IRS-1 acts as an endocytic regulator of IGF-I receptor to facilitate sustained IGF signaling
Figures
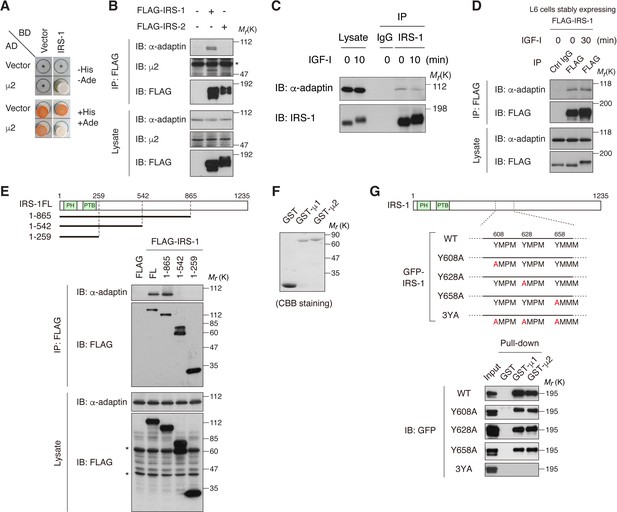
IRS-1 interacts with the clathrin adaptor AP2 complex through its YxxΦ motifs.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid assay indicating the interaction of IRS-1 with the μ2 subunit of AP2. (B) The association of IRS-1 or IRS-2 with endogenous AP2 subunits was analyzed by immunoprecipitation in HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-IRS-1 or FLAG-IRS-2. Asterisk indicates IgG band. (C, D) Changes in endogenous IRS-1- (C) and ectopically expressed FLAG-IRS-1- (D) associated AP2 following IGF-I stimulation in L6 cells were analyzed by immunoprecipitation. (E) AP2-binding region on IRS-1 was mapped with the indicated truncation mutants of FLAG-IRS-1 by immunoprecipitation of HEK293T cell lysates. Asterisks indicate nonspecific bands. (F, G) In vitro pull-down assay for the interaction between IRS-1 mutants and μ2 subunit. Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining of the recombinant proteins (GST, GST-μ1, and GST-μ2) used in the pull-down assay is shown (F). Three YxxΦ motifs in IRS-1, which contain Y608, Y628, and Y658 are depicted. The lysates from HEK293T cells expressing the indicated GFP-IRS-1 mutants were pulled down with GST-fused μ1 and μ2 (G).
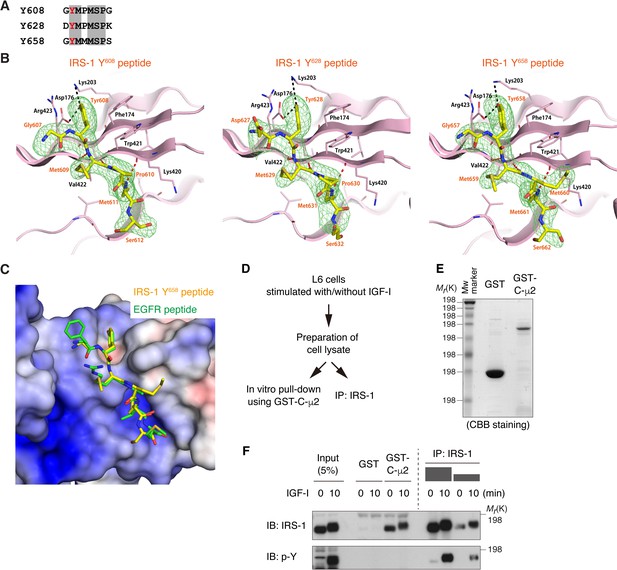
Three YxxΦ motifs in IRS-1 mediate the interaction with μ2 of AP2 complex.
(A) Sequence alignment of three IRS-1 YxxΦ peptides used for structural analysis. (B) Structural details of IRS-1 YxxΦ motif binding to C-μ2. The overall structures of C-μ2 with these peptides were similar to that with EGFR peptide (PDB 1BW8) with Cα root mean square deviations of 0.83, 0.611, and 0.55 Å for the complex with the Y608, Y628, and Y658 peptides, respectively. Six residues from Y-1 to Y + 4 were modeled into the density, whereas electron density for the C-terminal two residues was not clearly visible, indicating that they were disordered. Three IRS-1 YxxΦ motif peptides (Y608, Y628, and Y658) and μ2 residues important in the interaction are indicated. The side chains of the conserved Tyr residues (Y608, Y628, and Y658) are inserted in the binding pocket with their hydroxyl group forming hydrogen bonds with the side chains of Asp176 and Lys203, while the side chains make hydrophobic interactions with those of Phe174, Trp421, and Arg423. The side chains of the Met residues at Y + 3 (Met611, Met631, and Met661) are inserted in the second binding pocket on the opposite side of strand 16 from that for the Tyr residue, making hydrophobic interactions with the side chains of Leu175, Lys420 and Val422. IRS-1 peptide is shown in mFo – DFc electron density calculated without the peptide coordinates. The electron density is cropped around the peptide and contoured at 2.0 σ. Data collection and refinement statistics are shown in Table 1. (C) Surface charge distribution of C-μ2 around IRS-1 Y658 peptide (yellow) -binding interface is shown (colored from red at −6 kT/e to blue at +6 kT/e), including an overlay with the YxxΦ motif of EGFR (green) to compare binding of the two motifs. (D) Flow chart of the experiment shown in (E) and (F). Lysates were prepared from L6 cells stimulated with or without IGF-I, and then were split into in vitro pull-down using GST-C-μ2 and immunoprecipitation with anti-IRS-1 antibody. (E, F) In vitro pull-down assay showing the IRS-1 fraction capable of binding to μ2 in lysates of IGF-I-stimulated cells. Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining of the recombinant proteins (GST and GST-C-μ2) used in the pull-down assay is shown (E). The samples of immunoprecipitated IRS-1 were serially diluted to load the equivalent amount of IRS-1 pulled down with GST-C-μ2 (F). The tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS-1 was never detected in the pull-down fraction in IGF-I-stimulated condition.
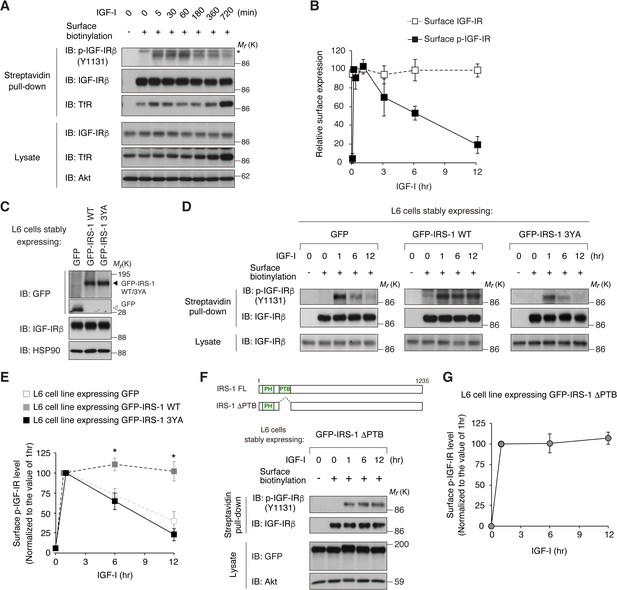
IRS-1 promotes cell surface retention of activated IGF-IR via its YxxΦ motifs.
(A) Changes in cell surface IGF-IR following IGF-I stimulation in L6 cells were analyzed by surface biotinylation assay. Transferrin receptor (TfR) was evaluated as a loading control for cell surface protein. (B) Immunoblots of surface IGF-IR for (A) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of four independent experiments. (C) Immunoblotting of GFP-IRS-1 wild-type (WT) and 3YA mutant in lysates from L6 cells stably expressing GFP, GFP-IRS-1 WT, or GFP-IRS-1 3YA. (D) Changes in surface phospho-IGF-IR following IGF-I stimulation were analyzed in L6 cells stably expressing GFP, GFP-IRS-1 WT, or GFP-IRS-1 3YA by surface biotinylation assay. (E) Immunoblots of surface IGF-IR for (D) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of four independent experiments. Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05 versus GFP. (F, G) Changes in surface phospho-IGF-IR following IGF-I stimulation were analyzed in L6 cells stably expressing GFP-IRS-1 ΔPTB by surface biotinylation assay (F). Immunoblots of surface IGF-IR for (F) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments (G).
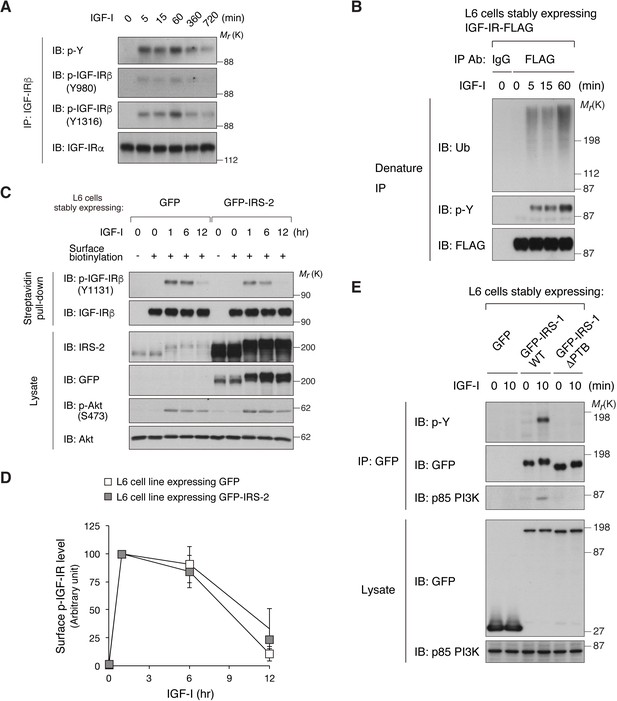
Expression of IRS-1, but not IRS-2, inhibits the down-regulation of activated IGF-IR induced by long-term IGF-I stimulation.
(A) Phosphorylation of multiple Tyr residues in IGF-IR in L6 cells stimulated with IGF-I for the indicated time was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-FLAG were collected at the indicated time periods following IGF-I stimulation. The cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody, and the bound proteins were eluted under denaturing conditions. The denatured fraction was then re-immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibody for ubiquitin assay as described in Materials and methods. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (C, D) Changes in surface phospho-IGF-IR following IGF-I stimulation were analyzed in L6 cells stably expressing GFP or GFP-IRS-2 by surface biotinylation assay (C). Immunoblots of surface IGF-IR for (C) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments (D). Statistical analyses by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test revealed no significant difference between two groups. (E) IGF-I-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and binding to p85 PI3K in L6 cells stably expressing GFP, GFP-IRS-1 WT, or GFP-IRS-1 ΔPTB were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
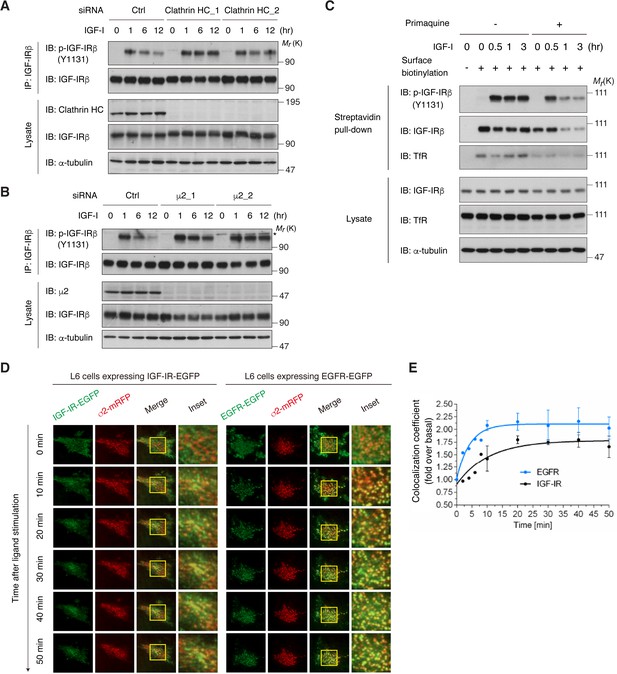
Internalization of activated IGF-IR is dependent on the clathrin/AP2-mediated endocytic pathway.
(A) Knockdown of clathrin heavy chain (HC) by two different siRNAs blocked long-term IGF-I-induced reduction of phospho-IGF-IR in L6 cells. Ctrl, control. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Knockdown of the μ2 subunit of AP2 by two different siRNAs blocked long-term IGF-I-induced reduction of phospho-IGF-IR in L6 cells. Asterisk indicates a nonspecific band. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. The μ2_1 siRNA was used in further experiments. (C) Changes in cell surface IGF-IR following IGF-I stimulation in L6 cells that were pre-treated with primaquine were analyzed by surface biotinylation assay. (D) Live cell TIRF-M imaging of L6 cells expressing IGF-IR-EGFP (left) or EGFR-EGFP (right) together with σ2-mRFP, which were stimulated for the indicated times with IGF-I or EGF, respectively. A representative region at higher magnification outlined by yellow rectangles is also shown in insets. (E) Quantification of colocalization between IGF-IR (black line) or EGFR (blue line) and AP2 in (D). Mean (fold over the value at 0 min)± SD is shown (n = 7 cells). The data are representative of three independent experiments.

AP2, but not AP1, is required for the targeting of activated IGF-IR from the plasma membrane into lysosomes.
(A) L6 cells were transfected with non-targeting or μ1 siRNA followed by IGF-I stimulation for the indicated time. Changes in phospho-IGF-IR were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-EGFP were transfected with non-targeting or μ2 siRNA. The cells were stimulated with IGF-I in the presence of leupeptin and pepstatin A for the indicated time. Prior to fixation, they were labeled with LysoTracker (magenta). The fixed cells were immunostained with anti-phospho-IGF-IR antibody (green), and the images were obtained by confocal microscopy. Insets show representative regions at higher magnification. Arrows are representative showing colocalization between phospho-IGF-IR and LysoTracker. Bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of colocalization between phospho-IGF-IR and LysoTracker in (B). The mean ±SD is shown (n > 20 cells). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05. The data are representative of three independent experiments.
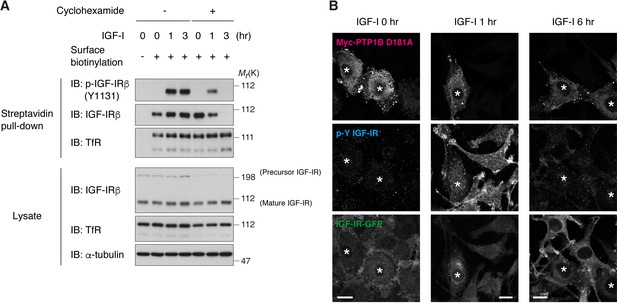
Effects of cycloheximide treatment and PTP1B D181A expression on surface IGF-IR changes after the ligand exposure.
(A) Changes in cell surface IGF-IR following IGF-I stimulation in L6 cells that were pre-treated with cycloheximide were analyzed by surface biotinylation assay. (B) L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-GFP were transiently transfected with Myc-PTP1B D181A. The cells were then stimulated with IGF-I for the indicated time. The fixed cells were immunostained to visualize phospho-IGF-IR and Myc-PTP1B D181A. Cells expressing Myc-PTP1B D181A were labeled with asterisks. Scale bar, 10 μm.
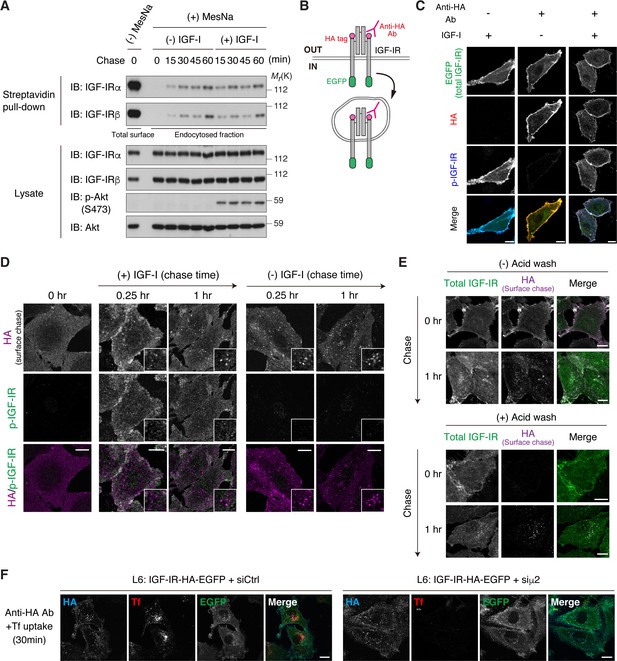
Chase of internalized IGF-IR.
(A) L6 cells were surface-labeled with a cleavable biotin reagent at 4°C and then warmed to 37°C in the presence or absence of IGF-I for the indicated time. Biotin was removed from surface proteins with MesNa treatment, and cells were lysed and subjected to pull-down with streptavidin. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Internalization assay using double-tagged IGF-IR. The HA tag is inserted into the exofacial region of IGF-IR so that the surface IGF-IR is susceptible to anti-HA antibody labeling and subsequent chasing for the internalization. (C) The binding of anti-HA antibody neither activated IGF-IR-HA-EGFP nor interfered the activation in response to the following treatment with IGF-I. L6 cells expressing IGF-IR-HA-EGFP were labeled with non-immunized IgG (-) or anti-HA antibody (+) on ice, and then transferred to media containing IGF-I for 5 min. Surface and phosphorylated IGF-IR levels were assessed by immunofluorescent staining followed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-HA-EGFP were labeled with anti-HA antibody prior to subsequent chase experiment in the presence or absence of IGF-I. Surface-derived IGF-IR was visualized by staining HA, whereas phosphorylated IGF-IR was stained with phospho-IGF-IR antibody. The cells were analyzed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) The resistance of incorporated HA antibody to acid stripping indicated the internalization of IGF-IR-HA-EGFP. L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-HA-EGFP were labeled with anti-HA antibody, and then were allowed for internalization in the culture media. Before fixation, the cells were washed with acid stripping buffer to remove surface-resident anti-HA antibody. The cells were immunostained and observed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Basal endocytosis of IGF-IR is independent on AP2. L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-HA-EGFP were transfected with non-targeting or μ2 siRNA. The cells were serum-starved and then surface-labeled with anti-HA antibody followed by chasing its uptake for 30 min. The μ2-depleted cells were discriminated by loss of Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated transferrin (Tf) uptake. The cells were immunostained and observed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm.

Colocalization of IGF-IR with AP2 in response to the ligand treatment.
(A, B) L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-EGFP were stimulated with or without IGF-I stimulation for 1 hr. Colocalization of phospho-IGF-IR with AP2 (A) or clathrin heavy chain (B) was analyzed in the stained cells by TIRF-M. Insets show representative regions at higher magnification. Arrows are representative showing the colocalization. Bar, 10 μm. (C) Quantification of colocalization between phospho-IGF-IR and AP2 in (A). The colocalization rate in each cell is plotted and the means are shown (n > 25 cells). Differences were analyzed by the two-tailed Student t-test. *p<0.05. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Live cell TIRF-M imaging of L6 cells expressing IGF-IR-EGFP and σ2-mRFP after IGF-I stimulation. A representative region at higher magnification outlined by yellow rectangles is also shown in insets. Arrows indicate AP2-positive spots existing prior to IGF-I stimulation.
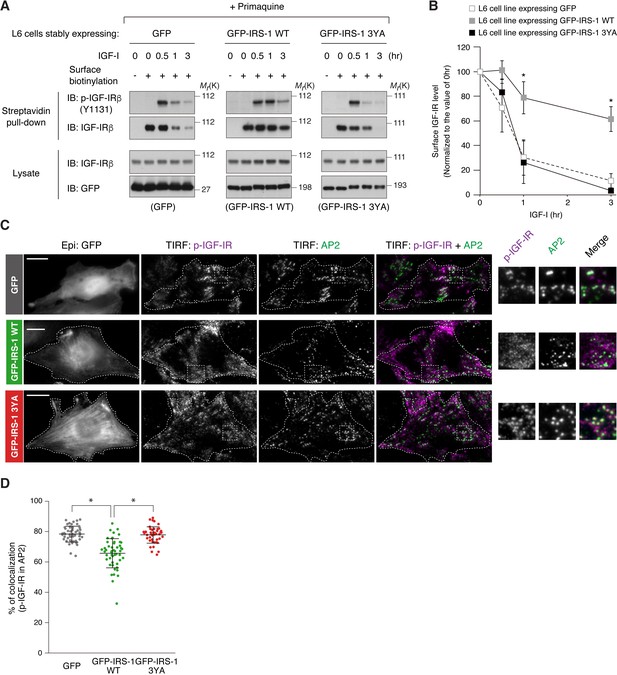
IRS-1 inhibits the recruitment of active IGF-IR into clathrin-coated structures.
(A) Changes in surface phospho-IGF-IR following IGF-I stimulation in the presence of primaquine were analyzed in L6 cells stably expressing GFP, GFP-IRS-1 WT, or GFP-IRS-1 3YA by surface biotinylation assay. (B) Immunoblots of surface IGF-IR for (A) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments. Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05 versus GFP. (C) L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-FLAG were transfected with the plasmid expressing GFP, GFP-IRS-1 WT, or GFP-IRS-1 3YA. The cells were stimulated with IGF-I for 1 hr. Colocalization of phospho-IGF-IR with AP2 was analyzed in the immunostained cells by TIRF-M. Insets show representative regions at higher magnification. Bar, 10 μm. (D) Quantification of colocalization between phospho-IGF-IR and AP2 in (C). The colocalization rate in each transfected cell is plotted and mean ±SD is shown (n > 50 cells in each condition). The data are representative of three independent experiments. Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05.
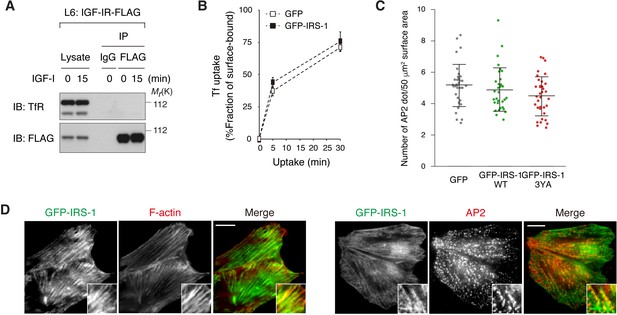
Effects of IRS-1 overexpression on AP2-positive spot formation and endocytosis of transferrin receptor.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation of IGF-IR and transferrin receptor (TfR) in L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-FLAG. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were performed with the indicated antibodies. (B) Transferrin (Tf) uptake in L6 cells stably expressing GFP or GFP-IRS-1 was analyzed by using Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated Tf. The internalization rate of surface-bound Tf is shown as mean ±SD (n > 70 cells). Statistical analyses by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test revealed no significant difference between two groups. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Quantification of the number of AP2-positive spots at the plasma membrane in L6 IGF-IR-FLAG cells transfected with GFP, GFP-IRS-1 WT, or GFP-IRS-1 3YA in the TIRF fields. The number of AP2 dot per 50 μm surface area in each transfected cell is plotted and mean ±SD is shown (n > 30 cells in each condition). Statistical analyses by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test revealed no significant difference between three groups. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) TIRF-M analysis of IRS-1 localization. In L6 cells stably expressing GFP-IRS-1, F-actin was stained with phalloidin (left panels), or AP2 was immunostained with anti-α-adaptin antibody (right panels). Insets show a representative region at higher magnification. Bar, 10 μm.
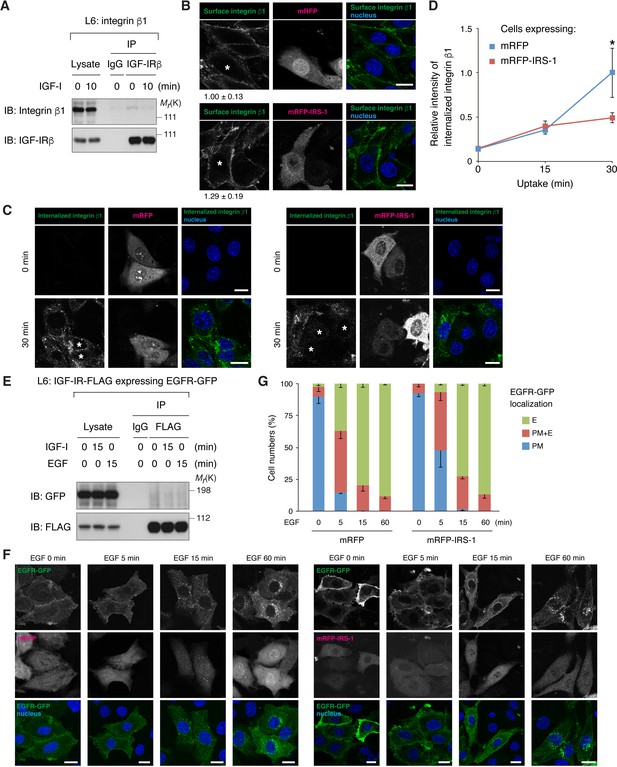
Effects of IRS-1 overexpression on endocytosis of integrin β1 and EGFR.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation of IGF-IR and integrin β1 in L6 cells stably expressing integrin β1. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were performed with the indicated antibodies. (B) L6 cells stably expressing integrin β1 were transfected with mRFP or mRFP-IRS-1. The serum-starved cells were incubated with anti-integrin β1 antibody at 4°C before fixation. Mean values and SD (20–40 cells) of pixel intensities were measured. mRFP- or mRFP-IRS-1-expressing cells were labeled with asterisks. Bar, 10 μm. (C, D) After surface-labeled cells were incubated for 30 min, surface anti-integrin β1 antibody was removed by acid striping, and internalized antibody was detected. mRFP- or mRFP-IRS-1-expressing cells were labeled with asterisks. Bar, 10 μm (C). The intensity of internalized integrin β1 is shown as mean ±SD (n > 50 cells; *p<0.05). The data are representative of two independent experiments (D). (E) Co-immunoprecipitation of IGF-IR and EGFR in L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-FLAG together with the transfected EGFR-GFP. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were performed with the indicated antibodies. (F, G) L6 cells transfected with EGFR-GFP together with mRFP or mRFP-IRS-1 were treated with 2 nM EGF for the indicated time (F). The cells expressing EGFR-GFP localized to the plasma membrane (PM), to the plasma membrane and endosomes (PM +E), or to the endosomes (E) were counted. In each condition, 40–90 cells were counted. Graphs display mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (G).
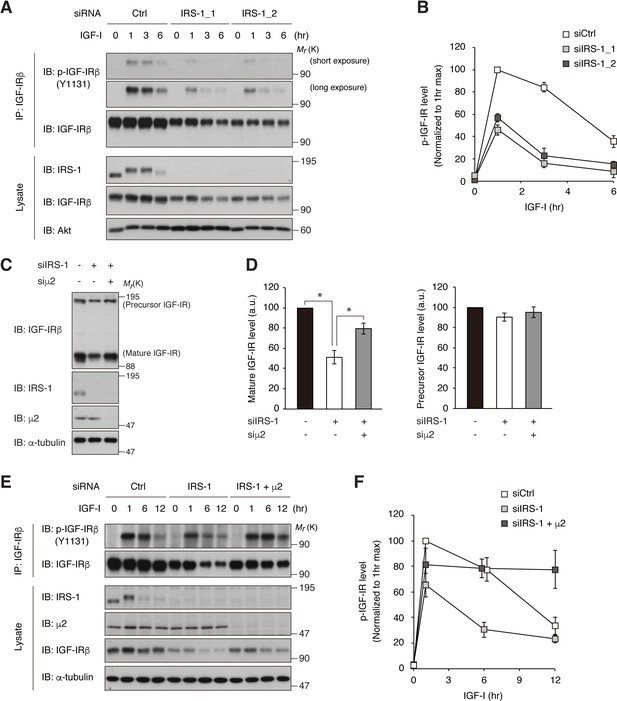
Depletion of IRS-1 accelerates AP2-dependent internalization of IGF-IR.
(A, B) L6 cells transfected with non-targeting (Ctrl) or IRS-1 siRNA were stimulated with IGF-I for the indicated time. Phosphorylation of IGF-IR was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (A). Both short and long exposed immunoblots of phospho-IGF-IR are shown. Immunoblots of phospho-IGF-IR for (A) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of four independent experiments (B). (C, D) L6 cells were transfected with IRS-1 siRNA combined with or without μ2 siRNA. The indicated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting (C). Immunoblots of mature and precursor IGF-IR for (C) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of four independent experiments (D). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05. a.u., arbitrary unit. (E, F) L6 cells were transfected with non-targeting or IRS-1 siRNA combined with or without μ2 siRNA. The cells were stimulated with IGF-I for the indicated time. Phosphorylation of IGF-IR was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (E). Immunoblots of phospho-IGF-IR for (E) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments (F).
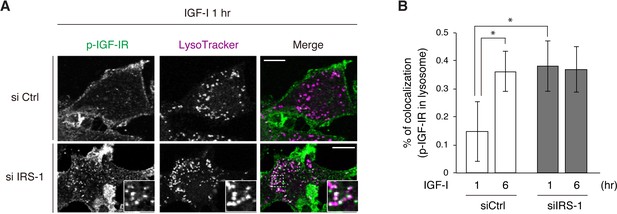
IRS-1 inhibits the targeting of IGF-IR into lysosomes.
(A) L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-EGFP were transfected with non-targeting or IRS-1 siRNA. The cells were stimulated with IGF-I in the presence of leupeptin and pepstatin A for 1 hr. Prior to fixation, they were incubated with LysoTracker (magenta) for staining lysosomes. The fixed cells were immunostained with anti-phospho-IGF-IR antibody (green), and the images were obtained by confocal microscopy. Insets show representative regions at higher magnification. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Quantification of colocalization between phospho-IGF-IR and LysoTracker in (A). The mean ± SD is shown (n > 20 cells). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05. The data are representative of three independent experiments.
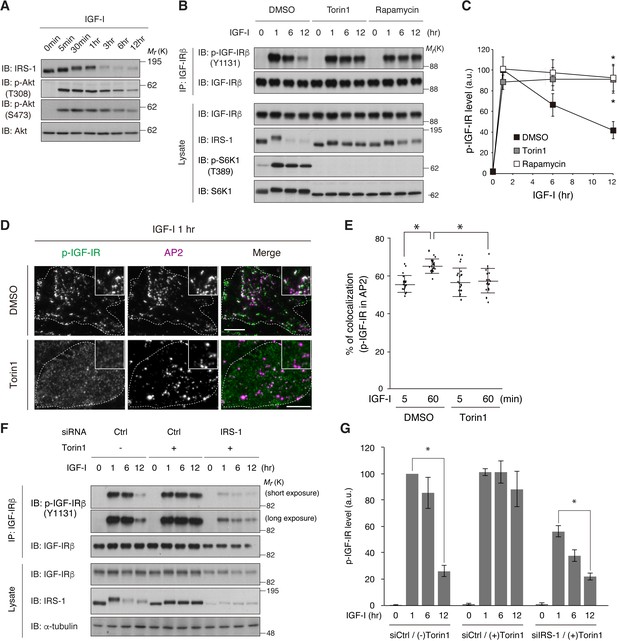
mTOR-dependent degradation of IRS-1 is required for the initiation of IGF-IR internalization.
(A) Changes in IRS-1 and Akt phosphorylation following IGF-I stimulation were analyzed in L6 cells by immunoblotting. (B, C) L6 cells were treated with Torin1 or rapamycin followed by IGF-I stimulation. Phosphorylation of IGF-IR was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (B). Immunoblots of phospho-IGF-IR for (B) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of four independent experiments (C). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05. (D, E) L6 cells stably expressing IGF-IR-EGFP were treated with or without Torin1 followed by IGF-I stimulation for 1 hr. Colocalization of phospho-IGF-IR with AP2 was analyzed in the immunostained cells by TIRF-M (D). Insets show a representative region at higher magnification. Bar, 10 μm. Quantification of colocalization between phospho-IGF-IR and AP2 in (D) in each cell is plotted and the means are shown (E; n > 25 cells). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (F, G) L6 cells were transfected with non-targeting or IRS-1 siRNA. The cells were treated with or without Torin1 followed by IGF-I stimulation for the indicated time. Phosphorylation of IGF-IR was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (F). Immunoblots of phospho-IGF-IR for (F) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of four independent experiments (G). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05.
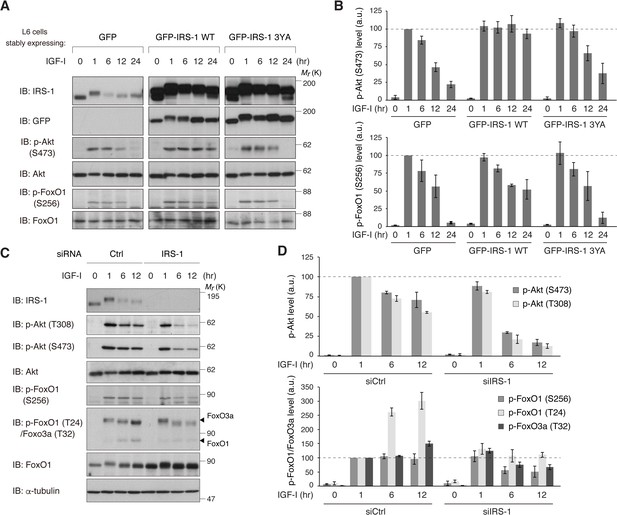
IRS-1 is required for sustained activation of Akt and FoxO inactivation in response to IGF-I.
(A, B) Immunoblotting after treating with IGF-I for the indicated time in L6 cells stably expressing GFP, GFP-IRS-1 WT, or GFP-IRS-1 3YA (A). Immunoblots of phospho-Akt (S473) and phospho-FoxO1 (S256) for (A) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments (B). (C, D) Immunoblotting after treating with IGF-I for the indicated time in L6 cells transfected with non-targeting or IRS-1 siRNA (C). Immunoblots of phospho-Akt (T308 and S473) and phospho-FoxO (S256 and T24 in FoxO1, and T32 in FoxO3a) for (C) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ±SEM of three independent experiments (D).
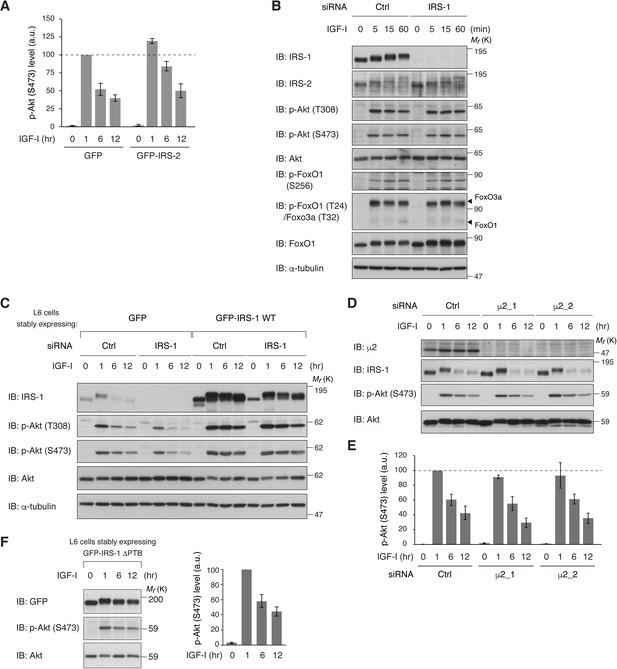
Neither overexpression of IRS-2 nor solely blocking of IGF-IR internalization leads to sustained activation of Akt.
(A) Immunoblots of phospho-Akt (S473) in Figure 2—figure supplement 1C were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (B) Immunoblotting after treating with IGF-I for the indicated time in L6 cells transfected with non-targeting or IRS-1 siRNA. (C) L6 cells stably expressing GFP or GFP-IRS-1 WT were transfected with non-targeting or IRS-1 siRNA (targeting 3’UTR of IRS-1 mRNA, thus not affecting ectopic GFP-IRS-1 expression), and then stimulated with IGF-I for the indicated time. Phosphorylation of Akt was analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D, E) Immunoblotting after treating with IGF-I for the indicated time in L6 cells transfected with non-targeting or μ2 siRNA (D). Immunoblots of phospho-Akt (S473) in (D) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (E). (F) Immunoblotting after treating with IGF-I for the indicated time in L6 cells stably expressing GFP-IRS-1 ΔPTB (left). Immunoblots of phospho-Akt (S473) were quantified and the graph is shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (right).
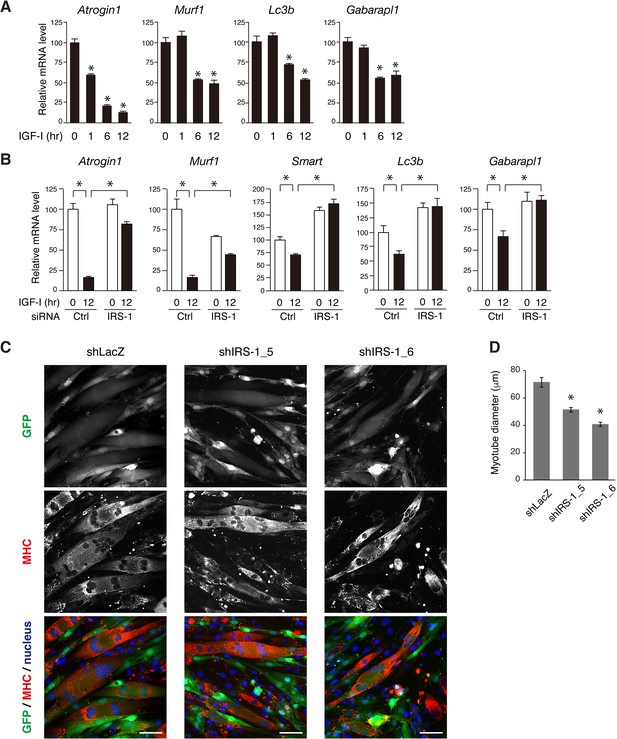
IRS-1 is required for efficient down-regulation of atrophy-related genes mediated by IGF-I.
(A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of atrophy-related genes from L6 myotubes stimulated with IGF-I. Data are expressed as fold of the value at 0 hr of IGF-I stimulation. Values are mean ±SEM (n = 3). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05 versus IGF-I 0 hr. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of atrophy-related genes from L6 myoblasts transfected with non-targeting or IRS-1 siRNA followed by IGF-I stimulation for 0 or 12 hr. Data are expressed as fold of the value at 0 hr of IGF-I stimulation in cells transfected with control siRNA. Values are mean ±SEM (n = 3). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05 versus IGF-I 0 hr. (C) L6 myotubes were infected with lentivirus containing LacZ- or IRS-1-targeting shRNA. The infected cells were visualized by GFP expression (green). The fixed cells were immunostained with anti-MHC antibody (red) together with Hoechst nuclear staining (blue). MHC, myosin heavy chain. Bar, 50 μm. (D) Measurement of myotube diameter after lentivirus-mediated knockdown of IRS-1 for (C). The data are presented as mean ±SEM (n > 100 cells per condition). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05.
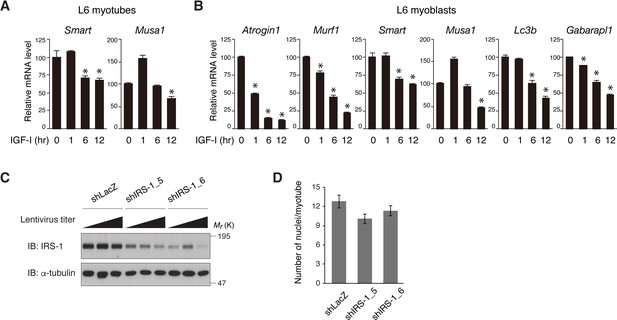
Long-term IGF-I stimulation suppresses the FoxO-regulated genes.
(A, B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Smart and Musa1 from L6 myotubes stimulated with IGF-I (A), and of the FoxO-regulated genes from L6 myoblasts stimulated with IGF-I (B) is shown. Data are expressed as fold of the value at 0 hr of IGF-I stimulation. Values are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3). Differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test. *p<0.05 versus IGF-I 0 hr. (C) Immunoblotting of IRS-1 in L6 myotubes infected with containing LacZ- or IRS-1-targeting shRNA at serially diluted titers. (D) Measurement of the number of nuclei per myotube after lentivirus-mediated knockdown of IRS-1 in Figure 8C. The data are presented as mean ± SEM (n > 100 cells per condition). Statistical analyses by ANOVA and the Tukey post hoc test revealed no significant difference between two groups.
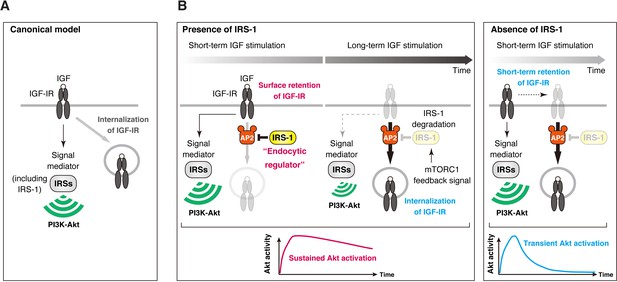
Model of IRS-1-mediated control for delayed IGF-IR internalization and its role in the sustained IGF signaling.
(A) The canonical view in which IRS-1 functions as a signaling mediator of IGF-IR to the PI3K-Akt pathway through their Tyr phosphorylation. The molecular basis for closed interactions between IGF-IR endocytosis and its signaling components has been poorly understood. (B) A proposed model for IRS-1-mediated surface retention of IGF-IR and sustained IGF signaling. The ability of IRS-1 to interact with AP2 prolongs the surface retention of active IGF-IR, which is caused by the inhibition of AP2-dependent IGF-IR internalization. After long-term stimulation of IGF, IRS-1 is degraded by mTORC1 feedback signal, which functions as a brake release to trigger the initiation of IGF-IR internalization. Accelerating IGF-IR internalization caused by IRS-1 depletion leads to the shift from sustained to transient Akt signaling.
Tables
Data collection and refinement statistics
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32893.005| Y608 peptide complex | Y628 peptide complex | Y658 peptide complex | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal parameters | |||
| Space group | P64 | P64 | P64 |
| Cell dimensions: | |||
| a, b, c (Å) | 126.07, 126.07, 73.40 | 126.19, 126.19, 74.11 | 125.48, 125.48, 74.14 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 120 | 90, 90, 120 | 90, 90, 120 |
| Data collection | |||
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Resolution (Å) | 50–2.63 (2.68–2.63)* | 50–3.10 (3.15–3.10) | 50–2.60 (2.64–2.60) |
| No. of unique reflections | 20035 | 12419 | 20659 |
| Multiplicity | 11.3 (10.9) | 11.3 (11.4) | 11.4 (11.5) |
| Completeness (%) | 100 (100) | 100 (100) | 100 (100) |
| Rmeas | 0.078 (1.504) | 0.103 (1.880) | 0.094 (2.069) |
| Rpim | 0.023 (0.455) | 0.031 (0.556) | 0.028 (0.608) |
| CC1/2 | (0.743) | (0.646) | (0.780) |
| Mean I/σ | 28.1 (1.8) | 24.8 (1.6) | 26.5 (1.6) |
| Refinement | |||
| Resolution (Å) | 43–2.62 | 36–3.10 | 36–2.60 |
| No. of reflections | 19977 | 12322 | 20589 |
| Rwork/Rfree | 0.185/0.223 | 0.194/0.251 | 0.192/0.227 |
| RMSD bond lengths (Å) | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.009 |
| RMSD bond angles (°) | 0.948 | 1.194 | 0.965 |
| No. of atoms | |||
| Protein/peptide | 2003 | 2121 | 2118 |
| Water/ion | 2 | 0 | 34 |
| Ramachandran plot | |||
| Favored (%) | 95.5 | 92.3 | 95.4 |
| Outliers (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| PDB accession code: | 5WRK | 5WRL | 5WRM |
-
*Values in parentheses are for highest resolution shell.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | BL21 | Agilent Technologies | Agilent Technologies: 200133 | |
| Strain, strain background(Escherichia coli) | BL21-CodonPlus(DE3)-RIL | Agilent Technologies | Agilent Technologies: 230245 | |
| Cell line (Rattus norvegicus) | L6 | ATCC | ATCC: CRL-1458; RRID: CVCL_0385 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | 293T | ATCC | ATCC: CRL-3216; RRID: CVCL_0063 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | PLAT-E | PMID: 10871756 | RRID: CVCL_B488 | A kind gift from T. Kitamura, The University of Tokyo |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-phospho-IGF-IRβ (Tyr1131) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 3021; RRID: AB_331578 | IB 1:1000; IF 1:200 |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-IGF-IRβ (Tyr980) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 4568; RRID: AB_2122279 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-phospho-IGF-IRβ (Tyr1316) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 6113; RRID: AB_10545762 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-IGF-IRβ | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 9750; RRID: AB_10950969 | IF 1:200 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Akt | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 9272; RRID: AB_329827 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-phospho-Akt (Thr308) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 9275; RRID: AB_329828 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-phospho-Akt (Ser473) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 9271; RRID: AB_329825 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-phospho-p70 S6K (Thr389) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 9234; RRID: AB_2269803 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-phospho-FoxO1 (Thr24)/FoxO3a (Thr32) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 9464; RRID: AB_329842 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-phospho-FoxO1 (Sere256) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 9461; RRID: AB_329831 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-FoxO1 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cell Signaling Technology: 2880; RRID: AB_2106495 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-IGF-IRα | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-712; RRID: AB_671788 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-IGF-IRβ | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-713; RRID: AB_671792 | IB 1:1000; IP 1:200 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-IRS-2 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-8299; RRID: AB_2125783 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-clathrin HC | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-12734; RRID: AB_627263 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-α-adaptin | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-17771; RRID: AB_2274034 | IB 1:1000; IF 1:200 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-p70 S6K | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-230; RRID: AB_632156 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-HSP90 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-7947; RRID: AB_2121235 | IB 1:2000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-γ-adaptin | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-10763; RRID: AB_2058329 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-GFP | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-9996; RRID: AB_627695 | IB 1:1000; IP 1:200 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-ubiquitin (P4D1) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz Biotechnology: sc-8017; RRID: AB_628423 | IB 1:200 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG M2 | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich: F3165; RRID: AB_259529 | IB 1:2000 |
| Antibody | Anti-FLAG M2 agarose affinity gel | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich: A2220; RRID: AB_10063035 | |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-α-tubulin (DM1A) | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich: T6199; RRID: AB_477583 | IB 1:2000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-phospho-Tyr (4G10) | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich: 05-1050X; RRID: AB_916370 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-IRS-1 | Upstate | Upstate: 06-248; RRID:AB_2127890 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-myosin heavy chain | Upstate | Upstate: 05-716; RRID: AB_309930 | IF 1:200 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Myc | Upstate | Upstate: 05-419; RRID: AB_309725 | IF 1:200 |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-p85 PI3 kinase | Upstate | Upstate: 06-195; RRID: AB_310069 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-μ2 | BD Transduction Laboratories | BD Transduction Laboratories: 611350; RRID: AB_398872 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-clathrin | abcam | abcam: ab2731; RRID: AB_303256 | IF 1:200 |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-integrin β1 | abcam | abcam: ab52971; RRID: AB_870695 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-transferrin receptor (H68.4) | Invitrogen | Invitrogen: 13-6800; RRID: AB_86623 | IB 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-integrin β1 (TS2/16) | Invitrogen | Invitrogen: 14-0299-82; RRID: AB_1210468 | IF 1:500 |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-HA (3F10) | Roche | Roche: 11-867-423-001; RRID: AB_10094468 | IF 1:200 |
| Antibody | Alexa 488-, 594- or 633- secondaries | Molecular Probes | IF 1:1000 | |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-IRS-1 | PMID: 23478262 | IP 1:200 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFLAG-CMV-IRS-1 1-865 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pFLAG-CMV; Insert: Rat IRS-1 1-865 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFLAG-CMV-IRS-1 1-542 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pFLAG-CMV; Insert: Rat IRS-1 1-542 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFLAG-CMV-IRS-1 1-259 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pFLAG-CMV; Insert: Rat IRS-1 1-259 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFLAG-CMV-IRS-1 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pFLAG-CMV; Insert: Rat IRS-1 full-length | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pFLAG-CMV-IRS-2 (plasmid) | PMID: 21168390 | Vector: pFLAG-CMV; Insert: human IRS-2 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-EGFP-IRS-1 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: EGFP-IRS-1 wild-type | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-EGFP-IRS-1 3YA (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: EGFP-IRS-1 3YA | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-EGFP-IRS-1ΔPTB (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: EGFP-IRS-1 DPTB | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-EGFP (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: EGFP | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-EGFP-IRS-2 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: EGFP-rat IRS-2 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIGF-IR-EGFP (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pEGFP-N1; Insert: human IGF-IR | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-IGF-IR-FLAG (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: IGF-IR-FLAG | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-IGF-IR-EGFP (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: IGF-IR-EGFP | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-IGF-IR-HA-EGFP (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: IGF-IR-HA-EGFP | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMXs-Puro-integrinβ1 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pMXs-Puro; Insert: human integrin b1 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | EGFR-GFP (plasmid) | Addgene | Addgene: 32751 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pσ2-mRFP (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pCS2-mRFP4; Insert: rat s2 subunit | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pmRFP-C1 (plasmid) | This paper | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pmRFP-IRS-1 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pmRFP-C1; Insert: rat IRS-1 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGEX-μ1 (plasmid) | PMID: 23478262 | Vector: pGEX-5X-3; Insert: mouse m1 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGEX-μ2 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pGEX-5X-3; Insert: mouse m2 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pGEX-C-μ2 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pGEX-5X-3; Insert: mouse m2 C-terminal domain | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET15b-C-μ2 (plasmid) | This paper | Vector: pET15b; Insert: rat m2 C-terminal domain | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pLV-hU6-EF1a-green | Biosettia | Biosettia: SORT-B05 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCAG-HIVgp | RIKEN | RDB04394 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCMV-VSV-G-RSV-Rev | RIKEN | REB04393 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA targeting clathrin #1 | RNAi Corp. | 5’-GUAUGCCUCUGAAUCGAAAGA-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA targeting clathrin #2 | RNAi Corp. | 5’-CAGAAGAAUCGACGUUAUUUU-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA targeting μ2 #1 | RNAi Corp. | 5’-CGAAGUGGCAUUUACGAAACC-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA targeting μ2 #2 | RNAi Corp. | 5’-CUGCUUUGGGAUAGUAUGAGC-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA targeting IRS-1 #1 | RNAi Corp. | 5’-CAAUGAGUGUGCAUAAACUUC-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA targeting IRS-1 #2 | RNAi Corp. | 5’-GCCUCGAAAGGUAGACACAGC-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA targeting μ1 | RNAi Corp. | 5’-CAGACGGAGAAUUCGAACUCA-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Non-targeting control siRNA | RNAi Corp. | 5’-GUACCGCACGUCAUUCGUAUC-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA targeting LacZ | Invitrogen | 5’-GCTACACAAATCAGCGATTT-3’(targeting sequence) | |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA targeting IRS-1 #5 | Invitrogen | 5’-GCAGGCACCATCTCAACAATCC-3’(targeting sequence) | |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA targeting IRS-1 #6 | Invitrogen | 5’-GAGAATATGTGAATATTGAATC-3’(targeting sequence) | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fbxo32-qPCR forward primer | Invitrogen | ACTTCTCGACTGCCATCCTG | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fbxo32-qPCR reverse primer | Invitrogen | TCTTTTGGGCGATGCCACTC | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Trim63-qPCR forward primer | Invitrogen | GGGAACGACCGAGTTCAGAC | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Trim63-qPCR reverse primer | Invitrogen | GCGTCAAACTTGTGGCTCAG | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fbxo30-qPCR forward primer | Invitrogen | TGCAGTGGGGGAAAAAGAAGT | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fbxo30-qPCR reverse primer | Invitrogen | TGCAGTACTGAATCGCCACA | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fbxo21-qPCR forward primer | Invitrogen | ACTCCATCGGGCTCGTTATG | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fbxo21-qPCR reverse primer | Invitrogen | TGTTTCGGATCCACTCGTGC | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Map1lc3b-qPCR forward primer | Invitrogen | GCCGGAGCTTCGAACAAAGA | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Map1lc3b-qPCR reverse primer | Invitrogen | GCTTCTCACCCTTGTATCGC | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gabarapl1-qPCR forward primer | Invitrogen | ACAACACTATCCCTCCCACC | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gabarapl1-qPCR reverse primer | Invitrogen | GCTTCTGCCTCATTTCCCGTA | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Rn18s-qPCR forward primer | Invitrogen | TCCCAGTAAGTGCGGGTCATA | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Rn18s-qPCR reverse primer | Invitrogen | CGAGGGCCTCACTAAACCATC | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | GST-μ1 | PMID: 23478262 | GST-tagged mouse m1 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | GST-μ2 | This study | GST-tagged mouse m2 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | GST-C-μ2 | This study | GST-tagged mouse m2 C-terminal domain | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | His-C-μ2 | This study | 6×His-tagged rat m2 C-terminal domain | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | GY(608)MPMSPG-IRS-1 peptide | Toray Research Center, Inc. | Used for co-crystalization | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | DY(628)MPMSPK-IRS-1 peptide | Toray Research Center, Inc. | Used for co-crystalization | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | GY(658)MMMSPS-IRS-1 peptide | Toray Research Center, Inc. | Used for co-crystalization | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | recombinant human IGF-I | Astellas Pharma Inc. | A kind gift from T. Ohkuma,Astellas Pharma Inc. | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | recombinant human EGF | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Thermo Fisher Scientific: PHG0315 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamine LTX | Invitrogen | Invitrogen: 15338100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamine RNAiMAX | Invitrogen | Invitrogen: 13778075 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | leupeptin | PEPTIDE INSTITUTE, INC. | PEPTIDE INSTITUTE: 4041 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | pepstatin A | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich: P5318-5MG | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Torin1 | Cayman Chemical | Cayman Chemical: 10997 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | rapamycin | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich: 37094-10MG | |
| Chemical compound, drug | primaquine bisphosphate | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich: 160393-1G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | cycloheximide | nacalai tesque | nacalai tesque: 06741-04 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EZ-Link NHS-LC-Biotin | Pierce | Pierce: 21336 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Biotin-SS-Sulfo-OSu | Dojindo | Dojindo: B572 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | LysoTracker Red DND-99 | Molecular Probes | Molecular Probes: L7528 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Transferrin from human serum, Alexa Fluor 546 conjugate | Molecular Probes | Molecular Probes: T23364 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hoechst 33342 | Molecular Probes | Molecular Probes: H3570 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ReverTra Ace qPCR Master Mix | TOYOBO | TOYOBO: FSQ-201 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | THUNDERBIRD SYBR qPCR Mix | TOYOBO | TOYOBO: QPS-201 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | cOmplete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail | Roche | Roche: 11873580001 | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | PMID: 22743772 | RRID: SCR_002285 | |
| Software, algorithm | HKL2000 | PMID: 27754618 | ||
| Software, algorithm | CCP4 suite | PMID: 21460441 | RRID: SCR_007255 | |
| Software, algorithm | MOLREP | doi:10.1107/S0021889897006766 | ||
| Software, algorithm | REFMAC5 | PMID: 15299926 | RRID: SCR_014225 | |
| software, algorithm | PHENIX | PMID: 20124702 | RRID: SCR_014224 | |
| Software, algorithm | COOT | PMID: 15572765 | RRID: SCR_014222 | |
| Software, algorithm | PyMOL | The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System | RRID: SCR_000305 | |
| Other | Lenti-X Concentrator | Clontech | Clonetech: 631231 | |
| Other | Glutathione Sepharose 4B | GE Healthcare | GE Healthcare: 17075601 | |
| Other | Protein G Seharose Fast Flow | GE Healthcare | GE Healthcare: 17061801 | |
| Other | Streptavidin Agarose | Pierce | Pierce: 20347 | |
| Other | HisTrap HP column | GE Healthcare | GE Healthcare: 17524801 | |
| Other | HiTrap SP HP column | GE Healthcare | GE Healthcare: 17115101 | |
| Other | HiLoad 16/60 Superdex200 column | GE Healthcare | GE Healthcare: 17-1069-01 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32893.024





