An intrinsic cell cycle timer terminates limb bud outgrowth
Figures
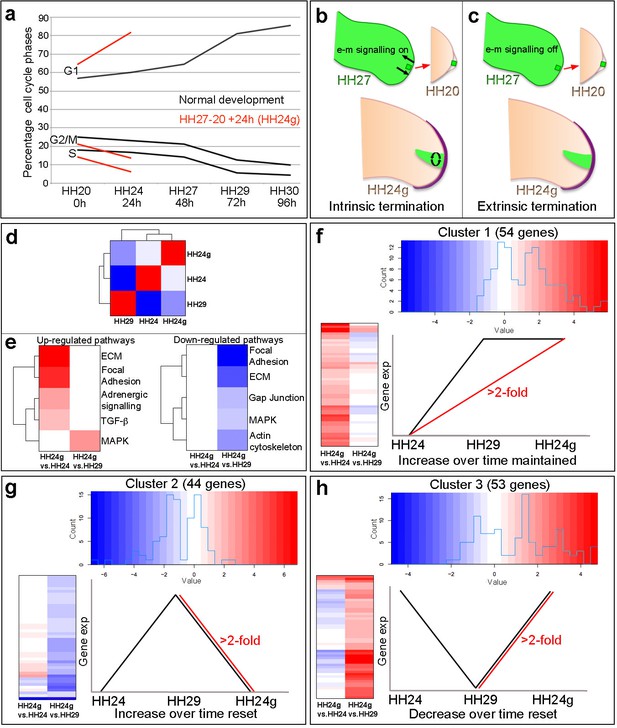
Cell cycle and RNA-seq analyses of chick wing distal tips.
(a) Decline in cell cycle rate determined by proportions of cells in G1-, S- and G2/M-phases between HH20 and HH30 in the distal chick wing bud (black lines Saiz-Lopez et al., 2017). Red lines show maintenance of cell cycle program in grafts of HH27 distal tips made to HH20 wing buds left for 24 hr until HH24 (HH24g - tissue would have progressed from HH27 to HH29 in donor) – note trajectories follow same pattern as black lines between HH27 and HH29. (b–c) Procedure for making HH27-20 grafts (Saiz-Lopez et al., 2017) and predictions for loss of proliferative growth in HH24g mesenchyme. (b) Intrinsic termination: e-m signalling (arrows in HH27 wing bud) maintained between mesenchyme and apical ridge but proliferation declines intrinsically in mesenchyme independently of e-m signalling (curved arrows in HH24g mesenchyme). (c) Extrinsic termination: e-m signalling irreversibly lost between graft and apical ridge in HH27 bud (arrows absent) and proliferation lost in graft. (d) Heat-map showing the correlation (Pearson) of the normalised RNA-seq data collapsed to the mean expression per group and the degree of correlation indicated by the colour (red: higher, blue: lower). (e) KEGG analyses across pairwise contrasts with degree in pathway change indicated by the colour (red: up-regulated, blue: down-regulated). (f–h) Clustering of RNA-seq data across pairwise contrasts with degree of gene expression change indicated by the colour (red: higher, blue: lower). (f) Cluster 1: genes that increase between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and are maintained in HH24g (red line - > 2 fold higher in HH24g than HH24). (g) Cluster 2: genes that increase between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and reset in HH24g (red line - > 2 fold lower in HH24g than HH29). (h) Cluster 3: genes that decrease between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and reset in HH24g (red line - > 2 fold higher in HH24g than HH29).
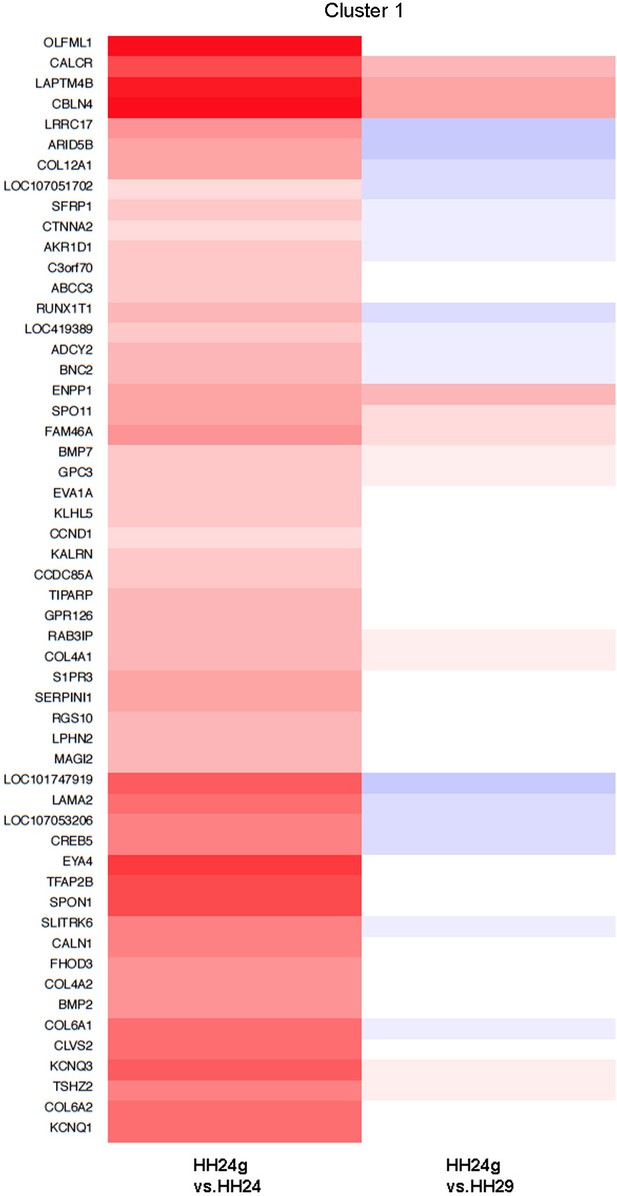
Cluster 1 Clustering of RNA-seq data across pairwise contrasts with degree of gene expression change indicated by the colour (red: higher, blue: lower).
Cluster 1: genes that increase between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and are maintained in HH24g distal mesenchyme (red line - > 2 fold higher in HH24g than HH24).
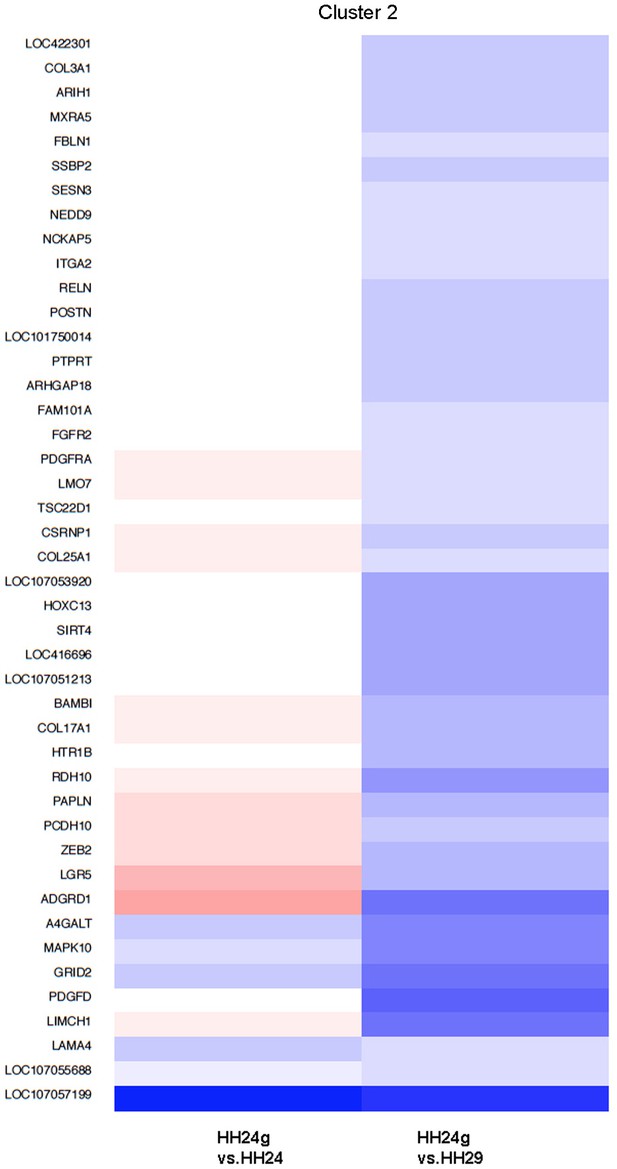
Cluster 2 Clustering of RNA-seq data across pairwise contrasts with degree of gene expression change indicated by the colour (red: higher, blue: lower).
Cluster 2: genes that increase between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and reset in HH24g distal mesenchyme (red line - > 2 fold lower in HH24g than HH29).
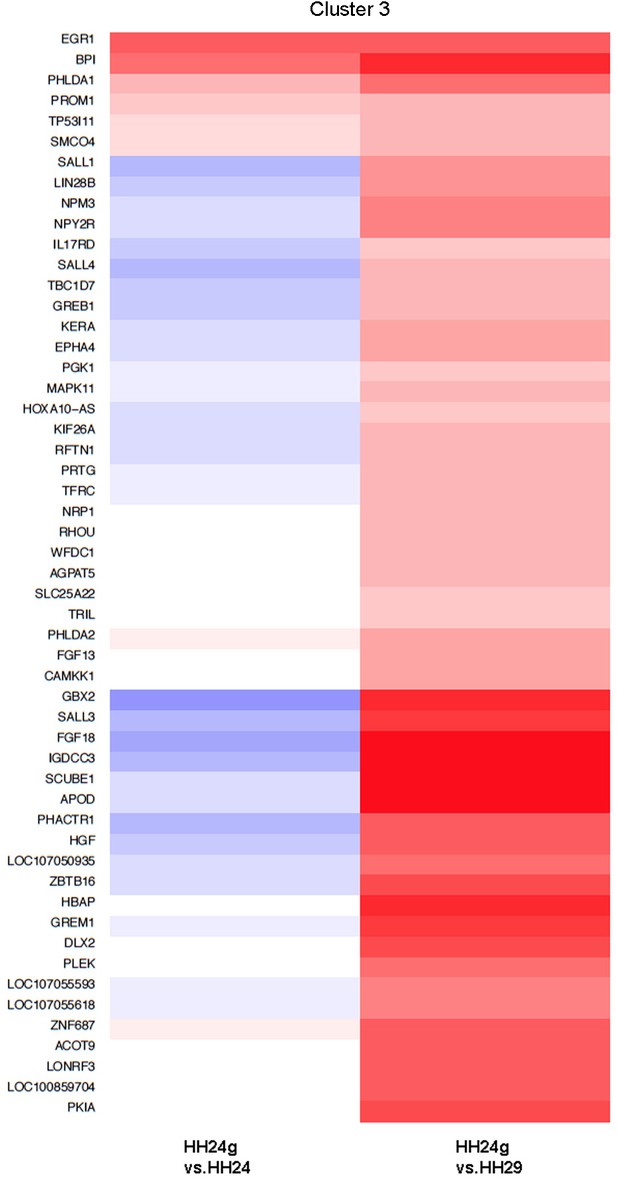
Cluster 3 Clustering of RNA-seq data across pairwise contrasts with degree of gene expression change indicated by the colour (red: higher, blue: lower).
Cluster 3: genes that decrease between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and reset in HH24g distal mesenchyme (red line - > 2 fold higher in HH24g than HH29).
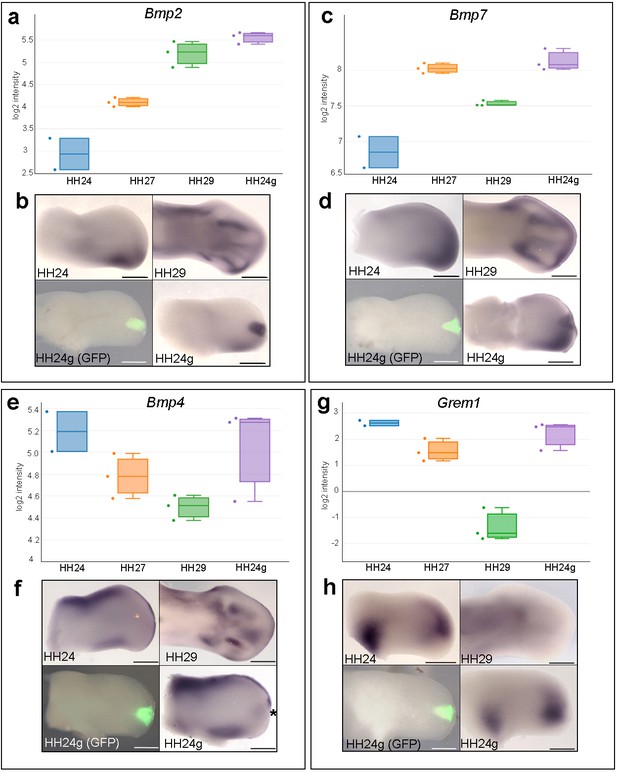
Bmp2/4/7 and Grem1 expression in HH24g mesenchyme.
(a) Histogram showing expression levels of Bmp2 as normalised log2 values of RNA sequencing read-count intensities. (b) In situ hybridization showing Bmp2 expression - note intense expression in HH24g mesenchyme in area of graft (n = 3/3, HH24 is the contralateral bud flipped horizontally). (c) Expression levels of Bmp7 determined by RNA-seq. (d) In situ hybridization showing Bmp7 expression - note intense region of expression in HH24g mesenchyme (n = 3/3). (e) Expression levels of Bmp4 determined by RNA-seq. (f) In situ hybridizations showing Bmp4 expression - note enhanced expression in HH24g mesenchyme in area of graft (asterisk - n = 2/3). (g) Expression levels of Grem1 determined by RNA-seq. (h) In situ hybridizations showing resetting of Grem1 expression (n = 7/9). Scale bars: HH24 buds - 500 μm; HH29 buds - 200 μm.
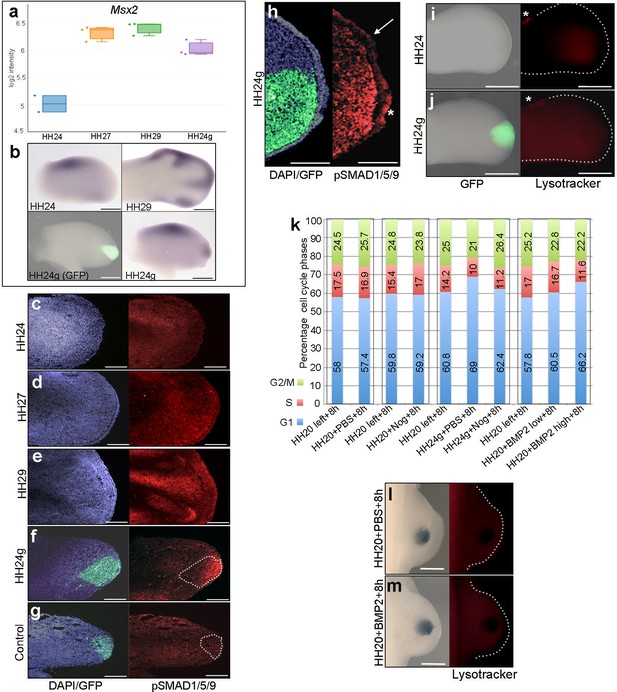
BMP signalling in HH24g mesenchyme
(a) Expression levels of Msx2 determined by RNA-seq. (b) In situ hybridization showing Msx2 expression - note intense expression in HH24g mesenchyme in grafted area (n = 3/4). (c–h) Immunostaining of pSMAD1/5/9: signal increases in the distal part of chick wing buds over time (c–e) and is enhanced in HH24g mesenchyme (f) compared to contralateral HH24 buds (n = 3/3 c) but not in HH20-HH20 grafts (n = 2/2 g); signal is enhanced in apical ectodermal ridge above grafts in HH24g mesenchyme (asterisk-h) but not adjacent regions of ridge (n = 2/2 - arrow-h). (i–j) Lysotracker staining of apoptotic cells reveals no difference in HH24 (i) and HH24g (j) mesenchyme (n = 5/5) – asterisks indicate anterior necrotic zone. (k) Flow cytometry of wing bud distal mesenchyme: PBS- and Noggin-soaked beads do not significantly affect proportion of cells in G1-phase after 8 hr compared to left wing controls (Pearson’s χ2 test – p=0.1 and p=0.4, respectively); Noggin-soaked beads implanted at HH20 (+Nog) produce a significant decrease in proportion of cells in G1-phase in HH24g grafts compared to PBS-treated controls (+PBS) after 8 hr (Pearson’s χ2 test - p<0.0001); BMP2-soaked beads implanted at HH20 significantly increase G1-phase cells after 8 hr compared to left wing controls (Pearson’s χ2 test - p<0.0001), note boxes indicate separate experiments. (l–m) Lysotracker staining of apoptotic cells reveals no difference in PBS (l) - n = 2/2) and BMP2 (m) - n = 2/2) treated mesenchyme after 8 hr. Scale bars: HH24 buds - 500 μm, HH29 buds - 200 μm in b; 150 μm in c-g; 75 μm in h; 300 μm in i-j and l-m.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Flow cytometry graphs for cell cycle analyses
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37429.008
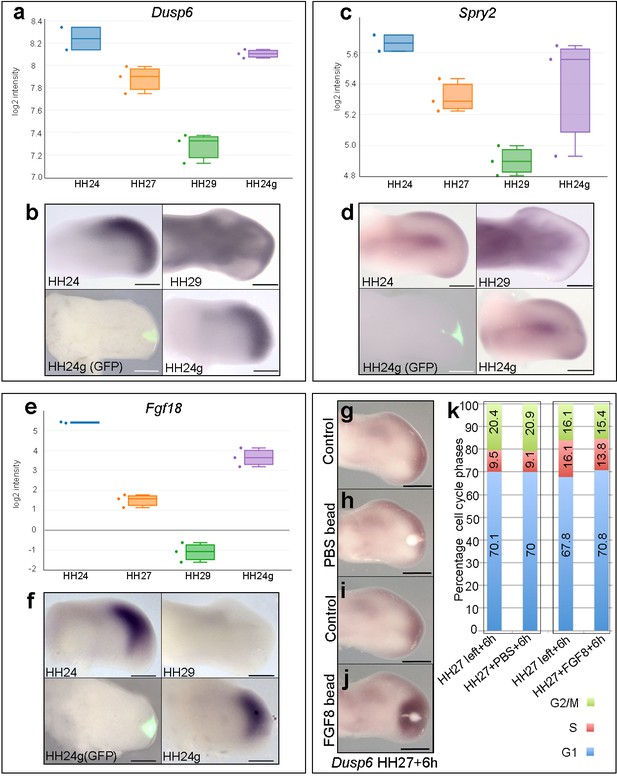
FGF signalling in HH24g mesenchyme.
(a-e) Resetting of gene expression in HH24g mesenchyme. Expression levels of Dusp6 (a), Spry2 (c) and Fgf18 (e) determined by RNA-seq. (b) In situ hybridization showing equivalent levels of Dusp6 (n = 3/3, (b), Spry2 (n = 3/3, (d), and Fgf18 (n = 3/3, (f) in HH24 and contralateral HH24g mesenchyme. (g–j) FGF-soaked beads (j) n = 3/3), but not PBS-soaked beads (h) n = 3/3), up-regulate expression of Dusp6 after 6 hr (control left wing buds flipped horizontally – (g) and (i). (k) Flow cytometry of wing bud distal mesenchyme: PBS-soaked beads do not significantly affect proportion of cells in G1-phase after 6 hr compared to left wing controls (Pearson’s χ2 test – p=0.5); FGF-soaked beads implanted at HH27 significantly increase G1-phase cells compared to left wing control after 6 hr (Pearson’s χ2 test - p<0.0001), note boxes indicate separate experiments. Scale bars: HH24 buds, HH27 buds - 300 μm; HH29 buds - 200 μm.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Flow cytometry graphs for cell cycle analyses
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37429.010
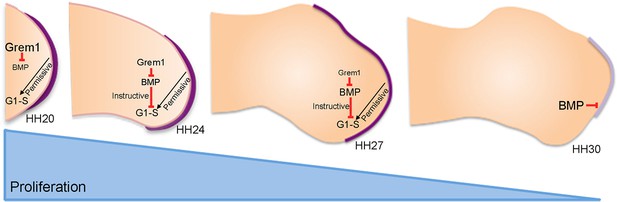
An intrinsic cell cycle timer terminates limb bud outgrowth.
HH20-HH24: antagonism of BMP signalling by Grem1 permits rapid mesenchyme proliferation and maintenance of the apical ectodermal ridge (purple) that permissively supports outgrowth. HH24-HH27: intrinsic rise in BMP signalling counters BMP antagonism and instructively decelerates mesenchyme proliferation rate. HH27-HH30: mesenchyme proliferation diminishes as patterning completes at HH28 and then BMP signalling inhibits FGF signalling in apical ectodermal ridge that then regresses.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
RNA sequencing of HH24g vs.
HH24 distal mesenchyme 55 genes are differentially expressed between HH24g and HH24 distal mesenchyme. 53 genes are increased in expression in HH24g distal mesenchyme and two genes are decreased in expression.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37429.012
-
Supplementary file 2
RNA sequencing of HH24g vs.
HH29 distal mesenchyme 99 genes are differentially expressed between HH24g and HH29 distal mesenchyme. 55 genes are increased in expression in HH24g distal mesenchyme and 44 genes are decreased in expression.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37429.013
-
Supplementary file 3
Cluster 1 Clustering of RNA-seq data across HH24g/HH24 and HH24g/HH29 pairwise contrasts.
Cluster 1: genes that increase between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and are maintained in HH24g distal mesenchyme.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37429.014
-
Supplementary file 4
Cluster 2 Clustering of RNA-seq data across HH24g/HH24 and HH24g/HH29 pairwise contrasts.
Cluster 2: genes that increase between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and reset in HH24g distal mesenchyme.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37429.015
-
Supplementary file 5
Cluster 3 Clustering of RNA-seq data across HH24g/HH24 and HH24g/HH29 pairwise contrasts.
Cluster 3: genes that decrease between HH24 and HH29 (black line) and reset in HH24g distal mesenchyme.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37429.016
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37429.017





