Shorter cortical adaptation in dyslexia is broadly distributed in the superior temporal lobe and includes the primary auditory cortex
Figures
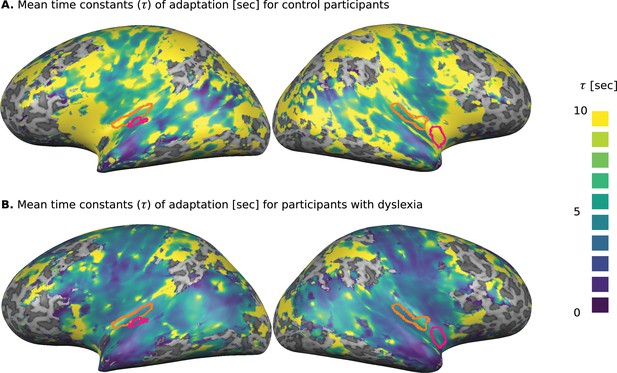
Cortical distribution of the groups’ mean estimated time constants () of adaptation, calculated separately for each of the responding voxels.
(A) Control participants. (B) Participants with dyslexia. The estimated s for participants with dyslexia were consistently shorter than those estimated for the control group. Significant group differences in the whole-brain analysis (Monte-Carlo cluster-level corrected: cluster threshold of 44 voxels; see 'Materials and methods') are outlined in magenta. The left and right primary auditory cortices, which were estimated as a source of P2 (ERP) component, are outlined in orange. An ROI analysis (see text) revealed a significant group difference in the left primary auditory cortex (Figure 2).
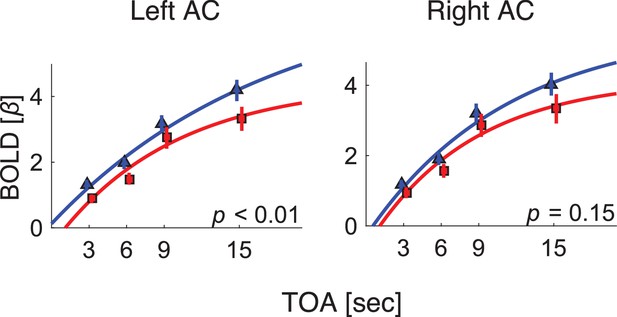
BOLD response as a function of TOA in the primary auditory cortex of each hemisphere.
Blue: control. Red: dyslexic. AC: the 3 subregions that comprise the primary auditory cortex, outlined in orange in Figure 1.
Tables
General characteristics of the participants in this study (mean and standard deviation).
The assessments used in this study were the same as in our previous study (Jaffe-Dax et al., 2017).
| Control group | Dyslexic group | Mann-Whitney z value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 19 | N = 20 | ||
| Age (years) | 25.9 (2.6) | 24.5 (2.6) | 1.7 n.s. |
| General cognitive (scaled) | |||
| Block design | 13.1 (3.2) | 12.4 (2.9) | 0.6 n.s. |
| Digit span | 11.1 (2.9) | 7.5 (1.9) | 4.0**** |
| Phonological speed [items/minute] | |||
| Pseudo-word reading rate | 64.0 (25.2) | 31.9 (9.7) | 3.9**** |
| Single-word reading rate | 101.6 (35.2) | 69.2 (21.3) | 3.0*** |
| Word pattern recognition rate | 69.8 (15.6) | 41.7 (11.8) | 4.5**** |
| Passage reading rate | 142.2 (23.9) | 100.7 (17.4) | 4.5**** |
| Spoonerism rate | 9.9 (3.0) | 5.7 (3.1) | 3.8**** |
| Phonological accuracy [% correct] | |||
| Pseudo-word reading accuracy | 90.6 (11.9) | 63.5 (18.4) | 4.0**** |
| Single-word reading accuracy | 97.2 (4.3) | 89.0 (6.5) | 3.7**** |
| Word pattern recognition accuracy | 100.0 (0.0) | 98.27 (3.1) | 2.5** |
| Passage reading accuracy | 98.7 (1.2) | 95.4 (2.3) | 4.1**** |
| Spoonerism accuracy | 90.8 (6.9) | 77.8 (17.2) | 2.5** |
-
*p < 0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.005; ****p<0.0005.
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30018.005





