Thalamocortical and corticothalamic pathways differentially contribute to goal-directed behaviors in the rat
Figures
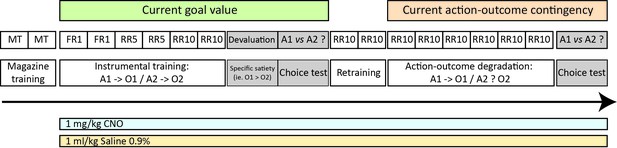
Experimental design.
After an initial magazine training phase (MT), all rats underwent instrumental training consisting in either pushing a lever or a tilt (see methods) using successively fixed (FR) and random ratios (RR) schedules. To assess how the animals can use current goal value to guide choice, we performed a choice test immediately after selective outcome devaluation, under extinction conditions (both the lever and the tilt are now present in the chamber). After retraining, all rats underwent further instrumental training consisting in a selective degradation procedure (see methods). Another choice test was conducted after this phase, identical to that conducted following outcome devaluation. For both experiments, separate groups of rats were treated with either 1 mg/kg CNO or 1 ml/kg Saline 0.9% given 60 mm prior each behavioral session except during MT. To rule out any potential confounding effect of CNO injection alone, an additional control experiment is provided as an appendix. For each action, instrumental performance during the last RR10 session or the last RR10 retraining session was considered baseline for the devaluation test and the degradation phase, respectively.
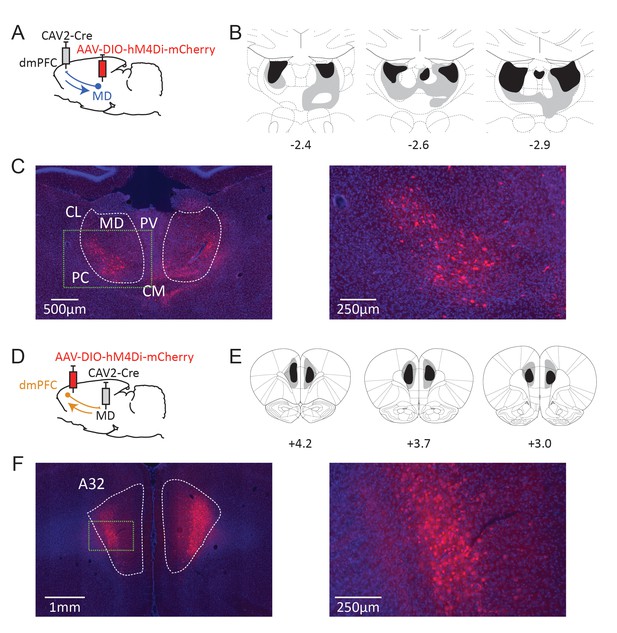
Dual-viral chemogenetic strategy to target TC (A) and CT pathways (D).
The CAV-2-Cre vector has a retrograde tropism. Maximal (grey) and minimal (dark) extent of DREADD expression in included rats at three rostrocaudal levels (expressed relative to Bregma, in mm) for CT (B) and TC (E) pathways. Representative examples of mCherry expression at thalamic (C) and cortical (F) levels. Insets in dashed green lines correspond to the higher magnification images provided on the right. CL: centrolateral thalamic nucleus, PC: paracentral thalamic nucleus, CM: centromedial thalamic nucleus, PV: paraventricular thalamic nucleus. A32 area corresponds to the prelimbic and most dorsal portion of the infralimbic areas in the seventh edition of the Paxinos and Watson atlas (Paxinos and Watson, 2014).
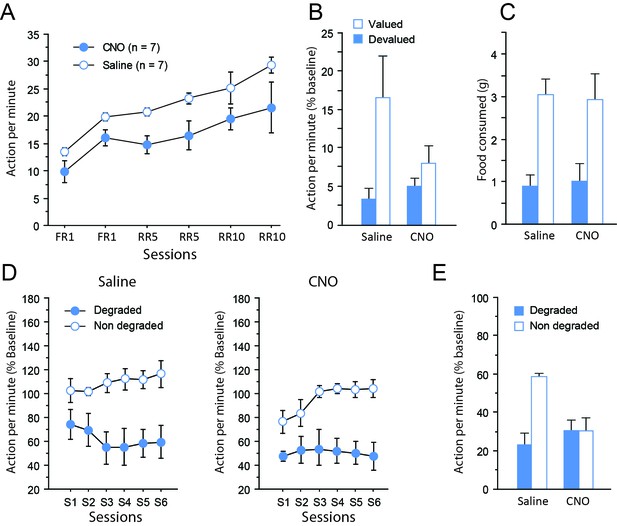
Chemogenetic inhibition of TC pathways.
(A) Mean number of lever presses (±sem) during instrumental training. (B) Mean number of lever presses (±sem, relative to baseline) during the instrumental choice test conducted immediately after selective outcome devaluation under extinction conditions. (C) Consumption test. (D) Mean number of lever presses (±sem, relative to baseline) during the contingency degradation procedure. (E) Mean number of lever presses (±sem, relative to baseline) for the final choice test conducted under extinction conditions.
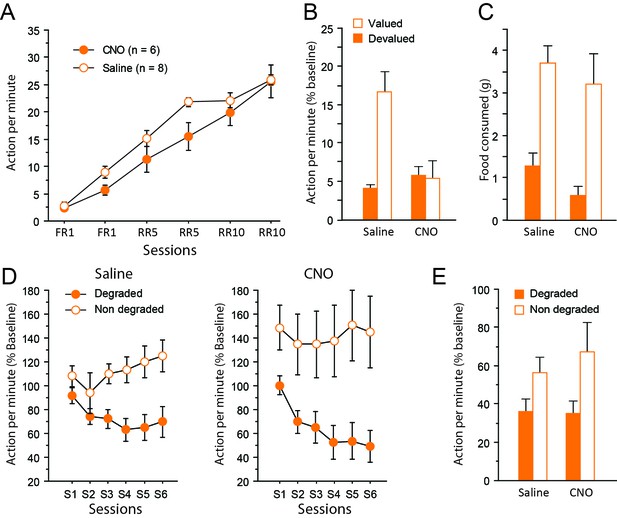
Chemogenetic inhibition of corticothalamic pathways.
(A) Mean number of lever presses (±sem) during instrumental training. (B) Mean number of lever presses (±sem, relative to baseline) during the instrumental choice test conducted immediately after selective outcome devaluation under extinction conditions. (C) Consumption test. (D) Mean number of lever presses (±sem, relative to baseline) during the degradation procedure. (E) Mean number of lever presses (±sem, relative to baseline), for the final choice test conducted under extinction.
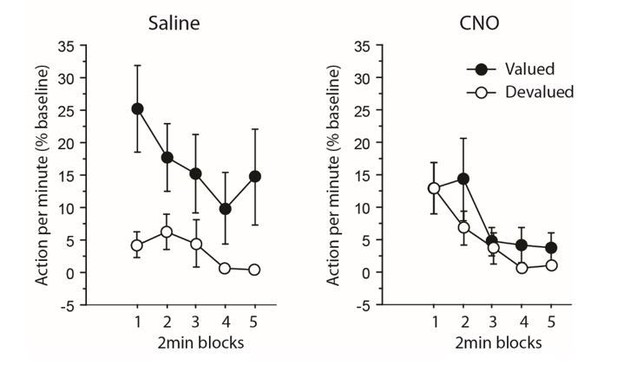
Experiment 1: inhibiting thalamocortical pathway.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32517.013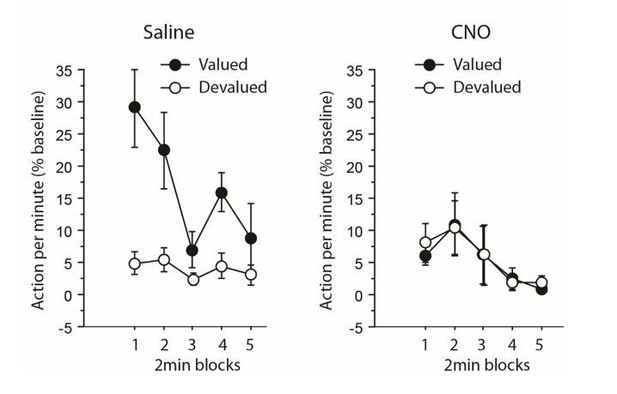
Experiment 2: inhibiting corticothalamic pathway.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32517.014Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32517.007





