An Eya1-Notch axis specifies bipotential epibranchial differentiation in mammalian craniofacial morphogenesis
Figures
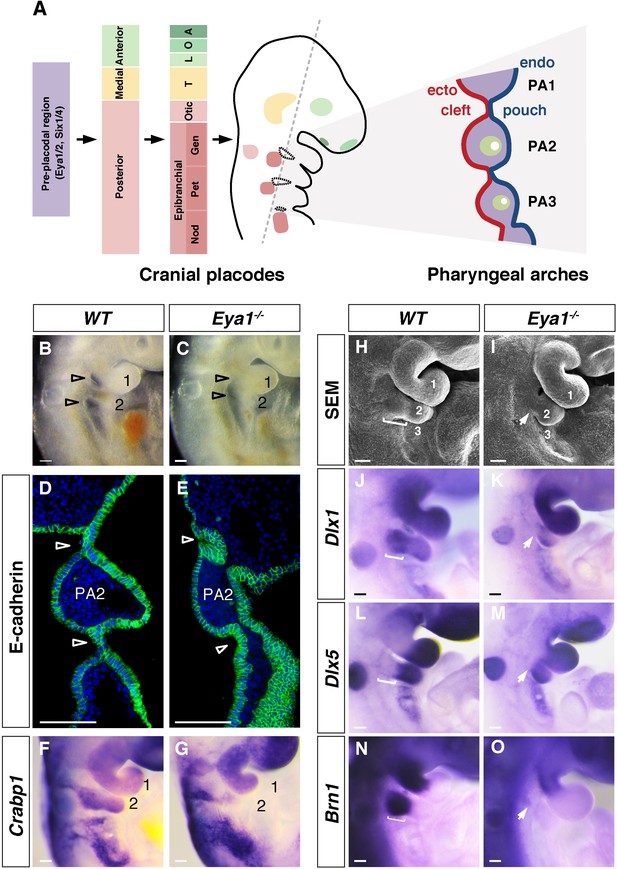
Cranial placode and pharyngeal arch development in wildtype and Eya1-/- mouse embryos.
(A) Schematic summary of the development of cranial placodes and pharyngeal arches (PA) in mouse embryos. The pre-placodal region, marked by expression of Eya and Six families of genes at E8.0, is divided into anterior, medial and posterior placodal regions at E8.5, which further develops into specific cranial placodes (A, adenohypophyseal; O, olfactory; L, lens; T, trigeminal; Gen, geniculate; Pet, petrosal; Nod, nodose) from E8.5–9.5. The epibranchial placodes are located in close proximity to the pharyngeal segmental plates (circled with black dotted lines). The grey dashed line indicates the plane of coronal section, which reveals the pharyngeal segmental plates and arch structures as shown in the diagram on the right (also panel D and E). The PA structures include the pharyngeal ectoderm (red), endoderm (blue) and the transient pharyngeal segmental plates, which form the clefts and pouches. The neural crest, mesoderm and aortic arch arteries are indicated in purple, green and white, respectively. (B and C) Lateral view of wildtype (WT) and Eya1-/- whole mount E9.5 embryos. Open arrowheads indicate positions of pharyngeal clefts; PA1 and PA2 are numbered (n > 20). (D and E) Immunostaining for E-cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue) on coronal sections of WT and Eya1-/- E9.5 embryos. Arrowheads indicate positions of the pharyngeal segmental plates, which are not formed in Eya1-/- embryos (n = 4). (F and G) Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing Crabp1 expression in WT and Eya1-/- E9.5 embryos (n = 5). (H and I) Scanning electron microscopy images of WT and Eya1-/- embryos at E10. White bracket in WT embryo indicates the proximal region of PA2, which was missing in Eya1-/- embryos (indicated by arrow) (n = 5). (J–O) Expression of Dlx1, Dlx5 and Brn1 in WT and Eya1-/- E9.5 embryos. White brackets indicate the proximal region of PA2 in WT embryos. Arrows indicate the missing proximal PA2 in Eya1-/- embryos (n > 5). Scale bars, 100 µm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data relating to Figure 1—figure supplement 1E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.004
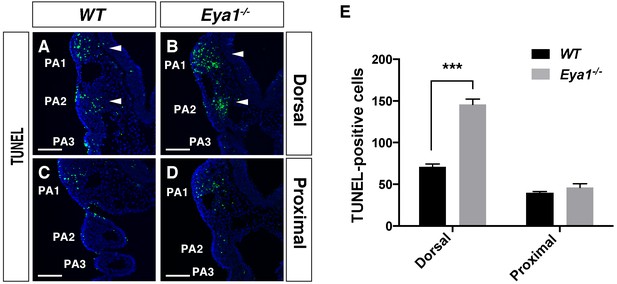
TUNEL assay in WT and Eya1-/- E9.5 embryos.
(A–D) TUNEL assay on coronal sections of WT and Eya1-/- embryos at E9.5, at the level above the pharyngeal clefts (dorsal) and at the level of the proximal PA. More apoptotic cells (arrowheads) were present in the Eya1-/- embryos. Scale bars, 100 µm. (E) Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells. There were more TUNEL-positive cells at the dorsal level in Eya1-/- embryos than in WT at E9.5 (n = 6). Apoptotic cells were counted on three sections per embryo. Analysis of variance was performed and significance was estimated using Student's t-test. All quantitative data are means ± SEM. ***p<0.001.
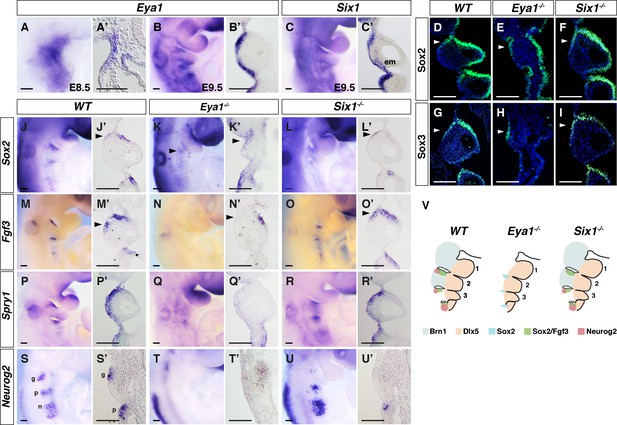
Differences in pharyngeal arch phenotypes in Eya1-/- and Six1-/- embryos.
(A–C’) In situ hybridization on whole-mount and coronal sections of Eya1 and Six1 in WT embryos at E8.5 (n = 5) and E9.5 (n = 5). (D–I) Immunostaining for Sox2 and Sox3 on coronal sections of E9.5 WT, Eya1-/- and Six1-/- embryos. (J–R’) In situ hybridization of Sox2, Fgf3, and Spry1 on whole-mount and coronal sections of E9.5 embryos (n ≥ 5). (S–U’) In situ hybridization of Neurog2 on whole-mount and coronal sections through the region of the geniculate and petrosal placodes of E9.5 embryos (n = 5). (V) Schematic summary of the abnormal PA phenotype and gene expression patterns in WT, Eya1-/- and Six1-/- embryos. Light blue and light orange label the Brn1+ proximal and Dlx5+ distal PA regions, respectively. The black dotted circles demarcate the pharyngeal segmentation plates. Green, blue, and red indicate Sox2+ and Fgf3+, single Sox2+ and Neurog2+ expression regions, respectively. em, ectomesenchyme; g, geniculate placode; p, petrosal placode; n, nodose placodes. Arrowheads indicate rostral-proximal ectodermal cells of PA2. Scale bars, 100 µm.

Expression of Eya1, Fgf8, Fgf15, and Fgfr1 in the pharyngeal ectoderm of E9.5 embryos.
(A) Immunostaining for Eya1 on coronal section of WT embryos at E9.5 (n = 5). The region demarcated by white dotted box in (A) is magnified in (A’), showing expression of Eya1 protein in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. (B–J) In situ hybridization of Fgf15, Fgf8 and Fgfr1 on whole mount or coronal sections of WT, Eya1-/- and Six1-/- embryos at E9.5 (n ≥ 5). Scale bars, 100 µm.
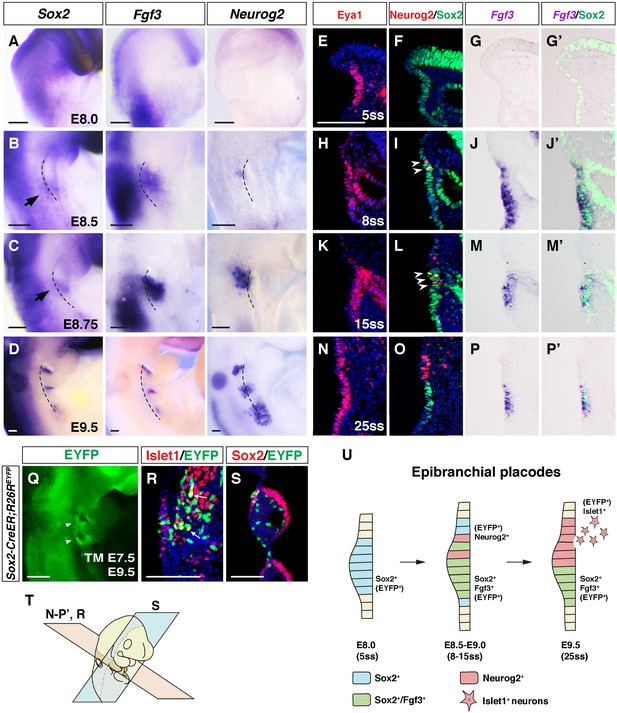
Bipotential Sox2+ progenitors give rise to both neurogenic and non-neuronal epibranchial placodal cells.
(A–D) Sox2, Fgf3 and Neurog2 expression in whole-mount WT embryos at E8.0, E8.5, E8.75 and E9.5. At E8.0, the pharyngeal surface ectoderm was induced to form the thickened posterior placode, which expressed Sox2 but not Fgf3 or Neurog2 (A). At E8.5, the first PA became morphologically identifiable and the pharyngeal ectoderm began to make contact with the endoderm. Fgf3 and Neurog2 expression could be detected in the epibranchial placode (B). At E8.75, the first pharyngeal cleft was already visible on the lateral side of the embryo, just rostral to the group of Sox2+cells, and Fgf3 and Neurog2 expression expanded ventrally and dorsally, respectively (C). At E9.5, the Sox2 and Fgf3 signals became more condensed and restricted to the rostral-proximal PA, while the Neurog2 expression expanded more dorsally in each PA (D), and the separation of the Sox2+/Fgf3+ and Neurog2+ cells became clear. Arrows indicate Sox2-expressing epibranchial placodal regions (n ≥ 5 for each stage). Black dashed lines indicate the position of foregut dorsal endoderm. (E–P’) Immunostaining for Eya1 (E, H, K and N) and co-immunostaining of Neurog2 and Sox2 (F, I, L and O) on adjacent transverse sections; and co-staining of Sox2 and in situ hybridization of Fgf3 (G, J, M and P) on transverse sections of WT embryos at different somite stages (ss) as indicated. Arrowheads indicate Neurog2+/Sox2+ double positive cells (n ≥ 4 per stage). (Q–S) Lineage tracing of Sox2+ placodal cells in Sox2-Cre; R26REYFP embryos. Tamoxifen was injected at E7.5 and embryos examined by whole-mount EYFP fluorescence at E9.5 (n = 10) (arrowheads indicate EYFP+ placodal regions) (Q). Co-immunostaining for Islet1/EYFP and Sox2/EYFP revealed the neurogenic lineage (n = 6) (R) and non-neuronal lineages (n = 4) (S). Arrow indicates Islet1+/EYFP+ positive cell. (T) Schematic diagram illustrating the coronal (blue; S) and transverse (pink; E–P’ and R) planes of sections for the respective panels in this figure. (U) Schematic diagram summarizing the differentiation of Sox2+ epibranchial placode progenitors (blue) into Neurog2+ neurogenic placodal cells and delaminating neurons (red); and Sox2+/Fgf3+ placodal cells (green). Scale bars, 100 µm.

Analysis of bipotential Sox2+ progenitors of the neurogenic and non-neuronal lineages in the epibranchial placodes.
(A–D’) Co-immunostaining for Neurog2/Sox2 on transverse sections of WT at 5ss and of Eya1-/- embryos at 5ss, 8ss, 16ss and 25ss (n = 3/stage). (E) Schematic diagram showing the development of Sox2+ epibranchial placode progenitors in Eya1-/- embryos. Sox2 progenitors (blue) remain present in the pharyngeal ectoderm of Eya1-/- embryos. (F and G) Co-immunostaining for Neurog2 and Sox2 on transverse sections of wildtype embryos at the petrosal and nodose placodal regions at E9.5. Sox2+ and Neurog2+ cells were intermingled at the placodal regions at 25ss (n = 5). (H and I) Lineage tracing of Sox2+ placodal cells in Sox2-Cre; R26REYFP embryos. Tamoxifen was injected at E9.5 and embryos were examined by immunostaining of EYFP at E12.5 (H) and E14.5 (I) (n = 3). Arrowheads indicate the EYFP+ cells. EAC, external auditory canal; Pi, pinna. Scale bars, 20 µm (A–D’) and 100 µm (H–I).
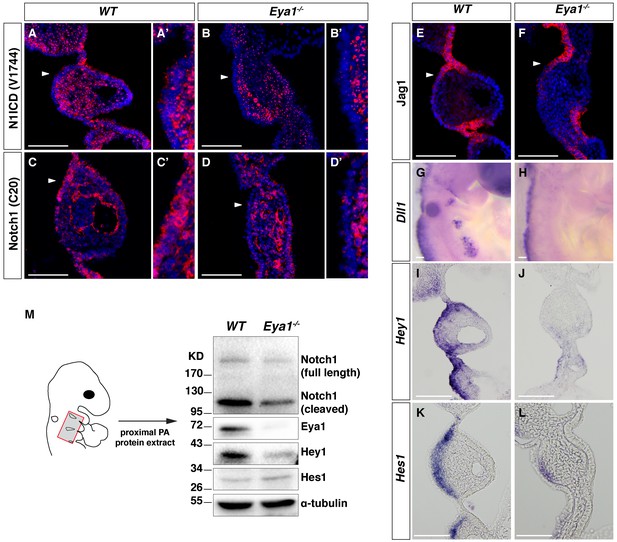
Downregulated Notch signaling in the ectoderm-derived pharyngeal epithelium of Eya1-/- embryos.
(A–D and A’–D’) Immunostaining for Notch1 ICD by V1744, which specifically recognizes Notch1 ICD (A–B’); or by C20, which recognizes an internal epitope on Notch1 ICD and thus both cleaved and uncleaved Notch1 receptor (C–D’) on coronal sections of WT and Eya1-/- embryos at E9.5 (n = 4). Arrowheads indicate the rostral-proximal pharyngeal ectoderm in (A-D), which are magnified in (A’-D’). (E–L) Immunostaining for Jag1 (E, F) and in situ hybridization of Dll1, Hey1 and Hes1 (G–L) on whole-mount or coronal sections of WT and Eya1-/- embryos at E9.5 (n ≥ 4). (M) Western blot analysis of tissue extracts from proximal PA2 and PA3 of WT and Eya1-/- embryos at E9.5 with the indicated antibodies. The red box in the embryo diagram indicates the dissected region. The Notch1 (C20) antibody recognizes both the full-length Notch1 receptor (Notch1 FL) and cleaved Notch1, which represents both the NEXT and ICD forms of the Notch1 receptor. One representative western blot of five. Scale bars, 100 µm.
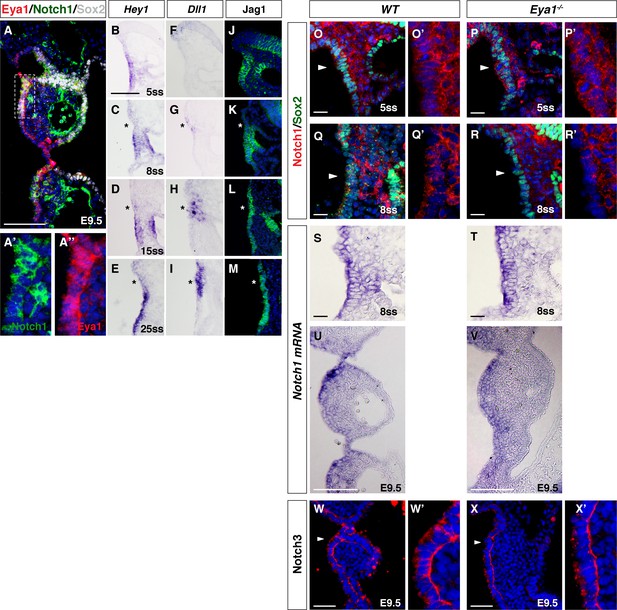
Expression of Notch signaling factors in the ectoderm-derived pharyngeal epithelium of WT and Eya1-/- embryos.
(A, A’ and A’’) Co-immunostaining of Notch1 (C20) with Eya1 and Sox2 in rostral-proximal pharyngeal ectoderm of WT at E9.5. Notch1 receptor is expressed in both nucleus and cytoplasm in the pharyngeal ectoderm (A’). Eya1 is also expressed in both nucleus and cytoplasm (A’’). Sox2 expression is shown as grey. The rostral-proximal pharyngeal ectoderm in (A) (boxed) is enlarged in (A’) and (A’’) (n = 3). (B–I) In situ hybridization showing Hey1 (B–E) and Dll1 (F–I) expression on transverse section of WT embryos at 5ss, 8ss, 15ss and 25ss (n = 4/stage). (J–M) Immunostaining of Jag1 on transverse section of WT embryos at 5ss, 8ss, 15ss and 25ss (n = 6/stage). Comparison to the expression profiles in Figure 3E–3P’, the asterisks represent the neurogenic region. (O–R) Co-staining of Notch1 (C20) and Sox2 on transverse sections of WT and Eya1-/- embryos at 5ss and 8ss. Arrowheads indicate Sox2+ pharyngeal ectoderm cells in (O)-(R), which are enlarged in (O’–R’) (n = 3). (S–V) In situ hybridization of Notch1 showing Notch1 mRNA expression in pharyngeal ectoderm of WT and Eya1-/- embryos at 8ss and E9.5 (n = 3). (W–X’) Immunostaining of Notch3 receptor on the coronal sections of WT and Eya1-/- embryos at E9.5. Arrowheads indicate the rostral-proximal pharyngeal ectoderm cells (n = 3). Scale bars, 100 µm.

Complete western blots for Figure 4M.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.011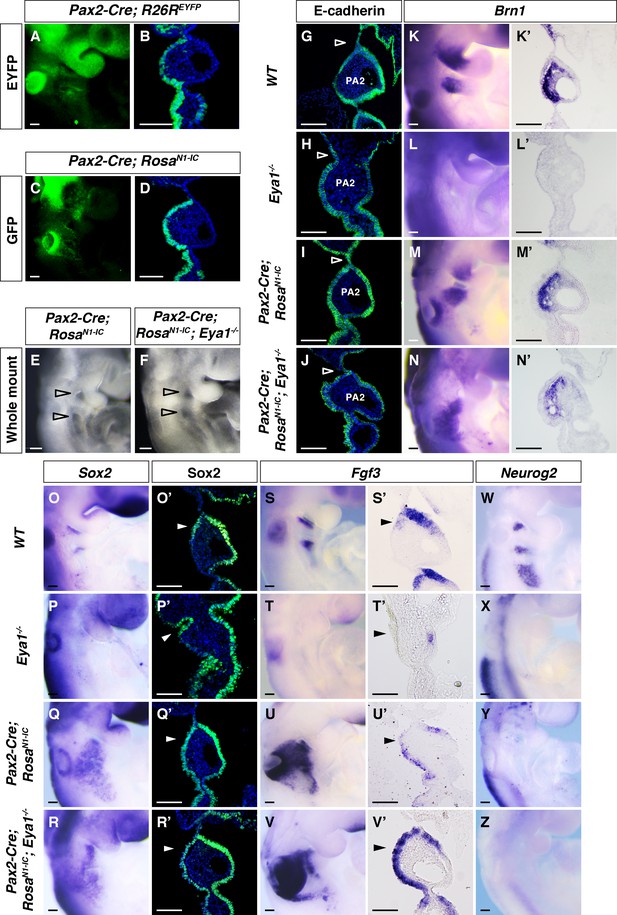
Over-expression of Notch1 ICD restores pharyngeal segmentation and Fgf3 expression in the pharyngeal epithelium of Eya1-/- embryos.
(A–D) Whole mount fluorescence and section immunostaining for EYFP in Pax2-Cre; R26REYFP (A, B) and GFP in Pax2-Cre;RosaN1-IC (C, D) at E9.5, to visualize Cre efficiency and expression of ectopic Notch1 ICD, respectively (n = 3). (E and F) Lateral view of Pax2-Cre; RosaN1-IC and Pax2-Cre; RosaN1-IC; Eya1-/- whole-mount embryos at E9.5 (n = 5). (G–Z) Expression of for E-cadherin (G–J), Brn1 (K–N’), Sox2 (O–R’), Fgf3 (S–V’), and Neurog2 (W–Z) on whole-mount or coronal sections of WT, Eya1-/-, Pax2-Cre; RosaN1-IC and Pax2-Cre; RosaN1-IC; Eya1-/- embryos at E9.5 (n ≥ 3). Open arrowheads indicate positions of the pharyngeal clefts. Arrowheads indicate the rostral-proximal pharyngeal ectodermal cells. Scale bars, 100 µm.
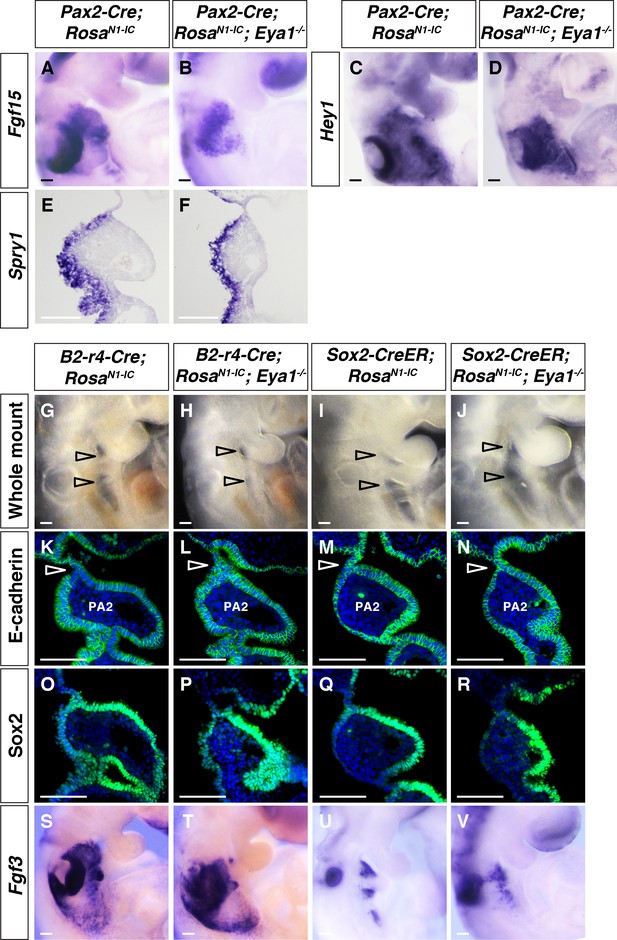
Over-expression of Notch1 ICD by Pax2-Cre, B2-r4-Cre and Sox2-CreER restored pharyngeal segmentation and morphogenesis in Eya1-/- embryos.
(A–F) In situ hybridization showing Fgf15, Hey1 and Spry1 expression in Pax2-Cre; RosaN1-IC and Pax2-Cre; RosaN1-IC; Eya1-/- embryos at E9.5 (n = 3). (G–J) Lateral view of Sox2-CreER; RosaN1-IC, Sox2-CreER; RosaN1-IC; Eya1-/-, B2-r4-Cre; RosaN1-IC and B2-r4-Cre; RosaN1-IC; Eya1-/- whole mount embryos at E9.5. Open arrowheads indicate pharyngeal clefts (n = 3). (K–N) Immunostaining for E-cadherin on coronal sections at E9.5 (n = 3). Open arrowheads indicate positions of the pharyngeal clefts. (O–R) Immunostaining for Sox2 on coronal sections at E9.5 (n = 3). (S–V) In situ hybridization showing Fgf3 expression in the pharyngeal ectoderm at E9.5 (n = 4). Scale bars, 100 µm.
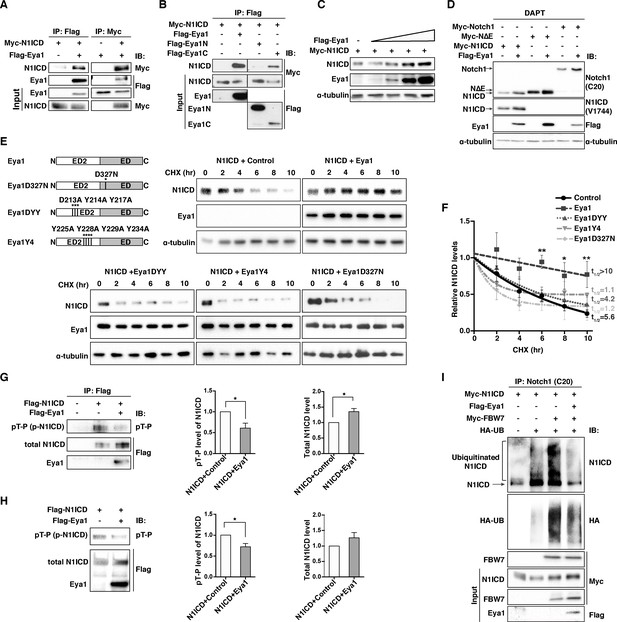
Eya1 stabilizes and dephosphorylates Notch1 ICD.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) analysis using 293T cells with (+) or without (-) transfected Myc-Notch1 ICD and Flag-Eya1, as indicated (n = 6). Pull-down assays (IP) using anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibodies. Western blot analyses (IB) using anti-Myc or anti-Flag antibodies. Input was 5% of the amount of proteins used for IP. (B) IP analysis using 293T cells transfected with Myc-Notch1 ICD, full-length Eya1, the N- or C-terminal portions of Eya1 (Eya1N and Eya1C, respectively) (n = 3). Input was 5% of the amount of proteins used for IP. (C) Increased amount of Flag-Eya1 was transfected into 293T cells with control or Myc-Notch1 ICD, leading to increased level of Notch1 ICD at higher amounts of Eya1. α-tubulin was used as internal control (n = 3). (D) Western blot analysis of 293T cells transfected with different plasmids as indicated. Cells were treated with 10 µM γ-secretase inhibitor (DAPT) for 48 hr prior to harvesting (n = 4). (E) Western blot analysis of cycloheximide (CHX) treated cells transfected with Myc-Notch1 ICD and wild-type or mutant Eya1 cDNAs at indicated time points using anti-Notch1 ICD (V1744), anti-Flag (Eya1), or anti-α-tubulin antibodies. Eya1 has a conserved transcriptional activation domain ED and an N-terminal ED2 domain. The DYY and Y4 mutants abolished the threonine phosphatase activity, while the D327N mutant abolished both the tyrosine- and threonine-phosphatase functions of Eya1 (n ≥ 3). (F) Summary graph showing quantification of the average Notch1 ICD protein levels relative to α-tubulin in experiments shown in (E). The relative protein levels were normalized to time point zero, fitted with one-phase decay, and the half-life (t1/2) calculated. Error bars represent SEM. *p<0.05. Statistical significance between two groups was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. (G) Western blot analysis of phosphorylation status of Notch1 ICD. Flag-Notch1 ICD was immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2 antibody with (+) or without (-) transfected Flag-Eya1, using pT-P antibodies (anti-phospho-Threonine-Proline antibody) or anti-Flag targeting the total Notch1 ICD. Graphs show quantification of the average levels of phosphorylated or total Notch1 ICD in the presence of control or Eya1 (n = 5). (H) Analysis of dephosphorylation of Notch1 ICD by Eya1 by an in vitro phosphatase assay. Flag-Notch1 ICD and Flag-Eya1 purified from 293T cells were incubated in vitro, after which the phosphorylation status of Notch1 ICD was examined by immunoblotting with anti-pT-P and anti-Flag antibodies. Graphs show quantification of the average levels of phosphorylated or total Notch1 ICD incubated with or without Eya1 (n = 4). (G and H) Error bars represent SEM, and p values were calculated using one sample t-test, *p<0.05. (H) Ubiquitination of Notch1 ICD was reduced in the presence of Eya1. Lysates from 293T cells transfected with indicated plasmids were treated with 20 µM MG132 for 6 hr before lysis (n = 3). The lysate were immunoprecipitated with anti-Notch1 (C20) and immunoblotted with anti-Notch1 ICD (V1744), anti-HA, anti-Myc and anti-Flag. Input was 5% of the amount of proteins used for IP.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Source data relating to Figure 6E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.017
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Source data relating to Figure 6F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.018
-
Figure 6—source data 3
Source data relating to Figure 6G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.019

Eya1 does not affect serine or tyrosine phosphorylation level of Notch1 ICD.
(A) Coomassie staining of SDS-PAGE showing purified Flag-Notch1 ICD, Flag-T2122A, Flag-Eya1 from 293T cells. (B–C) Analysis of phosphorylation status of Notch1 ICD. Transfected 293T cells in the presence (+) or absence (-) of Flag-Eya1 were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2 antibody. The phosphorylation status of Notch1 ICD was analysed by western blotting with antibodies targeting the phosphorylated S/T/Y residues anti-phospho-Serine-Proline-Proline antibody (pS-P-P), anti-phospho-Tyrosine antibody (pY) or anti-Flag antibody (n = 3).
Complete western blots for Figure 6 and Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.016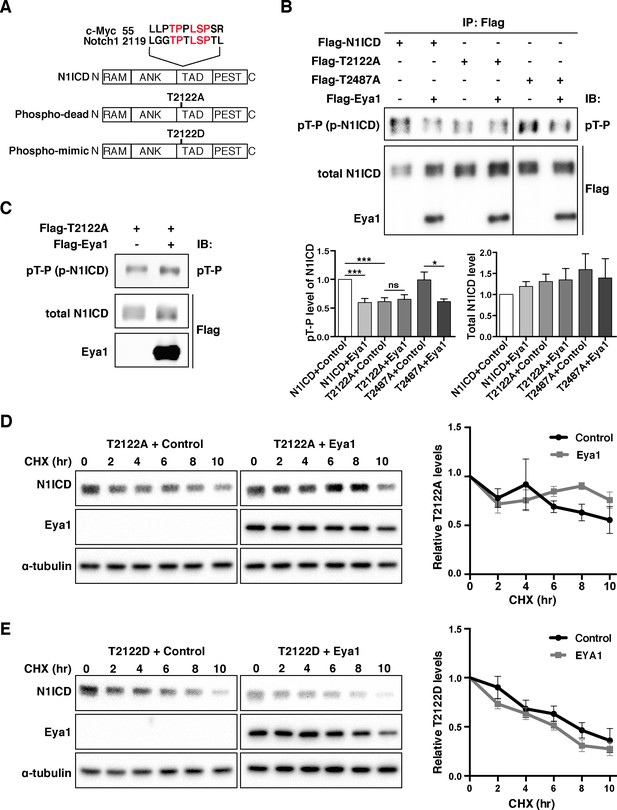
Eya1 targets the T2122 phosphorylation site of Notch1 ICD.
(A) Schematic diagram showing Notch1 ICD protein domains. Alignment of Notch1 ICD peptide sequence (from a.a. 2119) with c-Myc (from a.a. 55), positions of the phospho-dead (T2122A) and phospho-mimic (T2122D) mutations are indicated. Abbreviations: RAM, Rbp-associated molecule domain; ANK, ankyrin repeat domain; TAD, transcription activation domain; PEST, domain rich in proline, glutamic acid, serine and threonine. (B) Phosphorylation analysis of WT Notch1 ICD, Notch1 ICDT2122A, and Notch1 ICDT2487A by Eya1 phosphatase (n ≥ 3). Notch1 ICD was immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2 antibody and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-pT-P and anti-Flag antibodies. Graphs show quantification of the average levels of phosphorylated or total Notch1 ICD, Notch1 ICDT2122A and Notch1 ICDT2487A in the presence of control or Eya1. Statistical significance between two groups was determined by one sample t-test. Error bars represent SEM. ***p<0.001; *p<0.05; ns, not significant. (C) In vitro phosphatase treatment of Notch1 ICDT2122A by Eya1. Flag-T2122A and Flag-Eya1 purified from 293T cells were incubated in vitro, and then examined by immunoblotting with anti-pT-P and anti-Flag antibodies (n = 3). (D and E) Mutant Notch1 ICD protein stability analysis (n = 3). 293T cells transfected with indicated plasmids were treated with CHX. At indicated time points, cells were lysed and examined by immunoblotting with anti-Notch1 ICD (V1744), anti-Flag, or anti-α-tubulin antibodies. Graphs show quantification of the average Notch1 ICDT2122A or Notch1 ICDT2122D expression levels relative to α-tubulin. The relative protein levels were normalized to time point zero. No significance was observed between the groups transfected with control or Eya1 using unpaired two-tail t-test. Error bars represent SEM.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Source data relating to Figure 7B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.023
-
Figure 7—source data 2
Source data relating to Figure 7D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.024
-
Figure 7—source data 3
Source data relating to Figure 7E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.025

Eya1 does not affect the T2487 phosphorylation site of Notch1 ICD, related to Figure 7.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of 293T cells transfected with indicated cDNAs. Pull-down assays using anti-HA antibody and immunoblot with anti-Flag and anti-HA. Input was 5% of the amount of proteins used for IP. (B) Sequence alignment of Notch1 with c-Myc, Cyclin E and c-Jun. The alignment revealed two sites on Notch1, T2122 and T2487, which are similar to other Fbw7 substrates with the Cdc phosphodegrons (CPDs) consensus motif. (C) Notch1 ICD protein stability analysis. 293T cells transfected with indicated plasmids were treated with cycloheximide (CHX). At indicated time points, cells were lysed and examined by immunoblotting with anti-Notch1 ICD (V1744), anti-Flag, or anti-α-tubulin (loading control) antibodies. The results showed that Notch1 ICDT2487A mutant was more stable than WT Notch1 ICD, while Eya1 did not affect the stability of this mutant, indicating that T2487 may not be a target site of Eya1 (n = 3).
Complete western blots for Figure 7 and Figure 7—figure supplement 1.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.022
Model illustrating the role of Eya1 and Notch in regulating neurogenic and non-neuronal lineages during epibranchial placode development.
During PA development, the Eya1+/Sox2+ placodal progenitors formed at E8.0 are separated into two distinct cell populations by E9.0: the Neurog2+ neurogenic cells and the Sox2+/Fgf3+ non-neuronal cells in the proximal PA region, and with further spatial separation at E9.5. Our findings indicate that Notch1 ICD is dephosphorylated and stabilized by Eya1. The Notch1 ICD level is critical to control the cell fate decision for these two distinct cell populations and to regulate neurogenesis, pharyngeal segmentation and development of proximal arches.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Sox2 | Neuromics (Minnesota, USA) | GT15098-100, RRID: AB_2195800 | 1/500, IHC |
| antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Sox3 | R and D systems (Minnesota, USA) | AF2569, RRID: AB_2239933 | 1/500, IHC |
| antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-Jagged1 | DSHB (Iowa, USA) | Ts1.15h, RRID: AB_528317 | 1/300, IHC |
| antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-E-cadherin (24E10) | Cell Signaling Technology (Massachusetts, USA) | 3195, RRID: AB_2291471 | 1/1000, IHC |
| antibody | Mouse polyclonal anti-Eya1(A01) | Abnova (Taiwan) | H00002138-A01, RRID: AB_563241 | 1/300, IHC, WB |
| antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Notch1 (C20) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Texas, USA) | sc-6014; RRID: AB_650336 | 1/400, IHC, WB, IP |
| antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Cleaved Notch1 | Abcam (Hong Kong) | ab52301, RRID: AB_881726 | 1/500, IHC, WB |
| antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti- Cleaved Notch1 (Val1744) | Cell Signaling Technology | 2421S,RRID: AB_2314204 | 1/500, IHC, WB |
| antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Notch3 | BioLegend (California, USA) | 130502, RRID: AB_1227735 | 1/1000, IHC |
| antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti- Phospho-Threonine-Proline | Cell Signaling Technology | 9391S, RRID: AB_331801 | 1/3000, WB |
| antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Phospho-Serine-Proline-Proline motif [pSPP] | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#14390 | 1/1000, WB |
| antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-p-Tyrosine (PY99) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-7020, RRID:AB_628123 | 1/1000, WB |
| antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Neurog2 | R and D systems | MAB3314, RRID:AB_2149520 | 1/1000, IHC |
| antibody | Mouse polyclonal anti-Islet1 | DSHB | PCRP-ISL1-1A9, RRID:AB_2618775 | 1/400, IHC |
| antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-GFP | Abcam | ab6556, RRID:AB_305564 | 1/1000, IHC |
| antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Hes1 | Abcam | ab71559, RRID:AB_1209570 | 1/500, WB |
| antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Hey1 | Abcam | AB22614, RRID:AB_447195 | 1/500, WB |
| antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-GAPDH [6C5] | Abcam | Ab8245, RRID:AB_2107448 | 1/10000, WB |
| antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG(R) M2 | Sigma-Aldrich (Missouri, USA) | F1804, RRID:AB_262044 | 1/500 for IP, 1/4000 for WB |
| antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Flag | Sigma-Aldrich (Missouri, USA) | F7425, RRID:AB_439687 | 1/4000, WB |
| antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-c-Myc (9E10) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-40, RRID:AB_627268 | 1/1000, WB |
| antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Tubulin | DSHB | Cat#AA4.3-s; RRID: AB_579793 | 1/5000, WB |
| antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-HA-probe | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-805, RRID:AB_631618 | 1/1000, WB |
| antibody | Donkey anti-Goat IgG (H + L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 | Thermo Fisher Scientific (Hong Kong) | A-11055, RRID:AB_2534102 | 1/500, IHC |
| antibody | Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A21206, RRID:AB_2535792 | 1/500, IHC |
| antibody | Donkey anti-Rat IgG (H + L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-21208, RRID:AB_2535794 | 1/500, IHC |
| antibody | Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (H + L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 555 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-31570, RRID:AB_2536180 | 1/500, IHC |
| antibody | Donkey anti-Goat IgG (H + L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 594 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11058, RRID:AB_2534105 | 1/500, IHC |
| antibody | Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (H + L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, HRP | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A16017, RRID:AB_2534691 | 1/5000, WB |
| antibody | Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, HRP | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A16035, RRID:AB_2534709 | 1/5000, WB |
| antibody | Donkey anti-goat HRP Conjugate | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2020, RRID:AB_631728 | 1/5000, WB |
| antibody | Anti-Digoxigenin-AP, Fab fragments | Roche (Germany) | Cat#11093274910 | 1/2000, ISH |
| peptide, recombinant protein | 3XFLAG peptide | Sigma-Aldrich (Missouri, USA) | Cat# F4799 | |
| chemical compound, drug | X-tremeGENE 9 DNA Transfection Reagent | Roche | Cat#6365779001 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Proteinase K | Sigma-Aldrich (Missouri, USA) | Cat#P6556 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Cycloheximide | Sigma-Aldrich (Missouri, USA) | Cat#C7698 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Tamoxifen | Sigma-Aldrich (Wisconsin, USA) | Cat#06734 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-al | Sigma-Aldrich (Wisconsin, USA) | Cat#2211 | |
| chemical compound, drug | γ-Secretase inhibitor IX | Calbiochem (California, USA) | Cat#565770 | |
| chemical compound, drug | PhosStop | Roche | Cat#04906837001 | |
| chemical compound, drug | COmplete protease inhibitor cocktail | Roche | Cat#04693132001 | |
| chemical compound, drug | rProtein G Agarose | Invitrogen (Hong Kong) | Cat#15920–010 | |
| chemical compound, drug | DAPI | Sigma-Aldrich (Missouri, USA) | Cat# D9542 | |
| commercial assay or kit | In situ Cell Death Detection Kit, Fluorescein | Roche | Cat#11684795910 | |
| cell line (Human) | HEK 293T cells | ATCC (Virginia, USA) | CRL-3216, RRID: CVCL_0063 | |
| strain, strain background (C57BL/6N) | Mouse: C57BL/6N | Laboratory Animal Unit at the University of Hong Kong | N/A | |
| strain, strain background (C57BL/6N) | Mouse: Sox2-CreER | The Jackson Laboratory (Arnold et al., 2011) | RRID:IMSR_JAX:017593 | |
| strain, strain background (C57BL/6N) | Mouse: Pax2-Cre | A. Grove (Ohyama and Groves, 2004) | RRID:MMRRC_010569-UNC | |
| strain, strain background (C57BL/6N) | Mouse: B2-r4-Cre | K.S.E. Cheah (Szeto et al., 2009) | RRID:MGI:3849737 | |
| strain, strain background (C57BL/6N) | Mouse: Rosa26N1-IC | The Jackson Laboratory (Murtaugh et al., 2003) | RRID:IMSR_JAX:008159 | |
| strain, strain background (C57BL/6N) | Mouse: R26REYFP | The Jackson Laboratory (Srinivas et al., 2001) | RRID:IMSR_JAX:006148 | |
| strain, strain background (C57BL/6N) | Mouse: Eya1-/- | P.X. Xu (Xu et al., 1999) | RRID:MGI:3054666 | |
| strain, strain background (C57BL/6N) | Mouse: Six1-/- | P.X. Xu (Laclef et al., 2003) | RRID:MGI:2655196 | |
| sequence-based reagent | Full list of primers for cloning in Table 2 | N/A | N/A | |
| sequence-based reagent | Full list of primers for genotyping in Table 1 | N/A | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe : Dlx5 | (Liu et al., 1997) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe : Dlx1 | (Qiu et al., 1995) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe : Eya1 | (David et al., 2001) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe : Six1 | (Pandur and Moody, 2000) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe : Sox2 | (De Robertis et al., 1997) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe : Fgf8 | (Crossley and Martin, 1995) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe : Fgf3 | (Wilkinson et al., 1988) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe : Hes1 | (Zheng et al., 2000) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe: Fgfr1 | Addgene (Massachusetts, USA) | Cat# 14005 | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe: Crabp1 | (IMAGE 2922473) | N/A | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | In situ hybridization probe: Neurog2 | (IMAGE 468821) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pcDNA3.1+ | Addgene | Cat# V790-20 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pcDNA3.1-Myc-N1ICD | C.C. Hui (Toronto, Canada) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pCS2+-N1DEF-Myc | U. Lendahl (Chapman et al., 2006) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pcDNA5-FRT-TO-N1FL-Myc | U. Lendahl (Chapman et al., 2006) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | P3XFLAG-myc-CMV-26 | Sigma-Aldrich (Missouri, USA) | Cat# E6401 | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pCMV-3XFlag-N1ICD | This paper | N/A | Generated by cloning the N1ICD fragment into thepCMV-3XFlag-Myc-26 vector between BamHI and EcoRI sites |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pCMV-3XFlag-N1ICDT2122A | This paper | N/A | Point mutation, primers listed in Table 2 |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pCMV-3XFlag-N1ICDT2122D | This paper | N/A | Point mutation, primers listed in Table 2 |
| transfected construct (mouse) | pCMV-3XFlag-N1ICDT2487A | This paper | N/A | Point mutation, primers listed in Table 2 |
| transfected construct (mouse) | Flag-Eya1 | P.X. Xu (Li et al., 2017) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | HA-Eya1 | P.X. Xu (Li et al., 2017) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | Flag-Eya1D327N | P.X. Xu (Li et al., 2017) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | Flag-Eya1C | P.X. Xu (Li et al., 2017) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | Flag-Eya1N | P.X. Xu (Li et al., 2017) | N/A | |
| transfected construct (mouse) | Flag-Eya1-DYY | This paper | N/A | Point mutation, primers listed in Table 2 |
| transfected construct (mouse) | Flag-Eya1-Y4 | This paper | N/A | Point mutation, primers listed in Table 2 |
| transfected construct (human) | pCMV-Myc CDC4 WT* | Addgene | Cat# 16652 | |
| transfected construct (human) | HA-Ubiquitin | Addgene | Cat# 18712 | |
| software, algorithm | ImageJ | http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ | ImageJ, RRID:SCR_003070 | |
| software, algorithm | Prism Version 6 | http://www.graphpad.com | GraphPad Prism, RRID:SCR_002798 |
Sequences of primers for genotyping.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.027| Mouse line | Primer sequence | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Six1 knock-out | GenoFF: 5’ TCCCACCACTTCTTATCCTAG 3’ Exon1R: 5’ AGTGAGCAGAGCTGGGAGAG 3’ LacZR: 5’ TCTTCGCTATTACGCCAGCTG 3’ | Laclef et al. (2003) |
| Eya1 knock-out | GenoF2: 5’ ATGTCTGGTTTTAGTTAGGC 3’ WR2: 5’ AAACTCAGTCTGGGCACCAAG 3’ Neo240F: 5’ CAAGCAAAACCAAATTAAGGG 3’ | Xu et al., 1999 |
| Pax2-Cre Sox2-CreER B2-R4-Cre | Cre A: 5’ ACGGAAATCCATCGCTCGACCAGTT 3’ Cre S: 5’ GTCCGGGCTGCCACGACCAA 3’ | N/A |
| RosaN1-IC | WT F: 5’ TAACCTGGTGTGTGGGCGTTGT 3’ WT R: 5’ AATCTGTGGGAAGTCTTGTCC 3’ Mutant F: 5’ ACCCTGGACTACTGCGCCC 3’ Mutant R: 5’ CGAAGAGTTTGTCCTCAACCG 3’ | Murtaugh et al. (2003) |
Sequences of primers for cDNA cloning.
The bases in red indicate the mutated sites.
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| N1ICD_T2122A-F | CTGCCCTGGGTGGCCCCACTCTGTCTCC |
| N1ICD_T2122A-R | GGAGACAGAGTGGGGCCACCCAGGGCAG |
| N1ICD_T2122D-F | CTGCCCTGGGTGGCCCCACTCTGTCTCC |
| N1ICD_T2122D-R | GGAGACAGAGTGGGGCCACCCAGGGCAG |
| N1ICD_T2487A-F | AGCACCCCTTCCTCCCATCCCCTGAGTC |
| N1ICD_T2487A-R | GACTCAGGGGATGGGAGGAAGGGGTGCT |
| Eya1DYY-F | AGTTCACAGCAGCCGTCTCCCGGCTTTGGCCAG |
| Eya1DYY-R | CTGGCCAAAGCCGGGAGACGGCTGCTGTGAACT |
| Eya1Y4-F | CAGGGTCAGGCACAGAACAGCTCGCCGCCAGCACAC |
| Eya1Y4-R | GTGTGCTGGCGGCGAGCTGTTCTGTGCCTGACCCTG |
| Hey1-F | AGAACTAGTGGATCCATGAAGAGAGCTCAC |
| Hey1-R | CTTGATATCGAATTCTTAGAAAGCTCCGAT |
| Brn1 (Pou3f3)-F | AGAACTAGTGGATCCTCAAACAGCGGCGCA |
| Brn1 (Pou3f3)-R | CTTGATATCGAATTCAGTTCACGGGACCTT |
| Dll1-F | AGAACTAGTGGATCCATCTGTCTGCCAGGG |
| Dll1-R | CTTGATATCGAATTCGCACCGTTAGAACAA |
| Fgf15-F | AGAACTAGTGGATCCCAGTTGCTTTGTGGG |
| Fgf15-R | CTTGATATCGAATTCAGTTCACGGGACCTT |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30126.029





