BDNF-TrkB signaling in oxytocin neurons contributes to maternal behavior
Figures
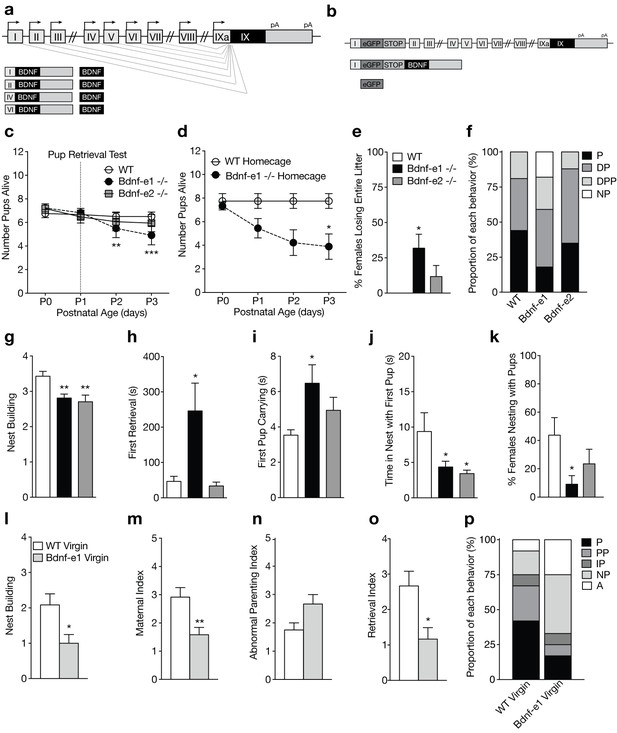
Disruption of BDNF from promoters I and II leads to impaired maternal care.
(a) Schematic of Bdnf transcript production. Transcription is initiated from promoters upstream of individual 5’-untranslated regions (UTRs) and spliced to the common coding exon IX. Each transcript produces an identical BDNF protein. (b) Design of Bdnf -/- mice using Bdnf-e1 -/- as a representative example. Targeting vectors were designed to insert an enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) upstream of the exon’s splice donor site. Bdnf-e1 -/- mice express a Bdnf-I-eGFP-STOP-Bdnf IX transcript leading to the production of GFP in lieu of BDNF. (c) Average litter size over time for WT, Bdnf-e1 -/-, and Bdnf-e2 -/- postpartum mothers exposed to the pup retrieval test one day after giving birth. Bdnf-e1 -/- mothers show significant pup loss compared to WT mothers (2-way ANOVA with mixed effect model; p<0.001). (d) Average litter size over time for WT and Bdnf-e1 -/- postpartum mothers remaining in the homecage. Bdnf-e1 -/- mothers show significant pup loss compared to WT mothers even in a naturalistic setting (2-way ANOVA with mixed effect model; p<0.001). (e) Percentage of postpartum mothers losing their entire litter by postnatal day 3 (P3). Approximately 1/3 of postpartum Bdnf-e1 -/- mothers lose their entire litter by P3 (1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons; p<0.05). (f) Proportion of WT, Bdnf-e1 -/- and Bdnf-e2 -/- with different maternal types including parenting (P), disorganized parenting (DP), partial parenting (PP), disorganized partial parenting (DPP), and non-parenting (NP). There is a significant decrease in the proportion of Bdnf-e1 -/- postpartum mothers with parenting behavior compared to WT (one-tailed Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon rank sum test, p<0.05). Bdnf-e1 -/- postpartum mothers show corresponding elevations in non-parenting behaviors. (g) Bar graph depicting nest building behavior before parturition. Bdnf-e1 and -e2 -/- show impaired nest building compared to WT (Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons, p<0.01). (h–j) Latency to first retrieval (h) time carrying first pup (i) and time nesting with first pup (j) during the pup retrieval test. Bdnf-e1 -/- postpartum mothers show increased latency to retrieval, longer time carrying the first pup to the nest, and reduced nesting time with first pup (1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons, p<0.05). Bdnf-e2 -/- postpartum mothers show similar, albeit milder phenotypes. (k) Percentage of postpartum mothers successfully retrieving all pups and nesting for at least 2 continuous minutes. Significantly fewer Bdnf-e1 -/- postpartum mothers successfully retrieve pups and continuously nest compared to WT (1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons, p<0.05). (l) Bar graph depicting nest building behavior of WT and Bdnf-e1virgins 24 hr prior to pup retrieval test. Bdnf-e1 -/- virgins show impairments in nest building compared to WT virgins (Mann-Whitney test, p<0.05). (m–o) Maternal (m), abnormal parenting (n) and retrieval (o) indices for WT and Bdnf-e1 -/- virgins during foreign pup retrieval test. Bdnf-e1 -/- virgin females show reductions in maternal and retrieval indices and a strong trend for increased abnormal parenting (Mann-Whitney tests, p<0.01, p<0.05, and p=0.0529, respectively). (p) Proportion of WT and Bdnf-e1 -/- virgin females with different maternal types including parenting (P) partial parenting (PP), irregular parenting (IP), non-parenting (NP), and attack (A). There is a significant decrease in the proportion of Bdnf-e1 -/- virgins with parenting behavior compared to WT. Bdnf-e1 -/- virgins show corresponding elevations in attack behavior (one-tailed Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon rank sum test, p<0.05). Data are means ± SEM. (n = 16 WT postpartum mothers; n = 22 Bdnf-e1 -/- postpartum mothers; n = 17 Bdnf-e2 -/- postpartum mothers; n = 12 WT virgins; n = 12 Bdnf-e1 -/- virgins; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and p<0.001, #p<0.0001).
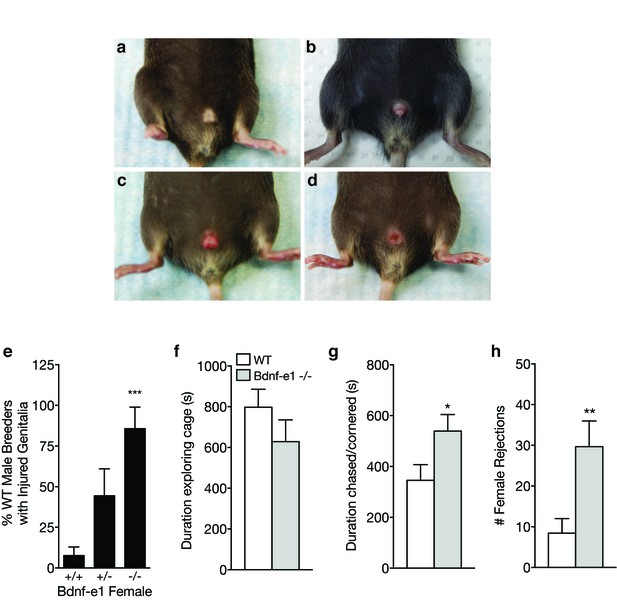
Bdnf-e1 -/- females show abnormal mating behaviors.
(a-d) Representative images depicting male genitalia injuries observed in Bdnf-e1 breeder cages. Breeder males frequently show inflamed, infected, and/or mutilated genitalia (b–d) compared to normal (a) when paired with heterozygous or homozygous Bdnf-e1 females. (e) Bar graph depicting the percentage of WT male breeders with injured genitalia when paired with females that are wild-type, heterozygous, or homozygous for promoter I-derived BDNF production. WT males rarely show injuries when paired with WT females; however, partial or complete loss of promoter I-derived BDNF leads to significant increases in injured males (1-way ANOVA; n = 26 + /+, n = 9 + /-, n = 7 -/-; p<0.001). (f–h) Quantification of mating behaviors between WT (n = 12) or Bdnf-e1 -/- (n = 12) estrous females and CD1 males, including duration exploring (f) duration chased/cornered (g) and number of female rejections (h). WT and Bdnf-e1 -/- females spend equal time exploring; however, Bdnf-e1 -/- females are more frequently cornered or chased by males (Student’s t test, p<0.05). Bdnf-e1 -/- females also show a significant increase in mounting rejections (Student’s t test, p<0.01). Data are means ± SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
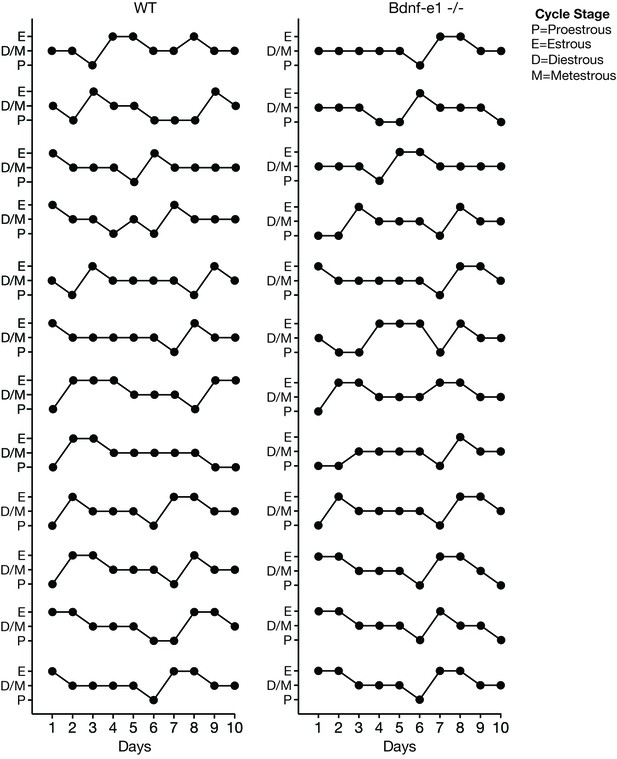
Bdnf-e1 -/- females have a normal estrous cycle.
Bdnf-e1 -/- virgin females enter all stages of the estrous cycle, including proestrous (P), estrous (E), diestrous (D), and metestrous (M), similar to WT females. Bdnf-e1 -/- virgins enter estrous ~every 5 days and remain in estrous for 24 – 48 hr.
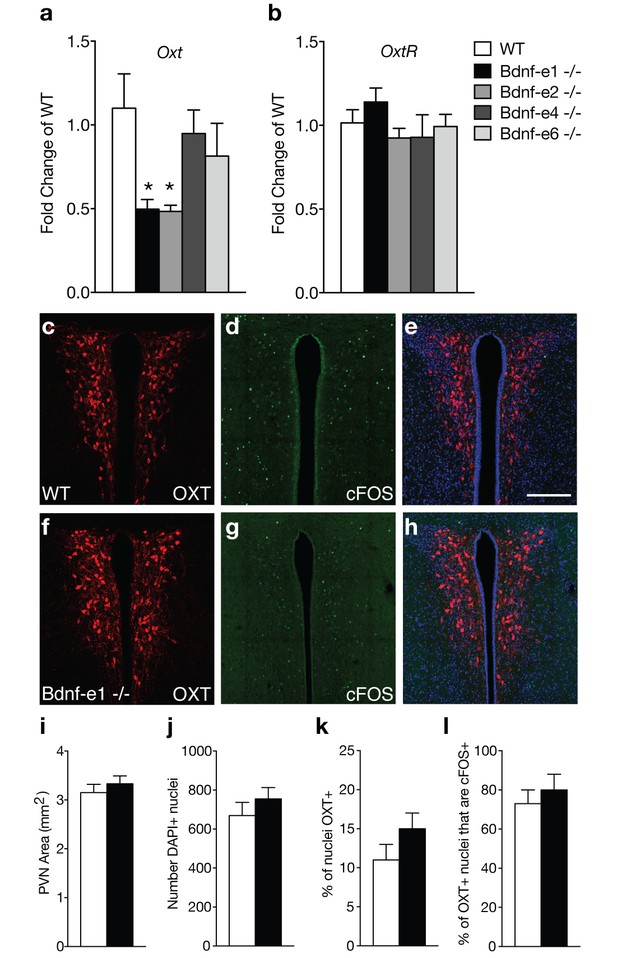
Oxytocin transcripts are reduced in Bdnf-e1 and -e2 -/- with impaired maternal care.
(a–b) qPCR demonstrating relative expression levels of oxytocin (a) and oxytocin receptor (b) transcripts in the HYP of 4 week old Bdnf-e1, -e2, -e4, and -e6 female mice (n = 4–5 per genotype; 1-way ANOVAs with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons, p<0.05). Oxt, but not Oxtr, transcripts are reduced in Bdnf-e1 and -e2 -/- females. (c–h) Confocal z-projections of PVN from WT (c–e) and Bdnf-e1 -/- (f–h) postpartum mothers collected 2 hr following pup retrieval testing. Immunolabeling of OXT (c, f) cFOS (d, g), and merged images (e, h). (i–l) Quantification of PVN area (i), number of PVN cells (j), % of PVN cells expressing OXT (k), and percentage of OXT neurons expressing cFOS following pup retrieval (l) in WT and Bdnf-e1-/- postpartum mothers (n = 6 – 9 images per animal; n = 3 animals per genotype; student’s t-test, Poisson regression, and binomial regression, respectively). There were no significant differences in PVN structure, OXT neuron number, or proportion of OXT neurons activated following pup retrieval. Data are means ± SEM; *p<0.05.
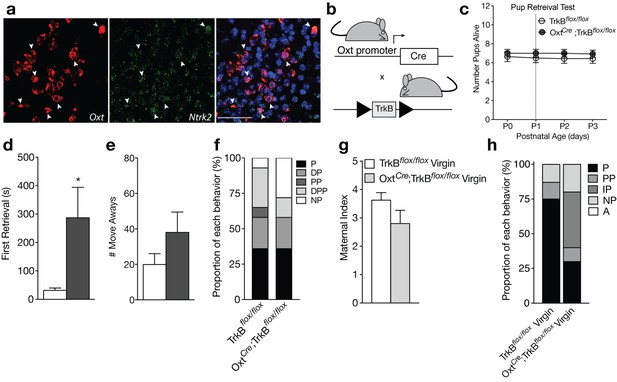
Loss of TrkB in OXT neurons leads to parenting deficits in postpartum mothers and virgin females.
(a) Confocal z-projections of Oxt and Ntrk2 transcripts in brain slices containing the PVN from an adult female visualized with RNAscope in situ hybridization. TrkB transcripts (green) are highly expressed in OXT neurons (red). (b) Breeding strategy used to obtain OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox mice. (c) Average litter size over time for TrkBflox/flox and OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox postpartum mothers exposed to the pup retrieval test one day post parturition. Mothers lacking TrkB in OXT neurons show normal pup survival compared to control (2-way ANOVA with mixed effect model; p>0.05). (d) Latency to first retrieval during pup retrieval test. OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox postpartum mothers show increased latency to retrieve first pup (Student’s t-test; p<0.05). (e) Number of times postpartum mothers move away from pups without retrieving. OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox mothers show a strong trend for increased move-aways. (f) Proportion of OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox and control mothers with different maternal types including parenting (P), disorganized parenting (DP), partial parenting (PP), disorganized partial parenting (DPP), and non-parenting (NP). There is no significant change in the proportion of OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox mothers with parenting behavior compared to control (one-tailed Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon rank sum test, p>0.05). However, a substantial proportion of OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox mothers show non-parenting behaviors. (g) Maternal index for control and OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox virgin females during foreign pup retrieval test. OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox virgin females show a trend for reduced maternal index. (h) Proportion of OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox and control mothers with different maternal types including parenting (P), partial parenting (PP), irregular parenting (IP), non-parenting (NP), and attack (A). There is a significant decrease in the proportion of OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox virgins with parenting behavior compared to control (one-tailed Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon rank sum test, p<0.05). Data are means ± SEM. (n = 14 TrkBflox/flox postpartum mothers; n = 14 OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox postpartum mothers; n = 8 TrkBflox/flox virgins; n = 10 OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox virgins; *p<0.05).
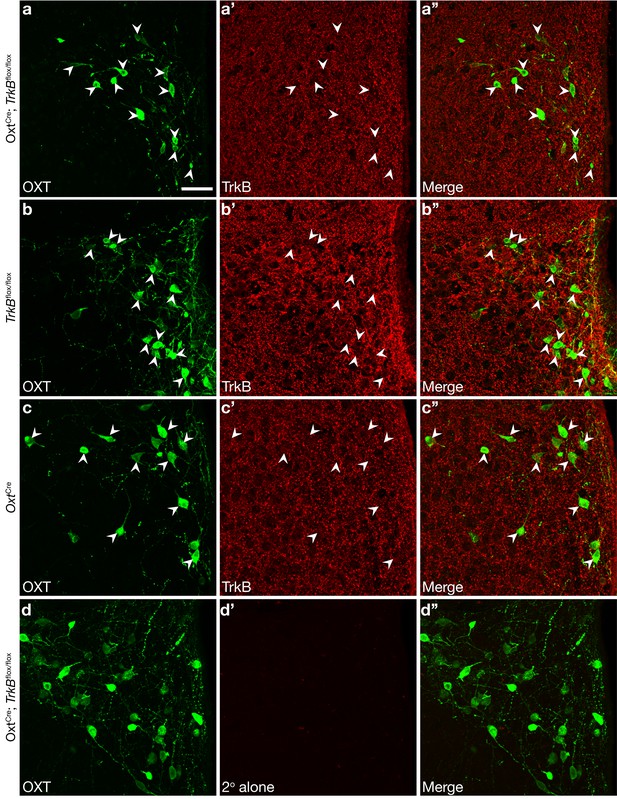
Ablation of TrkB protein in OXT neurons in OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox mice.
(a-d) Confocal z-projections of PVN from OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox (a, d), TrkBflox/flox (b), and OxtCre (c) adult mice. Immunolabeling of OXT (a, b, c, d), TrkB (a’, b’, c’), and merged images (a”, b”, c”, d”). In control section (d’) the secondary antibody for TrkB has been omitted to demonstrate low background and absence of bleed through from the OXT channel. While TrkB shows robust cell surface and synaptic expression, it appears absent in OXT neuron cell bodies in OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox, but not TrkBflox/flox or OxtCre mice. Scale bar is 50 μm.
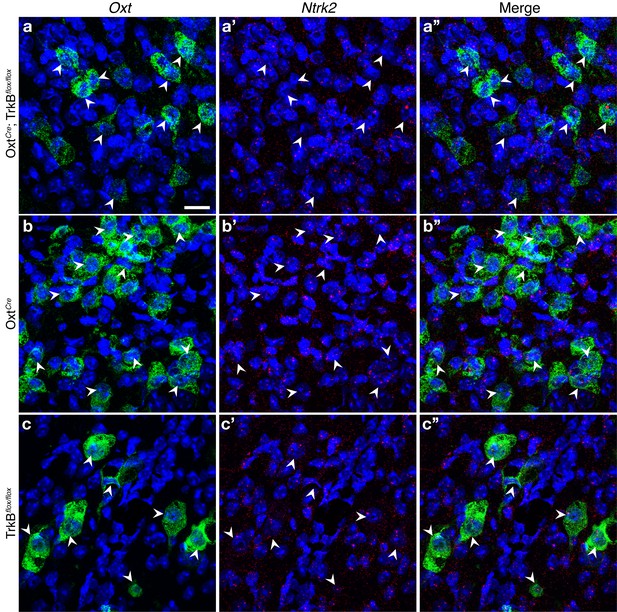
Selective loss of TrkB mRNA in OXT neurons in OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox mice.
(a-c) Confocal z-projections of Oxt (a, b, c) and Ntrk2 (a’, b’, c’) transcripts in brain sections containing the PVN from OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox (a), OxtCre (b), and TrkBflox/flox (c) visualized with RNAscope in situ hybridization. In the merged images (a”, b”, c”) Ntrk2 transcripts (red) localize to the nuclei of Oxt-expressing neurons (green) in OxtCre and TrkBflox/flox mice, but not OxtCre; TrkBflox/flox mice. The Ntrk2 probe was custom-designed to specifically target the floxed region in TrkBflox/flox mice, which includes the 5’UTR and Exon S.
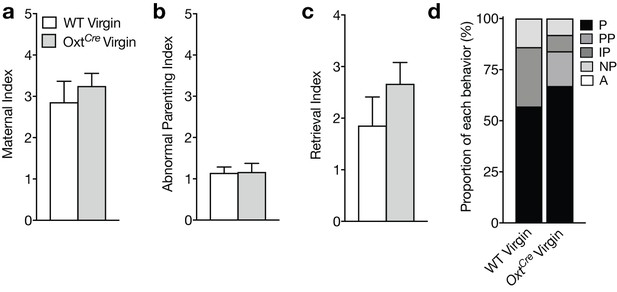
OxtCre mice show normal maternal behavior.
(a-c) Maternal (a), abnormal parenting (b), and retrieval (c) indices for WT and OxtCre virgins during foreign pup retrieval test. OxtCre virgin females show no differences on these indices compared to WT virgins (Mann-Whitney tests, p>0.05). (d) Proportion of WT and Bdnf-e1 -/- virgin females with different maternal types including parenting (P), partial parenting (PP), irregular parenting (IP), non-parenting (NP), and attack (A). OxtCre virgins show normal parenting behavior (Wilcoxon rank sum test, p>0.05). Data are means ±SEM. (n = 7 WT adult virgin females; n = 12 OxtCre adult virgin females).
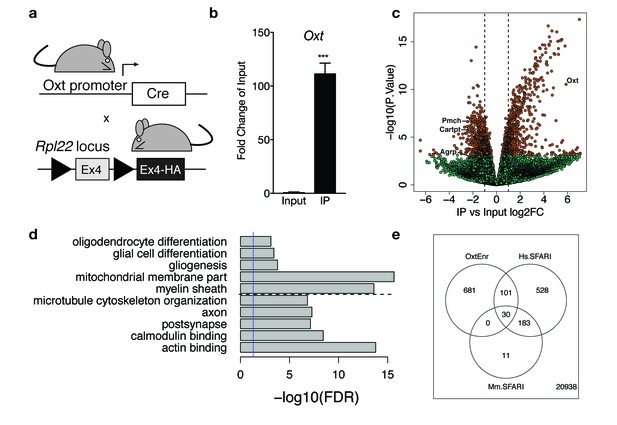
Identification of a unique molecular profile for OXT neurons using ribosomal tagging.
(a) Locus of the ribosomal protein Rpl22 in the Ribotag mouse and breeding strategy used to obtain OxtCre; Rpl22HA mice. (b) qPCR analysis validating significant enrichment of Oxt transcripts in IP compared to Input fractions. (c) Volcano plot of RNA-seq results with IP versus Input log2 fold change against –log10 p-value. Outer lines are 2-fold enriched/depleted genes. Red dots represent genes that are significantly different (<0.05) in IP versus Input. Green dots represent non-significant genes. A subset of differentially enriched marker genes is highlighted (Oxt, Agrp, Cartpt, Pmch). (d) Representative gene ontology (GO) terms in the cellular component, molecular function and biological processes categories for genes enriched and de-enriched in OXT neurons. Solid vertical line indicates p=0.05 and dotted horizontal line separates downregulated (top) and upregulated (bottom) pathways. (e) Venn diagram showing overlap of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in OXT neurons with mouse (Mm) and human (Hs) genes implicated in autism spectrum disorder by the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative (SFARI). Data are means ± SEM. (n = 3 Input, n = 3 IP; 5 OxtCre; Rpl22HA hypothalami pooled per sample).
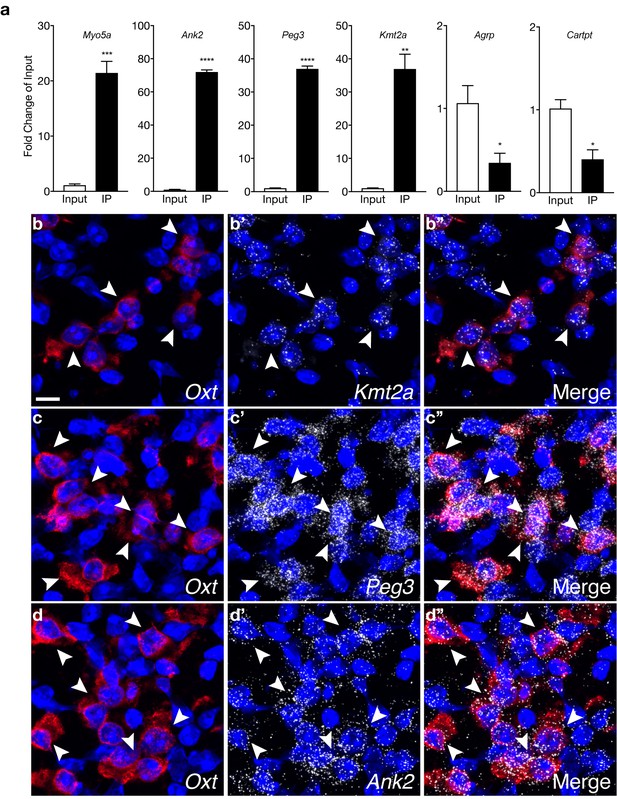
Validation of select genes enriched or de-enriched in OXT neurons.
(a) qPCR analysis validating significant enrichment (Myo5a, Ank2, Peg3, and Kmt2a) and de-enrichment (Agrp, Cartpt) of select transcripts in IP compared to Input fractions. (b–d) Representative confocal z-projections of Oxt (b, c, d), Kmt2a (b’), Peg3 (c’), and Ank2 (d’) transcripts in brain sections containing the PVN from an adult WT virgin female mouse visualized with RNAscope in situ hybridization. In the merged images (b”, c”, d”), Kmt2a, Peg3, and Ank2 transcripts (white) are enriched in Oxt-expressing neurons (red) independently corroborating RNA-seq and qPCR findings.
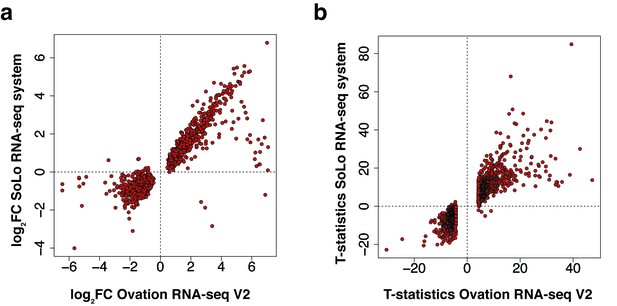
Validation of Ovation RNA-seq V2 system with SoLo RNA-seq system.
(a) Plot depicting log2 fold changes of DEGs in Oxt IP vs. Oxt Input using RNA-seq V2 system compared to the SoLo RNA-seq system. Fold changes are highly correlated between kits. (b) Plot depicting t-statistics for Oxt IP vs. Oxt Input using RNA-seq V2 system compared to SoLo RNA-seq system shows strong consistency between kits.
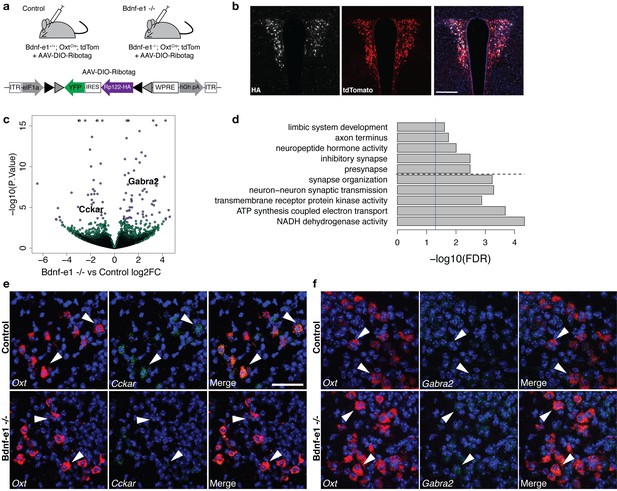
Perturbations in BDNF signaling impact gene pathways critical for plasticity in OXT neurons.
(a) Strategy for TRAP in OXT neurons from control and Bdnf-e1 -/- mice (n = 3 per genotype) using AAV-DIO-RiboTag and RNA-seq. (b) Confocal image showing HA (white) and tdTom (red) expression in hypothalamic sections containing the PVN of Bdnf-e1; OxtCre; tdTom mice injected bilaterally with AAV-DIO-Ribotag. Scale bar is 200 μm. (c) Volcano plot of RNA-seq results with Bdnf-e1 -/- IP vs. control IP log2 fold change against -log10 p-value. Blue dots represent genes that are significantly different in Bdnf-e1 -/- IP vs. control IP, including Cckar and Gabra2. Green dots represent non-significant genes. (d) Representative gene ontology (GO) terms in the molecular function, biological processes, and cellular component categories for genes enriched and de-enriched in OXT neurons following disruption of BDNF signaling. Solid vertical line indicates p=0.05 and dotted horizontal line separates downregulated (top) and upregulated (bottom) pathways. (e) Confocal z-projections of Oxt and Cckar transcripts in brain slices containing the PVN from adult control and Bdnf-e1 -/- females visualized with RNAscope in situ hybridization. Cckar transcripts (green) are enriched in Oxt-expressing neurons (red) in control, but not Bdnf-e1 -/- females. (f) Confocal z-projections of Oxt and Gabra2 transcripts in adult PVN of control and Bdnf-e1 -/- females visualized with RNAscope in situ hybridization. Gabra2 transcripts (green) co-localize with Oxt transcripts (red) in control females and appear elevated in Bdnf-e1 -/- females. Scale bar is 50 μm.
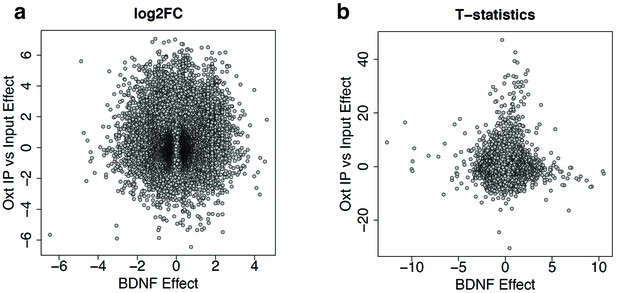
DEGs in Oxt Input vs. Oxt IP do not overlap with DEGs in control IP vs. Bdnf-e1 -/-IP.
(a) Plot depicting log2 fold changes of DEGs in Oxt IP vs. Oxt Input compared to the log2 fold changes of DEGs in control IP vs. Bdnf-e1 -/- IP. As expected, there is no correlation between the two sets of DEGs. (b) Plot depicting t-statistics for Oxt IP vs. Oxt Input compared to t-statistics for control IP vs. Bdnf-e1 -/- IP.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Bdnf-e1; Bdnf-e2 mice | PMID: 26585288 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Oxt-Cre mice | Jackson Labs | RRID:IMSR_JAX:024234 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | tdTomato mice | Jackson Labs | RRID:IMSR_JAX:007914 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Ntrk2 flox/ flox mice | PMID: 18511296 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Cort-Cre mice | Jackson Labs | RRID:IMSR_JAX:010910 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | RPL22-HA mice | Jackson Labs | RRID:IMSR_JAX:011029 | |
| Genetic reagent (Adeno-assoicated virus) | AAV1-DIO-RPL22HA-GFP | PMID: 25855171 | ||
| Antibody | anti-mouse HA | Covance | RRID:AB_291262 | |
| Antibody | goat anti-mouse Alexa 647 | Thermo-Fisher Scientific | RRID:AB_141693 | |
| Antibody | anti-mouse OXT | PMID: 3880813 | ||
| Antibody | anti-rabbit cFOS | Millipore | RRID:AB_2631318 | |
| Antibody | donkey anti-rabbit Alexa 488 | Thermo-Fisher Scientific | RRID:AB_141708 | |
| Antibody | anti-rabbit TrkB H-181 | Santa Cruz | RRID:AB_2155274 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Ovation RNA-Seq V2 kit | Nugen | Cat#: 7102 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Ovation SoLo RNA-seq System Mouse | Nugen | Cat#: 0502–32 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | KAPA Library Quantification Kit | KAPA Biosystems | Cat#: KR0405 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Miseq Reagent Kit v3 | Illumina | Cat#: MS-102–3001 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Ribogreen RNA assay kit | Invitrogen | Cat#: R11490 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Fluorescent Multiplex V1 | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 320850 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | A/G magnetic beads | Pierce | Cat#: 88803 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 10% NBF | Sigma | Cat#: HT501128 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fluoromount G | Southern Biotechnology | Cat#: 0100–01 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Oxt | Life Technologies | Cat#: Mm01329577_g1 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Oxtr | Life Technologies | Cat#: Mm01182684_m1 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Gapdh | Life Technologies | Cat#: 4352932E | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Myo5a | Life Technologies | Cat#: Mm00487823_m1 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Ank2 | Life Technologies | Cat#: Mm00618325_m1 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Peg3 | Life Technologies | Cat#: Mm01337379_m1 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Kmt2a | Life Technologies | Cat#: Mm01179235_m1 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Agrp | Life Technologies | Cat#: Mm00475829_g1 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | Taqman probe Cartpt | Life Technologies | Cat#: Mm04210469_m1 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | RNAscope probe Oxt | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 493171 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | RNAscope probeNtrk2 | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 423611 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | RNAscope probeGabra2 | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 435011 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | RNAscope probeCckar | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 313751 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | RNAscope probeNtrk2 (Exon S) | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 539481 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | RNAscope probe Kmt2a | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 408951 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | RNAscope probePeg3 | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 492581 | |
| Sequence- based reagent | RNAscope probe Ank2 | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | Cat#: 413221 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table Legends (Excel tables attached as separate tabs in a single file).
Table S1. Differential gene expression analysis of OXT Input vs. IP samples for all expressed genes. Table S2. Comparison of significant OXT neuron gene enrichment using Nugen Ovation RNA-seq System V2 kit vs. Nugen Ovation SoLo RNA-seq system. Table also includes comparison of differential gene expression between OXT neurons, Cort inhibitory interneurons, and Ntsr1 layer VI corticothalamic neurons versus their respective input RNA samples, as well as an overall OXT-IP versus pooled Cort-IP and Ntsr1-IP samples to assess specificity for these genes that were enriched in OXT neurons. Table S3. Gene Ontology analysis in OXT neurons. Enriched and depleted GO terms from differential expression analysis of OXT Input vs. IP. Table S4. Differential gene expression analysis of OXT-IP vs. Cort-IP and Ntsr1-IP samples for all expressed genes. Table S5. Gene ontology enrichment analysis for genes differentially expressed in OXT-IP vs. Cort-IP and Ntsr1-IP samples Table S6. OXT enriched mouse model genes in SFARI. List of genes enriched in OXT neurons implicated in genetic animal models of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative (SFARI). Table S7. OXT enriched human genes in SFARI. List of genes enriched in OXT neurons implicated in ASD by the SFARI Human Gene Module using the subset of mouse-expressed genes with human homologs. Table S8. Differential gene expression analysis of control IP vs. Bdnf-e1 -/- IP samples. Table S9. Gene Ontology analysis in OXT neurons with disruption of BDNF signaling. GO terms enriched from differential expression analysis of control IP vs. Bdnf-e1 -/- IP samples. Table S10. BDNF-dependent OXT genes in SFARI. List of genes perturbed in OXT neurons following disruption of BDNF signaling that are implicated in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative (SFARI).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33676.015
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33676.016





