Nanos promotes epigenetic reprograming of the germline by down-regulation of the THAP transcription factor LIN-15B
Figures
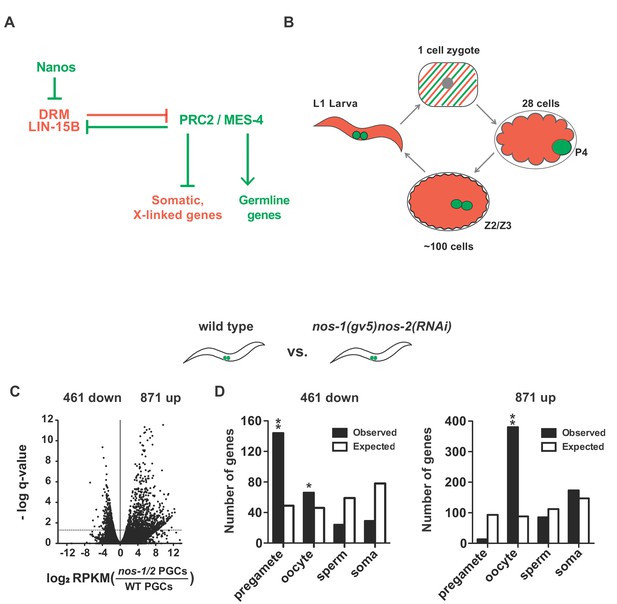
nos-1nos-2 PGCs upregulate transcripts expressed in oocytes.
(A) Mutual antagonism between DRM/LIN-15B transcription factor and PRC2/MES-4 chromatin modifiers balances activities that promote somatic (red) and germline (green) gene expression. In somatic lineages, LIN-15B and DRM transcription factors opposes PRC2 to silence germline genes (Petrella et al., 2011). In pregametic germ cells, PRC2 activates germline genes (with the help of MES-4) and silences somatic genes and X-linked genes, including genes expressed in oocytes (e.g. lin-15B) (Gaydos et al., 2012). In this study, we show that Nanos is required to remove maternally-inherited LIN-15B from PGCs to allow proper PRC2/MES-4 function. (B) Germline cycle in C. elegans. The zygote (stripped red and green) inherits from the oocyte maternal mRNAs that promote the development of somatic (red) and germline (green) cell fates during embryogenesis. P4 is the germline founder cell that gives rise to Z2 and Z3, the two primordial germ cells. Z2 and Z3 do not divide and remain mostly transcriptionally quiescent during embryogenesis. They resume division and transcription in the first larval stage (L1). (C–D). Transcriptome comparison between PGCs isolated from wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) L1 larvae using SMART-seq libraries (Materials and methods, See Figure 1—figure supplement 1B–C for results with Truseq libraries). (C) Volcano plot showing log2 fold-change in transcript abundance for each gene. The number of genes that were significantly up or downregulated in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) (designated as nos-1/2) PGCs are indicated. Dashed line marks the significance cutoff of q = 0.05 (Y axis) above which genes were counted as misexpressed. (D) Bar graphs showing expected and observed number of genes (Y axis) in different expression categories (X axis). Genes were assigned to a particular expression category based on their preferential expression patterns as determined in (Gaydos et al., 2012; Ortiz et al., 2014); Materials and methods and Supplementary file 1). The lists are non-overlapping and include 1694 pregamete genes, 1594 oocyte genes, 2042 sperm genes, and 2684 somatic genes. Oocyte genes include genes required for oogenesis and maternal genes required for embryogenesis. Because genes were categorized based on their preferential gene expression pattern, genes on one list may also be expressed in other tissues. See Supplementary file 1 for complete gene lists. Pregamete and oocyte genes are overrepresented among downregulated genes and oocyte genes are overrepresented among upregulated genes. Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.01 [*] or <0.001 [**]).
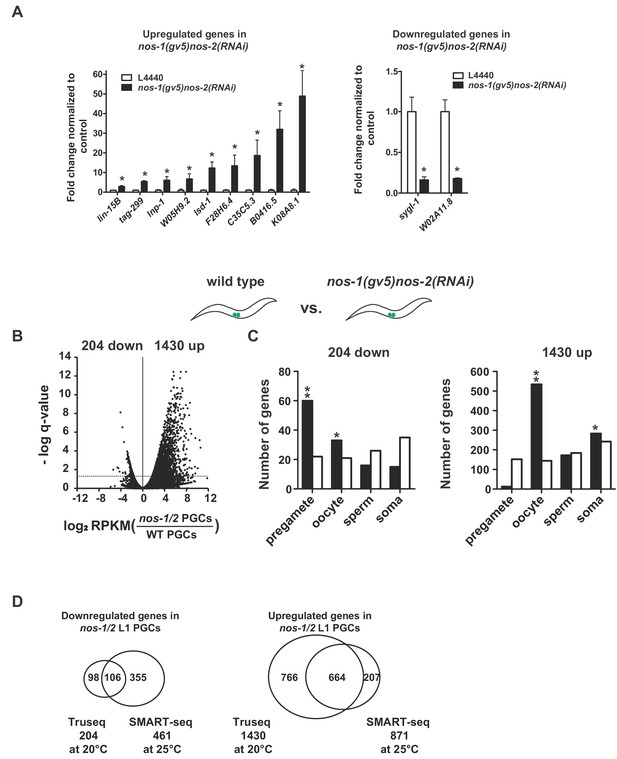
nos-1nos-2 PGCs upregulate transcripts expressed in oocytes.
(A) Bar graph showing results of quantitative RT-PCR of 11 genes significantly misexpressed in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) PGCs. (*p<0.05 using Student’s t-test). (B–C) Transcriptome comparison between PGCs isolated from wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) L1 larvae using Truseq libraries (see Materials and methods). (B) Volcano plot showing log2 fold-change of gene expression between PGCs isolated from wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) L1 larvae (designated as nos-1/2). The numbers of genes that were significantly up or downregulated in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) PGCs are indicated. Dashed lines mark the significance cutoff of q = 0.05 above which genes were counted as misexpressed. (C) Bar graph showing expected and observed number of genes (Y axis) in different expression categories (X axis). Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.01 [*] or <0.001 [**]). (D) Venn diagrams showing overlap between misregulated genes identified in the Truseq (Figure 1-figure supplement 1B and 1C) and SMART-seq analyses (Figure 1C and 1D) (transcriptome comparison between wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) L1 larvae).
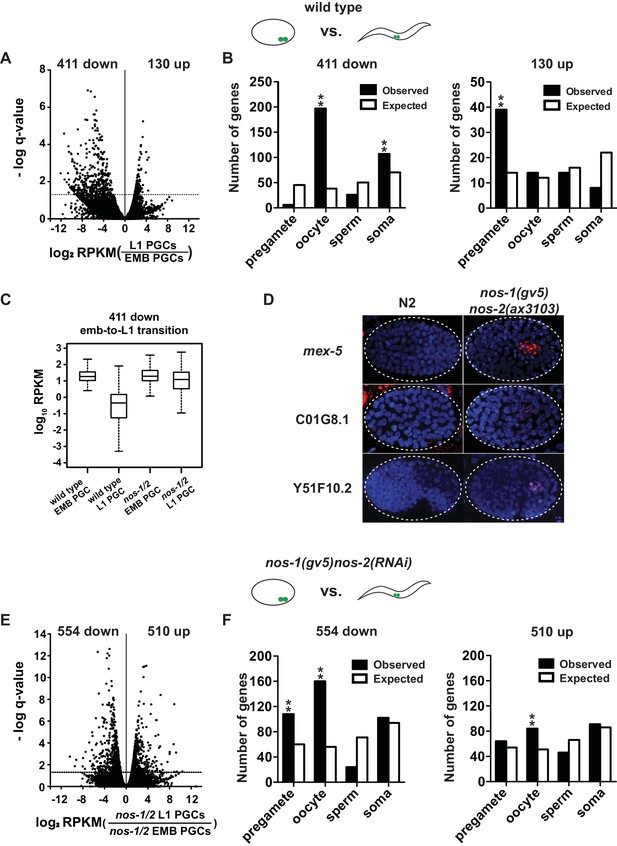
nos-1nos-2 PGCs are defective in maternal mRNA turnover during embryogenesis.
(A–B) Transcriptome comparison between PGCs isolated from wild-type embryos and wild-type L1 larvae. (A) Volcano plot showing log2 fold-change in transcript abundance for each gene. The numbers of genes whose expression were up or downregulated in L1 PGCs compared to embryonic PGCs are indicated. Dashed line marks the significance cutoff of q = 0.05 above which genes were counted as misexpressed. (B) Bar graphs showing expected and observed number of genes (Y axis) in the different expression categories (X axis). The lists of expression categories used here are the same as those in Figure 1B (Supplementary file 1). Oocyte and soma genes are overrepresented among downregulated genes and pregamete genes are overrepresented among upregulated genes. Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]). (C) Box and whisker plot showing the expression levels (log10) of 411 genes that are downregulated during embryogenesis in wild-type PGCs. Expression of these genes remains high on average in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) PGCs (designated as nos-1/2). Each box extends from the 25th to the 75th percentile, with the median indicated by the horizontal line; whiskers extend from the 2.5th to the 97.5th percentiles. (D) Photomicrograph of embryos hybridized with single molecule fluorescence probes (red) against mex-5, C01G8.1 and Y51F10.2. Wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) embryos were raised at 25°C and are compared here at the same stage (as determined by the number of DAPI-stained nuclei shown in blue). By the stages shown, all three transcripts have turned over in wild-type (N2), but are still present (red signal) in PGCs in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) embryos. At least 10 embryos were examined per probe set in different genotypes shown. (E–F) Transcriptome comparison between PGCs isolated from nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) embryos and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) (designated as nos-1/2) L1 larvae. (E) Volcano plot showing log2 fold-change in transcript abundance for each gene. The numbers of genes whose expression were up or downregulated in L1 PGCs compared to embryonic PGCs are indicated. Dashed lines mark the significance cutoff of q = 0.05 above which genes were counted as misexpressed. (F) Bar graphs showing expected and observed number of genes (Y axis) in the different expression categories (X axis). Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]).
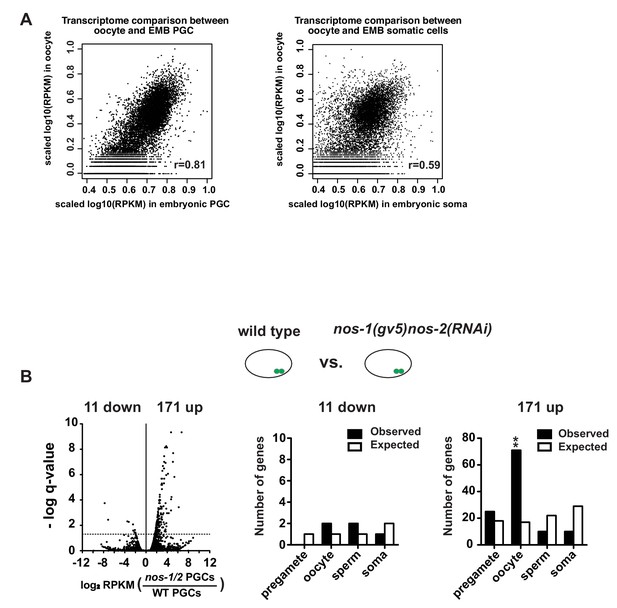
Maternal RNAs are maintained in early embryonic PGCs.
(A) XY scatter plots showing correlation of gene expression between wild-type embryonic PGCs (X axis) and oocyte transcriptome (Y axis) (Left panel) and correlation of gene expression between wild-type embryonic somatic blastomeres (X axis) and oocyte transcriptome (Y axis) (Right panel). High Pearson correlation value was obtained for embryonic PGCs versus oocyte (R = 0.81), but not for embryonic soma versus oocyte (R = 0.59). For these analyses, information of oocyte transcriptome was obtained from Stoeckius et al. (2014). To compare two transcriptomes, level of gene expression (RPKM) was first subjected to log10 transformation and followed by internal scaling with the range of gene expression in each transcriptome. Plots were generated using R. (B) Transcriptome comparison between PGCs isolated from wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) embryonic PGCs. Left: Volcano plot showing log2 fold-change of gene expression between PGCs isolated from nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi)(labeled as nos-1/2) and wild-type embryonic PGCs. Middle and Right: Bar graph showing expected and observed number of genes in the different expression categories. Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]).
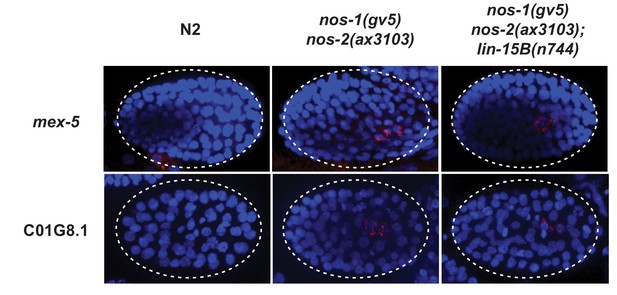
Perdurance of maternal RNAs is not suppressed by loss of lin-15B in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) PGCs.
Photomicrograph of embryos hybridized with single molecule fluorescence probes (red) against mex-5 and C01G8.1. Wild-type, nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103);lin-15B(n744) embryos were raised at 25°C for 8 hr prior for sample preparation. Samples are compared here at the same stage (as determined by the number of DAPI-stained nuclei shown in blue). By the stages shown, both transcripts have turned over in wild-type (N2), but are still present (red signal) in PGCs in both nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103);lin-15B(n744) embryos. At least 10 embryos were examined per probe set and for each genotype.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
R code for comparing transcriptome between oocyte and embryonic blastomeres.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.008
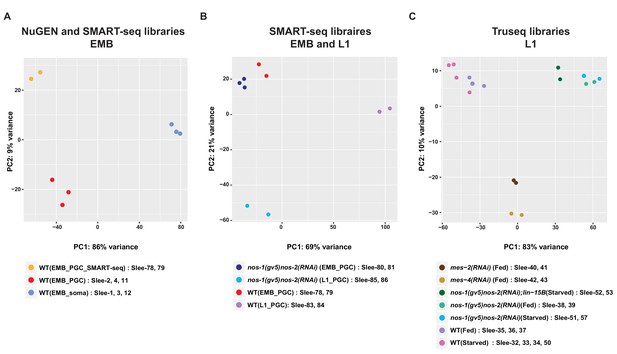
Principal component analysis (PCA) of transcriptomes from isolated PGCs.
PCA of biological replicates from different development stages and library preparation methods across two principal components (PC1 and PC2). (A) PCA of embryonic samples [embryonic PGCs and somatic cells] using NuGEN or SMARTseq library preparation methods. (B) PCA of transcriptomes from embryonic or L1 PGCs. (C) PCA of transcriptomes from 17 L1 PGC samples.
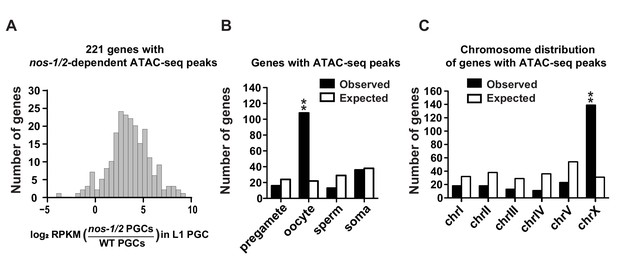
nos-1nos-2 L1 PGCs activate the transcription of oocyte and X-linked genes.
(A) Histogram showing the distribution of log2 fold change in gene expression between nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) (designated as nos-1/2) and wild-type L1 PGCs for 221 genes that acquired new ATAC-seq peaks in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) PGCs (Supplementary file 2). Consistent with ATAC-seq peaks denoting open chromatin, most genes are expressed at higher levels in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) PGCs compared to wild-type. (B) Bar graph showing expected and observed number of genes with nos-1nos-2 -dependent ATAC-seq peaks in the different expression categories. Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]). (C) Bar graph showing the chromosomal distribution of genes with nos-1nos-2 -dependent ATAC-seq peaks. Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]).
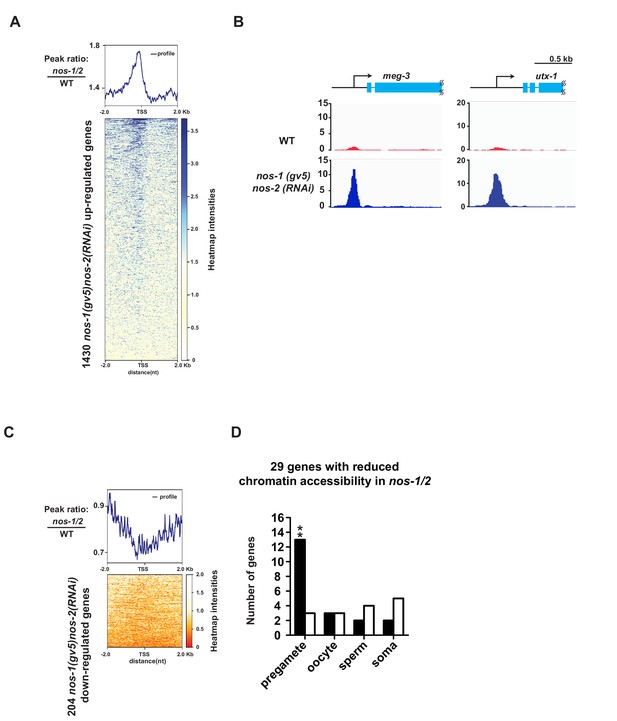
ATAC-seq reveals abnormal chromatin profile of nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) PGCs.
(A) Heat map showing accumulated ATAC-seq reads of 1430 genes (Y axis) that are upregulated genes in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) L1 PGCs compared to wild-type (as determined by Truseq, see Figure 1—figure supplement 1 and Materials and methods). 4 kb across transcription start site (TSS) are plotted on the heatmap (X axis). Darker color indicates accumulated ATAC-seq reads (open chromatin) in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi). See Materials and methods for detailed description of the data analysis. See Supplementary file 5 for lists of genes with differential expression in PGCs. nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) is labeled as nos-1/2 in this figure. (B) Genome browser view of ATAC-seq profiles for meg-3 and utx-1. Transcripts for both genes were significantly upregulated in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) over wild-type L1 PGCs (See expression level in Supplementary file 4). The promoters of meg-3 and utx-1 are more accessible in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) compared to wild-type PGCs. Y-axis shows normalized coverage read counts. (C) Heat map showing ATAC-seq reads for 204 downregulated genes in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) compared to wild-type L1 PGCs. 4 kb across transcription start site (TSS) were plotted on the heatmap. In the heatmap, darker color (red) indicates more reads (open chromatin) in wild-type PGCs. See Materials and methods for detail description of data analysis. (D) Bar graph showing expected and observed number of genes with reduced chromatin accessibility in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) compared to wild-type L1 in four different expression categories. Consistent with previous RNA-seq analysis, pregamete genes are overrepresented among genes with reduced chromatin accessibility. Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]).
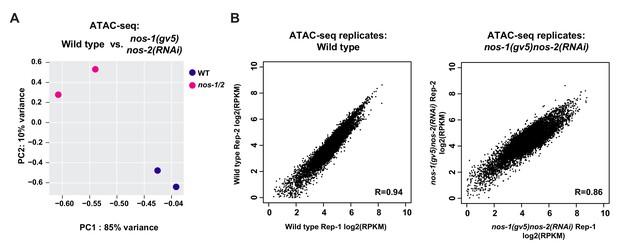
Analysis of reproducibility between ATAC-seq samples.
(A) PCA of ATAC-seq peaks between replicates. (B) Scatter plots comparing the ATAC-Seq peak scores (RPKM) between replicates. RPKM values for each replicate were obtained from DiffBind analysis. The Pearson correlation of the RPKM values are shown. Detail description of correlation analysis is listed in Materials and methods section.
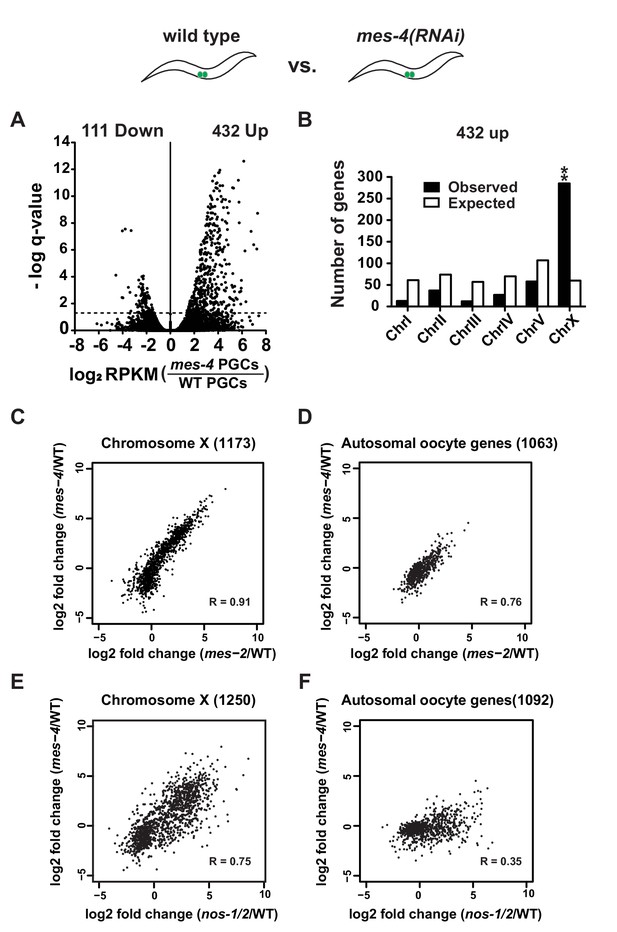
mes-4 and nos-1nos-2 PGCs exhibit a similar defect in X-chromosome silencing.
(A–B) Transcriptome comparison between PGCs isolated from wild-type and mes-4(RNAi) L1 larvae. See Figure 4—figure supplement 2 for comparison between wild-type and mes-2(RNAi). (A) Volcano plot showing log2 fold-change in transcript abundance for each gene. The numbers of genes whose expression were up or downregulated in mes-4(RNAi) PGCs are indicated. Dashed lines mark the significance cutoff of q = 0.05 above which genes were counted as misexpressed. (B) Bar graph showing chromosomal distribution of mes-4(RNAi) upregulated genes. Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]). (C–D) XY scatter plots showing correlation of the fold change in gene expression between mes-2(RNAi) (X-axis) and mes-4(RNAi)(Y-axis) PGCs compared to wild-type for X-linked genes and autosomal oocyte genes. Pearson correlation values are indicated. (E–F) XY scatter plots showing correlation of the fold change in gene expression between nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) (X-axis) and mes-4(RNAi) (Y-axis) PGCs compared to wild-type for X-linked genes and autosomal oocyte genes. Pearson correlation values are indicated.
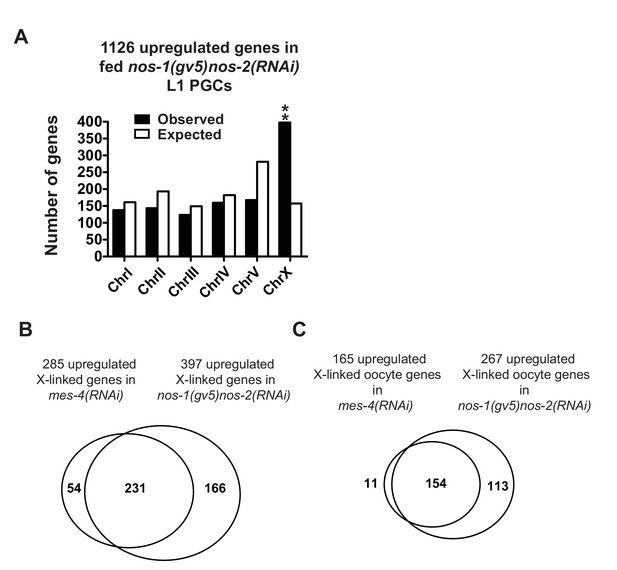
nos-1nos-2 PGCs share a defect in X chromosome silencing with mes-4 PGCs.
(A) Bar graph showing chromosomal distribution of nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) upregulated genes (fed L1, Truseq libraries). Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]). (B, C) Venn diagram showing overlap between nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) and mes-4(RNAi) L1 PGCs for upregulated X-linked genes (B) or for upregulated X-linked oocyte genes (C).
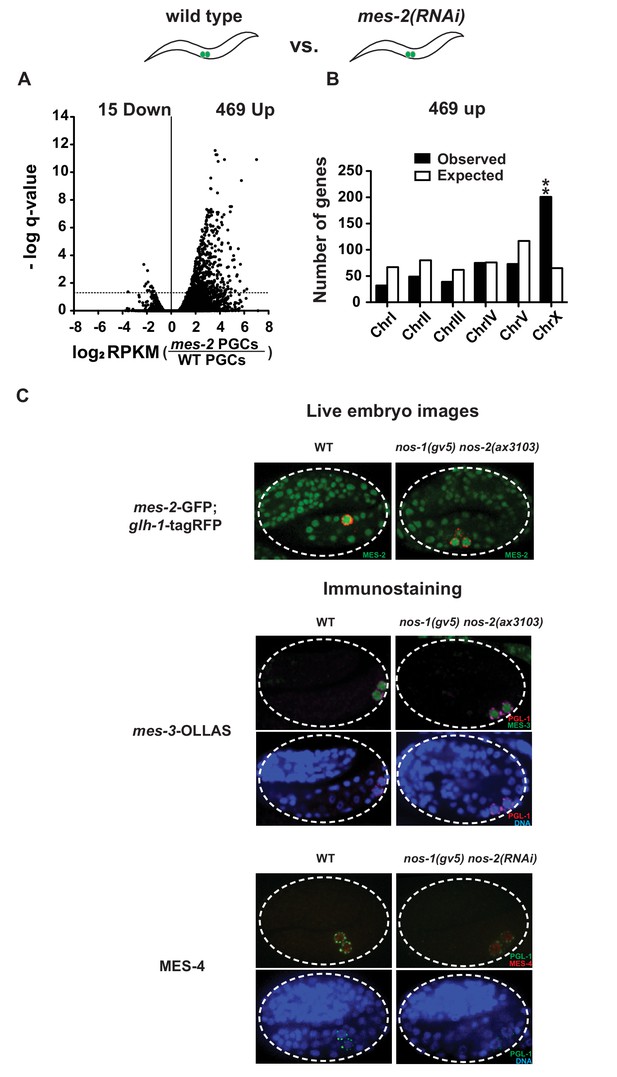
MES proteins are expressed in nos-1nos-2 embryonic PGCs.
Transcriptome comparison between PGCs isolated from wild-type and mes-2(RNAi) L1 larvae. (A) Volcano plot showing log2 fold change of gene expression between mes-2(RNAi) and wild-type L1 PGCs. The numbers of genes whose expression were up or downregulated in mes-2(RNAi) compared to wild-type L1 PGCs are indicated. Dashed lines mark the significance cutoff of q = 0.05 above which genes were counted as misexpressed. (B) Bar graph showing chromosomal distribution of mes-2(RNAi) upregulated genes. Asterisks indicate significantly more genes than expected (hypergeometric test, p-value<0.001 [**]). (C) Top: Photomicrograph of live embryo expressing GFP tagged MES-2 in wild- type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) embryos. Middle: Photomicrograph of fixed wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) embryos expressing OLLAS tagged MES-3. Bottom: Photomicrograph of fixed wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) embryos stained with α-MES-4 antibody and K76 α-PGL-1 antibody. Images of 2-fold+ stage embryos were taken.
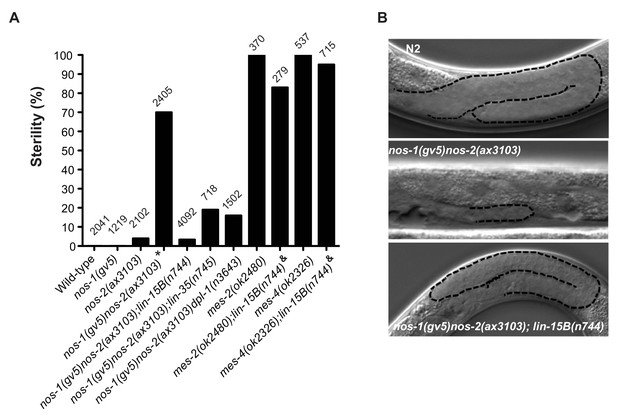
Suppression of nos-1nos-2 sterility by lin-15b and synMuvB mutants.
(A) Bar graph showing the % sterility at 20°C among progenies of hermaphrodites with the listed genotypes. lin-15B(n744) and lin-35(n745) are null alleles(Ferguson and Horvitz, 1989; Lu and Horvitz, 1998; Petrella et al., 2011). dpl-1(n3643) is a loss of function allele (Ceol and Horvitz, 2001) mes-2(ok2480) and mes-4(ok2326) are deletion alleles that causes 100% maternal-effect sterility (C. elegans Deletion Mutant Consortium et al., 2012). Number of progenies scored is written above indicated genotypes. * nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) hermaphrodites produce 70% sterile progenies at 20°C and 96% sterile progeny at 25°C with severely atrophied germlines (Figure 5B). nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103);lin-15B(n744) hermaphrodites produce 96.6% fertile progenies at 20°C, and arrest as larvae at 26°C as is true of lin-15B(n744) animals. & mes-2(ok2480);lin-15B(n744) and mes-4(ok2326);lin-15B(n744) hermaphrodites cannot be maintained as selfing populations. (B) Nomarski images of germlines (stippled) in L4 hermaphrodites of the indicated genotypes. Worms were staged according to vulva morphology. Note the atrophied germline in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) that is rescued to wild-type size in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103);lin-15B(n744).
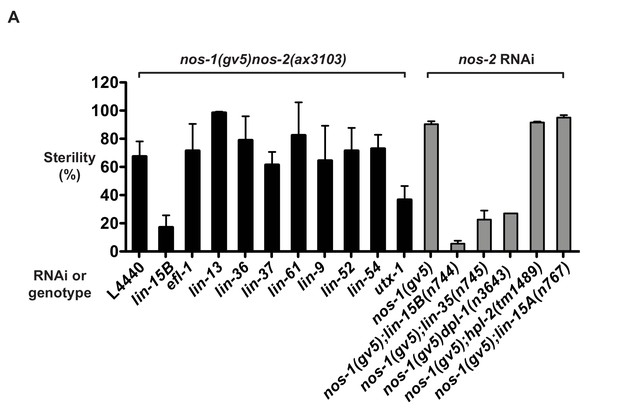
Suppression of nos-1nos-2 sterility by synMuvB mutants.
(A) Bar graphs showing percent sterility among worms of the indicated genotypes. Black bars: nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) mutant were fed with bacteria expressing dsRNA to genes indicated and the sterility of their progeny were scored. Gray bars: nos-1(gv5);synMuvB double mutants were fed with bacteria expressing nos-2 dsRNA and the sterility of their progenies were scored. Error bars report S.D. from ≥2 experiments.
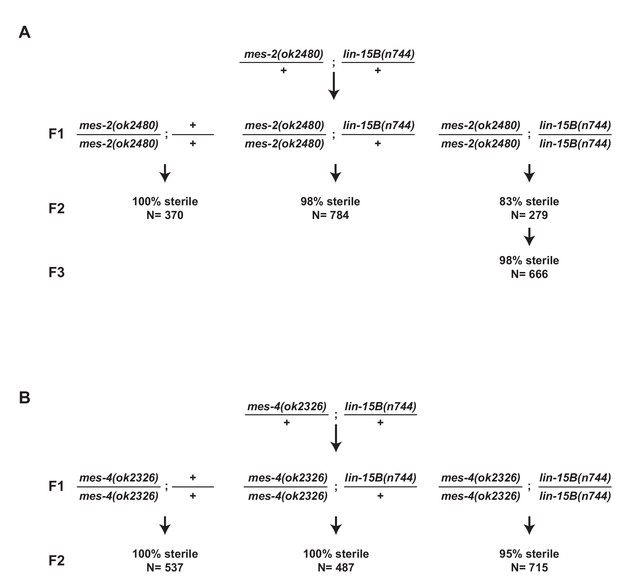
Loss of lin-15B does not rescue mes maternal effect sterility.
(A,B) Schemes for testing maternal effect sterility of mes-2(ok2480);lin-15B(n744) and mes-4(ok2326);lin-15B(n744) animals. (A) First generation (F1) mes-2(ok2480);lin-15B(n744) animals were derived from mes-2(ok2480)/+;lin-15B(n744)/+ hermaphrodites. The sterility of their progeny (F2) was scored. Loss of lin-15B suppressed mes-2(ok2480) maternal-effect sterility weakly for one generation (83% sterile F2). The percent sterility rose back up in the F3 generation (98%) and the line could not be maintained. (B) Loss of lin-15B suppressed mes-4(ok2326) maternal-effect sterility weakly (95% sterile F2). Line cannot be maintained as selfing populations.
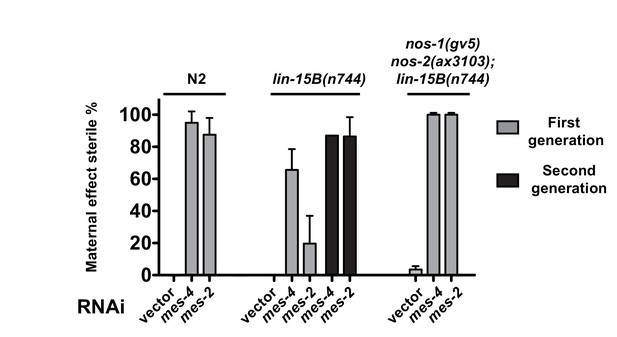
Suppression of nos-1nos-2 sterility by loss of lin-15B depends on mes activity.
Bar graphs showing percent sterility among animals with indicated genotypes and RNAi treatments. N2, lin-15B(n744) and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103);lin-15B(n744) were fed with bacteria expressing dsRNA to genes indicated and the sterility of their progeny were scored in either the first generation (gray bars) or the second generation (black bars). lin-15B(n744) partially suppresses mes maternal effect sterility in the first generation consistent with the result shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 2A, but not in the second generation (~86% sterility). Error bars report S.D. from ≥2 experiments.
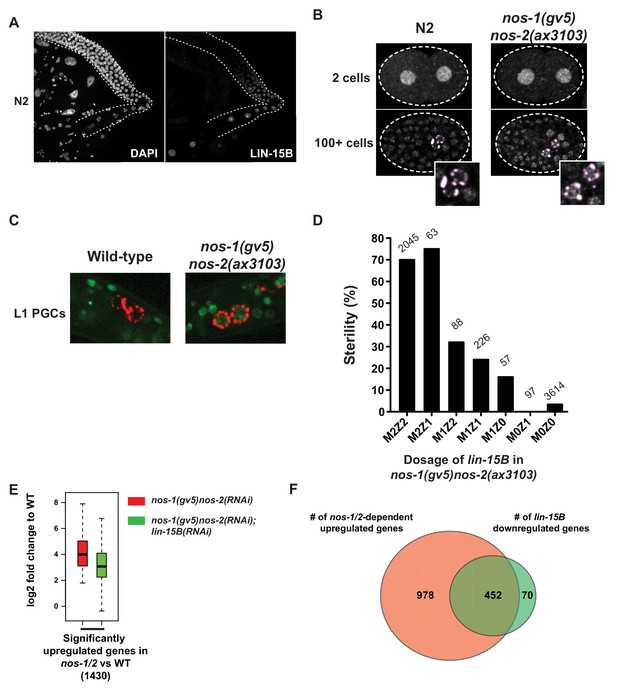
LIN-15B is inherited maternally and is downregulated in PGCs in a nos-1nos-2 dependent manner.
(A) Photomicrograph of a dissected wild-type gonad stained with anti-LIN-15B antibody and DAPI for DNA. LIN-15B protein is detected at the end of the pachytene region and in all oocyte nuclei. (B) Photomicrographs of fixed wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) embryos stained with α-LIN-15B and K76 (α-PGL-1, pink) antibodies. The α-LIN-15B polyclonal serum cross-reacts with perinuclear germ granules (pink color, see Materials and methods). 45/60 PGCs were positive for LIN-15B in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) embryos compared to 0/34 in wild-type. (C) Photomicrographs of newly hatched gonads from wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) L1 larvae with a paternal copy of the lin-15B transcriptional reporter (green). 12/16 nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) PGC doublets were positive for GFP compared to 0/28 in wild-type. See Figure 6—figure supplement 1B and C for description of the lin-15B transcriptional reporter. (D) Bar graph showing the sterility of nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) hermaphrodites with different dosages of maternal (M) and zygotic (Z) lin-15B at 20°C. M2Z2 denotes hermaphrodites with two doses of wild-type maternal LIN-15B and two doses of wild-type zygotic LIN-15B. Mating schemes are shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Number of hermaphrodites scored is written above each genotype. (E) Box and Whisker plot showing log2 fold change compared to wild-type of 1430 genes that are upregulated in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) (designated as nos-1/2) L1 PGCs. Each box extends from the 25th to the 75th percentile, with the median indicated by the horizontal line; whiskers extend from the 2.5th to the 97.5th percentiles. The upregulation is reduced in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi);lin-15B(RNAi) PGCs. See Figure 6—figure supplement 3 for additional comparisons. (F) Venn diagram showing overlap between 1430 genes upregulated in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) (designated as nos-1/2) compared to wild-type L1 PGCs (red) and downregulated genes in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi);lin-15B(RNAi) compared to nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) L1 PGCs (522 genes, green).
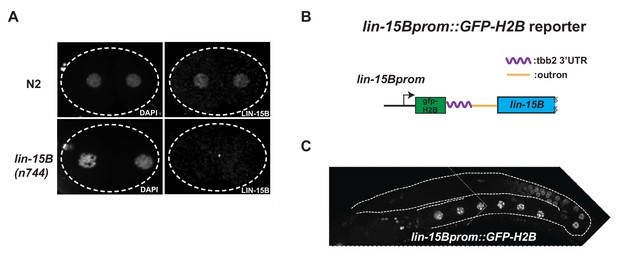
Expression oflin-15Bbegins in late pachytene germ cells.
(A) Photomicrograph of 2 cells wild-type and lin-15B(n744) embryos stained with α-LIN-15B antibody. α-LIN-15B is specific as no nuclear signal was detected in lin-15B(n744) embryos. (B) Cartoon diagram showing the lin-15B transcriptional reporter. GFP::Histone-H2B::tbb-2 3’ UTR::gpd-2/3 outron was inserted at 5’ end of lin-15B ORF in an operon configuration to preserve the function of endogenous lin-15B. (C) Photomicrograph of adult hermaphrodite expressing the lin-15B transcriptional reporter. Germline is outlined. Expression in the lin-15B promoter reporter begins in late pachytene germ cells committed to oogenesis.
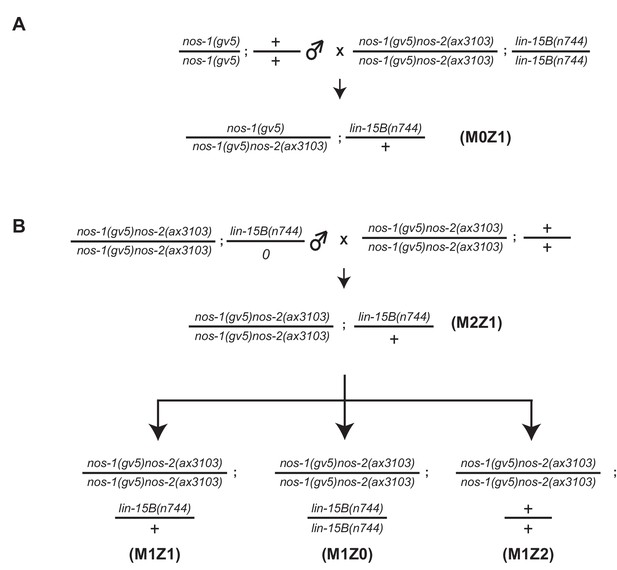
Assay for maternal and zygotic contribution of lin-15B in nos-1nos-2 sterility.
(A–B) Mating schemes to characterize the maternal and zygotic contribution of lin-15B in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103). lin-15B genotypes were determined by Sanger sequencing (See key resources table for PCR/sequencing oligos).
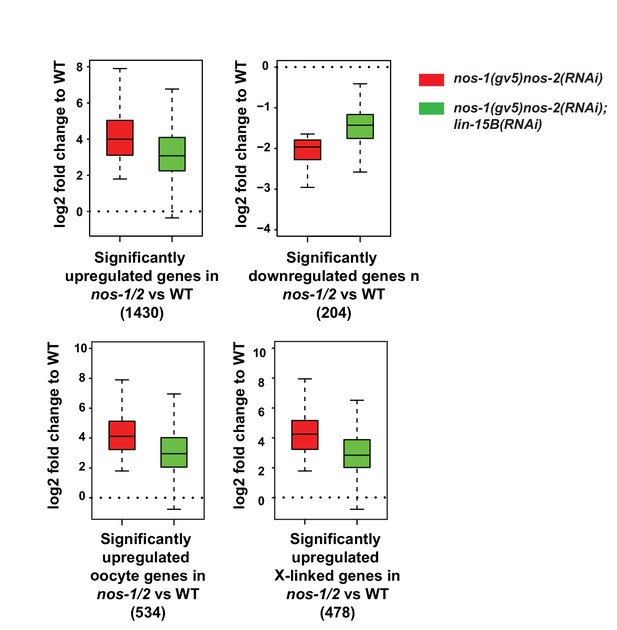
Loss of lin-15B activity mitigates gene expression changes in nos-1nos-2 PGCs.
Box and Whisker plot showing log2 fold change compared to wild-type of different gene sets as depicted under each plot. Each box extends from the 25th to the 75th percentile, with the median indicated by the horizontal line; whiskers extend from the 2.5th to the 97.5th percentiles. Misregulation of all gene sets is reduced in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi);lin-15B(RNAi) PGCs.
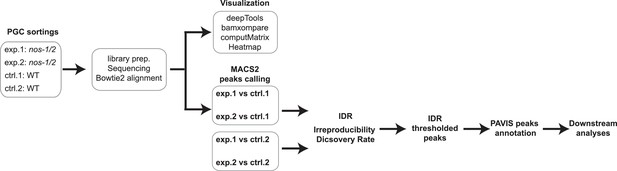
Experimental procedure for ATAC-seq analysis.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.024Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH1270 | Subramaniam and Seydoux (1999) | RRID:WB-STRAIN:JH1270 | nos-1(gv5) |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3103 | This study | nos-1(gv5); lin-15A(n767) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | TH206 | (http://www.modencode.org). | RRID:WB-STRAIN:TH206 | unc-119(ed3) III; ddEx16 |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3099 | This study | unc-119(ed3) III; ddEx16 out cross x2 | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | MT1806 | CGC | RRID:WB-STRAIN:MT1806 | lin-15A(n767) |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | PFR40 | CGC | RRID:WB-STRAIN:PFR40 | hpl-2(tm1489) |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | MT2495 | CGC | RRID:WB-STRAIN:MT2495 | lin-15B(n744) |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | MT10430 | CGC | RRID:WB-STRAIN:MT10430 | lin-35(n745) |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | MT11147 | CGC | RRID:WB-STRAIN:MT10430 | dpl-1(n3643) |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3109 | This study | nos-1(gv5); hpl-2(tm1489) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3119 | This study | nos-1(gv5); lin-35(n745) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3121 | This study | nos-1(gv5); lin-15B(n744) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3141 | This study | nos-1(gv5) dpl-1(n3643) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3357 | This study | nos-2(ax3103) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3367 | This study | nos-1(gv5) nos-2(ax3103)/MnC1 | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3401 | This study | nos-1(gv5); nos-2(ax3103); lin-15B(n744) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3428 | This study | mes-2(ax2509 [mes-2::GFP]); tagRFP::glh-1 | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3436 | This study | tagRFP::glh-1; nos-1(gv5); lin-15B(ax3104) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3484 | This study | mes-3(ax3105 [mes-3::OLLAS]) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3486 | This study | mes-3(ax3105 [mes-3::OLLAS]); nos-1(gv5) nos-2 (ax3103)/MnC1 | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3203 | CGC | RRID:WB-STRAIN:JH3203 | mes-2(ax2059 [mes-2::GFP]) |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3510 | This study | mes-2(ax2509[mes-2::GFP]); tagRFP::glh-1; nos-1(gv5) nos-2(ax3103)/MnC1 | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3513 | This study | gtbp-1(axls3105[gtbp-1 prom::GFP-H2B::lin-15B 3'utr]); tagRFP::glh-1; nos-1(gv5) nos-2(ax3103)/MnC1 | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3531 | This study | dpl-1(n3643) nos-1(gv5)nos-2(ax3103) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3538 | This study | lin-35(n745); nos-1(gv5) nos-2(ax3103) | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | VC2409 | CGC | RRID:WB-STRAIN:VC2409 | mes-2(ok2480)/mT1 II; +/mT1 [dpy-10(e128)] III |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | VC1874 | CGC | RRID:WB-STRAIN:VC1874 | mes-4(ok2326) V/nT1[qls51] (IV;V) |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3357 | This study | nos-2(ax3103). Deletion of nos-2 ORF. See Supplementary file 6 for description. | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3436 | This study | lin-15B(ax3104). lin-15B prom::GFP-H2B::tbb-2 3'UTR. See Supplementary file 6 for description. | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans) | JH3484 | This study | mes-3(ax3105). mes-3::OLLAS. See Supplementary file 6 for description. | |
| antibody | K76 | DSHB,PMID:28787592 | RRID:AB_531836 | (1:15) |
| antibody | Anti-FLAG M2 | Sigma-Aldrich Cat# F3165 | RRID:AB_259529 | (1:200) |
| antibody | Donkey-anti-mouse IgM 647 | Jackson Immuno Research Labs | RRID:AB_2340861 | (1:400) |
| antibody | Goat anti-Rabit IgG (H + L) 568 | Molecular probes cat# A-11011 | RRID:AB_143157 | (1:400) |
| antibody | Anti-OLLAS-L2 | Novus cat# NBP1-06713 | RRID:AB_1625979 | (1:200) |
| antibody | anti-LIN-15B | other | gift from Dr. Susan Strome, SDQ3183 1:40,000 | |
| antibody | anti-MES-4 | other | gift from Dr. Susan Strome. (1:400) | |
| antibody | anti-OLLAS | other | gift from Dr. Jeremy Nathans (1:80) | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL584 | This study | GAUCUUCUAGAAAGAAUCUU; crRNA cut at 3' end of nos-2 | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL669 | This study | AGAGUCGAAGUCGGUUCACU; crRNA cut at 5' end of nos-2 | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL823 | This study | GCACUGCUACUGCUGGAAGU; crRNA cut at 5' end of lin-15B | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL957 | This study | GGGAUAAUCTAAUUAGAAGA; crRNA cut at 3' end of mes-3 | |
| sequence-based reagent | AP691 | Paix et al. (2015) | GGCCTTAACCCAGAATAAGA; crRNA cut at 5' end of gtbp-1 | |
| sequence-based reagent | AP728 | Paix et al. (2015) | CACGAGGTGGTATGCGCAG; crRNA cut at 3' end of gtbp-1 | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL251 | This study | TGGAAAGTTGAGTGTGAGCA; Forward K08A8.1 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL252 | This study | GGAGAATGTTTGATGGCTTCAC; Reverse K08A8.1 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL259 | This study | CCTGAGAAGAAGCTGCAAATG; Forward W02A11.8 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL260 | This study | TTTATGTCCTTTGGCAAAACGG; Reverse W02A11.8 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL304 | This study | CTGCTATTGTGAAGTCTCCTG; Forward B0416.5 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL305 | This study | CCATTTGTGGCTTACTAGCG; Reverse B0416.5 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL308 | This study | TGTCAGTTTGTGATGTGCTG; Forward C35C5.3 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL309 | This study | GCTTCAAAATCGTCCTTTTCATG; Reverse C35C5.3 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL738 | This study | ACTGGACGATTTCAACGGAG; Forward lin-15B RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | CYL739 | This study | ACATACTGCACAGCGACG; Reverse lin-15B RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL994 | This study | AGTCGGTATTTTGAATGCGG; Forward lsd-1 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL995 | This study | CGTTTCCGAGTGATCTGATTG; Reverse lsd-1 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL998 | This study | AATCCGTTTGACTATGAGTGG; Forward W05H9.2 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL999 | This study | TCGTTTAGAAGCTACAATGACAG; Reverse W05H9.2 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL1006 | This study | GAAGTTACCCGTCGCAAG; Forward F28H6.4 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL1007 | This study | GCCACTGTTTTGTAATCCCG; Reverse F28H6.4 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL1010 | This study | ACTTTGCGATAAACTCCCTTC; Forward tag-299 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL1011 | This study | GCTTGCAGACACGAAGATAAG; Reverse tag-299 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL1020 | This study | CGAATGCGGACATCTTAATCC; Forward lnp-1 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL1021 | This study | GTTGACGGCTTCTGATTCTC; Reverse lnp-1 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL1044 | This study | TGGTTATGTGCAACACTTGG; Forward sygl-1 RT-PCR primer | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL1045 primer | This study | TCTCGCTACGATCCTTCTTC; Reverse sygl-1 RT-PCR | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL438 | This study | CAGCTCGAAACCTGAAAATTGT;Forward PCR primer for nos-2 locus. 179 bp upstream of nos-2 ATG. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL734 | This study | GCCATCACCTATGCGATTTG; Reverse PCR primer for nos-2 locus. 468 bp after nos-2 STOP. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL735 | This study | GTTGTGGCGGAAAGGAATAC; Reverse PCR primer for nos-2 locus, 154 bp after nos-2 ATG. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL43 | This study | ATGTTGATTTTCAGGACTTCTC; Forward PCR primer for nos-1 locus. seq from + 1- + 22 | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL45 | This study | ACGAAGCATCACCTGGAG; Forward PCR primer for nos-1 locus. seq from + 901–918 (ORF seq). | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL407 | This study | CGTTGAAACTTTGAAGAAAGACATC; Forward PCR primer for nos-1 locus. seq from + 901–918 (ORF seq). | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL361 | This study | GATGATTGTTGGAGAGGACG; Reverse PCR primer for lin-15B locus. Pair with oCYL363 to generated a PCR fragment contains n744 mutation. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL363 | This study | GCACAAACCTGGAGATCG; Forward PCR primer for lin-15B locus. 200 bp upstream of n744 mutation. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL374 | This study | AGAAGATGATGATTATGAGGAGG; Forward PCR primer for lin-35(n745) locus. 395 bp up stream of n745 mutation. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL375 | This study | GAAGAAGCAGCAGAGTAAATTC; Reverse PCR primer for lin-35(n745) locus. 276 bp down stream n745 mutation. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL402 | This study | TGGAGACTACAAATCCCACAG; Forward PCR primer for dpl-1 (n3643) locus, 270 bp up stream of n3643 site. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL405 | This study | GTACGTAATATCGTTTGGTAACGG; Reverse PCR primer for dpl-1(n3643) locus,270 bp down stream of n3643 site. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL668 | This study | Repair ssODN for nos-2 deletion. See Supplementary file S10 for sequence information. | |
| sequence-based reagent | oCYL977 | This study | Repair ssODN for mes-3 C'ter OLLAS tag. See Supplementary file S10 for sequence information. | |
| sequence-based reagent | gBLOCK4 | This study | First 138nt is gpd-2/3 outron followed by the sequence of recoded first 20 amino acid of LIN-15B. See Supplementary file S10 for sequence information. | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pSL270 | This study | contains GFP-H2B::tbb2 3'UTR from pCFJ420 and gpd-2/3 outron plus 60 nt lin-15B 5' sequence from gBLOCK4 | |
| software, algorithm | Diffbind | DOI: 10.18129/B9.bioc.DiffBind | RRID:SCR_012918 | |
| software, algorithm | hisat2 | DOI:10.1038/nprot.2016.095 | RRID:SCR_015530 | |
| software, algorithm | htseq-count | DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638 | RRID:SCR_011867 | |
| software, algorithm | cuffdiff | http://cole-trapnell-lab.github.io/cufflinks/ | RRID:SCR_001647 | |
| software, algorithm | Slidebook 6 | https://www.intelligent-imaging.com/slidebook | RRID:SCR_014300 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Gene categories.
These categories were based on previously published data sets as described in methods section.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.025
-
Supplementary file 2
Genes with nos-1nos-2-dependent chromatin features.
Excel sheet 1. List of 221 genes that acquired open chromatin in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) L1 PGCs. Excel sheet 2. List of 29 genes that acquired close chromatin in nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) L1 PGCs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.026
-
Supplementary file 3
Average gene expression level between x-linked and autosomal genes.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.027
-
Supplementary file 4
Expression level of selected genes.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.028
-
Supplementary file 5
Lists of differential expression analyses.
Data sheets contain significantly up- and downregulated genes from pairwise comparisons using ciffdiff as described in the methods section. FPKM values were extracted from differential expression analysis between wild-type and nos-1(gv5)nos-2(RNAi) PGCs using SMART-seq libraries.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.029
-
Supplementary file 6
Information for strains generated by CRISPR/cas9.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.030
-
Supplementary file 7
Information for sequencing libraries.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.031
-
Supplementary file 8
List of embryonic Z2/Z3 enriched genes.
From purified embryonic cells, we identified 1347 PGC enriched genes (enrichment over somatic blastomeres). In this table, we cross-referenced our embryonic PGC enriched gene set with other published PGC or germline enriched gene sets. 392/1347 embryonic PGC enriched genes were identified as PGC enriched genes in Spencer et al., 2011- Supplementary file 2 (in which 979 genes with enriched expression in Z2/Z3); 700/1347 were characterized as either germline specific or germline enriched genes in Gaydos et al., 2012.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.032
-
Supplementary file 9
Gene count tables for PCA plots.
Sheet 1. A table contains HTseq-count output using all Truseq libraries. Sheet 2. A table contains HTseq-count output using SMART-seq libraries.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.033
-
Supplementary file 10
Additional sequence information for oligos.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.034
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30201.035





