Oxytocin functions as a spatiotemporal filter for excitatory synaptic inputs to VTA dopamine neurons
Figures
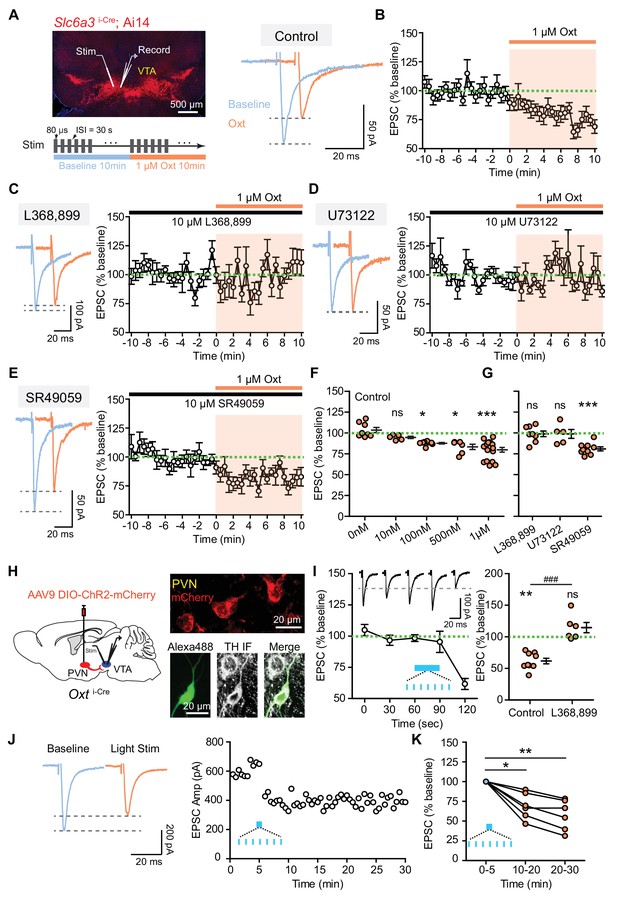
Oxytocin inhibits excitatory synaptic transmission in VTA DA neurons via the OxtR.
(A) Left, top: an image of a horizontal brain section from a Slc6a3i-Cre; A14 mouse. A stimulation electrode (Stim) was placed ~100 μm away from the recording electrode (Record). Left, bottom: experimental protocol schematic. Right: example traces of evoked EPSCs from one VTA DA neuron during baseline and following 1 μM oxytocin application. Blue, baseline; orange, following oxytocin application. (B) The amplitude of evoked EPSC decreased during the application of 1 μM oxytocin. n = 15 neurons from 10 mice. Green dashed line, baseline EPSC amplitude average; shaded region, time of oxytocin application. (C) OxtR antagonist L368,899 blocked oxytocin-induced EPSC amplitude attenuation. Left: example traces from one neuron before and during oxytocin application. Right: summary data for n = 8 neurons from six mice. (D) Same as (B), but with a phospholipase C blocker U73122. n = 5 neurons from four mice. (E) Same as (B), but with a vasopressin receptor (V1aR) antagonist SR49059. n = 9 neurons from six mice. (F) Summary data for EPSC amplitude changes induced by oxytocin at different concentrations (0 nM, 10 nM, 100 nM, 500 nM, and 1 μM). For each concentration respectively, n = 8 neurons from five mice, 5 neurons from two mice, 8 neurons from four mice, 6 neurons from five mice, and 15 neurons from 10 mice. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s Multiple Comparison post hoc test. (G) Summary data for oxytocin-induced EPSC amplitude changes in the presence of OxtR antagonist (L368,899), PLC blocker (U73122), and V1aR antagonist (SR49059). Wilcoxon signed rank test vs. baseline, ***p<0.001. (H) Left: Schematic of viral transduction strategy using AAV9-DIO-ChR2-mCherry to express ChR2 in PVN oxytocinergic neurons. Right, top: ChR2-mCherry (red) expression in PVN. Right, bottom: One example neuron identified as dopaminergic during whole-cell recording with Alexa Fluor 488 dye included in the internal solution (green). Post hoc immunofluorescent labeling against tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, grayscale) confirms its identity. (I) Left: Optical activation of oxytocin fibers in the VTA decreased evoked EPSC amplitude in DA neurons. Patterned light stimulation period is marked in blue. n = 9 neurons from six mice. Inset shows evoked EPSC traces from one VTA DA neuron before and after light stimulation, temporally matched to average data. Black dashed line shows EPSC amplitude of the example neuron at t = 120 s, 30 s after the end of optogenetic stimulation train. Right: Summary data for light stimulation-induced EPSC amplitude changes with and without OxtR antagonist (L368,899). n = 6 neurons from four mice in the presence of OxtR antagonist. **p<0.01, Wilcoxon signed rank test vs. baseline. ###p<0.001, Mann-Whitney test. Error bars reflect SEM. (J) Left: example traces of evoked EPSCs from one VTA DA neuron during baseline (blue) and after 30 s long light stimulation of PVN oxytocin fibers. Right: EPSC amplitudes recorded from one neuron (same as Left) during baseline and after light stimulation. (K) Summary data for light stimulation-induced EPSC amplitude changes 10–20 min and 20–30 min after light stimulation. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s Multiple Comparison post hoc test, n = 6 neurons from four mice.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Summary tables of evoked EPSC amplitudes from individual VTA DA neurons in response to oxytocin-signaling related pharmacological agents and optogenetic stimulation of oxytocin fibers.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33892.006
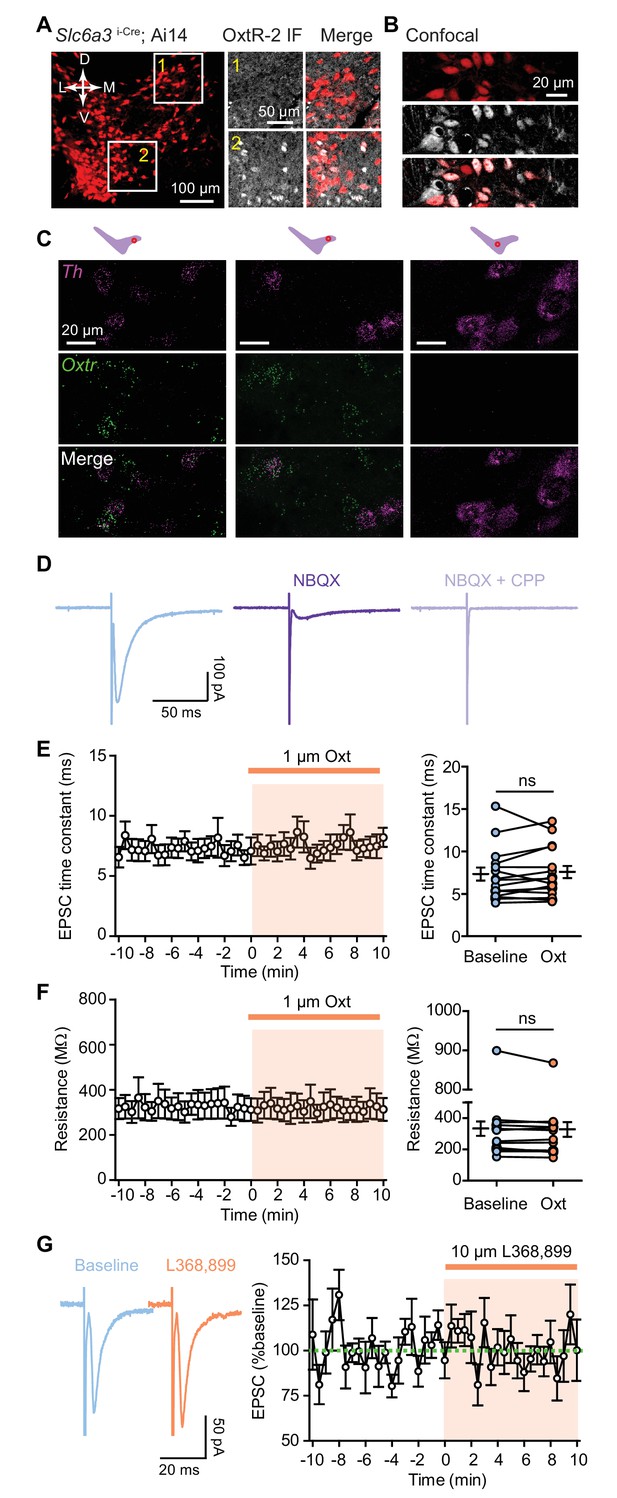
Characterization of targeted VTA subregions and physiological properties of recorded VTA DA neurons.
(A) Immunostaining with OxtR-2 antibody illustrates OxtR expression patterns in the VTA of Slc6a3i-Cre; Ai14 mice. Left: an image of a coronal brain section of VTA from a Slc6a3i-Cre; A14 mouse. Right: OxtR expression in different subregions of VTA, as indicated. (B) Confocal image highlights partial overlap between tdTomato-positive and OxtR-positive neurons in ventromedial VTA. (C) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) images in different subregions (indicated on top) of the VTA. Th (magenta) and Oxtr (green). (D) Example evoked EPSC traces from one VTA DA neuron in the baseline condition and following sequential application of AMPAR antagonist NBQX (10 µM) and NMDAR antagonist CPP (10 µM). Evoked EPSCs recorded at −70 mV are primarily driven by AMPA receptors, with a minor contribution of NMDARs. (E–F) Summary data showing that EPSC decay time constant and membrane resistance in VTA DA neurons are not altered by oxytocin application. p=0.303 or 0.266 respectively, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 15 neurons from 10 mice. (G) Left: example traces from one neuron before and during OxtR antagonist L368,899 application. Right: summary data for n = 6 neurons from three mice. Error bars reflect SEM.
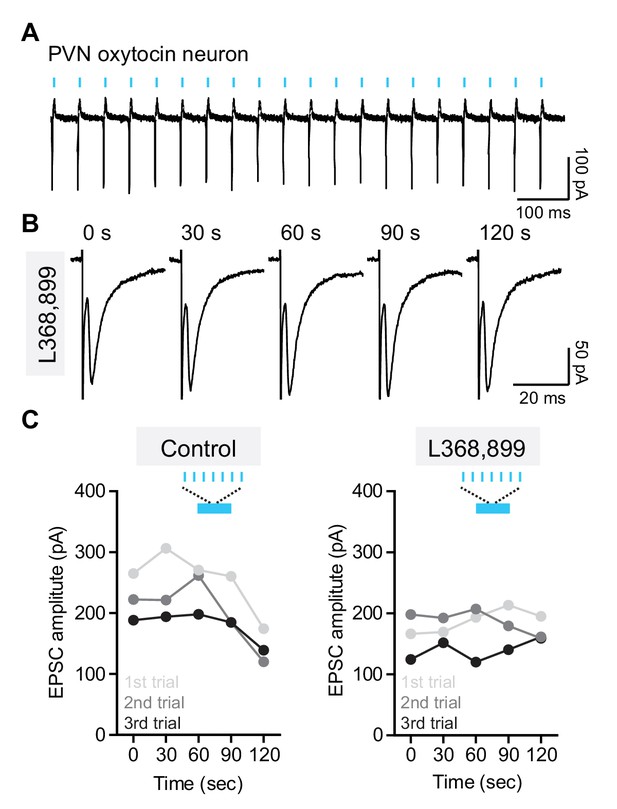
Optical stimulation of oxytocinergic fibers in the VTA modulates evoked EPSCs in DA neurons.
(A) Example cell-attached recording trace from one ChR2-positive PVN oxytocinergic neuron in response to 10 ms-long light pulses at 20 Hz delivered in 30 second-long bursts. Blue bars indicate the time of light stimulation. (B) Example evoked EPSC traces from one VTA DA neuron before and after light stimulation in the presence of OxtR antagonist (L368,899). Light stimulation was given between 60 s and 90 s. (C) Left: Example of light stimulation-induced EPSC amplitude changes in three sequential trials from one VTA DA neuron. Inter-trial interval was 6 min. Right: Same as left, but in the presence of OxtR antagonist (L368,899).
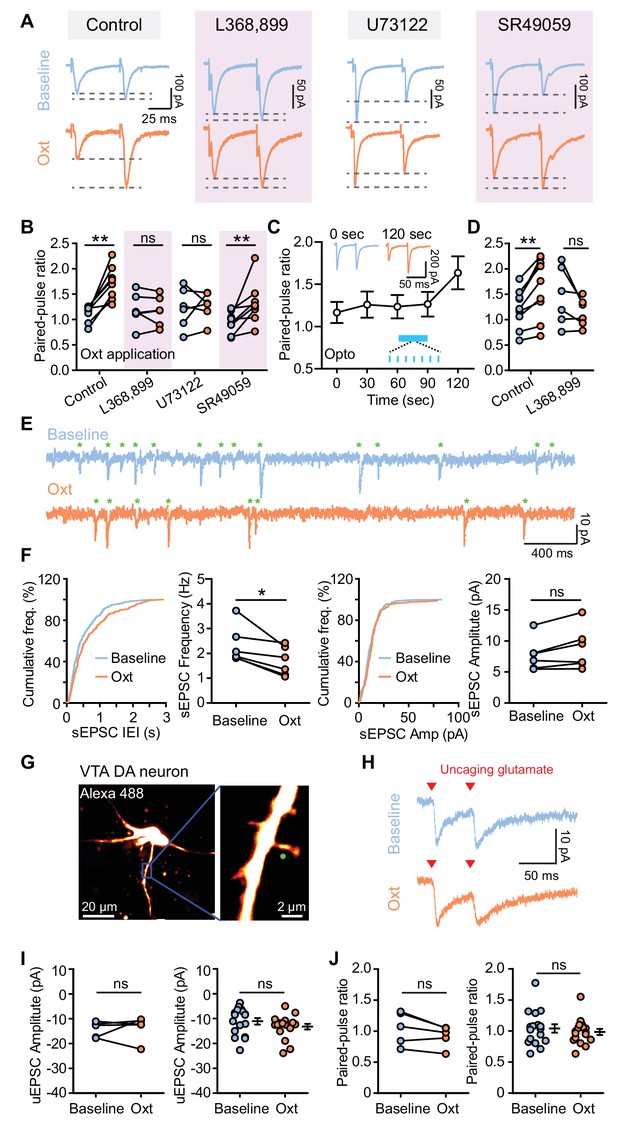
Oxytocin dampens excitatory synaptic transmission by presynaptic mechanisms.
(A) Traces from VTA DA neurons showing pairs of EPSCs (50 ms ISI) during baseline (top) and following oxytocin application (bottom). From left to right, example traces reflect: the control condition with no additional compounds, the OxtR antagonist L368,899, the PLC blocker U73122, and the V1aR antagonist SR49059. Traces for each neuron are normalized to the amplitude of the first evoked response in the baseline condition. (B) Summary results show paired-pulse ratio during baseline and following oxytocin application in control condition, in the presence of OxtR antagonist L368,899, PLC blocker U73122, and V1aR antagonist SR49059 separately. **p<0.01, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. For each condition respectively, n = 8 neurons from six mice, 6 neurons from five mice, 6 neurons from four mice, and 8 neurons from five mice. (C) Summary results show PPR change of the evoked EPSC of VTA DA neurons in response to light stimulation (marked in blue). n = 9 neurons from six mice. Insets show example pairs of EPSCs (50 ms ISI) from one VTA DA neuron at 0 s (before light stimulation) and 120 s (after light stimulation). (D) Summary data for light stimulation-induced EPSC PPR changes with and without OxtR antagonist (L368,899). **p<0.01, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 9 neurons from six mice for control condition, n = 6 neurons from four mice in the presence of OxtR antagonist. (E) Example traces show spontaneous EPSCs (sEPSCs, marked with green stars) during baseline (top) and following oxytocin application (bottom). (F) Left: distributions of sEPSC inter-event intervals (IEI) during baseline and following oxytocin application, with summary data for sEPSC frequency. Right: distributions of sEPSC amplitudes and summary data for sEPSC amplitude during baseline and oxytocin application. *p<0.05, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 6 neurons from five mice. (G) Left: projection of a z-stack from a VTA DA neuron filled with Alexa Fluor 488 acquired on a two-photon laser-scanning microscope. Right: higher magnification image of the dendrite. Green circle marks the uncaging spot. (H) Example traces of paired uncaging-evoked EPSCs (uEPSCs) at 50 ms ISI, from one dendritic spine during baseline condition (top) and oxytocin application (bottom). Red triangles mark uncaging time-points. (I) Left: summary data for uEPSC amplitudes in a group of dendritic spines from VTA DA neurons during baseline and following oxytocin application. p=0.813, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 5 dendritic spines from 4 neurons in three mice. Right: summary data for all uEPSC amplitudes across conditions. p=0.191, Mann-Whitney test, n = 17 dendritic spines for each condition from 16 neurons in four mice. (J) Same as (I), but for paired-pulse ratio. Error bars reflect SEM.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Summary tables of paired pulse ratios of evoked EPSCs, inter-event intervals of spontaneous EPSCs, and amplitudes of uncaging-evoked EPSCs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33892.010
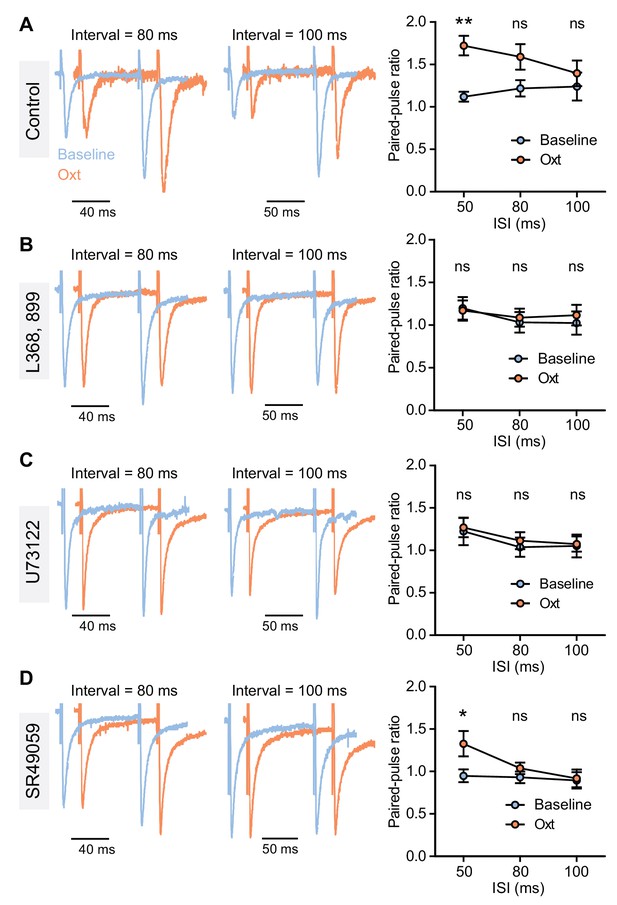
Oxytocinergic modulation of paired-pulse ratio in VTA DA neurons.
(A) Left: traces from a VTA DA neuron showing pairs of EPSCs (80 and 100 ms ISI) in baseline condition and following oxytocin application. Traces are normalized to the amplitude of the first evoked response. Right: summary results show paired-pulse ratio during baseline and following oxytocin application across all 3 ISI intervals sampled. **p<0.01, *p<0.05, Friedman’s 2-Way ANOVA by ranks test, n = 8 neurons from six mice. (B) Same as (A), but in the presence of OxtR antagonist L368,899. n = 6 neurons from five mice. (C) Same as (A), but in the presence of PLC blocker U73122. n = 6 neurons from four mice. (D) Same as (A), but in the presence of V1aR antagonist SR49059. n = 8 neurons from five mice. *p<0.05, Friedman’s 2-Way ANOVA by ranks test. Error bars reflect SEM.
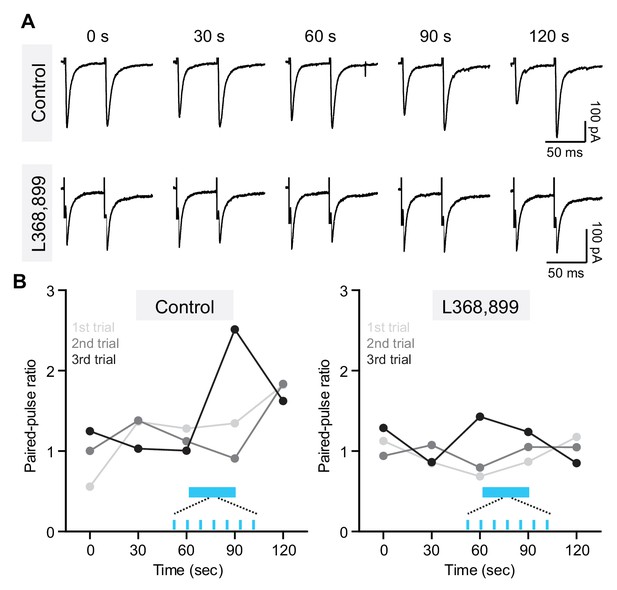
Optical stimulation of oxytocinergic fibers in VTA modulates paired-pulse ratio of evoked EPSCs in DA neurons.
(A) Top: traces from a VTA DA neuron showing pairs of EPSCs (50 ms ISI) before and after light stimulation. Light stimulation was delivered at t = 60–90 s. (B) Left: Example of light stimulation-induced EPSC PPR changes across three sequential trials from one VTA DA neuron. Inter-trial interval was 6 min. Right: Same as left, but in the presence of OxtR antagonist (L368,899).
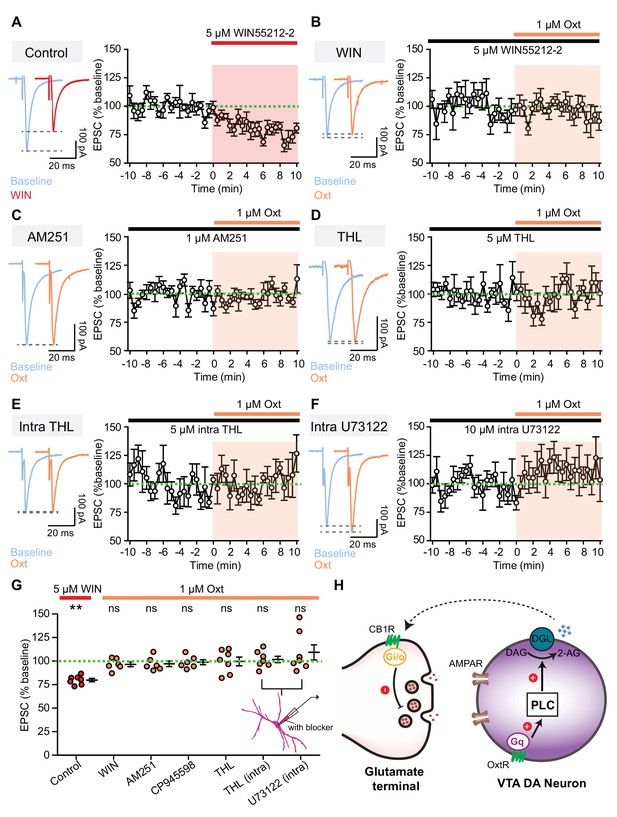
Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling underlies oxytocinergic modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission.
(A) Left: example traces of evoked EPSCs from one VTA DA neuron during baseline and following 5 μM CB1R agonist WIN55212-2 application. Right: summary data for EPSC amplitude over time, normalized to baseline. (B) Left: example traces of evoked EPSCs from one VTA DA neuron during baseline and following 1 μM oxytocin application in the presence of CB1R agonist WIN55212-2. Right: summary data for EPSC amplitude over time, normalized to baseline. (C) Same as (B), but in the presence of CB1R inverse agonist AM251. (D) Same as (B), but in the presence of orlistat (THL), a blocker of 2-AG synthesizing enzyme diacylglycerol lipase α (DGLα). (E) Same as (B), but with THL in the internal solution to block 2-AG synthesis. (F) Same as (B), but with U73122 in the internal solution to inhibit PLC activity. (G) Summary data for EPSC amplitude changes induced by CB1R agonist WIN55212-2 and oxytocin in the presence of WIN55212-2, CB1R inverse agonist AM251, CB1R antagonist CP945598, orlistat (THL), intracellular THL, and intracellular U73122, separately. **p<0.01, Wilcoxon signed rank test vs. baseline. For each condition respectively, n = 7 neurons from five mice, six neurons from four mice, six neurons from three mice, six neurons from four mice, six neurons from four mice, seven neurons from four mice, and seven neurons from four mice. Error bars reflect SEM. (H) Schematic summary of the mechanism underlying direct oxytocinergic regulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in VTA DA neurons. Oxytocin binds to Gq-coupled OxtR, activating the phospholipase C (PLC) pathway. PLC cleaves phosphatidylinositol 1,4,5-bisphosphate into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, and DAG is subsequently converted into 2-AG by DAG lipase (DGL). 2-AG released by VTA DA neurons binds to presynaptic Gi/o-coupled CB1R, decreasing glutamate release.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Summary tables of evoked EPSC amplitudes in response to endocannabinoid-signaling related pharmacological agents.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33892.013
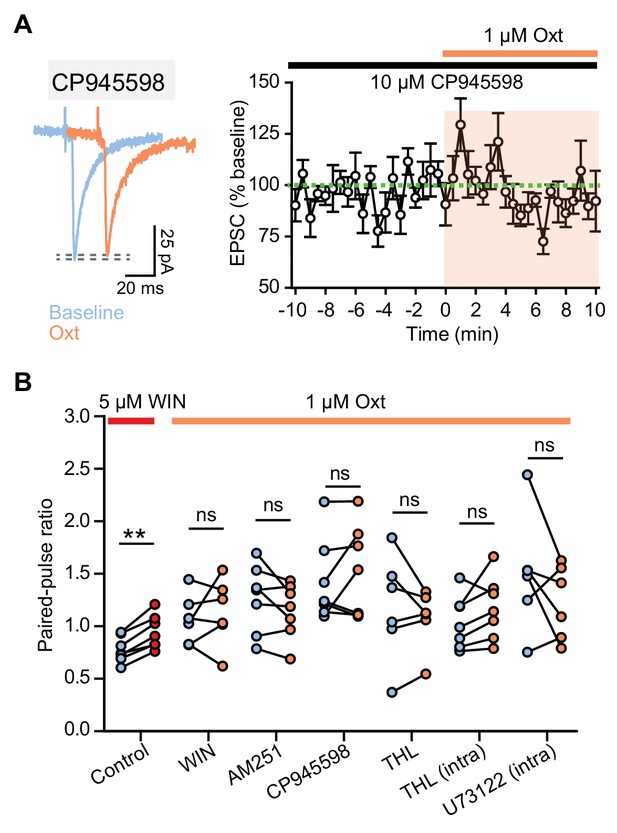
Endocannabinoid signaling underlies oxytocinergic regulation of the amplitude and PPR of evoked EPSCs in VTA DA neurons.
(A) Left: example traces of evoked EPSCs from one VTA DA neuron during baseline and following 1 μM oxytocin application in the presence of CB1R antagonist CP945598. Right: summary data for EPSC amplitude over time, normalized to baseline. n = 6 neurons from four mice. (B) Summary results show paired-pulse ratio during baseline and following CB1R agonist WIN55212-2 application and oxytocin application in the presence of WIN55212-2, CB1R inverse agonist AM251, CB1R antagonist CP945598, and orlistat (THL), separately. **p<0.01, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. For each condition respectively, n = 7 neurons from five mice, six neurons from four mice, six neurons from three mice, six neurons from four mice, six neurons from four mice, seven neurons from four mice, and six neurons from four mice. Error bars reflect SEM.
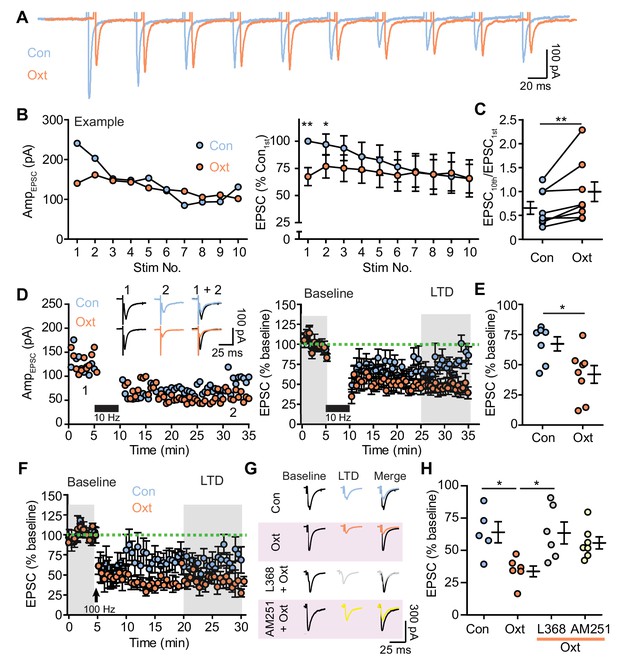
Oxytocin contributes to short and long-term synaptic plasticity of excitatory synaptic transmission.
(A) Example voltage-clamp traces from one VTA DA neuron evoked by repetitive electrical stimulation (20 Hz, 10 pulses) in control condition (blue) and during oxytocin application (orange). (B) Left: evoked EPSC amplitudes from the example neuron shown in (A) before and during oxytocin application. Right: summary results of normalized EPSC in control condition and following oxytocin application. EPSC amplitudes were normalized to the amplitude of the first EPSC in the control group. **p<0.001, *p<0.05, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 8 neurons from five mice. (C) Oxytocin increases the ratio between the 10th EPSC and the first EPSC within a train of stimuli. **p<0.01, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 8 neurons from five mice. (D) Oxytocin application adds to long-term depression (LTD) of EPSCs induced by 5 min, 10 Hz repetitive electrical stimulation (black bars). Left: EPSC amplitudes recorded from two representative neurons in the control condition and in the presence of oxytocin. Inset shows example traces from two neurons before and after LTD induction. Right: summary results show the normalized evoked EPSC amplitude across time in the control condition and in the presence of oxytocin. EPSC amplitudes were normalized based on a 5 min baseline recording (first shaded interval). n = 7 neurons from five mice for controls; eight neurons from six mice in the presence of oxytocin. (E) Summary data showing normalized EPSC amplitude after LTD induction (second shaded interval indicated in (D)). *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test, n = 7 and 8 neurons for control condition and in the presence of oxytocin. (F) Same as (D), but with LTD induction using 1 s long periods of 100 Hz stimulation, repeated four times with 10 second-long inter-train intervals (indicated by arrows). n = 5 neurons from five mice for controls, and six neurons from six mice for oxytocin condition. (G) Example traces before and after LTD induction in control condition, in the presence of oxytocin, in the presence of L368,899 and oxytocin, and in the presence of AM251 and oxytocin. (H) Summary data showing normalized EPSC amplitude after LTD induction (second shaded interval indicated in (F)) in the control condition, in the presence of oxytocin, in the presence of oxytocin and OxtR antagonist L368, 899, and in the presence of oxytocin and CB1 receptor inverse agonist AM251. *p<0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s Multiple Comparison post hoc test, n = 5 neurons for control, n = 6 neurons for oxytocin condition and oxytocin and L368, 899 condition, n = 7 neurons for oxytocin and AM251 condition.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Summary tables of amplitudes of repetitively evoked EPSCs in response to oxytocin and endocannabinoid-signaling related pharmacological agents.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33892.017
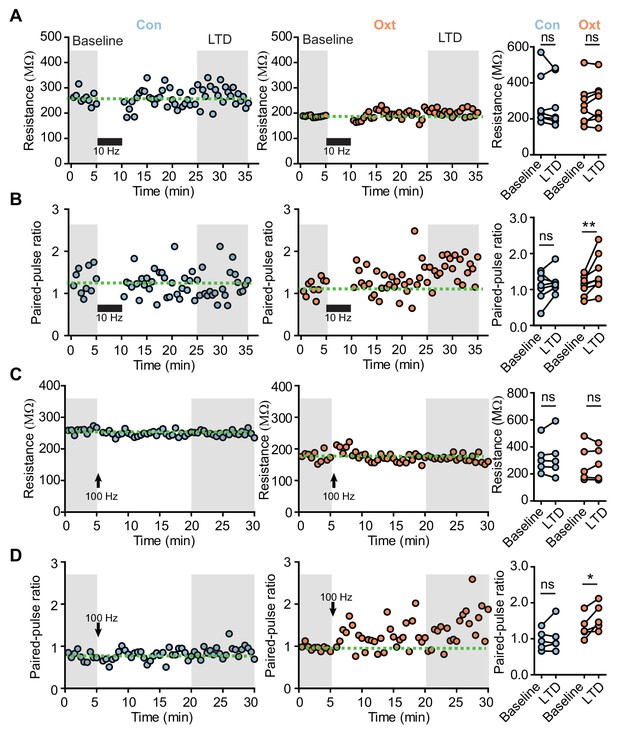
Oxytocin regulates presynaptic neurotransmitter release during LTD.
(A) Left: input resistance measurements from one VTA DA neuron in the control condition during LTD induction. Black bar marks the 5 min period of 10 Hz electrical pulses that were used to induce LTD. Middle: same measurements in another cell in the presence of oxytocin. Right: summary of input resistance in the control condition and in the presence of oxytocin. Shaded regions indicate time windows used to calculate average input resistance for baseline and LTD. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 7 neurons from five mice for control, eight neurons from six mice in the presence of oxytocin. (B) Same as (A), but for PPR. **p<0.01, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 7 neurons from five mice for control condition, eight neurons from six mice in the presence of oxytocin. (C) Left: input resistance measurements from one VTA DA neuron in the control condition during LTD induction. Black arrow indicates 1 s of 100 Hz stimulation, repeated four times at 10 s intervals. Middle: same measurements in another cell in the presence of oxytocin. Right: summary data for input resistance in the control condition and in the presence of oxytocin. Shaded regions indicate time windows used to calculate average input resistance for baseline and LTD. Paired t-test, n = 5 neurons from five mice for control and oxytocin groups. (D) Same as (C), but for PPR. *p<0.05, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 5 neurons from five mice for control and oxytocin groups.
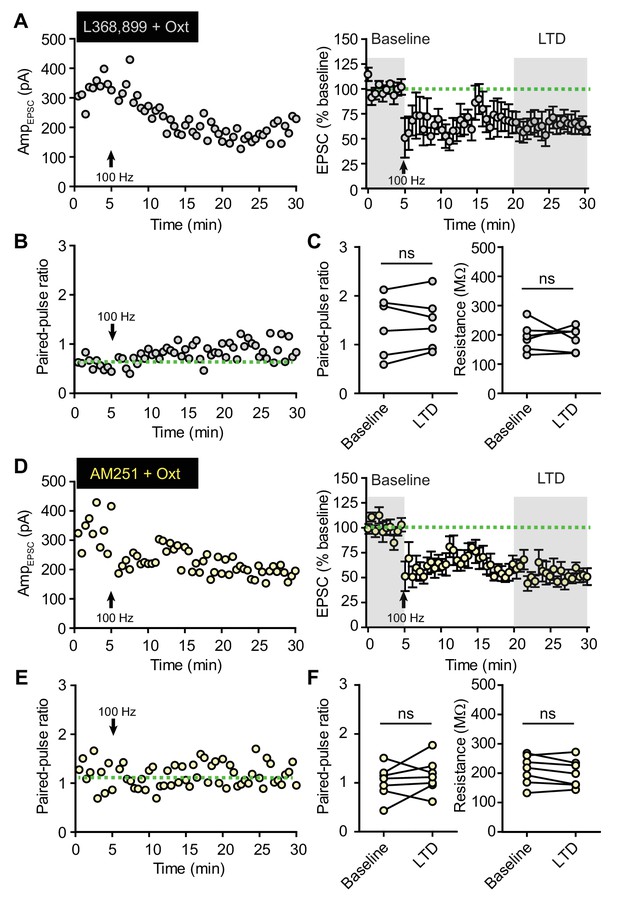
Oxytocin modulates EPSC amplitude during LTD through oxytocin and endocannabinoid receptors.
(A) EPSC amplitudes recorded from one VTA DA neuron in the presence of oxytocin and OxtR antagonist (L368, 899), with LTD induction using 1 s long periods of 100 Hz stimulation, repeated 4 times with 10 second-long inter-train intervals (indicated by arrows). Right: summary results show normalized evoked EPSC amplitude across time in the presence of oxytocin and OxtR antagonist. EPSC amplitudes were normalized based on a 5 min baseline recording (first shaded interval). n = 6 neurons from four mice. (B) PPR (50 ms ISI) measurements from one VTA DA neuron in the presence of oxytocin and OxtR antagonist during LTD induction. (C) Summary data for PPR and input resistance in the presence of oxytocin and OxtR antagonist during LTD induction. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, n = 6 neurons from four mice. (D–F) Same as (A–C), but with oxytocin and CB1 receptor inverse agonist (AM251). n = 7 neurons from four mice.
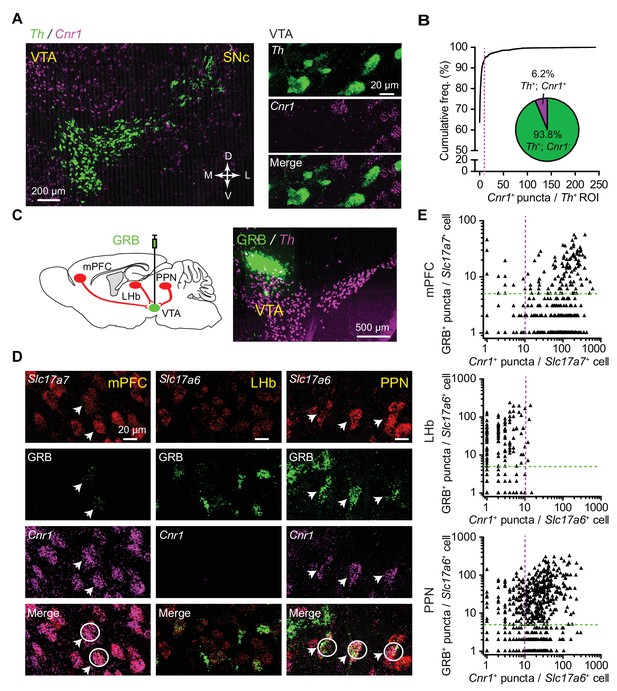
CB1 receptor transcripts selectively express in a subset of VTA DA neuron-targeting glutamatergic afferents.
(A) Left: fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) images of Th and CB1R (Cnr1) in midbrain VTA region. Green, Th; magenta, Cnr1. Right: confocal image of Th and Cnr1 in the VTA, showing separate channels and overlay. (B) Quantitative analysis of Th and Cnr1 co-expression by FISH in the VTA. Magenta line marks the cutoff used to classify a Th+ cell as Cnr1+ (>10 Cnr1+ puncta). Insert shows the proportion of Th+ neurons classified as Cnr1+ and Cnr1-. n = 1258 Th+ VTA cells from three mice. (C) Left: schematic showing combined retrograde labeling and FISH analysis. Right: example image of a green retrobead injection (GRB) in the VTA with follow up FISH for Th. (D) Left: confocal image of Slc17a7, GRB and Cnr1 in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), showing separate channels and overlay. Arrows and white circles mark glutamatergic neurons co-localizing GRB signal and Cnr1. Middle: confocal image of Slc17a6, GRB and Cnr1 in the lateral habenular nucleus (LHb). Right: same as middle, but in the pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN). (E) Top: Quantitative analysis of Slc17a7, Cnr1, and GRB co-expression by FISH in the mPFC. Magenta and green lines mark the cutoffs used to classify a cell as Cnr1+ or GRB+. 143 GRB+/Slc17a7+/Cnr1+ neurons of 188 GRB+/Slc17a7+ neurons from three mice. Middle: Same as (Top), but in LHb and labeled glutamatergic neurons with Slc17a6. 4 GRB+/Slc17a6+/Cnr1+ neurons of 178 GRB+/Slc17a6+ neurons from two mice. Bottom: Same as (Top), but in PPN and labeled glutamatergic neurons with Slc17a6. 306 GRB+/Slc17a6+/Cnr1+ neurons of 401 GRB+/Slc17a6+ neurons from three mice.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Summary tables of the number of FISH and green retrobead fluorescent puncta in each analyzed cell in regions of interest.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33892.020
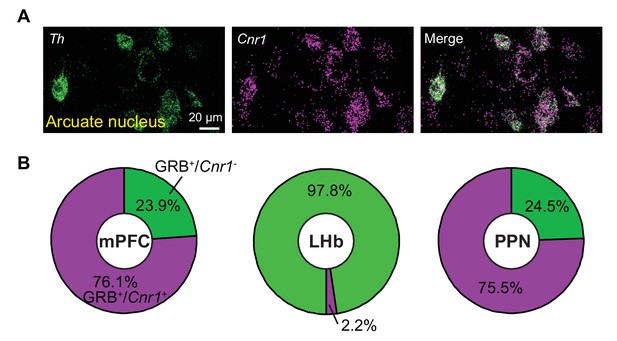
CB1 receptor transcripts expression in arcuate nucleus Th+ neurons and glutamatergic neurons projecting to VTA.
(A) Confocal image of Th and Cnr1 in arcuate nucleus, showing separate channels and overlay. Th+ neurons of the arcuate nucleus co-express Cnr1, in contrast to the VTA. (B) Quantitative analyses of Slc17a7/Slc17a6, GRB, and Cnr1 co-expression by FISH in the mPFC, LHb, and PPN. In mPFC, 143 GRB+/Slc17a7+/Cnr1+neurons of 188 GRB+/Slc17a7+ neurons from three mice; in LHb, 4 GRB+/Slc17a6+/Cnr1+neurons of 178 GRB+/Slc17a6+ neurons from two mice; in PPN, 306 GRB+/Slc17a6+/Cnr1+neurons of 401 GRB+/Slc17a6+ neurons from three mice.
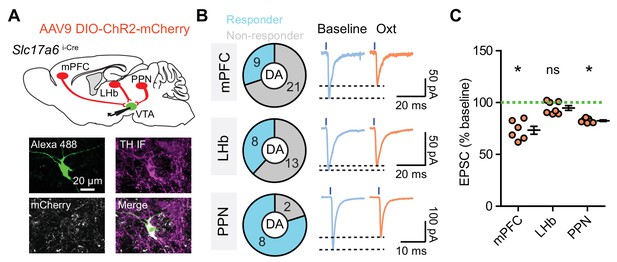
Oxytocin modulates pathway-specific excitatory synaptic transmission in VTA DA neurons.
(A) Top: Schematic of viral transduction strategy using AAV9-DIO-ChR2-mCherry to express ChR2 in glutamatergic neurons in mPFC, LHb, and PPN, respectively. Bottom: One example neuron labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 dye (green) during recording, identified as dopaminergic with TH post hoc immunolabeling (magenta). mCherry+ glutamatergic axons (gray) from the PPN are visible in the proximity of the dye-filled neuron. (B) Left: Quantification of VTA DA neurons receiving glutamatergic inputs from each brain region. Right: Examples of light-evoked EPSC traces of VTA DA neurons under baseline conditions and during oxytocin application with ChR2-mCherry virus delivered into mPFC, LHb, and PPN, respectively. Black dashed lines indicate the peak value of each trace. (C) Summary data for light-evoked EPSC amplitude at baseline and following oxytocin application with ChR2-mCherry virus delivered into mPFC, LHb, and PPN, respectively. *p<0.05, Wilcoxon signed rank test vs. baseline, n = 6 neurons from four mice for mPFC, seven neurons from four mice for LHb, and 7 neurons from two mice for PPN. Error bars reflect SEM.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Summary table of the effect of oxytocin on excitatory synaptic inputs from various regions to the VTA.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33892.023
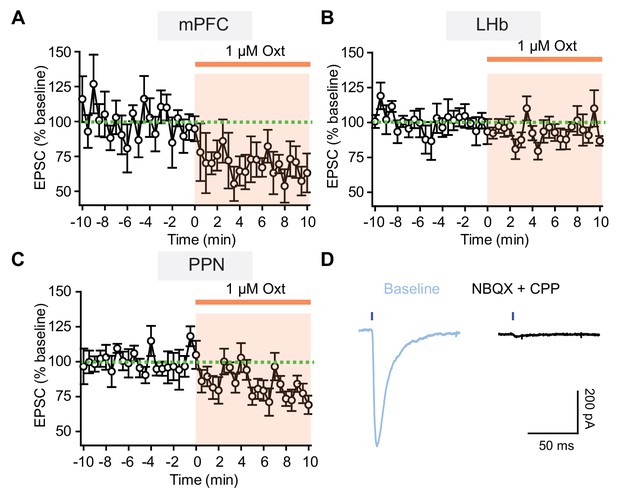
Oxytocin attenuates pathway-specific glutamatergic synaptic transmission in VTA DA neurons.
(A) Summary showing average normalized light-evoked EPSC amplitude in VTA DA neurons with AAV9-DIO-ChR2-mCherry virus injected into mPFC of Slc17a6i-Cre mice. n = 6 neurons from four mice. (B) Same as (A), but with ChR2-mCherry virus injected into LHb. n = 7 neurons from four mice. (C) Same as (A), but with ChR2-mCherry virus injected into PPN. n = 7 neurons from two mice. Error bars reflect SEM. (D) Example light-evoked EPSC in a VTA DA neuron, blocked by NMDA and AMPA receptor antagonists (NBQX and CPP).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| strain, strain background (Mouse) | C57BL/6 | Charles River | Cat#000664; RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664 | |
| strain, strain background (Mouse) | B6.SJL-Slc6a3 tm1.1(cre)Bkmn/J | Jackson Laboratory | Cat#006660; RRID: IMSR_JAX:006660 | |
| strain, strain background (Mouse) | B6.129S-Oxttm1.1(cre)Dolsn/J | Jackson Laboratory | Cat#024234; RRID:IMSR_JAX:024234 | |
| strain, strain background (Mouse) | Slc17a6 tm2(cre)Lowl/J | Jackson Laboratory | Cat#016963; RRID:IMSR_JAX:016963 | |
| strain, strain background (Mouse) | B6.Cg-Gt(ROSA) 26Sortm14(CAG-tdTomato)Hze/J | Jackson Laboratory | Cat#007914; RRID:IMSR_JAX:007914 | |
| strain, strain background (Mouse) | B6.129S-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm32 (CAG-COP4*H134R/EYFP)Hze/J | Jackson Laboratory | Cat#012569; RRID:IMSR_JAX:012569 | |
| antibody | Rabbit anti-tyrosine hydroxylase | Millipore | Cat#AB152; RRID:AB_390204 | concentration: 1:1000 |
| antibody | Rabbit anti-oxytocin receptor (OxtR-2) | NA | NA | Gift from R. Froemke (Marlin et al., 2015; Mitre et al., 2016) |
| recombinant DNA reagent | AAV9-EF1a-DIO-hChR2 (H134R)-mCherry | UPenn viral core | CS0543-3CS | |
| commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Fluorescence Multiplex Assay | ACDBio | ||
| commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Probe- Mm-Cnr1 | ACDBio | Cat#420721-C1 | |
| commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Probe- Mm-Th | ACDBio | Cat#317621-C2 | |
| commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Probe- Mm-Slc17a6 | ACDBio | Cat#319171-C2 | |
| commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Probe- Mm-Slc17a7 | ACDBio | Cat#416631-C2 | |
| commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Probe- Mm-Oxtr | ACDBio | Cat#412171-C1 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Oxytocin | Tocris | Cat#1910; CAS 50-56-6 | |
| chemical compound, drug | L-368,899 hydrochloride | Tocris | Cat#2641; CAS 160312-62-9 | |
| chemical compound, drug | SR 49059 | Tocris | Cat#2310; CAS 150375-75-0 | |
| chemical compound, drug | NBQX disodium salt | Tocris | Cat#1044; CAS 479347-86-9 | |
| chemical compound, drug | (RS)-CPP | Tocris | Cat#0173; CAS 100828-16-8 | |
| chemical compound, drug | SR95531 hydrobromide | Tocris | Cat#1262; CAS 104104-50-9 | |
| chemical compound, drug | U73122 | Tocris | Cat#1268; CAS 112648-68-7 | |
| chemical compound, drug | CP945598 hydrochloride | Tocris | Cat#4236; CAS 686347-12-6 | |
| chemical compound, drug | WIN55212-2 | Tocris | Cat#1038; CAS 131543-23-2 | |
| chemical compound, drug | AM251 | Tocris | Cat#1117; CAS 183232-66-8 | |
| chemical compound, drug | orlistat (THL) | Tocris | Cat#3540; CAS 96829-58-2 | |
| chemical compound, drug | MNI-L-glutamate | Tocris | Cat#1490; CAS 295325-62-1 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Alexa Fluor 488 hydrazide | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#A10436 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Alexa Fluor 594 hydrazide | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#A10438 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Green retrobeads (GRB) | Lumafluor Inc. | Cat#G180 | |
| software, algorithm | GraphPad Prizm 5 | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| software, algorithm | FIJI | Schindelin et al., 2012 | http://fiji.sc/; RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| software, algorithm | MATLAB | MathWorks | RRID:SCR_001622 | |
| software, algorithm | Igor Pro | Wavemetrics | RRID:SCR_000325 | |
| software, algorithm | SPSS | IBM | RRID:SCR_002865 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33892.024





