Cellular localization of the cell cycle inhibitor Cdkn1c controls growth arrest of adult skeletal muscle stem cells
Figures
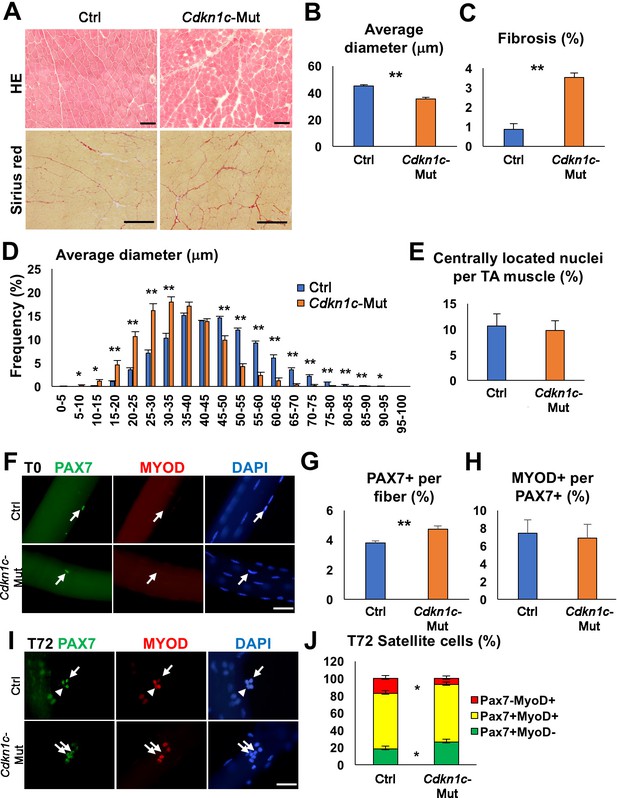
Cdkn1c deficiency impairs normal muscle growth.
(A) Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) and Sirius red staining of control (Ctrl) and Cdkn1c mutant (Cdkn1c-Mut) mouse Tibialis anterior (TA) muscles were performed to examine muscle histology, centrally located nucleated myofibers, and fibrosis. Scale bars, 100 μm. (B) Histogram showing the average of myofiber diameters (μm). (C) Histogram of average fibrotic area per TA muscle. (D) Fiber size (μm) distribution in control and Cdkn1c mutant mice. (E) Histogram of number of fibers with centrally located nuclei. (F) PAX7+ (green) MuSCs (arrows) on the myofibers isolated from EDL muscles of Cdkn1c mutant and control mice. MYOD (red) is not normally expressed in PAX7+ MuSCs at T0 (quiescence). DAPI (blue) shows all nuclei. Scale bars, 50 μm. (G) Numbers of PAX7+ satellite cells on the myofibers isolated from EDL. (H) Ratio of MYOD+ activated cells per PAX7+ MuSC on the myofibers isolated from EDL muscles of Cdkn1c mutant and control mice. (I) Immunofluorescence for PAX7 (green) and MYOD (red) at T72 in single myofiber cultures. Arrows and arrowheads show PAX7+MYOD- quiescent satellite cells and PAX7-MYOD+ differentiating cells, respectively. Scale bars, 50 μm. (J) Quantification of ratios of PAX7+ and MYOD+ cells per fiber at T72. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01.
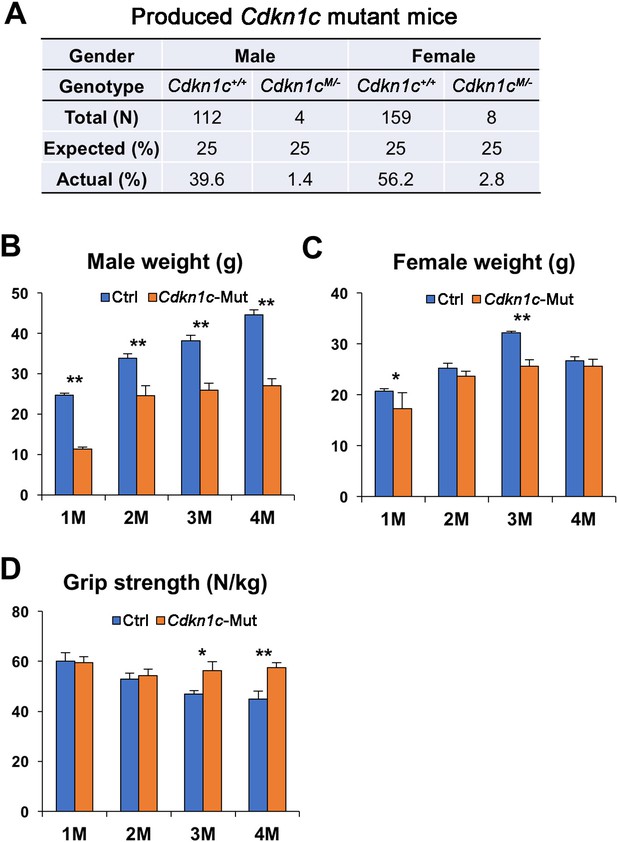
Cdkn1c mutant mice display smaller body weight.
(A) A few Cdkn1c mutant (Cdkn1cM/-) mice survived postnatally in a mixed CD1;B6 background. (B–C) Body weight average of control (Ctrl) and Cdkn1c mutant male (B) and female (C) mice. (D) Forelimb grip strength normalized for body weight control and Cdkn1c mutant mice. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01.
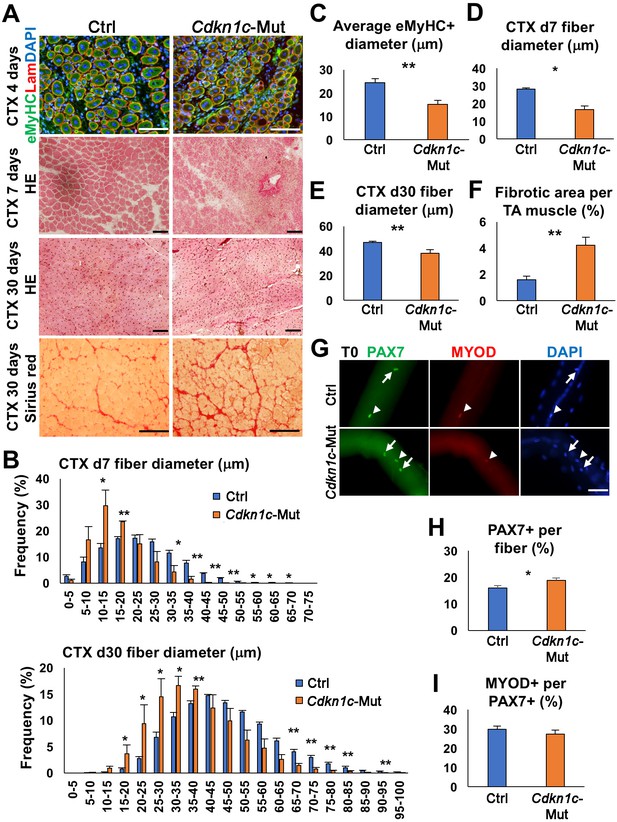
CDKN1c deficiency delays muscle regeneration.
(A) Embryonic myosin (eMyHC)/LAMININ/DAPI, Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE), and Sirius red staining of twelve- to fifteen-week-old control (Ctrl) and Cdkn1c mutant mouse TA muscles were performed for histological and fibrosis characterization 4, 7 or thirty days after cardiotoxin (CTX) injection. Scale bars, 100 μm. (B) Fiber size (μm) distribution in control (Ctrl) and Cdkn1c mutant (Cdkn1c-Mut) mice 7 (upper panel) or thirty (lower panel) days after CTX injection. (C) Histogram of average embryonic MyHC+ fiber diameters (μm) 4 days after CTX injection. (D) Histogram of average fiber diameters (μm) 7 and thirty days after CTX injection. (E) Fiber size (μm) distribution in control and Cdkn1c mutant mice thirty days after CTX injection. (F) Histogram of average fibrotic area per TA muscle. (G) PAX7+ (green) MuSCs (arrows) on the myofibers isolated from EDL muscles of Cdkn1c mutant and control mice thirty days after CTX injection. MYOD (red) is occasionally expressed in PAX7+ MuSCs (arrow heads). DAPI (blue) shows all nuclei. Scale bars, 50 μm. (H) Numbers of PAX7+ MuSCs on the EDL isolated myofibers . (I) Ratio of MYOD+ activated cells per PAX7+ MuSC on the myofibers isolated from EDL muscles of Cdkn1c mutant and control mice. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 100 μm. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01.
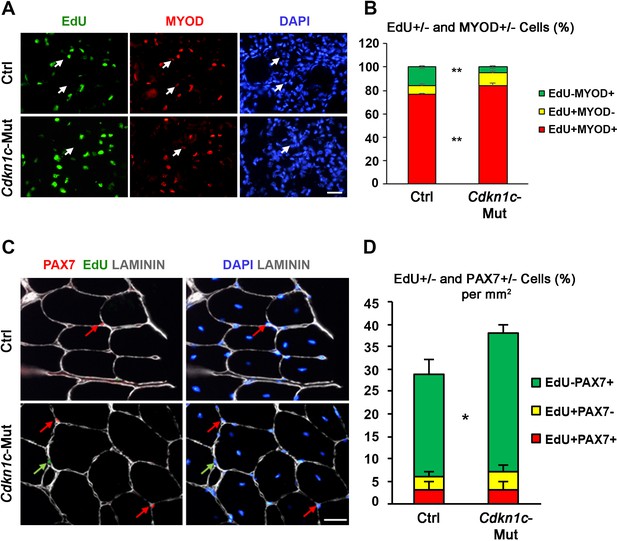
Myoblasts in Cdkn1c mutant mice display delayed cell cycle exit during muscle regeneration.
(A) EdU (green)/MYOD (red)/DAPI (blue) staining of TA muscle sections of control (Ctrl) and Cdkn1c mutant (Cdkn1c-Mut) mice at day 3 after CTX injection. Arrows indicate EdU-MYOD+ differentiating myoblasts. (B) Graph shows EdU±/MYOD ± cell ratio. (C) EdU (green)/PAX7 (red)/LAMININ (white)/DAPI (blue) staining of TA muscle sections of control (Ctrl) and Cdkn1c mutant (Cdkn1c-Mut) mice at day thirty after CTX injection. EdU+ or PAX7 + cells are indicated by green and red arrows, respectively. (D) Graph shows EdU±/PAX7± cell ratio per 1 mm2 section area. Scale bar, 50 μm. *p≤0.05 and **p≤0.01.
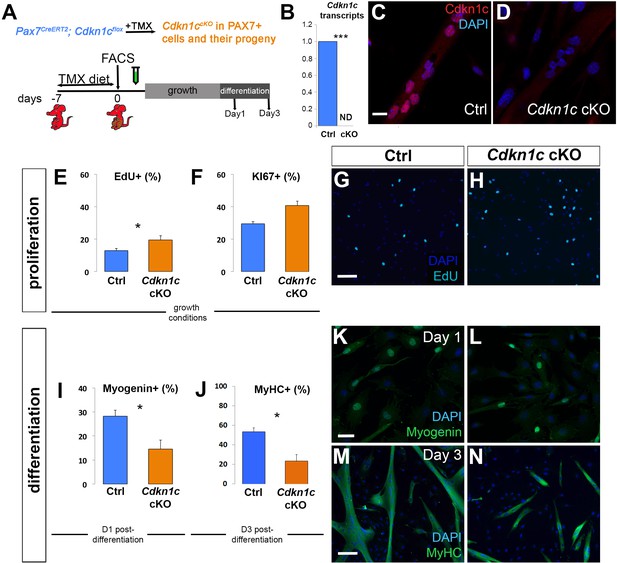
Cdkn1c deficiency impairs myogenic differentiation.
(A) Time-course of tamoxifen (TMX) administration, muscle satellite cell harvest (FACS arrow) and culture (light gray bar for growth culture conditions, dark gray bar for differentiation culture conditions). Analyzed animals were Pax7CreERT2/+; Cdkn1cFlox(m)/+;RosamTmG (Cdkn1c cKO) and Pax7CreERT2/+; Cdkn1c+/+;RosamTmG (control; Ctrl); maternal inheritance of the imprinted Cdkn1c is indicated by superscript (m). (B) Cdkn1c transcript levels of control and Cdkn1c cKO myoblast cultures 3 days post-differentiation. ND; not detected. (C–D) Control (C) and Cdkn1c cKO (D) myoblast cultures were examined for CDKN1c protein (red) following three days under differentiation conditions. (E–N) Control and Cdkn1c cKO myoblast cultures were examined for EdU+ (light blue) cells (E, G, H), KI67+ cells (F), MYOGENIN+ cells (green; I, K, L), and myotube formation (J, M, N). Nascent myotubes were marked with myosin heavy chain (MyHC; green; M, N). Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI (blue). Graphs show quantification of EdU and KI67 expression under growth conditions (E, F), MYOGENIN expression following 24 hr under differentiation conditions (I), and MyHC+ cells following 72 hr under differentiation conditions (J). Data show mean +SD, n = 3 animals. Asterisks indicate significance; *p≤0.05, ***p≤0.001. Scale bars, 40 μm (C, K), 1000 μm (G, M).
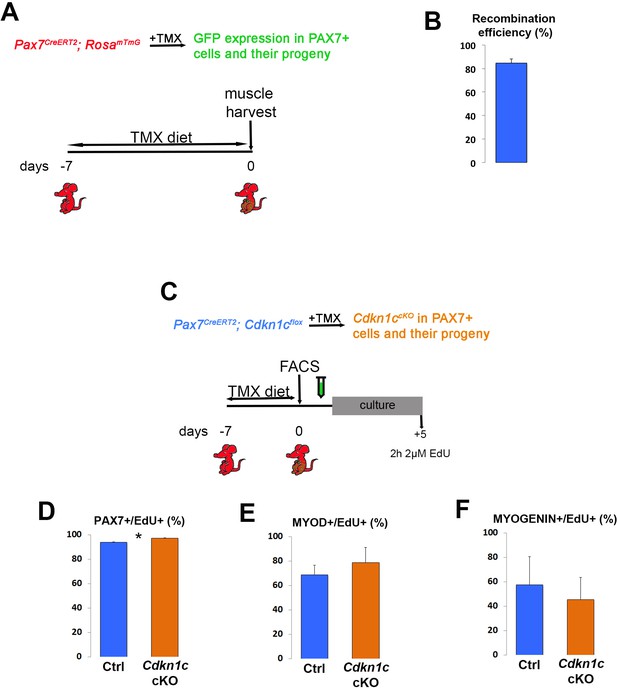
Myogenic marker expression in proliferating myoblasts.
(A) Time-course of tamoxifen administration, muscle satellite cell harvest (FACS arrow) and culture. Analyzed animals were Pax7CreERT2/+; Cdkn1cFlox(m)/+;RosamTmG (Cdkn1c cKO) and Pax7CreERT2/+; Cdkn1c+/+;RosamTmG (control; Ctrl); maternal inheritance of the imprinted Cdkn1c is indicated by superscript (m). (B–D) Control and Cdkn1c cKO myoblast cultures were examined for PAX7 (B), MYOD (C), and MYOGENIN (D) expression in the EdU+ fraction, following 2-hr incubation with 2 μM EdU prior to cell fixation. Data show mean +SD, n = 3 animals. Asterisks indicate significance; *p≤0.05.
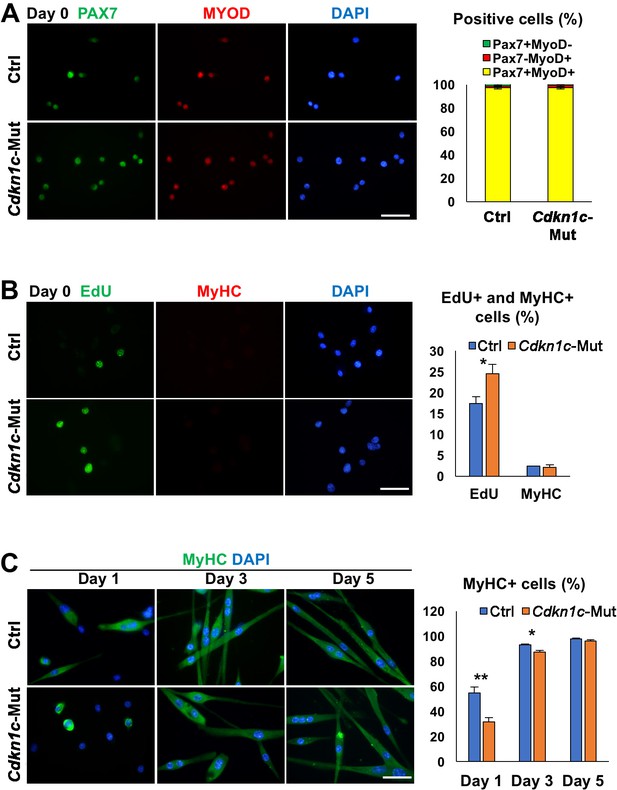
Cdkn1c mutant myoblasts display increased proliferation and reduced differentiation.
(A) Control (Ctrl) and Cdkn1c mutant (Cdkn1c-Mut) primary myoblasts are positive for both PAX7 and MYOD. (B) Under growth conditions, EdU+ cells are significantly higher in Cdkn1c mutant primary myoblasts compared with control cells. By contrast, there is no difference for MyHC+ differentiating cells. (C) Under differentiation conditions, Cdkn1c mutant primary myoblasts display reduced differentiation kinetics detected by MyHC in both day 1 and 3. However, in day 5, myogenic differentiation is almost saturated in both control and Cdkn1c mutant primary myoblasts. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 50 μm. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01.
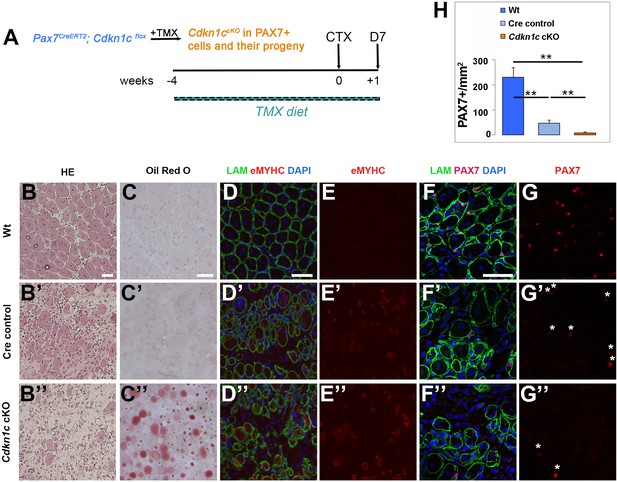
MuSC-specific Cdkn1c ablation hinders muscle regeneration.
(A) Time-course of tamoxifen administration, intramuscular injury of TA muscle (CTX arrow), and muscle harvest (D7 arrow). (B–G) Cryosections of TA muscle were stained for histological and satellite cell population characterization 7 days after CTX injection. Analyzed animals at (B-G) were wild-type littermates (Wt; Pax7+; Cdkn1c+; B–G), Cre control (Pax7CreERT2; B’–G’), and Cdkn1c cKO (Pax7CreERT2; Cdkn1cFlox; B’’–G’’). (B) HE staining for histologic characterization of the muscles. (C) Oil Red O staining for evaluation of fat infiltration of the muscles. (D–E) embryonic myosin (eMYHC, red)/LAMININ (LAM, green) immunofluorescence to mark newly formed myofibers post-regeneration. (F–G) PAX7 (red)/LAMININ (LAM, green) immunofluorescence to mark PAX7+ satellite cells. Nuclei in (D-G) were counter-stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 μm. (H) Quantification of (F-G). Data show mean +SD, n ≥ 5 animals. Asterisks indicate significance; **p≤0.01.
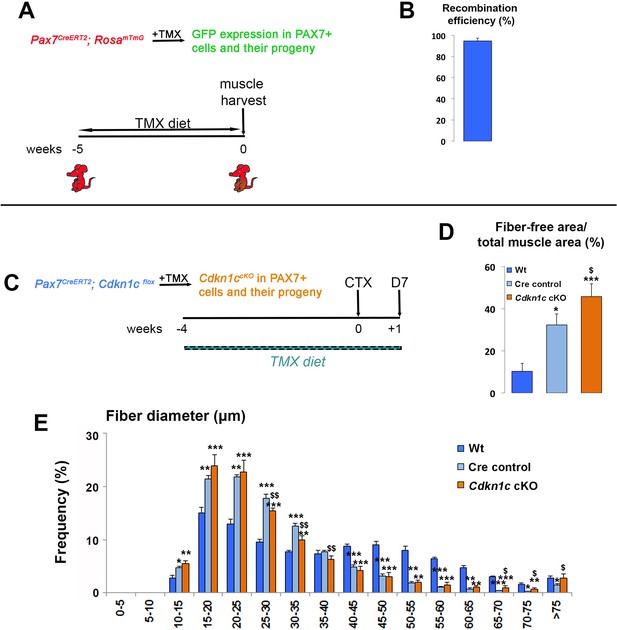
In vivo MuSC-specific Cdkn1c ablation.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33337.010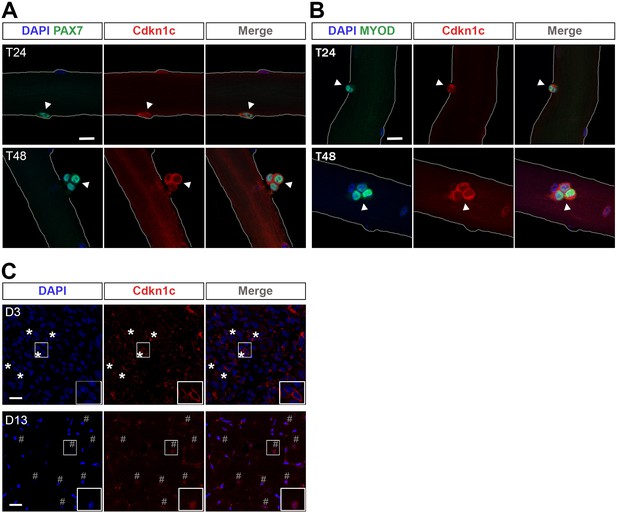
Cdkn1c cytoplasmic expression after satellite cell activation.
(A) Satellite-cell-derived myoblasts (T24–T48) of single EDL myofibers stained with PAX7 (green) and CDKN1c (red). Arrowheads indicate PAX7+ cells. (B) Satellite cell-derived myoblasts of single EDL myofibers stained with MYOD (green) and CDKN1c (red). Arrowheads indicate MYOD+ cells. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. n ≥ 3. Scale bars, 40 μm. (C) CDKN1c (red) staining of TA muscle at 3 (D3) or t (D13) days after CTX injection. Asterisks indicate regions with cytoplasmic CDKN1c. # indicates central nuclei of newly formed fibers during muscle regeneration. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm.
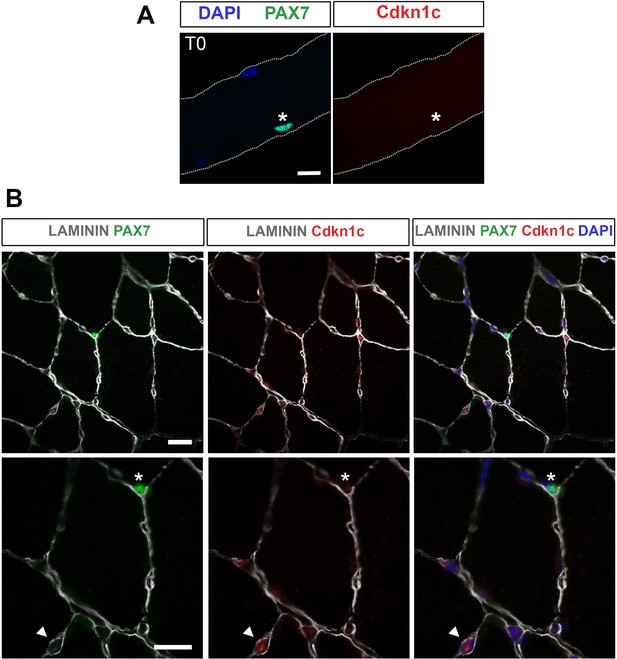
Cdkn1c is not expressed in quiescent satellite cells.
(A) Muscle satellite cells (MuSCs; T0) stained with PAX7 (green) and Cdkn1c (red) in single myofiber cultures of EDL muscles. (B) Cdkn1c (red) presence in TA muscle section. MuSCs were marked with PAX7 (green) and fibers were outlined with LAMININ (gray). Arrowheads indicate Cdkn1c + cells. Asterisks indicate satellite cells. Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 40 μm.
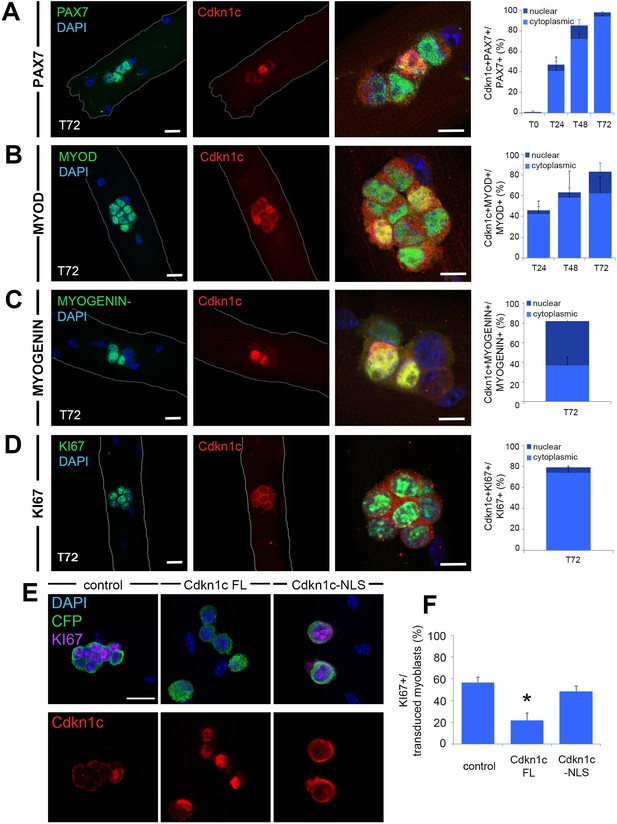
Cdkn1c expression and subcellular localization during satellite cell activation and differentiation.
(A–D) Immunofluorescence for PAX7 (A; green), MYOD (B; green), MYOGENIN (C; green) or KI67 (D; green) and Cdkn1c (red) at T72 in single myofiber cultures of EDL muscles and quantification of PAX7+ (A), MYOD+ (B), MYOGENIN+ (C) or KI67+ (D) cells that co-expressed CDKN1c over the time-course of the culture. Cytoplasmic (light blue) or nuclear (dark blue) localization of CDKN1c is indicated in the graphs. Scale bars, 40 μm. (E) Immunofluorescence for Cyant fluorescent protein (CFP, green), KI67 (purple), and CDKN1c (red) in transduced (i.e. CFP+) myoblasts at T72 in single myofiber cultures. Fibers were transduced with empty retroviruses (control; left panel), retroviruses expressing full-length Cdkn1c (Cdkn1c FL; middle panel) or Nuclear localization signal-deficient Cdkn1c (Cdkn1c–NLS; right panel). (F) Quantification of transduced (CFP+) myoblasts that were proliferating (KI67+). Nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 20 μm. Data show mean +SD, n ≥ 3 animals, 20–32 fibers/animal. *p≤0.05 compared to control virus.
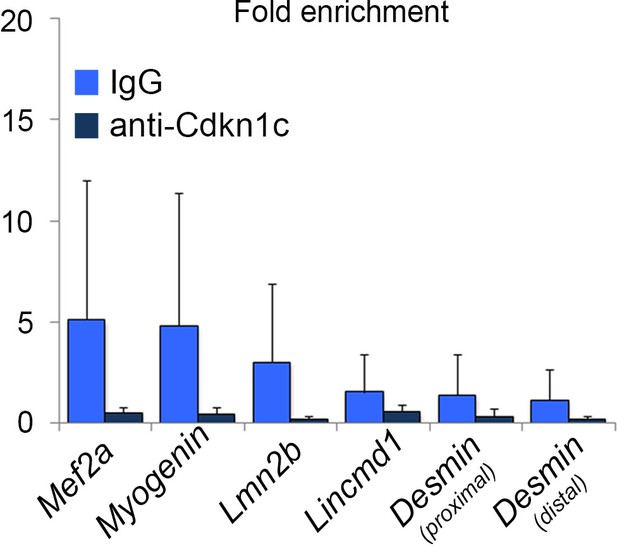
Lack of CDKN1c binding in myogenic regulatory regions.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by qPCR on C2C12 myogenic cells 4 days after differentiation induction. Enrichment was evaluated in myogenic regions that have previously been shown to be MYOD-regulated by the ChIP-sequencing study of Cao et al. (2010).
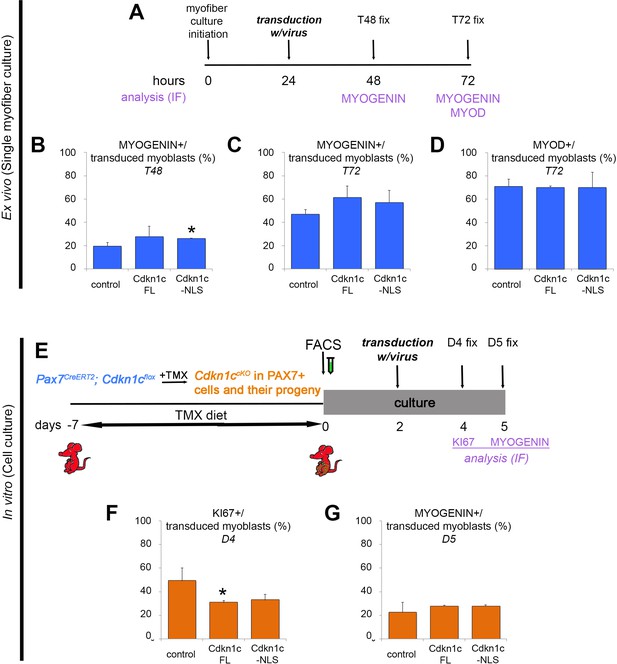
Uncoupling of cell cycle exit and differentiation.
(A) Time-course of single myofiber culture, transduction of activated myoblasts with virus, and readouts. (B–D) Quantification of transduced (CFP+) myoblasts that were differentiating, as evaluated by expression of MYOGENIN at T48 (B) and T72 (C) or MYOD (T72; D). Data show mean +SD, n = 3 animals, 20–30 fibers/animal. *p≤0.05 compared to control virus. (E) Time-course of tamoxifen administration, muscle satellite cell harvest (FACS arrow) and culture, transduction of activated myoblasts with virus, and readouts. (F–G) Quantification of transduced (CFP+) myoblasts that were proliferating (KI67+; F) or differentiating (MYOGENIN+; G). Data show mean +SD, n = 3 animals. *p≤0.05. (A–G) Myoblasts were transduced with empty retroviruses (control), retroviruses expressing full-length Cdkn1c (Cdkn1c FL) or Nuclear localization signal-deficient Cdkn1c (Cdkn1c–NLS). Analyzed animals in (A-D) were wild-type C57BL/6. Analyzed animals in (E-G) were Pax7CreERT2/+; Cdkn1cFlox(m)/+;RosamTmG (Cdkn1c cKO); maternal inheritance of the imprinted Cdkn1c is indicated by superscript (m).
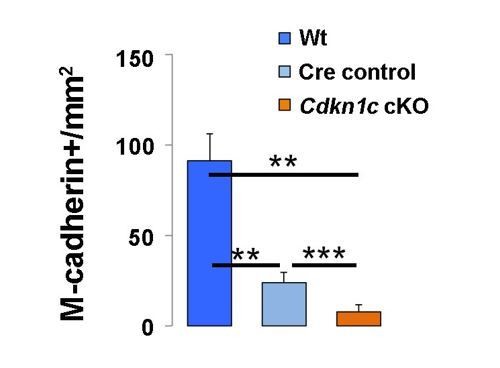
Quantification of M-cadherin+ MuSCs in regenerating muscle of wildtype littermate (Wt; Pax7+;Cdkn1c+), Cre control (Pax7CreERT2), and Cdkn1c cKO (Pax7CreERT2;Cdkn1cFlox) mice at D7 post-cardiotoxin injection.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33337.019Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Cdkn1ctm1Sje | The Jackson Laboratory; PMID: 9144284 | MGI: J40203, RRID:IMSR_JAX:003336 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | p57flox | PMID: 28196404 | Mouse line generated by the group of F.Relaix and characterized in Mademtzoglou et al. (2017); Genesis 55(4) doi: 10.1002/dvg.23025 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Pax7CreERT2/+ | The Jackson Laboratory; PMID: 19554048 | MGI: J:150962; RRID:IMSR_JAX:012476 | Mouse line obtained from C.M. Fan |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | RosamTmG | The Jackson Laboratory; PMID: 17868096 | MGI: J:124702; RRID:IMSR_JAX:007576 | |
| Genetic reagent (synthetic) | pGEMT-Easy vector | Promega | A1360 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | 293T | DSMZ | ACC635; RRID:CVCL_0063 | https://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/ACC-635.html?tx_dsmzresources_pi5%5BreturnPid%5D=192 |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | C2C12 | American Type Culture Collection (ATCC); PMID: 28966089 | CRL-1772; RRID: CVCL_0188 | Cell line maintained in E. Gomes lab |
| Antibody | anti-CD31-PE (monoclonal) | eBiosciences | 12-0311-81; RRID:AB_465631 | |
| Antibody | anti-CD45-PE (monoclonal) | eBiosciences | 12-0451-81; RRID:AB_465667 | |
| Antibody | anti-embryonic MyHC (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | F1.652; RRID:AB_528358 | |
| Antibody | anti-embryonic MyHC (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc53091; RRID:AB_670121 | |
| Antibody | anti-GFP (chicken polyclonal) | Abcam | ab13970; RRID:AB_300798 | |
| Antibody | anti-integrin a-biotin (mouse) | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-101-979; RRID:AB_2652472 | |
| Antibody | anti-IgG (rabbit) | Diagenode | C15410206 | |
| Antibody | anti-KI67 (mouse monoclonal) | BD Pharmingen | 556003; RRID:AB_396287 | |
| Antibody | anti-Laminin (rabbit polyclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | L9393; RRID:AB_477163 | |
| Antibody | anti-Laminin (rat monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | 4H8-2; RRID:AB_784266 | |
| Antibody | anti-Laminin (rabbit polyclonal) | Novus Biological | NB300-144AF647 | |
| Antibody | anti-MyHC (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | mf20-c; RRID:AB_2147781 | |
| Antibody | anti-MyoD (mouse monoclonal) | DAKO | M3512; RRID:AB_2148874 | |
| Antibody | anti-MyoD (rabbit polyclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc-760; RRID:AB_2148870 | |
| Antibody | anti-Myogenin (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | F5D; RRID:AB_2146602 | |
| Antibody | anti-p57 (goat polyclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc1039; RRID:AB_2078158 | |
| Antibody | anti-p57 (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc56431; RRID:AB_2298043 | |
| Antibody | anti-p57 (rabbit polyclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc8298; RRID:AB_2078155 | |
| Antibody | anti-Pax7 (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | PAX7-c; RRID:AB_528428 | |
| Antibody | anti-Sca-1-PE (mouse) | eBiosciences | 12-5981-81; RRID:AB_466085 | |
| Antibody | fab fragment affinity- purified antibody (goat) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 115-007-003 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | AGGGCATATCC AACAACAAACTT | Eurogentec | N/A | qPCR HPRT (Forward primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | GTTAAGCAGTA CAGCCCCAAA | Eurogentec | N/A | qPCR HPRT (Reverse primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | CTGAAGGACCA GCCTCTCTC | Eurogentec | N/A | qPCR p57 (Forward primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | AAGAAGTCGTT CGCATTGGC | Eurogentec | N/A | qPCR p57 (Reverse primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | ATCTGAGGTCA GCCATTTGGT | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Mef2a (Forward primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | GCTAAGGACAG CTGTGACCTG | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Mef2a (Reverse primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | TTAAAGACATGTG GCAACAGACTAC | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Lmn2b (Forward primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | TGCTCTTTCTGTA CTGTGTGGTG | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Lmn2b (Reverse primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | GGAGTGATTGA GGTGGACAGA | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Lincmd1 (Forward primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | CTCTCCCACCTG TTTGTGTCTT | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Lincmd1 (Reverse primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | AATTACAGCCG ACGGCCTCC | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Myogenin (Forward primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | CCAACGCCACA GAAACCTGA | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Myogenin (Reverse primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | CAGCTCCTTG CCCTGTGAAA | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Desmin-proximal (Forward primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | TGTAGCCCTCC TGACATCAC | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Desmin proximal (Reverse primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | CCAAAAGGG CCGATGAGGAA | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Desmin distal (Forward primer) |
| Sequence-based reagent | TAGAGACAGA CCAGTGGCGG | Eurogentec | N/A | ChIP qPCR Desmin distal (Reverse primer) |
| Commercial assay or kit | LightCycler 480 SYBR Green I Master | Roche-Sigma-Aldrich | 04887352001 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | iDeal ChIP-seq kit | Diagenode | C01010051 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNasy Micro Kit | QIAGEN | 74004 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Transcriptor First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit | Roche-Sigma-Aldrich | 4379012001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | bFGF | Peprotech | 450–33 | 20 ng/ml |
| Chemical compound, drug | bFGF | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PHG0263 | 20 ng/ml |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 10001620 | 0.2% |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cardiotoxin | Latoxan | L8102 | 10 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cardiotoxin | Sigma-Aldrich | 217503–1 mg | 10 µM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Chicken embryo extract | MP-Biomedical | 92850145 | 0.5% |
| Chemical compound, drug | Chicken embryo extract | Seralab | CE-650-J | 1% |
| Chemical compound, drug | collagen | BD Biosciences | 354236 | culture dish coating |
| Chemical compound, drug | Collagenase type I | Sigma-Aldrich | C0130 | 0.2% |
| Chemical compound, drug | Collagenase type I | Worthington Biochemical Corp | 9001-12-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Collagenase A | Roche-Sigma-Aldrich | 11088793001 | 0.2% w/v |
| Chemical compound, drug | DAPI (4’,6-diamidino-2- phenylindole dihydrochloride) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | D1306 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dispase II | Roche-Sigma-Aldrich | 4942078001 | 2.4 U/ml |
| Chemical compound, drug | DNaseI | Roche-Sigma-Aldrich | 11284932001 | 10 ng/mL |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 41966 | single myofiber culture |
| Chemical compound, drug | DMEM with GlutaMAX | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 61965 | myoblast culture |
| Chemical compound, drug | EdU | Thermo Fisher Scientific | C10340 | 2 μM |
| Chemical compound, drug | F-10 Ham's media | Sigma-Aldrich | N6635 | N/A |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 10270 | 20% |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fetal calf serum (FCS) | Eurobio | CVFSVF00-01 | 10% (prol/tion medium), 2% (diff/tion medium) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fluoromount-G | Southern Biotech | 0100–01 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hanks' Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 14025 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hepes | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15630 | 0.1M |
| Chemical compound, drug | Horse serum | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 26050088 | 5% (coating), 10% (culture) |
| Chemical compound, drug | L-glutamine | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 25030 | 20 mM |
| Chemical compound, drug | matrigel | Corning Life Sciences | 354230 | 1:20 in DMEM |
| Chemical compound, drug | Penicillin/streptomycin | Life Technologies | 15140 | 1X |
| Chemical compound, drug | Pyruvate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11360 | 10 mM |
| Software, algorithm | Photoshop CS5 | https://www.adobe.com/products/photoshop.html | RRID:SCR_014199 | |
| Other (anti-biotin beads) | anti-biotin beads | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-090-485; RRID:AB_244365 | MACS |
| Other (anti-PE beads) | anti-PE beads | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-048-801; RRID:AB_244373 | MACS |
| Other (chamber slides) | chamber slide | Nalge Nunc International | 177445 | myoblast culture |
| Other (culture plates) | petri dish | Sigma-Aldrich | Z692301 | single myofiber culture |
| Other (LD column) | LD column | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-042-901 | MACS |
| Other (MS column) | MS column | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-042-201 | MACS |
| Other (grip strength meter) | grip strength meter | Columbus Instruments | 1027CSM-D54 |
Sequences of primers used for the ChIP-qPCR.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33337.016| Regulated gene/region | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| Mef2a | ATCTGAGGTCAGCCATTTGGT | GCTAAGGACAGCTGTGACCTG |
| Lmn2b | TTAAAGACATGTGGCAACAGACTAC | TGCTCTTTCTGTACTGTGTGGTG |
| Lincmd1 | GGAGTGATTGAGGTGGACAGA | CTCTCCCACCTGTTTGTGTCTT |
| Myogenin | AATTACAGCCGACGGCCTCC | CCAACGCCACAGAAACCTGA |
| Desmin (proximal) | CAGCTCCTTGCCCTGTGAAA | TGTAGCCCTCCTGACATCAC |
| Desmin (distal) | CCAAAAGGGCCGATGAGGAA | TAGAGACAGACCAGTGGCGG |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33337.017





