A compartmentalized signaling network mediates crossover control in meiosis
Figures
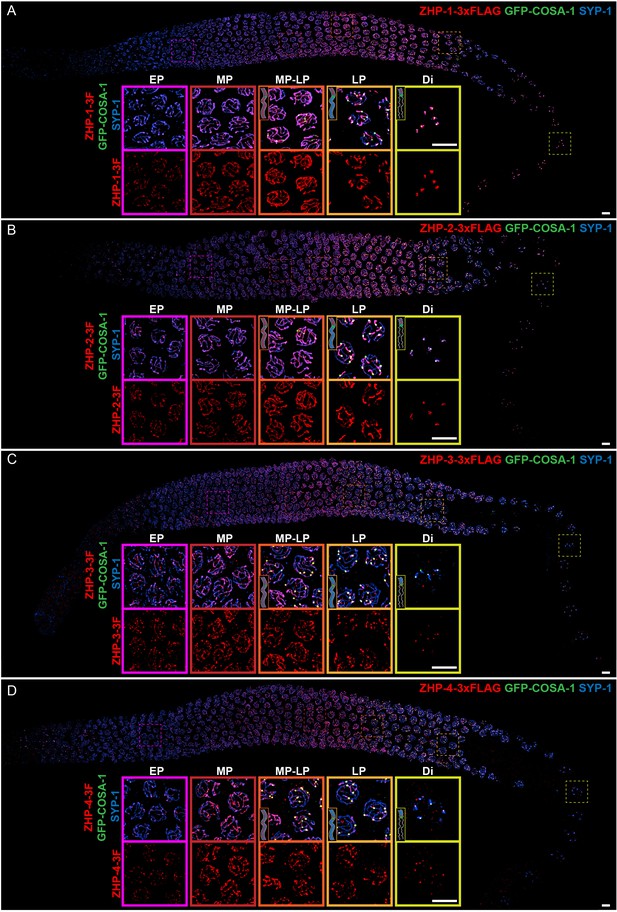
ZHP proteins exhibit two distinct patterns of dynamic localization.
(A–D) Projection images showing immunofluorescent localization of 3xFLAG tagged ZHP-1 (A), ZHP-2 (B), ZHP-3 (C) and ZHP-4 (D) relative to SCs (marked by SYP-1) and CO sites (marked by GFP-COSA-1) from mitosis to early diakinesis in the germ line. Insets in each panel show representative images of ZHP localization in (left to right) early pachytene (EP), mid-pachytene (MP), late pachytene (LP) and diplotene (Di) nuclei. Inserts show diagrams to clarify the localization patterns of ZHPs (red) from MP to Di. Gray lines, blue line and green focus represent the chromosome axis, central region of the synaptonemal complex (SC) and CO site, respectively. ZHP-1 and ZHP-2 show identical dynamics: they localize to assembling SCs, and upon the appearance of COSA-1 foci they become restricted to the short arm of each bivalent. ZHP-3 and ZHP-4 also mirror each other, localizing initially throughout the SC, and then accumulating at one site along each chromosome pair, concomitant with the appearance of COSA-1 at these sites. By late pachynema, 100% of GFP-COSA-1 foci colocalize with ZHP-4 puncta (n = 2,700 COSA-1 foci in 450 nuclei from eight gonads [11 rows of cells per gonad] were scored). 3F indicates 3xFLAG. Scale bars, 5 µm.
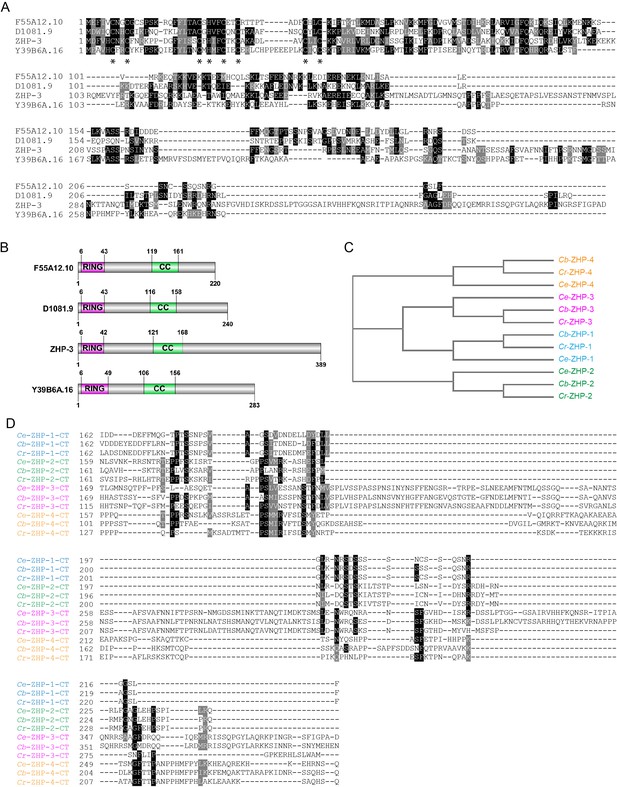
Sequence alignment of C. elegans ZHPs, and the evolution of ZHPs in nematodes.
(A) Sequence alignment of C. elegans F55A12.10 (ZHP-1), D1081.9 (ZHP-2), K02B12.8 (ZHP-3) and Y39B6A.16 (ZHP-4) generated with T-Coffee (Notredame et al., 2000). Dark and gray shading indicate identical and similar residues, respectively. Asterisks indicate residues involved in zinc coordination. (B) Schematic showing the domain organization of the four ZHP proteins. RING: RING finger domain; CC: coiled coil. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. (C) Phylogenetic relationship of ZHPs from different Caenorhabditids: Ce, C. elegans, Cb, C. briggsae; Cr, C. remanei. (D) Sequence alignment of the C-terminal domain of the four ZHPs from Caenorhabditids. The C-termini of the same ZHP protein from different nematodes are much more conserved than the C-termini of the different ZHPs from the same nematode. CT: C-terminus. Dark and gray shading indicate identical and similar residues, respectively.
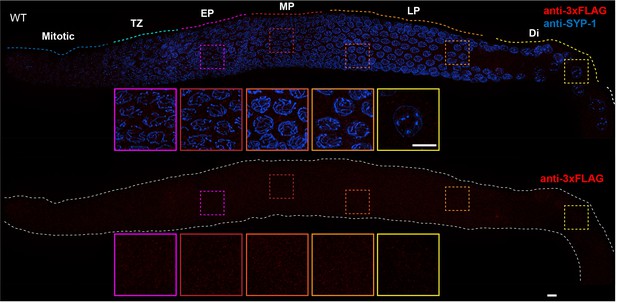
Absence of nonspecific staining with anti-FLAG antibodies in the C. elegans germline.
Projection images showing C. elegans germline immunostained with anti-3xFLAG epitope antibody (red) and anti-SYP-1 antibody (indicating synaptonemal complex (SC), blue). Insets in each panel show representative nuclei (left to right) in early pachytene (EP), mid-pachytene (MP), late pachytene (LP) and diplotene (Di). Anti-FLAG antibody staining shows no obvious unspecific signal in the germline. Mitotic and TZ indicate Mitotic zone and Transition Zone, respectively. WT: wild-type. Scale bars, 5 µm.
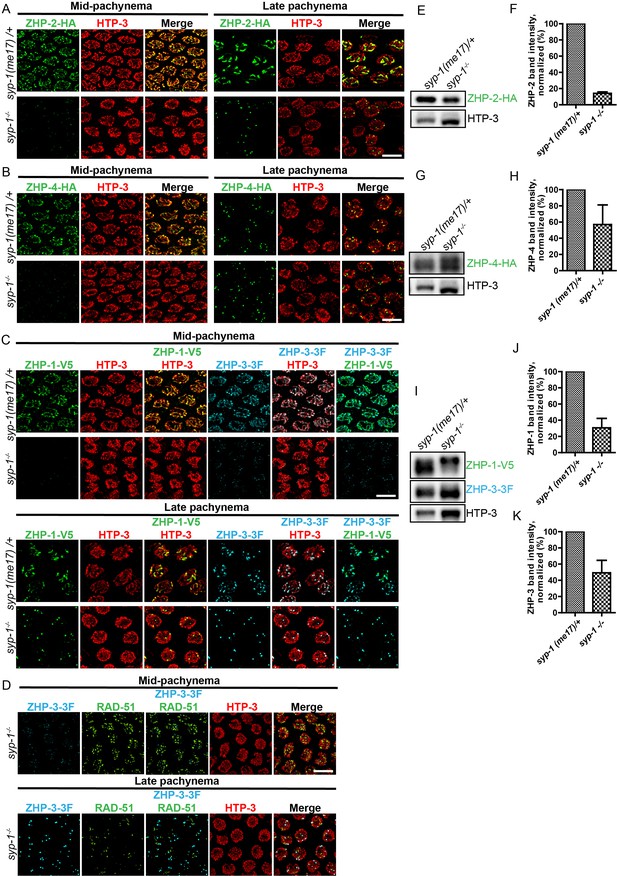
Localization of the ZHPs along meiotic chromosomes depends on SCs.
(A,B) Projection images of mid- and late pachytene nuclei, showing the localization of ZHP-2-HA (A) and ZHP-4-HA (B) in syp-1 mutant hermaphrodites and heterozygous controls. Chromosome axes are marked by HTP-3 (red). (C) Projection images of mid- and late pachytene nuclei showing the localization of ZHP-1-V5 (green) and ZHP-3-3xFLAG (cyan) in syp-1 mutants and control animals. Chromosome axes are marked by HTP-3 (red). Association of ZHPs along chromosomes was abolished in the absence of synapsis. (D) Projection images of mid- and late pachytene nuclei showing the localization of ZHP-3-3xFLAG (cyan) and RAD-51 (green) in syp-1 mutants. Chromosome axes are marked by HTP-3 (red). The nuclear puncta of ZHP-3 do not colocalize with DSB repair sites. Scale bars, 5 µm. (E,G,I) Western blots showing the abundance of ZHP proteins in syp-1 mutants and control worms. Protein from an equal number of animals was loaded in each lane, and HTP-3 was blotted as a loading control. (F,H,J,K) Quantification of Western blots. The ZHP band intensity was normalized against HTP-3 and expressed as percentage of the intensity in a control sample. Data are presented as mean ±SD protein levels from three independent experiments.
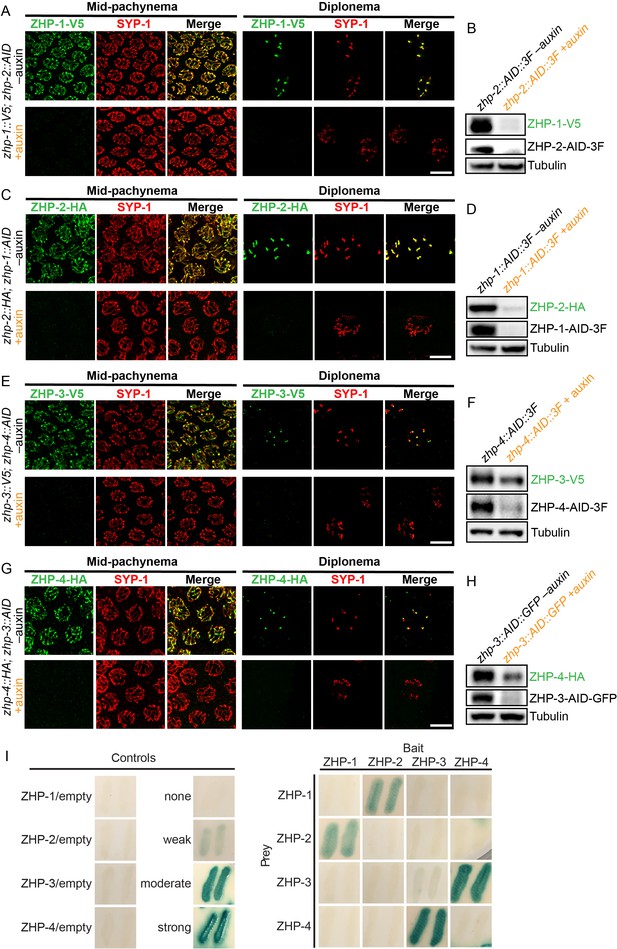
ZHPs likely act as two heterodimeric protein complexes.
(A–H) Projection images of mid-pachytene and diplotene nuclei, showing the localization of ZHPs (green), with corresponding Western blots to assess protein levels in the presence and absence of their partners. SCs are marked by SYP-1 (red). Tubulin was blotted as a loading control. Localization of each ZHP to SCs was abolished when its partner was depleted by auxin treatment for 24 hr. In the absence of their partners, the ZHPs were also destabilized. Scale bars, 5 µm. (I) Yeast 2-hybrid interactions monitored by β-galactosidase expression reveal specific interactions between ZHP-1 and ZHP-2, and ZHP-3 and ZHP-4, respectively. No interactions were detected for other combinations. ‘Empty’ indicates the same vector with no insert. None control: pPC97 and pPC86 with no insert; weak control: pPC97-human RB amino acids 302–928 and pPC86-human E2F1 amino acids 342–437; moderate control: pPC97-Drosophila DP amino acids 1–377 and pPC86-Drosophila E2F amino acids 225–433; and strong control: pPC97-rat cFos amino acids 132–211 and pPC86-mouse cJun amino acids 250–325.
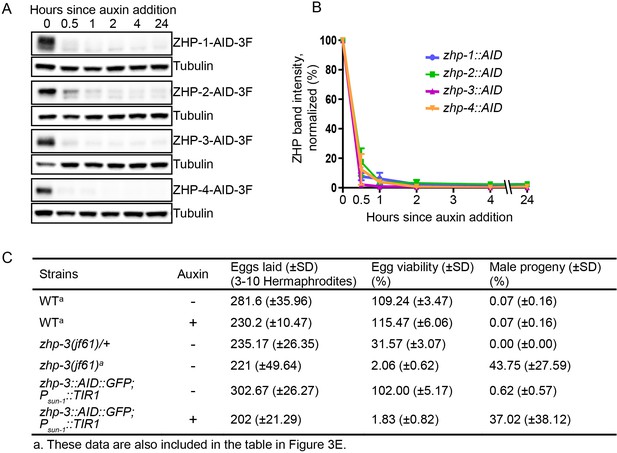
Depletion of ZHP proteins using the AID system.
(A) Western blots showing robust, rapid degradation of AID-tagged ZHP proteins in animals exposed to 1 mM auxin. Blots were done with anti-FLAG and anti-tubulin antibodies, respectively. Tubulin was blotted as a loading control. 3F: 3xFLAG. (B) Degradation kinetics of AID-tagged ZHPs. Proteins were quantified by Western blotting, normalized against tubulin controls. The graph shows the mean ±SD protein levels from three independent experiments. (C) Frequencies of males and viable embryos observed among whole broods for the indicated genotypes and conditions. No meiotic defects were observed in animals expressing ZHP-3-AID under standard culture conditions, but in the presence of 1 mM auxin this strain quantitatively phenocopies a zhp-3(jf61) null mutant. Reported viability of >100% is a consequence of failing to count some embryos.
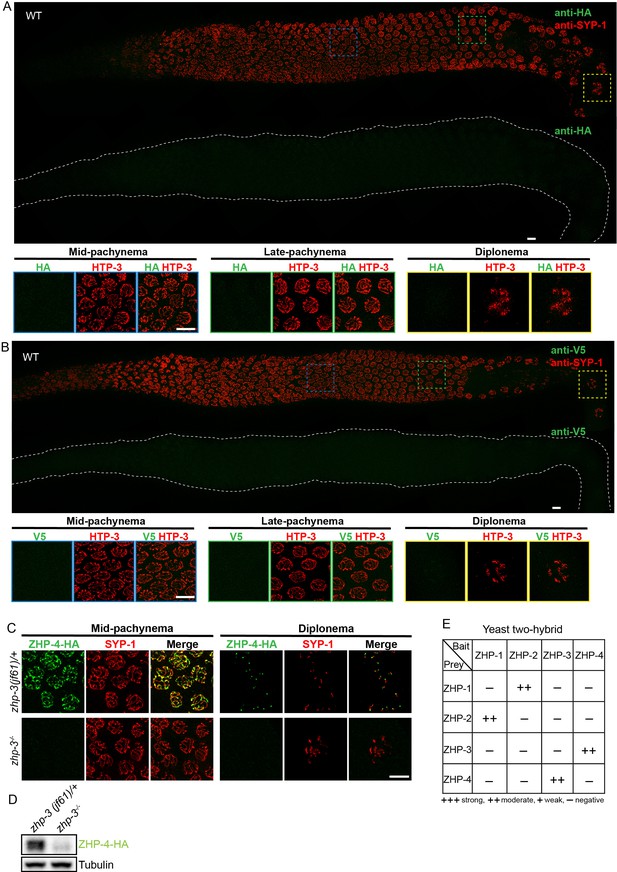
Additional antibody validation, ZHP-4 in zhp-3 mutants, and yeast 2-hybrid analysis of ZHP protein interactions.
(A,B) Projection images showing dissected C. elegans gonads stained with anti-HA antibodies (green) (A) or anti-V5 antibodies (green) (B), and anti-SYP-1 antibodies (red). Anti-epitope antibodies do not appear to detect endogenous proteins in wild-type C. elegans. WT: wild-type. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) Projection images of pachytene and diplotene nuclei in zhp-3 null mutants, revealing that the localization of ZHP-4 (green) to SCs depends on ZHP-3. Chromosome axes are marked by HTP-3 (red). Scale bars, 5 µm. (D) Western blot showing protein levels of ZHP-4 in zhp-3 null mutants and controls. (E) The yeast two-hybrid assay reveals specific interactions between ZHP-1 and -2, and ZHP-3 and -4. No interactions were detected among other combinations of ZHP proteins. Summary of the interactions derived from β-galactosidase, HIS+3AT, and URA expression assays are shown in this table. ++ indicates a moderately strong interaction.
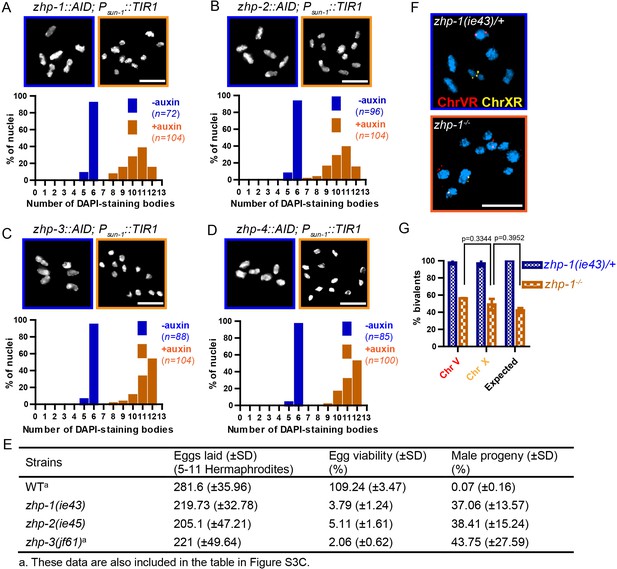
ZHP proteins play a central role in chiasma formation and meiotic chromosome segregation.
(A–D) Upper: DAPI-stained oocyte nuclei at late diakinesis. Each panel shows a representative nucleus. Lower: Graphs indicating the distribution of DAPI-staining bodies observed at diakinesis. ZHPs tagged with AID in a Psun-1::TIR1 background were treated with or without auxin for 24 hr. In the absence of auxin, each nucleus contains six bivalents (homolog pairs held together by chiasmata). Depletion of ZHP-1 or -2 leads to a marked decrease in bivalents per nucleus (8–12 DAPI-staining bodies, or 0–4 bivalents), while depletion of ZHP-3 or -4 results in a complete loss of bivalents (12 DAPI-staining bodies). n is the number of nuclei scored for each condition or genotype. Depletion of ZHP-1,–2, −3 or −4 significantly increase the number of DAPI-staining bodies (***p<0.0001 by Chi-square test for trend). The difference between ZHP-1 depletion and ZHP-2 depletion or ZHP-3 depletion and ZHP-4 depletion is not significant (p=0.7537 and 0.9760, respectively, by Chi-square test for trend). The difference between depletion of ZHP-1 or ZHP-2 and depletion of ZHP-3 or ZHP-4 is significant (***p<0.0001 by Chi-square test for trend). (E) Frequencies of males and viable embryos observed among the whole broods in wild-type, zhp-1, zhp-2 and zhp-3 null mutant hermaphrodites. (F–G) Sex chromosomes and autosomes show a similar reduction in chiasma formation in the absence of ZHP-1. (F) High magnification images of nuclei at late diakinesis from zhp-1 heterozygous controls and null mutant hermaphrodites, hybridized with FISH probes recognizing either the right end of X-chromosome or 5S rDNA on Chromosome V, and stained with DAPI. (G) Graph showing the frequency of bivalents observed for Chromosome V and the X Chromosome. ‘Expected value’ is the frequency for any single chromosome, given the average number of bivalents we observed, and assuming that they were distributed equally among six chromosome pairs. Data were derived from the number of DAPI-staining bodies in zhp-1 heterozygotes and null mutants. Data are represented as mean ±SEM from three independent experiments (n = 103 and 145 nuclei, respectively). Significance was tested using the two-sided Student’s t-test. Scale bars, 5 µm.
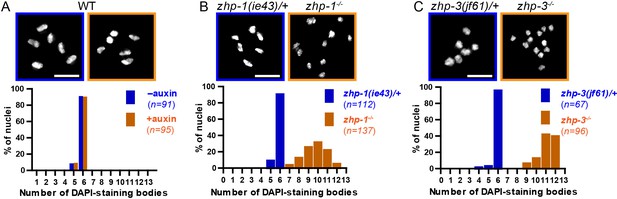
Chiasma formation in zhp-1 or zhp-3 null mutants.
(A–C) Null mutations in zhp-1 and zhp-3 quantitatively recapitulate the effects of AID-mediated depletion. Upper: Representative examples of DAPI-stained oocyte nuclei at diakinesis. Lower: Graphs indicating the distribution of nuclei containing various numbers of DAPI-staining bodies. Note: the observed number of DAPI-staining bodies, on average, is slightly lower than the true mean, since occasionally univalent or bivalent chromosomes in the same nucleus cannot be clearly resolved. (A) Auxin treatment does not impair chiasma formation in wild-type hermaphrodites (p=0.8670 by Chi-square test for trend). (B) A few bivalents are detected in zhp-1 null mutants, as in zhp-1::AID animals treated with 1 mM auxin. (C) No bivalents are observed in zhp-3 null mutants, as in zhp-3::AID hermaphrodites exposed to auxin. The difference in bivalents observed in zhp-1 and zhp-3 null mutants is significant (p<0.0001 by Chi-square test for trend). n is the number of nuclei scored for each condition or genotype. Scale bars, 5 µm.
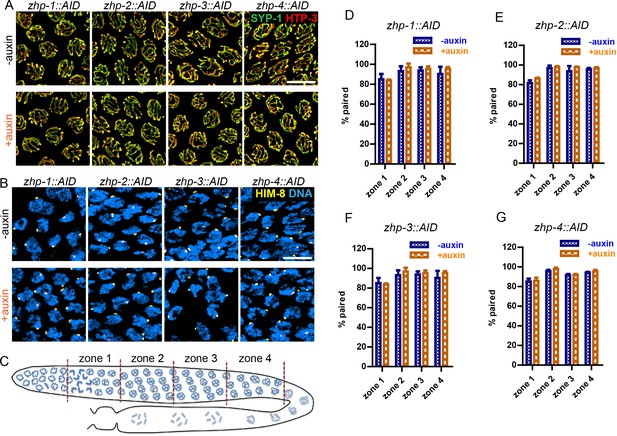
ZHP are dispensable for homolog pairing and synapsis.
(A) Projection images of representative pachytene nuclei stained for SYP-1 (green) and HTP-3 (red), revealing normal synapsis in ZHP-depleted worms. Animals expressing the indicated transgene, along with germline-expressed TIR1 protein (Zhang et al., 2015) were incubated on plates with or without 1 mM auxin for 24 hr before dissection. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Images of representative early prophase nuclei stained for HIM-8 (yellow), which specifically marks the pairing center region of the X chromosome (Phillips et al., 2005), and DNA (blue). Robust pairing of HIM-8 foci in early meiotic prophase is observed. Homologous pairing at other chromosomal loci was confirmed by FISH (data not shown). Scale bars, 5 µm. (C) Diagram of a hermaphrodite gonad, indicating the four zones in which homolog pairing was scored. (D–G) Quantification of the pairing of X chromosomes. Gonads were divided into four zones of equal length, spanning the meiotic entry through late pachytene region. Pairing was evaluated as previously described (Harper et al., 2011). The average percentage of nuclei with paired X chromosomes is plotted for each zone. Data are presented as mean ±SD (n = 3 gonads for each genotype or condition). No pairing defects were detected following depletion of ZHP-1,–2, −3, or −4 (p=0.7059, 0.3631, 0.6188, 0.3064, 0.0554, 0.5515, 0.2639, 0.4158, 0.1893, 0.9247, 0.8599, 0.3740, 0.7631, 0.1672, 0.7879 and 0.2935, respectively, from zone 1 to zone 4, and zhp-1::AID to zhp-4::AID, two-sided Student t-test).
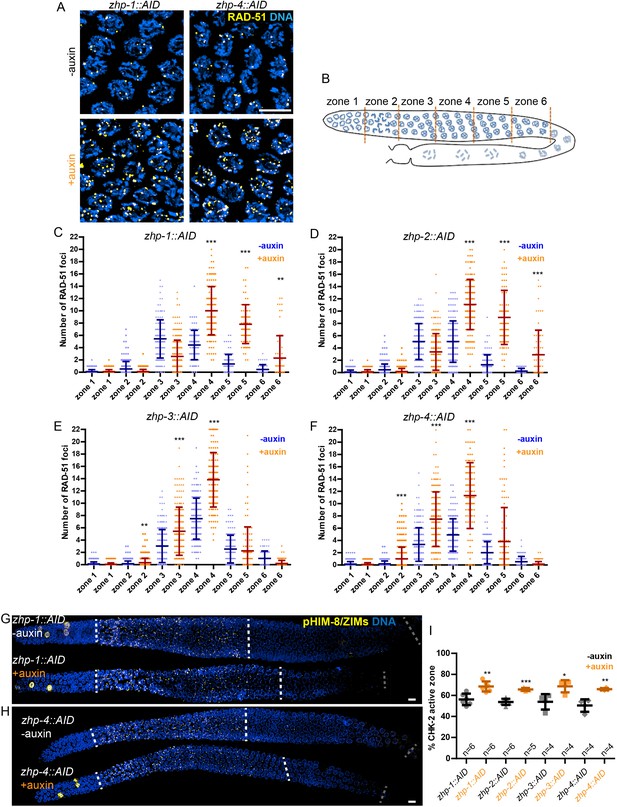
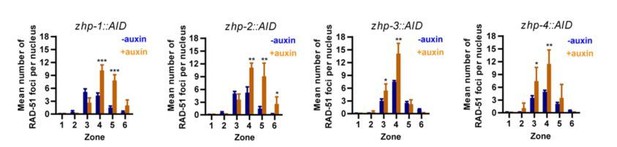
ZHPs are dispensable for DSB induction and the crossover assurance checkpoint.
(A) Projection images of mid-pachytene nuclei stained for RAD-51 (yellow) and DNA (blue), showing accumulation of DSB repair intermediates in the absence of ZHP-1 or ZHP-4. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Diagram of a hermaphrodite gonad, indicating the six zones in which RAD-51 foci were scored. (C–F) Quantification of RAD-51 foci. Gonads were divided into six zones of equal length, spanning the premeiotic through late pachytene region. The number of RAD-51 foci in each nucleus is presented for each zone. n = 167, 229, 160, 200, 133, 209, 100, 131, 87, 87, 44, 62, 222, 258, 227, 274, 190, 173, 158, 151, 109, 100, 68, 68, 352, 251, 283, 296, 197, 172, 167, 138, 124, 119, 76, 103, 338, 317, 281, 290, 227, 171, 194, 111, 134, 102, 74 and 102 nuclei, respectively, from zone 1 to zone 6, and zhp-1::AID to zhp-4::AID. four gonads were scored for each genotype or condition. **p=0.0084 and 0.0028, respectively, ***p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test. (G–I) CHK-2 activity is extended in the absence of ZHP proteins. Low magnification images of gonads stained for pHIM-8/pZIMs (yellow) and DNA (blue). The upper gonad in each panel is a non-auxin treated control, while lower panels show gonads from animals depleted of ZHP-1 (G) or ZHP-4 (H) for ~24 hr. Scale bars, 5 µm. (I) Quantification of the ‘CHK-2 active zone,’ defined as the length of the region of pHIM-8/ZIM staining as a fraction of the region from meiotic onset to the end of pachytene before nuclei form a single file. n = number of gonads scored for each genotype or condition. *p=0.0199, **p=0.0018 and 0.0021, respectively, ***p<0.0001, two-sided Student t-test.
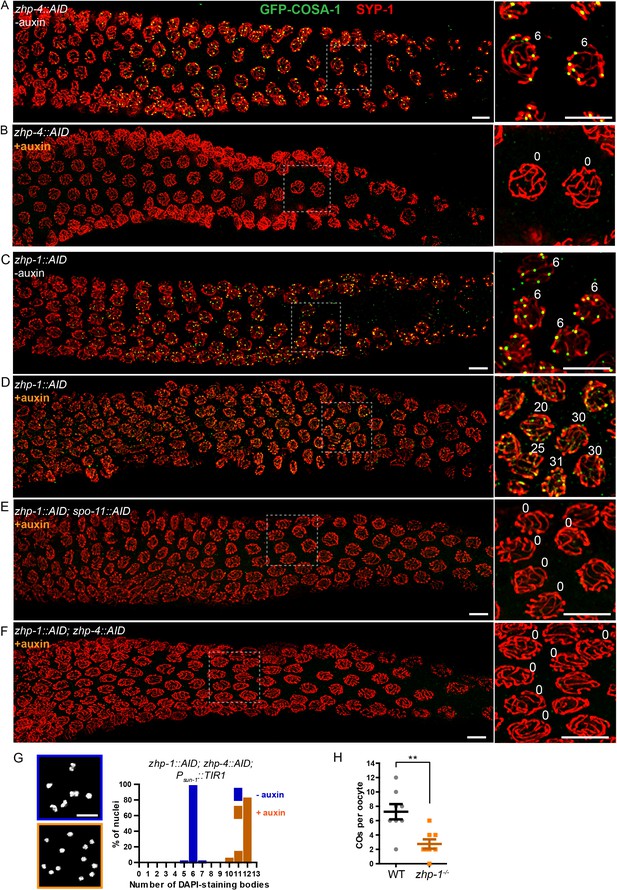
ZHP-3/4 are required to stabilize recombination intermediates, while ZHP-1/2 promote accumulation of pro-CO factors at a subset of intermediates during late prophase.
(A–F) Low-magnification images of mid- and late pachytene nuclei stained for GFP-COSA-1 (green) and SYP-1 (red). Insets on the right showing corresponding nuclei at late pachynema. (A) Representative zhp-4::AID; Psun-1::TIR1 germline showing six sites per nucleus marked by bright GFP-COSA-1 foci in the absence of auxin treatment. (B) Depletion of ZHP-4 by auxin treatment for 24 hr resulted in an absence of COSA-1 foci. (C) Control zhp-1::AID; Psun-1::TIR1 worm showing six bright GFP-COSA-1 foci per nucleus. (D) Depletion of ZHP-1 by auxin treatment for 24 hr results in a large number of recombination intermediates marked by dim GFP-COSA-1 foci. Image acquisition and display were adjusted to allow the dim foci to be visualized. (E, F) Co-depletion of ZHP-1 and SPO-11 (E) or of ZHP-1 and ZHP-4 (F) results in an absence of COSA-1 foci. (G) Left: Oocyte nuclei at late diakinesis, fixed and stained with DAPI. Each panel indicates a single representative nucleus. Right: Graphs of the distribution of DAPI-staining bodies at diakinesis. Co-depletion of ZHP-1 and ZHP-4 eliminates bivalents (12 DAPI-staining bodies). The number of nuclei scored for each condition was: n = 84 and 104, respectively. (H) Quantification of COs in wild type and zhp-1 null mutant oocytes by whole genome sequencing. n = 8 oocytes for each genotype. **p=0.0072, Mann-Whitney test. Scale bars, 5 µm.
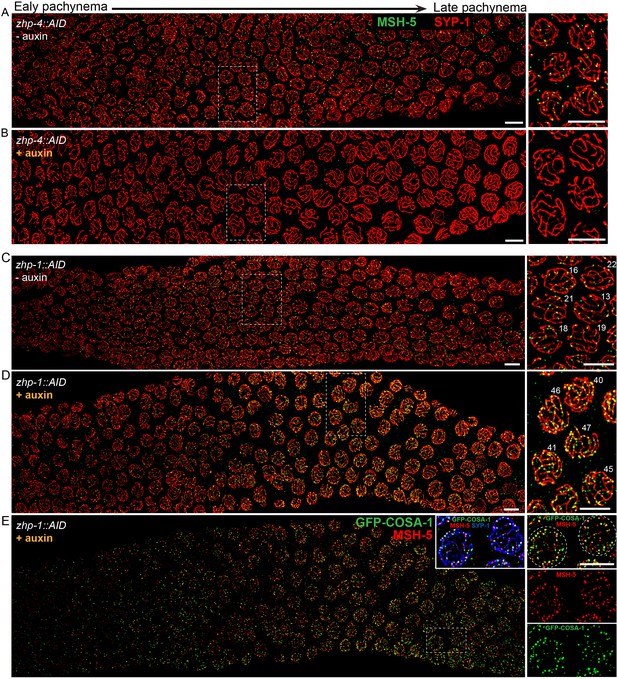
ZHP-3/4 are required for the appearance of MSH-5 foci, while ZHP-1/2 limit the number of foci during late prophase.
(A–D) Recombination intermediates visualized by immunolocalization of MSH-5. Low-magnification images of pachytene nuclei stained for MSH-5 (green) and SYP-1 (red). Larger magnification insets on the right show indicated nuclei at mid-or late pachynema. (A, C) MSH-5 foci normally peak at mid-pachytene, when 10–20 can be detected per nucleus (B) No MSH-5 foci were detected when ZHP-4 was depleted for 24 hr. (D) Depletion of ZHP-1 caused a large increase in the number of MSH-5-positive recombination intermediates. ~40–50 foci were detected in most nuclei at late pachynema. (E) The same gonad as in (D) showing the colocalization of dim GFP-COSA-1 foci with MSH-5 foci in the absence of ZHP-1. Scale bars, 5 µm.
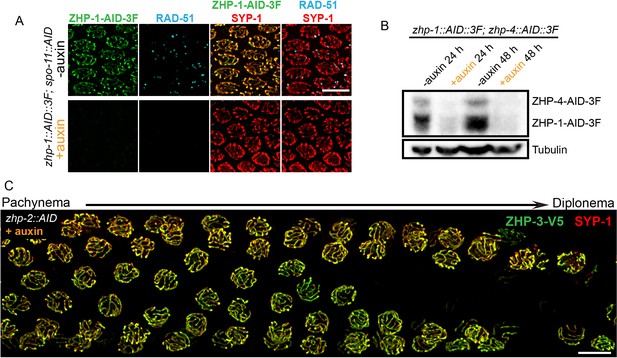
Robust protein co-depletion by the AID system and persistence of ZHP-3 throughout SCs following ZHP-1/2 depletion.
(A) Images of representative pachytene nuclei stained for ZHP-1-AID-3xFLAG (green), RAD-51 (cyan) and SYP-1 (red). ZHP-1 and recombination intermediates were undetectable following treatment with auxin for 24 hr. Scale bars, 5 µm. (B) Western blotting showing efficient co-depletion of ZHP-1 and ZHP-4. Blots were probed with anti-FLAG and anti-tubulin antibodies, respectively. Tubulin was blotted as a loading control. 3F: 3xFLAG. (C) Depletion of ZHP-2 by auxin treatment for 24 hr resulted in persistence of ZHP-3 throughout SCs in late pachytene nuclei. Scale bars, 5 µm.
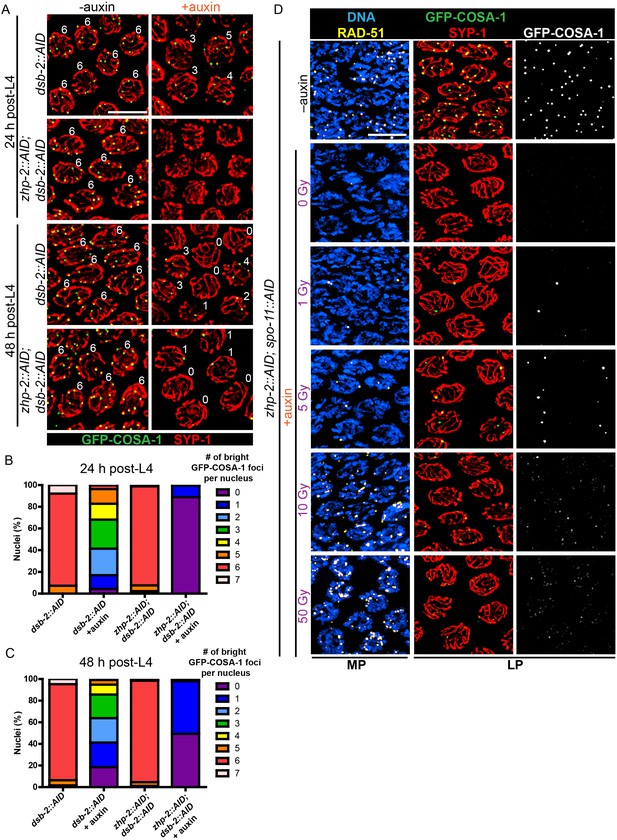
CO designation in the absence of ZHP-1/2.
(A) Projection images of representative late pachytene nuclei stained for GFP-COSA-1 (green) and SYP-1 (red). In the absence of DSB-2 at 24 hr post-L4, an average of 3 bright GFP-COSA-1 foci are detected in each nucleus. However, very few bright GFP-COSA-1 foci are observed when ZHP-2 is co-depleted. By 48 hr post-L4, only ~2 bright GFP-COSA-1 foci are observed per nucleus in the absence of DSB-2, and most nuclei display 0–1 bright GFP-COSA-1 focus when ZHP-2 is also depleted. (B) Quantification of bright GFP-COSA-1 foci at late pachynema, 24 hr post-L4. Worms of the indicated genotypes were maintained in the presence or in the absence of 1 auxin for 24 hr and then dissected for analysis. Data were derived from 4 to 8 gonads for each genotype or condition. n = 165, 348, 172 and 377 nuclei, respectively. The number of GFP-COSA-1 foci differed significantly between dsb-2::AID and zhp-2::AID; dsb-2::AID following auxin treatment (***p<0.0001 by Chi-square test for trend). (C) Quantification of bright GFP-COSA-1 foci in late pachytene nuclei 48 hr post-L4. Data were derived from 4 to 8 gonads for each genotype or condition. n = 252, 558, 263 and 416 nuclei, respectively. Depletion of ZHP-2 significantly reduces the number of GFP-COSA-1 foci in the absence of DSB-2 (***p<0.0001 by Chi-square test for trend). The distribution of GFP-COSA-1 foci is also significantly different between 24 hr and 48 hr post-L4 for auxin treated zhp-2::AID; dsb-2::AID hermaphrodites (***p<0.0001 by Chi-square test for trend). (D) Representative images of mid-pachytene (MP) and late pachytene (LP) nuclei stained for RAD-51 (yellow), GFP-COSA-1 (green), SYP-1 (red), and DNA (blue). GFP-COSA-1 foci in the absence of ZHP-1/2 was visualized following exposure of SPO-11-depleted worms to varying doses of ionizing radiation. L4 worms were maintained in the presence or in the absence of 1 mM auxin for 24 hr, followed by irradiation at the indicated dosage, and then incubated for additional 8 hr to allow irradiated nuclei to progress to late pachynema. Scale bars, 5 µm.
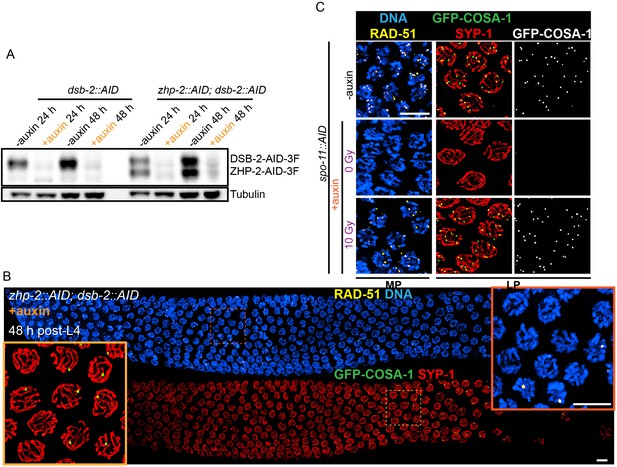
Validation of protein depletion, and further characterization of ZHP-1/2.
(A) Western blot showing efficient auxin-mediated depletion of DSB-2 alone, or co-depletion of ZHP-2 and DSB-2. Blots were probed with anti-FLAG and anti-tubulin antibodies, respectively. Tubulin was blotted as a loading control. 3F: 3xFLAG. (B) Low magnification images of gonads from worms at 48 hr post-L4 stained for RAD-51 (yellow), GFP-COSA-1 (green), SYP-1 (red) and DNA (blue). RAD-51 staining in the upper panel indicates that few DSBs are induced in the absence of DSB-2. The lower panel shows GFP-COSA-1 and SYP-1 staining in the same gonad. A few bright GFP-COSA-1 foci are detected in the absence of ZHP-2 when the number of DSBs is limited by DSB-2 depletion. Insets show enlargements of corresponding regions of the gonad. (C) SPO-11 activity is effectively abrogated by AID-mediated depletion. Projection images of pachytene nuclei stained for RAD-51 (yellow), GFP-COSA-1 (green), SYP-1 (red), and DNA (blue). DSBs were induced by ionizing radiation following depletion of SPO-11. No COSA-1 foci were observed in unirradiated animals, but CO designation was rescued following 10 Gy of irradiation. Scale bars, 5 µm.
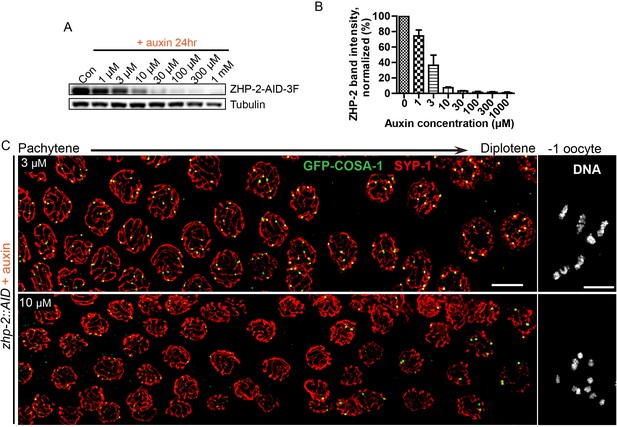
Partial depletion fails to separate the roles of ZHP-1/2 in limiting late recombination intermediates and promoting crossover maturation.
(A) Western blots showing partial depletion of AID-tagged ZHP-2 in animals exposed to low concentrations of auxin. Blots were probed with anti-FLAG and anti-tubulin antibodies, respectively. Tubulin was blotted as a loading control. 3F: 3xFLAG. (B) Quantification of ZHP-2 depletion. The intensity of ZHP-2 bands were normalized against the corresponding tubulin band, and expressed as percentage of the intensity in a control sample. The graph shows the mean ±SD protein levels from three independent experiments. (C) Low-magnification images of late pachytene nuclei stained for GFP-COSA-1 (green) and SYP-1 (red). Insets on the right show representative oocyte nuclei at late diakinesis under the same conditions. In the presence of 3 µM auxin for 24 hr, zhp-2:AID; Psun-1:TIR1 germline still show six designated CO sites per nucleus marked by bright GFP-COSA-1 foci. At 10 µM auxin, a reduced number of bright GFP-COSA-1 were detected. Nuclei with more than six bright foci were not observed under any depletion conditions. Similar results were obtained when ZHP-1-AID was depleted (data not shown) Scale bars, 5 µm.
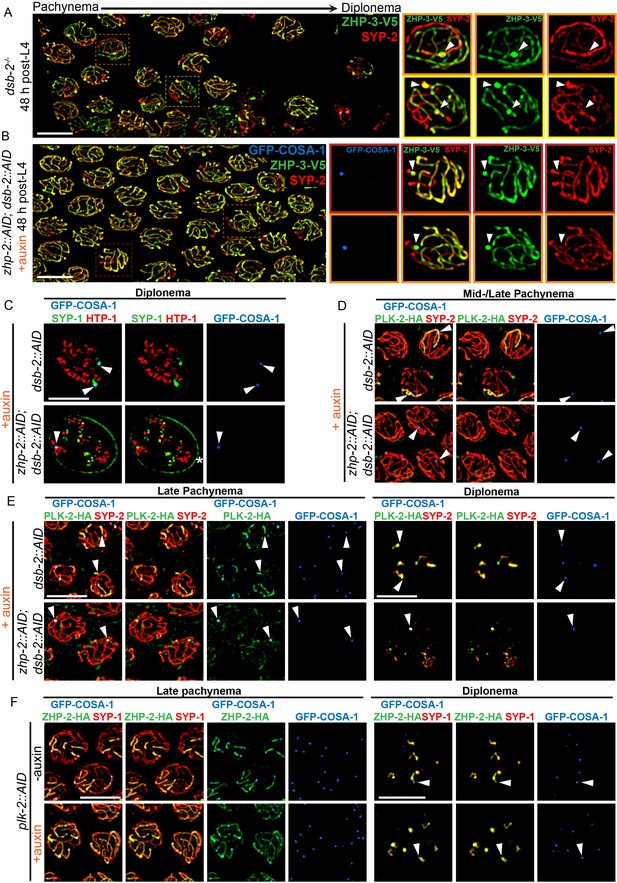
ZHP-1/2 act at the top of a hierarchy of chromosome remodeling factors.
(A) Late pachytene nuclei in a dsb-2 mutant at 48 hr post-L4, stained for ZHP-3-V5 (green) and SYP-2 (red). ZHP-3 is depleted and SYP-2 is enriched specifically along SCs with bright ZHP-3 foci. Boxed areas indicate nuclei shown at higher magnification to the right. Arrowheads in inset images indicate designated CO sites. (B) Late pachytene nuclei stained for ZHP-3-V5 (green), SYP-2 (red) and GFP-COSA-1 (blue). In the absence of ZHP-2 and DSB-2, ZHP-3 was still depleted from CO-designated SCs. However, enrichment of SYP proteins was not observed, (C) Higher-magnification images of diplotene nuclei from hermaphrodites depleted of DSB-2 alone or in combination with ZHP-2. The tissue was stained with antibodies against SYP-1 (green), HTP-1 (red) and GFP-COSA-1 (blue). In the absence of DSB-2 alone, SYP-1 and HTP-1 localized to reciprocal chromosome domains of bivalent chromosomes, as previously described (Machovina et al., 2016; Martinez-Perez et al., 2008). In worms depleted of both ZHP-2 and DSB-2, SYP-1 was restricted to CO sites at diplotene-diakinesis, while HTP-1/2 were retained on both short and long arms of bivalents. Asterisk indicates nuclear envelope staining due to cross-reactivity of our SYP-1 antibody, which becomes more prominent in late prophase. (D and E) Representative nuclei from the same genotypes as in (C), stained for PLK-2-HA (green), anti-SYP-2 (red) and GFP-COSA-1 (blue). In the absence of DSB-2, PLK-2 became enriched on CO-designated chromosomes, after which it relocalized to the short arm of CO-designated SCs at late pachynema, as recently described (Pattabiraman et al., 2017). However, when ZHP-2 and DSB-2 were co-depleted, PLK-2 was not enriched along CO-designated chromosomes, although foci were observed at CO sites. (F) Representative late pachytene and diplotene nuclei from hermaphrodites depleted of PLK-2, stained for ZHP-2-HA (green), SYP-1 (red) and GFP-COSA-1 (blue). In the absence of PLK-2, CO designation and asymmetric localization of ZHP-2 were delayed, and asymmetric disassembly of the SC was severely impaired, as previously described (Harper et al., 2011), but ZHP-2 still relocalized to the presumptive short arm during late prophase. Arrowheads indicate designated CO sites. Scale bars, 5 µm.
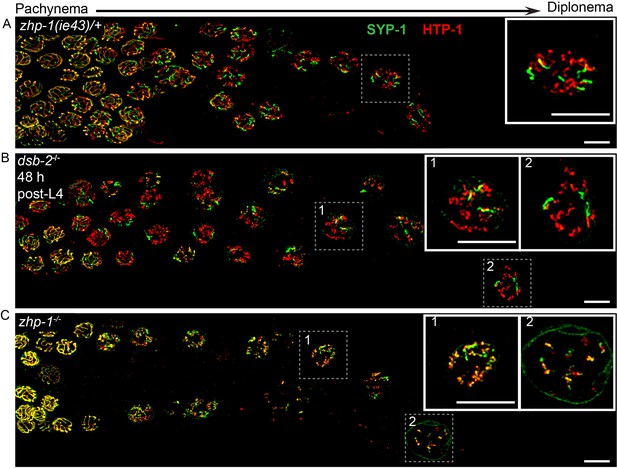
ZHP-1/2 are required for chromosome remodeling.
(A–C) Images of late pachytene nuclei stained for SYP-1 (green) and HTP-1 (red). (A) In zhp-1 heterozygotes, SYP-1 and HTP-1 show normal, reciprocal localization in late prophase. (B) In dsb-2 null mutants 48 hr post-L4, most late prophase nuclei display 2–4 bright COSA-1 foci. Although disassembly of SYP-1 and HTP-1 are delayed due to activation of the CO assurance checkpoint, these proteins eventually show reciprocal localization on these CO-designated chromosomes, while univalent chromosomes retain HTP-1 but not SYP-1. (C) In zhp-1 null mutants, SYP-1 and HTP-1 remain colocalized with each other on most chromosomes, despite the appearance of ~ 2–3 bright COSA-1 foci at late pachytene and a similar number of bivalents at diakinesis. Univalent chromosomes also show persistent staining with both HTP-1 and SYP-1. Insets showing enlarged views of the indicated nuclei. Scale bars, 5 µm.
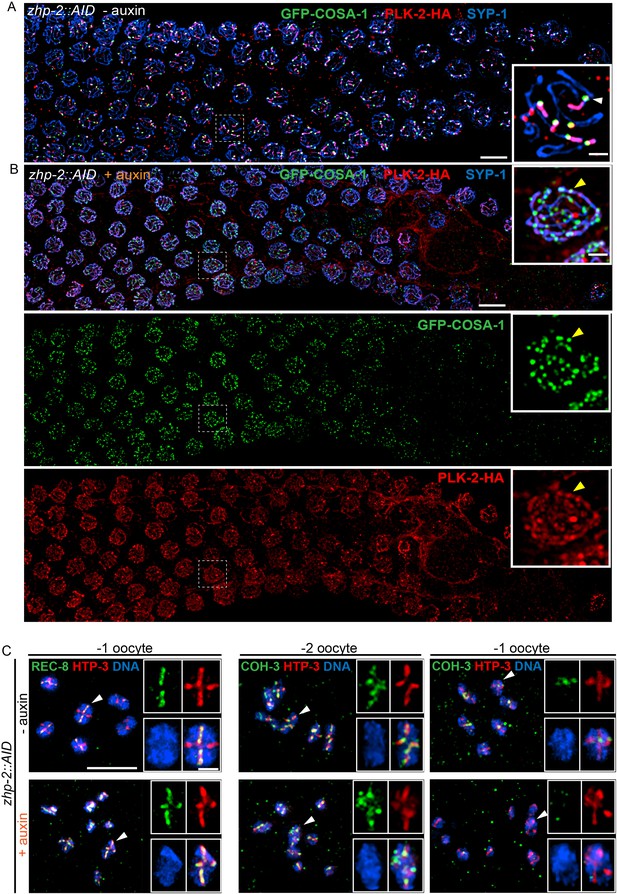
ZHP-1/2 are required for chromosome remodeling.
(A,B) ZHP-2 is required for asymmetric localization of PLK-2 following crossover designation. (A) In wild-type nuclei, and in animals expressing ZHP-AID in the absence of auxin, PLK-2 (red) concentrates along the presumptive short arms during late meiotic prophase. (B) When ZHP-2 is depleted, PLK-2 localizes to a subset of recombination intermediates, but does not show asymmetric localization along the SCs. (C) High-magnification images of maturing oocytes stained for the kleisin proteins REC-8 or COH-3 and the HORMA domain protein HTP-3, which persists along all arms of bivalents. Worms were treated with or without auxin for 48 hr. In the most mature, or ‘–1’ (relative to the spermatheca) oocyte in each arm of the gonad, REC-8 normally becomes enriched on the long arms, while COH-3 is retained on short arms. In the absence of ZHP-2, removal of REC-8 from short arms was defective and retention of COH-3 was rarely observed. Scale bars, 5 µm. Scale bar for insets, 1 µm.
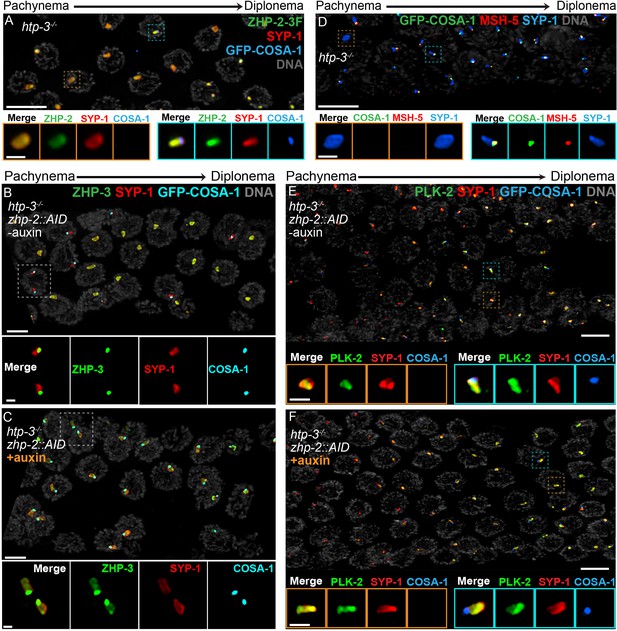
Compartmentalization of CO signaling within polycomplexes.
Polycomplexes assemble from SC proteins in meiotic nuclei of htp-3 mutants. During late meiotic prophase, a single focus containing COSA-1 and ZHP-3 appears on each polycomplex (Rog et al., 2017and data not shown). (A) ZHP-1 (not shown) and ZHP-2 (green) localize throughout polycomplexes (red) both before and after the appearance of COSA-1 foci (blue). Insets show higher magnification images of the indicated polycomplexes without (left) and with (right) COSA-1 foci. (B,C) Late prophase nuclei showing polycomplexes in the presence and absence of ZHP-2 (minus and plus auxin treatment, respectively). Insets show higher magnification views of the indicated polycomplexes. (B) In the presence of ZHP-2, ZHP-3 (green) colocalizes with COSA-1 foci (cyan) in late meiotic prophase and becomes depleted from the body of polycomplexes (red). (C) In the absence of ZHP-2, ZHP-3 (green) colocalizes with GFP-COSA-1, but also remains diffusely localized throughout polycomplexes. (D) Late prophase nuclei from htp-3 mutants showing colocalization of MSH-5 (red) with GFP-COSA-1 foci (green) on the surface of polycomplexes (blue). (E,F) Late prophase nuclei from the same genotypes depicted in (B,C). (E) PLK-2 (green) localizes throughout polycomplexes (red) prior to the appearance of GFP-COSA-1 foci (blue), but staining becomes more intense in late prophase. (F) Depletion of ZHP-2 does not affect the localization of PLK-2 to polycomplexes. Scale bars in lower magnification images, 5 µm; in insets, 1 µm.
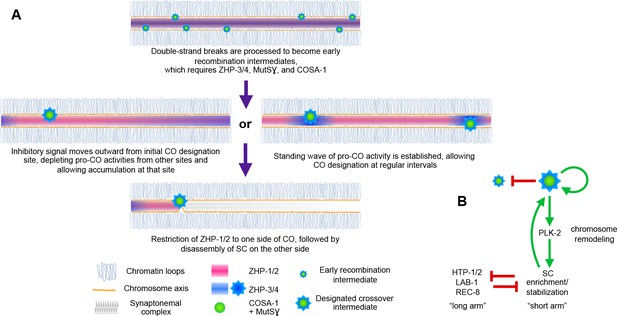
Schemata for crossover control and chromosome remodeling.
(A) Spatial regulation of CO designation by ZHP proteins. In early prophase, all 4 ZHPs concentrate within SCs at the interface between homologous chromosomes. DSBs are induced and homologous recombination is initiated through strand invasion. Recruitment or stabilization of MutSγ and COSA-1 at these early intermediates depends on the presence of ZHP-3/4 within the SC. As nuclei progress through mid-prophase, one such intermediate along each chromosome stochastically crosses a threshold activity level. [We note that this is analogous to a ‘cracking’ event posited in a beam-film model for crossover interference (Kleckner et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2014b)]. This event triggers positive and negative feedback that promotes accumulation of COSA-1, MutSγ, and ZHP-3/4 at this site. These pro-CO activities may be depleted from nearby recombination intermediates through a wave of inhibitory activity that travels outward from a designated CO site; alternatively, local activation and lateral inhibition may give rise to a periodic pattern of pro-CO activity along each pair of chromosomes. In either scenario, diffusion of proteins within the SC permits coordinated behavior of potential CO sites along each pair of chromosomes. (B) A circuit diagram for CO control and chromosome remodeling, incorporating the findings of this work. Coupled positive and negative feedback mechanisms mediated by ZHPs and other factors lead to accumulation of pro-CO factors at a single designated crossover site. ZHP-1/2 also act at the top of a hierarchy that leads to PLK-2 enrichment on one side of the crossover and retention of the SC within this domain, creating another positive feedback loop, although how ZHP-1/2 become enriched on one side of the crossover is currently unknown. Activities within the SC antagonize the retention of HTP-1/2 and associated factors along the axis, and vice versa, resulting in the differentiation of two distinct chromosome domains. This leads to eventual removal of REC-8 from the short arm and its retention on the long arm, promoting accurate, stepwise meiotic chromosome separation.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | zhp-1 | WormBase/This paper | WormBase ID: F55A12.10; WBGene00018867 | |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | zhp-2 | WormBase/This paper | WormBase ID: D1081.9; WBGene00008387 | |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | zhp-3 | WormBase/(Jantsch et al., 2004) PMID: 15340062 | WormBase ID: K02B12.8b; WBGene00006976 | |
| Gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | zhp-4 | WormBase/This paper | WormBase ID: Y39B6A.16; WBGene00012678 | |
| Strain, strain background (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | S. cerevisiae: MaV203 | Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA | Cat#11445012 | |
| Strain, strain background (Caenorhabditis elegans) | For C. elegans allele and strain information, see Supplementary file 1, Tables S2 and S4. | This paper | N/A | |
| Genetic reagent | For CRISPR/Cas9 reagents, see sequence-based reagent and peptide, recombinant protein. | This paper | N/A | |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-SYP-1 | (MacQueen et al., 2002) PMID: 12231631 | N/A | (1:500 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-SYP-2 | (Colaiácovo et al., 2003) PMID: 12967565 | N/A | (1:500 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-HTP-1 | (Martinez-Perez et al., 2008) PMID: 18923085 | N/A | (1:500 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-RAD-51 | Millipore Sigma, St. Louis, MO | Cat#29480002 | (1:5,000 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-pHIM-8/ZIMs | (Kim et al., 2015) PMID: 26506311 | N/A | (1:500 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-ZHP-3 | ModENCODE/SDIX; (Rog et al., 2017) PMID: 28045371 | Cat#SDQ3956 | (1:5,000 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-MSH-5 | ModENCODE/SDIX | Cat#SDQ2376 | (1:5,000 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-REC-8 | ModENCODE/SDIX | Cat#SDQ0802 | (1:5,000 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-COH-3 | ModENCODE/SDIX | Cat#SDQ3972 | (1:5,000 IF) |
| Antibody | Rat polyclonal anti-HIM-8 | (Phillips et al., 2005) PMID: 16360035 | N/A | (1:500 IF) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-SYP-1 | (Harper et al., 2011) PMID: 22018922 | N/A | (1:300 IF) |
| Antibody | Chicken polyclonal anti-HTP-3 | (MacQueen et al., 2005) PMID: 16360034 | N/A | (1:500 IF) |
| Antibody | Guinea pig polyclonal anti-HTP-3 | (MacQueen et al., 2005) PMID: 16360034 | N/A | (1:500 IF) (1:1,500 WB) |
| Antibody | Guinea pig polyclonal anti-PLK-2 | (Harper et al., 2011) PMID: 22018922 | N/A | (1:100 IF) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-V5 | Millipore Sigma | Cat#V8137; RRID:AB_261889 | (1:250 IF) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-V5 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#R960-25; RRID:AB_2556564 | (1:500 IF) (1:1,000 WB) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG M2 | Millipore Sigma | Cat#F1804; RRID:AB_262044 | (1:500 IF) (1:1,000 WB) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-HA, clone 2–2.2.14 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#26183; RRID:AB_10978021 | (1:400 IF) (1:1,000 WB) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-GFP | Millipore Sigma | Cat#11814460001; RRID:AB_390913 | (1:500 IF) (1:1,000 WB) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-α-tubulin, clone DM1A | Millipore Sigma | Cat#05–829; RRID:AB_310035 | (1:5,000 WB) |
Recombinant DNA reagent | Peft-3::AID::GFP::unc-54 3’UTR | (Zhang et al., 2015) PMID: 26552885; Addgene | pLZ29; Addgene plasmid #71719 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | cDNA zhp-1 | WormBase | WormBase ID: F55A12.10; WBGene00018867 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | cDNA zhp-2 | WormBase | WormBase ID: D1081.9; WBGene00008387 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | cDNA zhp-3 | WormBase | WormBase ID: K02B12.8b; WBGene00006976 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | cDNA zhp-4 | WormBase (codon-optimized byIntegrated DNA Technologies to facilitate gBlock synthesis) | WormBase ID: Y39B6A.16; WBGene00012678 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid: pDEST32-zhp-1-V5 | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid: pDEST32-zhp-2-3xFLAG | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid: pDEST32-zhp-3-3xFLAG | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid: pDEST32-zhp-4-HA | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid: pDEST22-zhp-1-V5 | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid: pDEST22-zhp-2-3xFLAG | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid: pDEST22-zhp-3-3xFLAG | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid: pDEST22-zhp-4-HA | This paper | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | FISH probe to the right arm of Chromosome V (5S rDNA) | (Dernburg et al., 1998) PMID: 9708740 | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | FISH Probe to the right arm of X Chromosome | (Phillips et al., 2005) PMID: 16360035 | N/A | |
| Sequence-based reagent | CRISPR tracrRNA | Integrated DNA Technologies, Skokie, IL | Cat#1072534 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | For crRNAs, repair templates and genotyping primers, see Supplementary file 1,Table S3 | This paper | N/A | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | S. pyogenes Cas9-NLS purified protein | QB3 MacroLab at UC Berkeley | N/A | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Auxin: 1H-Indole-3-acetic acid | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA | Cat#122160250; CAS:87-51-4 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NuSieve 3:1 agarose | Lonza, Walkersville, MD | Cat#50090 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nuclease-Free Duplex Buffer | Integrated DNA Technologies | Cat#11-01-03-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat #34095 | |
| Software, algorithm | SoftWorx package | Applied Precision; GE Healthcare Bio- Sciences, Pittsburgh, PA | http://www.gelifesciences.com/webapp/wcs/stores/servlet/productById/en/GELifeSciences-us/29065728 | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | NIH | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Adobe Photoshop CC 2014 | Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA | http://www.adobe.com/products/photoshop.html | |
| Software, algorithm | T-COFFEE | Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics; (Notredame et al., 2000) PMID:10964570 | http://tcoffee.vital-it.ch/apps/tcoffee/index.html | |
| Software, algorithm | IBS_1.0.1 | (Liu et al., 2015) PMID: 26069263 | http://ibs.biocuckoo.org/download.php | |
| Software, algorithm | Clustal Omega | EMBL-EBI | http://www.clustal.org/omega/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Graphpad Prism | Graphpad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA | http://www.graphpad.com/ | |
| Software, algorithm | MSG software package | (Andolfatto et al., 2011) PMID: 21233398 | https://github.com/JaneliaSciComp/msg |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
This file includes four tables (Table S1-S4).
Table S1 reports analysis of the progeny produced by animals expressing epitope-tagged proteins described in this work. In all cases, animals homozygous for these epitope-tagged alleles show no reduction in embryonic viability or increase in male production, indicating that the epitope tags used to detect various proteins do not impair their meiotic functions. Table S2 provides a list of all new alleles generated in this work, with details about the genome editing methods used to introduce epitope tags or mutations. Table S3 includes the sequences of RNA and DNA sequences used for genome editing, including synthetic CRISPR RNAs (crRNAs), repair templates, and DNA primers used for detecting or genotyping these mutations. In cases where restriction digests were used for genotyping, fragment sizes for wild-type and mutant alleles are also provided. Table S4 lists new worm strains constructed in the course of this work, as well as previously referenced strains.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.30789.025





