NECAPs are negative regulators of the AP2 clathrin adaptor complex
Figures
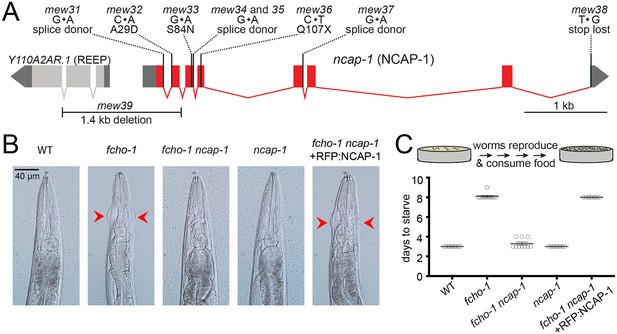
Loss of NCAP-1 suppresses fcho-1 mutants.
(A) Gene model of the C. elegans ncap-1 locus. Boxes represent exons. Mutations isolated from the fcho-1 suppressor screen are indicated. The deletion allele, mew39, was used throughout this study as ncap-1. The neighboring gene (Y110A2AR.1) is predicted to encode a receptor expression-enhancing protein (REEP). (B) Animal heads showing jowls phenotype (red arrows). Anterior is up. WT, wild type; RFP:NCAP-1, red fluorescent protein-tagged NCAP-1 single-copy transgene. (C) Starvation assay. Data represent days required for worms to reproduce and consume bacterial food source (top schematic). Bars indicate mean ±SEM for n = 10 biological replicates.
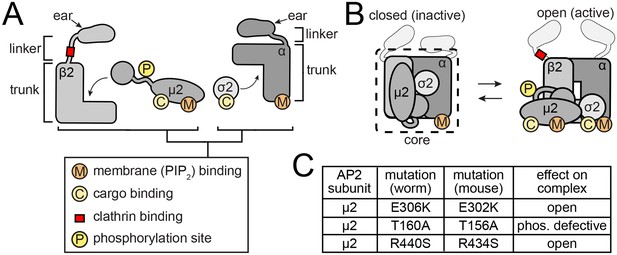
AP2 structures and mutations.
(A) AP2 is comprised of two large adaptins (α and β2) and two smaller subunits (µ2 and σ2). The adaptins, in turn, are comprised of appendage (ear), hinge (linker) and trunk domains. Phosphorylation site and binding pockets are diagrammed. (B) Cartoon representations of the closed (Collins et al., 2002) and open (Jackson et al., 2010 and Kelly et al., 2014) AP2 conformations. The core complex (dashed line) lacks ears and linkers. (C) Table of AP2 mutations used in this study.
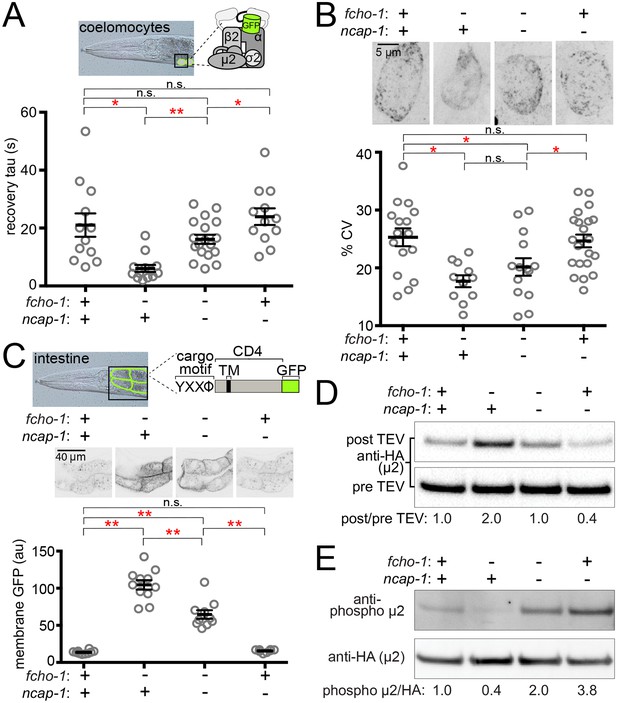
Loss of NCAP-1 restores AP2 activity in fcho-1 mutants.
(A) FRAP analysis of GFP-tagged AP2 α adaptin (APA-2:GFP) on membranes of coelomocytes (top schematic). Time constants (tau) of the fluorescence recovery are plotted. (B) AP2 localization in coelomocytes. Representative confocal images of coelomocytes in worms expressing APA-2:GFP. Micrographs (top) are representative maximum projections of Z-slices through approximately half of a cell. Data represent the coefficient of variance (%CV) of pixel intensities for individual cells. (C) Artificial AP2 cargo assay. Representative confocal micrographs of intestinal cells (middle) in worms expressing a GFP-tagged cargo (top schematic). TM, transmembrane domain. The average pixel intensity along a basolateral membrane was measured (bottom). (A–C) Bars indicate mean ±SEM for n ≥ 8 biological replicates. *p<0.05, **p<0.001, not significant (n.s.), unpaired, two-tailed T-test. (D) µ2 protease-sensitivity assay. Western blot analysis of whole worm lysates was used to quantify the amount of full-length µ2 (anti-HA, 50 kDa) before (pre TEV, bottom blot) and after protease induction (post TEV, top blot). Band intensities were compared to a tubulin loading control and normalized to the fcho-1(+) ncap-1(+) ratio (values below). (E) µ2 phosphorylation assay. Western blot analysis of whole worm lysates to quantify phosphorylated µ2 (top blot) relative to total µ2 subunit (bottom blot). Values indicate band intensity ratios of phospho µ2 compared to total µ2, normalized to the fcho-1(+) ncap-1(+) ratio (values below). (D and E) Blots are representative of ≥3 biological replicates. +, wild type allele; -, deletion allele.
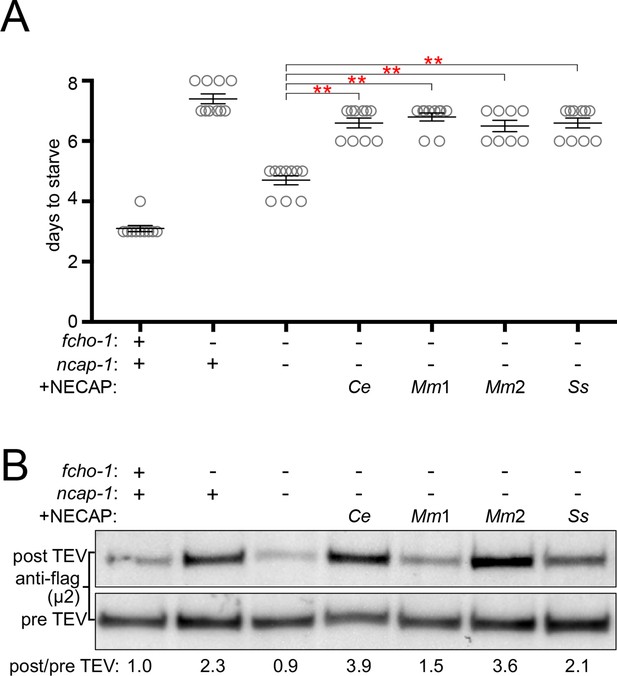
NECAPs restore closed AP2 in fcho-1 ncap-1 worms.
RFP-tagged NECAPs were expressed as single copy transgenes in fcho-1 ncap-1 worms. Ce, C. elegans; Mm, M. musculus; Ss, Sphaerobolus stellatus (multicellular fungus). +, wild type allele; -, deletion allele. (A) Starvation assay performed as in Figure 1C. Bars represent mean ±SEM for n ≥ 7 biological replicates. **p<0.001, unpaired, two-tailed T-test. (B) µ2 protease-sensitivity assay as in Figure 2D, except a flag-tagged µ2 subunit was used. Band intensities were compared to a histone loading control and normalized to the fcho-1(+) ncap-1(+) ratio (values below). Blot is representative of 2 biological replicates.
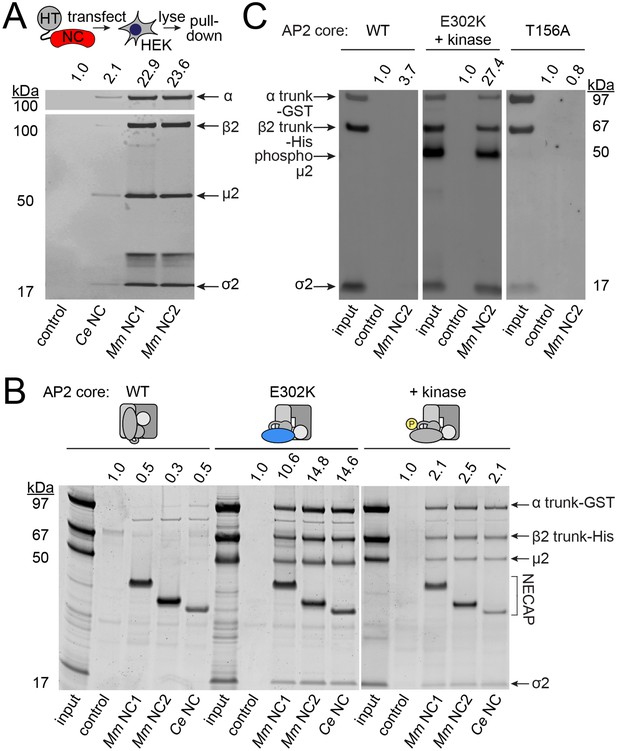
NECAPs bind the open and phosphorylated AP2 core.
Pulldown assays using affinity-tagged NECAPs. Proteins were cleaved from the affinity tag (HaloTag), electrophoretically separated and then blotted for AP2 subunits (A and C) or SYPRO-stained prior to imaging (B). Control, HaloTag alone; NC, NECAP; Ce, C. elegans; Mm, M. musculus. (A) Western blot analysis (middle) of samples purified from human cell lysates (top schematic) expressing the indicated NECAP bait (bottom). (B and C) In vitro pulldown assays using purified recombinant bait (NECAPs, bottom) and prey (vertebrate AP2 cores, top). Co-expression with the kinase domain from mouse AAK1 (+kinase) generates phosphorylated AP2. Amino acid changes in µ2 are indicated: E302K, constitutively open AP2; T156A, phosphorylation-defective AP2; see also Figure 1—figure supplement 1C. 20% of prey input was analyzed for comparison with 50% of the sample released by the protease. (A–C) Band intensities of the α subunit (A) or the α trunk (B and C) were quantified, background signal subtracted, and values normalized to the HaloTag control (values above). Data are representative of 2 biological (A), one technical (B), and two technical (C) replicates.
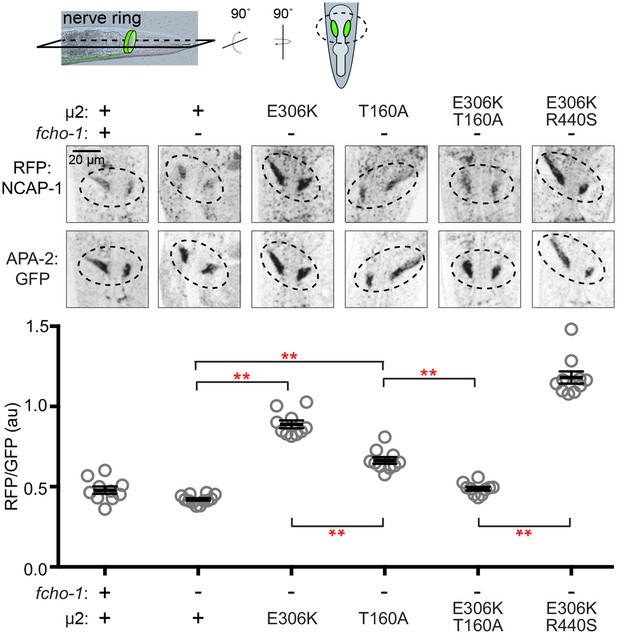
Phosphorylated AP2 recruits NCAP-1 in vivo.
Representative confocal slices (middle) through the approximate center of the nerve ring of worms (top schematic) expressing RFP:NCAP-1 and APA-2:GFP. RFP to GFP signal intensity at the nerve ring is plotted (bottom). Mutations in µ2 are indicated: E306K and R440S, constitutively open AP2; T160A, phosphorylation-defective AP2; see also Figure 1—figure supplement 1C. Bars indicate mean ±SEM for n ≥ 10 biological replicates. **p<0.001, unpaired, two-tailed T-test. au, arbitrary units; +, wild type allele; -, deletion allele.
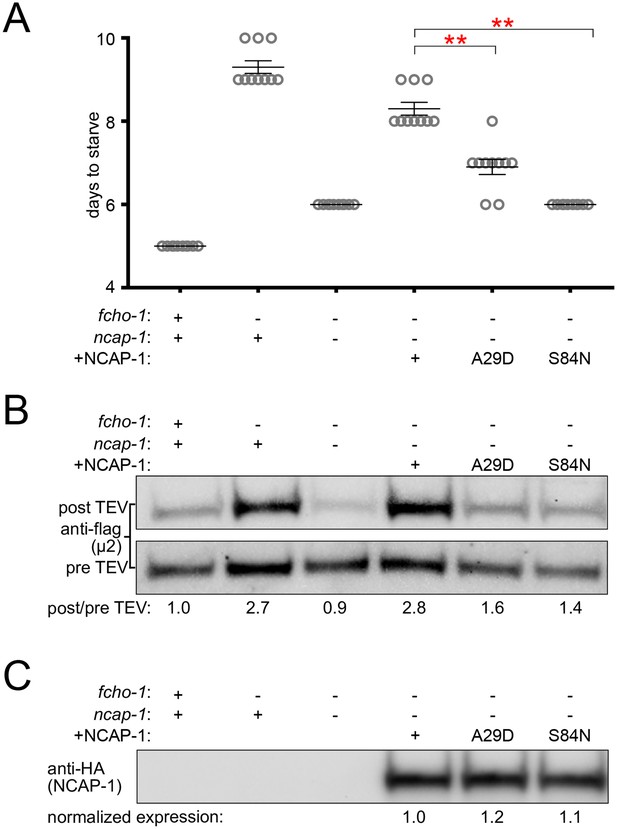
Missense mutations render NCAP-1 stable but functionally inactive.
Amino acid changes isolated from the fcho-1 suppressor screen (Figure 1A) were introduced into an RFP-tagged NCAP-1 transgene in fcho-1 ncap-1 worms. +, wild type allele; -, deletion allele. (A) Starvation assay performed as in Figure 1C. Bars represent mean ±SEM for n ≥ 9 biological replicates. **p<0.001, unpaired, two-tailed T-test. (B) µ2 protease-sensitivity assay as in Figure 3B. (C) Western blot analysis to detect HA epitope on NCAP-1 transgenic proteins. (B and C) Band intensities were compared to a beta actin loading control and normalized to the fcho-1(+) ncap-1(+) ratio (B) or to the transgenic wild type form of NCAP-1 (C) (values below). Blots are representative of 2 biological replicates.
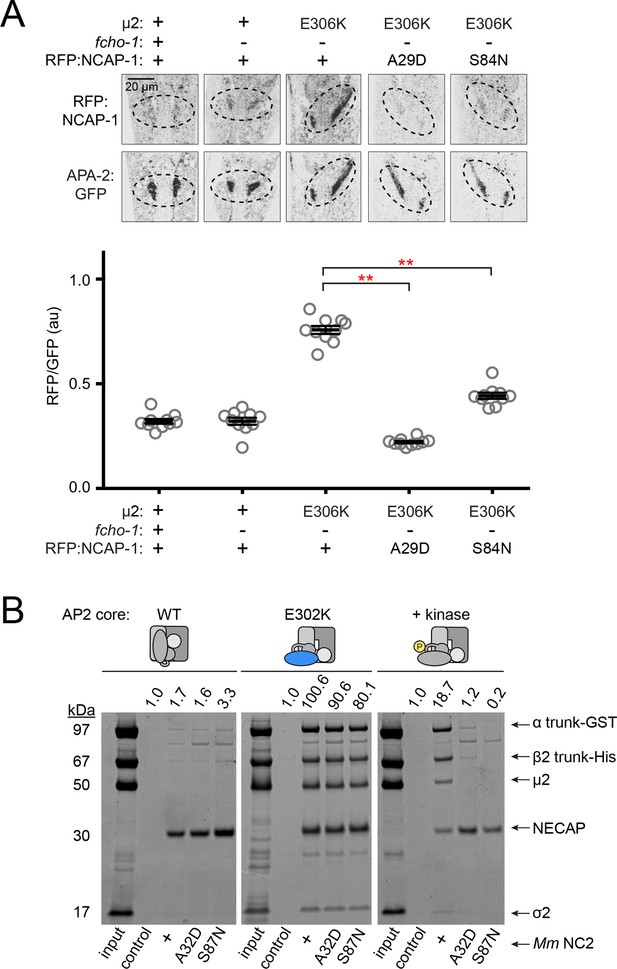
Missense mutations in NECAPs prevent association with phosphorylated forms of AP2.
(A) Confocal slices of worm nerve rings were acquired and analyzed as for Figure 5. Amino acid changes in µ2 (E306K, constitutively open AP2; see also Figure 1—figure supplement 1C) and in NCAP-1 are indicated. Bars indicate mean ±SEM for n = 10 biological replicates. **p<0.001, unpaired, two-tailed T-test. au, arbitrary units; +, wild type allele; -, deletion allele. (B) In vitro pulldown assays were performed as described in Figure 4B. Missense mutations in Mm NECAP2 bait are indicated (below). +, wild type allele. Data are representative of 1 technical replicate. Band intensities of the α trunk were quantified as in Figure 4 (values above).
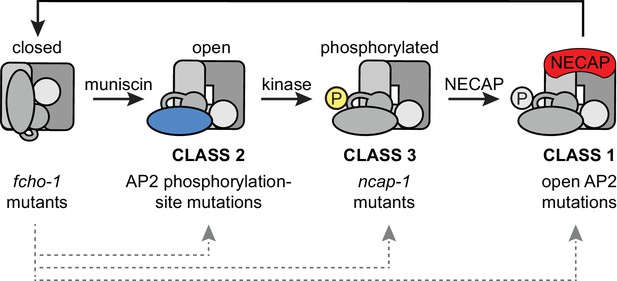
Model of AP2 activation and inactivation.
Muniscins allosterically activate AP2 to form a stable association with the membrane. Open AP2 is then phosphorylated on the µ2 subunit by the AP2-associated kinase. NECAPs subsequently bind to open, phosphorylated AP2 and recycle the complex. Generation of the closed form of AP2 presumably involves dephosphorylation and disengagement from the membrane. In the absence of muniscins, AP2 activation is greatly reduced. The fcho-1 suppressor screen isolated three classes of mutations that enable AP2 to remain active in lieu of muniscins (bottom). Each class disrupts the AP2 inactivation pathway and promotes accumulation of AP2 at discrete steps in the cycle (gray arrows).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gene (Caenorhabditis elegans) | ncap-1 | NA | CELE_Y110A2AR.3 | |
| gene (C. elegans) | fcho-1 | NA | CELE_F56D12.6 | |
| gene (C. elegans) | apm-2 | NA | CEAP50, apm-2, CELE_R160.1 | |
| gene (C. elegans) | apa-2 | NA | apt-4, CELE_T20B5.1 | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | N2 | NA | RRID:WB-STRAIN:N2_(ancestral)) | Wild type |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN109 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew31[splice donor]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN110 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew32[A29D]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN111 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew33[S84N]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN112 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew34[splice donor]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN113 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew35[splice donor]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN114 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew36[Q107X]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN115 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew37[splice donor]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN116 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew38[stop lost]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN101 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG6353 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II; unc-119(ed3) III | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN86 | this paper | ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN59 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II mewSi2 [Pdpy-30::RFP:NCAP1 unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG8012 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | oxSi254[Pdpy-30::APA-2::GFP unc-119(+)] II; unc-119(ed3) III | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG6650 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi254 [Pdpy-30::APA-2::GFP unc-119(+)] II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN98 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi254 [Pdpy-30::APA-2::GFP unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN97 | this paper | oxSi254[Pdpy-30::APA-2::GFP unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG8578 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | oxSi484[Pvha-6::GFP:CD4:YASV unc-119(+)] II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi876[Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG8579 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi484[Pvha-6::GFP:CD4:YASV unc-119(+)] II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi876[Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN65 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi484[Pvha-6::GFP:CD4:YASV unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi876[Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN66 | this paper | oxSi484[Pvha-6::GFP:CD4:YASV unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi876 [Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG8557 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEV(protease) unc-119(+)] II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi876[Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG8558 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEV(protease) unc-119(+)] II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi876[Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN100 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II; oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi876[Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN99 | this paper | oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi876[Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG8555 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877[Papm-2::3XFLAG:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | EG8556 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877[Papm-2::3xFLAG:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN96 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877[Papm-2::3xFLAG:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN106 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; mewSi3 [Pdpy-30::RFP:NCAP-1 unc-119(+)] IV; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877 [Papm-2::3xFLAG:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN91 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; mewSi15 [Pdpy-30::RFP:Mm_NECAP1 unc-119(+)] IV; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877[Papm-2::3xFLAG:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN93 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; mewSi8 [Pdpy-30::RFP:Mm_NECAP2 unc-119(+)] IV; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877[Papm-2::3xFLAG:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN95 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; mewSi17 [Pdpy-30::RFP:Ss_NECAP unc-119(+)] IV; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877 [Papm-2::3xFLAG:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN60 | this paper | mewSi1[Pdpy-30::APA2:GFP unc-119(+)] I; mewSi2[Pdpy-30:: RFP:NCAP1 unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN61 | this paper | mewSi1[Pdpy-30::APA2:GFP unc-119(+)] I; fcho-1(ox477:: unc-119(+)) II mewSi2[Pdpy-30:: RFP:NCAP1 unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN62 | this paper | mewSi1[Pdpy-30::APA2:GFP unc-119(+)] I; fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) II mewSi2[Pdpy-30::RFP:NCAP1 unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox562[E306K]) X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN53 | this paper | mewSi1[Pdpy-30::APA2:GFP unc-119(+)] I; fcho-1(ox477:: unc-119(+)) II mewSi2[Pdpy-30:: RFP:NCAP1 unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(mew44[T160A]) X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN55 | this paper | mewSi1[Pdpy-30::APA2:GFP unc-119(+)] I; fcho-1(ox477:: unc-119(+)) II mewSi2[Pdpy-30:: RFP:NCAP1 unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox562[E306K]+mew46[T160A]*) X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN56 | this paper | mewSi1[Pdpy-30::APA2:GFP unc-119(+)] I; fcho-1(ox477:: unc-119(+)) II mewSi2[Pdpy-30:: RFP:NCAP1 unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox562[E306K]+mew47[R440S]*) X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN128 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::cb-unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease Cb_unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; mewSi25[RFP:NCAP-1(A29D)*] IV; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877[Papm-2::3xFLAG:APM-2: tev-site Cb_unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN135 | this paper | fcho-1(ox477::cb-unc-119(+)) II oxSi883[Phsp-16.41::TEVprotease Cb_unc-119(+)] II ncap-1(mew39 [1.4 kb deletion]) II; mewSi35[RFP:NCAP-1(S84N)*] IV; apm-2(ox546[W64X]) X oxSi877 [Papm-2::3xFLAG:APM-2: tev-site Cb_unc-119(+)] X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN127 | this paper | mewSi1[APA2:GFP] I; fcho-1(ox477:: unc-119(+)) II mewSi24[RFP: NCAP1(A29D)*] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox562[E306K])X | |
| strain, strain background (C. elegans, hermaphrodite) | GUN122 | this paper | mewSi1[APA2:GFP] I; fcho-1(ox477:: unc-119(+)) II mewSi31[RFP: NCAP1(S84N)*] II ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) II; apm-2(ox562[E306K])X | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | fcho-1(ox477::unc-119(+)) | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew31[splice donor]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew32[A29D]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew33[S84N]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew34[splice donor]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew35[splice donor]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew36[Q107X]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew37[splice donor]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew38[stop lost]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | ncap-1(mew39[1.4 kb deletion]) | this paper | fcho-1 suppressor | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi2[Pdpy-30::RFP:NCAP1 unc-119(+)] | this paper | Generated with MosSCI | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi3[Pdpy-30::RFP:NCAP-1 unc-119(+)] | this paper | Generated with MosSCI | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi15[Pdpy-30::RFP: Mm_NECAP1 unc-119(+)] | this paper | Generated with MosSCI | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi8[Pdpy-30::RFP: Mm_NECAP2 unc-119(+)] | this paper | Generated with MosSCI | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi17[Pdpy-30::RFP: Ss_NECAP unc-119(+)] | this paper | Generated with MosSCI | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | oxSi254[Pdpy-30::APA-2:: GFP unc-119(+)] | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi1[Pdpy-30:: APA-2::GFP unc-119(+)] | this paper | Generated with MosSCI | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | oxSi484[Pvha-6::GFP:CD4: YASV unc-119(+)] | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | oxSi883[Phsp-16.41:: TEV(protease) unc-119(+)] | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | oxSi876[Papm-2::HA:APM-2: tev-site unc-119(+)] | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | oxSi880[Papm-2::HA:APM-2(E306K): tev-site unc-119(+)] | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | oxSi878[Papm-2::HA:APM-2(T160A): tev-site unc-119(+)] | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | oxSi877[Papm-2::3xFLAG: APM-2:tev-site unc-119(+)] | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | apm-2(ox562[E306K] +mew46[T160A]) | this paper | mew46[T160A] generated by CRISPR | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | apm-2(ox562[E306K] +mew47[R440S]) | this paper | mew47[R440S] generated by CRISPR | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi25[RFP:NCAP-1(A29D] | this paper | Generated by CRISPR | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi35[RFP:NCAP-1(S84N)] | this paper | Generated by CRISPR | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi24[RFP:NCAP1(A29D)] | this paper | Generated by CRISPR | |
| genetic reagent (C. elegans) | mewSi31[RFP:NCAP1(S84N)] | this paper | Generated by CRISPR | |
| cell line (Homo sapiens, female) | HEK293 | ATCC | RRID:CVCL_0045 | |
| transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pGH500, in HEK239 cells | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Tissue culture pulldowns’ | |
| transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pGH501, in HEK239 cells | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Tissue culture pulldowns’ | |
| transfected construct (H. sapiens) | pGH502, in HEK239 cells | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Tissue culture pulldowns’ | |
| antibody | mouse monoclonal anti-adaptin α | BD Biosciences | Cat# 610501, RRID:AB_397867 | (1:500) |
| antibody | rabbit polyclonal anti-AP2B1 | Abcam | 151961, RRID: AB_2721072 | (1:1000) |
| antibody | rabbit monoclonal anti-AP2M1 phospho T156 | Abcam | Cat# 109397, RRID:AB_10866362 | (1:1000) |
| antibody | rabbit monoclonal anti-AP2S1 | Abcam | Cat# 128950, RRID:AB_11140842 | (1:4000) |
| antibody | mouse monoclonal anti-flag | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F3165, RRID:AB_259529 | (1:1000) |
| antibody | mouse monoclonal anti-tubulin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# T5168, RRID:AB_477579 | (1:2000) |
| antibody | rabbit polyclonal anti-histone H3 | Abcam | Cat# 1791, RRID:AB_302613 | (1:4000) |
| antibody | rabbit polyclonal anti-beta actin | Abcam | Cat# 8227, RRID:AB_2305186 | (1:1000) |
| antibody | goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 | Life Technologies | Cat # A11029, RRID:AB_2534088 | (1:4000) |
| antibody | goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 647 | Life Technologies | Cat# A21244, RRID:AB_10562581 | (1:2000) |
| antibody | goat anti-rabbit StarBright Blue 700 | BioRad | Cat# 12004161, RRID: AB_2721073 | (1:5000) |
| antibody | goat anti-mouse IRDye 800CW | LI-COR | Cat# 925–32210, RRID:AB_2687825 | (1:20000) |
| antibody | rat monoclonal anti-HA- Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) | Roche | Cat# 12013819001 RRID:AB_390917 | (1:500) |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pEP29 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘C. elegans NECAP transgenes’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pEP41 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘C. elegans NECAP transgenes’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pEP58 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘C. elegans NECAP transgenes’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pEP71 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘C. elegans NECAP transgenes’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGH495 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘C. elegans NECAP transgenes’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGH505 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘C. elegans NECAP transgenes’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB19 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant AP2 cores’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB21 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant AP2 cores’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB27 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant NECAPs’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB28 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant NECAPs’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB29 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant NECAPs’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB31 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant AP2 cores’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB81 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant NECAPs’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pEP82 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant AP2 cores’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB91 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant NECAPs’ | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pGB94 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant NECAPs’ | |
| sequence-based reagent | pGH494 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | ||
| sequence-based reagent | pGH503 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant NECAPs’ | |
| sequence-based reagent | pGH504 | this paper | Cloning described in ‘Recombinant AP2 cores’ | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH678 | this paper | CGATAGAGAAGGCTTCAACACAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH679 | this paper | AGGTATTCAGACATTTTTC AAATGAAAATCTAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH680 | this paper | CAGTCAAAAAATGC GATAAAAGTACGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH681 | this paper | GGACAGGAAATTTC AATAAATTAGCGATG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP366 | this paper | AACGGGCGGTAGT GGAGGCACTGGTATG GGAGATTACGAGAACGTTTTAATG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP367 | this paper | TATCACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCT GGGTCTAGAAATCTAATAAA TTGCCAGACGTCG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP407 | this paper | GAGGAACGGGCGGTAGTGGAG GCACTGGTATGGAGGAGAGTG AGTACGAGTCTGTTCTGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP408 | this paper | TCACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGC TGGGTCTAGAACTGG ACCCAGCCGGTG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP409 | this paper | GGAGGAACGGGCGGTAGTGG AGGCACTGGTATGGCGGCA GAGCTGGAATATG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP410 | this paper | TCACCACTTTGTACAAGAAA GCTGGGTCTAAAACTGGA CCCAGTTAGATGGCTGTG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP391 | this paper | ACGTCGTGACTGGGAAAACCC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP392 | this paper | GCCAGGGTTTTCCCAGTCA CGACGTTGATCATTGGCA TGCTGAAATATTC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH526 | this paper | ATGGTTGTGTCGAAAGGCGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH528 | this paper | ACCAGTGCCTCCACTACCG CCCGTTCCTCCTGTGCCACC TTTGTACAGTTCATCCATTCC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH698 | this paper | GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAA AAGCAGGCTCAAAAATGG TTGTGTCGAAAGGCGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH731 | this paper | GTGACATTAAAGTC AAAAGCATCTCCTC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH733 | this paper | GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAA AAGCAGGCTCAAAAATGGGA GATTACGAGAACGTTTTAAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH734 | this paper | GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAA AGCTGGGTTTAGAAATCTAAT AAATTGCCAGACGTC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH736 | this paper | GAGGAGATGCTTTTGAC TTTAATGTCAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH738 | this paper | GCGGTAGTGGAGGCACTG GTATGGGAGATTACGAG AACGTTTTAATG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1011 | this paper | TAGACCCAGCTTTCTTGTA CAAAGTGGTGATA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1012 | this paper | ACCAGTGCCTCCAC TACCGCCCGTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH953 | this paper | CATGCTTCCGCCGGTACCT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH954 | this paper | GTTTAAACCCGCTGATCAGCCT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH955 | this paper | GTGGAGGTACCGGCGGAAG CATGGGAGATTACGAG AACGTTTTAATG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH956 | this paper | GCTGATCAGCGGGTTTAAACTT AGAAATCTAATAAATT GCCAGACGTCG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH957 | this paper | GTGGAGGTACCGGCGGAA GCATGGCGGCAGAGCTGGAA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH958 | this paper | GATCAGCGGGTTTAAACTT AAAACTGGACCCAGTTAGATGGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH959 | this paper | GTGGAGGTACCGGCGGAA GCATGGAGGAGAGTGAGTACGAGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH960 | this paper | GCTGATCAGCGGGTTTAAA CTTAGAACTGGACCCAGCCGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP13 | this paper | TAATTAACCTAGGCTGCTGCCACC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP17 | this paper | AAGAAGGAGATATACATAT GAAGAAGTTTTTCGACTCCAG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP18 | this paper | GGCAGCAGCCTAGGTTAATT ACTGTACATTTGGAACGGGGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB24 | this paper | CGCCGCCAGCCAATCTGCCCA GCCACCTGGCTGGTGA TCTGGGACTGTTC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB26 | this paper | ATGAATAAGCLCTCCGATCA TCATATGTATATCTCCTTCTTATA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB27 | this paper | GCATTTATGAAACCCGCT GCTAATTAACCTAGGC TGCTGCCACCG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB28 | this paper | ATGATCGGAGGCTTATTCATCT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB29 | this paper | GCAGCGGGTTTCATAAATGCCA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB33 | this paper | GGGCAGATTGGCTGGCG GCGAGAAGGCATCAAGTA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB34 | this paper | AGCAAGAGTCTGGTGCCGCG CGGCAGCGGTAAGCAGTC GATCGCCATTGATG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB35 | this paper | CTGCTTACCGCTGCCGCG CGGCACCAGACTCTTGCT TGTTTCATCAGCTGTG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB47 | this paper | TGAGATCCGGCTGC TAACAAAGCC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB48 | this paper | TTTAAGAAGGAGATATACA TATGGCAGAAATCGGTACTGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB49 | this paper | AGTGCATCTCCCGTGATGC AGAAATCTAATAAATTGCCA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB50 | this paper | AGTGCATCTCCCGTGATGC AAAACTGGACCCAGTTAGATGGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB51 | this paper | AGTGCATCTCCCGTGATGCA GAACTGGACCCAGCCGGTGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB52 | this paper | TGCATCACGGGAGATGCACT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB53 | this paper | GTTAGCAGCCGGATCTCAGT GGTGATGATGGTGATGTTG AAGCTGCCACAAGGCAGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB174 | this paper | AGTGCATCTCCCGTGATGC AGCTTCCGCCGGTACCTCCAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH338 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | CATATGTATATCTCCTTCTT ATACTTAACTAATATAC TAAGATG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP642 | this paper | CCGATATCCACGGT TGGTGGCCCG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP643 | this paper | ACCAACCGTGGATATCGGG ACTCAGAATGGCAACT GGACCAGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP644 | this paper | TCTAGATACTTCGTCATC CGAATTGAAGATGGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP645 | this paper | AATTCGGATGACGAAGT ATCTAGAGTTGTCTGT CACACTCTCCACTGCG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH847 | this paper | CCAAACTGAAGGTCAAGGTGGTC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH848 | this paper | CCTTGACCTTCAGTTTGGTGCGC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH853 | DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03648 | TAATTAACCTAGGC TGCTGCCACCG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1204 | this paper | GTTAATTAAAACAG ATGCACGACGGTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1205 | this paper | GTGCATCTGTTTTAATTAACA TGGAGGAGAGTGAGTACGAGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1206 | this paper | GCAGCAGCCTAGGTTAATTA GAACTGGACCCAGCCGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1227 | this paper | GGAAGTTCTGTTCCAGG GGCCCGGGTCCGG CATGTCCCCT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1228 | this paper | GCCCCTGGAACAGAACTTC CAGGCCGGATCCGCCCTTCTT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1231 | this paper | CATATGTATATCTCCTT CTTAAAGTTAAAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1246 | this paper | CCGCTGAGCAATAACT AGCATAAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1247 | this paper | CTAATGCAGGAGTCGCATAAGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1249 | this paper | GTTATGCTAGTTAT TGCTCAGCGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGH1250 | this paper | TTATGCGACTCCTGCATTAG GCGCGAGGCAGGATCTCG | |
| sequence-based reagent | rEP360 | this paper | Gene-specific target of crRNA: TGAAGTGTCTCGTAACAAGA | |
| sequence-based reagent | rGB156 | this paper | Gene-specific target of crRNA: CAAATCACGTCTCAAGTGAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | rGB155 | this paper | Gene-specific target of crRNA: TTGGGTGAAGTTCTAGCATC | |
| sequence-based reagent | rEP254 | this paper | Gene-specific target of crRNA: CGGGCTGTCGAGGTTCCAGT | |
| sequence-based reagent | rEP676 | this paper | Gene-specific target of crRNA: CACAAAATATCGAGAACTAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | rEP700 | this paper | Gene-specific target of crRNA: CCCTGGCAACGCAATTGAGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB154 | this paper | TCCCATTGGTTCGcGAAGTGTCT CGTAACAAGATGaAAGTTAA GGTATTTCACTTGTCAC | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB159 | this paper | TTCGTTACATTGGAcGATCG GGACTGTATGAAACtAGcTGC TAGAACTTCACCCAACCCT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oGB130 | this paper | GGAGCAGTCACAAATCACGT CTCAAGTtGCCGGCCAAATT GGATGGCGTCGGGAGGGTAT | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP674 | this paper | TTCGCTATAAAATCCCTATTT TTCAGAGatGCgGACTGGAAC CTCGACAGCCCGGCTTGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP680 | this paper | CCGCCGATCGGAACCAGCGG TCATAAAGatGCgGACTGGA ACCTCGACAGCCCGGCTTGG | |
| sequence-based reagent | oEP701 | this paper | GCCCGATCGATGCGCACCC TGGCAACGCAATTGAGGCcG TTTCgGATaacTCTaGATATTT TGTGATTCGTTTGCAG | |
| peptide, recombinant protein | AcTEV Protease | Invitrogen | 12575015 | |
| software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism (version 7.0 c for Mac) | GraphPad Software, www.graphpad.com | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| software, algorithm | Fiji | doi:10.1038/ nmeth.2019 | RRID:SCR_002285 |
-
*allele generated by CRISPR
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
(A) Strains (B) Plasmids (C) Oligonucleotides.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32242.011
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32242.012





