A two-hybrid antibody micropattern assay reveals specific in cis interactions of MHC I heavy chains at the cell surface
Figures
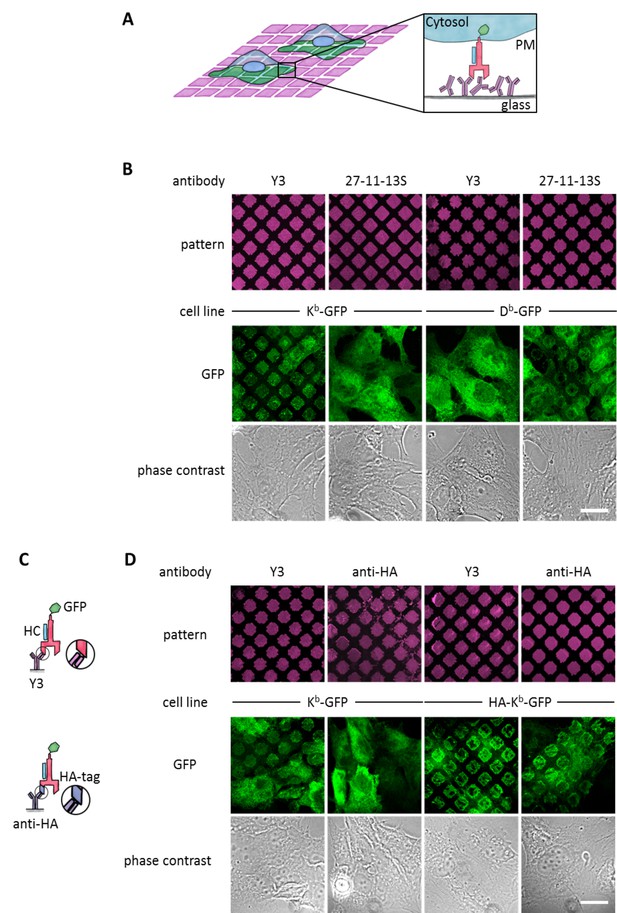
Specific capture of cell surface Kb on antibody micropatterns.
(A) Schematic presentation of the capture assay. Cells transduced with Kb (red) fused to GFP (green) are incubated on the Y3 antibody micropatterns (anti Kb; magenta). Upon specific antibody-antigen interaction, Kb-GFP is captured on its extracellular epitope by the Y3 antibody pattern elements (see enlargement). (B) Printed antibodies are target-specific. Control experiments demonstrate that Kb-GFP is only captured by the anti-Kb antibody Y3 and not by an antibody specific for Db (27-11-13S). (C) Schematic displaying the different antibody epitopes on the Kb molecule. The Y3 epitope reacts specifically with residues of the α2 helix of Kb-GFP whereas the anti-HA antibody recognizes the additional HA-tag that was N-terminally fused to Kb-GFP. (D) Surface Kb-GFP can be directly captured by the anti-Kb antibody Y3 or by the anti-HA antibody against the N-terminally tagged HA-Kb-GFP. Cells were transduced with Kb-GFP or HA-Kb-GFP and tested for specificity on Y3 or anti-HA antibody micropatterns. Y3 successfully captures both constructs, whereas HA only recognizes the HA-tagged molecules. Scale bar: 25 µm.
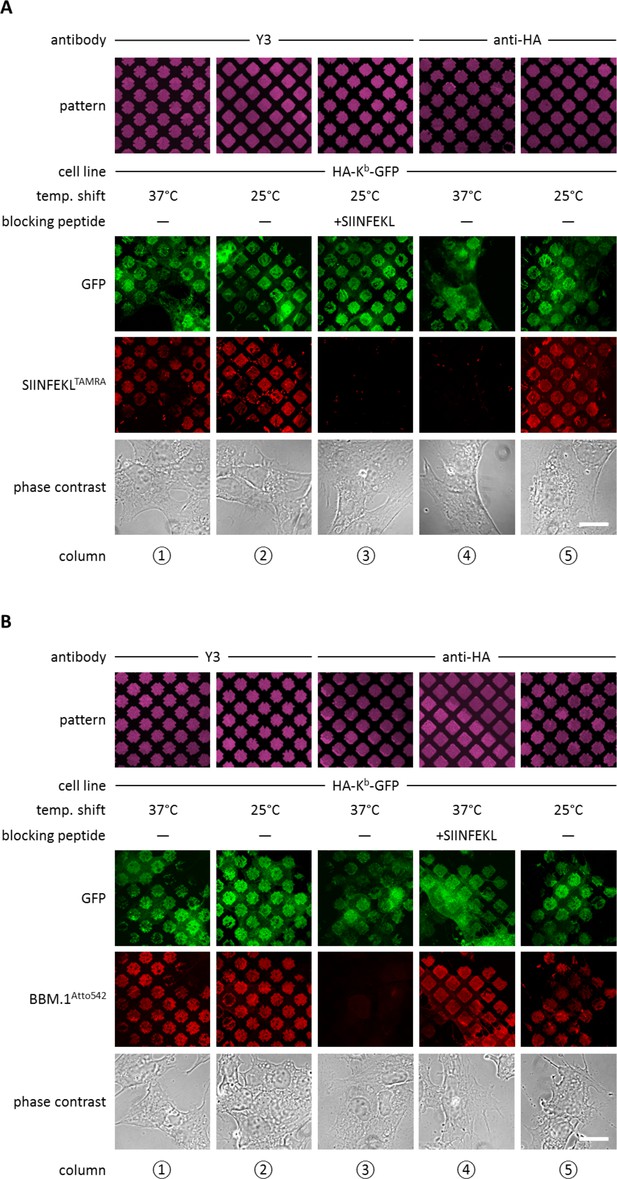
Antibody micropatterns determine stability of the captured Kb population.
(A) Cells expressing HA-Kb-GFP were captured on Y3 or anti-HA antibody micropatterns and incubated at 25 or 37°C to allow for the dissociation of β2m. To identify the nature of the captured Kb-GFP population (green channel), specific fluorescent peptide SIINFEKL (SL8TAMRA; red channel) was added to the samples. Based on their ability to bind peptide, one can distinguish between the peptide-receptive KbHC/β2m dimer and the Kb free heavy chains, which are incapable to bind peptide. (B) For further characterization of the captured HA-Kb-GFP on Y3 or anti-HA antibody micropatterns, immunostaining experiments were performed. Immunostaining of captured HA-Kb-GFP molecules with the anti-β2m antibody (BBM.1Atto542) reveals dissociation of β2m from anti-HA antibody micropatterns at 37°C (column 3). Addition of the specific ligand peptide SIINFEKL (SL8) during 37°C incubation prevents β2m dissociation (column 4). Scale bars: 25 µm.
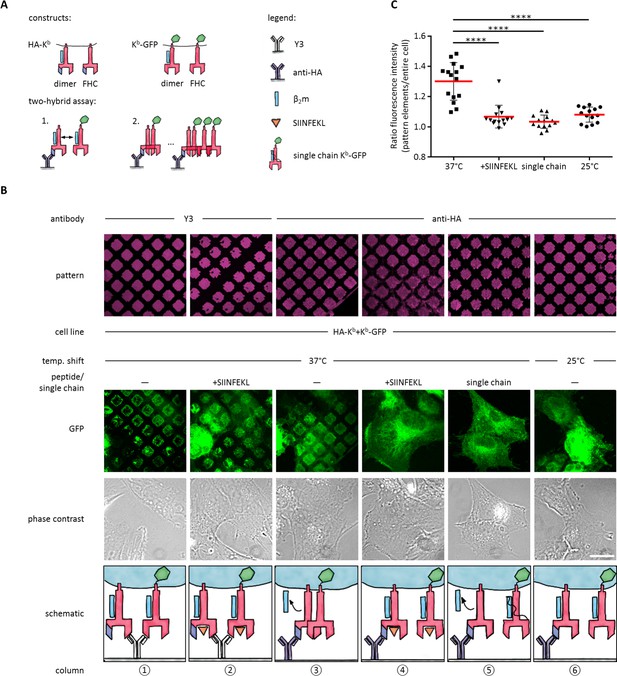
Antibody micropatterns reveal conformation-dependent in cis interaction of captured Kb-GFP.
(A) For the two-hybrid assay, cells were co-transduced with two Kb constructs: Kb with an N terminal HA tag (HA-Kb) and Kb-GFP (GFP fused to the cytoplasmic tail). (B) Cells were incubated on anti-HA or Y3 antibody micropatterns at different temperatures. Recruitment of Kb-GFP (green channel) to the anti-HA antibody micropatterns occurs specifically at 37°C and can be inhibited by addition of the SIINFEKL (SL8) peptide (column 3 and 4). The single chain mutant, scKb-GFP (which has β2m covalently linked to the Kb heavy chain) is also not recruited to the antibody micropatterns (column 5). From top to bottom: Antibody micropatterns, Kb-GFP, phase contrast, and schematic representation. Scale bar: 25 µm. (C) For quantification of co-capture, the mean fluorescence intensities of Kb-GFP of the total cell and the areas of pattern elements were determined. The redistribution of Kb-GFP leads to increased fluorescence intensity levels in the areas of the pattern elements and is represented as an increase of the ratio of the fluorescence intensity of the pattern elements over the fluorescence intensity of the entire cell (see Materials and methods). The plot shows the mean (red) ± SEM and the distribution of the calculated ratios from individual cells (black symbols; n (cells) ≥ 14) of ≥ 2 independent experiments (****: Significant difference, p<0.0001, two-tailed t-test).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Mean fluorescence intensities for quantification of cluster formation.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34150.007
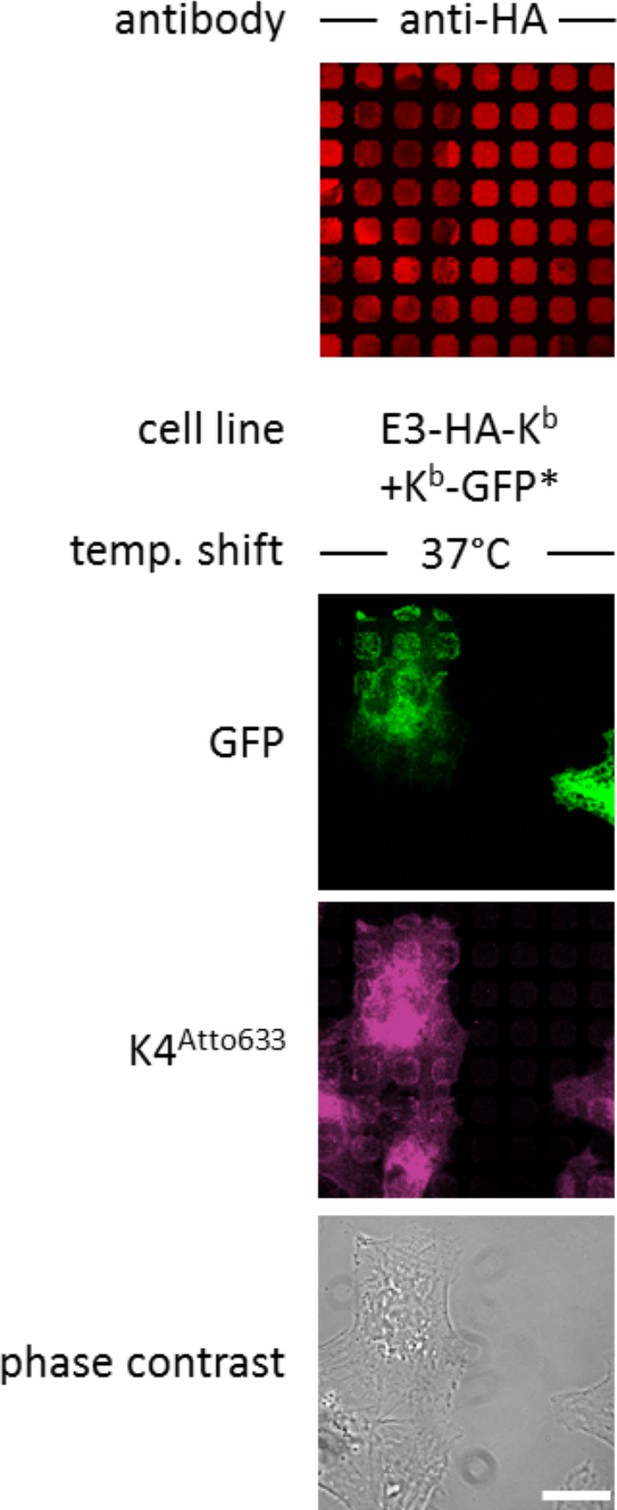
Staining E3-HA-Kb with K4-peptide.
The stable cell line STF1/E3 HA-Kb was electroporated (*) with Kb-GFP and incubated overnight on anti-HA micropatterns and either left at 25°C or shifted to 37°C to allow for co-capture as described. Cells were then stained with the K4Atto633 peptide, which binds specifically to the E3 tag of the E3-HA-Kb construct, which was captured by its HA-tag on the anti-HA micropatterns. Scale bar: 25 µm.
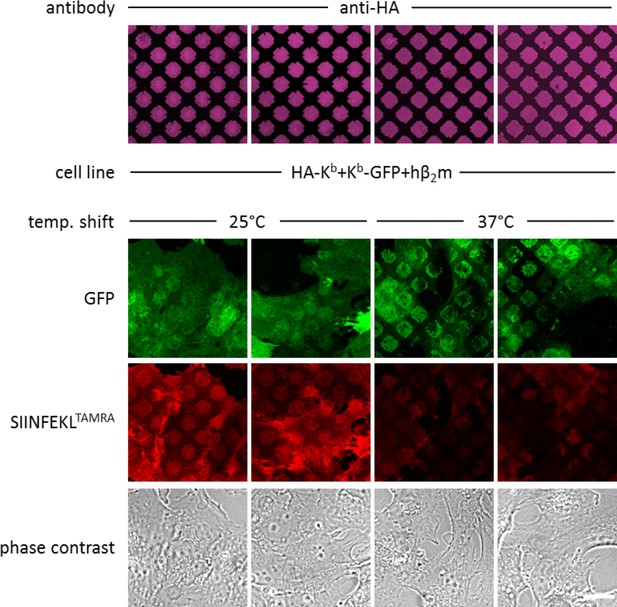
Binding SIINFEKLTAMRA to co-captured Kb-.
Co-transduced cells with E3-HA-Kb and Kb-GFP were incubated overnight on anti-HA micropatterns and either left at 25°C or shifted to 37°C to allow for co-capture as described. Cells were then incubated with SIINFEKLTAMRA (SL8TAMRA) peptide. Peptide binding was reduced in co-captured Kb at 37°C (columns 3 and 4), indicating that only free heavy chains interact in cis. Duplicates are shown. Scale bar: 25 µm.
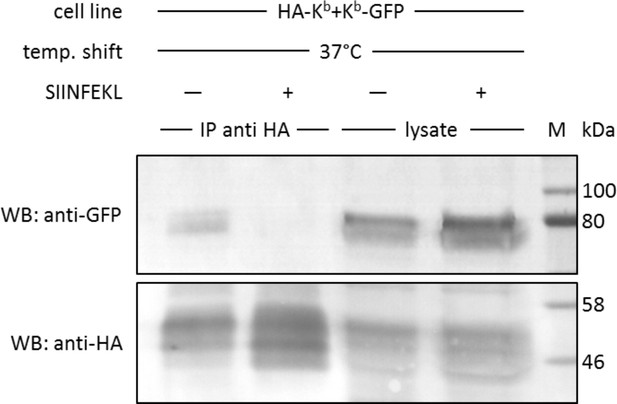
In cis interactions of Kb-GFP and HA-Kb are peptide-dependent and generally occur in cells at 37°C.
For co-immunoprecipitation, the same co-transduced cells from the previous experiment were used (STF1/HA-Kb and Kb-GFP). Cells were incubated at 25°C overnight to increase Kb cell surface levels and then shifted to 37°C to allow for the dissociation of β2m from the Kb heavy chain. The SIINFEKL (SL8) peptide was added as control to inhibit β2m dissociation (lanes 2 and 4). Cells were then lysed and successfully immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody (bottom row). Immunoisolates and lysate control samples were analysed by western blotting by sequential staining with an anti-GFP antibody (top row) and an anti-HA antibody (bottom row). The Kb-GFP construct was specifically co-immunoprecipitated in the absence of peptide, similar to the result on antibody micropatterns (lane 1).
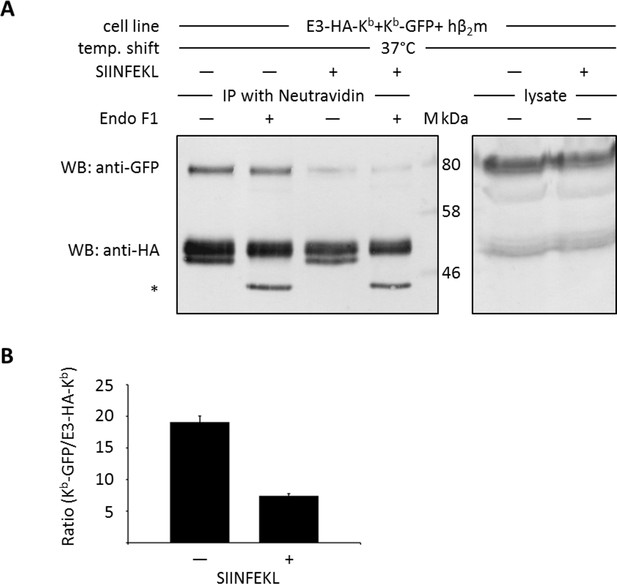
Co-immunoprecipitation of cell surface Kb molecules with K4-peptide.
For co-immunoprecipitation of cell surface proteins, stable STF1 cells co-transfected with E3-HA-Kb and Kb-GFP were used. Cells were incubated at 25°C overnight to enrich Kb cell surface levels and incubated in presence or absence of SIINFEKL (SL8) as indicated. For cell surface labeling, the biotinylated K4 peptide (K4biotin; binds to the extracellular E3 tag of E3-HA-Kb) was added and cells were shifted to 37°C to allow for β2m dissociation as described. Cells were lysed and co-immunoprecipitated with neutravidin agarose binding to the biotinylated E3-HA-Kb cell surface population. The immunoisolates were then treated with EndoF1 as indicated to distinguish the cell surface population (EndoF1 resistant, top bands) from the intracellular population of isolated Kb molecules (EndoF1 sensitive Kb molecules, see asterisk). (A) Sequential Western blot analysis with an anti-GFP antibody (top row) and anti-HA antibody (bottom row) demonstrates that only free heavy chains co-precipitate (lane 1) with E3-HA-Kb. (B) Quantification of (A): The ratio of co-precipitated Kb-GFP to total protein amounts was quantified.
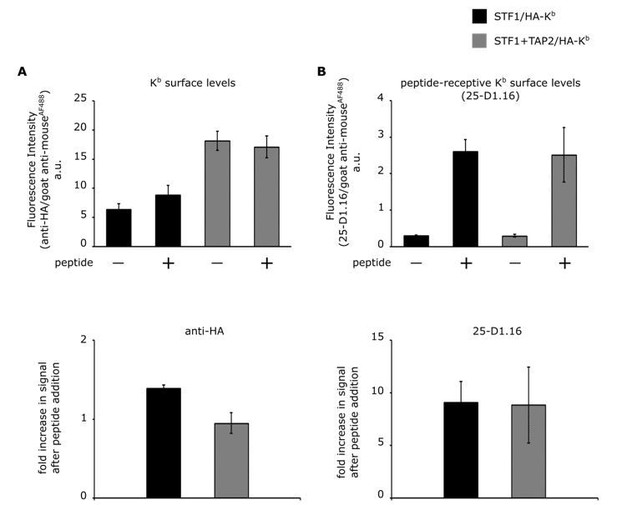
Comparison of cell surface expression of HA-Kb in STF1 and STF1+TAP2 cells by flow cytometry.
STF1 cells were transduced with HA-Kb and stained with anti-HA or 25-D1.16 and anti-mouse IgG conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 and subjected to flow cytometry. (A) Surface intensities of HA-Kb of both cell lines are represented as bar charts. TAP-deficient STF1 cells are represented in black and TAP2-proficient cells (STF1+TAP2) are represented in grey. Cells were incubated with (+) and without (-) 10 µM of the high affinity peptide SL8 and stained with the indicated antibodies. (B) The increase in surface signal after peptide addition in (A) for both antibodies is displayed as ratio. (n= 3; standard deviations as indicated).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (mus musculus) | H-2Kb | NCBI GenBank | NM_001001892.2 | |
| Gene (mus musculus) | H-2Db | NCBI GenBank | NM_010380.3 | |
| Cell line (homo sapiens) | STF1 | PMID:10074495 | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (mus musculus) | STF1/Kb-GFP | This paper | N/A | Stable cell lines were generated by lentiviral transduction and antibiotic selection as described in PMID: 24806963. |
| Transfected construct (mus musculus) | STF1/Db-GFP | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (mus musculus) | STF1/E3 HA-Kb-GFP | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (mus musculus) | STF1/E3 HA-Kb +Kb-GFP | This paper | N/A | |
| Transfected construct (mus musculus) | STF1/E3 HA-Kb +Kb-hβ2m-GFP (single chain) | This paper | N/A | |
| Antibody | Y3 | PMID: 6181513 | N/A | Produced and purified in house from hybridoma cells. 0.6 µg/µL for printing |
| Antibody | 27-11-13S | PMID: 6935293 | N/A | |
| Antibody | 12CA5 (Hemagglutinin; HA) | PMID: 6192445 | N/A | Produced and purified in house from hybridoma cells 0.6 µg/µL for printing; 1:100 dilution of hybridoma supernatant for Western blotting. |
| Antibody | BBM.1 | PMID: 91522 | N/A | Produced and purified in house from hybridoma. 0.1 µg/µL for staining. |
| Antibody | rabbit anti-GFP | Abcam | Cat #: ab290, RRID:AB_303395 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | rabbit antisera against H-2Kb and H-2Db | Charles River Laboratories | Rabbits were immunized with a peptide corresponding to residues 331–349 of the cytoplasmic tail of both heavy chains | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | goat anti-rabbit IgG-AP | Bio-Rad | Cat #: 170–6518, RRID:AB_11125338 | 1:10000 |
| Antibody | donkey anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 568 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat #: A10037, RRID:AB_2534013 | 1:400 for staining antibody micropatterns |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | puc2CL6Ipwo (lentiviral vector) | PMID: 21248040 | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | puc2CL6IPwo/ Kb-GFP (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | C-terminally GFP-tagged H-2Kb and H-2Db cDNA were cloned into the lentiviral vector via the XhoI and AgeI sites. |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | puc2CL6IPwo/ Db-GFP (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | puc2CL6IPwo/E3 -HA-Kb-GFP (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | N-terminally E3-tagged and HA-tagged) H-2Kb (±GFP) cDNA were cloned into the lentiviral vector via the XhoI and AgeI sites. |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | puc2CL6IPwo/ E3-HA-Kb (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | puc2CL6IPwo/ E3-HA-Kb (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | puc2CL6IPwo/Kb- hβ2m-GFP (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | Cloning strategy of the single chain construct according to PMID: 16049493 |
| Sequence-based reagent | forward primer E3 tag | This paper | N/A | 5´-ACTCAGACCCGCGCGGGCGAGATCG CAGCTCTGGAGAAGGAGATTGCCGCAT TGGAGAAGGAGATAGCGGCACTCGAG AAGTATCCATACGACGTCCC-3´ |
| Sequence-based reagent | reverse primer E3 tag | This paper | N/A | 5`-GGGACGTCGTATGGATACTTCTCGA GTGCCGCTATCTCCTTCTCCAATGCGG CAATCTCCTTCTCCAGAGCTGCGAT CTCGCCCGCGCGGGTCTGAGT-3´ |
| Sequence-based reagent | forward primer HA tag (1/2) | This paper | N/A | 5`-CCGACTCAGACCCGCGCGGGCC CATATCCATACGACGTCCCACACTC GCTGAGGTATTTCGTCACC-3´ |
| Sequence-based reagent | forward primer HA tag (1/2) | This paper | N/A | 5`-GGCCCATATCCATACGACGTCCCAG ATTATGCCGGCGGTGGACACTCGCTG AGGTATTTCGTCACC-3´ |
| Sequence-based reagent | reverse primer HA tag | This paper | N/A | 5`-GGTGACGAAATACCTCAGCGAGTG TGGGACGTCGTATGGATATGGGCCCG CGCGGGTCTGAGTCGG-3´ |
| Sequence-based reagent | reverse primer HA tag | This paper | N/A | 5`-GGTGACGAAATACCTCAGCGAGTG TCCACCGCCGGCATAATCTGGGACGTCG TATGGATATGGGCC-3´ |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | SIINFEKL peptide | GeneCust Ellange, Luxemburg | N/A | 2 µM final concentration |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | SIINFEKLTAMRA peptide | GeneCust Ellange, Luxemburg | N/A | 2 µM final concentration |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | K4Atto 633 peptide | emc microcollections | N/A | 25 nM final concentration |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | K4bio peptide | emc microcollections | N/A | 200 nM final concentration |
| Chemical compound, drug | Alexa Fluor 647 NHS ester | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat #: A37566 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Atto 542 NHS ester | ATTO-TEC, | Cat #: AD 542–31 | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | National Institutes of Health |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34150.010





