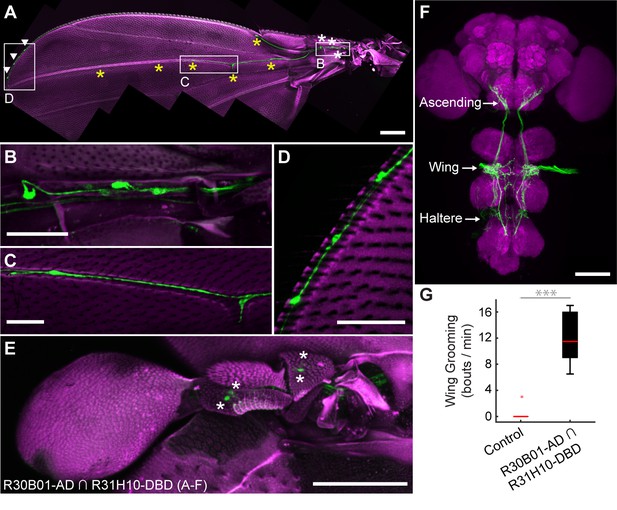
spGAL4 driver that expresses in wing and haltere sensory neurons whose activation elicits wing grooming.
(A–E) The expression pattern of R30B01-AD ∩ R31H10-DBD in sensory neurons of the wings and halteres. Native GFP fluorescence is shown in green and autofluorescence from the cuticle is in magenta. Maximum intensity projections are shown. The proximal wing is to the right and the distal wing is to the left. (A) Sensory neurons on the wing. White boxes and letters indicate the regions shown in B–D. The different symbols indicate the sensory neuron types on the wing as proximal campaniform sensilla (white asterisks), distal campaniform sensilla (yellow asterisks), or bristle mechanosensory (white arrowheads). Scale bar, 250 μm. (B–D) Larger images of the regions shown in A. Scale bars, 50 μm. Shown are the proximal campaniform sensilla (B), distal campaniform sensilla (C), and bristle mechanosensory neurons (D). (E) Expression in the haltere campaniform sensilla (asterisks). Scale bar, 100 μm (F) CNS expression visualized by co-stain with anti-GFP (green) and anti-Bruchpilot (magenta). Arrows indicate the CNS entry points of afferents from the wings and halteres, and the location of ascending projections from some of these afferents. Scale bar, 100 μm. (G) Wing grooming bout rate with optogentic activation of neurons targeted by R30B01-AD ∩ R31H10-DBD. Data are displayed as described for Figure 3C. Asterisks: p<0.0001.
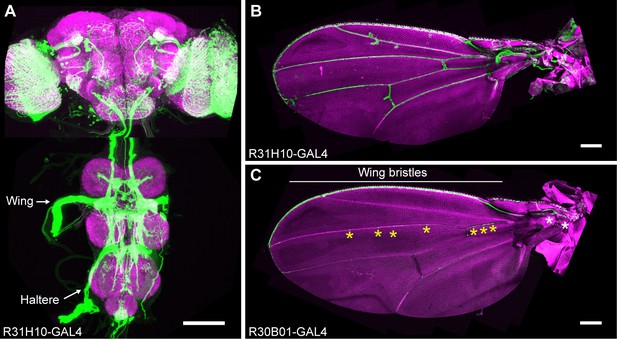
GAL4 lines that express in wing sensory neurons.
CNS (A) and wing (B) expression patterns of R31H10-GAL4 that targets neurons whose activation elicits wing grooming. Maximum intensity projections are shown. (A) The CNS expression is visualized by co-staining with anti-GFP (green) and anti-Bruchpilot (magenta). Arrows indicate the CNS entry points of afferents from the wings and halteres. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Wing expression pattern visualized using the native GFP fluorescence in green and autofluorescence from the cuticle in magenta. Scale bar, 250 μm. (C) Wing expression pattern of R30B01-GAL4. The different symbols indicate the sensory neuron types on the wing as proximal campaniform sensilla (white asterisks), distal campaniform sensilla (yellow asterisks), or bristle mechanosensory (white line). Scale bar, 250 μm.
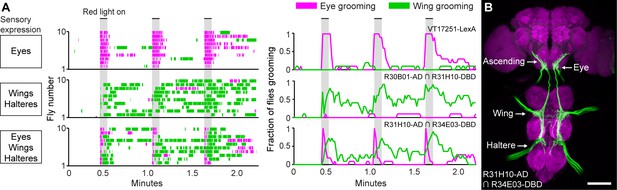
Simultaneous excitation of eye and wing/haltere sensory neurons produces sequential grooming.
(A) Ethograms (left) and histograms (right) showing eye grooming (magenta) or wing grooming (green) elicited with red light-activated CsChrimson expressed in different transgenic lines. The lines express in sensory neurons on the eyes (VT17251-LexA (top row)), wings and halteres (R30B01-AD ∩ R31H10-DBD (middle row)), or eyes, wings, and halteres (R31H10-AD ∩ R34E03-DBD (bottom row)). Data is plotted as described in Figure 2. See Video 6, Video 7, and Video 8 for representative examples. (B) GFP expression pattern of R31H10-AD ∩ R34E03-DBD in the CNS. Image shows a maximum intensity projection of a co-stain with anti-GFP (green) and anti-Bruchpilot (magenta). Arrows indicate the body part each sensory projection is from, and the location of ascending projections from the wings and halteres. Scale bars, 100 μm.
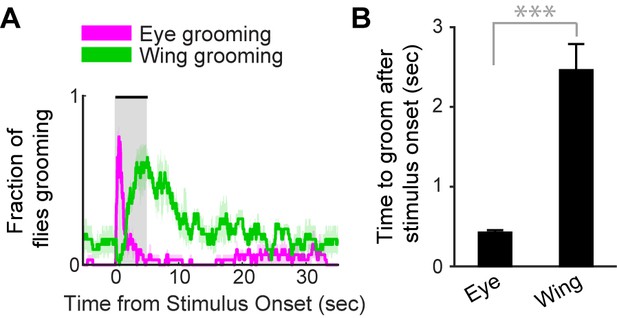
Simultaneous excitation of eye and wing/haltere sensory neurons produces sequential grooming.
(A) The mean fraction of flies performing head or posterior grooming for each frame before, during, and after the three different stimuli shown in Figure 5A (bottom). The envelope shows the standard error of the mean. The spGAL4 line (R31H10-AD ∩ R34E03-DBD) expresses CsChrimson in sensory neurons on the eyes, wings, and halteres. (B) The average time to perform head or posterior body grooming after the stimulus onset. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Statistical significance was assessed using a Mann-Whitney U test (***p<0.0001).
Videos
Grooming response to blue light illumination of the dorsal posterior body surface of a decapitated fly expressing ChR2 in sensory neurons.
ChR2 was expressed in sensory neurons across the body using R52A06-GAL4.
Grooming response to blue light illumination of the dorsal anterior body surface of a decapitated fly expressing ChR2 in sensory neurons.
ChR2 was expressed in sensory neurons across the body using R52A06-GAL4.
Grooming in response to the simultaneous optogenetic activation of sensory neurons across the body (R52A06-GAL4).
CsChrimson was expressed in sensory neurons using R52A06-GAL4. The infrared light in the bottom right corner indicates when the red light was on to activate the sensory neurons.
Grooming in response to the simultaneous optogenetic activation of sensory neurons across the body (R30B01-GAL4).
CsChrimson was expressed in sensory neurons using R30B01-GAL4. The infrared light in the bottom right corner indicates when the red light was on to activate the sensory neurons.
Grooming in response to the simultaneous optogenetic activation of sensory neurons across the body (R81E10-GAL4).
CsChrimson was expressed in sensory neurons using R81E10-GAL4. The infrared light in the bottom right corner indicates when the red light was on to activate the sensory neurons.
Grooming in response to the optogenetic activation of eye bristle mechanosensory neurons.
CsChrimson was expressed in eye bristle mechanosensory neurons using VT17251-LexA. The infrared light in the bottom right corner indicates when the red light was on to activate the sensory neurons.
Grooming in response to the optogenetic activation of wing/haltere sensory neurons.
CsChrimson was expressed in wing and haltere sensory neurons using R30B01-AD ∩ R31H10-DBD. The infrared light in the bottom right corner indicates when the red light was on to activate the sensory neurons.
Grooming in response to the simultaneous optogenetic activation of eye bristle mechanosensory and wing/haltere sensory neurons.
CsChrimson was expressed in eye, wing, and haltere sensory neurons using R31H10-AD ∩ R34E03-DBD. The infrared light in the bottom right corner shows when the red light was on to activate the sensory neurons.





