Association mapping from sequencing reads using k-mers
Figures
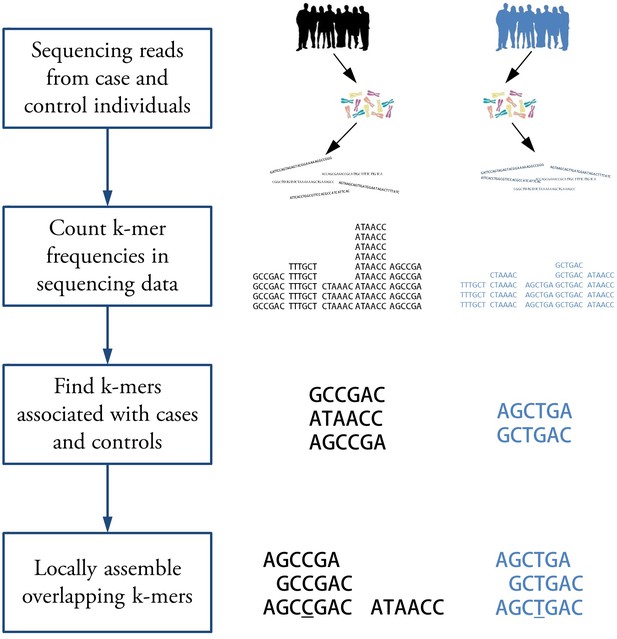
Workflow for association mapping using -mers.
The Hawk pipeline starts with sequencing reads from two sets of samples. The first step is to count -mers in reads from each sample. Then -mers with significantly different counts in two sets are detected. Finally, overlapping -mers are assembled into sequences to get a sequence, shown side by side, for each associated locus. The sequences may correspond to a SNP (underlined) in which case corresponding sequence may be detected in the other group. This may not be the case for other kinds of variations such as copy number variation.
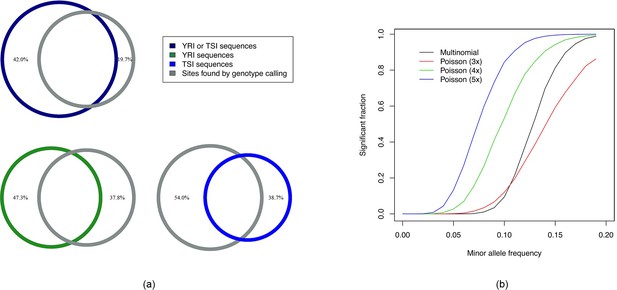
Intersection analysis and comparison of powers of tests.
(a) Venn diagrams showing intersections among sequences obtained using Hawk and significant sites found by genotype calling. The percentage values shown are fractions of the sites found using one method not covered by those found by the other method. of the sites overlapped with some sequence. Around of sequences do not overlap with any such site which can be explained by more types of variants found by Hawk as well as more power of the test using Poisson compared to Multinomial distribution. (b) Fraction of runs found significant (after Bonferroni correction) by tests against minor allele frequency of the case samples (with that of the controls fixed at 0) are shown. The curves labeled multinomial and Poisson correspond to likelihood ratio test using multinomial distribution and Poisson distributions with different -mer coverage.
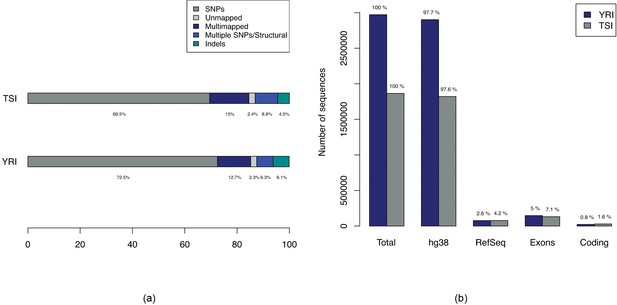
Breakdown of types of variations in comparison of YRI-TSI.
(a) Bars showing breakdown of 2,970,929 and 1,865,285 sequences enriched for in YRI and TSI samples respectively. The ‘Multiple SNPs/Structural’ entries correspond to sequences of length greater than 61, the maximum length of a sequence due to a single SNP with -mer size of 31 and ‘SNPs’ correspond to sequences of maximum length of 61. (b) Numbers of sequences with alignments to hg38, RefSeq mRNAs and Ensembl exons and coding regions.
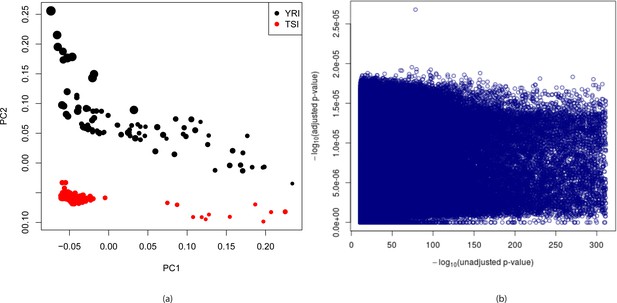
Detection and correction for population stratification in YRI-TSI dataset.
(a) Plots of first two principal components for YRI and TSI individuals from the 1000 genomes project. The PCA was run on a binary matrix indicating presence or absence of 3,483,820 randomly chosen -mers present in between 1% and 99% of the samples. The colors indicate population and sizes of circles are proportional to sequencing depth. (b) (adjusted p-values) are plotted against (unadjusted p-values) where adjusted p-values are calculated by fitting logistic regression models to predict population identity from -mer counts adjusting for population stratification, total number of -mers per sample and gender of individuals whereas unadjusted p-values are the p-values obtained using likelihood ratio test of -mer counts assuming Poisson distributions.
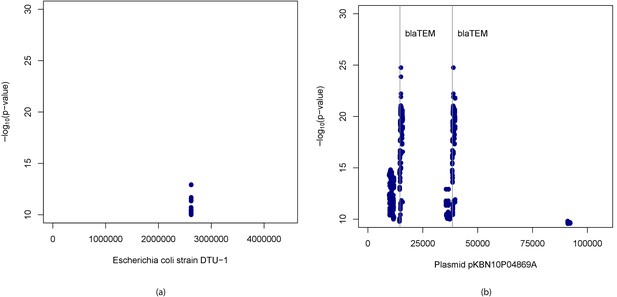
Manhattan plots for association mapping of ampicillin resistance in E.
coli using -mers. Manhattan plots showing (adjusted p-values) of -mers found significantly associated with ampicillin resistance and their start positions in (a) Escherichia coli strain DTU-1 genome and (b) plasmid pKBN10P04869A sequence. The vertical lines denote start positions of -lactamase TEM-1 gene, the presence of which is known to confer resistance to ampicillin.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5a.
Source file contains -mer sequences, corresponding p-values and their positions in Escherichia coli strain DTU-1 genome in SAM format.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32920.010
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Source data for Figure 5b.
Source file contains -mer sequences, corresponding p-values and their positions in plasmid pKBN10P04869A sequence in SAM format.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32920.011
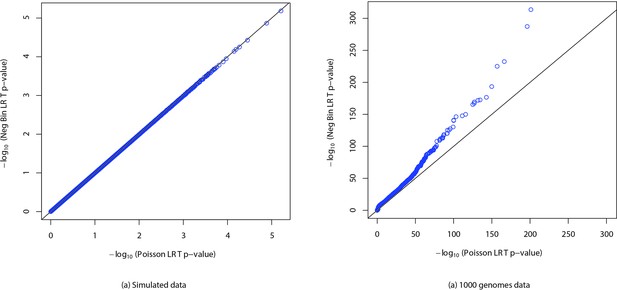
QQ plots of p-values.
QQ plots of p-values calculated using likelihood ratio test with Poisson and negative binomial distributions for (a) simulated data and (b) real data from the 1000 genomes project. The simulation was performed by sampling values from a negative binomial distribution with number of failures fixed at million and a uniformly chosen success probability between and . Half of the samples were assigned to cases and others were assigned to controls. Then p-values were computed using likelihood ratio tests with Poisson and negative binomial distributions. The process was repeated times and QQ plot was generated. Similarly p-values were computed for counts of randomly chosen -mers from YRI and TSI populations from the 1000 genomes project.
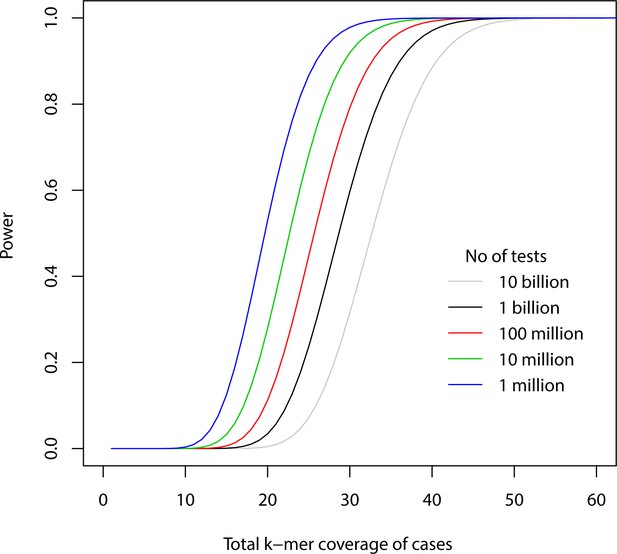
Power for different -mer coverages.
The figure shows power to detect a -mer present in all case samples and no control sample against total -mer coverage of cases using Bonferroni correction for different number of total tests for p-value=0.05.
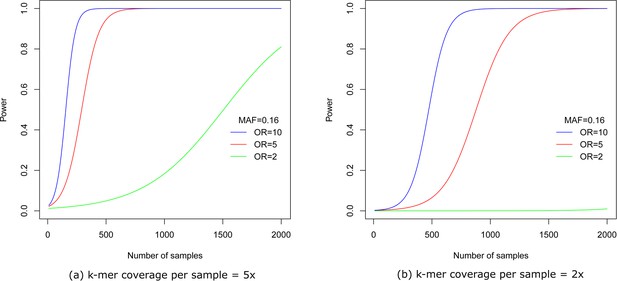
Power vs number of samples.
Figures show power to detect a -mer at MAF = 0.16 and different odds ratios for per sample -mer coverage of (a) five and (b) two after Bonferroni correction for 1 million tests.
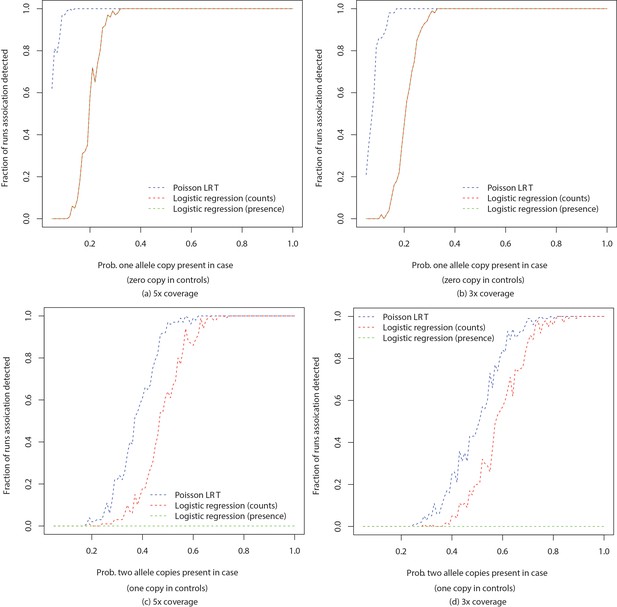
Comparison of powers of Poisson LRT and logistic regression based tests.
Figures show power to detect a -mer by Poisson based likelihood ratio test, logistic regression based tests using -mer counts and presence and absence of -mers with number of allele copies in controls fixed at (a), (b) 0 and (c), (d) 1. Simulation was performed by randomly choosing case individuals with specified number of copies of an allele according to varying probability. -mer counts were then generated according to Poisson distribution and detection of association was checked after Bonferroni correction for 1 million tests. The process was repeated 100 times for each set of parameters. Number of cases and number of controls were fixed at 100.
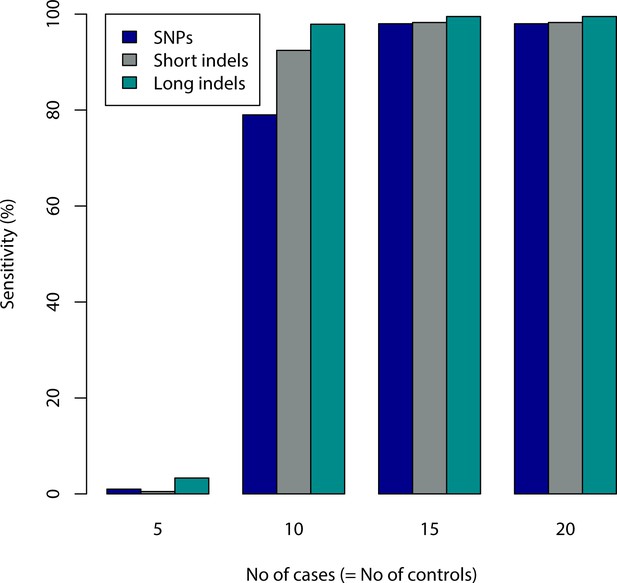
Sensitivity with simulated E. coli data.
The figure shows sensitivity for varying number of case and control samples for different types of mutations. Sensitivity is defined as the percentage of differing nucleotides that are covered by a sequence. All of the sequences covered some location of mutation.
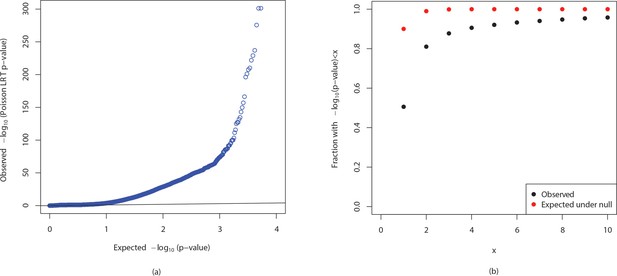
QQ plot and cumulative distributions of p-values.
The figures show (a) QQ plot and (b) cumulative distributions of (p-values) for observed p-values in the comparison of YRI and TSI populations from the 1000 genomes project and p-values expected if the null is true.
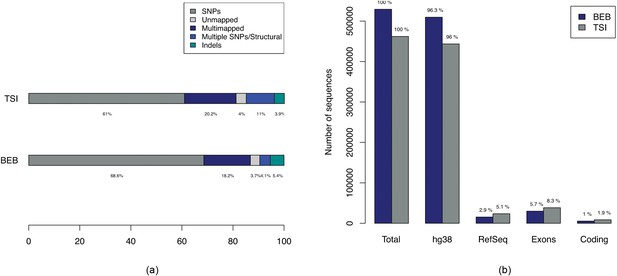
Breakdown of types of variations in BEB-TSI comparison.
(a) Bar plots showing breakdown of 529,287 and 462,122 sequences associated with BEB and TSI samples respectively. The ‘Multiple SNPs/Structural’ entries correspond to sequences of length greater than 61, the maximum length of a sequence due to a single SNP with -mer size of 31 and ‘SNPs’ correspond to sequences of maximum length of 61. (b) Numbers of sequences with alignments to hg38, RefSeq mRNAs and Ensembl exons and coding regions.
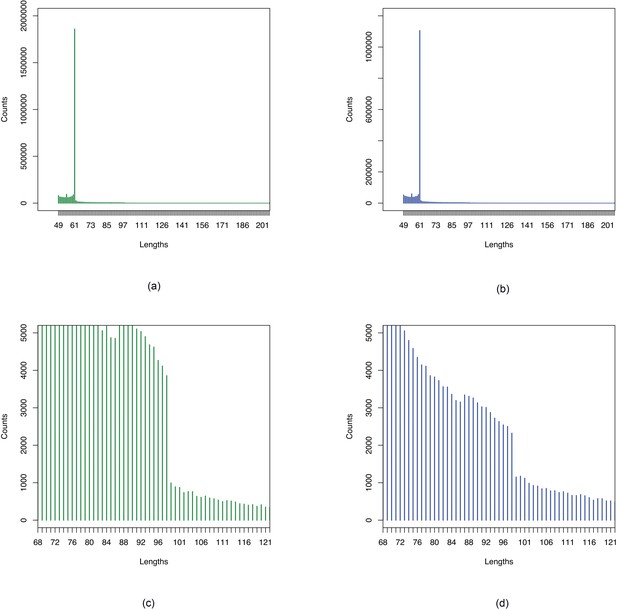
Histograms of sequence lengths in YRI-TSI comparison.
Figures show sections of histograms of lengths of sequences associated with (a, c) YRI and (b, d) TSI in comparison of YRI and TSI samples. Figures (a), (b) show peaks at 61, the maximum length corresponding to a single SNP with -mer size of 31. Figures (c), (d) show drop off after 98 which is the maximum length corresponding to two close-by SNPs as 31-mers were assembled using a minimum overlap of 24.
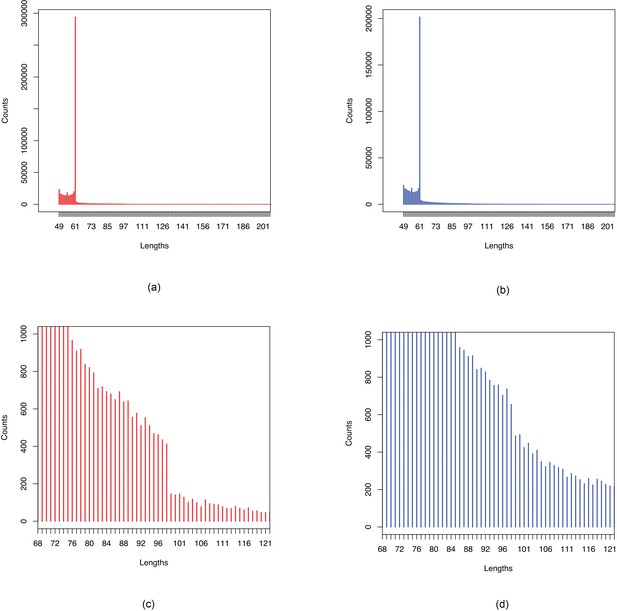
Histograms of sequence lengths in BEB-TSI comparison.
Figures show sections of histograms of lengths of sequences associated with (a, c) BEB and (b, d) TSI in comparison of BEB and TSI samples. Figures (a), (b) show peaks at 61, the maximum length corresponding to a single SNP with -mer size of 31. Figures (c), (d) show drop off after 98 which is the maximum length corresponding to two close-by SNPs as 31-mers were assembled using a minimum overlap of 24.
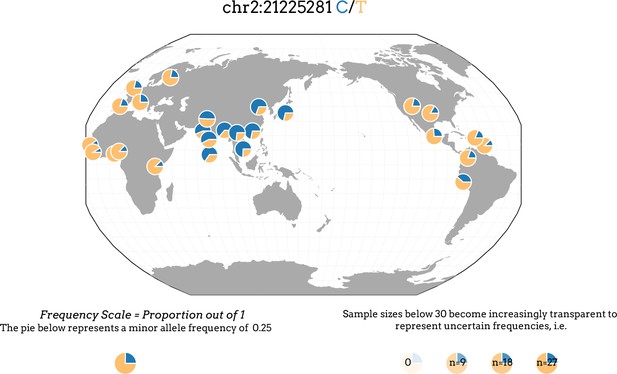
Distribution of the SNP rs1042034 alleles in 1000 genomes populations.
Plot obtained from the Geography of Genetic Variants Browser showing distribution of alleles at the SNP site rs1042034 revealing the ‘C’ allele is more prevalent in South, Southeast and East Asian populations compared to populations from other parts of the world.
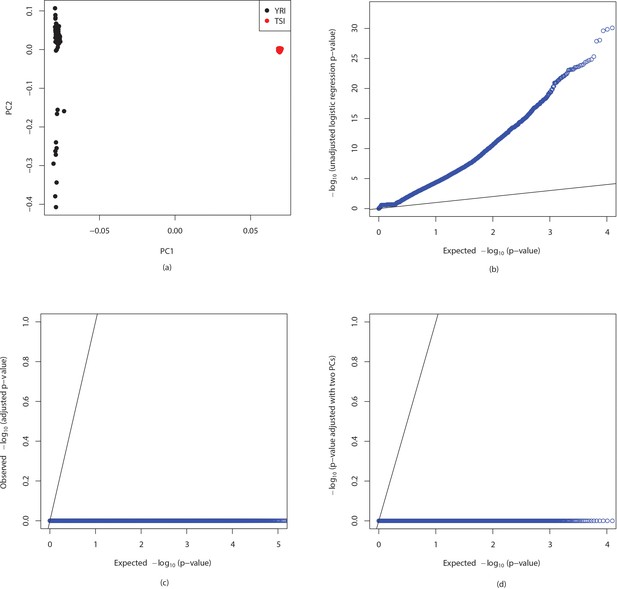
Detection and correction for population stratification in YRI-TSI dataset.
(a) Plots of first two principal components for YRI and TSI individuals where the PCA was run on variants called in the 1000 genomes project. QQ plots of ANOVA p-values of -mer counts computed by running logistic regression (b) without adjustment, (c) adjusted using first two principal components obtained from -mer counts, total number of -mers and sex of individuals, (d) adjusted using only first two principal components.
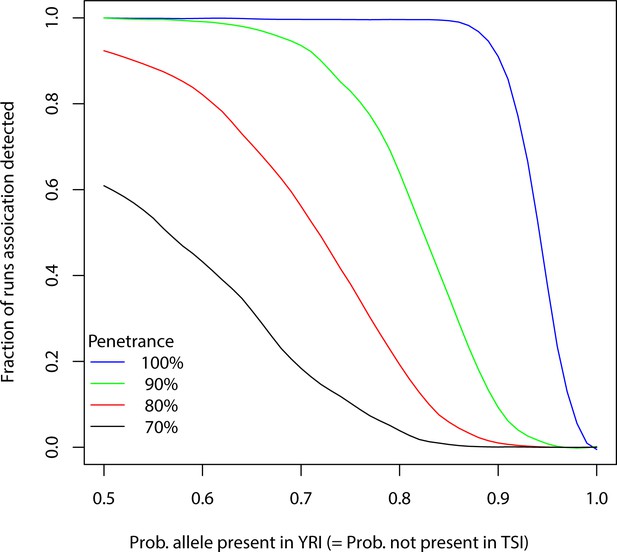
Detection of association after correcting for confounders.
A -mer (allele) is considered to be present in a YRI individual with probability and in a TSI individual with probability and counts are simulated using total numbers of -mers in the samples assuming Poisson distribution. The individuals with the -mer are randomly assigned to cases according to a penetrance value and the rest are assigned to controls. A p-value is then computed using logistic regression to predict phenotype from the counts correcting for population stratification, total number of -mers per sample and gender of individuals from the 1000 genomes data. The process is repeated 1000 times for a particular and penetrance and fraction of runs where the p-value passed the Bonferroni threshold is plotted. The process is repeated for various probabilities and penetrance.
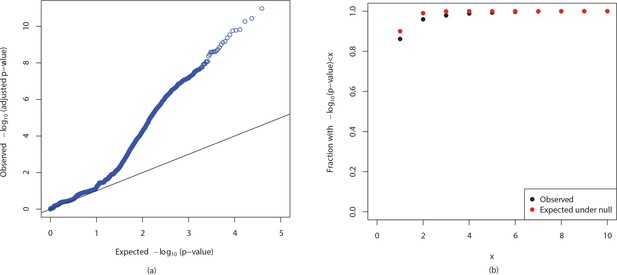
QQ plot and cumulative distributions of p-values.
The figures show (a) QQ plot and (b) cumulative distributions of (p-values) for observed p-values in association mapping of ampicillin resistance in E. coli and p-values expected if the null is true.
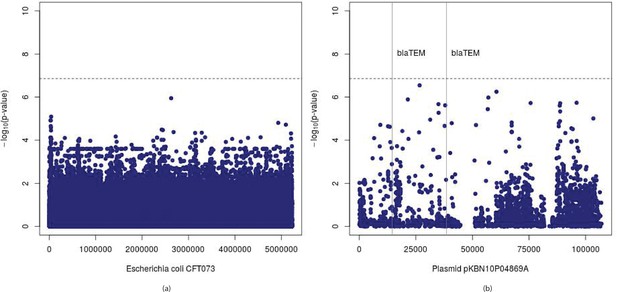
Manhattan plots for association mapping of ampicillin resistance in E. coli using conventional approach.
Manhattan plots showing (p-values) of SNPs and their positions in (a) Escherichia coli strain CFT073 genome and (b) plasmid pKBN10P04869A sequence. The vertical lines denote start positions of -lactamase TEM-1 gene, the presence of which is known to confer resistance to ampicillin. The horizontal lines denote Bonferroni threshold of .
Tables
Known variants in YRI-TSI comparison.
Table 1 shows p-values of sequences computed using likelihood ratio test at some well known sites of variation between populations. The (%) values denote fraction of individuals in the sample with the allele present. The p-values and % values are averaged over -mers constituting the associated sequences.
| Gene | SNP id | Description | Allele | p-value | %YRI | %TSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACKR1 | rs2814778 | Duffy antigen | C | 9.72 | 84.39% | 1.78% |
| SLC24A5 | rs1426654 | Skin pigmentation | G | 8.45 | 87.39% | 1.02% |
| SLC45A2 | rs16891982 | Skin/hair color | C | 1.89 | 92.18% | 4.67% |
| G6PD | rs1050829 | G6PD deficiency | C | 1.53 | 24.92% | 1.02% |
| G6PD | rs1050828 | G6PD deficiency | T | 5.83 | 18.32% | 0.00% |
Summary of sequences not in the human reference genome.
Table 2 shows summary of sequences associated with different populations that did not map to the human reference genome (hg38) or to the Epstein-Barr virus genome.
| Population | Population compared to | Total no. sequences | No. sequences with length1000bp | Total length in sequences with length1000 bp | No. sequences with length200bp | Total length in sequences with length200bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YRI | TSI | 94,795 | 41 | 59,956 | 478 | 225,426 |
| TSI | YRI | 66,051 | 10 | 13,896 | 184 | 77,383 |
| BEB | TSI | 19,584 | 3 | 3835 | 75 | 33,954 |
| TSI | BEB | 18,508 | 2 | 2105 | 81 | 28,134 |
Variants in genes linked to cardiovascular diseases.
Variants in genes linked to cardiovascular diseases found to be significantly more common in BEB samples compared to TSI samples. The (%) values denote fraction of individuals in the sample with the allele present. The p-values and % values are averaged over -mers constituting the associated sequences.
| Gene | SN id | Variant type | Allele | p-value | %BEB | %TSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOB | rs2302515 | Missense | C | 1.30 | 29.29% | 8.37% |
| APOB | rs676210 | Missense | A | 7.73 | 72.93% | 33.08% |
| APOB | rs1042034 | Missense | C | 2.28 | 68.67% | 31.91% |
| CYP11B2 | rs4545 | Missense | T | 1.31 | 31.33% | 0.91% |
| CYP11B1 | rs4534 | Missense | T | 9.36 | 33.00% | 0.91% |
| WNK4 | rs2290041 | Missense | T | 1.53 | 13.24% | 0.47% |
| WNK4 | rs55781437 | Missense | T | 1.30 | 15.21% | 0.91% |
| SLC12A3 | rs2289113 | Missense | T | 7.40 | 8.14% | 0.00% |
| SCNN1A | rs10849447 | Missense | C | 8.67 | 62.88% | 39.92% |
| ABO | - | 4 bp (CTGT) deletion | - | 1.17 | 29.15% | 10.55% |
| ABO | rs8176741 | Missense | A | 2.06 | 27.70% | 8.45% |
| SH2B3 | rs3184504 | Missense | C | 8.22 | 92.88% | 63.87% |
| RAI1 | rs3803763 | Missense | C | 1.32 | 75.86% | 51.17% |
| RAI1 | rs11649804 | Missense | A | 1.95 | 81.57% | 52.79% |
Variants in Titin of differential prevalence in BEB-TSI comparison.
Variants in Titin, a gene linked to cardiovascular diseases, that were found to be significantly more common in BEB samples compared to TSI samples. The (%) values denote fraction of individuals in the sample with the allele present. The p-values and % values are averaged over -mers constituting the associated sequences.
| Gene | SNP id | Variant type | Allele | p-value | %BEB | %TSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTN | rs9808377 | Missense | G | 1.70 | 66.44% | 41.91% |
| TTN | rs62621236 | Missense | G | 2.33 | 27.70% | 5.72% |
| TTN | rs2291311 | Missense | C | 1.06 | 25.77% | 7.77% |
| TTN | rs16866425 | Missense | C | 8.19 | 21.73% | 2.73% |
| TTN | rs4894048 | Missense | T | 2.00 | 22.65% | 2.26% |
| TTN | rs13398235 | Intron/missense | A | 2.04 | 41.00% | 17.40% |
| TTN | rs11888217 | Intron/missense | T | 4.18 | 27.25% | 4.55% |
| TTN | rs10164753 | Missense | T | 3.69 | 28.48% | 6.19% |
| TTN | rs10497520 | Missense | T | 1.66 | 54.76% | 18.86% |
| TTN | rs2627037 | Missense | A | 6.99 | 25.06% | 4.72% |
| TTN | rs1001238 | Missense | C | 1.66 | 64.66% | 38.21% |
| TTN | rs3731746 | Missense | A | 1.26 | 50.72% | 30.21% |
| TTN | rs17355446 | Intron/missense | A | 3.31 | 15.44% | 1.11% |
| TTN | rs2042996 | Missense | A | 1.03 | 71.41% | 35.87% |
| TTN | rs747122 | Missense | T | 1.59 | 28.57% | 7.24% |
| TTN | rs1560221 | Synonymous | G | 1.11 | 70.71% | 34.66% |
| TTN | rs16866406 | Missense | A | 2.17 | 35.60% | 17.51% |
| TTN | rs4894028 | Missense | T | 2.58 | 27.54% | 6.89% |
| TTN | - | Insertion | T | 1.09 | 34.11% | 8.59% |
| TTN | rs3829747 | Missense | T | 4.72 | 37.55% | 20.30% |
| TTN | rs2291310 | Missense | C | 2.18 | 36.63% | 8.04% |
| TTN | rs2042995 | Intron/Missense | C | 7.83 | 56.32% | 31.64% |
| TTN | rs3829746 | Missense | C | 5.30 | 75.94% | 37.60% |
| TTN | rs744426 | Missense | A | 1.36 | 37.15% | 18.92% |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32920.012





