Auditory experience controls the maturation of song discrimination and sexual response in Drosophila
Figures
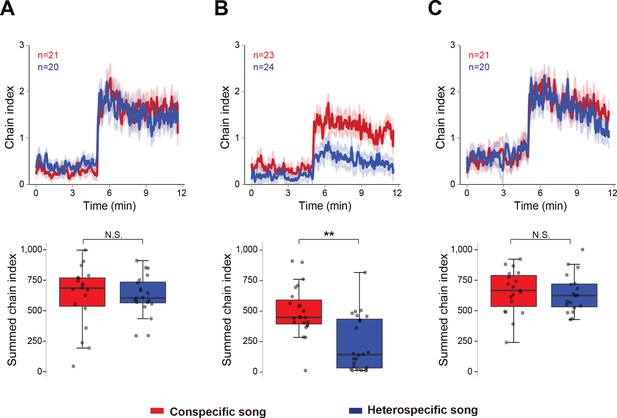
Social interaction shapes the preference to the song.
Chaining response of naïve male flies that were housed in different experimental conditions, grouped without wings (A), grouped with intact wings (B), and single-reared with intact wings (C). The time-courses of the chain index in response to playback of conspecific song (red) and heterospecific song (blue) are shown. Sound playback starts at 5 min. The bold line and ribbon represent the average value and standard error, respectively. The box plot shows the summed chain index between 5 min and 11.5 min. Boxplots display the median of each group with the 25th and 75th percentiles and whiskers denote 1.5x the inter-quartile range. N.S., not significant, p>0.05; **p<0.01; Mann-Whitney U test. n, number of behavioral chambers examined.
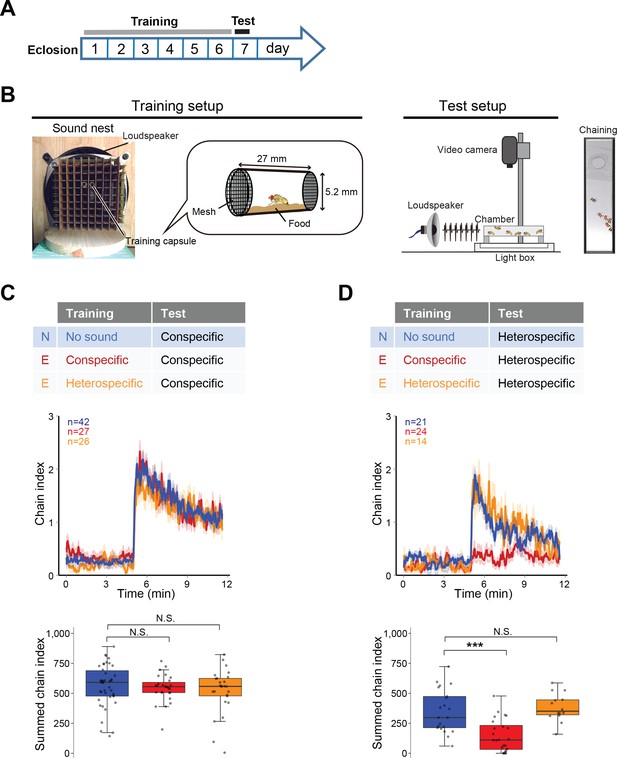
Fine-tuned song response of males after the training.
(A) Protocol for the training and test sessions. (B) Setup for the training and chaining test. In the training session, single-housed male flies were exposed to a training song for the first 6 days after eclosion. In the test session, song was delivered from a loudspeaker. Appropriate song typically drove the male flies to form male-male chains (chaining). Males in a chain are marked with red dots. (C, D) Chaining response to the conspecific song (C) or heterospecific song (D) after training. N, naïve group with no sound training (blue); E, experienced group with conspecific song training (red) or heterospecific song training (orange). The way to show the time courses of chaining behavior and the boxplot is similar to that depicted in Figure 1. N.S., not significant, p>0.05; ***p<0.001; Mann-Whitney U test versus naïve group.
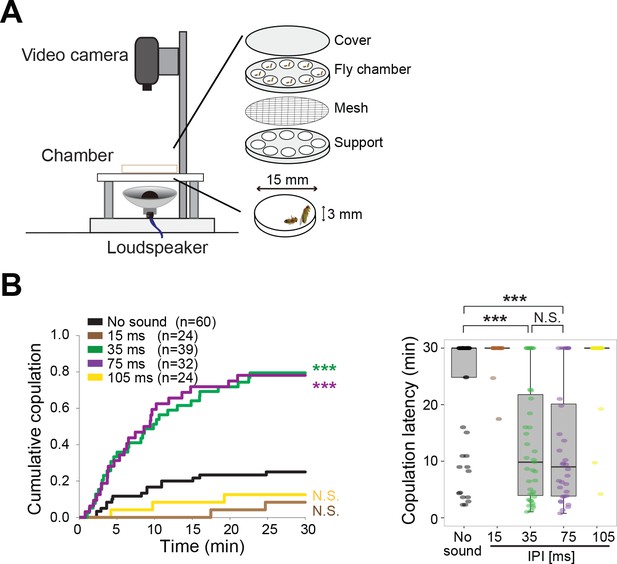
Playback of pulse song promotes copulation in wild-type fly pairs.
(A) Setup for song-induced copulation test. (B) Cumulative copulation rate and copulation latency with playback of artificial pulse songs of different inter-pulse interval (IPI). Copulation latency represents the latency to accept copulation in the 30 min observation period. Boxplots display the median of each group with the 25th and 75th percentiles and whiskers denote 1.5x the inter-quartile range. N.S., not significant, p>0.05; ***p<0.001; Log rank test versus no sound group (left panel); Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Scheffe’s test (right panel). n, number of fly pairs examined.
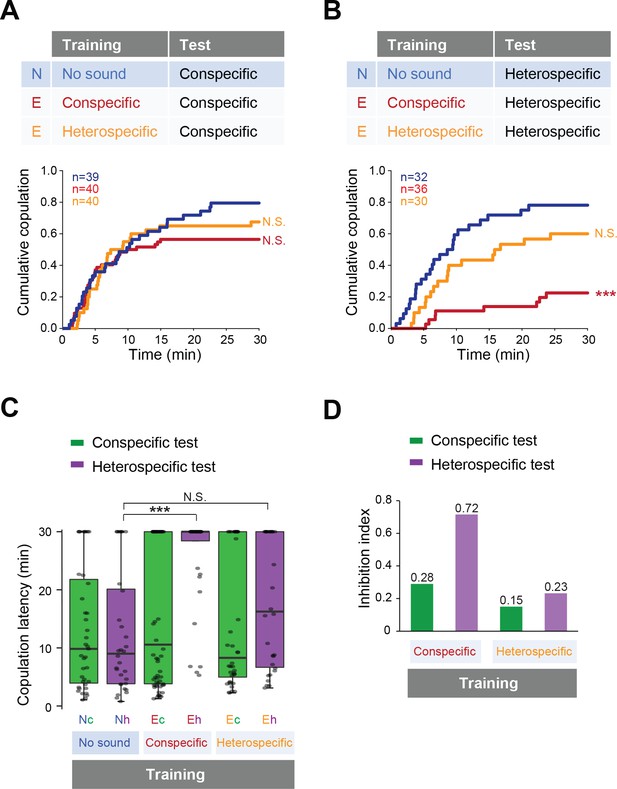
Fine-tuned song response of females after the training.
(A, B) Cumulative copulation rate in the conspecific song test (A) or heterospecific song test (B) after training females. Naïve group (no sound during training) and experienced groups (trained with conspecific song or heterospecific song) are shown. The color code is the same with that in Figure 2. N, naïve; E, experienced. (C) Copulation latencies of females under playback of conspecific song (green bars) or heterospecific song (purple bars). Nc and Nh, naïve flies tested with conspecific and heterospecific songs, respectively. Ec and Eh, experienced flies tested with conspecific and heterospecific songs, respectively. (D) Inhibition index under playback of conspecific song (green bars) or heterospecific song (purple bars) after training of conspecific song or heterospecific song. Inhibition index = (copulation ratioNaïve - copulation ratioExperienced)/copulation ratioNaive. N.S., not significant, p>0.05; ***p<0.001; Log rank test versus naïve group (A, B); Kruskal–Wallis test versus naïve group (C).
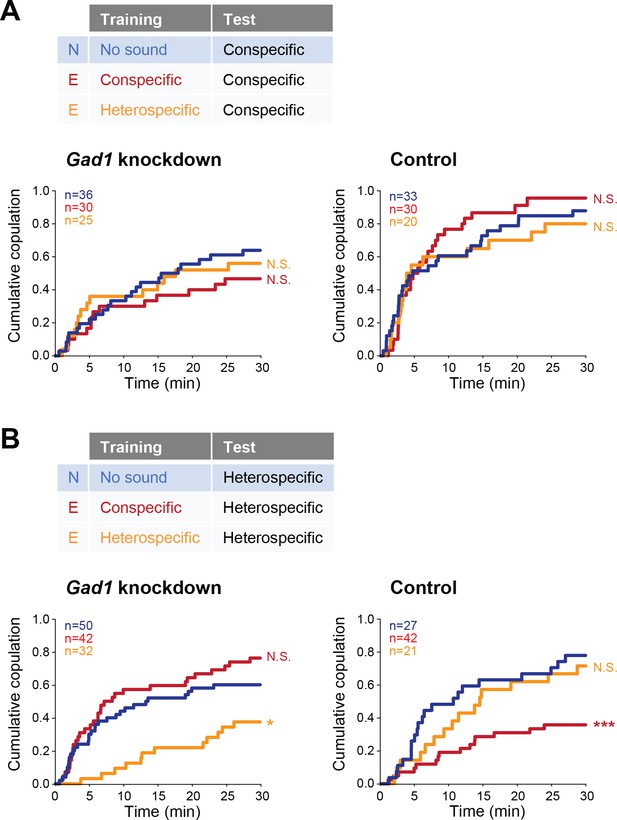
Involvement of Gad1 in the experience-dependent song preference in females.
(A, B) Cumulative copulation rate in the conspecific song test (A) or heterospecific song test (B) after training Gad1 knockdown (left) and control (right) females. Naïve group (no sound training) and experienced groups (conspecific song training and heterospecific song training) are shown. The color code is the same with that in Figure 2. N, naïve; E, experienced. N.S., not significant, p>0.05; *p<0.05; ***p<0.001; Log rank test versus naïve group.
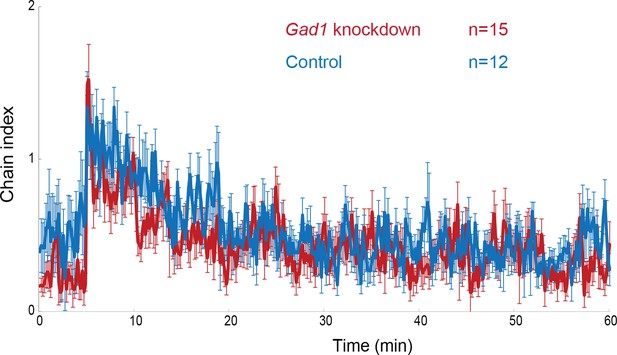
Male Gad1 knockdown flies responded normally to conspecific courtship song.
The time-courses of the chain index in response to playback of conspecific song in Gad1 knockdown group (red, Gad1-GAL4/+; UAS-Gad1 RNAi/+) and control group (blue, Gad1-GAL4/+; +/+) are shown. The way to perform chaining test is similar to that described in the Method part. Sound playback starts at 5 min and lasts until 60 min. Error bars denotes s.e.m. n, number of behavioral chambers examined.
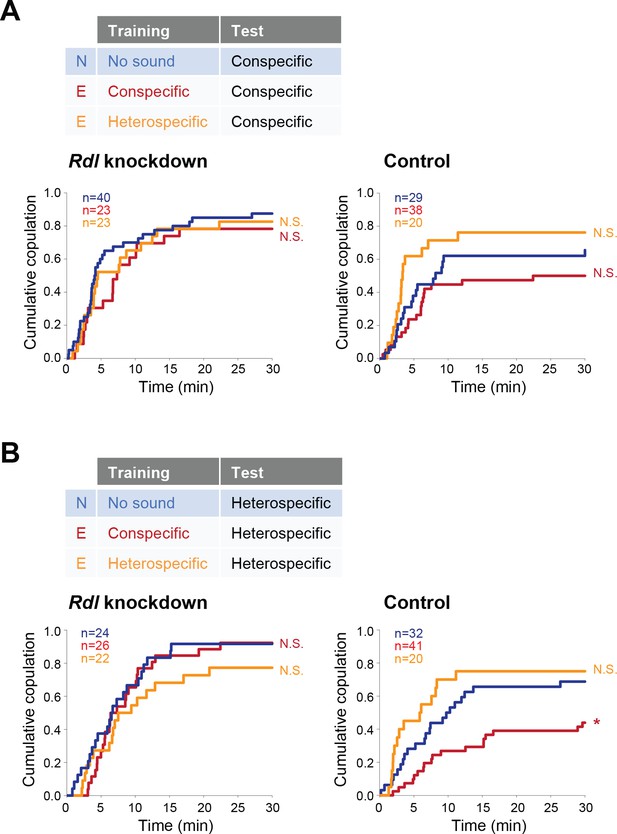
Rdl receptors in pC1 neurons modulate the experience-dependent song preference in females.
(A, B) Cumulative copulation rate in the conspecific song test (A) or heterospecific song test (B) after training Rdl knockdown (left) and control (right) females. Naïve group (no sound training) and experienced groups (conspecific song training or heterospecific song training) are shown. The color code is the same with that in Figure 2. N, naïve; E, experienced. N.S., not significant, p>0.05; *p<0.05; Log rank test versus naïve group.
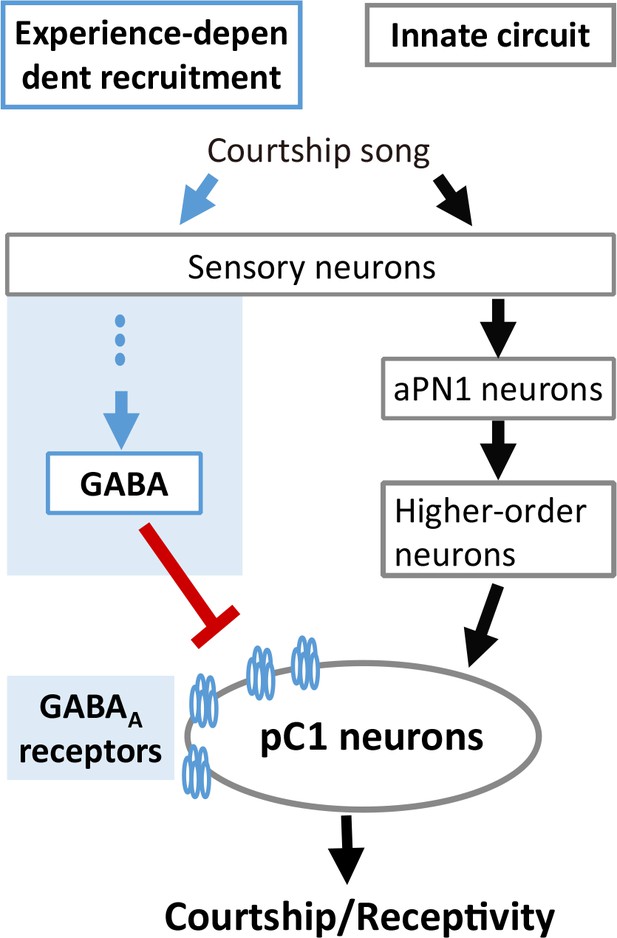
A model for experience-dependent tuning of IPI perception in Drosophila.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34348.010Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | Rdl | NA | FLYB: FBgn0004244 | |
| gene (Drosophila melanogaster) | GAD1 | NA | FLYB: FBgn0004516 | |
| strain, strain background (Drosophila melanogaster) | Canton-S | other | gift from K. Ito | |
| strain, strain background (Drosophila melanogaster) | Gad1-GAL4 | PMID: 12408848 | gift from K. Ito | |
| strain, strain background (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Gad1 RNAi | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | VDRC ID: 32344; RRID: Fly-Base_FBst0459538 | |
| strain, strain background (Drosophila melanogaster) | w1118 | Vienna Drosophila Resource Center | VDRC ID: 60000 | |
| strain, strain background (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Rdl RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC: 52903; RRID: BDSC_52903 | |
| strain, strain background (Drosophila melanogaster) | TRiP RNAi | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center | BDRC: 36304; RRID: BDSC_36304 | |
| strain, strain background (Drosophila melanogaster) | tubP>GAL80>; NP2631-GAL4/CyO; dsxFLP/TM2 | PMID: 27185554 | gift from D. Yamamoto | |
| software, algorithm | ChaIN (ver. 3) | PMID: 28701929 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Genotypes.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34348.011
-
Supplementary file 2
Statistical results.
The detailed statistical results in each figure are listed. N.S., not significant, p>0.05; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34348.012
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34348.013





