Septal secretion of protein A in Staphylococcus aureus requires SecA and lipoteichoic acid synthesis
Figures
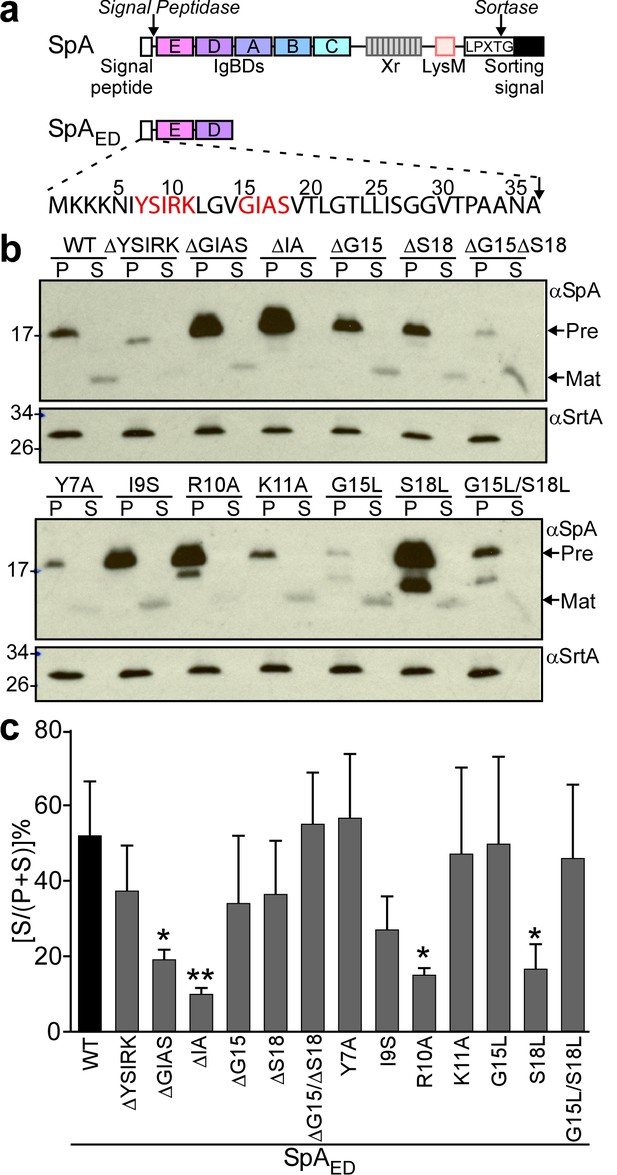
Mutagenesis of the signal peptide of staphylococcal protein A (SpA).
(a) Schematic illustrating the primary structure of SpA and of SpAED with the immunoglobulin binding domains (IgBDs, designated E, A, B, C and D), region X (Xr), LysM domain and LPXTG sorting signal. Cleavage sites for signal peptidase and sortase A are indicated. The amino acid sequence of the SpA signal peptide is displayed. YSIRK/GXXS motif residues are printed in red. (b) The structural genes for SpAED and its variants were cloned into pOS1, expressed from the spa promoter in S. aureus WY110 (∆spa ∆sbi) and secretion of SpAED was analyzed by immunoblotting with SpA-specific antibody in culture supernatant (S) and lysostaphin-digested bacterial pellet (P) samples. Signal peptide bearing SpAED precursors are labeled ‘Pre’ on the side of each blot; ‘Mat’ denotes mature protein without signal peptide. The calculated molecular weight (MW) of the variant precursors are: SpAED, 16.78 kD; SpAED/ΔYSIRK,16.13 kD; SpAED/ΔGIAS, 16.45 kD; SpAED/ΔIA, 16.59 kD; SpAED/ΔG15, 16.72 kD; SpAED/ΔS18, 16.69 kD; SpAED/ΔG15ΔS18, 16.63 kD; SpAED/Y7A, 16.68 kD; SpAED/I9S, 16.75 kD; SpAED/R10A, 16.69 kD; SpAED/K11A, 16.72 kD; SpAED/G15L, 16.83 kD; SpAED/S18L, 16.8 kD; SpAED/G15L/S18L, 16.86 kD. The MW of SpAED mature protein is 13.15 kD. Sortase A (SrtA, MW 23.54 kD) immunoblot serves as loading control. (c) Percent secretion of wild-type SpAED and its variants was quantified from triplicate experiments as the intensity of immunoblotting signals in the supernatant (S) divided by the sum signals in (S + P) fractions × 100. Statistical significance was analyzed with one-way ANOVA comparing each variant with wild-type and p values were recorded: WT vs. ∆GIAS, p=0.031; WT vs. ∆IA, p=0.0032; WT vs. R10A, p=0.0116; WT vs. S18L, p=0.0172. * denotes p<0.05, ** denotes p<0.01.
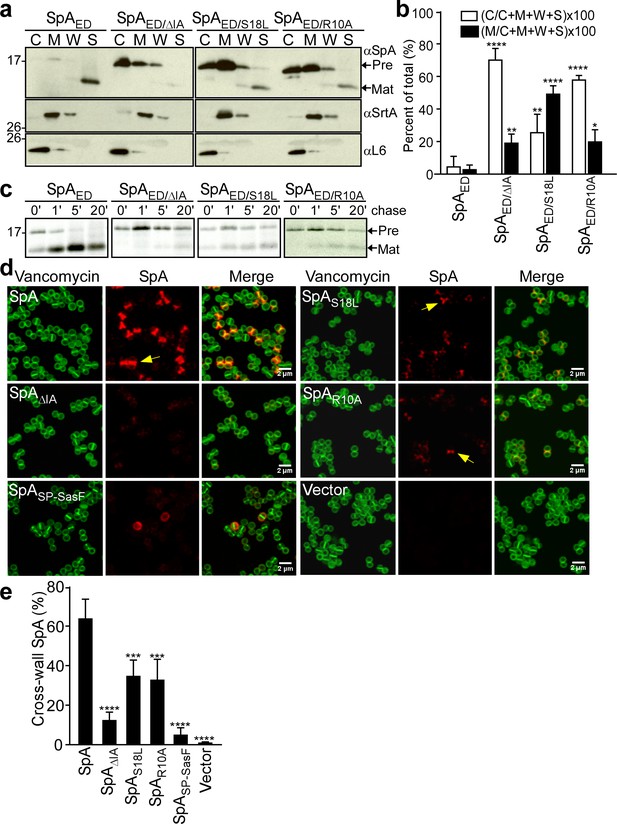
SpA signal peptide variants defective in precursor processing and septal secretion.
(a) S. aureus cultures were fractionated into cytoplasm (C), membrane (M), cell wall (W) and culture supernatant (S) and analyzed by immunoblotting with αSpA to reveal the subcellular location of wild-type SpAED precursor and secreted product of the SpAED/ΔIA, SpAED/S18L, and SpAED/R10A variants. Immunoblotting with αSrtA and αL6 was used to establish fractionation and loading controls. (b) Quantification of immunoblot signal intensity in (a) using Image J. Precursor abundance (%) the bacterial cytoplasm (C) and membrane (M) was quantified from triplicate experiments as the intensity of immunoblotting signals divided by the sum signals in all four fractions (C + M + W + S)×100. Statistical significance was analyzed with one-way ANOVA comparing each variant with wild-type and p values were recorded: for [C/(C + M + W + S)]×100, WT vs. ∆IA, p<0.0001; WT vs. S18L, p=0.0042; WT vs. R10A, p<0.0001; for [M/(C + M + W + S)]×100, WT vs. ∆IA, p=0.0056; WT vs. S18L, p<0.0001; WT vs. R10A, p=0.0405. **** denotes p<0.0001, ** denotes p<0.01, * denotes p<0.05. (c) S. aureus cultures were pulse-labeled for 60 s with [35S]methionine and labeling quenched by adding an excess of non-radioactive methionine (chase). At timed intervals during the pulse (0’) or 1 (1’), 5 (5’), and 20 (20’) minutes after the pulse (chase), culture aliquots were precipitated with trichloroacetic acid (TCA), lysostaphin-treated, immunoprecipitated with αSpA and analyzed by autoradiography. (d) S. aureus WY110 (∆spa ∆sbi) harboring chromosomal pCL55-insertions of wild-type spa (SpA), spaΔIA (SpAΔIA) spaS18L (SpAS18L), spaR10A (SpAR10A) spaSP-SasF (SpASP-SasF) or pCL55 alone (Vector) were treated with trypsin to remove SpA. Bacteria were incubated for 20 min to allow for secretion and cell wall deposition of newly synthesized SpA. Samples were incubated with BODIPY-FL vancomycin (Vancomycin) (green) to stain the bacterial cell wall and with SpA-specific monoclonal antibody and Alexa fluor 647-labeled secondary IgG (red) to reveal SpA. (e) SpA-positive staphylococci in images derived from samples in (d) were analyzed for SpA deposition at the cross wall of diplococci (n = 200). Data from three independent experiments were used to derive the mean (± SEM) and were analyzed for significant differences with one-way ANOVA for comparisons between wild-type and mutant SpA. p values were recorded: SpA vs. SpA∆IA, p<0.0001; SpA vs. SpAS18L, p=0.0006; SpA vs. SpAR10A, p=0.0004; SpA vs. SpASP-SasF, p<0.0001; SpA vs. Vector, p<0.0001. **** denotes p<0.0001, *** denotes p<0.001.
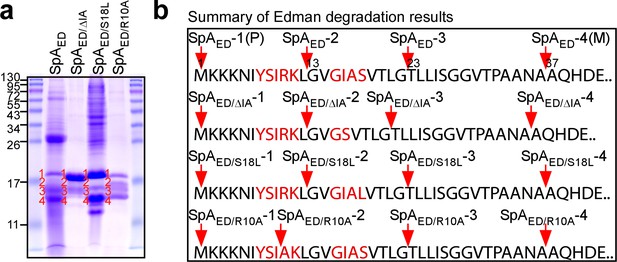
Proteolytic cleavage of the SpA signal peptide.
(a) Wild-type SpAED or SpAED/ΔIA, SpAED/S18L, and SpAED/R10A variant precursors and cleavage products were purified from detergent-solubilized staphylococcal membranes using affinity chromatography on IgG-sepharose and analyzed on Coomassie-Blue stained SDS-PAGE. Full length precursors (1) and their cleavage products (2-4) were analyzed by Edman degradation and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. See Table 1 for mass spectrometry data. (b) Schematic illustrating the proteolytic cleavage sites for each of the four precursors SpAED, SpAED/ΔIA, SpAED/S18L and SpAED/R10A.
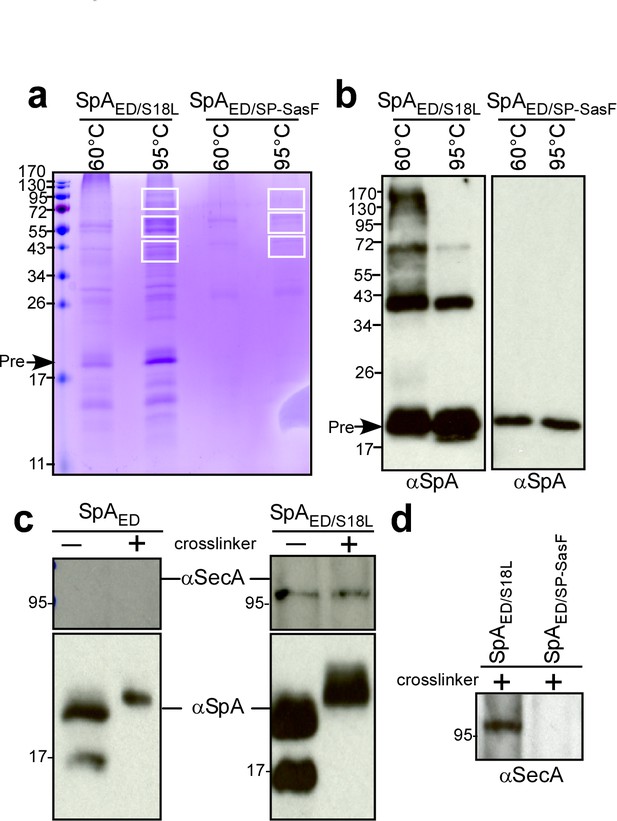
Crosslinking of staphylococcal proteins to SpAED/S18L or SpAED/SP-SasF.
(a) Bacteria from S. aureus WY110 (pSpAED/S18L) and S. aureus WY110 (pSpAED/ SP-SasF) cultures were crosslinked with 0.9% formaldehyde, membrane proteins detergent-solubilized and SpAED/S18L as well as SpAED/SP-SasF precursors purified by affinity chromatography on IgG-sepharose. Eluate was treated for 20 min at 95°C to reverse cross-linking or kept at 60°C (cross-linked control) and analyzed on Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE. Bands were excised as indicated and individual proteins identified via ESI-MS analyses of tryptic peptides and data comparison with in silico trypsin-cleaved translation products derived from the genome sequence of S. aureus. Immunoblotting of 60 and 95°C samples to validate crosslinking of SpAED/S18L (b). The identity of the SpA-immunoreactive species migrating at 43 and 72 kDa in the left panel of Figure 4b is not known. (c) Bacteria from S. aureus WY110 (pSpAED) and S. aureus WY110 (pSpAED/S18L) cultures were treated with 0.9% formaldehyde (+crosslinker) or left untreated (- crosslinker), membrane proteins detergent-solubilized, and SpAED/S18L as well as SpAED precursors purified by affinity chromatography on IgG-sepharose. Eluate was treated for 20 min at 95°C to reverse crosslinking and samples analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for SpA and SecA (MW 95.96 kD). (d) Eluates of crosslinked SpAED/S18L and SpAED/SP-SasF precursors were examined by immunoblotting for the presence of SecA. See Supplementary file 1 for a summary of proteins crosslinked to SpAED/S18L.
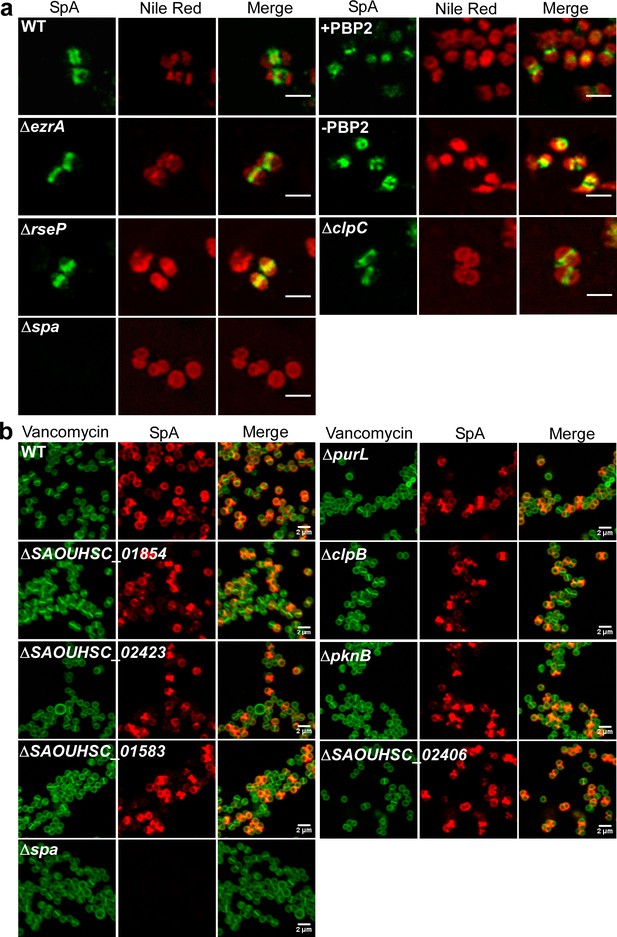
SpA septal secretion analysis in S. aureus mutants with knockout or conditional mutations in genes whose products were crosslinked to SpAED/S18L.
(a) Localization of SpA secretion in ΔezrA, ΔrseP, ΔclpC and PBP2-depleted S. aureus. To detect intracellular localization of SpA in mutants with known cell division or peptidoglycan synthesis defects, bacteria were trypsin treated to remove extracellular surface proteins and fixed with para-formaldehyde. Samples were treated with lysostaphin, incubated with detergent and SpA-specific rabbit antibodies and Alexa Fluor 488-labeled goat-anti-rabbit-IgG (green) and with Nile red to reveal bacterial membranes. Scale bar, 2 µm. (b) Localization of newly deposited SpA at the cross-wall in several staphylococcal mutants. To screen for surface protein targeting defects, wild-type staphylococci and the corresponding mutants were treated with trypsin to remove SpA. Bacteria were incubated for 20 min to allow for secretion and cell wall deposition of newly synthesized SpA. Samples were incubated with BODIPY-FL vancomycin (Vancomycin, green) to stain the bacterial cell wall and with SpA-specific monoclonal antibody and Alexa fluor 647-labeled secondary IgG (red) to reveal SpA.
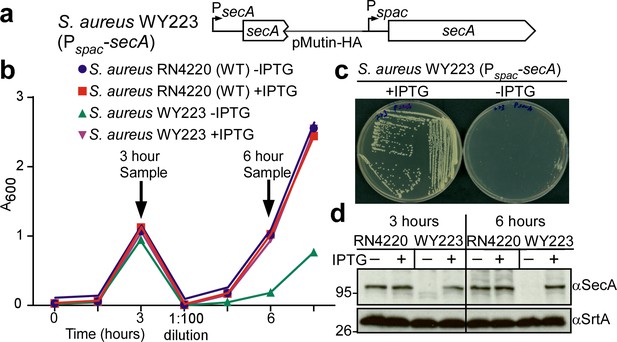
Depletion of SecA in S. aureus.
(a) Diagram of the secA gene locus in S. aureus RN4220 (wild-type parent, WT) and its Pspac-secA variant. (b) Bacteria from overnight cultures of wild-type S. aureus and S. aureus Pspac-secA grown in TSB with 1 mM IPTG were washed and suspended in fresh TSB with or without 1 mM IPTG. Subsequent growth was monitored as increased absorbance at 600 nm (A600). After three hours, cultures were diluted 1:100 into fresh TSB with or without 1 mM IPTG and incubated for additional growth measurements. (c) S. aureus Pspac-secA was streaked on tryptic soy agar with or without 1 mM IPTG supplement and incubated for 16 hr at 37°C for growth. (d) Culture samples retrieved after 3 and 6 hr in (b) were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against SecA (αSecA) and sortase A (αSrtA).
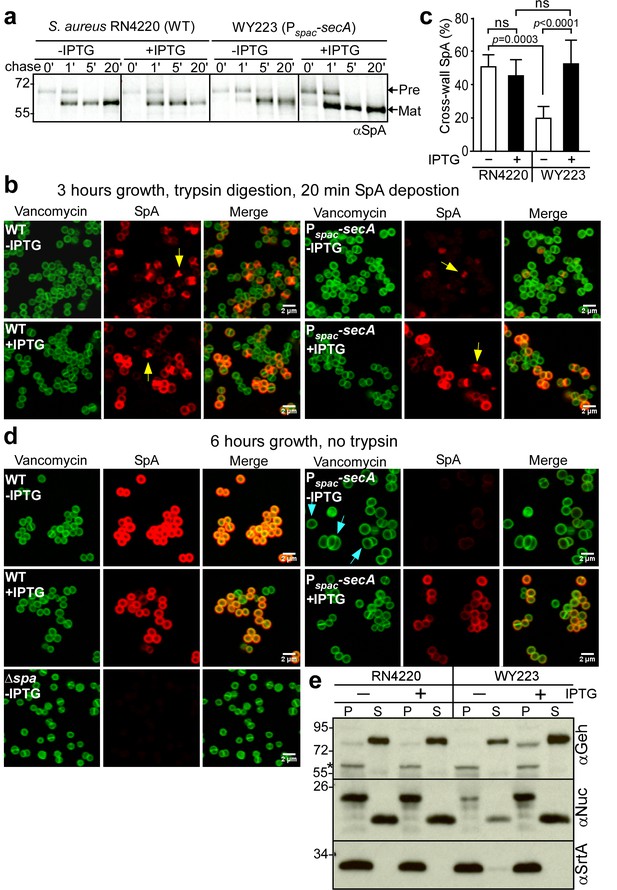
SecA depletion diminishes septal secretion of SpA in S. aureus.
(a) SpA precursor processing of [35S]methionine pulse-labeled S. aureus RN4220 (WT) or S. aureus Pspac-secA grown in the presence or absence of 1 mM IPTG. Bacteria were pulse-labeled for 60 s with radioactive methionine and then incubated with an excess of non-radioactive methionine. During the pulse (0’) or 1 (1’), 5 (5’) and 20 (20’) min after the addition of excess unlabeled methionine, culture aliquots were withdrawn, precipitated with TCA, digested with lysostaphin, and subjected to SDS-PAGE and autoradiography of immunoprecipitated SpA. Wild-type S. aureus (WT) and its Pspac-secA variant were grown for 3 (b) and 6 hr (d) in the presence or absence of 1 mM IPTG (see Figure 5). Samples in (b) were treated with trypsin to remove SpA from the bacterial surface. Bacteria were incubated for 20 min to allow for secretion and cell wall deposition of newly synthesized SpA. Samples were incubated with BODIPY-FL vancomycin (green) to stain the bacterial cell wall and with SpA-specific monoclonal antibody and Alexa Fluor 647-labeled secondary IgG (red) to reveal SpA. As a control for SpA-specific staining, the S. aureus ∆spa variant grown in the absence of IPTG was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. (c) SpA-positive staphylococci in images derived from samples in (b) were analyzed for SpA deposition at the cross wall of diplococci (n = 200). Data from three independent experiments were used to derive the mean (± SEM) and were analyzed for significant differences with one-way ANOVA and p values recorded: RN4220-IPTG vs. RN4220 +IPTG, non-significant (ns); RN4220-IPTG vs. WY223-IPTG, p=0.0003; WY223-IPTG vs. WY223 +IPTG, p<0.0001, RN4220 +IPTG vs. WY223 +IPTG, ns. (e) SecA depletion diminishes secretion of staphylococcal proteins. Protein samples from the extracellular supernatant (S) and bacterial pellet (P) of S. aureus RN4220 (WT) and S. aureus Pspac-secA cultures grown for 3 hr in the presence or absence of 1 mM IPTG were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against glycerol-ester hydrolase (αGeh) (precursor MW 76.39 kD, mature protein MW 72.26 kD), nuclease (αNuc) (precursor MW 25.12 kD, mature protein MW 18.78 kD) and sortase A (αSrtA). *Identifies unknown proteins crossreactive with αGeh.
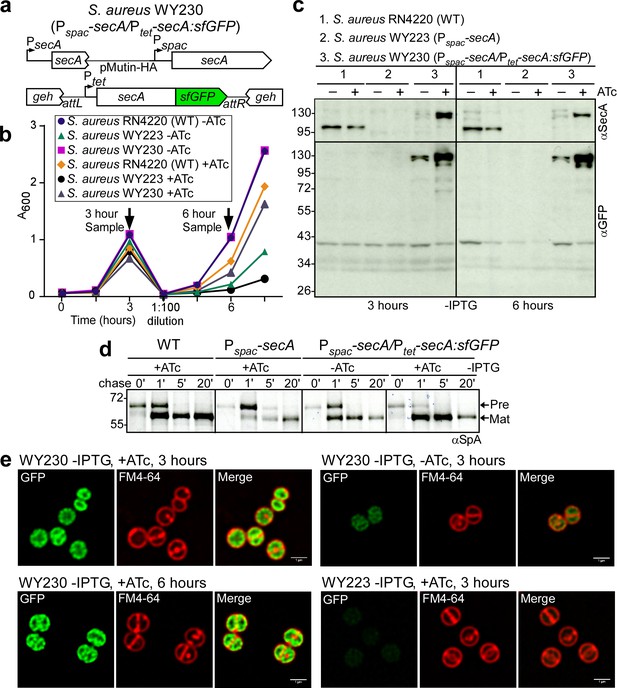
SecA localization in staphylococci.
(a) Diagram of the secA gene locus and of the pCL55-mediated att insertion site for secA-sfGFP in the staphylococcal genome. (b) Bacteria from overnight cultures of S. aureus RN4220 (WT), S. aureus Pspac-secA (WY223) and S. aureus Pspac-secA/Ptet-secA:sfGFP (WY230) grown in TSB with 1 mM IPTG were washed and suspended in fresh TSB without IPTG and with or without 0.43 µM anhydro-tetracycline (ATc); growth was monitored as increased absorbance at 600 nm (A600). After three hours, cultures were diluted 1:100 into fresh TSB without IPTG and with or without 0.43 µM ATc and incubated for further growth measurements. (c) Culture samples retrieved after 3 and 6 hr from the experiment detailed in (b) were analyzed by immunoblotting with rabbit antibodies against SecA (αSecA) and sfGFP (αGFP). (d) [35S]methionine-labeled S. aureus cultures incubated for 3 hr as described in (b) were analyzed during the 60 s pulse with radioactive methionine (0) and 1, 5 and 20 min after the addition of excess unlabeled methionine via SDS-PAGE and autoradiography of immunoprecipitated SpA. (e) Fluorescence microscopy of bacteria from S. aureus cultures incubated for 3 and 6 hr as described in (b). Bacteria were stained with the membrane dye FM4-64 (red) and analyzed for SecA-sfGFP fluorescence (green). Scale bar, 1 µm.
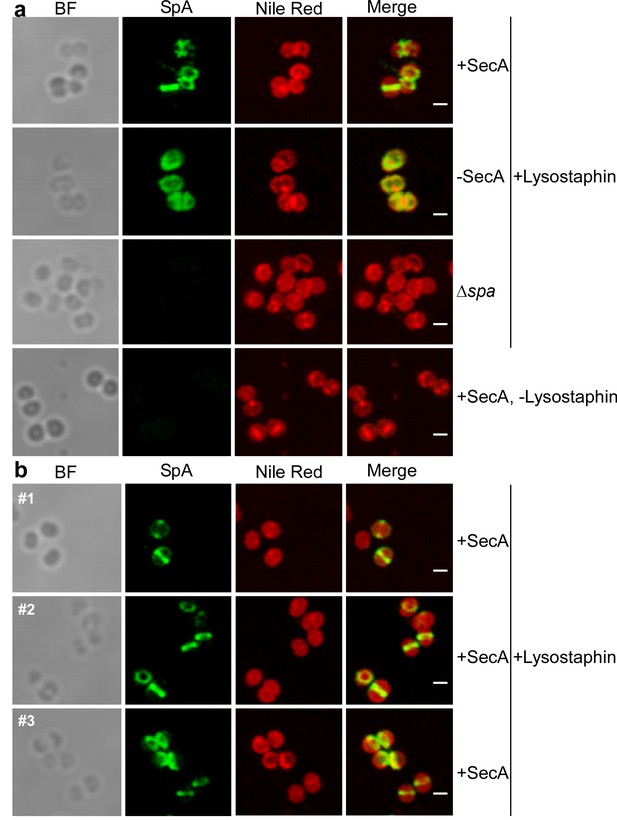
Intracellular trafficking of SpA in the presence and absence of SecA.
(a) S. aureus Pspac-secA cells were grown for 3 hr in the presence (+SecA) or absence of 1 mM IPTG (-SecA) and, alongside S. aureus ∆spa control cells, were trypsin treated to remove extracellular surface proteins and fixed with para-formaldehyde. Samples were then treated with lysostaphin (+Lysostaphin) or left untreated (-Lysostaphin), incubated with detergent and SpA-specific rabbit antibodies and Alexa Fluor 488-labeled goat-anti-rabbit-IgG (green) and with Nile red to reveal bacterial membranes. Bright-field microscopy (BF) images were acquired to reveal the contours of all bacterial cells. Scale bar, 1 µm. (b) Additional samples (#1, #2 and #3) of S. aureus Pspac-secA cells were grown in the presence of 1 mM IPTG (+SecA), trypsin treated, fixed with para-formaldehyde, lysostaphin treated, incubated with detergent and with SpA-specific antibody (green) and Nile red.
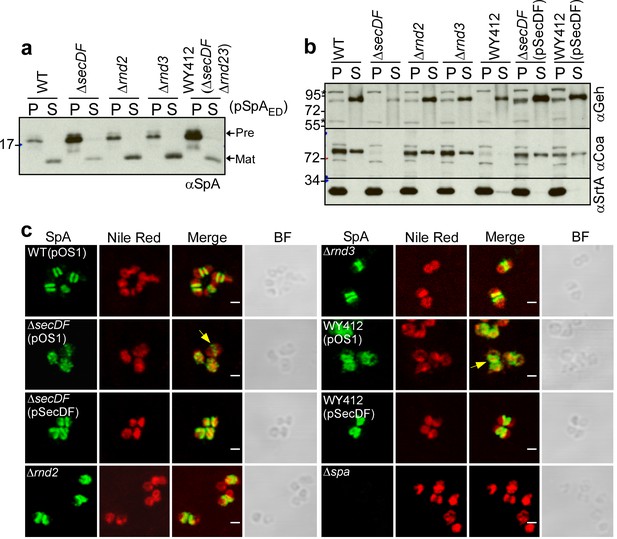
SecDF contributes to SpA secretion at septal membranes.
(a) S. aureus cultures were centrifuged to sediment the bacteria into the pellet (P) fraction and separate them from the extracellular medium (S, supernatant). Following lysostaphin digestion of bacteria, proteins in both fractions were precipitated with TCA and analyzed by immunoblotting with αSpA. (b) S. aureus cultures were fractionated as described in (a) and subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies specific for glycerol-ester hydrolase (αGeh), coagulase (αCoa) (precursor MW 71.72 kD, mature protein MW 68.96 kD) and sortase A (αSrtA). (c) Fluorescence microscopy of bacteria from cultures of S. aureus RN4220 (WT, wild-type), WY418 (∆secDF), WY416 (∆rnd2), WY400 (∆rnd3) and WY412 (∆secDF ∆rnd23) mutants with and without expression plasmid for wild-type secDF (pSecDF) as well as S. aureus SEJ1 (∆spa) as control. Bacteria were trypsin treated to remove extracellular surface proteins and fixed with para-formaldehyde. Samples were treated with lysostaphin, incubated with detergent and SpA-specific rabbit antibodies and Alexa Fluor 488-labeled goat-anti-rabbit-IgG (green) and with Nile red to reveal bacterial membranes. BF identifies the bright-field microscopy view of fluorescence microscopy images. Scale bar, 1 µm.
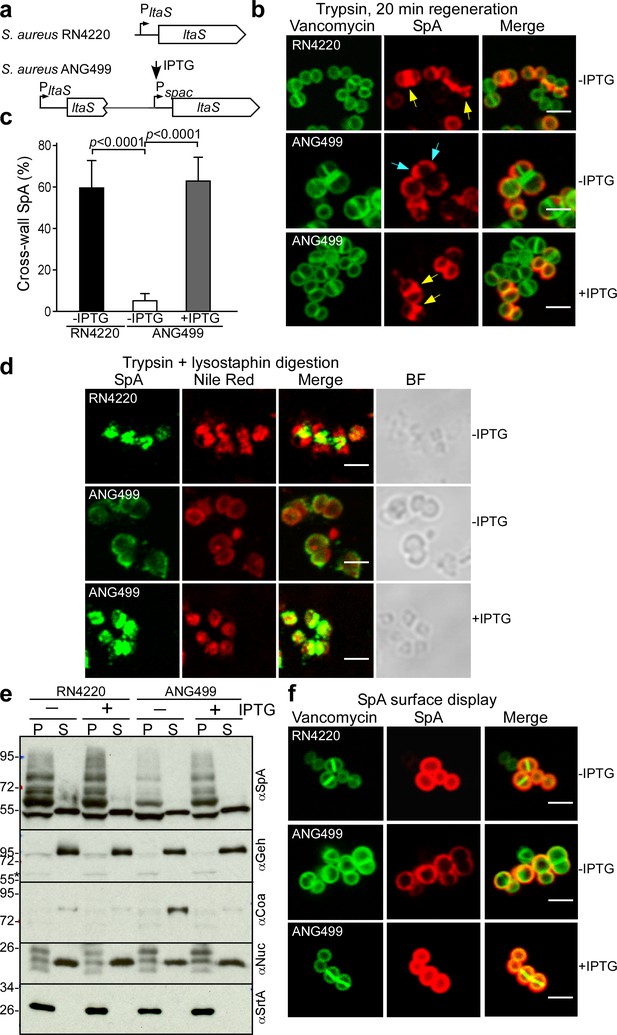
Localization of SpA secretion in LtaS-depleted S. aureus.
(a) Schematic to illustrate the ltaS locus in S. aureus RN4220 and ANG499. (b) Fluorescence microscopy with BODIPY-FL-vancomycin (green) and αSpA (red) stained samples 20 min after trypsin removal of surface proteins from the staphylococcal envelope to detect newly synthesized SpA. Scale bar, 2 µm. (c) SpA-positive staphylococci in images derived from samples in (b) were analyzed for SpA deposition at the cross wall of diplococci (n = 200). Data from three independent experiments were used to derive the mean (± SEM) and were analyzed for significant differences with one-way ANOVA for comparisons between S. aureus RN4220 (WT) and ANG499 grown with (+LtaS) and without IPTG (-LtaS). p values were recorded: RN4220-IPTG vs. ANG499-IPTG, p<0.0001; ANG499-IPTG vs. ANG499 +IPTG, p<0.0001. (d) Fluorescence microscopy to localize intracellular SpA in S. aureus strains RN4220 (WT) and ANG499 (Pspac-ltaS) grown with and without IPTG induction for 3 hr. Bacteria were trypsin treated to remove extracellular surface proteins and fixed with para-formaldehyde. Samples were then treated with lysostaphin, incubated with detergent and SpA-specific rabbit antibodies and Alexa Fluor 488-labeled goat-anti-rabbit-IgG (green) and with Nile red to reveal bacterial membranes. BF identifies the bright-field microscopy view of fluorescence microscopy images. Scale bar, 2 µm. (e) The culture supernatant (S) and bacterial pellet (P) samples of S. aureus RN4220 and ANG499 grown for three hours in the presence or absence of IPTG were immunoblotted with antibodies specific for SpA (αSpA), glycerol-ester hydrolase (αGeh), coagulase (αCoa), nuclease (αNuc) and sortase A (αSrtA). (f) Fluorescence microscopy of staphylococci to measure surface display of protein A in bacteria stained with BODIPY-FL-vancomycin (green) and αSpA (red) without trypsin treatment. Scale bar, 2 µm.
Tables
MALDI-TOF-MS ion signals of purified SpAED species and their variants
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34092.005| Protein | Observed m/z | Calculated m/z* | ∆obs.- calc. |
|---|---|---|---|
| SpAED-1 | 16776.47 | 16777.7 | 1.23 |
| SpAED-2 | 15273.92 | 15273.78 | 0.14 |
| SpAED-3 | 14418.92 | 14418.78 | 0.14 |
| SpAED-4 | 13152.40 | 13152.32 | 0.08 |
| SpAED/S18L-1 | 16803.02 | 16803.78 | 0.76 |
| SpAED/S18L-2 | 15298.89 | 15299.86 | 0.97 |
| SpAED/S18L-3 | 14417.89 | 14418.78 | 0.89 |
| SpAED/S18L-4 | 13152.22 | 13152.32 | 0.10 |
| SpAED/∆IA-1 | 16592.95 | 16593.46 | 0.51 |
| SpAED/∆IA-2 | 15088.71 | 15089.54 | 0.83 |
| SpAED/∆IA-3 | 14417.86 | 14418.78 | 0.92 |
| SpAED/∆IA-4 | 13151.55 | 13152.32 | 0.77 |
| SpAED/R10A-1 | 16692.99 | 16692.59 | 0.40 |
| SpAED/R10A-2 | 15584.97 | 15586.2 | 1.23 |
| SpAED/R10A-3 | 14418.46 | 14418.78 | 0.32 |
| SpAED/R10A-4 | 13152.07 | 13152.32 | 0.25 |
-
*Based on average mass calculated with the online ExPASy tool.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of ESI-MS identified tryptic peptides crosslinked to SpAED/S18L.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34092.014
-
Supplementary file 2
Strains and plasmids used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34092.015
-
Supplementary file 3
Oligonucleotide primers used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34092.016
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34092.017





