Live-cell mapping of organelle-associated RNAs via proximity biotinylation combined with protein-RNA crosslinking
Figures
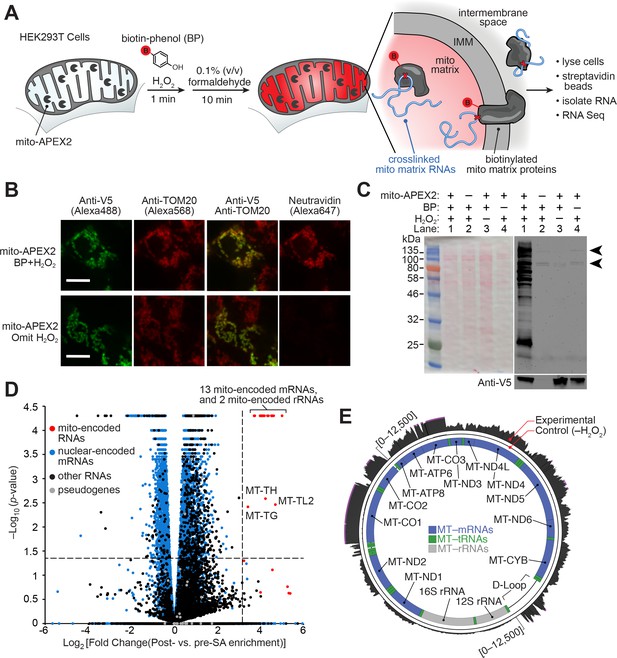
APEX-RIP in mitochondria.
(A) Overview of the APEX-RIP workflow. Live cells expressing APEX2 (grey ‘pacmen’) targeted to the compartment of interest (here, the mitochondrial matrix) are incubated with the APEX substrate biotin-phenol (BP; red B: biotin). A one-minute pulse of H2O2 initiates biotinylation of proximal endogenous proteins (Rhee et al., 2013), which are subsequently crosslinked to nearby RNAs by 0.1% formaldehyde. Following cell lysis, biotinylated species are enriched by streptavidin pulldown, and coeluting RNAs are analyzed by qRT-PCR or RNA-Seq. IMM: inner mitochondrial membrane. (B) Imaging APEX2 biotinylation in situ. HEK 293T cells expressing V5-tagged mito-APEX2 were biotinylated using the APEX-RIP workflow, fixed, and stained as indicated. The bottom row is a negative control in which H2O2 treatment was omitted. Scale bars, 10 µm. TOM20 is a mitochondrial outer membrane protein; neutravidin staining detects biotinylation. (C) In situ biotinylation of the mitochondrial matrix proteome requires mito-APEX2, BP, and H2O2. Streptavidin blot analysis of whole cell lysates prepared following the protocol described in (A), or after omitting components of the APEX reaction. Arrowheads denote endogenous biotinylated proteins (Chapman-Smith and Cronan, 1999). Anti-V5 blot (bottom) detects expression of mito-APEX2. (D–E) mito-APEX-RIP efficiently recovers the mitochondrial transcriptome. (D) Gene-level RNA-Seq analysis of mito-APEX-RIP; data are the average values of three experimental replicates. Fold change is defined as (FPKMpost-enrichment/FPKMpre-enrichment); dashed lines indicate significance thresholds for fold enrichment (determined by ROC analysis, see Materials and methods) and p-values calculated by CuffDiff2 (Trapnell et al., 2013). Mitochondrial genomes encode 13 mRNAs, two rRNAs and 22 tRNAs (red). Note that three mitochondrial tRNA genes, MT-TH, MT-TL2, and MT-TG, were also enriched. See Supplementary file 1A. (E) Nucleotide-level RNA-Seq analysis of mito-APEX-RIP, mapped to the human mitochondrial genome (innermost circle). Outermost circle: reads from the full APEX-RIP protocol; middle circle: reads from the negative control. Note the enrichment of several mitochondrially-encoded tRNAs and the D-loop leader transcript. Ribosomal RNAs were removed during library preparation (see Materials and methods). See also: Figure 1—figure supplements 1,2.
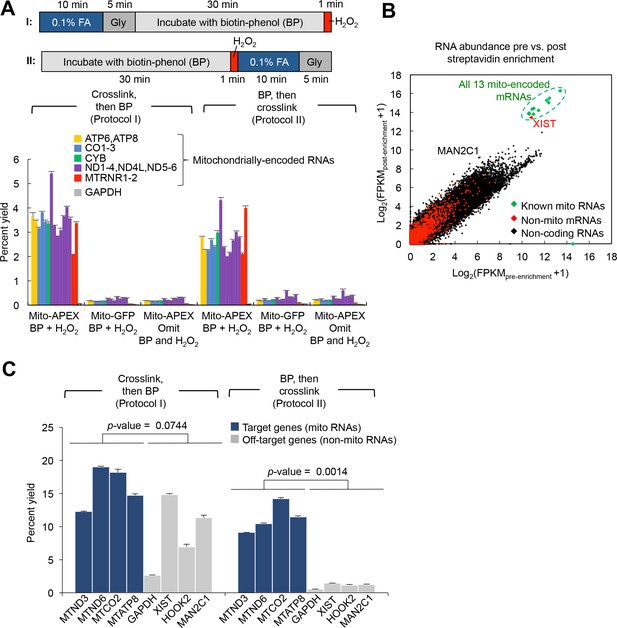
Optimization of APEX-RIP protocol.
(A) Top: Alternative labeling and crosslinking protocols. In protocol I., cells are crosslinked with formaldehyde (FA) and quenched with Glycine (Gly) prior to the introduction of biotin-phenol (BP) and the initiation of APEX-catalyzed biotinylation with H2O2. In Protocol II., live cells are incubated in BP, and in situ biotinylation is initiated prior to FA crosslinking. In both cases, cell lysis, streptavidin enrichment and RNA purification proceed as described (see Materials and methods). Bottom: qRT-PCR analysis comparing Protocols I and II. Negative control experiments replace mito-APEX with mito-GFP, or omit BP and H2O2. All constructs were APEX1 derivatives, transiently expressed in HEK 293T cells. Data are the means of three replicates ± one standard deviation. (B) RNA-Seq analysis of RNAs enriched by protocol I. Although all 13 mitochondrially-encoded mRNAs (green) were enriched, these were accompanied by substantial contaminating RNAs, including XIST and MAN2C1. Data from one experimental replicate are shown. (C) qRT-PCR analysis comparing Protocols I. and II., including off-target controls designed using the results from RNA-Seq in (B). Note the superior enrichment obtained using Protocol II. Cells in this experiment stably-expressed mito-APEX2. This protocol and cell line were used to collect all data in Figure 1. Data are the means of four replicates ± one standard deviation. Significance testing: Student’s two-tailed t-test.
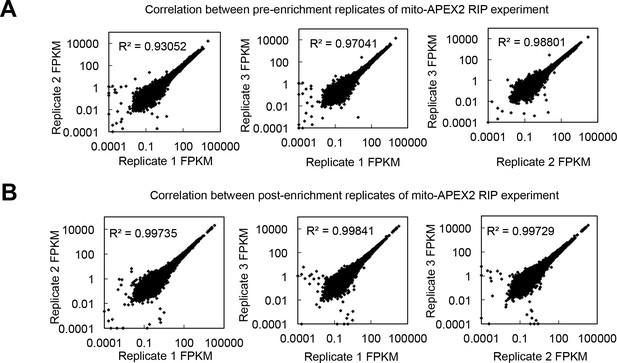
Reproducibility of the mito-APEX2 RIP experiment.
Pairwise correlations between global RNA abundances (FPKM) in biological replicates (A) prior to enrichment, and (B) following mito-APEX2-RIP.
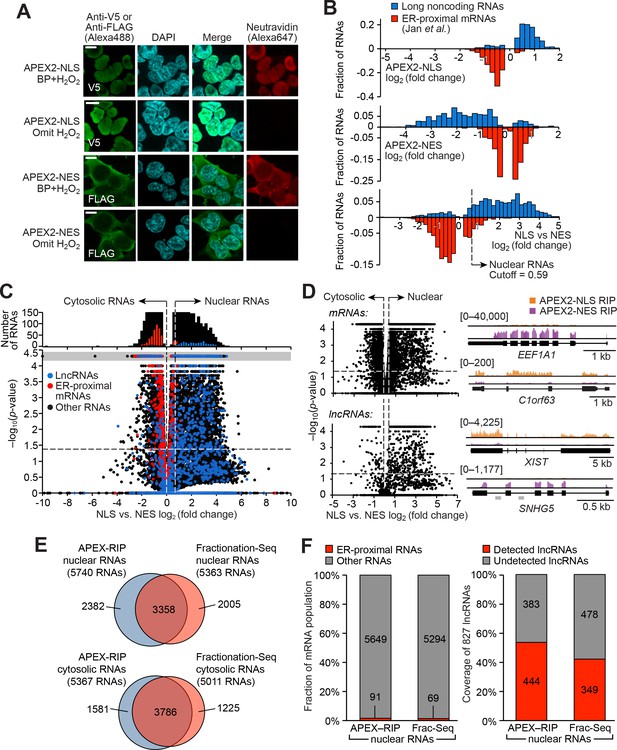
APEX-RIP mapping of the nuclear-cytoplasmic RNA distribution.
(A) Fluorescence imaging of nuclear and cytosol-targeted APEX2 fusion constructs. HEK 293T cells expressing the indicated constructs (‘NLS,’ nuclear localization signal; ‘NES,’ nuclear export signal) were labeled with biotin-phenol, crosslinked and stained as indicated. Scale bars, 10 µm. DAPI is nuclear stain. (B) APEX-RIP recovers known nuclear and cytosolic standard RNAs, defined here as long noncoding RNAs (nuclear markers, blue) and RNAs proximal to the Endoplasmic Reticulum (cytoplasmic markers,red—defined by (Jan et al., 2014), with measured p-values≤0.05—see Materials and methods). Top: APEX2–NLS-RIP enriches nuclear standards. Middle: APEX2–NES-RIP enriches cytoplasmic standards. Bottom: Combined analysis of the APEX2–NLS and APEX2–NES RIP experiments distinguish the two classes. Fold changes are defined as (FPKMpost-enrichment/FPKMpre-enrichment); combined fold change as [FPKMNLS–post-enrichment /FPKMNES–post-enrichment]. Dotted line indicates the significance threshold for nuclear localization. (C) Global analysis of nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA localization by combined APEX2-NLS and APEX2-NES RIP. Vertical dashed lines indicate the cutoffs for nuclear and cytosolic RNAs. Horizontal dash line indicates p-value=0.05. Top histogram illustrates the distribution of RNAs with p-value=5×10−5, which are boxed in gray in the scatter plot. The average of data from three biological replicates are shown. See Supplementary file 2A-B. (D) APEX-RIP reveals classes of RNAs with canonical and noncanonical nuclear-cytoplasmic distributions. Left: the same data as in (C), separately parsed into mRNAs (top) and lncRNAs (bottom). Right: read density plots of example RNAs from each class that exhibit stereotypical and atypical localization. EEF1A1 and C1orf63 are mRNAs; XIST and SNHG5 are lncRNAs. For each gene, a common y-scale is used for all read tracks. SnoRNAs encoded in the SNHG5 gene body are indicated as gray rectangles. (E) Venn diagrams comparing APEX-RIP and fractionation-based RNA datasets (Sultan et al., 2014). (F) Nuclear APEX-RIP is more sensitive than is biochemical fractionation. Left: Specificity of the APEX-RIP and nuclear RNA datasets (Sultan et al., 2014). Off-target RNAs were defined as actively translated ER-proximal mRNAs (Jan et al., 2014). Right: Recall of nuclear standard RNAs, defined as a set of 827 lncRNAs annotated by GENCODE hg19 with average pre-enrichment FPKM ≥ 1.0. See also: Figure 2—figure supplements 1–2.
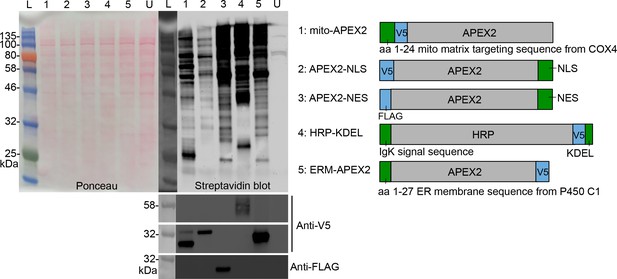
Characterization of APEX2 fusion constructs.
HEK 293 T cells stably expressing the indicated constructs (right) were labeled and crosslinked via Protocol II (Figure 1—figure supplement 1A). Cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, blotting with streptavidin-HRP, anti-V5 and anti-FLAG. L: ladder; U: untransfected HEK 293T cells. Anti-V5 and anti-FLAG blots (bottom left) measure fusion construct expression.
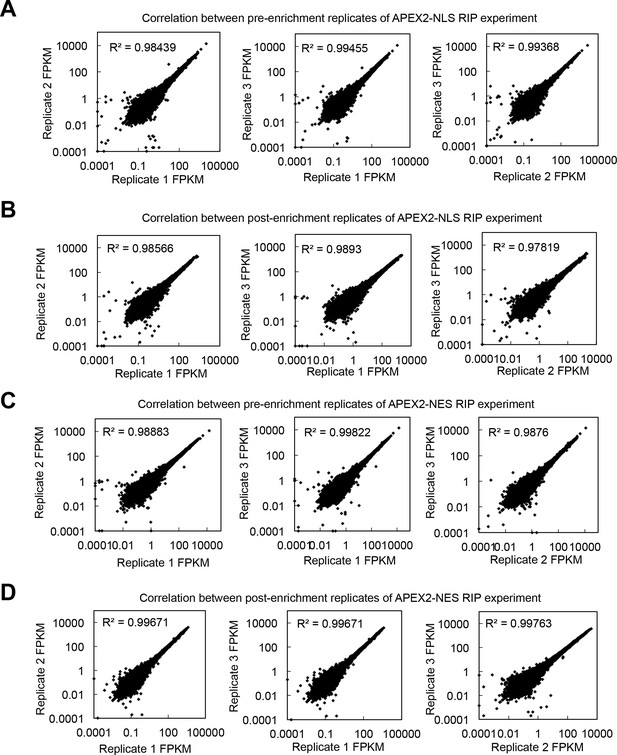
Reproducibility of nuclear–cytoplasmic APEX-RIP experiments.
Pairwise correlations between global RNA abundances (FPKM) in biological replicates of the APEX2–NLS-RIP experiment, (A) prior to, and (B), following enrichment, and similarly, of the APEX2–NES-RIP experiment, (C) prior to, and (D) following enrichment.
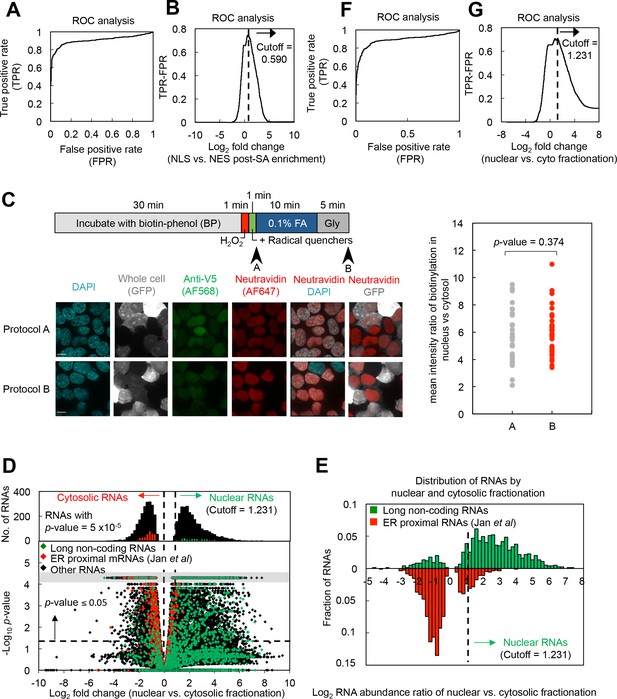
Precision and specificity of nuclear–cytoplasmic APEX-RIP, and its comparison to subcellular fractionation.
(A–B) Determination of cutoffs for APEX-RIP data by ROC analysis (see Materials and methods). (C) APEX protein localization isn’t perturbed during the APEX-RIP labeling and crosslinking protocol. APEX2-NLS HEK293T cells expressing a whole-cell GFP marker were processed using the optimized APEX-RIP protocol (bar diagram). Cells were fixed prior to, and following the mild formaldehyde crosslinking step (arrowheads), and imaged by immunofluorescence. Left: Representative images for cells fixed at each time point. Right: average nuclear-vs-cytosolic biotinylation signal ratio measured at both time points; each dot represents an individual cell (n = 30). p-value: student’s paired t-test. (D-—E) APEX-RIP recapitulates the results of nuclear-cytosolic fractionation-sequencing. (D) Global analysis of nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA localization [FPKMnuclear/FPKMcytosolic] by biochemical fractionation-sequencing of HEK293 cells (Sultan et al., 2014). Horizontal dash line indicates p-value = 0.05. Top histogram illustrates the distribution of RNAs with p-value = 5×10−5, which are boxed in gray in the scatter plot. Average data from two biological replicates are shown. (E) Distribution of RNAs based on enrichment of nuclear over cytosolic fractionation, similar to the bottom panel of Figure 2B (see Materials and methods). (F–G) Determination of cutoffs for fractionation data (Sultan et al., 2014) by ROC analysis (see Materials and methods).
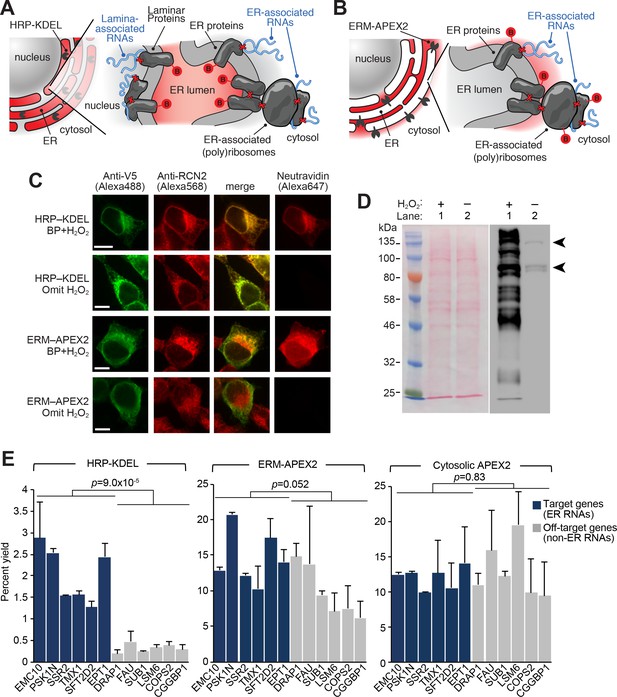
APEX-RIP at the Endoplasmic Reticulum membrane.
(A—B) Schematics summarizing alternating ER-targeting strategies. (A) HRP, targeted to the ER lumen with a KDEL sequence, biotinylates proteins within the ER. Red B: biotin. Red X’s: chemical crosslinks induced by 0.1% formaldehyde treatment. Note that RNAs enriched by this approach may reside at the cytosolic face of the ER, or at the nuclear lamina, as shown. (B) APEX2, targeted to the ER membrane (ERM) by fusing it to the transmembrane segment of rabbit P450 C1, biotinylates proteins proximal to the cytosolic face of the ER. (C) Imaging of biotinylation from HRP-KDEL and ERM-APEX2 catalyzed reactions. HEK293T cells stably expressing HRP-KDEL or ERM-APEX2 were labeled with BP, fixed and imaged as in Figure 1B. Scale bars, 10 μm. Anti-RCN2 was used to mark ER lumen. (D) Streptavidin blot detection of resident ER proteins biotinylated by HRP-KDEL, as in Figure 1C. Arrowheads denote endogenously biotinylated proteins (Chapman-Smith and Cronan, 1999). (E) qRT-PCR analysis, comparing the specificities of the labeling schemes shown in (A–B). Target and off-target genes were selected using previously-reported RNA abundances at the ER membrane (Jan et al., 2014). Cytosolic APEX2 (APEX2–NES, as in Figure 2) serves as a negative control. Data are the mean of four replicates ± one standard deviation. Significance testing: Student’s two-tailed t-test.
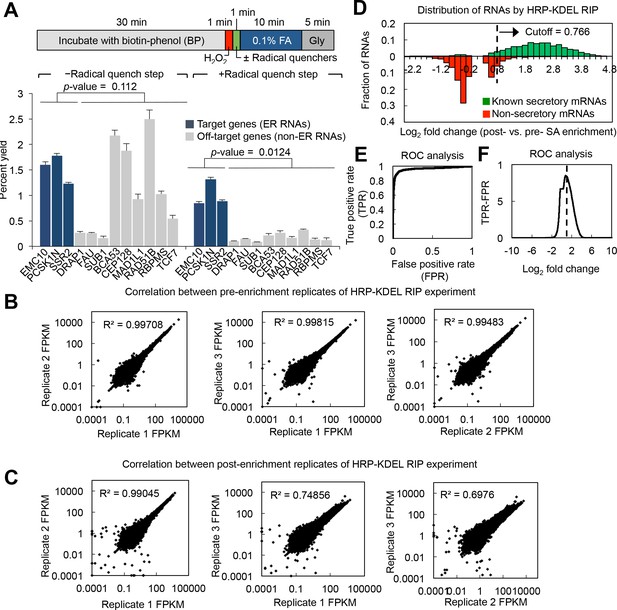
Further optimization of the APEX-RIP protocol; additional HRP-KDEL RIP data.
(A) Addition of a radical quenching step between APEX2 labeling and formaldehyde crosslinking improves APEX-RIP specificity. Top: schematic of the revised labeling–crosslinking workflow. The radical quenchers used were Trolox and ascorbic acid; these were included in the 0.1% FA and Gly steps regardless of whether the discrete radical quenching step is included. Bottom: qRT-PCR analysis of the ER-APEX-RIP experiment with and without this additional quenching step, as in (Figure 1—figure supplement 1C). Data are the mean of four replicates,±one standard deviation. Significance testing: Student’s two-tailed t-test. (B–C) Correlation of RNA abundance (in FPKM) for each replicate. (B) and (C) are pre- and post-enrichment replicates, respectively. Given the low correlation between post-enrichment replicate three and other replicates, only data from replicates 1 and 2 were included in further analysis. (D) Histograms showing the distribution of RNA enrichment values–log2 fold change (defined as FPKMpost-enrichment/FPKMpre-enrichment), for all RNAs with p-values ≤ 0.05. Green denotes mRNAs encoding known secretory proteins and red denotes mRNAs encoding non-secretory proteins. Significance cutoffs were determined using ROC analysis (see below). Known secretory and non-secretory standard mRNAs were cataloged as described (see Materials and methods). (E–F) Determination of significance thresholds ratio cutoffs by ROC analysis (see Materials and methods).
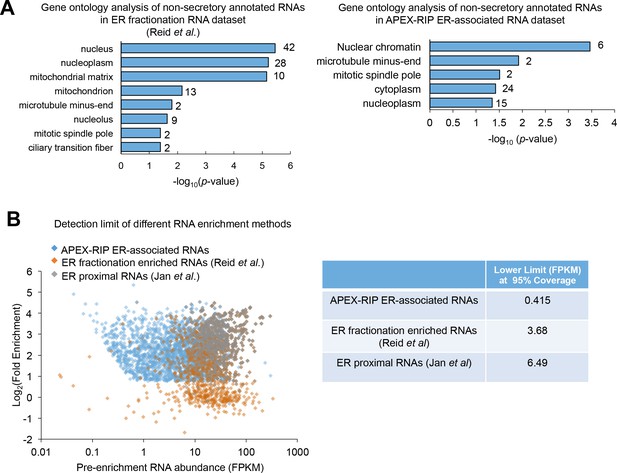
Additional analysis comparing HRP-KDEL RIP data and other ER-RNA data sets.
(A) Gene ontology (GO) analysis of mRNAs that were enriched in ER datasets, but which lack secretory annotation. The number of RNA species in each class is indicated to the right of the corresponding bar.
Left: non-secretory mRNAs enriched by biochemical fractionation (99 mRNAs, 9% of total enriched mRNAs) (Reid and Nicchitta, 2012) predominantly exhibit nuclear and mitochondrial annotation. Right: non-secretory mRNAs enriched by HRP-KDEL RIP (87 mRNAs, 3.5% of total APEX-RIP-enriched mRNAs) have predominantly cytosolic annotation, with a minority exhibiting nuclear annotation. All terms shown have p<0.05, as assessed using DAVID (Huang et al., 2009). (B) APEX-RIP recovers low-abundance targets with greater efficiency than do alternative approaches. Left: RNAs enriched by ER-APEX-RIP exhibit a broader range in starting abundances than do RNAs recovered by ER biochemical fractionation or ER-proximity restricted ribosome profiling. Right: Table summarizing the lower bound (i.e. the lowest starting FPKM) for 95% of the RNA species enriched by each method.
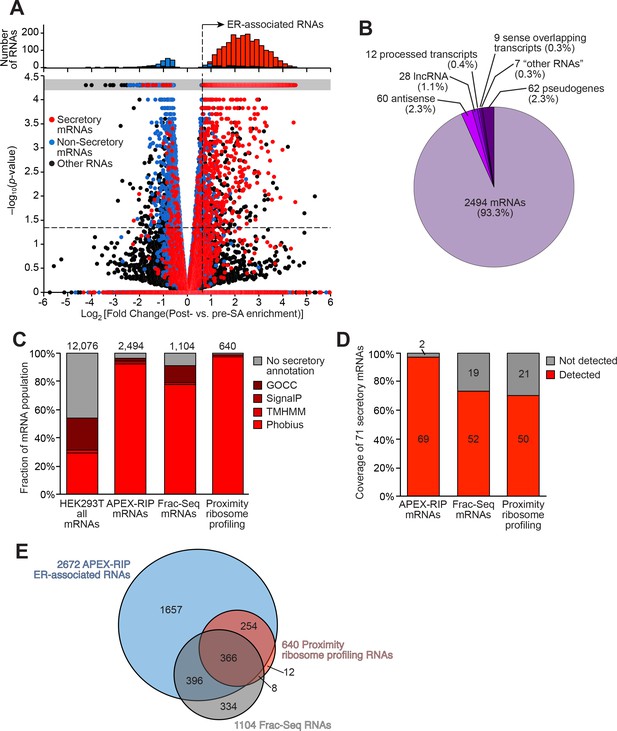
Mapping the ER-proximal transcriptome with APEX–RIP.
(A) Global analysis of RNA localization at the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Fold change = (FPKMpost-enrichment/FPKMpre-enrichment). Horizontal dashed line indicates p-value = 0.05. Top histogram illustrates the distribution of RNAs with p-value = 5×10−5, which are boxed in gray in the scatter plot. Average data from two biological replicates are shown. Standard mRNAs encoding known secretory and non-secretory proteins are highlighted in red and blue, respectively (see Materials and methods). (B) Classification of APEX-RIP enriched, ER-associated RNAs. Collectively, all classes of non-coding RNAs constitute 6.7% of enriched genes (178 of 2672 RNAs). (C) Specificity analysis for protein-coding mRNAs in the APEX-RIP-derived ER-associated RNA list. The total number of RNA species in each condition is indicated above each column. 96.5% of the 2494 APEX-RIP ER-enriched mRNAs exhibit some form of secretory annotation (as predicted by Phobius, TMHMM, SignalP, or GOCC, see methods), whereas only 53.8% of total mRNAs expressed in HEK293T cells (FPKM ≥ 1.0) are similarly classified (left). (D) Target recall of ER APEX-RIP exceeds those of proximity-restricted ribosome profiling (Jan et al., 2014: see Supplementary file 3D) and biochemical fractionation (Reid and Nicchitta, 2012; see Supplementary file 3C). See also: Supplementary file 3E. (E) Venn diagram comparing RNA datasets. Note that all enriched RNAs in Reid et al. ER fractionation-Seq dataset were mRNAs. See also: Figure 3—figure supplements 1–2.
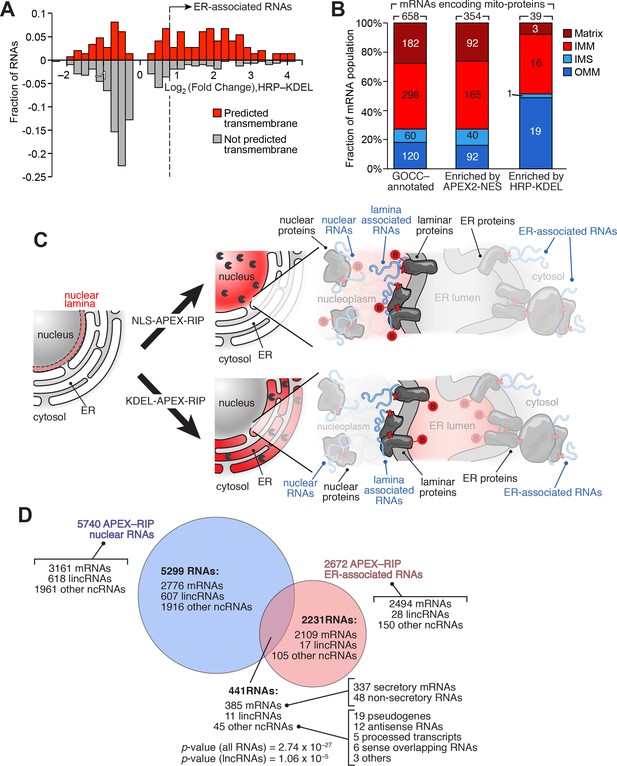
APEX-RIP reveals RNAs with potentially novel localization.
(A) Many mitochondrial transmembrane proteins appear to be translated at the ER. mRNAs encoding mitochondrial proteins (defined by GOCC and MitoCarta 1.0 (Ashburner et al., 2000; Pagliarini et al., 2008) with predicted transmembrane helices (predicted by TMHMM (Krogh et al., 2001); red distribution) are preferentially enriched by HRP-KDEL APEX-RIP, relative to those encoding mitochondrial proteins lacking transmembrane domains (gray distribution). See Supplementary file 3A. (B) Mitochondrial proteins encoded by ER-proximal mRNAs are enriched for outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) destined proteins, and de-enriched for matrix and intermembrane space (IMS) destined proteins. Predicted sub-mitochondrial localization of all GOCC-annotated mitochondrial proteins (left), those with mRNAs enriched by APEX2–NES (middle), and those enriched by HRP–KDEL (right). IMM: Inner mitochondrial membrane. The total number of mRNA species with annotated mitochondrial sublocalization is indicated above each column. See Supplementary file 4A. (C) Scheme for identifying putative RNAs associated with the nuclear lamina. Since subsets of laminar proteins should be biotinylated both by APEX2-NLS (top right) and by HRP-KDEL (bottom right and Figure 3A), we can intersect these two datasets to obtain a candidate list of nuclear lamina-localized RNAs. Notation as in Figure 3A. (D) Venn diagram identifying putative lamina-associated RNAs, defined as the overlap between HRP-KDEL- and APEX2-NLS-enriched RNAs. See also: Supplementary file 4B. Significance testing: hypergeometric test.

Fractionation-Seq and APEX-RIP recover similar populations of intronic sequences from each compartment.
A. Both methods quantify the nuclear enrichment and cytosolic de-enrichment of intronic reads (GENCODE hg19) to similar extents. We ascribe the greater number of intronic reads in the APEX pre-enrichment samples–relative to the Fractionation-Seq starting material–to our use of ribosome depletion, rather than poly(A) selection, in our starting samples (methods). B. Intronic reads exhibit similar subcellular partitioning by each method. Data shown are for all introns with starting RPKM≥1.0 in at least one experimental replicate. The data correlate with a Spearman’s r=0.88, p-value=0.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cell line (human) | HEK293T | ATCC | CRL3216; RRID: CVCL_0063 | |
| cell line (human) | mito-APEX2 (HEK293T) | this paper | mito-BamHI-V5-APEX2 CMV promoter Mito is a 24-amino acidmitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) derived from COX4. V5: GKPIPNPLLGLDST | |
| cell line (human) | APEX2-NLS (HEK293T) | this paper | NotI-V5-APEX2-EcoRI-3xNLS-NheI CMV promoter NLS: DPKKKRKV | |
| cell line (human) | APEX2-NES (HEK293T) | PMID: 28441135 | BstBI-FLAG-APEX2-NES-NheI CMV promoter NES: LQLPPLERLTLD | |
| cell line (human) | ERM-APEX2 (HEK293T) | PMID: 28441135 | BstBI-ERM-APEX2-V5-NheI CMV promoter ERM is ER membrane targeting sequence derived from N-terminal 27 amino acids of rabbit P450 C1 (MDPVVVLGLCLSCLLLLSLWKQSYGGG) | |
| cell line (human) | HRP-KDEL (HEK293T) | this paper | NotI-IgK-HRP-V5-KDEL-IRES-puromycin-XbaI CMV promoter IgK is N-terminal signaling sequence that brings protein to ER (METDTLLLWVLLLWVPGSTGD). KDEL is ER-retaining sequence | |
| antibody | Anti V5 | Life Technologies | R960-25; RRID: AB_2556564 | Dilution 1:1000 |
| antibody | Anti FLAG | Agilent | 200472 | Dilution 1:500 |
| antibody | Anti TOM20 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-11415; RRID: AB_2207533 | Dilution 1:400 |
| antibody | Anti RCN2 | Proteintech | 10193–2-AP; RRID: AB_2180018 | Dilution 1:200 |
| antibody | Anti Mouse-AlexaFlour488 | Life Technologies | A-11029; RRID: AB_2534088 | Dilution 1:1000 |
| antibody | Anti Mouse-AlexaFlour568 | Life Technologies | A-11031; RRID: AB_144696 | Dilution 1:1000 |
| antibody | Streptavidin-HRP | ThermoFisher | S-911 | Dilution 1:1000 |
| recombinant DNA reagent | Mito-APEX (plasmid) | PMID: 23371551 | pCDNA vector | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | mito-APEX2 (plasmid) | this paper | pLX304 vector | mito-BamHI-V5-APEX2 CMV promoter Mito is a 24-amino acidmitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) derived from COX4. V5: GKPIPNPLLGLDST |
| recombinant DNA reagent | APEX2-NLS (plasmid) | this paper | NotI-V5-APEX2-EcoRI-3xNLS-NheI CMV promoter NLS: DPKKKRKV | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | HRP-KDEL (plasmid) | this paper | NotI-IgK-HRP-V5-KDEL-IRES-puromycin-XbaI CMV promoter IgK is N-terminal signaling sequence that brings protein to ER (METDTLLLWVLLLWVPGSTGD). KDEL is ER-retaining sequence | |
| sequence-based reagent | Ribo-Zero Gold rRNA removal kit (Illumina) | Illiumina | MRZG12324 | |
| sequence-based reagent | Truseq RNA sample preparation kit V2 | Illiumina | RS-122–2001 | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND1 forward | this paper | CACCTCTAGCCTAGCCGTTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND1 reverse | this paper | CCGATCAGGGCGTAGTTTGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND2 forward | this paper | CTTAAACTCCAGCACCACGAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND2 reverse | this paper | AGCTTGTTTCAGGTGCGAGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND3 forward | this paper | CCGCGTCCCTTTCTCCATAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND3 reverse | this paper | AGGGCTCATGGTAGGGGTAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND4 forward | this paper | ACAACACAATGGGGCTCACT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND4 reverse | this paper | CCGGTAATGATGTCGGGGTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND4L forward | this paper | TCGCTCACACCTCATATCCTC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND4L reverse | this paper | AGGCGGCAAAGACTAGTATGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND5 forward | this paper | TCCATTGTCGCATCCACCTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND5 reverse | this paper | GGTTGTTTGGGTTGTGGCTC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND6 forward | this paper | GGGTTGAGGTCTTGGTGAGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ND6 reverse | this paper | ACCAATCCTACCTCCATCGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-CYTB forward | this paper | TCTTGCACGAAACGGGATCA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-CYTB reverse | this paper | CGAGGGCGTCTTTGATTGTG | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-COX1 forward | this paper | TCCTTATTCGAGCCGAGCTG | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-COX1 reverse | this paper | ACAAATGCATGGGCTGTGAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-COX2 forward | this paper | AACCAAACCACTTTCACCGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-COX2 reverse | this paper | CGATGGGCATGAAACTGTGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-COX3 forward | this paper | CTAATGACCTCCGGCCTAGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-COX3 reverse | this paper | AGGCCTAGTATGAGGAGCGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ATP6 forward | this paper | TTCGCTTCATTCATTGCCCC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ATP6 reverse | this paper | GGGTGGTGATTAGTCGGTTGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ATP8 forward | this paper | ACTACCACCTACCTCCCTCAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-ATP8 reverse | this paper | GGCAATGAATGAAGCGAACAGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-RNR1 forward | this paper | CATCCCCGTTCCAGTGAGTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-RNR1 reverse | this paper | TGGCTAGGCTAAGCGTTTTGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-RNR2 forward | this paper | CAGCCGCTATTAAAGGTTCGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MT-RNR2 reverse | this paper | AAGGCGCTTTGTGAAGTAGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | GAPDH forward | this paper | TTCGACAGTCAGCCGCATCTTCTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | GAPDH reverse | this paper | GCCCAATACGACCAAATCCGTTGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | XIST forward | this paper | CCCTACTAGCTCCTCGGACA | |
| sequence-based reagent | XIST reverse | this paper | ACACATGCAGCGTGGTATCT | |
| sequence-based reagent | EMC10 forward | this paper | TTCATTGAGCGCCTGGAGAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | EMC10 reverse | this paper | TTCATTGAGCGCCTGGAGAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | PCSK1N forward | this paper | GAGACACCCGACGTGGAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | PCSK1N reverse | this paper | AATCCGTCCCAGCAAGTACC | |
| sequence-based reagent | SSR2 forward | this paper | GTTTGGGATGCCAACGATGAG | |
| sequence-based reagent | SSR2 reverse | this paper | CTCCACGGCGTATCTGTTCA | |
| sequence-based reagent | TMX1 forward | this paper | ACGGACGAGAACTGGAGAGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | TMX1 reverse | this paper | ATTTTGACAAGCAGGGCACC | |
| sequence-based reagent | SFT2D2 forward | this paper | CCATCTTCCTCATGGGACCAG | |
| sequence-based reagent | SFT2D2 reverse | this paper | GCAGAACACAGGGTAAGTGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | EPT1 forward | this paper | TGGCTTTCTGCTGGTCGTAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | EPT1 reverse | this paper | AATCCAAACCCAGTCAGGCA | |
| sequence-based reagent | DRAP1 forward | this paper | ACATCCCACCTGAAGCAGTG | |
| sequence-based reagent | DRAP1 reverse | this paper | GATGCCACCAGGTCCTTCAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | FAU forward | this paper | TCCTAAGGTGGCCAAACAGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | FAU reverse | this paper | GTGGGCACAACGTTGACAAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | SUB1 forward | this paper | CGTCACTTCCGGTTCTCTGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | SUB1 reverse | this paper | TGATTTAGGCATCGCTTCGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | LSM6 forward | this paper | CGGACGACCAGTTGTGGTAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | LSM6 reverse | this paper | CCAGGACCCCTCGATAATCC | |
| sequence-based reagent | COPS2 forward | this paper | AGGAGGACTACGACCTGGAAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | COPS2 reverse | this paper | GCCGCTTTTGGGTCATCTTC | |
| sequence-based reagent | CGGBP1 forward | this paper | GCCTCGTCCACTTTCCCTAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | CGGBP1 reverse | this paper | TCATGCCTTTACGTAGGATCGAG | |
| sequence-based reagent | BCA53 forward | this paper | TCTTGCCTGCTCCACAGTTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | BCA53 reverse | this paper | CAAACACCAAGGAGGGGTCT | |
| sequence-based reagent | CEP128 forward | this paper | TACAGTAATGGACAGGCGGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | CEP128 reverse | this paper | TCCGGAGTTGGTCGATTGAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | MAD1L1 forward | this paper | CGAGTCTGCCATCGTCCAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MAD1L1 reverse | this paper | GCACTCTCCACCTGCTTCTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | RAD51B forward | this paper | TTTGGACGAAGCCCTGCAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | RAD51B reverse | this paper | CACAACCTGGTGGACCTGTA | |
| sequence-based reagent | RBPMS forward | this paper | ACAGTCGCTCAGAAGCAGAG | |
| sequence-based reagent | RBPMS reverse | this paper | CGAAGCGGATGCCATTCAAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | TCF7 forward | this paper | TCAACAGCCCACATCCCAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | TCF7 reverse | this paper | AGAGGCCTGTGAACTTGCTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | HOOK2 forward | this paper | TTTGCTGAAAAGGAAGCTGGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | HOOK2 reverse | this paper | GCAACTCCAGATCTGCCTCA | |
| sequence-based reagent | MAN2C1 forward | this paper | ATGAGGCCCACAAGTTCCTG | |
| sequence-based reagent | MAN2C1 reverse | this paper | TCTCATAGGTGGCCTGGGAA | |
| peptide, recombinant protein | ||||
| commercial assay or kit | ||||
| chemical compound, drug | Biotin-phenol (BP) | PMID: 23371551 | ||
| software, algorithm | Tophat v2.1.1 | DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36 | RRID:SCR_013035 | |
| software, algorithm | CuffDiff2 | RRID:SCR_001647 | ||
| software, algorithm | Slidebook 6.0 | RRID:SCR_014300 | ||
| software, algorithm | DAVID bioinformatics analysis | RRID:SCR_003033 | ||
| other |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Mitochondrial APEX-RIP Data.
(A) RNAs enriched by mito-APEX2-RIP. (B) Unfiltered mito-APEX-RIP RNA-Seq data. (C) Column definitions.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29224.014
-
Supplementary file 2
Nuclear and Cytosolic APEX-RIP Data.
(A) APEX2-RIP-enriched nuclear RNAs. (B) APEX2-RIP-enriched cytosolic RNAs. (C) Unfiltered APEX-RIP RNA-Seq data. (D) Unfiltered nuclear and cytosolic fractionation-seq data (Sultan et al., 2014). (E) Fractionation-Seq-enriched Nuclear RNAs. (F) Fractionation-Seq-enriched cytosolic RNAs. (G) lncRNAs used to determine coverage analysis (Figure 2F). (H) Column definitions.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29224.015
-
Supplementary file 3
KDEL-RIP Data (ER-proximal RNAs).
(A) KDEL-RIP-enriched ER-proximal RNAs. (B) Unfiltered KDEL-RIP RNA-Seq data. (C) ER-associated RNAs enriched by Fractionation-Seq (Reid and Nicchitta, 2012). (D) ER-associated RNAs enriched by proximity-dependent ribosome profiling (Jan et al., 2014). (E) True positive list: RNAs encoding established ER-resident proteins. (F) Column definitions.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29224.016
-
Supplementary file 4
Additional analysis of ER and nuclear datasets.
(A) Mitochondrial mRNAs (nuclear-encoded) enriched at the ER membrane. (B) RNAs that may be enriched at the nuclear lamina. (C) Column definitions.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29224.017
-
Supplementary file 5
Materials used in this study.
(A) Genetic constructs used in this study. (B) Antibodies used for immunofluorescence. RRID: Research Resource Identifier (https://scicrunch.org/resources). (C) qRT-PCR primers used in this study. (D) Column definitions.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29224.018
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29224.019





