Site-specific monoubiquitination downregulates Rab5 by disrupting effector binding and guanine nucleotide conversion
Figures
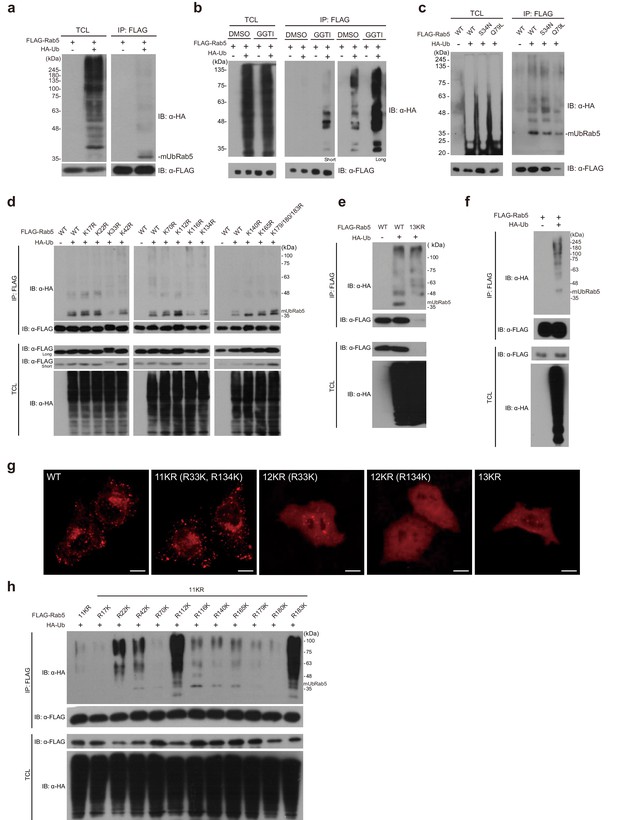
Rab5 is monoubiquitinated in the cellular environment.
(a) Monoubiquitination of FLAG-Rab5 in HEK 293T cells. FLAG-Rab5 was co-transfected with HA-ubiquitin or HA vector and immunoprecipitated from total cell lysates (TCL). Immunoblotting was performed with the indicated antibodies. (b) Cells were treated with a geranylgeranyl transferase inhibitor (GGTI-298) or DMSO. After 24 hr of treatment, cells were harvested and subjected to ubiquitination assay. Short and long refer to exposure time during immunoblotting (c) GDP/GTP-bound mutants of Rab5 (S34N, Q79L) were examined by the ubiquitination assay (d) Each of 13 lysine (K) residues was mutated to arginine (R), and all single mutants were subjected to ubiquitination assay. (e) A 13KR (no lysine) mutant of Rab5 was generated and subjected to the ubiquitination assay. (f) FLAG-Rab5 was co-transfected with HA-ubiquitin or HA vector and subjected to ubiquitination assay in HeLa cells. (g) Immunofluorescence assay of 13KR, 12KR (13KR with R33K or R134K), and 11KR (13KR with R33/134K) mutants. FLAG-Rab5 WT and mutants were transfected into HeLa cells that were then stained with FLAG-mouse-IgG/rhodamine (red). Scale bar, 10 μm. (h) Ubiquitination assay of single lysine mutants in HEK 293T cells. The 11KR mutant was used as a negative control. Each of 11 arginine (R) residues was mutated back to lysine residues as indicated.
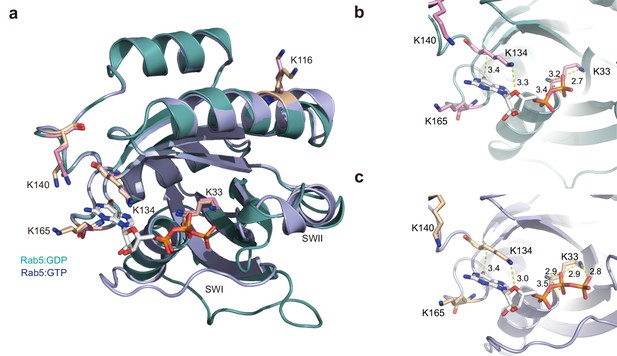
Structural and biochemical analyses of putative ubiquitination sites of Rab5.
(a) Putative lysine residues responsible for Rab5 ubiquitination are depicted in the crystal structures of Rab5:GDP and Rab5:GTP complexes (PDB ID: 1TU4 and 3MJH, respectively). (b, c) Structural analysis of lysine residues as putative ubiquitination sites based on the crystal structures of Rab5:GDP and Rab5:GTP (PDB ID: 1TU4 and 3MJH, respectively). Lysine residues and guanine nucleotides are shown as stick models. Polar interactions are shown as yellow dotted lines with distances shown. This figure was prepared in PyMOL (Schrődinger).
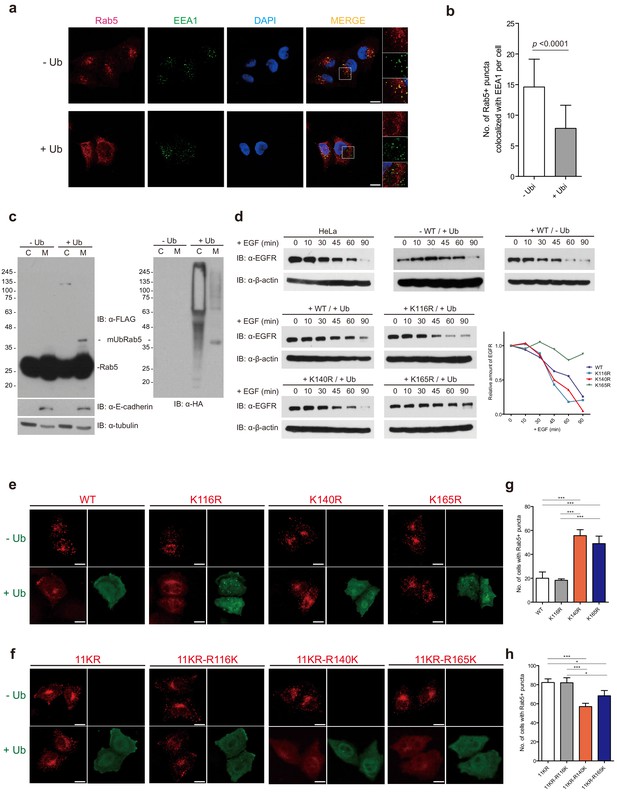
Endosome delocalization of Rab5 through overexpression of ubiquitin.
(a) HeLa cells were transfected with HA-ubiquitin or HA vector. Endogenous Rab5 and EEA1 were immunostained with Rab5-mouse-IgG/rhodamine (red) and EEA1-rabbit-IgG/Alexa-fluor-488 (green). Images were obtained by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) Quantification of immunofluorescence results in b. Number of Rab5 positive puncta co-localized with EEA1 is counted per cell (n = 45). p-value is calculated by t-test. (c) Fractionation assay. Cytosol and membrane fractions were subjected to immunoprecipitation and analyzed by immunoblotting as indicated. (d) EGF-induced EGF receptor (EGFR) degradation was monitored in HeLa cells. Cells were treated with EGF, harvested at the indicated time points, and analyzed by immunoblotting. (e) FLAG-Rab5 WT and K-to-R mutants were transfected with or without HA-ubiquitin into HeLa cells as indicated. (f) FLAG-Rab5 K11R and indicated 11KR/single R-to-K mutants were transfected with or without HA-ubiquitin into HeLa cells. Cells were immunostained with FLAG-mouse-IgG/Rhodamine (red) and HA-rabbit-IgG/Alexa-fluor-488 (green). Images were obtained by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (g, h) Quantification of immunofluorescence results in f and g, respectively. Number of cells with Rab5-positive endosomes were counted from 100 cells transfected with ubiquitin. Data are presented as mean ± S.D (n = 3, *p < 0.1, ***p < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA).
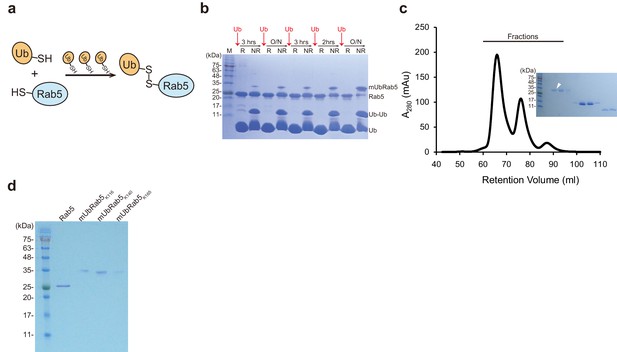
Chemical synthesis of mUbRab5s by iterative addition of ubiquitinG76C.
(a) Schematic diagram of the chemical ubiquitination of Rab5 by iterative addition of ubiquitinG76C. (b) Production of mUbRab5K140 was monitored by SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) or non-reducing (NR) conditions. Intervals between addition of ubiquitinG76C (Ub) are indicated. O/N, overnight. Data for the production of mUbRab5K116 and mUbRab5K165 are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1c,d. (c) A representative size exclusion chromatography chromatogram of the final reaction mixture for mUbRab5K140 synthesis. (Inset) Fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. White arrowhead indicates a fraction containing pure mUbRab5K140. (d) Final products of chemically synthesized mUbRab5K116, mUbRab5K140, and mUbRab5K165.
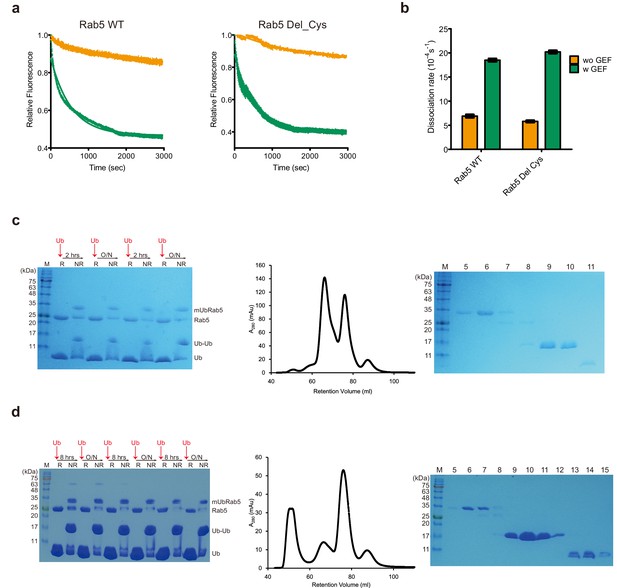
Functional comparison of Rab5 Del_Cys and WT, and chemical synthesis of mUbRab5K116 and mUbRab5K165.
(a) Rab5 WT and Rab5 Del_Cys mutant (C19S/C63S/deletion of C-terminal four amino acids) were subjected to MANT-GDP release assay with (green) or without a GEF (orange; Rabex-5132-393). Raw data and fitted one-phase exponential dissociation curves are shown. (b) Dissociation rates of MANT-GDP with or without the GEF are shown as mean ± S.D (n = 3). (c, d) Chemical synthesis of mUbRab5K116 and mUbRab5K165, respectively. (Left) Reaction was monitored by SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) or non-reducing (NR) conditions. (Middle) Size exclusion chromatography chromatogram of final reaction mixture for mUbRab5K140 synthesis. (Right) Fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE.
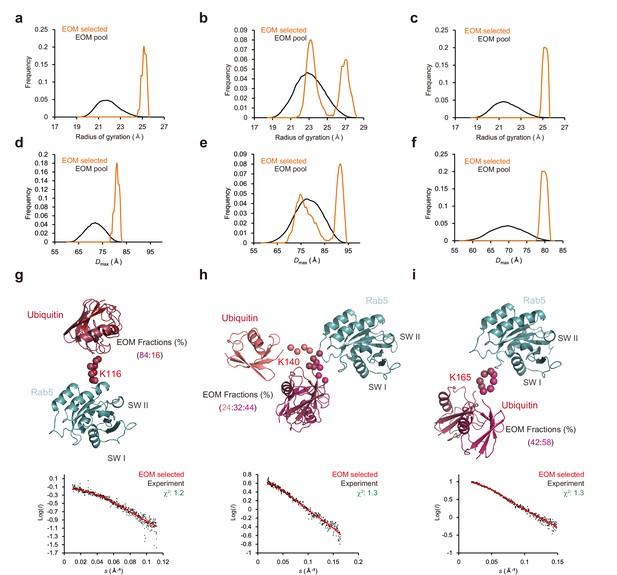
Ensemble models of mUbRab5s from small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) obtained using the ensemble optimized method (EOM).
(a, b, c) Radius of gyration (Rg) and (d, e, f) maximum inter-atomic distance (Dmax) plots of the randomly generated pool (solid black) and EOM-selected model (orange) are shown for mUbRab5K116, mUbRab5K140, and mUbRab5K165, respectively. (g, h, i) (Upper) Final ensemble models of mUbRab5K116, mUbRab5K140, and mUbRab5K165. Each EOM-selected ensemble and switch I and II regions of Rab5 (SW I and SW II) are labeled. Rab5 is colored in cyan and ubiquitin is colored in series of red. (Lower) Raw data with the calculated SAXS curve for each model are plotted.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
SAXS raw data and EOM results of mUbRab5K116.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.013
-
Figure 4—source data 2
SAXS raw data and EOM results of mUbRab5K140.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.014
-
Figure 4—source data 3
SAXS raw data and EOM results of mUbRab5K165.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.015
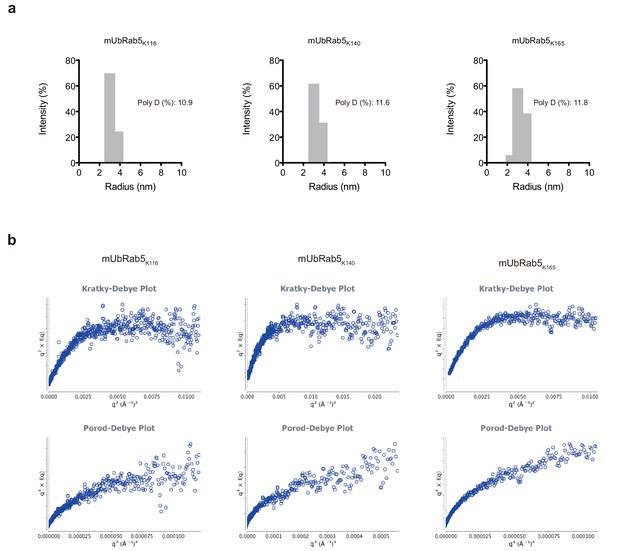
Polydispersity and flexibility analyses of mUbRab5s.
(a) Polydispersity of chemically synthesized mUbRab5s was measured by dynamic light scattering. (b) Flexibility analysis of mUbRab5s was performed by ScÅtter (http://www.biosis.net) using the SAXS data. Kratky-Debye plot reveals a plateau, while the Porod-Debye plot showed loss of the plateau. This result suggests that all mUbRab5s are flexible in solution.
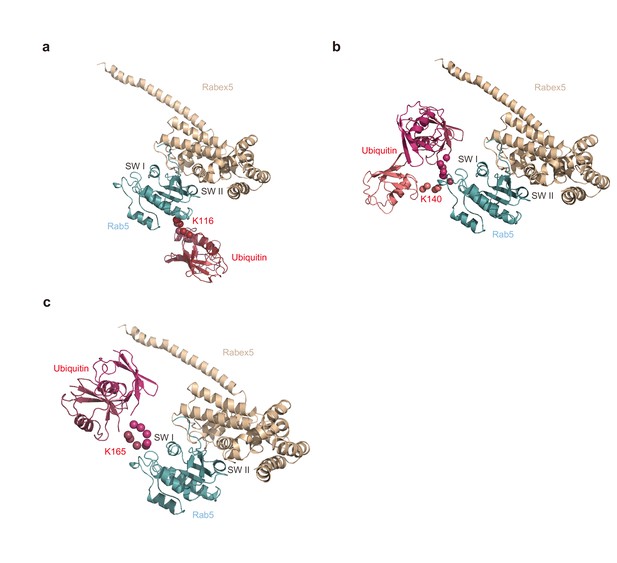
Structural models of mUbRab5s with a GEF.
Ensemble models of mUbRab5K116, mUbRab5K140, and mUbRab5K165 derived by SAXS were superimposed with the crystal structures of (a, b, c) Rab5:Rabex-5 (a GEF) complex (PDB ID: 4DQU).
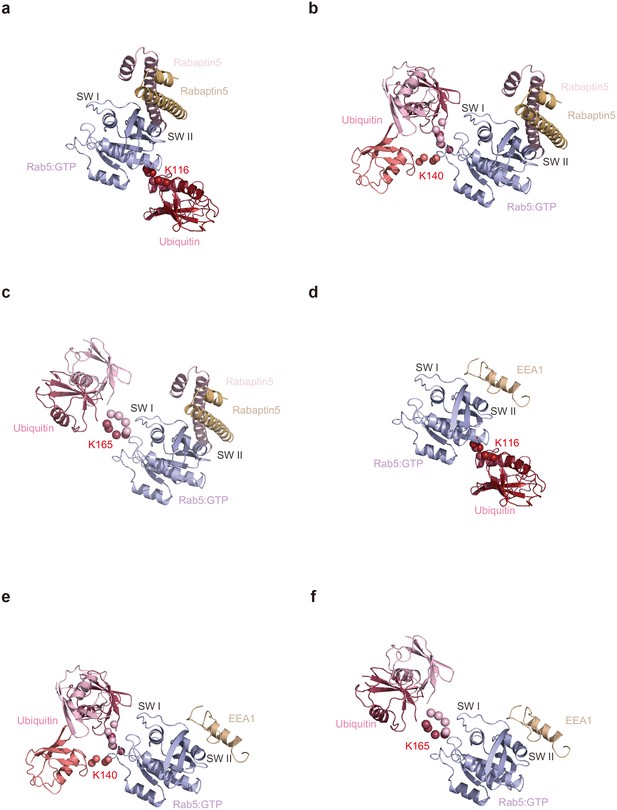
Structural models of mUbRab5s with effector proteins.
Ensemble models of mUbRab5K116, mUbRab5K140, and mUbRab5K165 derived by SAXS were superimposed with the crystal structures of (a, b, c) Rab5:Rabaptin5 (an effector) complex (PDB ID: 1TU3), and (d, e, f) Rab5:EEA1 (an effector) complex (PDB ID: 3MJH)
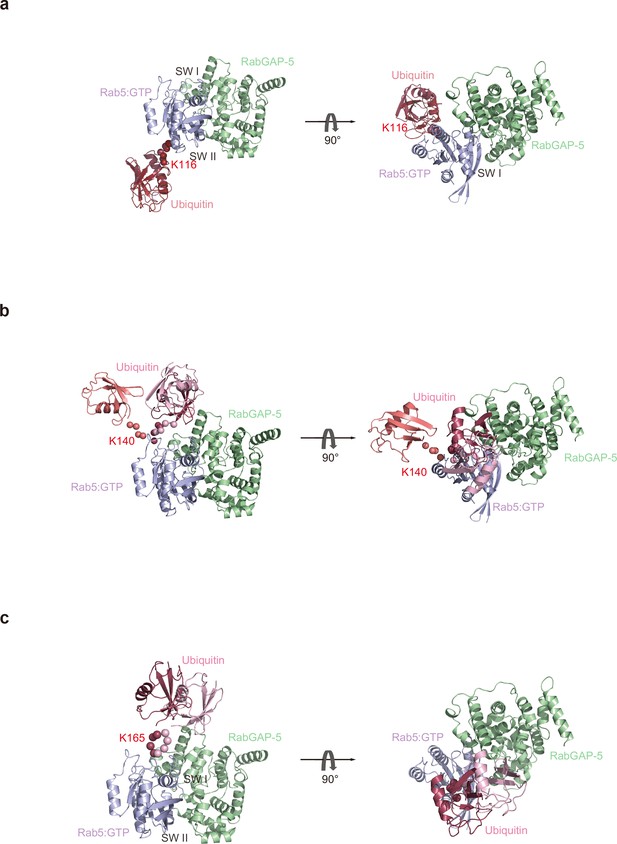
Structural models of mUbRab5s with a GAP.
Ensemble models of mUbRab5K116, mUbRab5K140, and mUbRab5K165 derived by SAXS were superimposed with the crystal structures of (a, b, c) Rab1B:RabGAP-5 (a GAP) (PDB ID: 4HLQ).
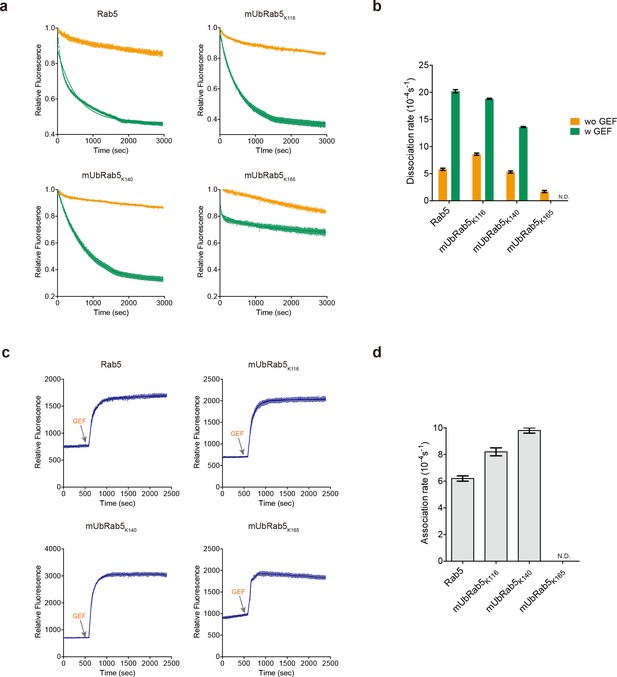
Intrinsic and GEF-mediated GDP release and GTP loading activities of mUbRab5s.
(a) MANT-GDP release assay with (green) or without a GEF (orange; Rabex-5132-393). Raw data and fitted one-phase exponential dissociation curves are shown. (b) Dissociation rates of MANT-GDP with or without the GEF are shown as mean ± standard deviation (S.D.; n = 3). (c) MANT-GTP loading was monitored by fluorescence emission at different time points. GEF was added to the reaction mixture to facilitate the GTP loading at the indicated time (gray arrow). (d) Association rates of MANT-GTP with the GEF are shown as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). Raw data and fitted one-phase exponential association curves are shown. (b, d) Dissociation and association rates of mUbRab5K165 with GEF were not determined (labeled ‘N.D.”) because the data could not be fitted to one-phase exponential dissociation and association curves.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Raw data of GDP release assay for Rab5 and mUbRab5s.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.018
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Raw data of GTP loading assay for Rab5 and mUbRab5s.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.019
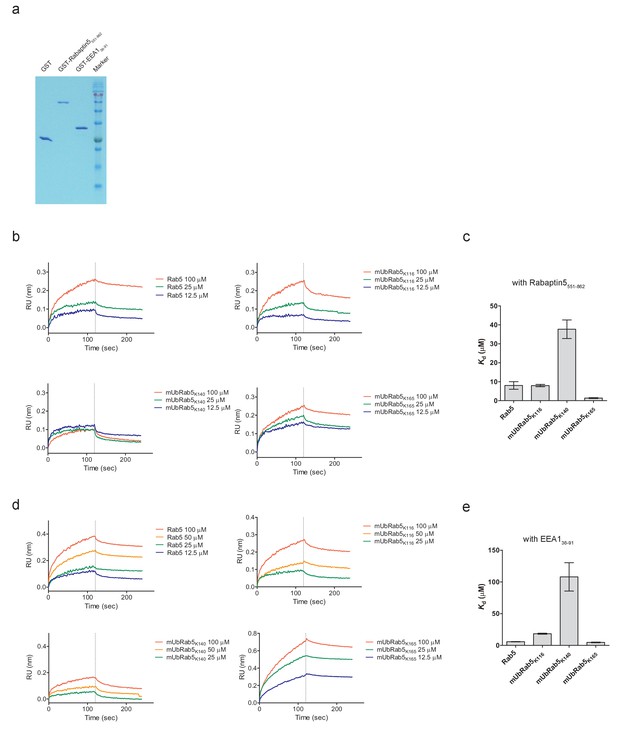
Impairment of the interaction of mUbRab5K140 with effector proteins (Rabaptin5 and EEA1).
(a) Highly purified GST-tagged Rabaptin5551-862, GST-EEA136-91, and GST proteins were prepared. (b, d) Bio-layer interferometry assay was performed to determine dissociation constants (Kd) for mUbRab5K140 and either Rabpatin-5 or EEA1. Several concentrations of Rab5 or mUbRab5s were used as indicated. (c, e) Dissociation constants were calculated by global binding fitting. Kd values are shown as mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Raw data of BLI assays of Rab5 and mUbRab5s with Rabaptin5.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.022
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Raw data of BLI assays of Rab5 and mUbRab5s with EEA1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.023
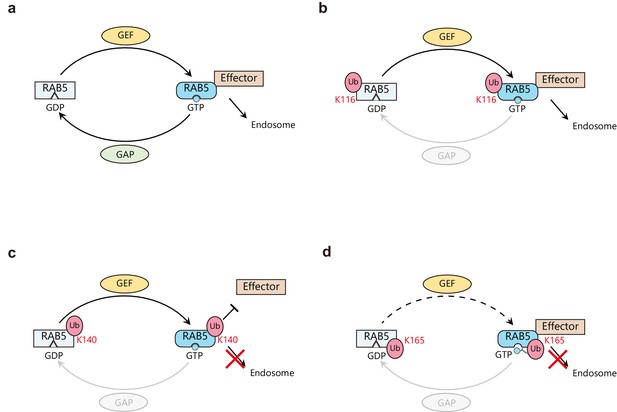
Proposed model of Rab5 regulation by site-specific monoubiquitination.
(a) Canonical Rab5 regulatory cycle. Inactive GDP-bound Rab5 is activated by a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF such as Rabex-5) through the exchange of GDP to GTP. The activated GTP-bound Rab5 interacts with various effector proteins to form early endosomes. Activated Rab5 is switched-off by a GTPase activating protein (GAP) through the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP. (b) Monoubiquitination on K116 has no effect on the regulatory cycle. Thus, mUbRab5K116 is regulated in the same way as unmodified Rab5. (c) Monoubiquitination of K140 causes the ubiquitin moiety to impair the interaction of Rab5 with its effector proteins. Therefore, mUbRab5K140 cannot form early endosomes. (d) Monoubiquitination of K165 alters the GDP/GTP conversion cycle by interfering with the activities of GEF, thus lowering affinity to GTP. mUbRab5K165 cannot form early endosomes.

Multiple sequence alignment of human and mouse Rab GTPases reported to be ubiquitinated.
Rab GTPases in the ubiquitination database (mUbSiDa [Chen et al., 2014b]) were obtained, and their sequences were aligned to human Rab5A (this study) using Clustal X2 (Larkin et al., 2007). The graphical representation of the aligned sequences was prepared using BoxShade (ExPASy server). Ubiquitination sites from proteomic studies are indicated with the letter ‘K’ in the red background (K). Ubiquitination sites and structural key lysine residues revealed from this study are marked as inverse triangles in black ( ) and green (
) and green ( ), respectively. ‘h’ and ‘m’ refer to human and mouse, respectively. (b) Rab5 GTPases from different species were aligned to human Rab5A. Ubiquitination sites from this study are indicated with the letter ‘K’ on a red background (K).
), respectively. ‘h’ and ‘m’ refer to human and mouse, respectively. (b) Rab5 GTPases from different species were aligned to human Rab5A. Ubiquitination sites from this study are indicated with the letter ‘K’ on a red background (K).
Tables
Putative ubiquitination sites of Rab5A based on published studies.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.004| Lysine site | Peptide from mass spectrometry | Predicted protein |
|---|---|---|
| 116 | RAKNWVKELQRQA | hRab5a (K116/215)(Chen et al., 2014b; Wagner et al., 2011) |
| 134 | IALSGNKADLANK | mRab5a (K134/215)(Chen et al., 2014b; Wagner et al., 2012) |
| 140 | KADLANKRAVDFQ | mRab5a (K140/215)(Chen et al., 2014b; Wagner et al., 2012) |
SAXS data collection and analysis statistics.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.016| mUbRab5K116 | mUbRab5K140 | mUbRab5K165 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data-collection parameters | |||
| Synchrotron beamlines | PAL-4C | ||
| Beam geometry | Capillary | ||
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.24 | ||
| Exposure time (sec) | 10 | ||
| Concentration range (mg/ml) | 0.4–2.9 | 0.9–7.3 | 1.0–2.6 |
| Sample parameters | |||
| Polydispersity (%, by DLS) | 10.9 | 11.6 | 11.8 |
| Structural parameters | |||
| I(0) (cm−1) [from Guinier] | 0.73 ± 0.01 | 4.29 ± 0.03 | 10.69 ± 0.05 |
| Rg (Å) [from Guinier] | 25.54 ± 0.24 | 23.38 ± 0.34 | 27.23 ± 0.34 |
| I(0) (cm−1) [from P(r)] | 0.73 | 4.35 | 10.74 |
| Rg (Å) [from P(r)] | 26.55 | 24.61 | 27.81 |
| Dmax (Å) | 86.56 | 83.51 | 93.69 |
| Porod volume estimate (Å3) | 44428.4 | 32040.2 | 46685.0 |
| Software employed | |||
| Primary data reduction | RAW | ||
| Dara processing | PRIMUS | ||
| Ensemble analysis | EOM and FoXS MES | ||
| Three-dimensional representations | PyMOL | ||
GDP dissociation and GTP association rates for Rab5 and mUbRab5s.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.020| GDP dissociation rate ± SD* (10−4 s−1) | GTP association rate ± SD (10−4 s−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without GEF | With GEF | |||
| Rab5 | 5.8 ± 0.2 | 20.2 ± 0.3 | 6.2 ± 0.2 | |
| mUbRab5K116 | 8.6 ± 0.2 | 18.8 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 0.2 | |
| mUbRab5K140 | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 13.6 ± 0.2 | 9.8 ± 0.2 | |
| mUbRab5K165 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | ND† | ND† | |
-
* SD, standard deviation
† ND, not determined.
Binding kinetics of Rab5 and mUbRab5s to Rabaptin5551-862 and EEA136-91.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.024| Rabaptin5 | EEA1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kon ± SEM* (102 M−1s−1) | koff ± SEM (10 −3s−1) | Kd ±SEM (μM) | kon ±SEM (102 M−1s−1) | koff ± SEM (10 −3s−1) | Kd ±SEM (μM) | |
| Rab5 | 6.6 ± 2.8 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 8.0 ± 3.4 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 5.8 ± 0.3 |
| mUbRab5K116 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 18.4 ± 0.8 |
| mUbRab5K140 | 13.9 ± 1.8 | 52.3 ± 1.4 | 37.7 ± 4.9 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 19.7 ± 0.8 | 108.0 ± 22.0 |
| mUbRab5K165 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.5 |
-
* SEM, standard error of the mean
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29154.027





