Neural retina-specific Aldh1a1 controls dorsal choroidal vascular development via Sox9 expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells
Figures
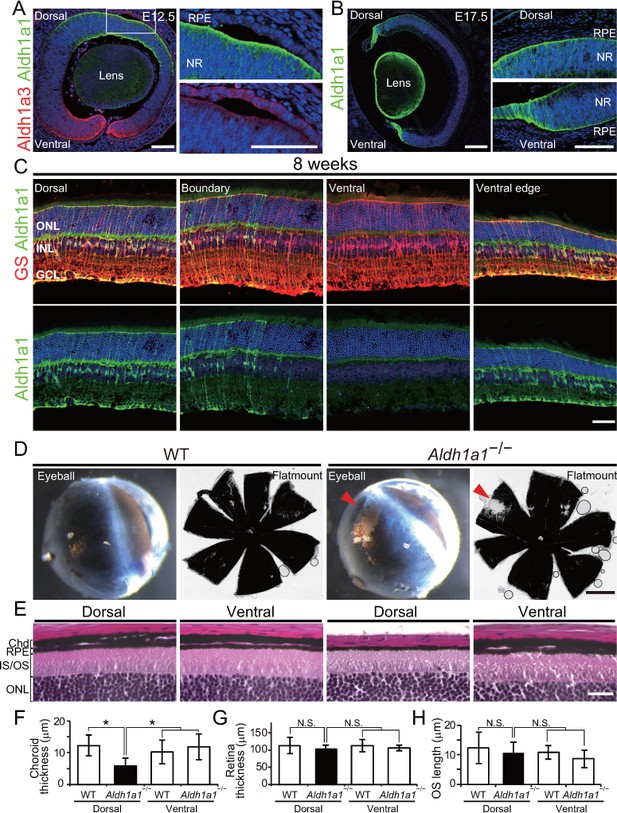
Aldh1a1 is predominantly expressed in the dorsal neural retina during embryonic and adult stages, and Aldh1a1–/– mice have less pigmentation and a thin choroid in the dorsal area.
(A–C) Section immunohistochemistry of the mouse retinas labeled with Aldh1a1, Aldh1a3 and glutamine synthetase (GS) antibodies. (A) At E12.5, Aldh1a1 (green) and Aldh1a3 (red) are expressed in dorsal and ventral neural retina (NR), respectively. At the dorsal edge (white box), Aldh1a1 is expressed only in NR, not in RPE (right upper panel), while some RPE cells are Aldh1a3-positive (right lower panel). (B) At E17.5, Aldh1a1 (green) is expressed in the dorsal half and the ventral edge of the retina, but no Aldh1a1-positive RPE cells were detected in the dorsal (right upper panel) and ventral (right lower panel) regions. (C) At 8 weeks, Aldh1a1 (green)-positive cells were double-labeled with GS (red) at the dorsal, boundary, and ventral edge regions (see Figure 1—figure supplement 1A, B; for the ‘boundary’ region). ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer. (D) Dissected eyeballs and choroidal flat-mounts of adult (8-week-old) wild-type (WT) and Aldh1a1–/– mice. Loss of pigmentation was observed in the dorsonasal region (red arrowhead) of Aldh1a1–/– eyes. (E) Hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) staining of WT and Aldh1a1–/– retinal sections. The pigmented layer (choroid) of the dorsal Aldh1a1–/– retina is thinner than those on the other sides. ONL, outer nuclear layer; IS/OS, inner segment/outer segment; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; Chd, choroid. (F–H) Quantitative evaluation of choroidal thickness (F), retinal thickness (G), and the length of outer segments (H) of the H and E-stained retinal sections. Data represent the average ±SD; n = 8–9 from 4 to 5 mice per group. *p<0.05. N.S., not significant. [Scale bars, 50 μm (A and C), 200 μm (B), 1 mm (D), and 20 μm (E).].
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 1F–H.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.005
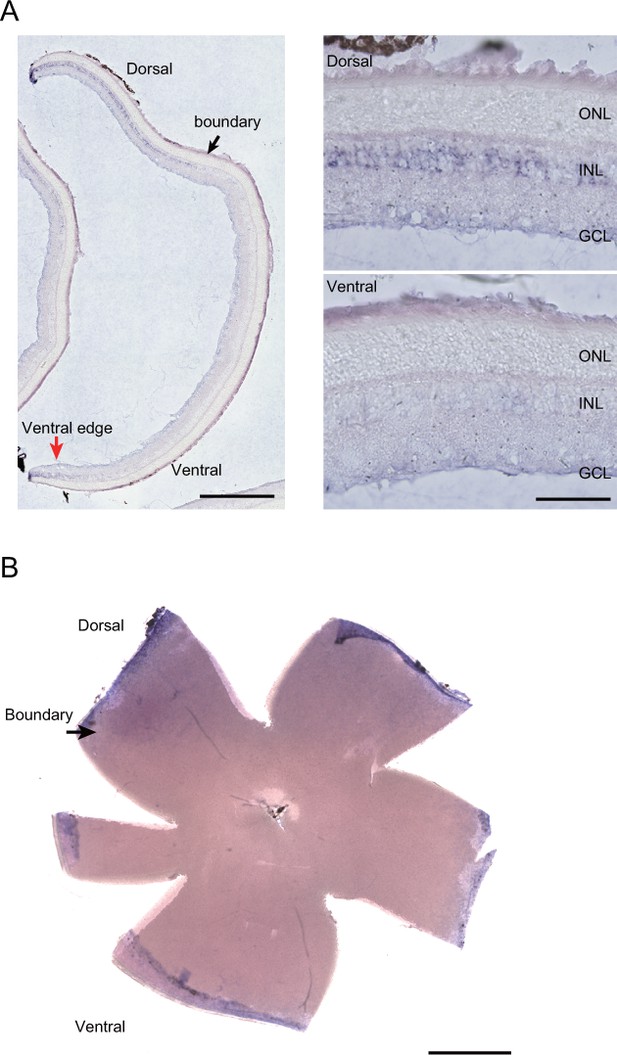
In situ hybridization (ISH) with the Aldh1a1 probe in the adult (8-week-old) mouse retina.
(A) Section ISH. Aldh1a1-positive cells were localized in the inner nuclear layer (INL) from the dorsal to the ‘boundary’ regions (black arrow) and the ventral edge (red arrow). Right panels show the high-magnification images of the section ISH. No Aldh1a1-positive cells were found in outer nuclear layer (ONL). GCL, ganglion cell layer. (B) Flat-mount ISH. Aldh1a1-positive cells were predominantly observed in the dorsal portion of the neural retina (black arrow). [Scale bars, 1 mm (left panel in A and B), 100 μm (right panels in A).].
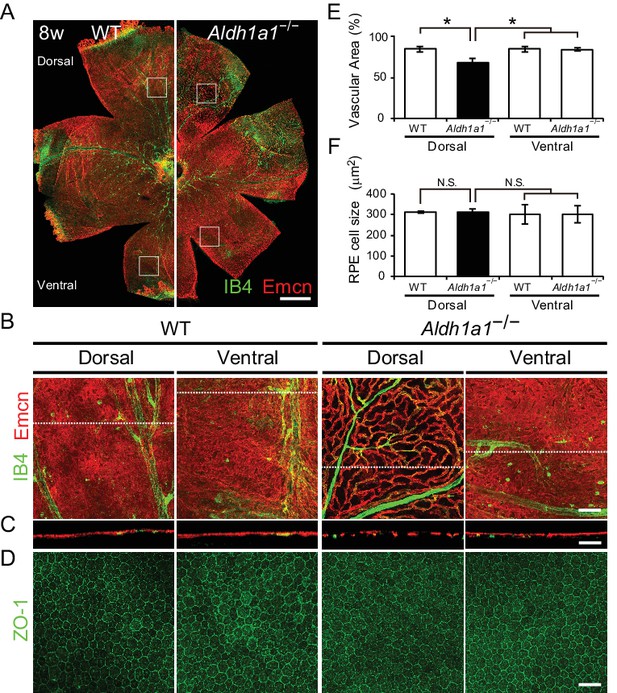
Hypoplasia at the dorsal side of choroid in Aldh1a1–/– mice.
(A) Representative choroidal flat-mount immunohistochemistry of adult (8-week-old) WT (left panel) and Aldh1a1–/– (right panel) posterior eyes stained for endomucin (Emcn, red) and isolectin B4 (IB4, green). (B) High-magnification Z-stack images of the choroidal flat-mounts collected from the dorsal and ventral areas of WT and Aldh1a1–/– mice (four white boxes shown in (A)) stained with Emcn (red) and IB4 (green). The dorsal image of Aldh1a1–/– mice indicates poor vascularization. (C) Orthogonal images of the Z-stacks (broken lines in (B)) showing breaks/holes in the dorsal region of Aldh1a1–/– eyes stained with Emcn antibody (red) and IB4 (green). (D) RPE flat-mount immunohistochemistry of WT and Aldh1a1–/– stained with ZO-1 (green). (E and F) Quantitative evaluation of the vascular density and size of RPE cells of adult WT and Aldh1a1–/– mice. Data represent the average ± SD; n = 8 per group. *p<0.05. N.S., not significant. [Scale bars, 500 μm (A), 50 μm (B–D).].
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 2E,F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.007
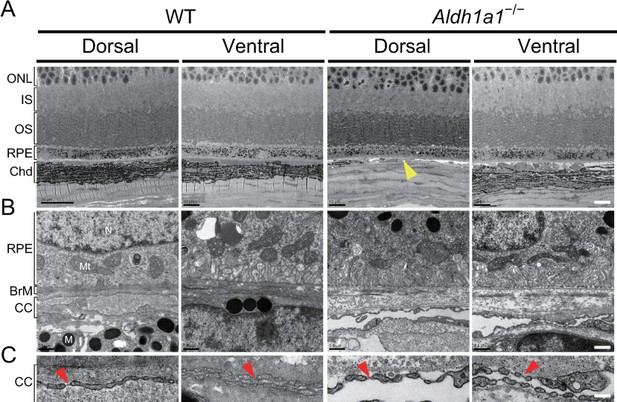
Choroidal vessels of Aldh1a1–/– mice have features of capillaries.
(A) Electron micrographs of the dorsal and ventral areas from adult (8-week-old) WT and Aldh1a1–/– mice. The absence of choroidal pigmentation and a thin choroid layer is observed in the dorsal section of Aldh1a1–/– mice (yellow arrowhead). (B) Higher magnification of electron micrographs of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and Bruch’s membrane (BrM). There are no differences between WT and Aldh1a1–/– mice in the morphology of RPE and BrM. M, melanocyte; Mt, mitochondria; N, nucleus. (C) The higher magnification of electron micrography allows visualization of the fenestrations in the choriocapillaris. Representative fenestrated structures are indicated by red arrowheads. In the dorsal section of Aldh1a1–/– mice, the choriocapillaris shows fenestrations similar to those in the dorsal and ventral sides of WT and the ventral side of Aldh1a1–/– mice. [Scale bars, 10 μm (A), 0.5 μm (B), and 0.1 μm (C).].
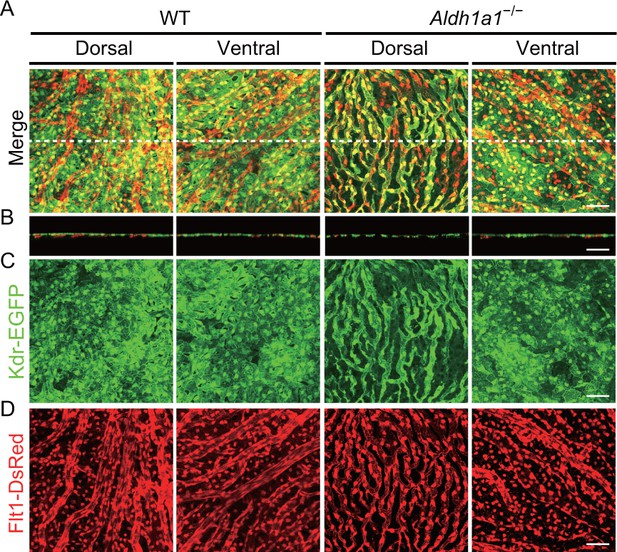
Choroidal vessels of the Aldh1a1–/– mice have both Flt1 and Kdr expression.
(A–D) Z-stack images of choroidal flat-mounts of adult (4-week-old) wild type (WT) and Aldh1a1–/–;Flt1-BAC-DsRed;Kdr-BAC-EGFP mice. Merged (A), Kdr-EGFP (C, green) and Flt1-DsRed (D, red) images show poorly vascularized choroid co-expressing both Flt1-DsRed and Kdr-EGFP in the dorsal region of Aldh1a1–/– mice. (B) Orthogonal images of the Z-stacks (broken lines in (A)). [Scale bars, 50 μm (A–D).].
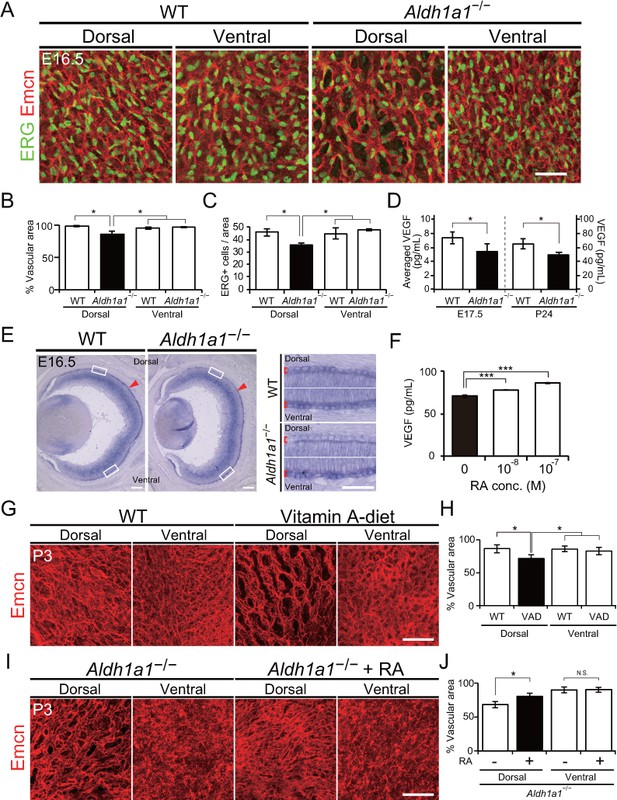
Retinoic acids modulate VEGF secretion by RPE cells.
(A) Choroidal flat-mount immunohistochemistry of E16.5 WT and Aldh1a1–/– embryos stained for endomucin (Emcn, red) and ETS-related gene (ERG, green). Note that hypovascularization and fewer vascular endothelial cells were observed in the dorsal region of Aldh1a1–/– embryonic eyes. (B and C) Quantitative evaluation of the density of Emcn-positive vessels and the number of ERG-positive cells in E16.5 WT and Aldh1a1–/– embryos. Data represent the average ±SD; n = 4 per group. *p<0.05. (D) ELISA analysis of VEGF secreted from WT and Aldh1a1–/– RPE-choroid complex at E17.5 and P24. Data represent the average ±SD; n = 4 independent samples per group. *p<0.05. (E) In situ hybridization on E16.5 WT and Aldh1a1–/– eyes with the Vegfa probe (DIG-labeled, purple). Vegfa expression was reduced in the dorsal RPE cells of Aldh1a1–/– eyes (upper RPEs from red arrowhead). Right panels show the higher magnification images of left panels (four white boxes) and red square brackets indicate RPE layer. (F) Retinoic acid (RA)-dependent enhancement of VEGF secretion of human primary RPE cells evaluated by ELISA. Data are means three times ELISA determinations. ***p<0.001. (G) Choroidal flat-mount immunohistochemistry of P3 WT and Vitamin-A-deficient (VAD) mice stained for endomucin (Emcn, red). Dorsal choroidal hypoplasia was observed in VAD mice. (H) Quantitative evaluation of the vascular density of P3 WT and VAD mice. Data represent the average ±SD; n = 5–6 per group. *p<0.05. (I) Choroidal flat-mount of P3 Aldh1a1–/– and Aldh1a1–/– mice from a mother treated with RA by oral gavage between E10 and E16, immunostained with anti-endomucin antibody (Emcn, red) This RA treatment of the mother restored the choroidal vascularization in P3 Aldh1a1–/– pups. (J) Quantitative evaluation of the vascular density in Aldh1a1–/– mice and Aldh1a1–/– mice from a mother treated with RA. Data represent the average ± SD; n = 4 per group. *p<0.05. N.S., not significant. [Scale bars, 50 μm (A, right panels in E, (G and I), 200 μm (left panels in E)].
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 4B–D,F,H,J.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.013
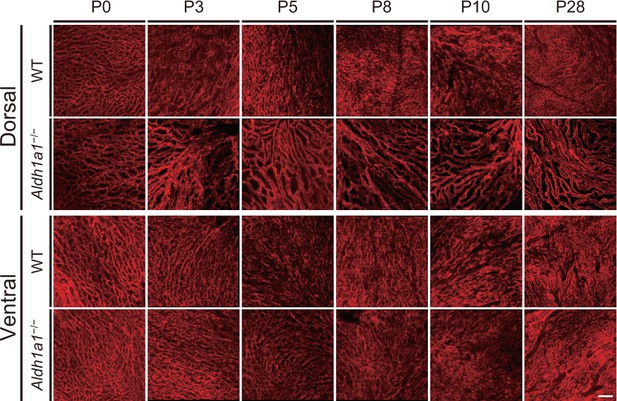
Developmental flat-mount immunohistochemical analysis of choroid in the Aldh1a1–/– mice.
P0–28 choroidal flat-mounts of WT and Aldh1a1–/– eyes were immunostained with the endomucin antibody (Emcn, red), and images of the dorsal and ventral areas were collected. Poor vascularization was already detectable in the P0 dorsal choroid of Aldh1a1–/– mice. [Scale bar, 50 μm.].
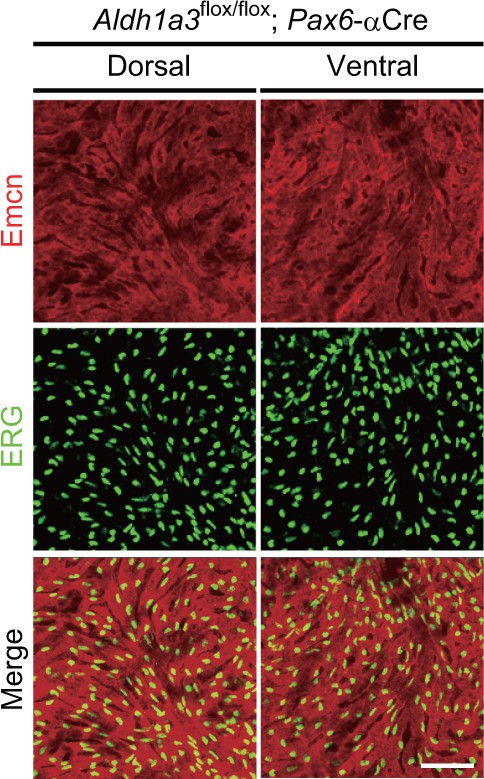
Neural retina-specific conditional disruption of Aldh1a3 did not show choroidal hypoplasia in the ventral retina.
Choroidal flat-mount immunohistochemistry of adult (5-week-old) Aldh1a3 L2/L2;Pax6-αCre mice labeled with endomucin (Emcn, red) and ETS-related gene antibodies. Both dorsal and ventral choroids show normal vascularization. [Scale bar, 50 μm.].
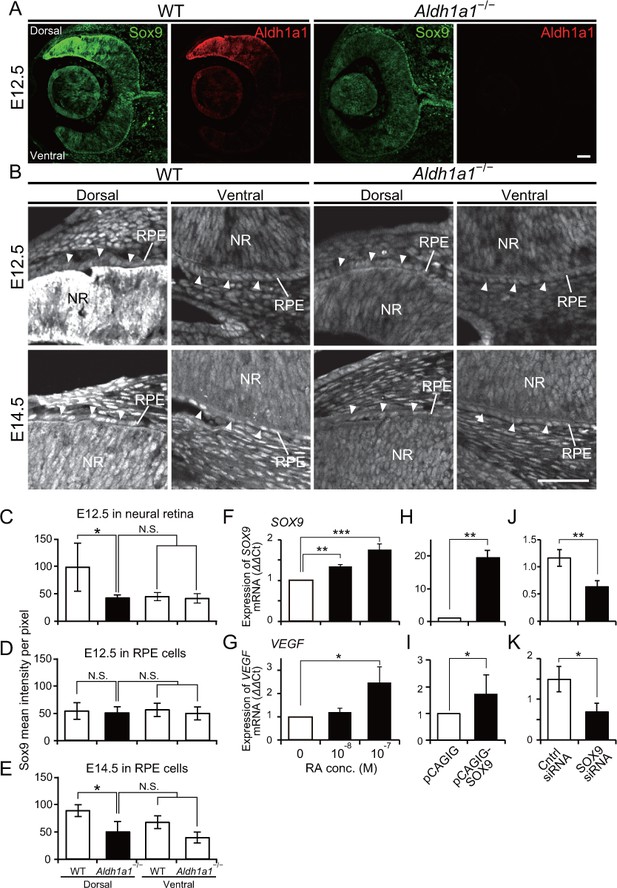
Sox9 expression is downregulated in RPE cells of Aldh1a1–/– mice.
(A) Sox9 (green) and Aldh1a1 (red) staining of WT and Aldh1a1–/– eyes at E12.5. (B) Sox9 (white) expression in neural retina and RPE (white arrowheads) of WT and Aldh1a1–/– eyes at E12.5 (upper panels) and E14.5 (lower panels). Sox9 was strongly expressed in the dorsal neural retinas of E12.5 WT eyes, and downregulated in RPE cells of E14.5 Aldh1a1–/– eyes. [Scale bars, 50 μm (A and B).]. (C–E) Quantitative evaluation of the Sox9 immunofluorescence intensity in embryonic WT and Aldh1a1–/– eyes. Sox9 intensity was quantified in the E12.5 neural retina (C), E12.5 RPE cells (D), and E14.5 RPE cells (E). Data represent the average ±SD; n = 4 per group. *p<0.05. N.S., not significant. (F–K) Sox9 and Vegfa mRNA expression in primary RPE cells in response to RA exposure (F and G), Sox9 overexpression (H and I), and Sox9 knockdown (J and K). Relative expression of Sox9 mRNA (F, H, and J) and Vegfa mRNA (G, I, and K) normalized to β-actin mRNA are shown. Data are representative of three experiments. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. N.S., not significant.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 5C–K.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.016
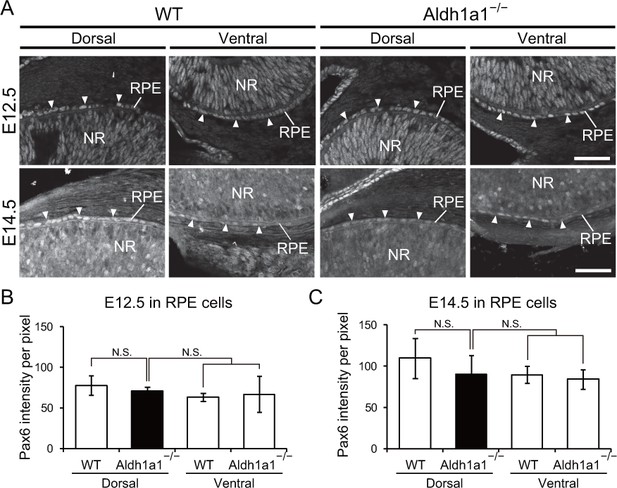
Pax6 expression in the developing RPE cells of WT and Aldh1a1–/– mice.
(A) Section immunohistochemistry labeled with the Pax6 antibody (white) in neural retina and RPE cells of WT and Aldh1a1–/– eyes at E12.5 (upper panels) and E14.5 (lower panels). NR, neural retina; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. [Scale bar, 50 μm.]. (B and C) Quantitative evaluation of the intensity of Pax6 expression suggested that there was not a significant difference in Pax6 expression in RPE cells between WT and Aldh1a1–/– embryos. N.S., not significant.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 5—figure supplement 1B and C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.017
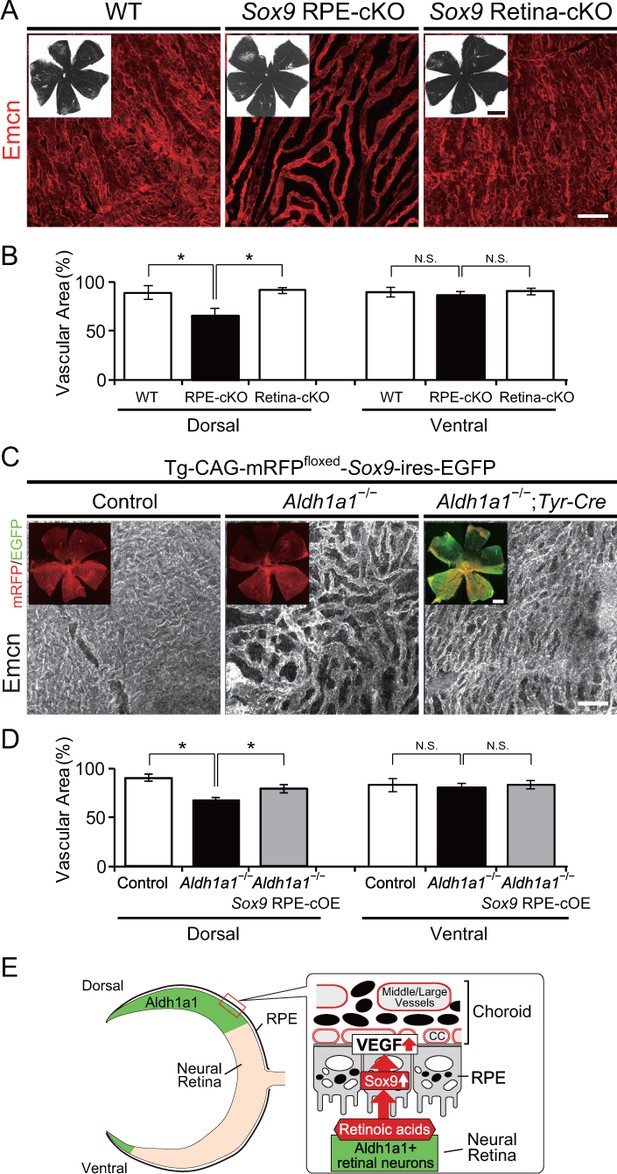
RPE-derived Sox9 controls choroidal vasculature development.
(A) Endomucin expression (Emcn, red) in 5-week-old choroidal flat-mounts. RPE-specific conditional knockout of Sox9 (Sox9 RPE-cKO) mimicked the choroidal hypoplasia seen in Aldh1a1–/– mice (middle panel), but retina-specific conditional knockout of Sox9 (Sox9 Retina-cKO) did not (right panel). Insets represent each choroidal flat-mount. (B) Quantitative evaluation of the vascular density of 5-week-old WT, Sox9 RPE-cKO, and Sox9 Retina-cKO. Data represent the average ±SD; n = 4–5 per group. *p<0.05. N.S., not significant. (C) Endomucin (Emcn, white) expression in P7 choroidal flat-mounts. The choroid was hypovascularized in Tg-CAG-mRFPfloxed-SOX9-ires-EGFP;Aldh1a1–/– eyes (middle panel). Choroidal hypoplasia in Aldh1a1–/– mice was rescued in Aldh1a1–/–;RPE-specific conditional overexpression of Sox9 (Aldh1a1–/–;Tyr-Cre, right panel). Insets represent reporter (mRFP and EGFP) expression. (D) Quantitative evaluation of the vascular density of P7 control, Aldh1a1–/–, and Aldh1a1–/–;Sox9 RPE-cOE. Data represent the average ±SD; n = 5 per group. *p<0.05. N.S., not significant. [Scale bars, 1 mm (insets in A), 50 μm (A and C), 500 μm (insets in C).]. (E) Model summarizing that neural retina-specific Aldh1a1 controls choroidal vascularization in the dorsal region. Retinoic acids (RA) synthesized by Aldh1a1 regulate Sox9 expression, and then Sox9 enhances VEGF secretion from the dorsal RPE cells.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 6B and D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.020
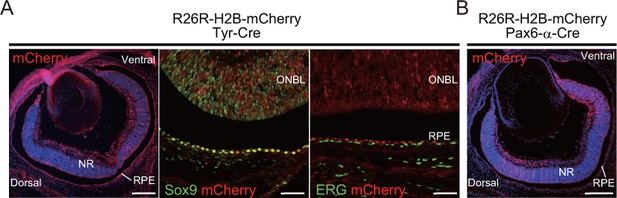
Cre reporter assay of Tyr-Cre and Pax6-α-Cre mice using albinized R26R-H2B-mCherry mice.
(A) Section immunohistochemistry of E16.5 Tyr-Cre eyes labeled with the Sox9 (green, middle panel) antibody and ETS-related gene (ERG, green, right panel) antibody. Cre activity (mCherry, red) could be detected mainly in retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells, with limited staining in the neural retina (NR), and was not detected in the choroid. Cre-expression is colocalized with Sox9 in RPE cells. ONBL, outer neuroblastic layer. (B) Section immunohistochemistry of E16.5 Pax6-α-Cre eyes. Cre activity (mCherry, red) could be detected in the NR without a central area of retinal progenitor cells, but at no stage in RPE cells. [Scale bar, 200 μm (left panel in A and B) and 50 μm (middle and right panels in A)].
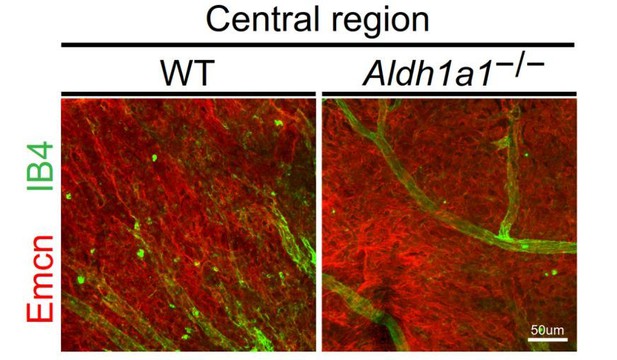
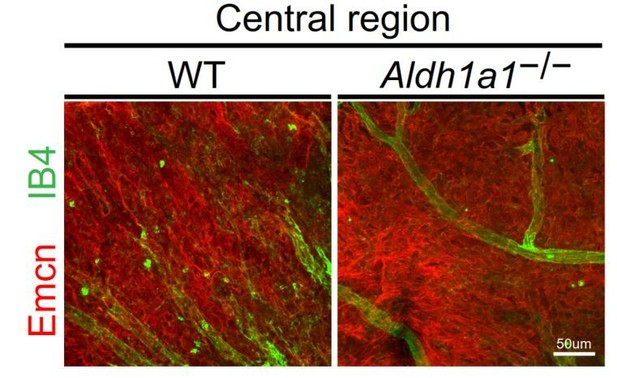
Representative choroidal flat-mount IHC of the central region of adult (8-week-old) WT (left panel) and Aldh1a1–/– (right panel) eyes immunostained with FITC-labeled isolectin B4 (IB4, green) and anti-endomucin antibody (Emcn, red).
There was no difference in choroidal vascular density between WT and Aldh1a1–/– mice.
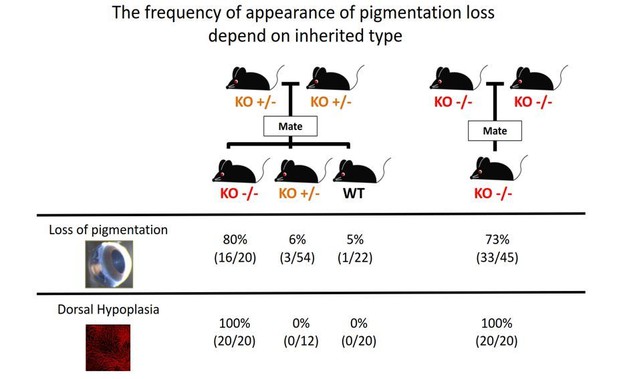
The frequency of appearance of pigmentation loss did not correspond with the principles of Mendelian inheritance.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.025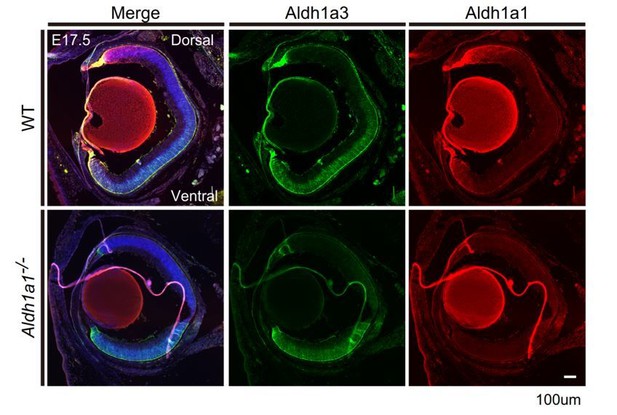
Section IHCs of E17.5 mouse eyes labeled with anti-Aldh1a3 (green) and anti-Aldh1a1 (red) antibodies.
The region of Aldh1a3 expression did not expand.
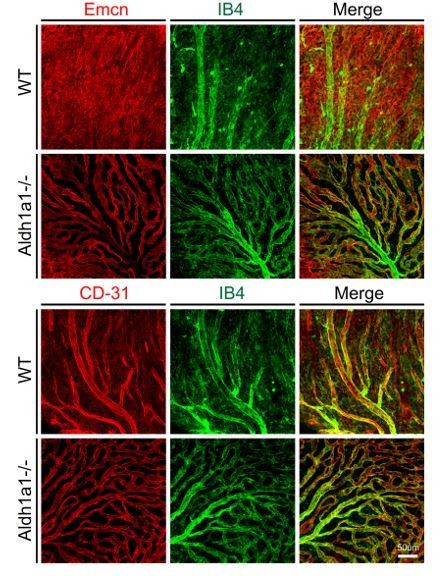
The representative dorsal region of choroidal flat-mounts of 8-week-old WT and Aldh1a1–/– mice stained with FITC-isolectin B4 (IB4, green), anti-endomucin (Emcn, red; upper panels), and anti-CD-31 (red; lower panels).
Emcn specifically visualized choriocapillaris, whereas CD-31 visualized medium-sized/large vessels that were IB4-positive.
Representative dorsal choroidal flat-mounts of adult (8-week-old) WT (left panel) and Aldh1a1–/– (right panel) eyes immunostained with anti-endomucin (Emcn, red) and anti-ZO-1 (green) antibodies.
There is no difference in the size of RPE between WT and Aldh1a1–/– mice.
Tables
Oligonucleotides used in this study
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.021| Mouse primers | Oligonucleotide sequences (5’−3’) | |
|---|---|---|
| Aldh1a1-/- | Forward | TGAGCAAATCCTCCACAGCCCTGTTC |
| Reverse | CTGCTAAAGCGCATGCTCCAGACTG | |
| Aldh1a3 flox | Forward | TCTCTGACCAGCTTTCCAACCTTCAG |
| Reverse | CTCAAACCAGCACCACCTCCATATTG | |
| Sox9 flox | Forward | TCAGCAAGACTCTGGGCAAGCTCT |
| Reverse | CTCAAAATCTGAGCCACTCCCTC | |
| Tyr-Cre, Pax6-α-Cre | Forward | CCTGGAAAATGCTTCTGTCCGT |
| Reverse | GTGTCCACATAGTCATTGGCAGAGTG | |
| Sox9-Tg, Kdr-BAC-EGFP | Forward | AGCTGACCCTGAAGTTCATCTG |
| Reverse | GTCGTCCTTGAAGAAGATGGTG | |
| Flt1-BAC-tdsRed | Forward | GCTGCAGGCGCGGAGAAGGGCTCTC |
| Reverse | CTTCACGTACACCTTGGAGC | |
| IL2 (internal control) | Forward | GCCTAGAAGATGAACTTGGACCTCTG |
| Reverse | GTGGAAGGATTCACTTGCACAGTGAC | |
| Human RPE primers | ||
| Sox9 | Forward | CGTACCCGCACTTGCACAAC |
| Reverse | TCTCGCTCTCGTTCAGAAGTC | |
| Vegfa | Forward | TGCCCGCTGCTGTCTAAT |
| Reverse | TCTCCGCTCTGAGCAAGG | |
| β-actin | Forward | CCAACCGCGAGAAGATGA |
| Reverse | CCAGAGGCGTACAGGGATAG |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32358.022





