The zinc-finger transcription factor Hindsight regulates ovulation competency of Drosophila follicles
Figures
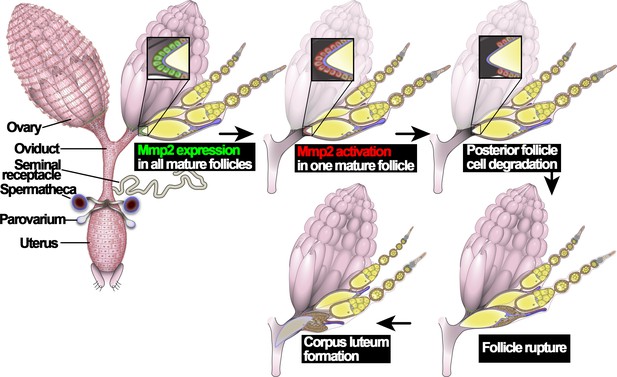
An illustration of Drosophila ovulation process.
The female reproductive system, consisting of two ovaries, oviduct, uterus, seminal receptacle, and a pair of spermathecae and parovaria, was depicted in the cartoon. Two representative ovarioles with different staged egg chambers were highlighted in the right ovary. Oocytes and nurse cells are in yellow. Mmp2 expression is shown in green and Mmp2 activity is shown in red.
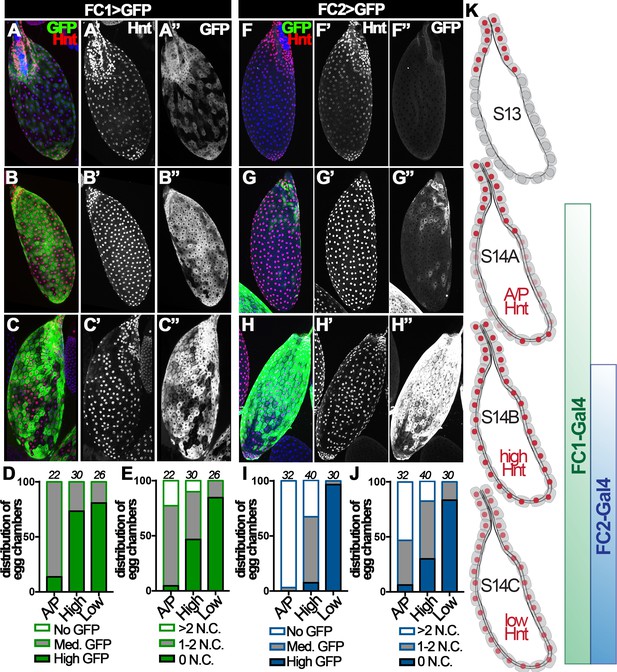
Hindsight expression in stage-14 egg chambers.
(A–C) Hnt expression (red in A-C and white in A’-C’) in A/P-Hnt (A), high-Hnt (B), and low-Hnt (C) egg chambers. FC1 expression (FC1 Gal4 driving UAS-eGFP, FC1 > GFP) is shown in green (A–C) and white in (A”–C”). Nuclei are shown by DAPI in blue (A–C). (D–E) Quantification of FC1 expression (D) and residual nurse cell nuclei (E) in A/P-Hnt, high-Hnt, and low-Hnt egg chambers. The number of stage-14 egg chambers analyzed is noted above each bar. (F–H) Hnt expression (red in F-H and white in F’-H’) in A/P-Hnt (F), high-Hnt (G), and low-Hnt (H) egg chambers. FC2 expression (FC2 > GFP) is shown in green (F–H) and white (F”–H”). Nuclei are shown in blue (F–H). (I–J) Quantification of FC2 expression (I) and residual nurse cell nuclei (J) in A/P-Hnt, high-Hnt, and low-Hnt egg chambers. (K) A schematic cartoon shows the temporal pattern of Hnt, FC1 and FC2 expression in stage-14 egg chambers. FC1-related graphs are colored green and FC2-relaed graphs are colored blue.
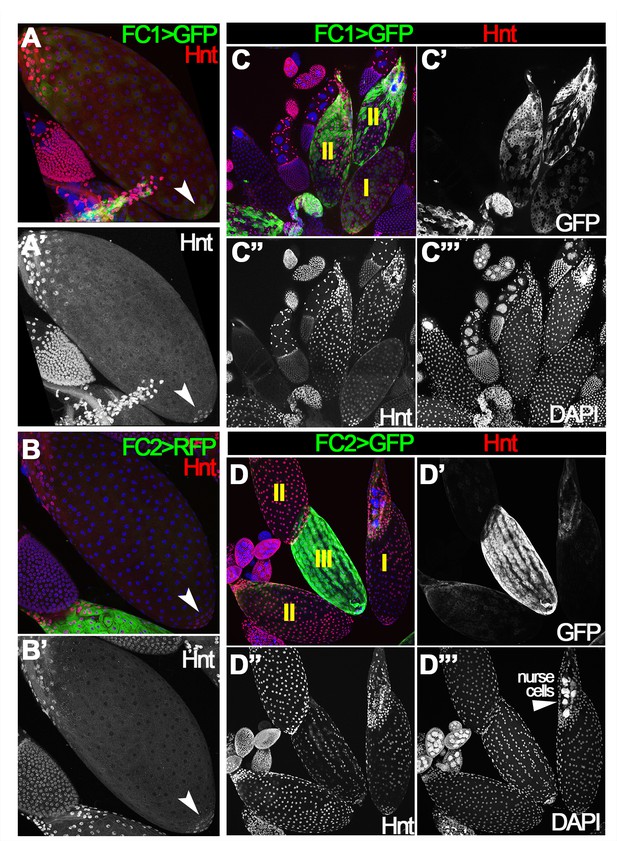
Egg chambers with different patterns of Hindsight expression.
(A–B’) Hnt (red in A-B and white in A’-B’) is expressed in posterior tip follicle cells (arrowheads) in youngest stage-14 egg chambers, which have faint FC1 (A) but no FC2 (B) expression (green). (C–D”’) Representative images show all three types of egg chambers with differential Hnt expression. (I) A/P-Hnt (stage-14A) egg chambers; (II) high-Hnt (stage-14B) egg chambers; (III) low-Hnt (stage-14C) egg chambers. DAPI labeling nuclei is shown in blue (A–D), or white (C”’, D”’).
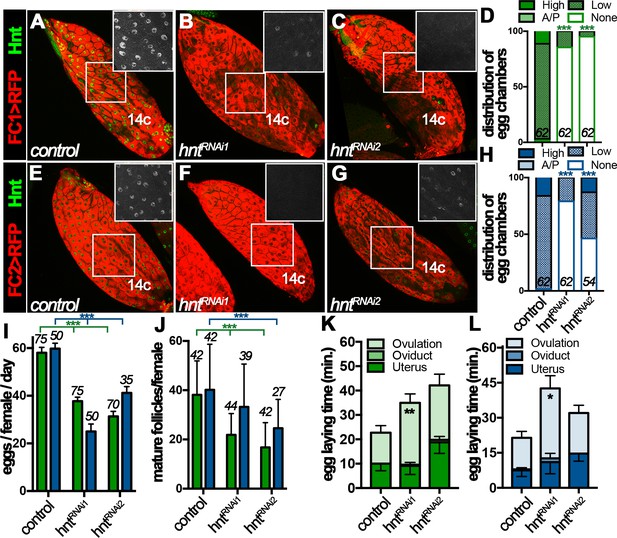
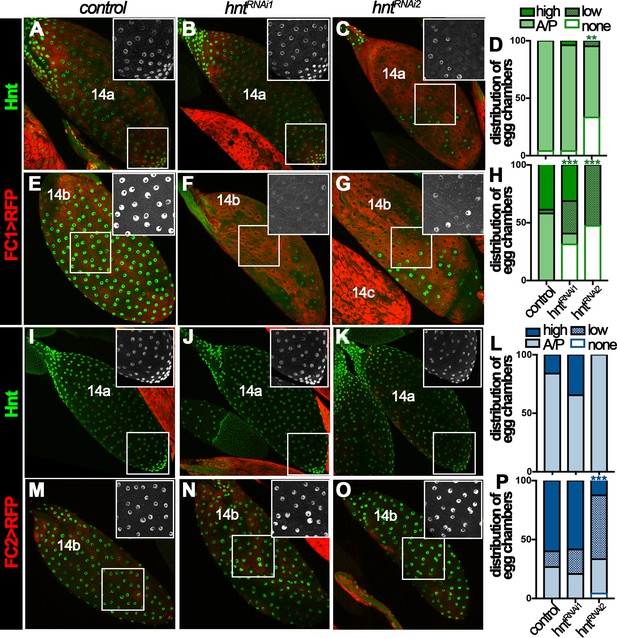
Hindsight expression in stage-14 follicle cells is essential for normal ovulation.
(A–D) Hnt expression (green) in control (A) and hntRNAi (B–C) stage-14C egg chambers with FC1. FC1 expression (FC1 > RFP) is shown in red. Inserts are high magnification of Hnt expression in squared areas. The quantification of Hnt expression (categorized as high-Hnt, low-Hnt, A/P-Hnt, and None-Hnt) in stage-14C egg chambers is shown in (D). The number of stage-14C egg chambers (selected according to no nurse-cell nuclei/high FC1 expression) analyzed is noted above each bar. (E–H) Hnt expression (green) in control (E) and hntRNAi (F–G) stage-14C egg chambers with FC2. FC2 expression (FC2 > RFP) is shown in red. Inserts are high magnification of Hnt expression in squared areas. The quantification of Hnt expression in stage-14C egg chambers is shown in (H). The stage-14C egg chambers are selected according to no nurse-cell nuclei/high FC2 expression. (I–J) The quantification of egg laying (I) and mature egg chambers in each female’s ovaries after egg laying (J) in control or hntRNAi females with FC1 (green bars) or FC2 Gal4 (blue bars). The number of females is noted above each bar. (K–L) The egg-laying time in control or hntRNAi females with FC1 (K) or FC2 (L). Also see Supplementary file 1. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Hnt expression in stage-14A and stage-14B egg chambers.
(A–H) Hnt expression (green in A-C and E-G) in stage-14A (A–D) and stage-14B (E–H) egg chambers with FC1 driving RFP (control, A and E) or hntRNAi (B–C and F–G). Quantification of Hnt expression is shown in (D) and (H). (I–P) similar as in (A–H) but using FC2 Gal4 instead.
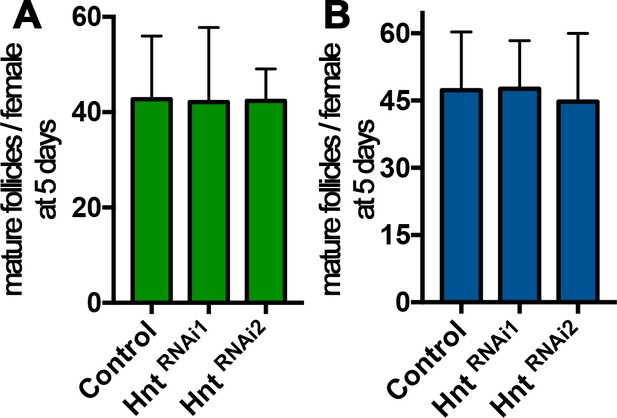
hnt depletion in stage-14 follicle cells does not affect oogenesis in virgin females.
(A–B) Quantification of stage-14 egg chambers in virgin females before egg laying experiment. (A) is using FC1 Gal4, while (B) is using FC2-Gal4.
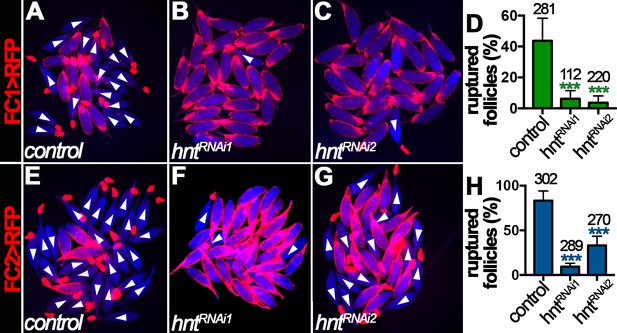
Hindsight is required for OA-induced follicle rupture.
(A–D) Representative images show control (A) and hntRNAi (B–C) egg chambers with FC1 after three-hour culture with 20 μM OA. Quantification of OA-induced follicle rupture is shown in (D). (E–H) Representative images show control (E) and hntRNAi (F–G) egg chambers with FC2 after three-hour culture with 20 μM OA. Quantification is shown in (H). Egg chambers were isolated according to FC1 > RFP (red in A-C) or FC2 > RFP (red in E-G) expression. Bright-field images of the egg chambers are shown in blue, and ruptured egg chambers are marked by white arrowheads. The number of egg chambers is listed above each bar. ***p<0.001.
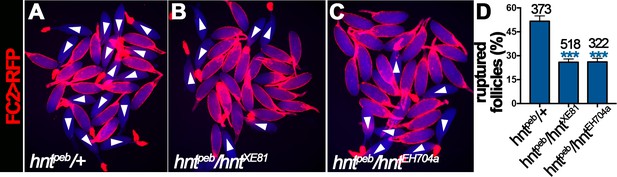
hnt mutant mature follicles are defective for OA-induced follicle rupture.
(A–C) Representative images show hntpeb/+ (A), hntpeb/hntXE81 (B), and hntpeb/hntEH704a (C) mature follicles after three-hour culture with OA. Mature follicles were isolated according to FC2 > RFP expression showing in red. Bright-field images of the egg chambers are shown in blue, and ruptured follicles are marked by white arrowheads. (D) Quantification of OA-induced rupture is shown. ***p<0.001.
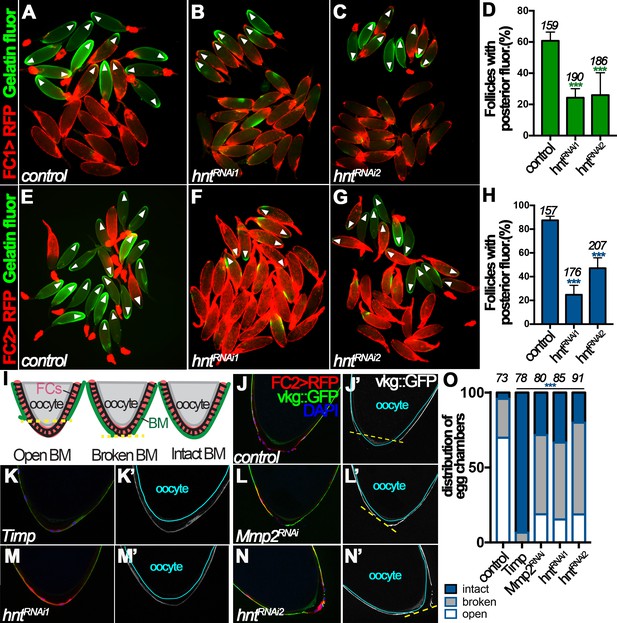
Hindsight regulates Mmp2 activity in stage-14 follicle cells.
(A–C) Representative images show OA-induced Mmp2 activity (green) in control (A) and hntRNAi (B–C) egg chambers with FC1 after three-hour culture with OA. Egg chambers with posterior Mmp2 activity are marked by arrowheads. Quantification is shown in (D). (E–H) Representative images show OA-induced Mmp2 activity (green) in control (E) and hntRNAi (F–G) egg chambers with FC2 after three-hour culture with OA. The quantification is shown in (H). (I) A diagram shows the three categories of basement-membrane (BM) configurations (according to Vkg::GFP expression) of follicle cells in isolated stage-14 egg chambers. When a line connecting the posterior-most Vkg edges bisects the oocyte, it is defined as an open-BM configuration, whereas when the line does not bisect the oocyte, it is defined as a broken-BM configuration. The intact-BM configuration is defined as intact, continuous Vkg::GFP throughout the posterior of the egg chamber. (J–J') A control egg chamber identified according to FC2 >RFP expression shows the open-BM configuration. (K–K’) An egg chamber with overexpression of Timp shows the intact-BM configuration. (L–L’) An Mmp2RNAi egg chamber shows the broken-BM configuration. (M–N) hntRNAi egg chambers show intact-BM (M–M’) and broken-BM (N–N’) configurations. (O) Quantification of BM configurations of FC2-expressing egg chambers with respective genotypes. The number of egg chambers analyzed is noted above each bar. ***p<0.001.
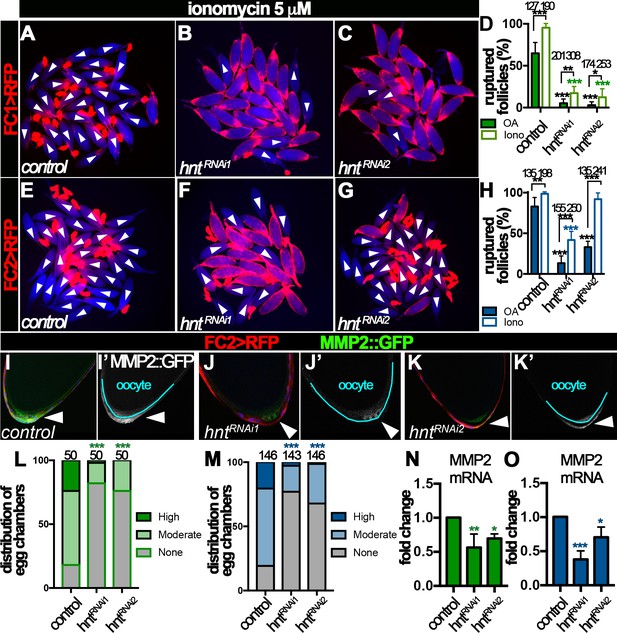
Hindsight regulates Mmp2 expression in stage-14 follicle cells.
(A–H) Response of egg chambers isolated according to FC1 (A–D) or FC2 (E–H) to ionomycin-induced rupture in three hours. (A–C and E–G) Representative images show control (A and E) and hntRNAi (B–C and F–G) egg chambers after the culture. Bright field images of the egg chambers are shown in blue, and white arrowheads mark ruptured egg chambers. Quantification of rupture response to OA or to ionomycin is shown in (D and H). (I–K) Representative images show Mmp2::GFP expression (green in I-K and white in I’-K’) in control (I–I’) or hntRNAi (J–K’) egg chambers with FC2 Gal4 (Red). Nuclei are labeled with DAPI and shown in blue (I–K). Arrowheads point to posterior follicle cells, and oocytes are outlined in cyan (I’–K’). (L–M) Quantification of Mmp2::GFP expression in control and hntRNAi egg chambers using FC1 (L) or FC2 (M) Gal4. (N–O) Quantification of Mmp2 mRNA levels in hntRNAi egg chambers with FC1 (N) or FC2 (O) Gal4. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
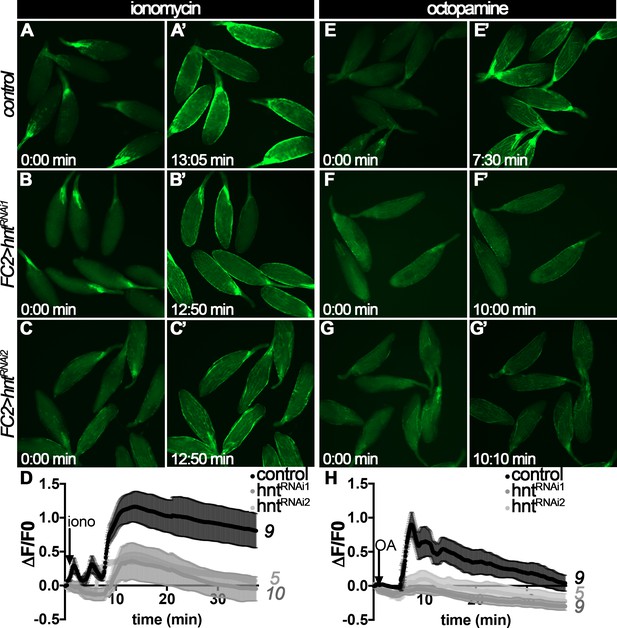
Measurement of intracellular Ca22+in follicle cells after ionomycin or octopamine stimulation.
(A–D) Intracellular Ca2+ depicted by GCaMP5G (green in A-C’) increase in response to ionomycin stimulation in both control (A–A’) and hntRNAi (B–C’) egg chambers with FC2 Gal4, although hntRNAi egg chambers show slightly weaker response. The frames with peak GCaMP5G signal after ionomycin stimulation are shown in A’-C’. Quantification of intracellular Ca2+ level (ΔF/F0) is shown in D and the number of egg chambers analyzed is noted at the end of each trace. (E–H) Intracellular Ca2+ depicted by GCaMP5G (green in E-G’) increase in control egg chambers (E–E’) after OA stimulation but does not in hntRNAi egg chambers with FC2 Gal4 (F–G’). The frames with peak GCaMP5G signal after OA stimulation are shown in E’-G’. Quantification of intracellular Ca2+ level (ΔF/F0) is shown in H and the number of egg chambers analyzed is noted at the end of each trace. Also see Videos 1–6.
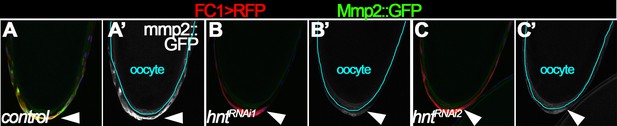
hnt depletion disrupts Mmp2 expression in posterior follicle cells.
Mmp2::GFP (green in A-C and white in A’-C’) is highly expressed in posterior follicle cells of control stage-14 egg chambers (A–A’), but is weakly detected in posterior follicle cells of hntRNAi egg chambers (B–C’) with FC1 Gal4. The oocyte is outlined in cyan (A’–C’), and nuclei are labeled with DAPI and shown in blue (A–C).
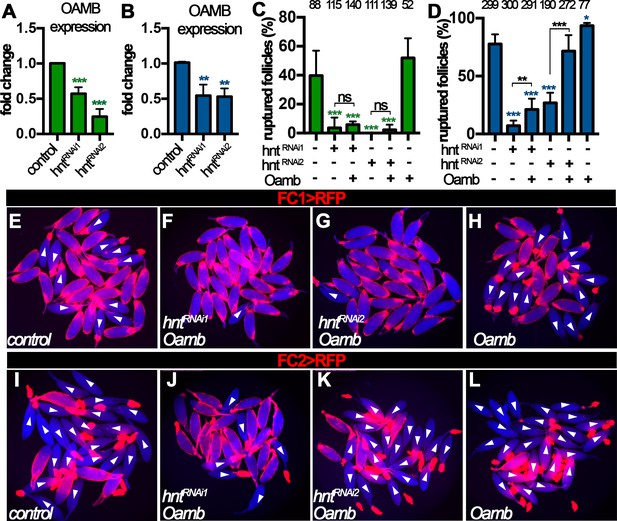
Hnt regulates Oamb expression in stage-14 follicle cells.
(A–B) Quantification of Oamb mRNA levels in hntRNAi egg chambers with FC1 (A) or FC2 (B) Gal4. (C–D) Quantification of egg chambers in response to OA-induced follicle rupture. hntRNAi and/or Oamb overexpression is driven by FC1 (C) or FC2 (D) Gal4. (E–L) Representative images of the quantification in (C–D). FC1 >RFP (E–H) or FC2 >RFP (I–L) is shown in red, bright-field images of the egg chambers are shown in blue, and ruptured egg chambers are marked by white arrowheads. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
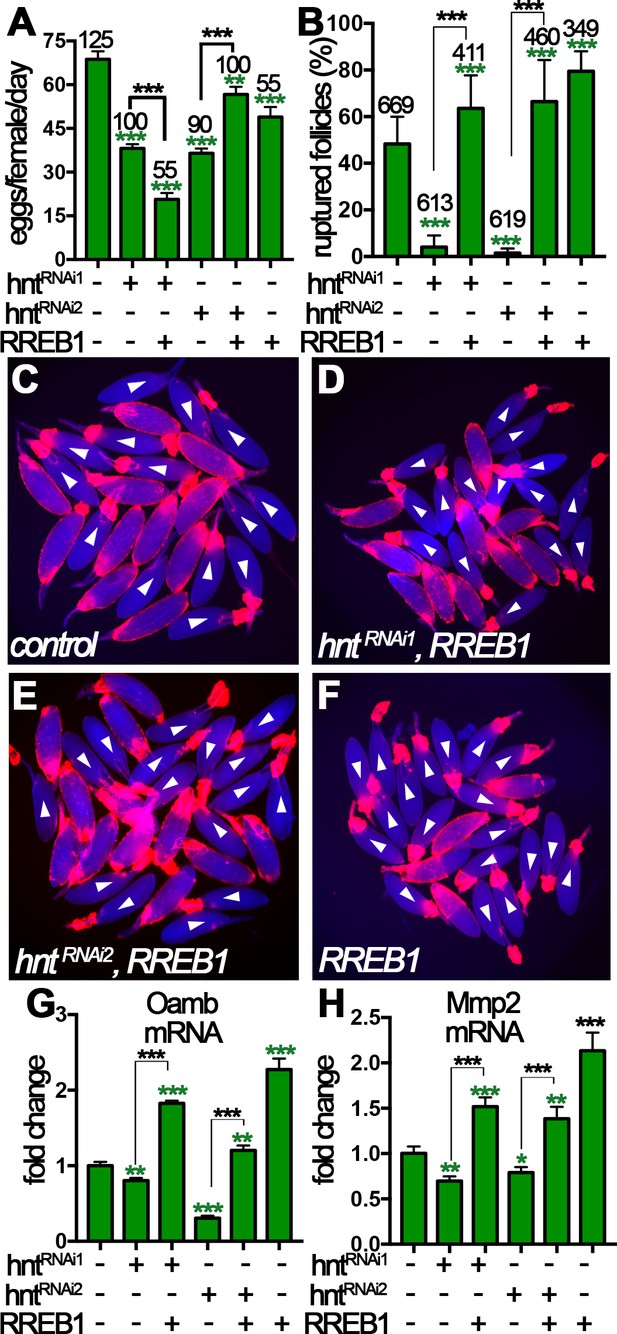
Human RREB-1 can replace Hindsight’s role in regulating follicle’s competency to ovulation.
(A) The quantification of egg-laying capacity of females with FC1 driving hntRNAi and/or RREB-1 overexpression. (B–F) The quantification of OA-induced follicle rupture (B) in egg chambers with hntRNAi and/or RREB-1 overexpression using FC1 Gal4. Representative images are shown in (C–F). FC1 >RFP is shown in red, bright-field images of egg chambers are shown in blue, and white arrowheads mark ruptured follicles. (G–H) Quantification of Oamb (G) and Mmp2 (H) mRNA level in egg chambers with FC1 Gal4 driving hntRNAi and/or RREB-1 overexpression. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
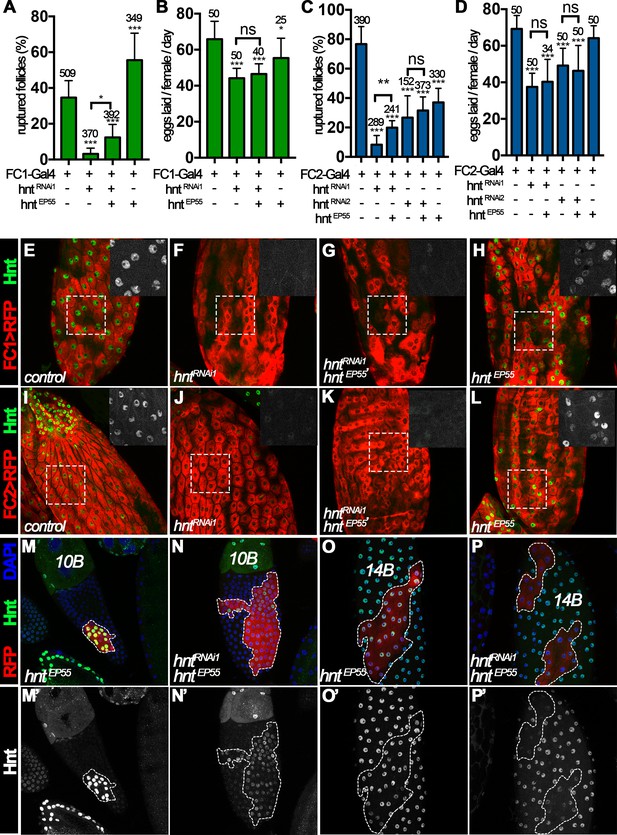
Rescue of ovulation defect in hntRNAi females with hnt overexpression.
(A–D) Quantification of OA-induced follicle rupture (A, C) and the egg-laying number (B, D) from females with FC1 (A–B) and FC2 (C–D) Gal4 driving hntRNAi and/or hntEP55 overexpression. (E–L) Hnt expression (green, white in insets of outlined area) in stage-14C control (E, I), hntRNAi1 (F, J), hntRNAi1/hntEP55 (G, K), and hntEP55 (H, L) follicles with FC1 (FC1 > RFP in red, (E–H) or FC2 (FC2 > RFP in red, (I–L). (M–P’) Hnt expression (green in M-P and white in M’-P’) in stage-10B (M–N) and stage-14B (O–P) egg chambers. Hnt is highly overexpressed in a flip-out clone with actin-Gal4 and hntEP55 (M and O) but is barely detected in the clone with actin-Gal4 and hntEP55/hntRNAi1 (N and P). Clone cells are marked by act-Gal4 driving UAS-RFP expression (red) and DNA is labeled with DAPI in blue (M–P). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
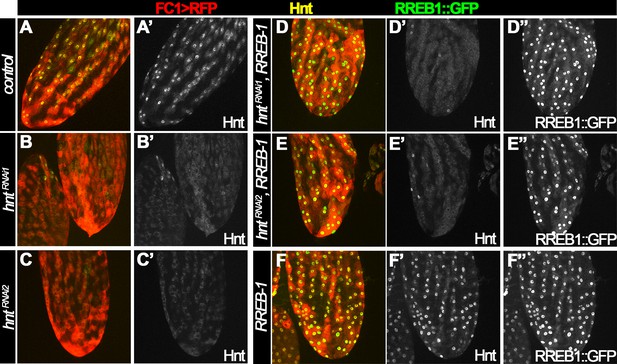
Human RREB-1::GFP does not interfere with Hnt expression in control or hntRNAi egg chambers.
Hnt expression is shown in yellow (A–F) and white (A’–F’), and RREB1::GFP expression is shown in green (D–F) and white (D”–F”). (A–C) Hnt expression is detected in control follicle cells (A) and is reduced in follicle cells with FC1 driving hntRNAi expression (B–C). (D–E) Hnt expression is still reduced in follicle cells with FC1 driving hntRNAi/RREB-1::GFP expression. (F) Both Hnt and RREB-1::GFP is highly expressed in follicle cells with FC1 driving RREB-1::GFP expression.
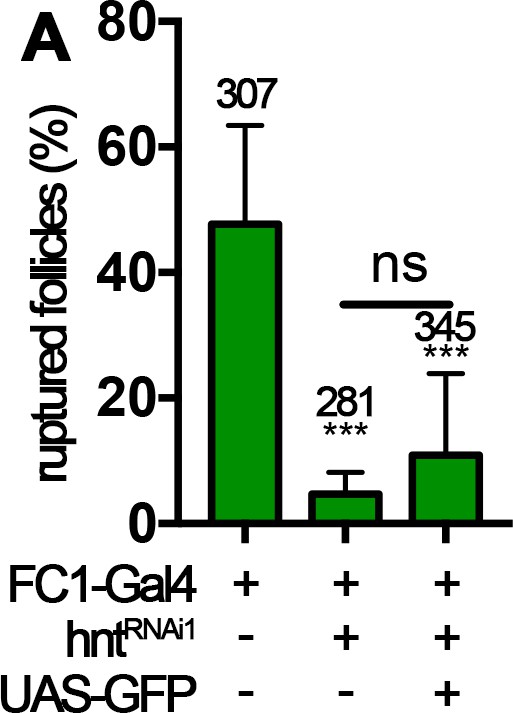
Overexpression of GFP is not sufficient to rescue rupture defect of hntRNAi follicles with FC1 Gal4.
Quantification of OA-induced follicle rupture is shown.
***p<0.001.
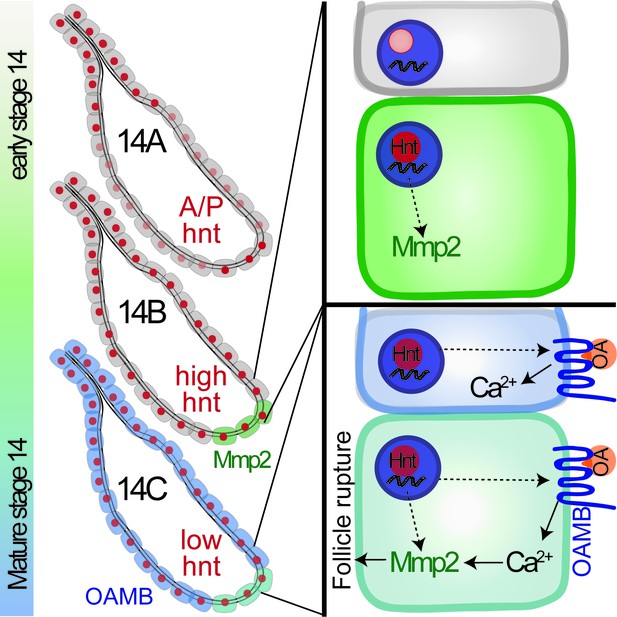
A schematic cartoon summarizes the role of Hindsight in stage-14 follicle cells.
Hnt expression is shown in red with different intensity indicating different expression level. Mmp2 expression is shown in green and Oamb expression is shown in blue. OA stands for octopamine.
Videos
Signal of GCaMP5G driven by FC2 in Control follicles with ionomycin stimulation (FC2 > GCaMP5G).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29887.015Signal of GCaMP5G driven by FC2 in hntRNAi1 follicles with ionomycin stimulation (FC2 > GCaMP5G/hntRNAi1).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29887.016Signal of GCaMP5G driven by FC2 in hntRNAi2 follicles with ionomycin stimulation (FC2 > GCaMP5G/hntRNAi2).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29887.017Signal of GCaMP5G driven by FC2 in Control follicles with octopamine stimulation (FC2 > GCaMP5G).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29887.018Signal of GCaMP5G driven by FC2 in hntRNAi1 follicles with octopamine stimulation (FC2 > GCaMP5G/hntRNAi1).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29887.019Signal of GCaMP5G driven by FC2 in hntRNAi2 follicles with octopamine stimulation (FC2 > GCaMP5G/hntRNAi2).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29887.020Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
The egg laying, egg distribution within the reproductive tract, and egg-laying time of females with various genotypes.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29887.027
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.29887.028





